2001 DODGE RAM power steering
[x] Cancel search: power steeringPage 455 of 2889

²Horn relay control - high-line/premium version
only
²VTSS indicator driver - high-line/premium ver-
sion only
²Wiper motor relay control
MESSAGING
The high-line/premium CTM uses the following
messages received from other electronic modules over
the CCD data bus:
²Airbag Deploy (ACM)
²Charging System Failure (PCM)
²Engine RPM (PCM)
²System Voltage (PCM)
²Vehicle Speed (PCM)
²Voltage Fault (PCM)
The high-line/premium CTM provides the following
messages to other electronic modules over the CCD
data bus:
²Engine Enable (PCM)
²Radio Seek Up (Radio)
²Radio Seek Down (Radio)
²Radio Volume Up (Radio)
²Radio Volume Down (Radio)
²Preset Scan (Radio)
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - CENTRAL TIMER
MODULE
The hard wired inputs to and outputs from the
Central Timer Module (CTM) may be diagnosed and
tested using conventional diagnostic tools and meth-
ods. Refer to the appropriate wiring information. The
wiring information includes wiring diagrams, proper
wire and connector repair procedures, further details
on wire harness routing and retention, as well as
pin-out and location views for the various wire har-
ness connectors, splices and grounds.
However, conventional diagnostic methods may not
prove conclusive in the diagnosis of the high-line/pre-
mium CTM. In order to obtain conclusive testing of
the high-line/premium CTM, the Chrysler Collision
Detection (CCD) data bus network and all of the elec-
tronic modules that provide inputs to or receive out-
puts from the CTM must also be checked. The most
reliable, efficient, and accurate means to diagnose
the high-line/premium CTM, the CCD data bus net-
work, and the electronic modules that provide inputs
to or receive outputs from the high-line/premium
CTM requires the use of a DRBIIItscan tool and the
appropriate diagnostic information. The DRBIIIt
scan tool can provide confirmation that the CCD data
bus network is functional, that all of the electronic
modules are sending and receiving the proper mes-
sages over the CCD data bus, and that the CTM is
receiving the proper hard wired inputs and respond-ing with the proper hard wired outputs needed to
perform its many functions.
WARNING: ON VEHICLES EQUIPPED WITH AIR-
BAGS, DISABLE THE AIRBAG SYSTEM BEFORE
ATTEMPTING ANY STEERING WHEEL, STEERING
COLUMN, OR INSTRUMENT PANEL COMPONENT
DIAGNOSIS OR SERVICE. DISCONNECT AND ISO-
LATE THE BATTERY NEGATIVE (GROUND) CABLE,
THEN WAIT TWO MINUTES FOR THE AIRBAG SYS-
TEM CAPACITOR TO DISCHARGE BEFORE PER-
FORMING FURTHER DIAGNOSIS OR SERVICE. THIS
IS THE ONLY SURE WAY TO DISABLE THE AIRBAG
SYSTEM. FAILURE TO TAKE THE PROPER PRE-
CAUTIONS COULD RESULT IN ACCIDENTAL AIR-
BAG DEPLOYMENT AND POSSIBLE PERSONAL
INJURY.
NOTE: The following tests may not prove conclu-
sive in the diagnosis of the high-line or premium
versions of the Central Timer Module (CTM). The
most reliable, efficient, and accurate means to diag-
nose the high-line or premium CTM requires the
use of a DRBIIITscan tool and the appropriate diag-
nostic information.
(1) Check the fused B(+) fuse (Fuse 13 - 10
ampere) in the Junction Block (JB). If OK, go to Step
2. If not OK, repair the shorted circuit or component
as required and replace the faulty fuse.
(2) Check for battery voltage at the fused B(+) fuse
(Fuse 13 - 10 ampere) in the JB. If OK, go to Step 3.
If not OK, repair the open fused B(+) circuit between
the JB and the Power Distribution Center (PDC) as
required.
(3) For a base version CTM, check the fused igni-
tion switch output (st-run) fuse (Fuse 11 - 10 ampere)
in the JB. For a high-line/premium version CTM,
check the fused ignition switch output (run-acc) fuse
(Fuse6-25ampere) in the JB. If OK, go to Step 4. If
not OK, repair the shorted circuit or component as
required and replace the faulty fuse.
(4) Turn the ignition switch to the On position. For
a base version CTM, check for battery voltage at the
fused ignition switch output (st-run) fuse (Fuse 11 -
10 ampere) in the JB. For a high-line/premium ver-
sion CTM, check for battery voltage at the fused igni-
tion switch output (run-acc) fuse (Fuse6-25
ampere) in the JB. If OK, go to Step 5. If not OK,
repair the shorted circuit or component as required
and replace the faulty fuse.
