2001 DODGE TOWN AND COUNTRY tire type
[x] Cancel search: tire typePage 28 of 2321

LUBRICANTS AND GREASES
Lubricating grease is rated for quality and usage
by the NLGI. All approved products have the NLGI
symbol (Fig. 7) on the label. At the bottom NLGI
symbol is the usage and quality identification letters.
Wheel bearing lubricant is identified by the letter
ªGº. Chassis lubricant is identified by the latter ªLº.
The letter following the usage letter indicates the
quality of the lubricant. The following symbols indi-
cate the highest quality.
OPERATION
The cooling system is designed around the coolant.
The coolant must accept heat from engine metal, in
the cylinder head area near the exhaust valves and
engine block. Then coolant carries the heat to the
radiator where the tube/fin radiator can transfer the
heat to the air.
WARNING: ANTIFREEZE IS AN ETHYLENE GLYCOL
BASE COOLANT AND IS HARMFUL IF SWAL-
LOWED OR INHALED. IF SWALLOWED, DRINK
TWO GLASSES OF WATER AND INDUCE VOMIT-
ING. IF INHALED, MOVE TO FRESH AIR AREA.
SEEK MEDICAL ATTENTION IMMEDIATELY. DO NOT
STORE IN OPEN OR UNMARKED CONTAINERS.
WASH SKIN AND CLOTHING THOROUGHLY AFTER
COMING IN CONTACT WITH ETHYLENE GLYCOL.
KEEP OUT OF REACH OF CHILDREN. DISPOSE OF
GLYCOL BASE COOLANT PROPERLY, CONTACT
YOUR DEALER OR GOVERNMENT AGENCY FOR
LOCATION OF COLLECTION CENTER IN YOUR
AREA. DO NOT OPEN A COOLING SYSTEM WHEN
THE ENGINE IS AT OPERATING TEMPERATURE OR
HOT UNDER PRESSURE, PERSONAL INJURY CAN
RESULT. AVOID RADIATOR COOLING FAN WHEN
ENGINE COMPARTMENT RELATED SERVICE IS
PERFORMED, PERSONAL INJURY CAN RESULT.
FLUID FILL/CHECK
LOCATIONS
DESCRIPTION
The fluid check/fill points and lubrication locations
are located in each applicable Sections.
MAINTENANCE SCHEDULES
DESCRIPTION
There are two maintenance schedules that show
proper service for your vehicle.
First is Schedule ±A. It lists all the scheduled
maintenance to be performed under ªnormalº operat-
ing conditions.
Second is Schedule ±B. It is a schedule for vehi-
cles that are operated under the following conditions:
²Frequent short trip driving less than 10 miles
(16.2 km)
²Frequent driving in dusty conditions
²Frequent off-road or desert operation
²Frequent trailer towing
²Day and night temperatures are below freezing
²Frequent long periods of engine idling
²Frequent stop and go driving
²More than 50% of your driving is at sustained
high speeds during hot weather, above 90ÉF (32ÉC)*
²Taxi, police or delivery service
²If equipped for and operation with E-85
(ethanol) fuel.
DESCRIPTION
At Each Stop For Fuel
²Check engine oil level and add as required.
²Check windshield washer solvent and add as
required.
Once A Month
²Check tire pressure and look for unusual wear
or damage.
²Check fluid levels of coolant reservoir, brake
master cylinder, power steering and transmission.
Add fluid as required.
²Check all lights and all other electrical items for
correct operation.
At Each Oil Change
²Change oil filter
²Inspect the exhaust system.
²Inspect brake hoses.
²Inspect the CV joints and front suspension com-
ponent boots and seals.
²Rotate the tires at each oil change interval
shown on Schedule ± A (7,500 miles - 12 000 km) or
Fig. 7 NLGI Symbol
1 - WHEEL BEARINGS
2 - CHASSIS LUBRICATION
3 - CHASSIS AND WHEEL BEARINGS
RSLUBRICATION & MAINTENANCE0-7
FLUID TYPES (Continued)
ProCarManuals.com
Page 44 of 2321

FLUID FILL/CHECK
LOCATIONS
DESCRIPTION
The fluid check/fill points and lubrication locations
are located in each applicable service manual section.
