2001 DODGE TOWN AND COUNTRY torque
[x] Cancel search: torquePage 1519 of 2321

REMOVAL.............................118
INSTALLATION..........................118
THROTTLE VALVE CABLE
REMOVAL.............................118
INSTALLATION..........................118
ADJUSTMENTS.........................120
TORQUE CONVERTER
DESCRIPTION..........................120
OPERATION............................123
REMOVAL.............................125
INSTALLATION..........................125
TRANSFER SYSTEM - OUTPUT SHAFT/GEAR/
BEARING
REMOVAL.............................126
INSTALLATION..........................129
ADJUSTMENTS.........................132TRANSFER SYSTEM - TRANSFER SHAFT/
GEAR/BEARING
REMOVAL.............................134
INSTALLATION..........................137
ADJUSTMENTS.........................142
VALVE BODY
REMOVAL.............................142
DISASSEMBLY..........................145
CLEANING.............................151
INSPECTION...........................152
ASSEMBLY............................152
INSTALLATION..........................155
ADJUSTMENTS.........................157
VEHICLE SPEED SENSOR/PINION GEAR
REMOVAL.............................157
INSTALLATION..........................157
AUTOMATIC - 31TH
DESCRIPTION
This transaxle combines torque converter, three
speed transmission, final drive gearing, and differen-
tial into a front wheel drive system.
Within this transaxle, there are three primary
areas:
(1) Main center line plus valve body.
(2) Transfer shaft center line (includes governor
and parking sprag).
(3) Differential center line.
Center distances between the main rotating parts
in these three areas are held precise to maintain a
low noise level.
The torque converter, transaxle area, and differen-
tial are housed in an integral aluminum die casting.
The differential oil sump is common with the
transaxle sump. Separate filling of the differen-
tial is NOT necessary.
The torque converter is attached to the crankshaft
through a flexible driving plate. Cooling of the con-
verter is accomplished by circulating the transaxle
fluid through a remote cooler. There are two types of
coolers used. An oil-to-water type cooler located in
the radiator side tank and/or an oil-to-air heat
exchanger. The torque converter assembly is a sealed
unit that cannot be disassembled.
The transaxle fluid is filtered by an internal filter
attached to the lower side of the valve body assembly.Engine torque is transmitted to the torque con-
verter and then through the input shaft to multiple-
disc clutches in the transaxle. The power flow
depends on the application of the clutches and bands.
Refer to Elements in Use Chart in Diagnosis and
Tests section.
The transaxle consists of:
²Two multiple-disc clutches
²An overrunning clutch
²Two servos
²A hydraulic accumulator
²Two bands
²Two planetary gear sets
This provides three forward ratios and a reverse
ratio. The common sun gear of the planetary gear
sets is connected to the front clutch by a driving
shell. The driving shell is splined to the sun gear and
front clutch retainer. The hydraulic system consists
of an oil pump and a single valve body which con-
tains all of the valves except the governor valves.
The transaxle sump and differential sump are both
vented through the dipstick. Output torque from the
main center line is delivered through helical gears to
the transfer shaft. This gear set is a factor in the
transaxle final drive (axle) ratio. The shaft also car-
ries the governor and parking sprag. An integral heli-
cal gear on the transfer shaft drives the differential
ring gear.