(5) Turn the ignition switch to the Off position.
Disconnect and isolate the battery negative cable.
Remove the CTM from its mounting bracket to access
the CTM wire harness connector(s). Disconnect the
instrument panel wire harness connector(s) for the
8E - 4 ELECTRONIC CONTROL MODULESBR/BE
BODY CONTROL/CENTRAL TIMER MODULE (Continued)
Page 463 of 2889
²ABS Warning Lamp
²Brake Warning Lamp
REMOVAL
(1) Disconnect battery negative cable.
(2) Push the harness connector locks to release the
locks, (Fig. 11) then remove the connectors from the
CAB.
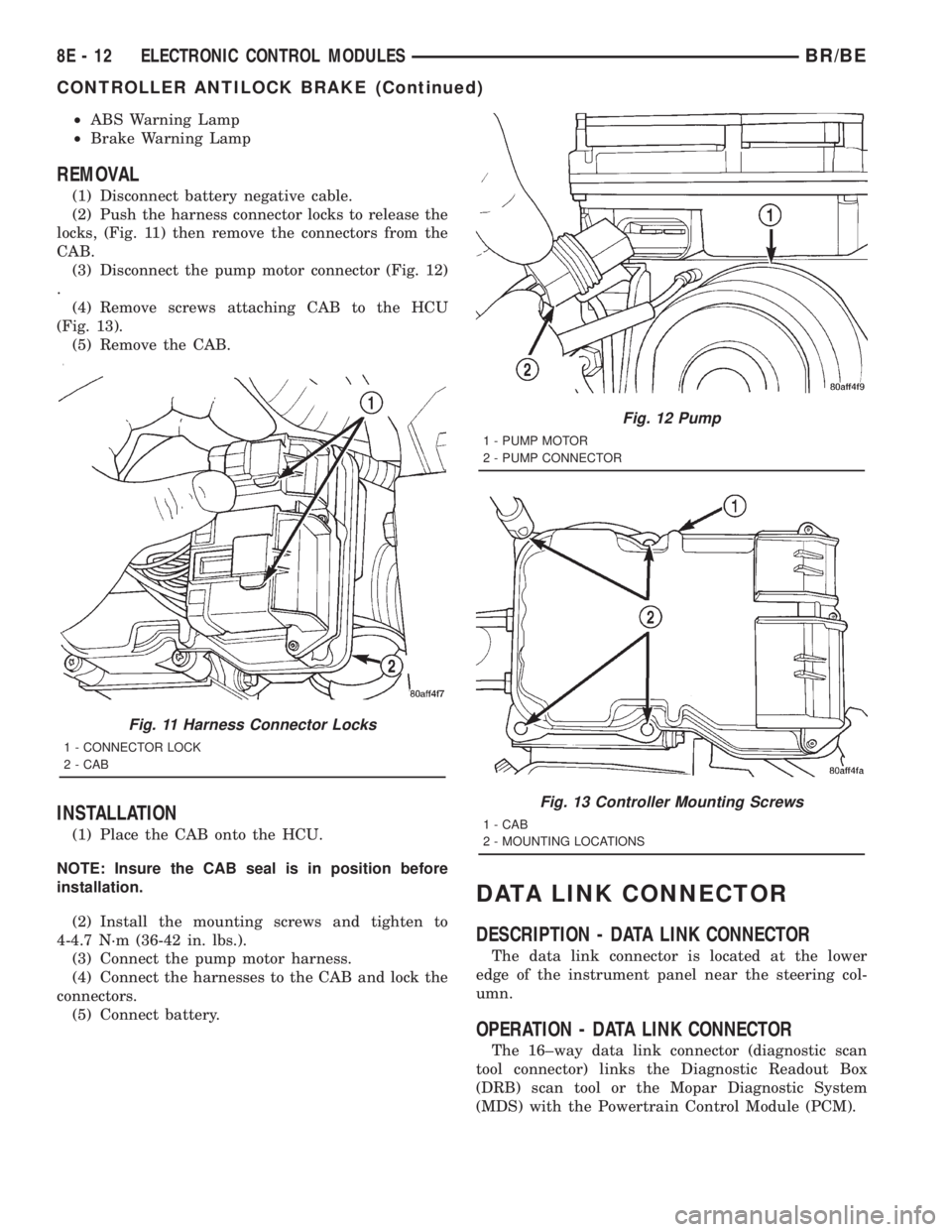
(3) Disconnect the pump motor connector (Fig. 12)
.
