2001 DODGE RAM service
[x] Cancel search: servicePage 1265 of 2889

DIAGNOSIS AND TESTINGÐENGINE
DIAGNOSIS - INTRODUCTION
Engine diagnosis is helpful in determining the
causes of malfunctions not detected and remedied by
routine maintenance.
These malfunctions may be classified as either
mechanical (e.g., a strange noise), or performance
(e.g., engine idles rough and stalls).
(Refer to 9 - ENGINE - DIAGNOSIS AND TEST-
ING - Preformance) or (Refer to 9 - ENGINE - DIAG-
NOSIS AND TESTING - Mechanical). Refer to 14 -
FUEL SYSTEM for fuel system diagnosis.Additional tests and diagnostic procedures may be
necessary for specific engine malfunctions that can-
not be isolated with the Service Diagnosis charts.
Information concerning additional tests and diagno-
sis is provided within the following:
²Cylinder Compression Pressure Test
²Cylinder Combustion Pressure Leakage Test
²Cylinder Head Gasket Failure Diagnosis
²Intake Manifold Leakage Diagnosis
²Lash Adjuster (Tappet) Noise Diagnosis
²Engine Oil Leak Inspection
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTINGÐPERFORMANCE
PERFORMANCE DIAGNOSIS CHARTÐGASOLINE ENGINES
CONDITION POSSIBLE CAUSES CORRECTION
ENGINE WILL NOT CRANK 1. Weak or dead battery 1. Charge/Replace Battery. (Refer to
8 - ELECTRICAL/BATTERY
SYSTEM/BATTERY - STANDARD
PROCEDURE). Check charging
system. (Refer to 8 - ELECTRICAL/
CHARGING - DIAGNOSIS AND
TESTING).
2. Corroded or loose battery
connections2. Clean/tighten suspect battery/
starter connections
3. Faulty starter or related circuit(s) 3. Check starting system. (Refer to
8 - ELECTRICAL/STARTING -
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING)
4. Seized accessory drive
component4. Remove accessory drive belt and
attempt to start engine. If engine
starts, repair/replace seized
component.
5. Engine internal mechanical
