2001 DODGE RAM width
[x] Cancel search: widthPage 2515 of 2889
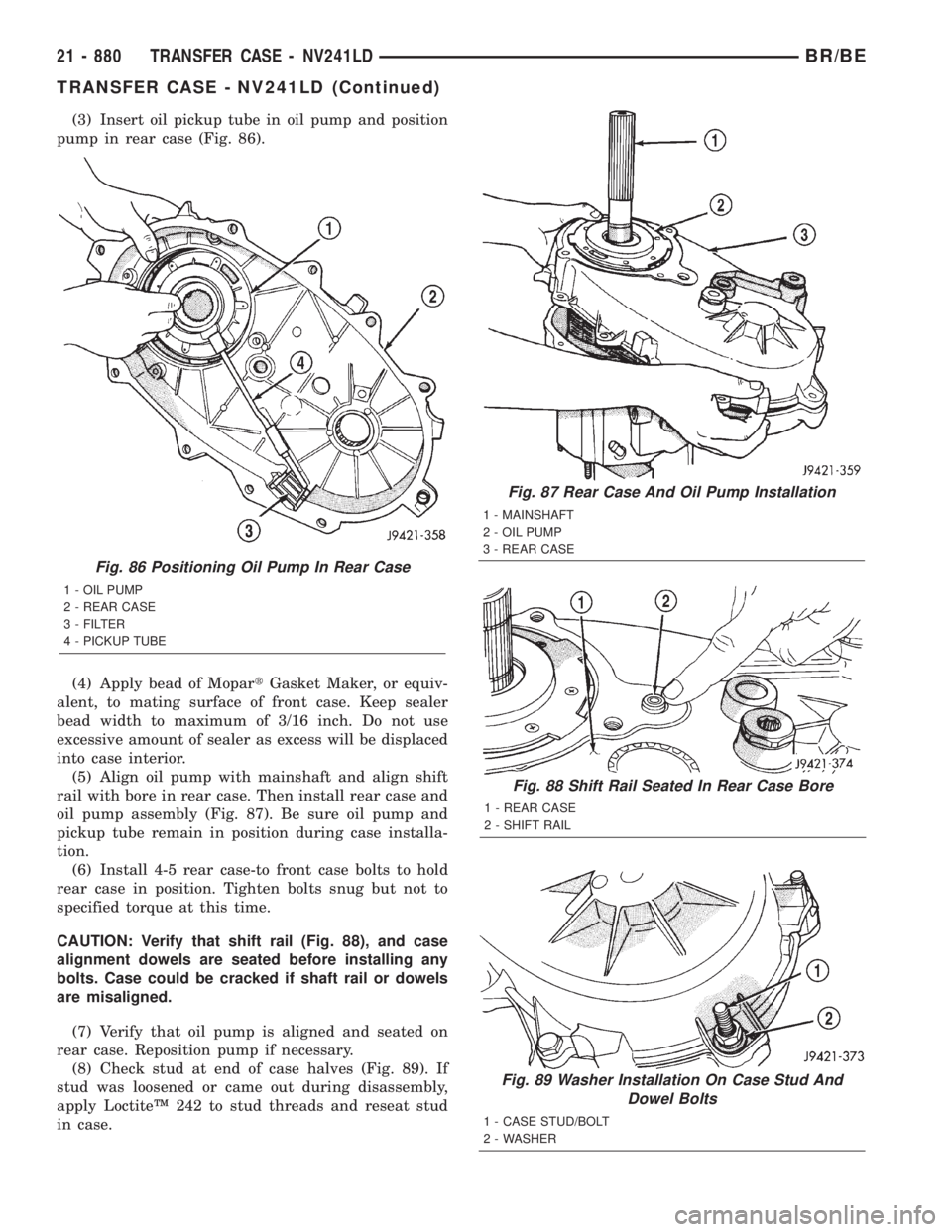
(3) Insert oil pickup tube in oil pump and position
pump in rear case (Fig. 86).
(4) Apply bead of MopartGasket Maker, or equiv-
alent, to mating surface of front case. Keep sealer
bead width to maximum of 3/16 inch. Do not use
excessive amount of sealer as excess will be displaced
into case interior.
(5) Align oil pump with mainshaft and align shift
rail with bore in rear case. Then install rear case and
oil pump assembly (Fig. 87). Be sure oil pump and
pickup tube remain in position during case installa-
tion.