(4) Remove screws attaching CAB to the HCU
(Fig. 13).
(5) Remove the CAB.
INSTALLATION
(1) Place the CAB onto the HCU.
NOTE: Insure the CAB seal is in position before
installation.
(2) Install the mounting screws and tighten to
4-4.7 N´m (36-42 in. lbs.).
(3) Connect the pump motor harness.
(4) Connect the harnesses to the CAB and lock the
connectors.
(5) Connect battery.
DATA LINK CONNECTOR
DESCRIPTION - DATA LINK CONNECTOR
The data link connector is located at the lower
edge of the instrument panel near the steering col-
umn.
OPERATION - DATA LINK CONNECTOR
The 16±way data link connector (diagnostic scan
tool connector) links the Diagnostic Readout Box
(DRB) scan tool or the Mopar Diagnostic System
(MDS) with the Powertrain Control Module (PCM).
Fig. 11 Harness Connector Locks
1 - CONNECTOR LOCK
2 - CAB
Fig. 12 Pump
1 - PUMP MOTOR
2 - PUMP CONNECTOR
Fig. 13 Controller Mounting Screws
1 - CAB
2 - MOUNTING LOCATIONS
8E - 12 ELECTRONIC CONTROL MODULESBR/BE
CONTROLLER ANTILOCK BRAKE (Continued)
Page 491 of 2889

DIESEL ENGINE
Diesel engine models feature a clamping type
female battery terminal made of soft lead die cast
onto one end of the battery cable wire. A square
headed pinch-bolt and hex nut are installed at the
open end of the female battery terminal clamp. The
pinch-bolt on the left side battery positive cable
female terminal clamp also has a stud extending
from the head of the bolt. Large eyelet type terminals
are crimped onto the opposite end of the battery
cable wire and then solder-dipped. The battery posi-
tive cable wires have a red insulating jacket to pro-
vide visual identification and feature a larger female
battery terminal clamp to allow connection to the
larger battery positive terminal post. The battery
negative cable wires have a black insulating jacket
and a smaller female battery terminal clamp.
OPERATION
The battery cables connect the battery terminal
posts to the vehicle electrical system. These cables
also provide a return path for electrical current gen-
erated by the charging system for restoring the volt-
age potential of the battery. The female battery
terminal clamps on the ends of the battery cable
wires provide a strong and reliable connection of the
battery cable to the battery terminal posts. The ter-
minal pinch bolts allow the female terminal clamps
to be tightened around the male terminal posts on
the top of the battery. The eyelet terminals secured
to the ends of the battery cable wires opposite the
female battery terminal clamps provide secure and
reliable connection of the battery to the vehicle elec-
trical system.
GASOLINE ENGINE
The battery positive cable terminal clamp is
crimped onto the ends of two wires. One wire has an
eyelet terminal that connects the battery positive
cable to the B(+) terminal stud of the Power Distri-
bution Center (PDC), and the other wire has an eye-
let terminal that connects the battery positive cable
to the B(+) terminal stud of the engine starter motor
solenoid. The battery negative cable terminal clamp
is also crimped onto the ends of two wires. One wire
has an eyelet terminal that connects the battery neg-
ative cable to the vehicle powertrain through a stud
on the front of the left engine cylinder head. The
other wire has an eyelet terminal that connects the
battery negative cable to the vehicle body through a
ground screw on the left front fender inner shield,
just ahead of the battery. An additional ground wire
with two eyelet terminals is used to provide ground
to the vehicle frame. One eyelet terminal of this
ground wire is installed under the head of the bat-
tery negative cable terminal clamp pinch-bolt, andthe other eyelet terminal is secured with a ground
screw to the outer surface of the left frame rail,
below the battery.
DIESEL ENGINE
The left battery positive cable terminal clamp is
die cast onto the ends of two wires. One wire has an
eyelet terminal that connects the left battery positive
cable to the B(+) terminal stud of the Power Distri-
bution Center (PDC), and the other wire has an eye-
let terminal that connects the left battery positive
cable to the B(+) terminal stud of the engine starter
motor solenoid. The right battery positive cable ter-
minal clamp is die cast onto the end of a single wire.