21 - 22 AUTOMATIC - 31THRS
ProCarManuals.com
Page 1520 of 2321
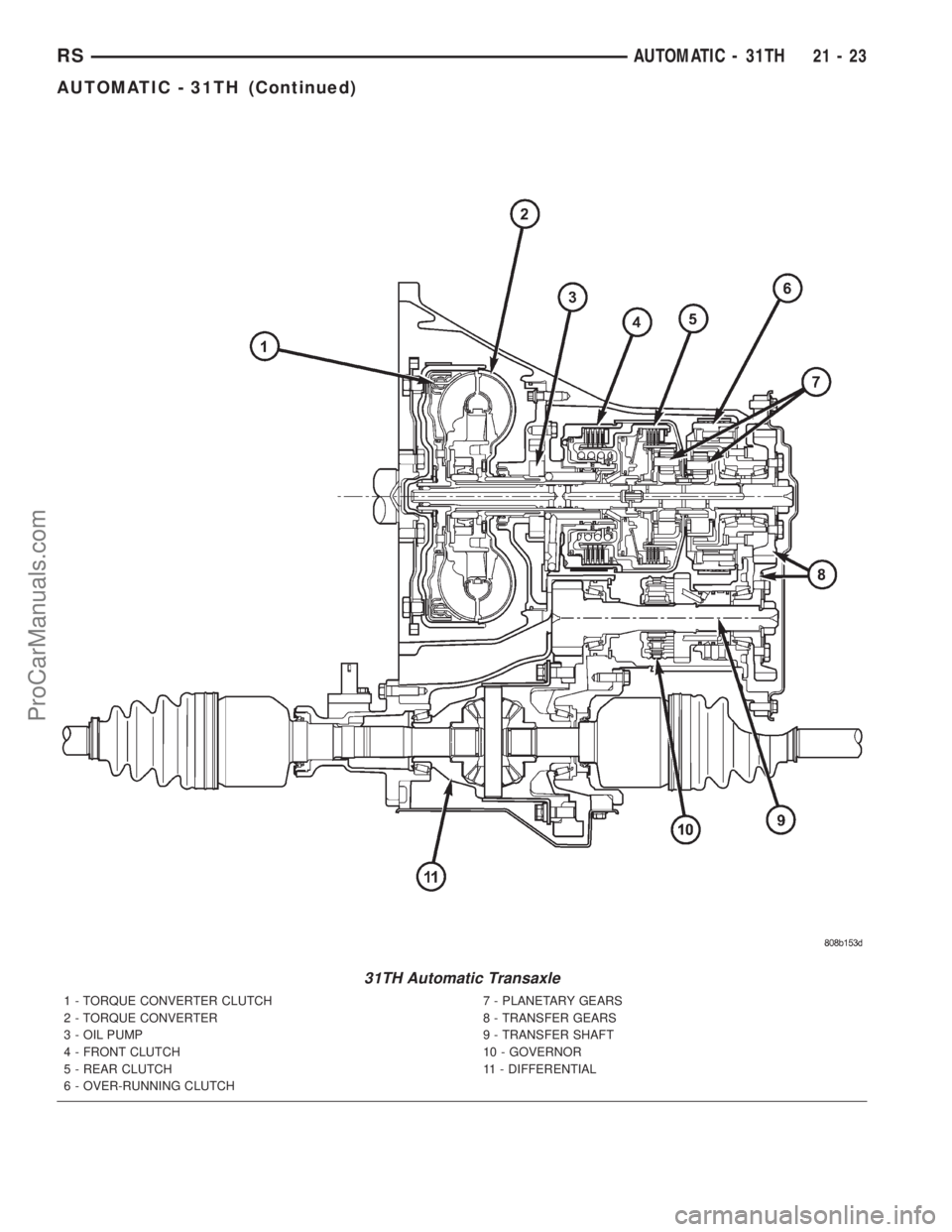
31TH Automatic Transaxle
1 - TORQUE CONVERTER CLUTCH
2 - TORQUE CONVERTER
3 - OIL PUMP
4 - FRONT CLUTCH
5 - REAR CLUTCH
6 - OVER-RUNNING CLUTCH7 - PLANETARY GEARS
8 - TRANSFER GEARS
9 - TRANSFER SHAFT
10 - GOVERNOR
11 - DIFFERENTIAL
RSAUTOMATIC - 31TH21-23
AUTOMATIC - 31TH (Continued)
ProCarManuals.com
Page 1523 of 2321

CONDITION POSSIBLE CAUSES CORRECTION
NO DRIVE OR
REVERSE (VEHICLE
WILL NOT MOVE)1. Fluid Level Low. 1. Add fluid and check for leaks if drive is
restored.
