2001 DODGE RAM wiring
[x] Cancel search: wiringPage 498 of 2889

CHARGING
TABLE OF CONTENTS
page page
CHARGING
DESCRIPTION...........................27
OPERATION.............................27
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING.................27
CHARGING SYSTEM....................27
SPECIFICATIONS........................28
BATTERY TEMPERATURE SENSOR
DESCRIPTION...........................29
OPERATION.............................29
REMOVAL..............................29INSTALLATION...........................29
GENERATOR
DESCRIPTION...........................29
OPERATION.............................29
REMOVAL..............................30
INSTALLATION...........................30
VOLTAGE REGULATOR
DESCRIPTION...........................31
OPERATION.............................31
CHARGING
DESCRIPTION
The charging system consists of:
²Generator
²Electronic Voltage Regulator (EVR) circuitry
within the Powertrain Control Module (PCM)
²Ignition switch (refer to Ignition System for
information)
²Battery (refer to 8, Battery for information)
²Battery temperature sensor
²Check Gauges Lamp (if equipped)
²Voltmeter (refer to 8, Instrument Panel and
Gauges for information)
²Wiring harness and connections (refer to 8, Wir-
ing Diagrams for information)
OPERATION
The charging system is turned on and off with the
ignition switch. The system is on when the engine is
running and the ASD relay is energized. When the
ASD relay is on, voltage is supplied to the ASD relay
sense circuit at the PCM. This voltage is connected
through the PCM and supplied to one of the genera-
tor field terminals (Gen. Source +) at the back of the
generator.
The amount of direct current produced by the gen-
erator is controlled by the EVR (field control) cir-
cuitry contained within the PCM. This circuitry is
connected in series with the second rotor field termi-
nal and ground.
A battery temperature sensor, located in the bat-
tery tray housing, is used to sense battery tempera-
ture. This temperature data, along with data from
monitored line voltage, is used by the PCM to vary
the battery charging rate. This is done by cycling the
ground path to control the strength of the rotor mag-netic field. The PCM then compensates and regulates
generator current output accordingly.
All vehicles are equipped with On-Board Diagnos-
tics (OBD). All OBD-sensed systems, including EVR
(field control) circuitry, are monitored by the PCM.
Each monitored circuit is assigned a Diagnostic Trou-
ble Code (DTC). The PCM will store a DTC in elec-
tronic memory for certain failures it detects. Refer to
On-Board Diagnostics in 25, Emission Control Sys-
tem for more DTC information and a list of codes.
The Check Gauges Lamp (if equipped) monitors:
charging system voltage,engine coolant tempera-
ture and engine oil pressure. If an extreme condition
is indicated, the lamp will be illuminated. This is
done as reminder to check the three gauges. The sig-
nal to activate the lamp is sent via the CCD bus cir-
cuits. The lamp is located on the instrument panel.
Refer to 8, Instrument Panel and Gauges for addi-
tional information.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - CHARGING
SYSTEM
The following procedures may be used to diagnose
the charging system if:
²the check gauges lamp (if equipped) is illumi-
nated with the engine running
²the voltmeter (if equipped) does not register
properly
²an undercharged or overcharged battery condi-
tion occurs.
Remember that an undercharged battery is often
caused by:
²accessories being left on with the engine not
running
²a faulty or improperly adjusted switch that
allows a lamp to stay on. Refer to Ignition-Off Draw
Test in 8, Battery for more information.
BR/BECHARGING 8F - 27
Page 504 of 2889

When the starter relay coil is energized, the nor-
mally open relay contacts close. The relay contacts
connect the relay common feed terminal to the relay
normally open terminal. The closed relay contacts
energize the starter solenoid coil windings.
The energized solenoid pull-in coil pulls in the sole-
noid plunger. The solenoid plunger pulls the shift
lever in the starter motor. This engages the starter
overrunning clutch and pinion gear with the starter
ring gear on the manual transmission flywheel or on
the automatic transmission torque converter or
torque converter drive plate.
As the solenoid plunger reaches the end of its
travel, the solenoid contact disc completes the high-
amperage starter feed circuit and energizes the sole-
noid plunger hold-in coil. Current now flows between
the solenoid battery terminal and the starter motor,
energizing the starter.