(6) Install 4-5 rear case-to front case bolts to hold
rear case in position. Tighten bolts snug but not to
specified torque at this time.
CAUTION: Verify that shift rail (Fig. 88), and case
alignment dowels are seated before installing any
bolts. Case could be cracked if shaft rail or dowels
are misaligned.
(7) Verify that oil pump is aligned and seated on
rear case. Reposition pump if necessary.
(8) Check stud at end of case halves (Fig. 89). If
stud was loosened or came out during disassembly,
apply LoctiteŸ 242 to stud threads and reseat stud
in case.
Fig. 87 Rear Case And Oil Pump Installation
1 - MAINSHAFT
2 - OIL PUMP
3 - REAR CASE
Fig. 88 Shift Rail Seated In Rear Case Bore
1 - REAR CASE
2 - SHIFT RAIL
Fig. 89 Washer Installation On Case Stud And
Dowel Bolts
1 - CASE STUD/BOLT
2 - WASHER
Fig. 86 Positioning Oil Pump In Rear Case
1 - OIL PUMP
2 - REAR CASE
3 - FILTER
4 - PICKUP TUBE
21 - 880 TRANSFER CASE - NV241LDBR/BE
TRANSFER CASE - NV241LD (Continued)
Page 2517 of 2889

(4) Apply MopartSilicone Sealer to threads of rear
retainer bolts. Then install retainer bolts finger tight.
(5) Install output bearing on mainshaft and seat it
in rear retainer with suitable size pipe tool (Fig. 94).
(6) Install output bearing retaining ring (Fig. 95).
(7) Tighten rear retainer bolts to 27-34 N´m (20-25
ft. lbs.) torque.
(8) Install new seal in rear extension housing seal
with suitable size installer tool.
(9) Apply bead of MopartGasket Maker, or equiv-
alent, to mating surface of rear extension housing.
Keep sealer bead width to maximum of 3/16 inch. Do
not use excessive amount of sealer as excess could be
displaced into output bearing.
(10) Align and install rear extension on retainer
(Fig. 96).(11) Apply MopartSilicone Sealer to threads of
rear extension housing bolts. Then install and
tighten bolts to 27-34 N´m (20-25 ft. lbs.) torque.
INSTALLATION
(1) Align and seat transfer case on transmission.
Be sure transfer case input gear splines are aligned
with transmission output shaft. Align splines by
rotating transfer case rear output shaft yoke if nec-
essary. Do not install any transfer case attaching
nuts until the transfer case is completely seated
against the transmission.
(2) Install and tighten transfer case attaching
nuts. Tighten nuts to 30-41 N´m (20-30 ft.lbs.).
(3) Install rear crossmember.
(4) Remove jack stand from under transmission.
(5) Align and connect propeller shafts. (Refer to 3 -
DIFFERENTIAL & DRIVELINE/PROPELLER
SHAFT/PROPELLER SHAFT - INSTALLATION)
(6) Connect vacuum harness and vent hose.
(7) Connect shift rod to transfer case lever or floor
shift arm. Use channel lock style pliers to press rod
back into lever grommet.
(8) Adjust shift linkage, if necessary.
(9) Fill transfer case with recommended transmis-
sion fluid and install fill plug.
(10) Install skid plate, if equipped. (Refer to 13 -
FRAMES & BUMPERS/FRAME/TRANSFER CASE
SKID PLATE - INSTALLATION)
(11) Lower vehicle
Fig. 94 Output Bearing Installation
1 - OUTPUT BEARING
2 - PIPE TOOL
Fig. 95 Output Bearing Retaining Ring Installation
1 - OUTPUT BEARING
2 - RETAINING RING
Fig. 96 Rear Extension Installation
1 - REAR EXTENSION
2 - RETAINER
3 - EXTENSION SEAL
21 - 882 TRANSFER CASE - NV241LDBR/BE
TRANSFER CASE - NV241LD (Continued)
Page 2544 of 2889

(8) Install retaining ring (Fig. 59).
INPUT AND PLANETARY GEAR
(1) Lubricate planetary pinions and annulus gear
with transmission fluid.
(2) Install planetary/input gear assembly in case
(Fig. 60).
(3) Start planetary pinions in low range annulus
gear. Then tap PTO gear, with hammer handle to
seat planetary pinions in annulus gear.
