2002 DODGE RAM length
[x] Cancel search: lengthPage 1240 of 2255

INSPECTION
(1) Visually inspect the tappet the tappet socket,
stem, and face for excessive wear, cracks, or obvious
damage (Fig. 118).
(2) Measure the tappet stem diameter. Replace the
tappet if it falls below the minimum size (Fig. 118).
INSTALLATION
(1) Insert the trough the full length of the cam-
shaft bore (Fig. 115). Again, make sure the cap end
goes in first and the open side faces up (towards tap-
pets).
(2) Lower the tappet installation tool through the
push rod hole (Fig. 119) and into the trough.
(3) Retrieve the tappet installation tool using the
hooked rod provided with the tool kit (Fig. 120).
(4) Lubricate the tappet with clean engine oil or
suitable equivalent and install the tappet to the
installation tool (Fig. 121).
(5) Pull the tappet up and into position (Fig. 121).
If difficulty is experienced getting the tappet to make
the turn into the tappet bore, wiggle the trough
whilegentlypulling up on the tappet.(6) With the tappet in place, rotate the trough one
half turn so the open side is down (toward crank-
shaft) (Fig. 122).
(7) Remove the tappet installation tool from the
tappet.
(8) Re-install a dowel rod and secure the rod with
a rubber band.
(9) Rotate the trough one half turn and repeat the
procedure for the remaining tappets.
(10) Install the camshaft (Refer to 9 - ENGINE/
ENGINE BLOCK/CAMSHAFT & BEARINGS (IN
BLOCK) - INSTALLATION).
PISTON & CONNECTING ROD
DESCRIPTION
The piston (Fig. 123) is constructed of aluminum
and is gravity cast, free floating design. The piston
Fig. 116 Secure Dowel/Tappet to Adjacent Cylinder
Fig. 117 Lift Dowel Rod to Disengage from Tappet
Fig. 118 Tappet Inspection
TAPPET STEM DIAMETER
15.925 mm (0.627 in.) MIN.
15.977 mm (0.629 in.) MAX.
Fig. 119 Insert Installation Tool through Push Rod
Hole
BR/BEENGINE 5.9L DIESEL 9 - 165
SOLID LIFTERS/TAPPETS (Continued)
Page 1250 of 2255
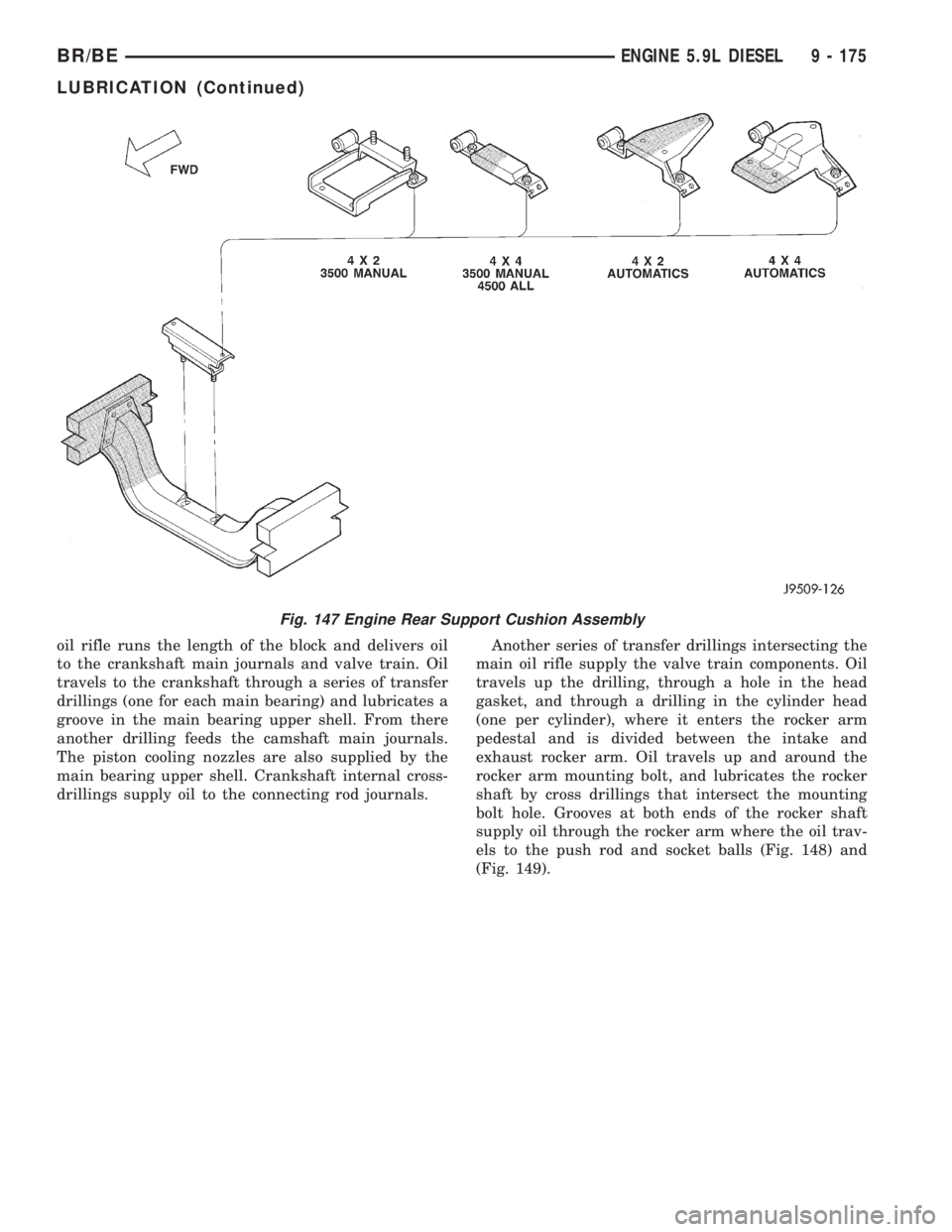
oil rifle runs the length of the block and delivers oil