failure or hydro-static lock5. Refer to (Refer to 9 - ENGINE -
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING)
ENGINE CRANKS BUT WILL NOT
START1. No spark 1. Check for spark. (Refer to 8 -
ELECTRICAL/IGNITION CONTROL
- DESCRIPTION)
2. No fuel 2. Perform fuel pressure test, and if
necessary, inspect fuel injector(s)
and driver circuits. (Refer to 14 -
FUEL SYSTEM/FUEL DELIVERY/
FUEL PUMP - DIAGNOSIS AND
TESTING).
3. Low or no engine compression 3. Perform cylinder compression
pressure test. (Refer to 9 - ENGINE
- DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING).
9 - 118 ENGINE 5.9LBR/BE
ENGINE 5.9L (Continued)
Page 1276 of 2889
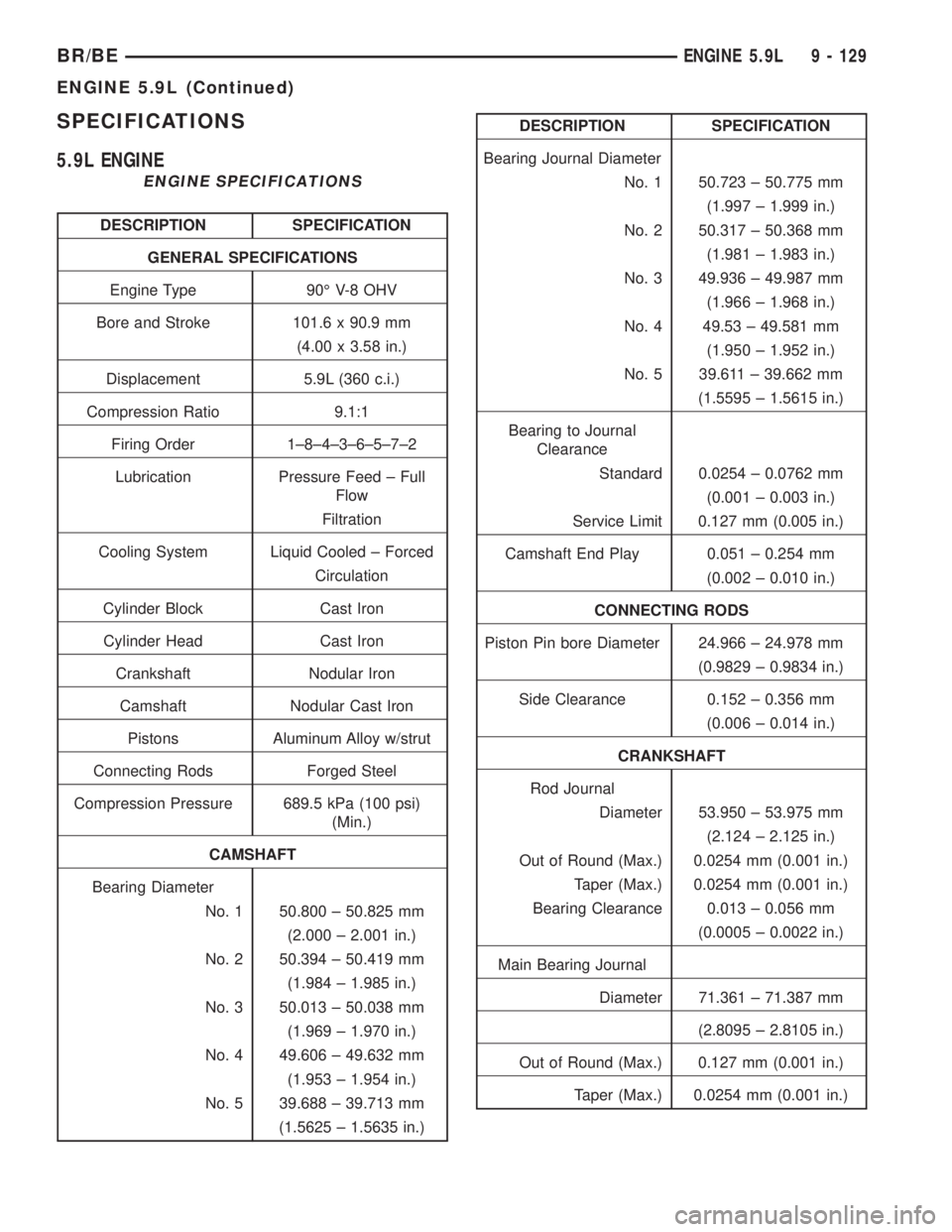
SPECIFICATIONS
5.9L ENGINE
ENGINE SPECIFICATIONS
DESCRIPTION SPECIFICATION
GENERAL SPECIFICATIONS
Engine Type 90É V-8 OHV
Bore and Stroke 101.6 x 90.9 mm
(4.00 x 3.58 in.)
Displacement 5.9L (360 c.i.)
Compression Ratio 9.1:1
Firing Order 1±8±4±3±6±5±7±2
Lubrication Pressure Feed ± Full
Flow
Filtration
Cooling System Liquid Cooled ± Forced
Circulation
Cylinder Block Cast Iron
Cylinder Head Cast Iron
Crankshaft Nodular Iron
Camshaft Nodular Cast Iron
Pistons Aluminum Alloy w/strut
Connecting Rods Forged Steel
Compression Pressure 689.5 kPa (100 psi)
(Min.)
CAMSHAFT
Bearing Diameter
No. 1 50.800 ± 50.825 mm
(2.000 ± 2.001 in.)
No. 2 50.394 ± 50.419 mm
(1.984 ± 1.985 in.)
No. 3 50.013 ± 50.038 mm
(1.969 ± 1.970 in.)
No. 4 49.606 ± 49.632 mm
(1.953 ± 1.954 in.)
No. 5 39.688 ± 39.713 mm
(1.5625 ± 1.5635 in.)
DESCRIPTION SPECIFICATION
Bearing Journal Diameter
No. 1 50.723 ± 50.775 mm
(1.997 ± 1.999 in.)
No. 2 50.317 ± 50.368 mm
(1.981 ± 1.983 in.)
No. 3 49.936 ± 49.987 mm
(1.966 ± 1.968 in.)
No. 4 49.53 ± 49.581 mm
(1.950 ± 1.952 in.)
No. 5 39.611 ± 39.662 mm
(1.5595 ± 1.5615 in.)
Bearing to Journal
Clearance
Standard 0.0254 ± 0.0762 mm
(0.001 ± 0.003 in.)