The eyelet terminal on the other end of the right bat-
tery positive cable is connected to the stud on the
pinch-bolt of the left battery positive cable terminal
clamp. This stud also provides a connection point for
the eyelet terminals from the fuel heater relay and
intake air heater relay jumper harness take outs. All
of these eyelet terminals are secured to the left bat-
tery positive cable terminal clamp pinch-bolt stud
with a single hex nut.
The left battery negative cable terminal clamp is
die cast onto the ends of two wires. One wire has an
eyelet terminal that connects the left battery nega-
tive cable to the vehicle powertrain through a ground
screw on the left side of the engine block, below the
power steering and vacuum pumps. The other wire
has an eyelet terminal that connects the left battery
negative cable to the vehicle body through a ground
screw on the left front fender inner shield, just ahead
of the left battery. An additional ground wire with
two eyelet terminals is used to provide ground to the
vehicle frame. One eyelet terminal of this ground
wire is installed under the nut of the left battery
negative cable terminal clamp pinch-bolt, and the
other eyelet terminal is secured with a ground screw
to the outer surface of the left frame rail, below the
left battery. The right battery negative cable terminal
is also die cast onto the ends of two wires. One wire
has an eyelet terminal that connects the right bat-
tery negative cable to the vehicle powertrain through
a ground screw on the right side of the engine block,
just forward of the right engine mount. The other
wire has an eyelet terminal that connects the right
battery negative cable to the vehicle body through a
ground screw on the right front fender inner shield,
just behind the right battery.
DIAGNOSIS & TESTING - BATTERY CABLES
A voltage drop test will determine if there is exces-
sive resistance in the battery cable terminal connec-
tions or the battery cables. If excessive resistance is
found in the battery cable connections, the connec-
tion point should be disassembled, cleaned of all cor-
8F - 20 BATTERY SYSTEMBR/BE
BATTERY CABLE (Continued)
Page 494 of 2889

(4) Connect the voltmeter to measure between the
battery negative cable terminal clamp and a good
clean ground on the engine block (Fig. 25). Rotate
and hold the ignition switch in the Start position.
Observe the voltmeter. If the reading is above 0.2
volt, clean and tighten the battery negative cable
eyelet terminal connection to the engine block.
Repeat the test. If the reading is still above 0.2 volt,
replace the faulty battery negative cable.
NOTE: If the vehicle is equipped with a dual battery
system, Step 4 must be performed twice, once for
each battery.
POSITIVE CABLE REMOVAL - GASOLINE
Both the battery negative cable and the battery
positive cable are serviced in the battery wire har-
ness. If either battery cable is damaged or faulty, the
battery wire harness assembly must be replaced.
(1) Remove the positive battery cable from the bat-
tery.
(2) Remove the cover from the PDC.
(3) Remove the positive battery cable from the
PDC.
(4) Disconnect the starter motor signal wire har-
ness connector, located on the PDC housing.
(5) Disengage wire harness assembly pushpin
retainers.
(6) From under the vehicle, disengage wire har-
ness assembly pushpin retainers.
(7) Remove the positive battery cable from the
starter motor B+ terminal stud.
(8) Remove the starter motor trigger wire from the
starter motor.
(9) Remove the positive cable wire harness assem-
bly from the vehicle.
NEGATIVE CABLE REMOVAL - GASOLINE
Both the battery negative cable and the battery
positive cable are serviced in the battery wire har-
ness. If either battery cable is damaged or faulty, the
battery wire harness unit must be replaced.
(1) Turn the ignition switch to the Off position. Be
certain that all electrical accessories are turned off.
(2) Loosen the battery negative cable terminal
clamp pinch-bolt hex nut.
(3) Disconnect the battery negative cable terminal
clamp from the battery negative terminal post. If
necessary, use a battery terminal puller to remove
the terminal clamp from the battery post.
(4) Remove the negative cable jumper from the left
side of the radiator closure panel.
(5) Remove the negative cable jumper from the left
side of the frame assembly.
(6) Remove the PDC cover and remove the gener-
ator output wire from the PDC.
(7) Following the wire, remove the pushpin retain-
ers holding the wire assembly in place.
(8) Remove the negative cable eyelet from the
power steering pump pivot bolt.
(9) Remove the generator output wire from the
generator.
(10) Remove the negative battery cable assembly,
by fishing out from under the compressor mounting
bracket, if equipped.
POSITIVE CABLE INSTALLATION - GASOLINE
(1) Position the battery wire harness into the
engine compartment.
(2) Install the positive battery cable on the battery.
(3) Install the positive battery cable on the PDC.
(4) Install the cover on the PDC.
(5) Connect the starter motor signal wire harness
connector, located on the PDC housing.