to the crankshaft main journals and valve train. Oil
travels to the crankshaft through a series of transfer
drillings (one for each main bearing) and lubricates a
groove in the main bearing upper shell. From there
another drilling feeds the camshaft main journals.
The piston cooling nozzles are also supplied by the
main bearing upper shell. Crankshaft internal cross-
drillings supply oil to the connecting rod journals.Another series of transfer drillings intersecting the
main oil rifle supply the valve train components. Oil
travels up the drilling, through a hole in the head
gasket, and through a drilling in the cylinder head
(one per cylinder), where it enters the rocker arm
pedestal and is divided between the intake and
exhaust rocker arm. Oil travels up and around the
rocker arm mounting bolt, and lubricates the rocker
shaft by cross drillings that intersect the mounting
bolt hole. Grooves at both ends of the rocker shaft
supply oil through the rocker arm where the oil trav-
els to the push rod and socket balls (Fig. 148) and
(Fig. 149).
Fig. 147 Engine Rear Support Cushion Assembly
BR/BEENGINE 5.9L DIESEL 9 - 175
LUBRICATION (Continued)
Page 1295 of 2255
FRAME FASTENERS
Bolts, nuts and rivets can be used to repair frames
or to install a reinforcement section on the frame.
Bolts can be used in place of rivets. When replacing
rivets with bolts, install the next larger size diameter
bolt to assure proper fit. If necessary, ream the hole
out just enough to sufficiently receive the bolt.
Conical-type washers are preferred over the split-
ring type lock washers. Normally, grade-5 bolts are
adequate for frame repair.Grade-3 bolts or softer
should not be used.Tightening bolts/nuts with thecorrect torque, refer to the Introduction Group at the
front of this manual for tightening information.
SPECIFICATIONS
FRAME DIMENSION
Frame dimensions are listed in Millimeters (mm)
scale. All dimensions are from center to center of
Principal Locating Point (PLP), or from center to cen-
ter of PLP and fastener location (Fig. 10) .