MAINTENANCE SCHEDULES
MAINTENANCE SCHEDULES - DIESEL ENGINE
There are two maintenance schedules that show
proper service for the vehicle.
First is ScheduleªAº. It lists all the scheduled
maintenance to be performed under ªnormalº operat-
ing conditions.
Second is ScheduleªBº. It is a schedule for vehi-
cles that are operated under the conditions listed at
the beginning of the schedule.
Use the schedule that best describes the driving
conditions.
Where time and mileage are listed, follow the
interval that occurs first.
At Each Stop for Fuel
²Check the engine oil level, add as required.
²Check the windshield washer solvent and add if
required.
Once a Month
²Check the tire pressure and look for unusual
wear or damage.
²Inspect the battery and clean and tighten termi-
nals as required.
²Check the fluid levels of coolant reservoir, brake
master cylinder, power steering and transaxle and
add as needed.
²Check all lights and all other electrical items for
correct operation.
²Check the rubber seals on each side of the radi-
ator for proper fit.
At Each Oil Change
²Replace the engine oil filter at each oil change.
²Inspect exhaust system.
²Inspect brake hoses
²Inspect the CV joints and front suspension com-
ponents
²Rotate the tires at each oil change interval
shown on schedule ªAº 20 000 km or every other
interval shown on schedule ªBº 20 000 km.
²Check the coolant level, hoses, and clamps.
²Inspect brake linings, hoses and calipers.
²Inspect engine accessory drive belts.
²Inspect for presence of water in fuel filter/water
separator, drain if necessary.
SCHEDULE ªAº
20 000 km (12 000 miles)
²Change engine oil. (1)
²Replace engine oil filter.
²Inspect air filter element. Replace as necessary.
40 000 km (24 000 Miles)
²Change engine oil. (1)
²Replace engine oil filter.
²Replace air filter element.
²Replace fuel filter/water separator element. (2)
²Check alignment.
60 000 km (37 000 Miles)
²Change engine oil. (1)
²Replace engine oil filter.
²Inspect air filter element. Replace as necessary.
80 000 km (49 000 Miles)
²Change engine oil. (1)
²Replace engine oil filter.
²Replace air filter element.
²Replace fuel filter/water separator element. (2)
²Check alignment.
100 000 km (62 000 Miles)
²Change engine oil. (1)
²Replace engine oil filter.
²Inspect air filter element. Replace as necessary.
120 000 km (75 000 Miles)
²Change engine oil. (1)
²Replace engine oil filter.
²Replace air filter element.
²Replace fuel filter/water separator element. (2)
²Check alignment.
140 000 km (86 000 miles)
²Change engine oil. (1)
²Replace engine oil filter.
²Inspect air filter element. Replace as necessary.
Fig. 6 Engine Oil Viscosity Recommendation ±
Diesel Engines
RGLUBRICATION & MAINTENANCE - RG - 2.5 L TURBO DIESEL0a-5
FLUID TYPES (Continued)
ProCarManuals.com
Page 53 of 2321

BUSHINGS
REMOVAL - STABILIZER BAR CUSHION
(1) Raise Vehicle. Refer to Hoisting in Lubrication
and Maintenance.
(2) Remove the 2 bolts fastening the emission leak
detection pump to the cradle crossmember reinforce-
ment.
(3) Move the leak detection pump to the side
allowing access to the stabilizer bar cushion retain-
ers.
(4) Remove the nut and bolt securing each stabi-
lizer bar cushion retainer to the cradle crossmember
(Fig. 2) and remove the retainers.
(5) Remove each stabilizer bar cushion from the
stabilizer bar by opening the slit in the cushion and
peeling it off the stabilizer bar.
INSTALLATION - STABILIZER BAR CUSHION
(1) Install each new cushion on stabilizer bar by
spreading cushion at slit and forcing it onto stabilizer
bar.
