Page 309 of 4323
A15651
ECM
Intake Air Temp. Sensor
(Built into Mass Air Flow Meter)
54 Y±G5 V
THA 22R
E8
E8 G±W28
E2
E1 M1
THA
E2
± DIAGNOSTICSENGINE
DI±115
309 Author�: Date�:
2005 SEQUOIA (RM1146U)
WIRING DIAGRAM
INSPECTION PROCEDURE
HINT:
�If DTCs related to different systems that have terminal E2 as the ground terminal are output simulta-
neously, terminal E2 may have an open circuit.
�Read freeze frame data using the hand-held tester. Freeze frame data records the engine conditions
when a malfunction is detected. When troubleshooting, freeze frame data can help determine if the
vehicle was running or stopped, if the engine was warmed up or not, if the air±fuel ratio was lean or
rich, as well as other data from the time when a malfunction occurred.
Page 315 of 4323
FI6448
ECM
5 V
THW E2
Engine Coolant Temp. Sensor
2
1G±Y
G±W
E1 E2
E8
E8
2821
± DIAGNOSTICSENGINE
DI±121
315 Author�: Date�:
2005 SEQUOIA (RM1146U)
WIRING DIAGRAM
INSPECTION PROCEDURE
HINT:
�If DTCs related to different system that have terminal E2 as the ground terminal are output simulta-
neously, terminal E2 may have an open circuit.
�Read freeze frame data using the hand-held tester. Freeze frame data records the engine conditions
when a malfunction is detected. When troubleshooting, freeze frame data can help determine if the
vehicle was running or stopped, if the engine was warmed up or not, if the air±fuel ratio was lean or
rich, as well as other data from the time when a malfunction occurred.
Page 326 of 4323
A19212
T14
Throttle Control Motor
and Position Sensor
4
6
1
2G±W
G±B
P±L
B±Y28
23
19
20
4
5
17 E8
P
VECM
E2
VC
VTA2
VTA1 3
5
(Shielded)
L±RM±
M+
GE01 E8
E8
E8
E8
E8
E8 DI±132
± DIAGNOSTICSENGINE
326 Author�: Date�:
2005 SEQUOIA (RM1146U)
WIRING DIAGRAM
INSPECTION PROCEDURE
HINT:
�If DTCs related to different system that have terminal E2 as the ground terminal are output simulta-
neously, terminal E2 may have an open circuit.
�Read freeze frame data using the hand-held tester. Freeze frame data records the engine conditions
when a malfunction is detected. When troubleshooting, freeze frame data can help determine if the
vehicle was running or stopped, if the engine was warmed up or not, if the air±fuel ratio was lean or
rich, as well as other data from the time when a malfunction occurred.
Page 342 of 4323
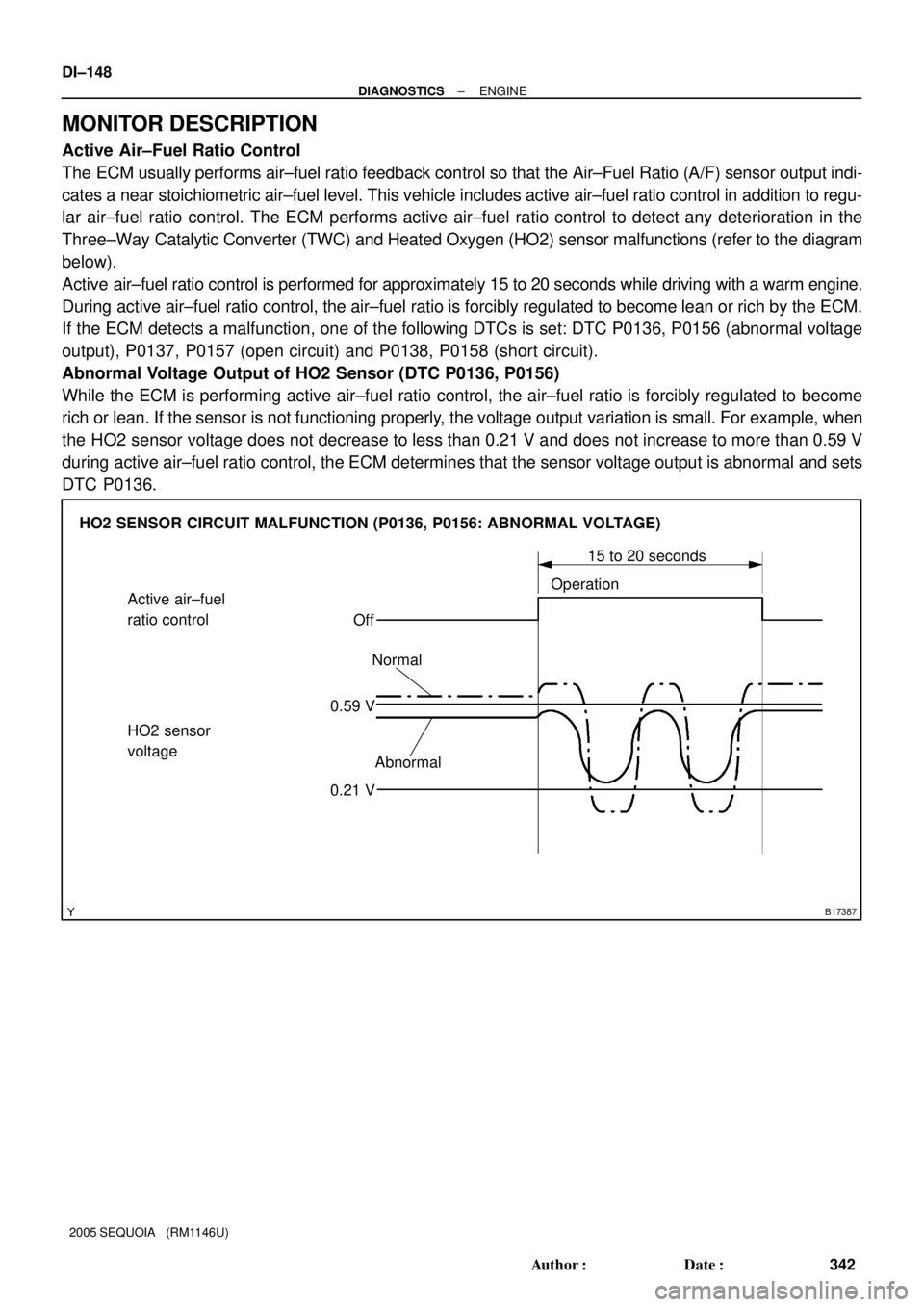
B17387
Active air±fuel
ratio control