2. Gearshift Linkage/Cable Loose/
Misadjusted.2. Inspect, adjust and reassemble linkage
as needed. Replace worn/damaged parts.
3. Filter Plugged. 3. Remove and disassemble transmission.
Repair or replace failed components as
needed. Replace filter. If filter and fluid
contained clutch material or metal
particles, an overhaul may be necessary.
Perform lube flow test. Flush oil. Replace
cooler as necessary.
4. Oil Pump Damaged. 4. Perform pressure test to confirm low
pressure. Replace pump body assembly if
necessary.
5. Valve Body Malfunctioned. 5. Check press and inspect valve body.
Replace valve body (as assembly) if any
valve or bore is damaged. Clean and
reassemble correctly if all parts are in
good condition.
6. Transmission Internal Component
Damaged.6. Remove and disassemble transmission.
Repair or replace failed components as
needed. Remove and disassemble
transmission. Repair or replace failed
components as needed.
7. Park Sprag not Releasing - Check Stall
Speed, Worn/Damaged/Stuck.7. Remove, disassemble, repair.
8. Torque Converter Damage. 8. Inspect and replace as required.
SHIFTS DELAYED OR
ERRATIC (ALSO
SHIFTS HARSH AT
TIMES)1. Fluid Level Low/High. 1. Correct fluid level and check for leaks if
low.
2. Fluid Filter Clogged. 2. Replace filter. If filter and fluid
contained clutch material or metal
particles, an overhaul may be necessary.
Perform lube flow test.
3. Throttle Linkage Misadjusted. 3. Adjust linkage as described in service
section.
4. Throttle Linkage Binding. 4. Check cable for binding. Check for
return to closed throttle at transmission.
5. Gearshift Linkage/Cable Misadjusted. 5. Adjust linkage/cable as described in
service section.
6. Governor Valve Sticking. 6. Inspect, clean or repair.
7. Governor Seal Rings Worn/Damaged. 7. Inspect/replace.
8. Clutch or Servo Failure. 8. Remove valve body and air test clutch,
and band servo operation. Disassemble
and repair transmission as needed.
9. Front Band Misadjusted. 9. Adjust band.
10. Pump Suction Passage Leak. 10. Check for excessive foam on dipstick
after normal driving. Check for loose
pump bolts, defective gasket. Replace
pump assembly if needed.
21 - 26 AUTOMATIC - 31THRS
AUTOMATIC - 31TH (Continued)
ProCarManuals.com
Page 1526 of 2321

CONDITION POSSIBLE CAUSES CORRECTION
SLIPS IN FORWARD
DRIVE RANGES1. Fluid Level Low. 1. Add fluid and check for leaks.
2. Fluid Foaming. 2. Check for high oil level, bad pump
gasket or seals, dirt between pump halves
and loose pump bolts. Replace pump if
necessary.
3. Throttle Linkage Misadjusted. 3. Adjust linkage.
4. Gearshift Linkage Misadjusted. 4. Adjust linkage.
5. Rear Clutch Worn. 5. Inspect and replace as needed.
6. Low Hydraulic Pressure Due to Worn
Pump, Incorrect Control Pressure
Adjustments, Valve Body Warpage or
Malfunction, Sticking Governor, Leaking
Seal Rings, Clutch Seals Leaking, Servo
Leaks, Clogged Filter or Cooler Lines6. Perform hydraulic and air pressure
tests to determine cause.
7. Rear Clutch Malfunction, Leaking Seals
or Worn Plates.7. Air pressure check clutch-servo
operation and repair as required.
8. Overrunning Clutch Worn, Not Holding
(Slips in 1 Only).8. Replace Clutch.
SLIPS IN LOW GEAR
9D9ONLY, BUT NOT IN
1 POSITIONOverrunning Clutch Faulty. Replace overrunning clutch.
GROWLING, GRATING
OR SCRAPING
NOISES1. Drive Plate Broken. 1. Replace.
2. Torque Converter Bolts Hitting Dust
Shield.2. Dust shield bent. Replace or repair.