Service Limit 0.127 mm (0.005 in.)
Camshaft End Play 0.051 ± 0.254 mm
(0.002 ± 0.010 in.)
CONNECTING RODS
Piston Pin bore Diameter 24.966 ± 24.978 mm
(0.9829 ± 0.9834 in.)
Side Clearance 0.152 ± 0.356 mm
(0.006 ± 0.014 in.)
CRANKSHAFT
Rod Journal
Diameter 53.950 ± 53.975 mm
(2.124 ± 2.125 in.)
Out of Round (Max.) 0.0254 mm (0.001 in.)
Taper (Max.) 0.0254 mm (0.001 in.)
Bearing Clearance 0.013 ± 0.056 mm
(0.0005 ± 0.0022 in.)
Main Bearing Journal
Diameter 71.361 ± 71.387 mm
(2.8095 ± 2.8105 in.)
Out of Round (Max.) 0.127 mm (0.001 in.)
Taper (Max.) 0.0254 mm (0.001 in.)
BR/BEENGINE 5.9L 9 - 129
ENGINE 5.9L (Continued)
Page 1277 of 2889
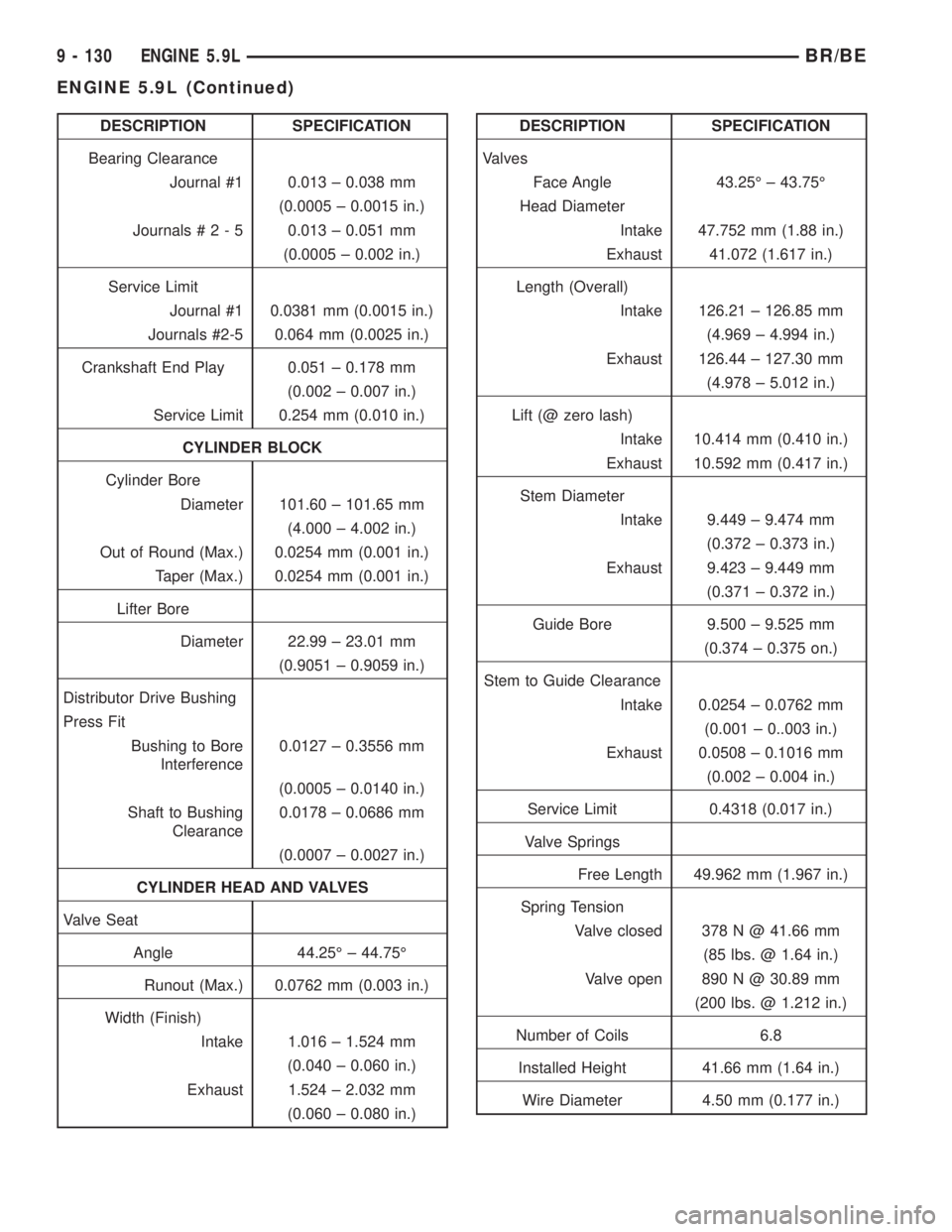
DESCRIPTION SPECIFICATION
Bearing Clearance
Journal #1 0.013 ± 0.038 mm
(0.0005 ± 0.0015 in.)