OffOperation15 to 20 seconds
HO2 sensor
voltage
Abnormal Normal
0.21 V 0.59 V HO2 SENSOR CIRCUIT MALFUNCTION (P0136, P0156: ABNORMAL VOLTAGE) DI±148
± DIAGNOSTICSENGINE
342 Author�: Date�:
2005 SEQUOIA (RM1146U)
MONITOR DESCRIPTION
Active Air±Fuel Ratio Control
The ECM usually performs air±fuel ratio feedback control so that the Air±Fuel Ratio (A/F) sensor output indi-
cates a near stoichiometric air±fuel level. This vehicle includes active air±fuel ratio control in addition to regu-
lar air±fuel ratio control. The ECM performs active air±fuel ratio control to detect any deterioration in the
Three±Way Catalytic Converter (TWC) and Heated Oxygen (HO2) sensor malfunctions (refer to the diagram
below).
Active air±fuel ratio control is performed for approximately 15 to 20 seconds while driving with a warm engine.
During active air±fuel ratio control, the air±fuel ratio is forcibly regulated to become lean or rich by the ECM.
If the ECM detects a malfunction, one of the following DTCs is set: DTC P0136, P0156 (abnormal voltage
output), P0137, P0157 (open circuit) and P0138, P0158 (short circuit).
Abnormal Voltage Output of HO2 Sensor (DTC P0136, P0156)
While the ECM is performing active air±fuel ratio control, the air±fuel ratio is forcibly regulated to become
rich or lean. If the sensor is not functioning properly, the voltage output variation is small. For example, when
the HO2 sensor voltage does not decrease to less than 0.21 V and does not increase to more than 0.59 V
during active air±fuel ratio control, the ECM determines that the sensor voltage output is abnormal and sets
DTC P0136.
Page 347 of 4323

± DIAGNOSTICSENGINE
DI±153
347 Author�: Date�:
2005 SEQUOIA (RM1146U) Heated oxygen sensor impedance
348.1 MW or more
Heated oxygen sensor output voltage (Extremely high):
Duration of following condition10 sec. or more
Heated oxygen sensor voltageMore than 1.2 V
COMPONENT OPERATING RANGE
ParameterStandard Value
Heated oxygen sensor voltageVaries between 0.1 to 0.9 V
MONITOR RESULT
Refer to page DI±24 for detailed information.
The test value and test limit information are described as shown in the following table. Check the monitor
result and test values after performing the monitor drive pattern (refer to ºConfirmation Monitorº).
�MID (Monitor Identification Data) is assigned to each emissions±related component.
�TID (Test Identification Data) is assigned to each test value.