DIMENSIONS FOR DIFFERING WHEELBASES*
WHEELBASE LENGTH
ALENGTH
BLENGTH
C
118 2118.0 3663.6 4185.4
134 2118.0 3994.5 4693.4
138 2626.0 4096.1 4693.4
154 2626.0 4502.5 5201.4
162 2118.0 4705.0 5042.5
*Measurements are in Millimeters (mm).
13 - 8 FRAME & BUMPERSBR/BE
FRAME (Continued)
Page 1377 of 2255

DESCRIPTIONÐHIGH PRESSURE FUEL LINES
The high-pressure fuel lines are the 6 lines located
between the fuel injection pump and the fuel injector
connector tubes (Fig. 45). All other fuel lines are con-
sidered low-pressure lines.
OPERATIONÐHIGH PRESSURE FUEL LINES
CAUTION: The high-pressure fuel lines must be
held securely in place in their holders. The lines
cannot contact each other or other components. Do
not attempt to weld high-pressure fuel lines or to
repair lines that are damaged. If lines are ever
kinked or bent, they must be replaced. Use only the
recommended lines when replacement of high-pres-
sure fuel line is necessary.
High-pressure fuel lines deliver fuel under pres-
sure of up to approximately 120,000 kPa (17,405 PSI)
from the injection pump to the fuel injectors. The
lines expand and contract from the high-pressure
fuel pulses generated during the injection process. All
high-pressure fuel lines are of the same length and
inside diameter. Correct high-pressure fuel line usage
and installation is critical to smooth engine opera-
tion.
WARNING: USE EXTREME CAUTION WHEN
INSPECTING FOR HIGH-PRESSURE FUEL LEAKS.
INSPECT FOR HIGH-PRESSURE FUEL LEAKS WITH
A SHEET OF CARDBOARD. HIGH FUEL INJECTION
PRESSURE CAN CAUSE PERSONAL INJURY IF
CONTACT IS MADE WITH THE SKIN.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - HIGH-PRESSURE
FUEL LINE LEAKS
High-pressure fuel line leaks can cause starting
problems and poor engine performance.
WARNING: DUE TO EXTREME FUEL PRESSURES
OF UP TO 120,000 kPa (17,400 PSI), USE EXTREME
CAUTION WHEN INSPECTING FOR HIGH-PRES-
SURE FUEL LEAKS. DO NOT GET YOUR HAND
NEAR A SUSPECTED LEAK. INSPECT FOR HIGH-
PRESSURE FUEL LEAKS WITH A SHEET OF CARD-
BOARD. HIGH FUEL INJECTION PRESSURE CAN
CAUSE PERSONAL INJURY IF CONTACT IS MADE
WITH THE SKIN.
Start the engine. Move the cardboard over the
high-pressure fuel lines and check for fuel spray onto
the cardboard (Fig. 46). If a high-pressure line con-
nection is leaking, bleed the system and tighten the
connection. Refer to the Air Bleed Procedure in this
group for procedures. Replace damaged, restricted or
leaking high-pressure fuel lines with the correct
replacement line.
Fig. 45 High-Pressure Fuel Lines
Fig. 46 Typical Test for Leaks with Cardboard
1 - HIGH-PRESSURE LINE
2 - CARDBOARD
3 - FITTING
14 - 78 FUEL DELIVERY - DIESELBR/BE
FUEL LINES (Continued)
Page 1378 of 2255

CAUTION: The high-pressure fuel lines must be
clamped securely in place in the holders. The lines
cannot contact each other or other components. Do
not attempt to weld high-pressure fuel lines or to
repair lines that are damaged. Only use the recom-
mended lines when replacement of high-pressure
fuel line is necessary.
REMOVAL
High-pressure lines are used between the fuel
injection pump and the fuel injectors only. All high-
pressure fuel lines are of the same length and inside
diameter. Correct high-pressure fuel line usage and
installation is critical to smooth engine operation.