NOTE: Cushions must be installed on stabilizer bar
so the square corner of the bushing will be down
and slit in cushion will be facing the rear of the
vehicle when the stabilizer bar is installed (Fig. 3).
(2) Place stabilizer bar into mounted position with
cushions properly aligned.
(3) Hook each retainer into cradle crossmember
mounting hole and over cushion.(4) Install each mounting bolt from rear of cradle
crossmember through retainer. Install the two nuts
and tighten to 68 N´m (50 ft. lbs.) torque.
(5) Reattach emission leak detection pump to cra-
dle crossmember reinforcement with two mounting
bolts.
(6) Lower the vehicle.
HUB / BEARING
DESCRIPTION
The front wheel bearing and front wheel hub of
this vehicle are a hub and bearing unit type assem-
bly. This unit combines the front wheel mounting
hub (flange) and the front wheel bearing into a
sealed one-piece unit. The hub and bearing is
mounted to the center of the steering knuckle (Fig.
1). It is retained by four mounting bolts accessible
from the rear of the steering knuckle. The hub flange
has five wheel mounting studs.
The wheel mounting studs used to mount the tire
and wheel to the vehicle are the only replaceable
components of the hub and bearing assembly. Other-
wise, the hub and bearing is serviced only as a com-
plete assembly.
OPERATION
The hub and bearing has internal bearings that
allow the hub to rotate with the driveshaft, along
with the tire and wheel. The five wheel mounting
studs mount the tire and wheel, and brake rotor to
the vehicle.
Fig. 2 Front Stabilizer Bar Cushion Retainers
1 - STEERING GEAR
2 - STABILIZER BAR
3 - RAISED BEAD
4 - FRONT CRADLE CROSSMEMBER
5 - RETAINERS
Fig. 3 Correctly Installed Stabilizer Bar Cushion
1 - SLIT
2 - SQUARE CORNER
3 - STABILIZER BAR
4 - STABILIZER BAR CUSHION (BUSHING)
2 - 4 FRONTRS
ProCarManuals.com
Page 54 of 2321
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - HUB AND
BEARING (FRONT)
The condition of the front hub and bearing assem-
bly is diagnosed using the inspection and testing pro-
cedure detailed below.
The bearing contained in the Unit III front hub/
bearing assembly will produce noise and vibration
when worn or damaged. The noise will generally
change when the bearings are loaded. A road test of
the vehicle is normally required to determine the
location of a worn or damaged bearing.
Find a smooth level road surface and bring the
vehicle up to a constant speed. When vehicle is at a
constant speed, swerve the vehicle back and forth
from the left and to the right. This will load and
unload the bearings and change the noise level.
Where axle bearing damage is slight, the noise is
usually not noticeable at speeds above 48 km/h (30
mph).
REMOVAL - HUB AND BEARING
NOTE: Replacement of the Unit III front hub/bearing
assembly can be normally done without having to
remove the steering knuckle from the vehicle. In the
event that the hub/bearing is frozen in the steering
knuckle and cannot be removed by hand, it will
have to be pressed out of the steering knuckle. The
steering knuckle will require removal from the vehi-
cle to allow the hub/bearing assembly to be
pressed out of the steering knuckle. (Refer to 2 -
SUSPENSION/FRONT/KNUCKLE - REMOVAL)
(1) Raise vehicle on jack stands or centered on a
frame contact type hoist. See Hoisting in Lubrication
and Maintenance.
(2) Remove wheel lug nuts, and front tire and
wheel assembly.