HO2S bank 1 sensor 2
MIDTIDScalingDescription of Test ValueMinimum Test LimitMaximum Test Limit
$02$07Multiply by 0.001
(V)Minimum sensor voltageMinimum test limitMaximum test limit
$02$08Multiply by 0.001
(V)Maximum sensor voltageMinimum test limitMaximum test limit
$02$8FMultiply by 0.001
(g)Maximum oxygen storage capacity0Maximum test limit
HO2S bank 2 sensor 2
MIDTIDScalingDescription of Test ValueMinimum Test LimitMaximum Test Limit
$06$07Multiply by 0.001
(V)Minimum sensor voltageMinimum test limitMaximum test limit
$06$08Multiply by 0.001
(V)Maximum sensor voltageMinimum test limitMaximum test limit
$06$8FMultiply by 0.001
(g)Maximum oxygen storage capacity0Maximum test limit
WIRING DIAGRAM
Refer to DTC P2195 on page DI±383.
Page 362 of 4323
DI±168
± DIAGNOSTICSENGINE
362 Author�: Date�:
2005 SEQUOIA (RM1146U)
TYPICAL ENABLING CONDITIONS
ItSpecificationItemMinimumMaximum
The monitor will run whenever these
DTCs are not presentSee page DI±18
Battery voltage11 V±
Fuel system statusClosed±loop
Throttle position learningCompleted
Either of the following conditions is met:Condition 1 or 2
1. Engine RPM±1,000 rpm
2. Intake air amount per revolution0.26 g/sec.±
Catalyst monitorNo executed
TYPICAL MALFUNCTION THRESHOLDS
Detection CriteriaThreshold
Purge±cutExecuting
Either of the following conditions is metCondition 1 or 2
1. Average between short±term fuel trim and long±term fuel
trim35% or more (varies with ECT)
2. Average between short±term fuel trim and long±term fuel
trim±35% or less (varies with ECT)
WIRING DIAGRAM
Refer to DTC P2195 on page DI±383.
INSPECTION PROCEDURE
HINT:
Hand±held tester only:
Malfunctioning areas can be identified by performing the A/F CONTROL function provided in the ACTIVE
TEST. The A/F CONTROL function can help to determine whether the Air±Fuel Ratio (A/F) sensor, Heated
Oxygen (HO2) sensor and other potential trouble areas are malfunctioning.
The following instructions describe how to conduct the A/F CONTROL operation using a hand±held tester.
(1) Connect a hand±held tester to the DLC3.
(2) Start the engine and turn the tester ON.
(3) Warm up the engine at an engine speed of 2,500 rpm for approximately 90 seconds.
(4) On the tester, select the following menu items: DIAGNOSIS / ENHANCED OBD II / ACTIVE
TEST / A/F CONTROL.
(5) Perform the A/F CONTROL operation with the engine in an idling condition (press the RIGHT
or LEFT button to change the fuel injection volume).