Once the engine starts, the overrunning clutch pro-
tects the starter motor from damage by allowing the
starter pinion gear to spin faster than the pinionshaft. When the driver releases the ignition switch to
the On position, the starter relay coil is de-energized.
This causes the relay contacts to open. When the
relay contacts open, the starter solenoid plunger
hold-in coil is de-energized.
When the solenoid plunger hold-in coil is de-ener-
gized, the solenoid plunger return spring returns the
plunger to its relaxed position. This causes the con-
tact disc to open the starter feed circuit, and the shift
lever to disengage the overrunning clutch and pinion
gear from the starter ring gear.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - STARTING
SYSTEM
The battery, starting, and charging systems oper-
ate in conjunction with one another, and must be
tested as a complete system. For correct starting/
charging system operation, all of the components
involved in these 3 systems must perform within
specifications.
Starting System Diagnosis
CONDITION POSSIBLE CAUSE CORRECTION
STARTER FAILS TO
OPERATE.1. Battery discharged or
faulty.1. Refer to Battery. Charge or replace battery, if required.
2. Starting circuit wiring
faulty.2. Refer to 8, Wiring Diagrams. Test and repair starter
feed and/or control circuits, if required.
3. Starter relay faulty. 3. Refer to Starter Relay in the Diagnosis and Testing
section of this group. Replace starter relay, if required.
4. Ignition switch faulty. 4. Refer to Ignition Switch and Key Lock Cylinder.
Replace ignition switch, if required.
5. Clutch pedal position
switch faulty.5. Refer to Clutch Pedal Position Switch.
6. Park/Neutral position
switch faulty or
misadjusted.6. Refer to Park/Neutral Position Switch. Replace
park/neutral position switch, if required.
7. Starter solenoid faulty. 7. Refer to Starter Motor. Replace starter motor assembly,
if required.
8. Starter motor faulty. 8. If all other starting system components and circuits test
OK, replace starter motor.
STARTER ENGAGES,
FAILS TO TURN
ENGINE.1. Battery discharged or
faulty.1. Refer to Battery. Charge or replace battery, if required.
2. Starting circuit wiring
faulty.2. Refer to 8, Wiring Diagrams. Test and repair starter
feed and/or control circuits, if required.
3. Starter motor faulty. 3. If all other starting system components and circuits test
OK, replace starter motor assembly.
4. Engine seized. 4. Refer to Engine Diagnosis in the Diagnosis and Testing
section of 9, Engine.
BR/BESTARTING 8F - 33
STARTING (Continued)
Page 505 of 2889

Starting System Diagnosis
CONDITION POSSIBLE CAUSE CORRECTION
STARTER ENGAGES,
SPINS OUT BEFORE
ENGINE STARTS.1. Starter ring gear faulty. 1. Refer to Starter Motor in Removal and Installation.
Remove starter motor to inspect starter ring gear.
Replace starter ring gear, if required.
2. Starter motor faulty. 2. If all other starting system components and circuits test
OK, replace the starter motor assembly.
STARTER DOES NOT
DISENGAGE.1. Starter motor
improperly installed.1. Refer to Starter Motor in the Removal and Installation
section of this group. Tighten the starter mounting
hardware to the correct tightness specifications.
2. Starter relay faulty. 2. Refer to Starter Relay in the Diagnosis and Testing
section of this group. Replace starter relay, if required.
3. Ignition switch faulty. 3. Refer to Ignition Switch and Key Lock Cylinder.
Replace ignition switch, if required.
4. Starter motor faulty. 4. If all other starting system components and circuits test
OK, replace starter motor.
INSPECTION
For complete starter wiring circuit diagrams, refer
to 8, Wiring Diagrams. Before removing any unit
from starting system for repair or diagnosis, perform
the following inspections:
WARNING: ON VEHICLES EQUIPPED WITH AIR-
BAGS, REFER TO 8, PASSIVE RESTRAINT SYS-
TEMS, BEFORE ATTEMPTING ANY STEERING
WHEEL, STEERING COLUMN, OR INSTRUMENT
PANEL COMPONENT DIAGNOSIS OR SERVICE.
FAILURE TO TAKE THE PROPER PRECAUTIONS
COULD RESULT IN ACCIDENTAL AIRBAG DEPLOY-
MENT AND POSSIBLE PERSONAL INJURY.