(6) Install wire harness assembly pushpin retain-
ers in their original position.
(7) From under the vehicle, install wire harness
assembly pushpin retainers.
(8) Install and tighten the nut that secures the
battery positive cable eyelet terminal to the B(+) ter-
minal stud on the starter solenoid. Tighten the nut to
10 N´m (90 in. lbs.).
(9) Connect the starter motor trigger wire on the
starter motor.
(10) Reconnect the battery positive cable terminal
clamp to the battery positive terminal post. Tighten
the terminal clamp pinch-bolt hex nut to 4 N´m (35
in. lbs.).
(11) Apply a thin coating of petroleum jelly or
chassis grease to the exposed surfaces of the battery
cable terminal clamps and the battery terminal
posts.
Fig. 25 Test Ground Circuit
1 - VOLTMETER
2 - BATTERY
3 - ENGINE GROUND
BR/BEBATTERY SYSTEM 8F - 23
BATTERY CABLE (Continued)
Page 495 of 2889

NEGATIVE CABLE INSTALLATION - GASOLINE
(1) Position the battery wire harness into the
engine compartment and under the compressor
mounting bracket, if equipped.
(2) Install and tighten the nut that secures the
battery negative cable ground eyelet terminal to the
stud on the power steering pump pivot bolt.
(3) Install the generator output cable eyelet termi-
nal onto the generator output terminal stud.
(4) Install and tighten the nut that secures the
generator output cable eyelet terminal to the genera-
tor output terminal stud. Tighten the nut to 8.4 N´m
(75 in. lbs.).
(5) Position the cover for the generator output ter-
minal stud housing onto the back of the generator
and snap it into place.
(6) Secure wire assembly in place with pushpin
retainers in there original positions.
(7) Install and tighten the screw that secures the
battery negative cable eyelet terminal to the radiator
closure panel, near the battery. Tighten the screw to
40 in. lbs.
(8) Install and tighten the screw that secures the
battery negative cable eyelet terminal to the left
front side of the frame assembly. Tighten the screw
to 80 in. lbs.
(9) Install and tighten the nut that secures the
battery positive cable eyelet terminal and the gener-
ator output cable eyelet terminal to the PDC B(+)
terminal stud. Tighten the nut to 80 in. lbs.
(10) Reconnect the battery negative cable terminal
clamp to the battery negative terminal post. Tighten
the terminal clamp pinch-bolt hex nut to 35 in. lbs.
(11)
Apply a thin coating of petroleum jelly or chassis
grease to the exposed surfaces of the battery cable ter-
minal clamps and the battery terminal posts.
BATTERY TRAY
DESCRIPTION
The battery is mounted in a molded plastic tray (Fig.
26) with an integral support located in the left front cor-
ner of the engine compartment. A U-nut held in a
molded formation on each side of the battery tray pro-
vides anchor points for the battery hold down bolts. The
battery tray is secured on the outboard side to the inner
fender shield by two hex screws with washers, and from
underneath the integral battery tray support is secured
to the left front wheelhouse inner panel by two stud
plates. Each stud plate has two studs and is secured by
two nuts with washers. The stud plate that secures the
front of the battery tray support to the wheelhouse innerpanel is installed through the wheelhouse panel from
the top. The stud plate that secures the rear of the bat-
tery tray support to the wheelhouse inner panel is
installed through the wheelhouse panel from the bottom.
A hole in the bottom of the battery tray is fitted
with a battery temperature sensor. Refer toBattery
Temperature Sensorin the index of this service
manual for the location of more information on the
battery temperature sensor. Models that are
equipped with an optional vehicle speed control sys-
tem have the speed control servo secured to the inte-
gral battery tray support. Refer toSpeed Control
Servoin the index of this service manual for the
location of more information on the speed control
servo and its mounting.
Models that are equipped with the diesel engine
option have a second battery tray located in the right
front corner of the engine compartment. This second
battery tray and its mounting are mirror image of
the standard equipment left battery tray. However,
the right battery tray and support have no provisions
for a battery temperature sensor or a speed control
servo mounting bracket.