(4) Install retaining ring on input gear (Fig. 61).
(5) Apply bead of MopartGasket Maker, or equiv-
alent, to mating surface of input retainer. Keep
sealer bead width to maximum of 3/16 inch. Do not
use excessive amount of sealer as excess could be dis-
placed into oil channel and feed hole in case.(6) Align oil channel in retainer with oil feed hole
in front case (Fig. 62).
(7) Install retainer on input gear shaft and front
case (Fig. 63).
Fig. 59 Retaining Ring Installation
1 - RETAINING RING
Fig. 60 Planetary/Input Gear Assembly Installation
1 - WOOD/RUBBER HAMMER HANDLE
2 - PLANETARY ASSEMBLY
Fig. 61 Installing Input Gear Retaining Ring
1 - INPUT BEARING RETAINING RING
2 - SNAP-RING PLIERS
3 - INPUT GEAR
Fig. 62 Aligning Retainer Oil Channel and Case
Feed Holes
1 - FEED HOLE
2 - FRONT CASE
3 - FEED CHANNEL
4 - BEARING RETAINER
BR/BETRANSFER CASE - NV241HD 21 - 909
TRANSFER CASE - NV241HD (Continued)
Page 2552 of 2889

(4) Apply bead of MopartGasket Maker, or equiv-
alent, to mating surface of front case. Keep sealer
bead width to maximum of 3/16 inch. Do not use
excessive amount of sealer as excess will be displaced
into case interior.
(5) Align oil pump with mainshaft and align shift
rail with bore in rear case. Then install rear case and
oil pump assembly (Fig. 92). Be sure oil pump and
pickup tube remain in position during case installa-
tion.
(6) Install 4-5 rear case-to front case bolts to hold
rear case in position. Tighten bolts snug but not to
specified torque at this time.
CAUTION: Verify that shift rail (Fig. 93), and case
alignment dowels are seated before installing any
bolts. Case could be cracked if shaft rail or dowels
are misaligned.
(7) Verify that oil pump is aligned and seated on
rear case. Reposition pump if necessary.
Fig. 91 Positioning Oil Pump In Rear Case
1 - OIL PUMP
2 - REAR CASE
3 - FILTER
4 - PICKUP TUBE
Fig. 92 Rear Case And Oil Pump Installation
1 - MAINSHAFT
2 - OIL PUMP
3 - REAR CASE
Fig. 93 Shift Rail Seated In Rear Case Bore
1 - REAR CASE
2 - SHIFT RAIL
BR/BETRANSFER CASE - NV241HD 21 - 917
TRANSFER CASE - NV241HD (Continued)
Page 2553 of 2889

(8) Check stud at end of case halves (Fig. 94). If
stud was loosened or came out during disassembly,
apply LoctiteŸ 242 to stud threads and reseat stud
in case.
(9) Apply LoctiteŸ 242 to remainder of rear case-
to-front case bolt threads and install bolts. Be sure
lock washers are used on studs/bolts at case ends.
Tighten bolts, or stud nuts as follows:
²flange head bolts to 47-61 N´m (35-45 ft. lbs.)
²all other bolts/nuts to 27-34 N´m (20-25 ft. lbs.)
(10) Install oil pump retaining ring on mainshaft
(Fig. 95).
(11) Install rear output bearing and snap-ring to
output shaft.
COMPANION FLANGE
(1) Install companion flange seal on front shaft
(Fig. 96).
(2) Install companion flange on front shaft (Fig.
97). Then install and tighten flange nut to 176-271
N´m (130-200 ft. lbs.) torque.
EXTENSION HOUSING AND PTO COVER
(1) Apply bead of MopartGasket Maker, or equiv-
alent, to mating surface of extension housing. Keep
sealer bead width to maximum of 3/16 inch. Do not
use excessive amount of sealer as excess could be dis-
placed into oil pump.
(2) Position extension housing over output shaft.
(3) Spread extension housing retaining ring and
seat extension housing on rear case. Verify that the
retaining ring is seated in output shaft rear bearing.
(4) Install retaining ring access cover.
(5) Apply MopartSilicone Sealer, or equivalent, to
threads of extension housing bolts. Then install bolts
finger tight.
(6) Tighten extension housing bolts to 27-34 N´m
(20-25 ft. lbs.) torque.