²Battery- Visually inspect battery for indica-
tions of physical damage and loose or corroded cable
connections. Determine the state-of-charge and
cranking capacity of battery. Charge or replace bat-
tery, if required. Refer toBatteryin 8, Battery.
Note: If equipped with diesel engine, a dual bat-
tery system is used, and both batteries must be
inspected.
²Ignition Switch- Visually inspect ignition
switch for indications of physical damage and loose
or corroded wire harness connections. Refer toIgni-
tion Switch and Key Lock Cylinder.
²Clutch Pedal Position Switch- If equipped
with manual transmission, visually inspect clutch
pedal position switch for indications of physical dam-
age and loose or corroded wire harness connections.
Refer toClutch Pedal Position Switchin 6,
Clutch.
²Park/Neutral Position Switch- If equipped
with automatic transmission, visually inspect park/
neutral position switch for indications of physical
damage and loose or corroded wire harness connec-tions. Refer toPark/Neutral Position Switchin
21, Transmission.
²Starter Relay- Visually inspect starter relay
for indications of physical damage and loose or cor-
roded wire harness connections.
²Starter Motor- Visually inspect starter motor
for indications of physical damage and loose or cor-
roded wire harness connections.
²Starter Solenoid- Visually inspect starter sole-
noid for indications of physical damage and loose or
corroded wire harness connections.
²Wiring- Visually inspect wire harnesses for
damage. Repair or replace any faulty wiring, as
required. Refer to 8, Wiring Diagrams.
TESTING
COLD CRANKING TEST
For complete starter wiring circuit diagrams, refer
to 8, Wiring Diagrams. The battery must be fully-
charged and load-tested before proceeding. Refer to
Batteryin 8, Battery.
(1) Connect volt-ampere tester to battery terminals
(Fig. 1). See instructions provided by manufacturer of
volt-ampere tester being used.Note: If equipped
with dual battery system (diesel), tester should
be connected to driver side battery only. Also,
tester current reading must be taken from bat-
tery positive cable lead that connects to starter
motor.
(2) Fully engage parking brake.
(3) If equipped with manual transmission, place
gearshift selector lever in Neutral position and block
clutch pedal in fully depressed position. If equipped
with automatic transmission, place gearshift selector
lever in Park position.
8F - 34 STARTINGBR/BE
STARTING (Continued)
Page 506 of 2889

(4) Verify that all lamps and accessories are
turned off.
(5) To prevent a gasoline engine from starting,
remove Automatic ShutDown (ASD) relay. To prevent
a diesel engine from starting, remove Fuel Pump
Relay. These relays are located in Power Distribution
Center (PDC). Refer to label on PDC cover for relay
location.
WARNING: IF EQUIPPED WITH DIESEL ENGINE,
ATTEMPT TO START ENGINE A FEW TIMES
BEFORE PROCEEDING WITH FOLLOWING STEP.
(6) Rotate and hold ignition switch in Start posi-
tion. Note cranking voltage and current (amperage)
draw readings shown on volt-ampere tester.
(a) If voltage reads below 9.6 volts, refer to
Starter Motorin Diagnosis and Testing. If starter
motor is OK, refer toEngine Diagnosisin 9,
Engine for further testing of engine. If starter
motor is not OK, replace faulty starter motor.
(b) If voltage reads above 9.6 volts and current
(amperage) draw reads below specifications, refer
toFeed Circuit Testin this section.
(c) If voltage reads 12.5 volts or greater and
starter motor does not turn, refer toControl Cir-
cuit Testingin this section.
(d) If voltage reads 12.5 volts or greater and
starter motor turns very slowly, refer toFeed Cir-
cuit Testin this section.
NOTE: A cold engine will increase starter current
(amperage) draw reading, and reduce battery volt-
age reading.FEED CIRCUIT TEST
The starter feed circuit test (voltage drop method)
will determine if there is excessive resistance in
high-amperage feed circuit. For complete starter wir-
ing circuit diagrams, refer 8, Wiring Diagrams.
When performing these tests, it is important to
remember that voltage drop is giving an indication of
resistance between two points at which voltmeter
probes are attached.
Example:When testing resistance of battery posi-
tive cable, touch voltmeter leads to battery positive
cable clamp and cable connector at starter solenoid.
If you probe battery positive terminal post and cable
connector at starter solenoid, you are reading com-
bined voltage drop in battery positive cable clamp-to-
terminal post connection and battery positive cable.