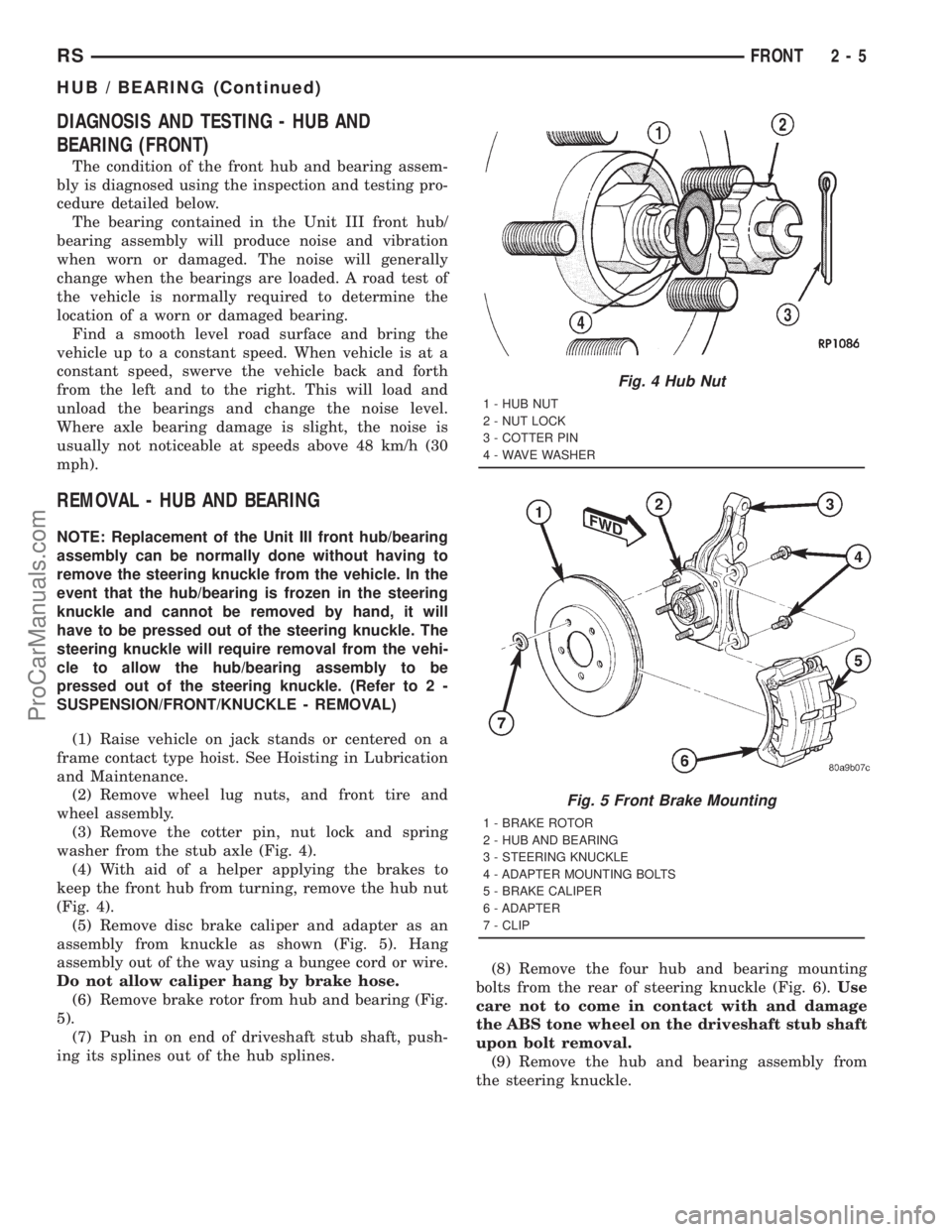
(3) Remove the cotter pin, nut lock and spring
washer from the stub axle (Fig. 4).
(4) With aid of a helper applying the brakes to
keep the front hub from turning, remove the hub nut
(Fig. 4).
(5) Remove disc brake caliper and adapter as an
assembly from knuckle as shown (Fig. 5). Hang
assembly out of the way using a bungee cord or wire.
Do not allow caliper hang by brake hose.
(6) Remove brake rotor from hub and bearing (Fig.
5).
(7) Push in on end of driveshaft stub shaft, push-
ing its splines out of the hub splines.(8) Remove the four hub and bearing mounting
bolts from the rear of steering knuckle (Fig. 6).Use
care not to come in contact with and damage
the ABS tone wheel on the driveshaft stub shaft
upon bolt removal.
(9) Remove the hub and bearing assembly from
the steering knuckle.