Fig. 94 Washer Installation On Case Stud And
Dowel Bolts
1 - CASE STUD/BOLT
2 - WASHER
Fig. 95 Oil Pump Retaining Ring Installation
1 - RETAINING RING
2 - OIL PUMP
Fig. 96 Installing Flange Seal On Front Shaft
1 - FRONT OUTPUT SHAFT
2 - FLANGE SEAL
Fig. 97 Installing Companion Flange On Front Shaft
1 - COMPANION FLANGE
21 - 918 TRANSFER CASE - NV241HDBR/BE
TRANSFER CASE - NV241HD (Continued)
Page 2571 of 2889

OPERATION
The wheel (Fig. 19) has raised sections between
the rim flanges and the rim well. Initial inflation of
the tire forces the bead over these raised sections. In
case of tire failure, the raised sections hold the tire
in position on the wheel until the vehicle can be
brought to a safe stop.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - WHEEL
INSPECTION
Inspect wheels for:
²Excessive run out
²Dents or cracks
²Damaged wheel lug nut holes
²Air Leaks from any area or surface of the rim
NOTE: Do not attempt to repair a wheel by hammer-
ing, heating or welding.
If a wheel is damaged an original equipment
replacement wheel should be used. When obtaining
replacement wheels, they should be equivalent in
load carrying capacity. The diameter, width, offset,
pilot hole and bolt circle of the wheel should be the
same as the original wheel.
WARNING: FAILURE TO USE EQUIVALENT
REPLACEMENT WHEELS MAY ADVERSELY
AFFECT THE SAFETY AND HANDLING OF THE
VEHICLE. USED WHEELS ARE NOT RECOM-
MENDED. THE SERVICE HISTORY OF THE WHEEL
MAY HAVE INCLUDED SEVERE TREATMENT OR
VERY HIGH MILEAGE. THE RIM COULD FAIL WITH-
OUT WARNING.
STARDARD PROCEDURE - DUAL REAR WHEEL
INSTALLATION
Dual rear wheels use a special heavy duty lug nut
wrench. It is recommended to remove and install
dual rear wheels only when the proper wrench is
available. The wrench is also use to remove wheel
center caps for more information refer to Owner's
Manual.
The tires on both wheels must be completely raised
off the ground when tightening the lug nuts. This
will ensure correct wheel centering and maximum
wheel clamping.
A two piece flat face lug nut with right-hand
threads is used for retaining the wheels on the hubs
(Fig. 20).
The dual rear wheel lug nuts should be tightened
according to the following procedure:
²Place two drops of oil to the interface of the nut/
washer (Fig. 20) before installing on the wheel stud.
NOTE: Do not use more then two drops of oil on
the nut/washer, since the center caps attach in this
area.
²Tighten the wheel lug nuts in the numbered
sequential pattern until they are snug tight. Then
tighten lug nut to specified torque following same
number sequence, (Refer to 22 - TIRES/WHEELS/
WHEELS - SPECIFICATIONS).
Fig. 18 Dual Rear Wheels
1 - INBOARD WHEEL VALVE STEM
2 - OUTBOARD WHEEL VALVE STEM
Fig. 19 Safety Rim
1 - FLANGE
2 - RIDGE
3 - WELL
22 - 10 TIRES/WHEELSBR/BE
WHEELS (Continued)
Page 2803 of 2889

tional to the amount of oxygen in the exhaust. The
information obtained by the sensor is used to calcu-
late the fuel injector pulse width. This maintains a
14.7 to 1 Air Fuel (A/F) ratio. At this mixture ratio,
the catalyst works best to remove hydrocarbons (HC),
carbon monoxide (CO) and nitrogen oxide (NOx) from
the exhaust.
The O2S is also the main sensing element for the
Catalyst and Fuel Monitors.
The O2S can fail in any or all of the following
manners:
²slow response rate
²reduced output voltage
²dynamic shift
²shorted or open circuits
Response rate is the time required for the sensor to
switch from lean to rich once it is exposed to a richer
than optimum A/F mixture or vice versa. As the sen-
sor starts malfunctioning, it could take longer to
detect the changes in the oxygen content of the
exhaust gas.