3. Planetary Gear Set Broken/Seized. 3. Check for debris in oil pan and repair
as required.
4. Overrunning Clutch Worn/Broken. 4. Inspect and check for debris in oil pan.
Repair as required.
5. Oil Pump Components Scored/Binding. 5. Remove, inspect and repair as
required.
6. Output Shaft Bearing or Bushing
Damaged.6. Remove, inspect and repair as
required.
7. Clutch Operation Faulty. 7. Perform air pressure check and repair
as required.
8. Front and Rear Bands Misadjusted. 8. Adjust bands.
DRAGS OR LOCKS UP 1. Fluid Level Low. 1. Check and adjust level.
2. Clutch Dragging/Failed 2. Air pressure check clutch operation and
repair as required.
3. Front or Rear Band Misadjusted. 3. Adjust bands.
4. Case Leaks Internally. 4. Check for leakage between passages
in case.
5. Servo Band or Linkage Malfunction. 5. Air pressure check servo operation and
repair as required.
6. Overrunning Clutch Worn. 6. Remove and inspect clutch. Repair as
required.
7. Planetary Gears Broken. 7. Remove, inspect and repair as required
(look for debris in oil pan).
RSAUTOMATIC - 31TH21-29
AUTOMATIC - 31TH (Continued)
ProCarManuals.com
Page 1527 of 2321

CONDITION POSSIBLE CAUSES CORRECTION
WHINE/NOISE
RELATED TO ENGINE
SPEED1. Fluid Level Low. 1. Add fluid and check for leaks.
2. Shift Cable Incorrect Routing. 2. Check shift cable for correct routing.
Should not touch engine or bell housing.
TORQUE CONVERTER
LOCKS UP IN
SECOND AND/OR
THIRD GEARLockup Solenoid, Relay or Wiring
Shorted/Open.Test solenoid, relay and wiring for
continuity, shorts or grounds. Replace
solenoid and relay if faulty. Repair wiring
and connectors as necessary.
HARSH 1-2 OR 2-3
SHIFTSLockup Solenoid Malfunction. Remove valve body and replace solenoid
assembly.
NO START IN PARK
OR NEUTRAL1. Gearshift Linkage/Cable Misadjusted. 1. Adjust linkage/cable.
2. Neutral Switch Wire Open/Cut. 2. Check continuity with test lamp. Repair
as required.
3. Neutral Switch Faulty. 3. Refer to service section for test and
replacement procedure.
4. Neutral Switch Connect Faulty. 4. Connectors spread open. Repair.
5. Valve Body Manual Lever Assembly
Bent/Worn/Broken.5. Inspect lever assembly and replace if
damaged.
NO REVERSE (OR
SLIPS IN REVERSE)1. Direct Clutch Pack (front clutch) Worn. 1. Disassemble unit and rebuild clutch
pack.
2. Rear Band Misadjusted. 2. Adjust band.
3. Front Clutch Malfunctioned/Burnt. 3. Air pressure test clutch operation.
Remove and rebuild if necessary.
OIL LEAKS (ITEMS
LISTED REPRESENT
POSSIBLE LEAK
POINTS AND SHOULD
ALL BE CHECKED.1. Fluid Lines and Fittings Loose/Leaks/
Damaged.1. Tighten fittings. If leaks persist, replace
fittings and lines if necessary.
2. Filler Tube (where tube enters case)
Leaks/Damaged.2. Replace tube seal. Inspect tube for
cracks in tube.
3. Pressure Port Plug Loose Loose/
Damaged.3. Tighten to correct torque. Replace plug
or reseal if leak persists.
4. Pan Gasket Leaks. 4. Tighten pan screws to 150 inch
pounds. If leaks persist, replace gasket.
Do no over tighten screws.
5. Valve Body Manual Lever Shaft Seal
Leaks/Worn.5. Replace shaft seal.
6. Rear Bearing Access Plate Leaks. 6. Replace gasket. Tighten screws.
7. Gasket Damaged or Bolts are Loose. 7. Replace bolts or gasket or tighten both.
8. Adapter/Extension Gasket Damaged
Leaks/Damaged.8. Replace gasket.