CAUTION: Refer to Cleaning Fuel System Parts.
(1) Disconnect both negative battery cables from
both batteries. Cover and isolate ends of cables.
(2) Thoroughly clean fuel lines at cylinder head
and injection pump ends.
(3) Remove cable cover (Fig. 47). Cable cover is
attached with 2 Phillips screws, 2 plastic retention
clips and 2 push tabs (Fig. 47). Remove 2 Phillips
screws and carefully pry out 2 retention clips. After
clip removal, push rearward on front tab, and
upward on lower tab for cover removal.Do not
remove any cables at lever.(4) Disconnect wiring harness (clip) at bottom of
Accelerator Pedal Position Sensor (APPS) mounting
bracket (Fig. 48).
(5) Using 2 small screwdrivers, pry front wiring
clip (Fig. 49) from cable bracket housing. Position
wiring harness towards front of engine.
(6) Remove electrical connector from APPS by
pushing connector tab rearward while pulling down
on connector (Fig. 50).
(7) Disconnect 2 electrical cables from cable
mounting studs (Fig. 51) at intake air heater on top
of intake manifold.
(8) Remove engine oil dipstick from engine.
(9) Remove engine oil dipstick tube support
mounting bolt (Fig. 51) and position tube to side.
(10) Disconnect clamps and remove air tube
(intake manifold-to-intercooler) (Fig. 49).
(11) Remove 4 air intake housing mounting bolts
and remove housing (Fig. 52) and (Fig. 51). Position
ground cable at top of air intake housing to front of
engine.
(12) Remove intake manifold air heater element
block from engine (Fig. 53). Discard old upper and
lower gaskets
(13) Remove 3 cable bracket housing mounting
bolts (Fig. 52). Carefully position cable bracket and
cable assembly to side of engine.Leave cables con-
nected to lever.
Fig. 47 Cable/Lever/Throttle Linkage Cover
1 - CABLE/LEVER/LINKAGE COVER
2 - PUSH UP LOWER TAB
3 - SCREWS/CLIPS (2)
4 - TAB PUSH HERE
Fig. 48 Wiring Clip at APPS
1 - LEVER
2 - MOUNTING BOLTS (6)
3 - WIRE HARNESS CLIP
4 - CALIBRATION SCREWS (NO ADJUSTMENT)
5 - APPS ASSEMBLY
BR/BEFUEL DELIVERY - DIESEL 14 - 79
FUEL LINES (Continued)
Page 1380 of 2255

(14) Remove engine lifting bracket at rear of
intake manifold (2 bolts) (Fig. 54).
(15) Remove bolts from all fuel injection line sup-
port brackets at intake manifold.
(16) Place shop towels around fuel lines at fuel
injectors. Do not allow fuel to drip down side of
engine.CAUTION: WHEN LOOSENING OR TIGHTENING
HIGH-PRESSURE FITTINGS AT INJECTION PUMP,
USE A BACK-UP WRENCH ON DELIVERY VALVE AT
PUMP. DO NOT ALLOW DELIVERY VALVE TO
ROTATE.
(17) Loosen high-pressure line fittings at injection
pump (Fig. 55) beginning with cylinders 1, 2 and 4.
(18) Loosen high-pressure lines at cylinder head
for cylinders 1, 2 and 4 (Fig. 54).
(19) Carefully remove front line bundle from
engine.Do not bend lines while removing.While
removing front line bundle, note line position.
(20) Loosen high-pressure lines at injection pump
beginning with cylinders 3, 5 and 6.
(21) Loosen high-pressure lines at cylinder head
for cylinders 3, 5 and 6 (Fig. 54).
(22) Carefully remove rear line bundle from
engine.Do not bend lines while removing.While
removing rear line bundle, note line position.
INSTALLATION
High-pressure lines are used between the fuel
injection pump and the fuel injectors only. All high-
pressure fuel lines are of the same length and inside
diameter. Correct high-pressure fuel line usage and
installation is critical to smooth engine operation.