Journals#2-50.013 ± 0.051 mm
(0.0005 ± 0.002 in.)
Service Limit
Journal #1 0.0381 mm (0.0015 in.)
Journals #2-5 0.064 mm (0.0025 in.)
Crankshaft End Play 0.051 ± 0.178 mm
(0.002 ± 0.007 in.)
Service Limit 0.254 mm (0.010 in.)
CYLINDER BLOCK
Cylinder Bore
Diameter 101.60 ± 101.65 mm
(4.000 ± 4.002 in.)
Out of Round (Max.) 0.0254 mm (0.001 in.)
Taper (Max.) 0.0254 mm (0.001 in.)
Lifter Bore
Diameter 22.99 ± 23.01 mm
(0.9051 ± 0.9059 in.)
Distributor Drive Bushing
Press Fit
Bushing to Bore
Interference0.0127 ± 0.3556 mm
(0.0005 ± 0.0140 in.)
Shaft to Bushing
Clearance0.0178 ± 0.0686 mm
(0.0007 ± 0.0027 in.)
CYLINDER HEAD AND VALVES
Valve Seat
Angle 44.25É ± 44.75É
Runout (Max.) 0.0762 mm (0.003 in.)
Width (Finish)
Intake 1.016 ± 1.524 mm
(0.040 ± 0.060 in.)
Exhaust 1.524 ± 2.032 mm
(0.060 ± 0.080 in.)DESCRIPTION SPECIFICATION
Valves
Face Angle 43.25É ± 43.75É
Head Diameter
Intake 47.752 mm (1.88 in.)
Exhaust 41.072 (1.617 in.)
Length (Overall)
Intake 126.21 ± 126.85 mm
(4.969 ± 4.994 in.)
Exhaust 126.44 ± 127.30 mm
(4.978 ± 5.012 in.)
Lift (@ zero lash)
Intake 10.414 mm (0.410 in.)
Exhaust 10.592 mm (0.417 in.)
Stem Diameter
Intake 9.449 ± 9.474 mm
(0.372 ± 0.373 in.)
Exhaust 9.423 ± 9.449 mm
(0.371 ± 0.372 in.)
Guide Bore 9.500 ± 9.525 mm
(0.374 ± 0.375 on.)
Stem to Guide Clearance
Intake 0.0254 ± 0.0762 mm
(0.001 ± 0..003 in.)
Exhaust 0.0508 ± 0.1016 mm
(0.002 ± 0.004 in.)
Service Limit 0.4318 (0.017 in.)
Valve Springs
Free Length 49.962 mm (1.967 in.)
Spring Tension
Valve closed 378 N @ 41.66 mm
(85 lbs. @ 1.64 in.)
Valve open 890 N @ 30.89 mm
(200 lbs. @ 1.212 in.)
Number of Coils 6.8
Installed Height 41.66 mm (1.64 in.)
Wire Diameter 4.50 mm (0.177 in.)
9 - 130 ENGINE 5.9LBR/BE
ENGINE 5.9L (Continued)
Page 1286 of 2889

(2) Attach dial indicator Tool C-3339 to cylinder
head and set it at right angles to valve stem being
measured (Fig. 9).
(3) Move valve to and from the indicator. The total
dial indicator reading should not exceed 0.432 mm
(0.017 in.). Ream the guides for valves with oversize
stems if dial indicator reading is excessive or if the
stems are scuffed or scored.
VALVE GUIDES
Service valves with oversize stems are available.
Refer to REAMER SIZES CHART
REAMER SIZES CHART
REAMER O/S VALVE GUIDE SIZE
0.076 mm 8.026 - 8.052 mm
(0.003 in.) (0.316 - 0.317 in.)