Fig. 4 Hub Nut
1 - HUB NUT
2 - NUT LOCK
3 - COTTER PIN
4 - WAVE WASHER
Fig. 5 Front Brake Mounting
1 - BRAKE ROTOR
2 - HUB AND BEARING
3 - STEERING KNUCKLE
4 - ADAPTER MOUNTING BOLTS
5 - BRAKE CALIPER
6 - ADAPTER
7 - CLIP
RSFRONT2-5
HUB / BEARING (Continued)
ProCarManuals.com
Page 56 of 2321

REMOVAL - STEERING KNUCKLE
(1) Raise vehicle on jack stands or centered on a
frame contact type hoist. Refer to Hoisting in Lubri-
cation And Maintenance.
(2) Remove the wheel and tire assembly from the
vehicle.
(3) Remove the cotter pin, nut lock and spring
washer from the end of the stub axle and hub nut
(Fig. 8).
(4) Have a helper apply the vehicle's brakes to
keep hub from turning,loosen and removethe hub
nut (Fig. 8).
(5) Remove disc brake caliper and adapter as an
assembly from knuckle as shown (Fig. 9). Hang
assembly out of the way using a bungee cord or wire
(Fig. 10).Do not allow caliper to hang by brake
hose.
(6) Remove nut attaching outer tie rod end to
steering knuckle by holding the tie rod end stud
while loosening and removing nut with a wrench
(Fig. 11).
(7) Remove tie rod end from steering knuckle
using Remover, Special Tool C-3894±A (Fig. 12).
(8) If equipped with antilock brakes, remove the
front wheel speed sensor from the steering knuckle
(Fig. 13).
(9) Remove the two steering knuckle-to-strut clevis
bracket attaching bolts.
(10) Tip the knuckle outward and remove the
driveshaft stub axle from the hub and bearing. Sus-
pend driveshaft straight outward using a bungee
cord or wire (Fig. 10).Do not allow driveshaft to
hang by inner joint.
Fig. 8 Hub Nut
1 - HUB NUT
2 - NUT LOCK
3 - COTTER PIN
4 - WAVE WASHER
Fig. 9 Front Brake Mounting
1 - BRAKE ROTOR
2 - HUB AND BEARING
3 - STEERING KNUCKLE
4 - ADAPTER MOUNTING BOLTS
5 - BRAKE CALIPER
6 - ADAPTER
7 - CLIP
Fig. 10 CALIPER AND DRIVESHAFT SUSPENDED
1 - HANGER SUSPENDING CALIPER
2 - HANGER SUSPENDING DRIVESHAFT
3 - DRIVESHAFT
4 - BRAKE CALIPER
RSFRONT2-7
KNUCKLE (Continued)
ProCarManuals.com
Page 59 of 2321

(5) Install steering knuckle in clevis bracket of
strut damper assembly. Install the strut clevis-to-
steering knuckle attaching bolts. Tighten both bolts
to a torque of 81 N´m (60 ft. lbs.) plus an additional
1/4 (90É) turn.
(6) Install tie rod end into knuckle steering arm.
Start nut onto stud of tie rod end. While holding stud
of tie rod end stationary using a socket (Fig. 11),
tighten tie rod end to steering knuckle attaching nut.
Then using a crowfoot on a torque wrench (Fig. 17),
tighten the tie rod end nut to a torque of 75 N´m (55
ft. lbs.).
(7) If equipped with antilock brakes, install wheel
speed sensor and mounting bolt on steering knuckle
(Fig. 13). Tighten the speed sensor bolt to a torque of
7 N´m (60 in. lbs.).
(8) Install brake rotor on hub and bearing (Fig. 9).
(9) Install disc brake caliper and adapter assembly
on steering knuckle. Install adapter amounting bolts
and tighten to 169 N´m (125 ft. lbs.).
(10) Clean any debris from the threads of the
outer C/V joint stub axle.
(11) Install the washer and hub nut on stub axle.
(12) Have a helper apply the vehicle's brakes to
keep hub from turning, then tighten hub nut to a
torque of 244 N´m (180 ft. lbs.).