Fig. 53 Intake Manifold Air Heater (Elements)
1 - AIR HEATER ELEMENTS
2 - LOWER GASKET
3 - BLOCK
4 - UPPER GASKET
Fig. 54 High-Pressure Fuel Lines
Fig. 55 High Pressure Lines at Fuel Injection Pump
1 - FPCM ELECTRICAL CONNECTOR
2 - HIGH-PRESSURE FUEL LINES
3 - FITTINGS
4 - FUEL INJECTION PUMP
5 - FPCM
BR/BEFUEL DELIVERY - DIESEL 14 - 81
FUEL LINES (Continued)
Page 1569 of 2255

(4) Remove throttle and shift levers from valve
body manual shaft and throttle lever shaft.
(5) Remove transmission oil pan and gasket.
(6) Remove filter from valve body (Fig. 17). Keep
filter screws separate from other valve body screws.
Filter screws are longer and should be kept with fil-
ter.
(7) Remove park/neutral position switch and seal.
(8) Remove hex head bolts attaching valve body to
transmission case (Fig. 18). A total of 10 bolts are
used. Note different bolt lengths for assembly refer-
ence.
(9) Remove valve body assembly. Push valve body
harness connector out of case. Then work park rod
and valve body out of case (Fig. 19).
(10) Remove accumulator outer spring, piston and
inner spring (Fig. 20). Note position of piston and
springs for assembly reference. Remove and discard
piston seals if worn or cut.
(11) Remove pump oil seal with suitable pry tool or
slide-hammer mounted screw.
Fig. 17 Oil Filter Removal
1 - OIL FILTER
2 - VALVE BODY
3 - FILTER SCREWS (2)
Fig. 18 Valve Body Bolt Locations
1 - VALVE BODY BOLTS
2 - VALVE BODY BOLTS
Fig. 19 Valve Body Removal
1 - GOVERNOR PRESSURE SENSOR
2 - VALVE BODY
3 - PARK ROD
4 - ACCUMULATOR PISTON
5 - GOVERNOR PRESSURE SOLENOID
21 - 116 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 46REBR/BE
AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 46RE (Continued)
Page 1584 of 2255

(16) Install crankshaft position sensor. (Refer to 14
- FUEL SYSTEM/FUEL INJECTION/CRANKSHAFT
POSITION SENSOR - INSTALLATION)
(17) Install new plastic retainer grommet on any
shift linkage rod or lever that was disconnected.
Grommets should not be reused. Use pry tool to
remove rod from grommet and cut away old grom-
met. Use pliers to snap new grommet into lever and
to snap rod into grommet at assembly.
(18) Connect gearshift and throttle cable to trans-
mission.
(19) Connect wires to park/neutral position switch,
transmission solenoid(s) and oxygen sensor. Be sure
transmission harnesses are properly routed.
CAUTION: It is essential that correct length bolts be
used to attach the converter to the driveplate. Bolts
that are too long will damage the clutch surface
inside the converter.
(20) Install torque converter-to-driveplate bolts.
On models with 10.75 in. converter, tighten bolts to31 N´m (270 in. lbs.). On models with 12.2 in. con-
verter, tighten bolts to 47 N´m (35 ft. lbs.).
(21) Install converter housing access cover.
(22) Install starter motor and cooler line bracket.
(Refer to 8 - ELECTRICAL/STARTING/STARTER
MOTOR - INSTALLATION)
(23) Connect cooler lines to transmission.
(24) Install transmission fill tube. Install new seal
on tube before installation.
(25) Install exhaust components.
(26) Align and connect propeller shaft. (Refer to 3 -
DIFFERENTIAL & DRIVELINE/PROPELLER
SHAFT/PROPELLER SHAFT - INSTALLATION)
(27) Adjust gearshift linkage and throttle valve
cable if necessary.
(28) Lower vehicle.
(29) Fill transmission with MopartATF +4, type
9602, Automatic Transmission fluid.
BR/BEAUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 46RE 21 - 131
AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 46RE (Continued)