The following operation will require a voltmeter
accurate to 1/10 (0.10) volt. Before performing tests,
be certain that following procedures are accom-
plished:
²Battery is fully-charged and load-tested. Refer to
Batteryin 8, Battery.
²Fully engage parking brake.
²If equipped with manual transmission, place
gearshift selector lever in Neutral position and block
clutch pedal in fully depressed position. If equipped
with automatic transmission, place gearshift selector
lever in Park position.
²Verify that all lamps and accessories are turned
off.
²To prevent a gasoline engine from starting,
remove Automatic ShutDown (ASD) relay. To prevent
a diesel engine from starting, remove Fuel Pump
Relay. These relays are located in Power Distribution
Center (PDC). Refer to label on PDC cover for relay
location.
(1) Connect positive lead of voltmeter to battery
negative terminal post. Connect negative lead of volt-
meter to battery negative cable clamp (Fig. 2). Rotate
and hold ignition switch in Start position. Observe
voltmeter. If voltage is detected, correct poor contact
between cable clamp and terminal post.Note: If
equipped with a dual battery system (diesel),
procedure must be performed twice, once for
each battery.
(2) Connect positive lead of voltmeter to battery
positive terminal post. Connect negative lead of volt-
meter to battery positive cable clamp (Fig. 3). Rotate
and hold ignition switch in Start position. Observe
voltmeter. If voltage is detected, correct poor contact
between cable clamp and terminal post.Note: If
equipped with a dual battery system (diesel),
this procedure must be performed twice, once
for each battery.
Fig. 1 Volts-Amps Tester Connections - Typical
1 - POSITIVE CLAMP
2 - NEGATIVE CLAMP
3 - INDUCTION AMMETER CLAMP
BR/BESTARTING 8F - 35
STARTING (Continued)
Page 508 of 2889

(5) Connect positive lead of voltmeter to starter
housing. Connect negative lead of voltmeter to bat-
tery negative terminal post (Fig. 6). Rotate and hold
ignition switch in Start position. Observe voltmeter.
If reading is above 0.2 volt, correct poor starter to
engine block ground contact.Note: If equipped
with a dual battery system (diesel), this proce-
dure must be performed on driver side battery
only.(6) If equipped with dual battery system (diesel),
connect positive lead of voltmeter to driver side bat-
tery positive cable clamp. Connect negative lead of
voltmeter to passenger side battery positive terminal
post. Rotate and hold ignition switch in Start posi-
tion. Observe voltmeter. If reading is above 0.2 volt,
clean and tighten passenger side battery positive
cable eyelet connection at driver side battery positive
cable clamp bolt. Repeat test. If reading is still above
0.2 volt, replace faulty passenger side battery posi-
tive cable.
If resistance tests detect no feed circuit problems,
refer toStarter Motorin the Diagnosis and Testing.
CONTROL CIRCUIT TESTING
The starter control circuit components should be
tested in the order in which they are listed, as fol-
lows:
²Starter Relay- Refer toStarter RelayDiag-
nosis and Testing.
²Starter Solenoid- Refer toStarter Motor
Diagnosis and Testing.
²Ignition Switch- Refer toIgnition Switch
and Key Lock Cylinder
²Clutch Pedal Position Switch- If equipped
with manual transmission, refer toClutch Pedal
Position Switchin 6, Clutch.
²Park/Neutral Position Switch- If equipped
with automatic transmission, refer toPark/Neutral
Position Switchin 21, Transmission.
²Wire harnesses and connections- Refer to 8,
Wiring Diagrams.