The output voltage of the O2S ranges from 0 to 1
volt. A good sensor can easily generate any output
voltage in this range as it is exposed to different con-
centrations of oxygen. To detect a shift in the A/F
mixture (lean or rich), the output voltage has to
change beyond a threshold value. A malfunctioning
sensor could have difficulty changing beyond the
threshold value.
OXYGEN SENSOR HEATER MONITOR
If there is an oxygen sensor (O2S) shorted to volt-
age DTC, as well as a O2S heater DTC, the O2S
fault MUST be repaired first. Before checking the
O2S fault, verify that the heater circuit is operating
correctly.
Effective control of exhaust emissions is achieved
by an oxygen feedback system. The most important
element of the feedback system is the O2S. The O2S
is located in the exhaust path. Once it reaches oper-
ating temperature 300É to 350ÉC (572 É to 662ÉF), the
sensor generates a voltage that is inversely propor-
tional to the amount of oxygen in the exhaust. The
information obtained by the sensor is used to calcu-
late the fuel injector pulse width. This maintains a
14.7 to 1 Air Fuel (A/F) ratio. At this mixture ratio,
the catalyst works best to remove hydrocarbons (HC),
carbon monoxide (CO) and nitrogen oxide (NOx) from
the exhaust.
The voltage readings taken from the O2S sensor
are very temperature sensitive. The readings are not
accurate below 300ÉC. Heating of the O2S sensor is
done to allow the engine controller to shift to closed
loop control as soon as possible. The heating element
used to heat the O2S sensor must be tested to ensure
that it is heating the sensor properly.The O2S sensor circuit is monitored for a drop in
voltage. The sensor output is used to test the heater
by isolating the effect of the heater element on the
O2S sensor output voltage from the other effects.
LEAK DETECTION PUMP MONITOR (IF EQUIPPED)
The leak detection assembly incorporates two pri-
mary functions: it must detect a leak in the evapora-
tive system and seal the evaporative system so the
leak detection test can be run.
The primary components within the assembly are:
A three port solenoid that activates both of the func-
tions listed above; a pump which contains a switch,
two check valves and a spring/diaphragm, a canister
vent valve (CVV) seal which contains a spring loaded
vent seal valve.
Immediately after a cold start, between predeter-
mined temperature thresholds limits, the three port
solenoid is briefly energized. This initializes the
pump by drawing air into the pump cavity and also
closes the vent seal. During non test conditions the
vent seal is held open by the pump diaphragm
assembly which pushes it open at the full travel posi-
tion. The vent seal will remain closed while the
pump is cycling due to the reed switch triggering of
the three port solenoid that prevents the diaphragm
assembly from reaching full travel. After the brief
initialization period, the solenoid is de-energized
allowing atmospheric pressure to enter the pump
cavity, thus permitting the spring to drive the dia-
phragm which forces air out of the pump cavity and
into the vent system. When the solenoid is energized
and de energized, the cycle is repeated creating flow
in typical diaphragm pump fashion. The pump is con-
trolled in 2 modes:
Pump Mode: The pump is cycled at a fixed rate to
achieve a rapid pressure build in order to shorten the
overall test length.
Test Mode: The solenoid is energized with a fixed
duration pulse. Subsequent fixed pulses occur when
the diaphragm reaches the Switch closure point.
The spring in the pump is set so that the system
will achieve an equalized pressure of about 7.5º H20.
The cycle rate of pump strokes is quite rapid as the
system begins to pump up to this pressure. As the
pressure increases, the cycle rate starts to drop off. If
there is no leak in the system, the pump would even-
tually stop pumping at the equalized pressure. If
there is a leak, it will continue to pump at a rate rep-
resentative of the flow characteristic of the size of the
leak. From this information we can determine if the
leak is larger than the required detection limit (cur-
rently set at .040º orifice by CARB). If a leak is
revealed during the leak test portion of the test, the
test is terminated at the end of the test mode and no
further system checks will be performed.
25 - 16 EMISSIONS CONTROLBR/BE
EMISSIONS CONTROL (Continued)
Page 2804 of 2889

After passing the leak detection phase of the test,
system pressure is maintained by turning on the
LDP's solenoid until the purge system is activated.
Purge activation in effect creates a leak. The cycle
rate is again interrogated and when it increases due
to the flow through the purge system, the leak check
portion of the diagnostic is complete.
The canister vent valve will unseal the system
after completion of the test sequence as the pump
diaphragm assembly moves to the full travel position.