0.381 mm 8.331 - 8.357 mm
(0.015 in.) (0.328 - 0.329 in.)(1)
Slowly turn reamer by hand and clean guide thor-
oughly before installing new valve.Ream the valve
guides from standard to 0.381 mm (0.015 in.). Use
a two step procedure so the valve guides are
reamed true in relation to the valve seat:
²Step 1ÐReam to 0.0763 mm (0.003 inch).
²Step 2ÐReam to 0.381 mm (0.015 inch).
REFACING VALVES AND VALVE SEATS
The intake and exhaust valves have a 43-1/4É to
43-3/4É face angle and a 44-1/4É to 44-3/4É seat angle
(Fig. 10).
VALVE FACE AND VALVE SEAT ANGLE CHART
ITEM DESCRIPTION SPECIFICATION
ASEAT WIDTH
INTAKE 1.016 - 1.524 mm
(0.040 - 0.060 in.)
EXHAUST 1.524 - 2.032 mm
(0.060 - 0.080 in.)
BFACE ANGLE
(INT. AND EXT.) 43òÉ - 43ôÉ
CSEAT ANGLE
(INT. AND EXT.) 44òÉ - 44ôÉ
DCONTACT
SURFACE Ð
Fig. 8 Positioning Valve with Tool C-3973
1 - VALVE
2 - SPACER TOOL
Fig. 9 Measuri2ng Valve Guide Wear
1 - VALVE
2 - SPECIAL TOOL C-3339
Fig. 10 Valve Face and Seat Angles
1 - CONTACT POINT
A,B,C and D Refer to VALVE FACE AND VALVE SEAT ANGLE
CHART
BR/BEENGINE 5.9L 9 - 139
INTAKE/EXHAUST VALVES & SEATS (Continued)
Page 1289 of 2889

ROCKER ARM / ADJUSTER
ASSY
REMOVAL
(1) Remove cylinder head cover and gasket (Refer
to 9 - ENGINE/CYLINDER HEAD/CYLINDER
HEAD COVER(S) - REMOVAL).
(2) Remove the rocker arm bolts and pivots (Fig.
16). Place them on a bench in the same order as
removed.
(3) Remove the push rods and place them on a
bench in the same order as removed.
INSTALLATION
(1) Rotate the crankshaft until the ªV8º mark lines
up with the TDC mark on the timing chain case
cover. This mark is located 147É ATDC from the No.1
firing position.
(2) Install the push rods in the same order as
removed.
(3) Install rocker arm and pivot assemblies in the
same order as removed. Tighten the rocker arm bolts
to 28 N´m (21 ft. lbs.) torque.
CAUTION: DO NOT rotate or crank the engine dur-
ing or immediately after rocker arm installation.
Allow the hydraulic roller tappets adequate time to
bleed down (about 5 minutes).
(4) Install cylinder head cover (Refer to 9 -
ENGINE/CYLINDER HEAD/CYLINDER HEAD
COVER(S) - INSTALLATION).
ENGINE BLOCK
CLEANING
Clean cylinder block thoroughly and check all core
hole plugs for evidence of leakage.
INSPECTION
Examine block for cracks or fractures.
The cylinder walls should be checked for out-of-
round and taper. Refer to Honing Cylinder Bores in
the Service Procedures portion of this Section.
Inspect the oil line plug, the oil line plug is located
in the vertical passage at the rear of the block
between the oil-to-filter and oil-from-filter passages
(Fig. 17). Improper installation or missing plug could
cause erratic, low, or no oil pressure.
The oil plug must come out the bottom. Use flat
dowel, down the oil pressure sending unit hole from
the top, to remove oil plug.
(1) Remove oil pressure sending unit from back of
block.
(2) Insert a 3.175 mm (1/8 in.) finish wire, or
equivalent, into passage.
(3) Plug should be 190.0 to 195.2 mm (7-1/2 to
7-11/16 in.) from machined surface of block (Fig. 17).
If plug is too high, use a suitable flat dowel to posi-
tion properly.