(6) Monitor the voltage outputs of the A/F and HO2 sensors (AFS B1S1 (AFS B2S1) and OS2 B1S2
(O2S B2S2)) displayed on the tester.
HINT:
�The A/F CONTROL operation lowers the fuel injection volume by 12.5 % or increases the injection
volume by 25 %.
�Each sensor reacts in accordance with increases and decreases in the fuel injection volume.
Page 373 of 4323
A21043
Starter Relay EFI Relay
Circuit Opening
Relay
Fuel Pump RelayMREL
FPRTr2
Tr1 EFI No.1
IGNECM
FC
NE Fuel Pump
Battery
StarterFuel Pump Resistor
AM2Ignition Switch
STA
Crankshaft Position
Sensor (NE Signal)
± DIAGNOSTICSENGINE
DI±179
373 Author�: Date�:
2005 SEQUOIA (RM1146U)
DTC P0230 Fuel Pump Primary Circuit
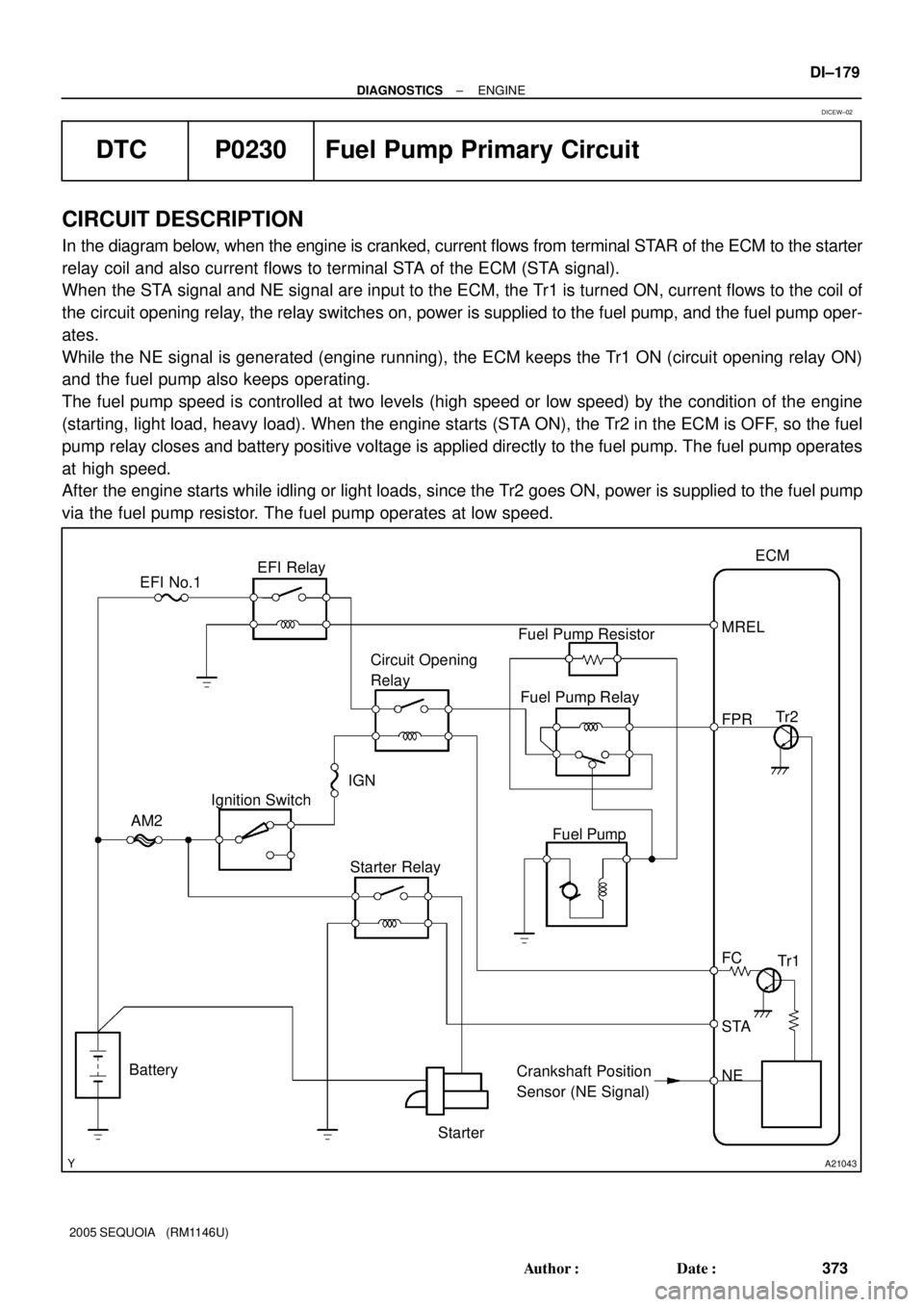
CIRCUIT DESCRIPTION
In the diagram below, when the engine is cranked, current flows from terminal STAR of the ECM to the starter
relay coil and also current flows to terminal STA of the ECM (STA signal).
When the STA signal and NE signal are input to the ECM, the Tr1 is turned ON, current flows to the coil of
the circuit opening relay, the relay switches on, power is supplied to the fuel pump, and the fuel pump oper-
ates.
While the NE signal is generated (engine running), the ECM keeps the Tr1 ON (circuit opening relay ON)
and the fuel pump also keeps operating.
The fuel pump speed is controlled at two levels (high speed or low speed) by the condition of the engine
(starting, light load, heavy load). When the engine starts (STA ON), the Tr2 in the ECM is OFF, so the fuel
pump relay closes and battery positive voltage is applied directly to the fuel pump. The fuel pump operates
at high speed.
After the engine starts while idling or light loads, since the Tr2 goes ON, power is supplied to the fuel pump
via the fuel pump resistor. The fuel pump operates at low speed.
DICEW±02
Page 375 of 4323
A23553
G±R
1 28
A 6
BECM
AM2
W±B6
32
15 3
2 121
3 2B IA1
J5
J/CL±O
I18
Ignition SW
3
7
F10
Fusible Link BlockB±R
BI530
10 26 4
12
2
114
68
1 41
5 3L±B
AM2
52HE6
2D
2F 1J1C2F
IA4
E4
E4 IG4
IA4 2H
2H 2C 1C
1JFPR
FC
MREL B±O5
J44
J45J/C E
L
BB1G±RG±REngine Room J/B
4
2F
5V V V
IL2
25
G±O G±O
B
IG2
W±B
W±BA
ED 5 4G±RIG1
B±WB±W
Instrument Panel J/B
F9
Fuel Pump
Resister
Battery2C
W±R W±R5
6
EFI No.15
C/OPN Relay Fuel Pump
Relay
EFI Relay F19
Fuel Pump
± DIAGNOSTICSENGINE
DI±181
375 Author�: Date�:
2005 SEQUOIA (RM1146U)
WIRING DIAGRAM
HINT:
This diagnostic chart is based on premise that engine is started. If the engine is not started, proceed to prob-
lem symptoms table on DI±33.