Fig. 6 Test Starter Ground - Typical
1 - STARTER MOTOR
2 - BATTERY
3 - VOLTMETER
BR/BESTARTING 8F - 37
STARTING (Continued)
Page 512 of 2889
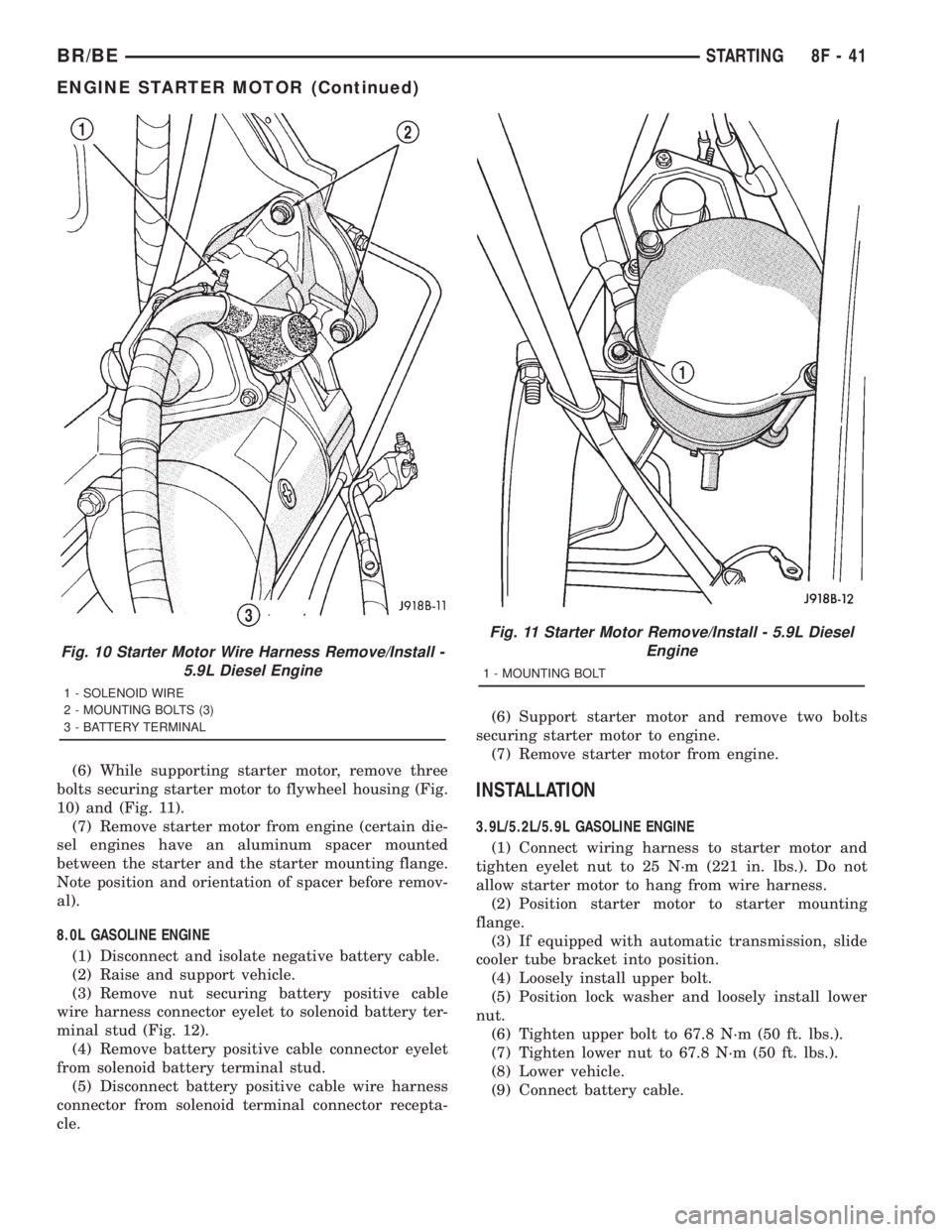
(6) While supporting starter motor, remove three
bolts securing starter motor to flywheel housing (Fig.
10) and (Fig. 11).
(7) Remove starter motor from engine (certain die-
sel engines have an aluminum spacer mounted
between the starter and the starter mounting flange.
Note position and orientation of spacer before remov-
al).
8.0L GASOLINE ENGINE
(1) Disconnect and isolate negative battery cable.
(2) Raise and support vehicle.
(3) Remove nut securing battery positive cable
wire harness connector eyelet to solenoid battery ter-
minal stud (Fig. 12).
(4) Remove battery positive cable connector eyelet
from solenoid battery terminal stud.
(5) Disconnect battery positive cable wire harness
connector from solenoid terminal connector recepta-
cle.(6) Support starter motor and remove two bolts
securing starter motor to engine.
(7) Remove starter motor from engine.
INSTALLATION
3.9L/5.2L/5.9L GASOLINE ENGINE
(1) Connect wiring harness to starter motor and
tighten eyelet nut to 25 N´m (221 in. lbs.). Do not
allow starter motor to hang from wire harness.
(2) Position starter motor to starter mounting
flange.