(4) If plug is too low, remove oil pan and No. 4
main bearing cap. Use suitable flat dowel to position
properly. Coat outside diameter of plug with Mopart
Fig. 16 Rocker Arms
1 - ROCKER ARMS
2 - CYLINDER HEAD
Fig. 17 Oil Line Plug
1 - RIGHT OIL GALLERY
2 - CYLINDER BLOCK
3 - OIL FROM FILTER TO SYSTEM
4 - OIL TO FILTER
5 - FROM OIL PUMP
6 - CRANKSHAFT
7 - PLUG
9 - 142 ENGINE 5.9LBR/BE
Page 1294 of 2889

²0.254 mm (0.010 inch)
²0.305 mm (0.012 inch)
REMOVAL
(1) Remove the oil pan (Refer to 9 - ENGINE/LU-
BRICATION/OIL PAN - REMOVAL).
(2) Remove the oil pump from the rear main bear-
ing cap (Refer to 9 - ENGINE/LUBRICATION/OIL
PUMP - REMOVAL).
(3) Identify bearing caps before removal. Remove
bearing caps one at a time.
(4) Remove upper half of bearing by inserting
Crankshaft Main Bearing Remover/Installer Tool
C-3059 into the oil hole of crankshaft (Fig. 27).
(5) Slowly rotate crankshaft clockwise, forcing out
upper half of bearing shell.
INSTALLATION
Only one main bearing should be selectively fitted
while all other main bearing caps are properly tight-
ened. All bearing capbolts removed during service
procedures are to be cleaned and oiled before instal-
lation.
When installing a new upper bearing shell, slightly
chamfer the sharp edges from the plain side.
(1) Start bearing in place, and insert Crankshaft
Main Bearing Remover/Installer Tool C-3059 into oil
hole of crankshaft (Fig. 27).
(2) Slowly rotate crankshaft counterclockwise slid-
ing the bearing into position. Remove Tool C-3059.
(3) Install the bearing caps. Clean and oil the
bolts. Tighten the capbolts to 115 N´m (85 ft. lbs.)
torque.
(4) Install the oil pump (Refer to 9 - ENGINE/LU-
BRICATION/OIL PUMP - INSTALLATION).
(5) Install the oil pan (Refer to 9 - ENGINE/LU-
BRICATION/OIL PAN - INSTALLATION).
(6) Start engine check for leaks.
CRANKSHAFT OIL SEAL -
FRONT
DESCRIPTION
The crankshaft rear seal is a two piece viton seal.
The crankshaft front seal is a one piece viton seal
with a steel housing. The front seal is located in the
engine front cover. One part of the two piece rear
seal is located in a slot in the number four (4) crank-
shaft main bore, the second part of the two piece seal
is located in the number four (4) main bearing cap.
OPERATION
The crankshaft seals prevent oil from leaking from
around the crankshaft, either from the rear of the
engine or from the engine front cover.
REMOVAL
The oil seal can be replaced without removing the
timing chain cover, provided that the cover is not
misaligned.
(1) Disconnect the negative cable from the battery.
(2) Remove vibration damper (Refer to 9 -
ENGINE/ENGINE BLOCK/VIBRATION DAMPER -
REMOVAL).
(3) If front seal is suspected of leaking, check front
oil seal alignment to crankshaft. The seal installa-
tion/alignment Tool 6635, should fit with minimum
interference. If tool does not fit, the cover must be
removed and installed properly.
Fig. 26 Main Bearing
Fig. 27 Upper Main Bearing Removal and
Installation with Tool C-3059
1 - SPECIAL TOOL C-3059
2 - BEARING
3 - SPECIAL TOOL C-3059
4 - BEARING
BR/BEENGINE 5.9L 9 - 147
CRANKSHAFT MAIN BEARINGS (Continued)
Page 1296 of 2889

REMOVAL
The service seal is a two piece, Viton seal. The
upper seal half can be installed with crankshaft
removed from engine or with crankshaft installed.
When a new upper seal is installed, install a new
lower seal. The lower seal half can be installed only
with the rear main bearing cap removed.
UPPER SEAL ÐCRANKSHAFT REMOVED
(1) Remove the crankshaft (Refer to 9 - ENGINE/
ENGINE BLOCK/CRANKSHAFT - REMOVAL). Dis-
card the old upper seal.
UPPER SEALÐCRANKSHAFT INSTALLED
(1) Remove the oil pan (Refer to 9 - ENGINE/LU-
BRICATION/OIL PAN - REMOVAL).
(2) Remove the oil pump (Refer to 9 - ENGINE/
LUBRICATION/OIL PUMP - REMOVAL).