9. Neutral Switch Leaks/Damaged. 9. Replace switch and gasket.
10. Converter Housing Area Leaks. 10. Check for leaks at seal caused by
worn seal or burr on converter hub
(cutting seal), worn bushing, missing oil
return, oil in front pump housing or hole
plugged. Check for leaks past O-ring seal
on pump or past pump-to-case bolts;
pump housing porous, oil coming out vent
due to overfill or leak past front band shaft
access plug.
21 - 30 AUTOMATIC - 31THRS
AUTOMATIC - 31TH (Continued)
ProCarManuals.com
Page 1528 of 2321
CONDITION POSSIBLE CAUSES CORRECTION
11. Pump Seal Leaks/Worn/Damaged. 11. Replace seal.
12. Torque Converter Weld Leak/Cracked
Hub.12. Replace converter.
13. Case Porosity Leaks. 13. Replace case.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - ROAD TEST
Prior to performing a road test, check the fluid
level and throttle valve cable adjustments.
During the road test, the transaxle should be oper-
ated in each position to check for slipping and any
variation in shifting.
If vehicle operates at high speeds, but has poor
acceleration, the converter's overrunning clutch may
be slipping. If acceleration is normal, but high throt-
tle opening is needed for high speeds, the stator
clutch may have seized.Observe closely for slipping or engine speed flare-
up. Slipping or flare-up in any gear usually indicates
clutch, band, or overrunning clutch problems. If the
condition is far advanced, an overhaul will probably
be necessary to restore normal operation.
In most cases, the clutch or band that is slipping
can be determined by noting the transaxle operation
in all selector positions and then comparing which
internal units are applied in those positions. The Ele-
ments±in±Use Chart provides a basis for road test
analysis.
CLUTCHES BANDS
LEVER START PARK
FRONT REAR LOCKUPOVER-
RUNNING(KICKDOWN) LOW/REV
POSITION SAFETY SPRAG FRONT REAR
PÐ
PARKXX
RÐ
REVERSEXX
NÐ
NEUTRALX
DÐ
DRIVE
First X X
Second X X
Third X X X
2Ð
SECOND
First X X
Second X X
1 Ð Low X X
The rear clutch is applied in both the D first gear
and 1 first gear positions. Also, the overrunning
clutch is applied in D first gear and the low/reverse
band is applied in 1 first gear position. If the trans-
axle slips in D range first gear, but does not slip in 1
first gear, the overrunning clutch is slipping. Simi-
larly, if the transaxle slips in any two forward gears,
the rear clutch is slipping.Using the same procedure, the rear clutch and
front clutch are applied in D third gear. If the trans-
axle slips in third gear, either the front clutch or the
rear clutch is slipping. By selecting another gear that
does not use one of those units, the unit that is slip-
ping can be determined. If the transaxle also slips in
reverse, the front clutch is slipping. If the transaxle
does not slip in reverse, the rear clutch is slipping.
RSAUTOMATIC - 31TH21-31
AUTOMATIC - 31TH (Continued)
ProCarManuals.com
Page 1531 of 2321

(5) Low line pressure in all positions indicates a
defective pump, a clogged filter, or a stuck pressure
regulator valve.
GOVERNOR PRESSURE
Test only if transaxle shifts at wrong vehicle
speeds when throttle cable is correctly adjusted.
(1) Connect a 100 psi gauge to governor pressure
port. It is located at lower right side of case, below
differential cover (Fig. 2).
(2) Operate transaxle in third gear to read pres-
sures. The governor pressure should respond
smoothly to changes in mph and should return to 0
to 3 psi when vehicle is stopped. High pressure
(above 3 psi) at standstill will prevent the transaxle
from downshifting.
THROTTLE PRESSURE
No gauge port is provided for throttle pressure.
Incorrect throttle pressure should be suspected if
part throttle upshift speeds are either delayed or
occur too early in relation to vehicle speed. Engine
runaway on shifts can also be an indicator of low
throttle pressure setting, or misadjusted throttle
cable.