(13) Install the spring wave washer on the end of
the stub axle.
(14) Install the hub nut lock, and anewcotter pin
(Fig. 8). Wrap cotter pin prongs tightly around the
hub nut lock.(15) Install wheel and tire assembly. Install and
tighten the wheel mounting nuts in proper sequence
until all nuts are torqued to half the required speci-
fication. Then repeat the tightening sequence to the
full specified torque of 135 N´m (100 ft. lbs.).
(16) Lower vehicle.
(17) Set front wheel alignment camber and toe as
necessary. (Refer to 2 - SUSPENSION/WHEEL
ALIGNMENT - STANDARD PROCEDURE)
LOWER BALL JOINT
DESCRIPTION
The ball joint is an integral part of the lower con-
trol arm (Fig. 1). The ball joint has a tapered stud
that is pressed into the aluminum knuckle. The ball
joint stud is threaded on the end for a retainer nut.
The ball joint has a non-vented seal boot. The seal
boot has an integrated heat shield (Fig. 18).
The ball joint used in the lower control arm of this
vehicle is a sealed-for-life ball joint and requires no
maintenance lubrication. The ball joint has been
lubricated-for-life during the manufacturing process.
A special fitting cap is installed on the fill port. This
cap must not be removed and replaced with a com-
mon zirc fitting. The special cap is there to eliminate
the possibility of lubrication latter during the ball
joints life, thus damaging the non-vented seal boot.
NOTE: The ball joint does not require any type of
additional lubrication for the life of the vehicle. No
attempt should be made to ever add any lubrication
to the lower ball joint.
Fig. 17 Torquing Tie Rod End Attaching Nut
(Typical)
1 - STEERING KNUCKLE
2 - TIE ROD END
3 - CROWFOOT
4 - SOCKET
5 - TORQUE WRENCH
Fig. 18 Ball Joint Seal Boot (Typical)
1 - BALL JOINT SEAL BOOT
2 - BALL JOINT STUD
3 - LOWER CONTROL ARM
4 - SHIELD
2 - 10 FRONTRS
KNUCKLE (Continued)
ProCarManuals.com
Page 61 of 2321

The lower control arm is an iron casting with two
rubber bushings and a ball joint. The lower control
arm front bushing is the spool type and is pressed
into the lower control arm. The standard lower con-
trol arm rear bushing is a push-on bushing that is
pushed over a stem on the rear of the lower control
arm. The optional lower control arm rear bushing is
a hydro-bushing that is pressed on. It has liquid
filled voids that provide more effective dampening
than the standard bushing. Vehicles with rear hydro-
bushings utilize a different lower control arm than
vehicles with standard bushings. They have a
straight slightly tapered round stem where the
hydro-bushing is mounted whereas the standard arm
has a straight stem with a squared knob on the end
to retain the bushing.
The lower control arm ball joint is pressed into the
outer end of the arm. The ball joint has a tapered
stud and retainer nut for fastening it to the steering
knuckle.
OPERATION
The lower control arm supports the lower end of
the steering knuckle and allows for the up and down
movement of the suspension during the jounce and
rebound travel. The lower control arm ball joint con-
nects the arm to the steering knuckle.
REMOVAL - LOWER CONTROL ARM
(1) Raise vehicle on jack stands or centered on a
frame contact type hoist. See Hoisting in Lubrication
and Maintenance.
(2) Remove wheel and tire assembly.(3) Remove the steering knuckle. (Refer to 2 -
SUSPENSION/FRONT/KNUCKLE - REMOVAL)
(4) Remove the bolts fastening the power steering
cooler to the front suspension cradle crossmember
reinforcement (Fig. 22).
(5) Remove the lower control arm rear bushing
retainer bolts located on each side of each lower con-
trol arm rear bushing.
NOTE: The bolts fastening the cradle crossmember
reinforcement are of two different thread sizes. Note
the location of the various sizes.
(6) Remove the bolts attaching the cradle cross-
member reinforcement to the front suspension cradle
crossmember (Fig. 23). Remove the 2 bolts fastening
the reinforcement and rear of cradle crossmember to
the body of the vehicle. Remove the reinforcement.