(3) If equipped with automatic transmission, slide
cooler tube bracket into position.
(4) Loosely install upper bolt.
(5) Position lock washer and loosely install lower
nut.
(6) Tighten upper bolt to 67.8 N´m (50 ft. lbs.).
(7) Tighten lower nut to 67.8 N´m (50 ft. lbs.).
(8) Lower vehicle.
(9) Connect battery cable.
Fig. 10 Starter Motor Wire Harness Remove/Install -
5.9L Diesel Engine
1 - SOLENOID WIRE
2 - MOUNTING BOLTS (3)
3 - BATTERY TERMINAL
Fig. 11 Starter Motor Remove/Install - 5.9L Diesel
Engine
1 - MOUNTING BOLT
BR/BESTARTING 8F - 41
ENGINE STARTER MOTOR (Continued)
Page 513 of 2889

5.9L DIESEL ENGINE
(1) If equipped, position aluminum spacer to rear
of starter.
(2) Position starter motor to engine.
(3) Support starter and loosely install three
mounting bolts.
(4) Tighten 3 bolts to 43.4 N´m (32 ft. lbs.).
(5) Position wiring eyelets to starter studs and
install nuts. Tighten small nut to 6.2 N´m (55 in.
lbs.). Tighten large nut to 13.6 N´m (120 in. lbs.).
(6) Install protective rubber boot over stud.
(7) Lower vehicle.
(8) Connect battery cables to both batteries.
8.0L GASOLINE ENGINE
(1) Support starter motor and loosely install two
bolts securing starter motor to engine.
(2) Tighten 2 bolts to 67.8 N´m (50 ft. lbs.).
(3) Connect solenoid wire to solenoid terminal.
(4) Position battery cable eyelet to starter stud.
Install nut and tighten to 13.6 N´m (120 in. lbs.).
(5) Lower vehicle.
(6) Connect battery cable.
ENGINE STARTER MOTOR
RELAY
DESCRIPTION
The starter relay is an electromechanical device
that switches battery current to the pull-in coil of the
starter solenoid when ignition switch is turned to
Start position. The starter relay is located in the
Power Distribution Center (PDC) in the engine com-
partment. See PDC cover for relay identification and
location.
The starter relay is a International Standards
Organization (ISO) relay. Relays conforming to ISO
specifications have common physical dimensions, cur-
rent capacities, terminal patterns, and terminal func-
tions.
The starter relay cannot be repaired or adjusted
and, if faulty or damaged, it must be replaced.
OPERATION
The ISO relay consists of an electromagnetic coil, a
resistor or diode, and three (two fixed and one mov-
able) electrical contacts. The movable (common feed)
relay contact is held against one of the fixed contacts
(normally closed) by spring pressure. When electro-
magnetic coil is energized, it draws the movable con-
tact away from normally closed fixed contact, and
holds it against the other (normally open) fixed con-
tact.
When electromagnetic coil is de-energized, spring
pressure returns movable contact to normally closed
position. The resistor or diode is connected in parallel
with electromagnetic coil within relay, and helps to
dissipate voltage spikes produced when coil is de-en-
ergized.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - STARTER RELAY
The starter relay (Fig. 13) is located in Power Dis-
tribution Center (PDC). Refer to PDC cover for relay
identification and location. For complete starter relay
wiring circuit diagrams, refer to 8, Wiring Diagrams.
(1) Remove starter relay from PDC.
(2) A relay in de-energized position should have
continuity between terminals 87A and 30, and no
continuity between terminals 87 and 30. If OK, go to
Step 3. If not OK, replace faulty relay.
(3) Resistance between terminals 85 and 86 (elec-
tromagnet) should be 7565 ohms. If OK, go to Step
4. If not OK, replace faulty relay.
(4) Connect 12V battery to terminals 85 and 86.
There should now be continuity between terminals
30 and 87, and no continuity between terminals 87A
and 30. If OK, perform Relay Circuit Test that fol-
lows. If not OK, replace faulty relay.