Fig. 26 Battery Tray - Typical
1 - STUD PLATE (2)
2 - NUT AND WASHER (4)
3 - FRONT WHEELHOUSE INNER PANEL
4 - SPEED CONTROL SERVO
5 - TRAY
6 - SCREW AND WASHER (2)
7 - BATTERY TREMPERATURE SENSOR
8 - U-NUT (2)
9 - FENDER INNER SHIELD
8F - 24 BATTERY SYSTEMBR/BE
BATTERY CABLE (Continued)
Page 517 of 2889

OPERATION - HEATED MIRROR SYSTEM
The solid state electronic control logic and timer
circuitry for the heated mirror system receives bat-
tery current from a fuse in the Junction Block (JB)
only when the ignition switch is in the On or Start
positions. After the heated mirror system is turned
On, the electronic control logic and timer circuitry
will automatically turn the system off after a pro-
grammed time interval of about fifteen minutes.
After the initial time interval has expired, if the
heated mirror switch is depressed and released a sec-
ond time during the same ignition cycle, the elec-
tronic control logic and timer circuitry will
automatically turn the heated mirror system off after
a programmed time interval of about five minutes.
The heated mirror system will be shut off automati-
cally if the ignition switch is turned to the Off or
Accessory positions. After the heated mirror system
is turned On, it can also be turned off manually by
depressing and releasing the heated mirror switch a
second time.
When the heated mirror system is turned On, the
heated mirror system control logic and timer cir-
cuitry energizes the heated mirror system indicator
lamp and the heated mirror relay. When energized,
the heated mirror relay supplies fused ignition
switch output (run/start) current from a fuse in the
JB to the outside mirror heating grids located behind
the mirror glass of each of the outside rear view mir-
rors. When energized, each of the outside mirror
heating grids produces enough heat to warm the
glass of the outside rear view mirrors.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - HEATED MIRROR
SYSTEM
If only one of the outside mirror heating grids is
inoperative, perform continuity checks on the circuits
and heater grid for that mirror only. If both outside
mirror heating grids are inoperative, proceed with
the heated mirror system diagnosis as follows. (Refer
to Appropriate Wiring Information).
WARNING: ON VEHICLES EQUIPPED WITH AIR-
BAGS, DISABLE THE AIRBAG SYSTEM BEFORE
ATTEMPTING ANY STEERING WHEEL, STEERING
COLUMN, OR INSTRUMENT PANEL COMPONENT
DIAGNOSIS OR SERVICE. DISCONNECT AND ISO-
LATE THE BATTERY NEGATIVE (GROUND) CABLE,
THEN WAIT TWO MINUTES FOR THE AIRBAG SYS-
TEM CAPACITOR TO DISCHARGE BEFORE PER-
FORMING FURTHER DIAGNOSIS OR SERVICE. THIS
IS THE ONLY SURE WAY TO DISABLE THE AIRBAG
SYSTEM. FAILURE TO TAKE THE PROPER PRE-
CAUTIONS COULD RESULT IN ACCIDENTAL AIR-
BAG DEPLOYMENT AND POSSIBLE PERSONAL
INJURY.The operation of the heated mirror system can be
confirmed in one of the following manners:
²Turn the ignition switch to the On position.
While monitoring the instrument panel voltmeter,
momentarily depress and release the heated mirror
switch. When the heated mirror system is turned On,
a distinct voltmeter needle deflection should be
noted.
²Turn the ignition switch to the On position.
Momentarily depress and release the heated mirror
switch to turn the heated mirror system On. The
heated mirror operation can be checked by feeling
the outside rear view mirror glass. A distinct differ-
ence in temperature between the unheated and
heated mirror glass can be detected within three to
four minutes of system operation.
The above checks will confirm system operation.
Illumination of the heated mirror system indicator
lamp means that there is electrical current available
at the heated mirror relay, but does not confirm that
the electrical current is reaching the outside mirror
heating grids.
If the heated mirror system does not operate, the
problem should be isolated in the following manner:
(1) Confirm that the ignition switch is in the On
position.
(2) Check the fuses in the Power Distribution Cen-
ter (PDC) and in the Junction Block (JB). The fuses
must be tight in their receptacles and all electrical
connections must be secure.
When the above steps have been completed and
both outside mirror heating grids are still inopera-
tive, one or more of the following is faulty:
²Heated mirror switch, electronic control logic
and timer circuitry, and heated mirror relay.
²Heated mirror wire harness circuits or connec-
tors.
²Outside mirror heating grid (both mirror grids
would have to be faulty).
If turning On the heated mirror system produces a
severe voltmeter deflection or fuse failures, check for
a shorted circuit between the output of the heated
mirror relay and the outside mirror heating grids.
8G - 2 HEATED MIRRORSBR/BE
HEATED MIRRORS (Continued)
Page 521 of 2889

OPERATION
The heated seat module receives fused battery cur-
rent through the energized heated seat relay in the
Junction Block (JB) only when the engine is running.