In no case should throttle pressure be adjusted
until the transaxle throttle cable adjustment has
been verified to be correct.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - TORQUE
CONVERTER HOUSING FLUID LEAKAGE
When diagnosing converter housing fluid leaks,
three actions must be taken before repair:
(1) Verify proper transmission fluid level.
(2) Verify that the leak originates from the con-
verter housing area and is transmission fluid.
(3) Determine the true source of the leak.
Fluid leakage at or around the torque converter
area may originate from an engine oil leak (Fig. 3).
The area should be examined closely. Factory fill
fluid is red and, therefore, can be distinguished from
engine oil.
Some suspected converter housing fluid leaks may
not be leaks at all. They may only be the result of
residual fluid in the converter housing, or excess
fluid spilled during factory fill, or fill after repair.
Converter housing leaks have several potential
sources. Through careful observation, a leak source
can be identified before removing the transmission
for repair.
Pump seal leaks tend to move along the drive hub
and onto the rear of the converter (Fig. 3). Pump
o-ring or pump body leaks follow the same path as a
seal leak. Pump attaching bolt leaks are generally
deposited on the inside of the converter housing and
not on the converter itself. Pump seal or gasket leaksusually travel down the inside of the converter hous-
ing (Fig. 3).
TORQUE CONVERTER LEAKAGE
Possible sources of torque converter leakage are:
²Torque converter weld leaks at the outside diam-
eter weld (Fig. 4).
²Torque converter hub weld (Fig. 4).
Fig. 3 Converter Housing Leak Paths
1 - PUMP SEAL
2 - PUMP VENT
3 - PUMP BOLT
4 - PUMP GASKET
5 - CONVERTER HOUSING
6 - CONVERTER
7 - REAR MAIN SEAL LEAK
Fig. 4 Converter Leak PointsÐTypical
1 - OUTSIDE DIAMETER WELD
2 - TORQUE CONVERTER HUB WELD
3 - STARTER RING GEAR