Fig. 12 Starter Motor Remove/Install - 8.0L Gasoline
Engine
1 - ENGINE
2 - BATTERY POSITIVE CABLE WIRE HARNESS
3 - NUT
4 - STARTER MOTOR
5 - SCREW AND WASHER (2)
8F - 42 STARTINGBR/BE
ENGINE STARTER MOTOR (Continued)
Page 517 of 2889

OPERATION - HEATED MIRROR SYSTEM
The solid state electronic control logic and timer
circuitry for the heated mirror system receives bat-
tery current from a fuse in the Junction Block (JB)
only when the ignition switch is in the On or Start
positions. After the heated mirror system is turned
On, the electronic control logic and timer circuitry
will automatically turn the system off after a pro-
grammed time interval of about fifteen minutes.
After the initial time interval has expired, if the
heated mirror switch is depressed and released a sec-
ond time during the same ignition cycle, the elec-
tronic control logic and timer circuitry will
automatically turn the heated mirror system off after
a programmed time interval of about five minutes.
The heated mirror system will be shut off automati-
cally if the ignition switch is turned to the Off or
Accessory positions. After the heated mirror system
is turned On, it can also be turned off manually by
depressing and releasing the heated mirror switch a
second time.
When the heated mirror system is turned On, the
heated mirror system control logic and timer cir-
cuitry energizes the heated mirror system indicator
lamp and the heated mirror relay. When energized,
the heated mirror relay supplies fused ignition
switch output (run/start) current from a fuse in the
JB to the outside mirror heating grids located behind
the mirror glass of each of the outside rear view mir-
rors. When energized, each of the outside mirror
heating grids produces enough heat to warm the
glass of the outside rear view mirrors.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - HEATED MIRROR
SYSTEM
If only one of the outside mirror heating grids is
inoperative, perform continuity checks on the circuits
and heater grid for that mirror only. If both outside
mirror heating grids are inoperative, proceed with
the heated mirror system diagnosis as follows. (Refer
to Appropriate Wiring Information).
WARNING: ON VEHICLES EQUIPPED WITH AIR-
BAGS, DISABLE THE AIRBAG SYSTEM BEFORE
ATTEMPTING ANY STEERING WHEEL, STEERING
COLUMN, OR INSTRUMENT PANEL COMPONENT
DIAGNOSIS OR SERVICE. DISCONNECT AND ISO-
LATE THE BATTERY NEGATIVE (GROUND) CABLE,
THEN WAIT TWO MINUTES FOR THE AIRBAG SYS-
TEM CAPACITOR TO DISCHARGE BEFORE PER-
FORMING FURTHER DIAGNOSIS OR SERVICE. THIS
IS THE ONLY SURE WAY TO DISABLE THE AIRBAG
SYSTEM. FAILURE TO TAKE THE PROPER PRE-
CAUTIONS COULD RESULT IN ACCIDENTAL AIR-
BAG DEPLOYMENT AND POSSIBLE PERSONAL
INJURY.The operation of the heated mirror system can be
confirmed in one of the following manners:
²Turn the ignition switch to the On position.
While monitoring the instrument panel voltmeter,
momentarily depress and release the heated mirror
switch. When the heated mirror system is turned On,
a distinct voltmeter needle deflection should be
noted.
²Turn the ignition switch to the On position.
Momentarily depress and release the heated mirror
switch to turn the heated mirror system On. The
heated mirror operation can be checked by feeling
the outside rear view mirror glass. A distinct differ-
ence in temperature between the unheated and
heated mirror glass can be detected within three to
four minutes of system operation.
The above checks will confirm system operation.
Illumination of the heated mirror system indicator
lamp means that there is electrical current available
at the heated mirror relay, but does not confirm that
the electrical current is reaching the outside mirror
heating grids.
If the heated mirror system does not operate, the
problem should be isolated in the following manner:
(1) Confirm that the ignition switch is in the On
position.
(2) Check the fuses in the Power Distribution Cen-
ter (PDC) and in the Junction Block (JB). The fuses
must be tight in their receptacles and all electrical
connections must be secure.
When the above steps have been completed and
both outside mirror heating grids are still inopera-
tive, one or more of the following is faulty:
²Heated mirror switch, electronic control logic
and timer circuitry, and heated mirror relay.
²Heated mirror wire harness circuits or connec-
tors.
²Outside mirror heating grid (both mirror grids
would have to be faulty).
If turning On the heated mirror system produces a
severe voltmeter deflection or fuse failures, check for
a shorted circuit between the output of the heated
mirror relay and the outside mirror heating grids.
8G - 2 HEATED MIRRORSBR/BE
HEATED MIRRORS (Continued)