The heated seat switches receive battery current
through a fused ignition switch output (run) circuit
only when the ignition switch is in the On position.
The heated seat module shares a common ground cir-
cuit with each of the heated seat elements. The
heated seat elements will only operate when the sur-
face temperature of the seat cushion cover at the
heated seat sensors is below the designed tempera-
ture set points of the system.
The heated seat module will automatically turn off
the heated seat elements if it detects a short in the
heated seat element circuit or a heated seat sensor
value that is out of range. The heated seat system
will also be turned off automatically whenever the
ignition switch is turned to any position except On or
if the engine quits running. If the ignition switch is
turned to the Off position or if the engine quits run-
ning while a heated seat is turned ON, the heated
seat will remain Off after the engine is restarted
until a heated seat switch is depressed again.
The heated seat module monitors inputs from the
heated seat sensors and the heated seat switches. In
response to these inputs the heated seat module uses
its internal programming to control outputs to the
heated seat elements in both front seats and to con-
trol the heated seat LED indicator lamps located in
both of the heated seat switches. The heated seat
module is also programmed to provide a self-diagnos-
tic capability. When the module detects certain fail-
ures within the heated seat system, it will provide a
visual indication of the failure by flashing the indica-
tor lamps in the heated seat switches.
DIAGNOSIS & TESTING - HEATED SEAT
SYSTEM
SELF-DIAGNOSIS
The heated seat system is capable of performing
some self-diagnostics. The following table depicts the
various failure modes which will be reported to the
vehicle operator or technician by flashing the individ-
ual heated seat switch Light Emitting Diode (LED)
indicator lamps. See the Heated Seat System Self-Di-
agnosis table for the diagnostic routines. The driver
side heated seat switch indicator lamps will flash if a
failure occurs in the driver side heated seat, and the
passenger side heated seat switch indicator lamps
will flash for a passenger side heated seat failure. If
a monitored heated seat system failure occurs, the
switch indicator lamps will flash at a pulse rate of
about one-half second on, followed by about one-half
second off for a duration of about one minute afterthe switch for the faulty heated seat is depressed in
either the Low or High direction. This process will
repeat every time the faulty heated seat switch is
actuated until the problem has been corrected.
Heated Seat System Self-Diagnosis
Monitored FailureSwitch High
Indicator LampSwitch Low
Indicator Lamp
Heated Seat
Element ShortedFlashing Flashing
Heated Seat
Element OpenFlashing Off
Heated Seat
Sensor Value Out
of RangeOff Flashing
TESTING
Refer toPower Seatin the index of this service
manual for the location of complete heated seat sys-
tem wiring diagrams. Before testing the individual
components in the heated seat system, perform the
following preliminary checks:
WARNING: ON VEHICLES EQUIPPED WITH AIR-
BAGS, DISABLE THE AIRBAG SYSTEM BEFORE
ATTEMPTING ANY STEERING WHEEL, STEERING
COLUMN, OR INSTRUMENT PANEL COMPONENT
DIAGNOSIS OR SERVICE. DISCONNECT AND ISO-
LATE THE BATTERY NEGATIVE (GROUND) CABLE,
THEN WAIT TWO MINUTES FOR THE AIRBAG SYS-
TEM CAPACITOR TO DISCHARGE BEFORE PER-
FORMING FURTHER DIAGNOSIS OR SERVICE. THIS
IS THE ONLY SURE WAY TO DISABLE THE AIRBAG
SYSTEM. FAILURE TO TAKE THE PROPER PRE-
CAUTIONS COULD RESULT IN ACCIDENTAL AIR-
BAG DEPLOYMENT AND POSSIBLE PERSONAL
INJURY.
²If the heated seat switch back lighting and the
cluster illumination lamps do not illuminate with the
headlamps or park lamps turned On, refer toInstru-
ment Clusterin the index of this service manual for
the location of the proper cluster illumination lamps
diagnosis and testing procedures. If the heated seat
switch back lighting does not illuminate, but the
cluster illumination lamps do illuminate with the
headlamps or park lamps turned On, refer to
Heated Seat Switchin this section for the location
of the proper heated seat switch diagnosis and test-
ing procedure.
²If a single indicator lamp for one heated seat
switch does not operate and the heated seat elements
do heat, refer toHeated Seat Switchin this section
for the location of the proper heated seat switch diag-
nosis and testing procedure.