Evaporative system functionality will be verified by
using the stricter evap purge flow monitor. At an
appropriate warm idle the LDP will be energized to
seal the canister vent. The purge flow will be clocked
up from some small value in an attempt to see a
shift in the 02 control system. If fuel vapor, indicated
by a shift in the 02 control, is present the test is
passed. If not, it is assumed that the purge system is
not functioning in some respect. The LDP is again
turned off and the test is ended.
MISFIRE MONITOR
Excessive engine misfire results in increased cata-
lyst temperature and causes an increase in HC emis-
sions. Severe misfires could cause catalyst damage.
To prevent catalytic convertor damage, the PCM
monitors engine misfire.
The Powertrain Control Module (PCM) monitors
for misfire during most engine operating conditions
(positive torque) by looking at changes in the crank-
shaft speed. If a misfire occurs the speed of the
crankshaft will vary more than normal.
FUEL SYSTEM MONITOR
To comply with clean air regulations, vehicles are
equipped with catalytic converters. These converters
reduce the emission of hydrocarbons, oxides of nitro-
gen and carbon monoxide. The catalyst works best
when the Air Fuel (A/F) ratio is at or near the opti-
mum of 14.7 to 1.
The PCM is programmed to maintain the optimum
air/fuel ratio of 14.7 to 1. This is done by making
short term corrections in the fuel injector pulse width
based on the O2S sensor output. The programmed
memory acts as a self calibration tool that the engine
controller uses to compensate for variations in engine
specifications, sensor tolerances and engine fatigue
over the life span of the engine. By monitoring the
actual fuel-air ratio with the O2S sensor (short term)
and multiplying that with the program long-term
(adaptive) memory and comparing that to the limit,
it can be determined whether it will pass an emis-
sions test. If a malfunction occurs such that the PCM
cannot maintain the optimum A/F ratio, then the
MIL will be illuminated.
CATALYST MONITOR
To comply with clean air regulations, vehicles are
equipped with catalytic converters. These converters
reduce the emission of hydrocarbons, oxides of nitro-
gen and carbon monoxide.
Normal vehicle miles or engine misfire can cause a
catalyst to decay. A meltdown of the ceramic core can
cause a reduction of the exhaust passage. This can
increase vehicle emissions and deteriorate engine
performance, driveability and fuel economy.
The catalyst monitor uses dual oxygen sensors
(O2S's) to monitor the efficiency of the converter. The
dual O2S's sensor strategy is based on the fact that
as a catalyst deteriorates, its oxygen storage capacity
and its efficiency are both reduced. By monitoring
the oxygen storage capacity of a catalyst, its effi-
ciency can be indirectly calculated. The upstream
O2S is used to detect the amount of oxygen in the
exhaust gas before the gas enters the catalytic con-
verter. The PCM calculates the A/F mixture from the
output of the O2S. A low voltage indicates high oxy-
gen content (lean mixture). A high voltage indicates a
low content of oxygen (rich mixture).
When the upstream O2S detects a lean condition,
there is an abundance of oxygen in the exhaust gas.
A functioning converter would store this oxygen so it
can use it for the oxidation of HC and CO. As the
converter absorbs the oxygen, there will be a lack of
oxygen downstream of the converter. The output of
the downstream O2S will indicate limited activity in
this condition.
As the converter loses the ability to store oxygen,
the condition can be detected from the behavior of
the downstream O2S. When the efficiency drops, no
chemical reaction takes place. This means the con-
centration of oxygen will be the same downstream as
upstream. The output voltage of the downstream
O2S copies the voltage of the upstream sensor. The
only difference is a time lag (seen by the PCM)
between the switching of the O2S's.
To monitor the system, the number of lean-to-rich
switches of upstream and downstream O2S's is
counted. The ratio of downstream switches to
upstream switches is used to determine whether the
catalyst is operating properly. An effective catalyst
will have fewer downstream switches than it has
upstream switches i.e., a ratio closer to zero. For a
totally ineffective catalyst, this ratio will be one-to-
one, indicating that no oxidation occurs in the device.
The system must be monitored so that when cata-
lyst efficiency deteriorates and exhaust emissions
increase to over the legal limit, the MIL will be illu-
minated.
BR/BEEMISSIONS CONTROL 25 - 17
EMISSIONS CONTROL (Continued)