4 - LUG
21 - 34 AUTOMATIC - 31THRS
AUTOMATIC - 31TH (Continued)
ProCarManuals.com
Page 1532 of 2321
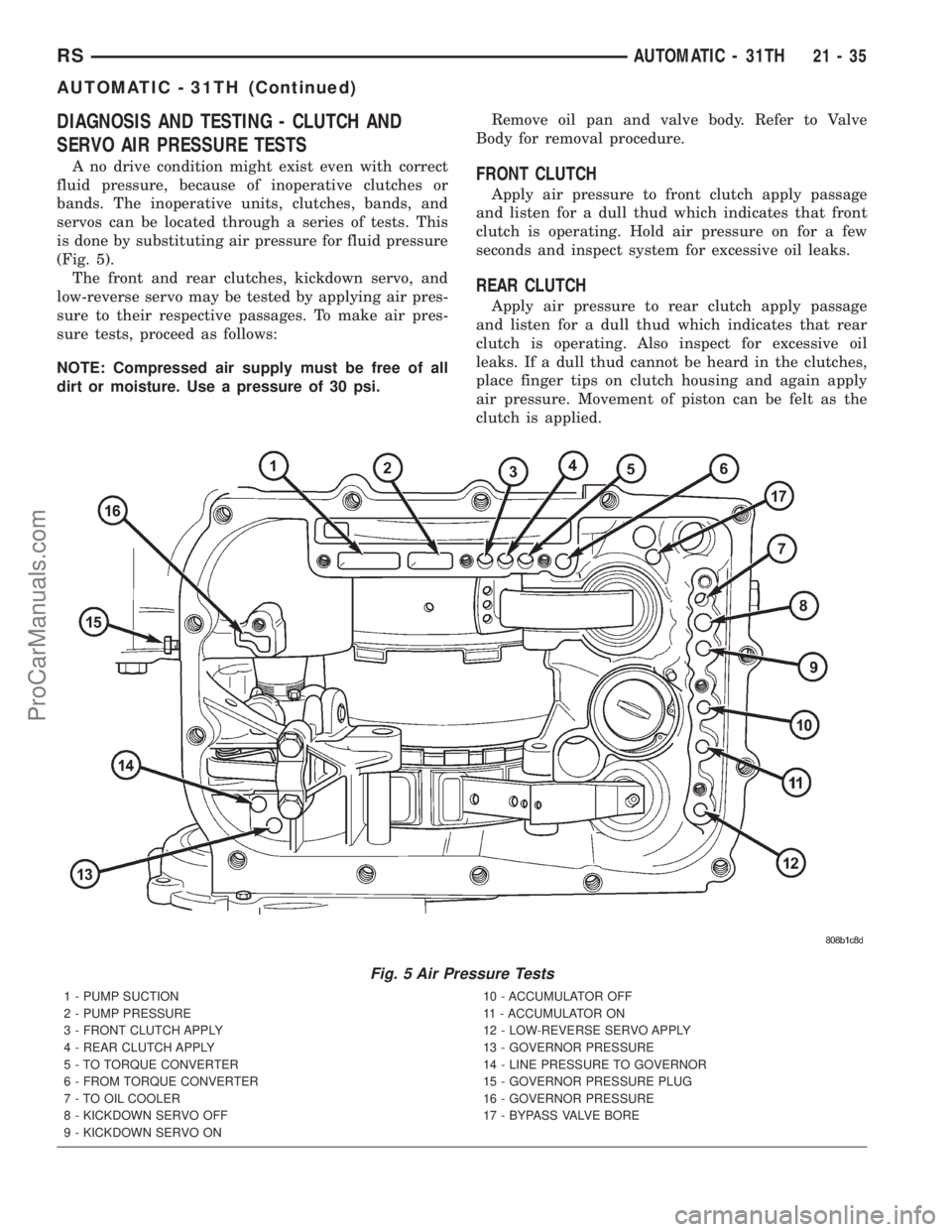
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - CLUTCH AND
SERVO AIR PRESSURE TESTS
A no drive condition might exist even with correct
fluid pressure, because of inoperative clutches or
bands. The inoperative units, clutches, bands, and
servos can be located through a series of tests. This
is done by substituting air pressure for fluid pressure
(Fig. 5).
The front and rear clutches, kickdown servo, and
low-reverse servo may be tested by applying air pres-
sure to their respective passages. To make air pres-
sure tests, proceed as follows:
NOTE: Compressed air supply must be free of all
dirt or moisture. Use a pressure of 30 psi.Remove oil pan and valve body. Refer to Valve
Body for removal procedure.FRONT CLUTCH
Apply air pressure to front clutch apply passage
and listen for a dull thud which indicates that front
clutch is operating. Hold air pressure on for a few
seconds and inspect system for excessive oil leaks.
REAR CLUTCH
Apply air pressure to rear clutch apply passage
and listen for a dull thud which indicates that rear
clutch is operating. Also inspect for excessive oil
leaks. If a dull thud cannot be heard in the clutches,
place finger tips on clutch housing and again apply
air pressure. Movement of piston can be felt as the
clutch is applied.
Fig. 5 Air Pressure Tests
1 - PUMP SUCTION
2 - PUMP PRESSURE
3 - FRONT CLUTCH APPLY
4 - REAR CLUTCH APPLY
5 - TO TORQUE CONVERTER
6 - FROM TORQUE CONVERTER
7 - TO OIL COOLER
8 - KICKDOWN SERVO OFF
9 - KICKDOWN SERVO ON10 - ACCUMULATOR OFF
11 - ACCUMULATOR ON
12 - LOW-REVERSE SERVO APPLY
13 - GOVERNOR PRESSURE
14 - LINE PRESSURE TO GOVERNOR
15 - GOVERNOR PRESSURE PLUG
16 - GOVERNOR PRESSURE
17 - BYPASS VALVE BORE
RSAUTOMATIC - 31TH21-35
AUTOMATIC - 31TH (Continued)
ProCarManuals.com