8G - 6 HEATED SEAT SYSTEMBR/BE
HEATED SEAT SYSTEM (Continued)
Page 527 of 2889

ifications have common physical dimensions, current
capacities, terminal patterns, and terminal functions.
The ISO micro-relay terminal functions are the same
as a conventional ISO relay. However, the ISO micro-
relay terminal pattern (or footprint) is different, the
current capacity is lower, and the physical dimen-
sions are smaller than those of the conventional ISO
relay.
The heated seat relay cannot be repaired or
adjusted and, if faulty or damaged, it must be
replaced.
OPERATION
The ISO relay consists of an electromagnetic coil, a
resistor or diode, and three (two fixed and one mov-
able) electrical contacts. The movable (common feed)
relay contact is held against one of the fixed contacts
(normally closed) by spring pressure. When the elec-
tromagnetic coil is energized, it draws the movable
contact away from the normally closed fixed contact,
and holds it against the other (normally open) fixed
contact. When the electromagnetic coil is de-ener-
gized, spring pressure returns the movable contact to
the normally closed position. The resistor or diode is
connected in parallel with the electromagnetic coil in
the relay, and helps to dissipate voltage spikes that
are produced when the coil is de-energized.
The heated seat relay is controlled by the premium
version of the Central Timer Module (CTM), which
controls the ground feed to the coil ground terminal
of the relay to energize and de-energize the electro-
magnetic coil of the relay. The CTM monitors engine
operation through messages it receives from the Pow-
ertrain Control Module (PCM) over the Chrysler Col-
lision Detection (CCD) data bus network. The CTM is
programmed to energize the relay only when the
engine is running, and to de-energize the relay when
the engine is not running. Refer toCentral Timer
Modulein the index of this service manual for the
location of more information on the premium CTM.
DIAGNOSIS & TESTING - HEATED SEAT RELAY
The heated seat relay (Fig. 7) is located in the
Junction Block (JB) on the left end of the instrument
panel in the passenger compartment of the vehicle.
Refer toWiring Diagramsfor the location of com-
plete heated seat system wiring diagrams.
WARNING: ON VEHICLES EQUIPPED WITH AIR-
BAGS, DISABLE THE AIRBAG SYSTEM BEFORE
ATTEMPTING ANY STEERING WHEEL, STEERING
COLUMN, OR INSTRUMENT PANEL COMPONENT
DIAGNOSIS OR SERVICE. DISCONNECT AND ISO-
LATE THE BATTERY NEGATIVE (GROUND) CABLE,
THEN WAIT TWO MINUTES FOR THE AIRBAG SYS-
TEM CAPACITOR TO DISCHARGE BEFORE PER-FORMING FURTHER DIAGNOSIS OR SERVICE. THIS
IS THE ONLY SURE WAY TO DISABLE THE AIRBAG
SYSTEM. FAILURE TO TAKE THE PROPER PRE-
CAUTIONS COULD RESULT IN ACCIDENTAL AIR-
BAG DEPLOYMENT AND POSSIBLE PERSONAL
INJURY.
RELAY TEST
(1) Remove the heated seat relay from the JB.
Refer toHeated Seat Relayin this section for the
location of the proper heated seat relay removal pro-
cedures.
(2) A relay in the de-energized position should
have continuity between terminals 87A and 30, and
no continuity between terminals 87 and 30. If OK, go
to Step 3. If not OK, replace the faulty relay.
(3) Resistance between terminals 85 and 86 (elec-
tromagnet) should be 75 5 ohms. If OK, go to Step
4. If not OK, replace the faulty relay.
(4) Connect a battery to terminals 85 and 86.
There should now be continuity between terminals
30 and 87, and no continuity between terminals 87A
and 30. If OK, perform the Relay Circuit Test that
follows. If not OK, replace the faulty relay.
RELAY CIRCUIT TEST
(1) The relay common feed terminal cavity (30) is
connected to battery voltage and should be hot at all
times. If OK, go to Step 2. If not OK, repair the open
circuit to the fused B(+) fuse in the Power Distribu-
tion Center (PDC) as required.
(2) The relay normally closed terminal (87A) is
connected to terminal 30 in the de-energized position,
but is not used for this application. Go to Step 3.
Fig. 7 Heated Seat Relay
TERMINAL LEGEND
NUMBER IDENTIFICATION
30 COMMON FEED
85 COIL GROUND
86 COIL BATTERY
87 NORMALLY OPEN
87A NORMALLY CLOSED
8G - 12 HEATED SEAT SYSTEMBR/BE
HEATED SEAT RELAY (Continued)