(7) Remove the pivot bolt attaching the front bush-
ing of the lower control arm to the front suspension
cradle crossmember.
(8) Remove the lower control arm.
DISASSEMBLY - LOWER CONTROL ARM
(REAR BUSHING - STANDARD)
(1) Remove the lower control arm from the front
suspension cradle. (Refer to 2 - SUSPENSION/
FRONT/LOWER CONTROL ARM - REMOVAL)
(2) Mount the lower control arm in a visewithout
using excessive clamping force.
Fig. 21 Installing Ball Joint Seal Boot
1 - SHIELD
2 - SPECIAL TOOL 6758
3 - LOWER CONTROL ARM
4 - BALL JOINT SEAL BOOT
Fig. 22 POWER STEERING COOLER
1 - CRADLE CROSSMEMBER REINFORCEMENT
2 - POWER STEERING COOLER
2 - 12 FRONTRS
LOWER CONTROL ARM (Continued)
ProCarManuals.com
Page 65 of 2321

(10) Install the wheel and tire assembly. Install
and tighten the wheel mounting stud nuts in proper
sequence until all nuts are torqued to half specifica-
tion. Then repeat the tightening sequence to the full
specified torque of 135 N´m (100 ft. lbs.).
(11) Raise vehicle, remove jack stands and lower
vehicle to the ground.
(12) Perform front wheel alignment as necessary.
(Refer to 2 - SUSPENSION/WHEEL ALIGNMENT -
STANDARD PROCEDURE)
STABILIZER BAR
DESCRIPTION
The stabilizer bar interconnects both front struts of
the vehicle and is attached to the front crossmember
(Fig. 1) .
Attachment of the stabilizer bar to the front cross-
member is through 2 rubber-isolator cushion bush-
ings and retainers. A double ball jointed stabilizer
bar link is used to attach each end of the stabilizer
bar to the front strut assemblies. All parts of the sta-
bilizer bar are replaceable as individual components.
The stabilizer bar to front crossmember cushion
bushings are split for easy removal and installation.
The split in the bushings should be positioned toward
the rear of the vehicle, with the square corner facing
down, when the stabilizer bar is installed.
OPERATION
Jounce and rebound movements affecting one
wheel are partially transmitted to the opposite wheel
of the vehicle through the stabilizer bar. This helpsto minimize the body roll of the vehicle during sus-
pension movement.
Connecting the stabilizer bar links to the strut
assemblies helps reduce the fore-and-aft rate of the
stabilizer bar from the rest of the front suspension.
REMOVAL - STABILIZER BAR
(1) Raise vehicle on jack stands or centered on a
frame contact type hoist. See Hoisting in Lubrication
and Maintenance.
(2) Remove the bolts fastening the power steering
cooler to the front suspension cradle crossmember
reinforcement (Fig. 32).
(3) Remove the lower control arm rear bushing
retainer bolts located on each side of each lower con-
trol arm rear bushing.
NOTE: The bolts fastening the cradle crossmember
reinforcement are of two different thread sizes. Note
the location of the various sizes.
(4) Remove the bolts attaching the cradle cross-
member reinforcement to the front suspension cradle
crossmember (Fig. 33). Remove the 2 bolts fastening
the reinforcement and rear of cradle crossmember to
the body of the vehicle. Remove the reinforcement.
CAUTION: When removing the nut from the stud of
the stabilizer bar link, do not allow the stud to
rotate in it's socket. Hold the stud from rotating by
placing an open-end wrench on the flat machined
into the stud (Fig. 34).
Fig. 31 Jack Stands Supporting Vehicle Weight
1 - LOWER CONTROL ARMS
2 - BALL JOINT
3 - JACK STANDS
4 - BALL JOINT
Fig. 32 POWER STEERING COOLER
1 - CRADLE CROSSMEMBER REINFORCEMENT
2 - POWER STEERING COOLER
2 - 16 FRONTRS
LOWER CONTROL ARM (Continued)
ProCarManuals.com