(3) Remove the rear main bearing cap. Remove
and discard the old lower oil seal.
(4) Carefully remove and discard the old upper oil
seal.
LOWER SEAL
(1) Remove the oil pan (Refer to 9 - ENGINE/LU-
BRICATION/OIL PAN - REMOVAL).
(2) Remove the oil pump (Refer to 9 - ENGINE/
LUBRICATION/OIL PUMP - REMOVAL).
(3) Remove the rear main bearing cap and discard
the old lower seal.
INSTALLATION
The service seal is a two piece, Viton seal. The
upper seal half can be installed with crankshaft
removed from engine or with crankshaft installed.
When a new upper seal is installed, install a new
lower seal. The lower seal half can be installed only
with the rear main bearing cap removed.
UPPER SEAL ÐCRANKSHAFT REMOVED
(1) Clean the cylinder block rear cap mating sur-
face. Be sure the seal groove is free of debris. Check
for burrs at the oil hole on the cylinder block mating
surface to rear cap.
(2) Lightly oil the new upper seal lips with engine
oil.
(3) Install the new upper rear bearing oil seal with
the white paint facing toward the rear of the engine.
(4) Position the crankshaft into the cylinder block.
(5) Lightly oil the new lower seal lips with engine
oil.
(6) Install the new lower rear bearing oil seal into
the bearing cap with the white paint facing towards
the rear of the engine.
(7) Apply 5 mm (0.20 in.) drop of MopartGasket
Maker, or equivalent, on each side of the rear mainbearing cap (Fig. 31). DO NOT over-apply sealant or
allow the sealant to contact the rubber seal. Assem-
ble bearing cap to cylinder block immediately after
sealant application.
(8) To align the bearing cap, use cap slot, align-
ment dowel, and cap bolts. DO NOT remove excess
material after assembly. DO NOT strike rear cap
more than two times for proper engagement.
(9) Clean and oil all cap bolts. Install all main
bearing caps. Install all cap bolts and alternately
tighten to 115 N´m (85 ft. lbs.) torque.
(10) Install oil pump (Refer to 9 - ENGINE/LU-
BRICATION/OIL PUMP - INSTALLATION).
(11) Apply MopartGEN II Silicone Rubber Adhe-
sive Sealant, or equivalent, at bearing cap-to-block
joint to provide cap to block and oil pan sealing (Fig.
32). Apply enough sealant so that a small amount is
squeezed out. Withdraw nozzle and wipe excess seal-
ant off the oil pan seal groove.
(12) Install new front crankshaft oil seal (Refer to
9 - ENGINE/ENGINE BLOCK/CRANKSHAFT OIL
SEAL - FRONT - INSTALLATION).
(13)
Immediately install the oil pan (Refer to 9 -
ENGINE/LUBRICATION/OIL PAN - INSTALLATION).
UPPER SEALÐCRANKSHAFT INSTALLED
(1) Clean the cylinder block mating surfaces before
oil seal installation. Check for burrs at the oil hole on
the cylinder block mating surface to rear cap.
(2) Lightly oil the new upper seal lips with engine
oil. To allow ease of installation of the seal, loosen at
least the two main bearing caps forward of the rear
bearing cap.
Fig. 31 Sealant Application to Bearing Cap
1 - MOPAR SILICONE RUBBER ADHESIVE SEALANT SLOTS
2 - MOPARTGASKET MAKER (OR EQUIVALENT)
3 - CAP ALIGNMENT SLOT
4 - REAR MAIN BEARING CAP
BR/BEENGINE 5.9L 9 - 149
CRANKSHAFT OIL SEAL - REAR (Continued)
Page 1307 of 2889

DIAGNOSIS AND TESTINGÐENGINE OIL
LEAKS
Begin with a through visual inspection of the
engine, particularly at the area of the suspected leak.
If an oil leak source is not readily identifiable, the
following steps should be followed:
(1) Do not clean or degrease the engine at this
time because some solvents may cause rubber to
swell, temporarily stopping the leak.
(2) Add an oil-soluble dye (use as recommended by
manufacturer). Start the engine and let idle for
approximately 15 minutes. Check the oil dipstick to
be sure the dye is thoroughly mixed as indicated
with a bright yellow color under a black light source.
(3) Using a black light, inspect the entire engine
for fluorescent dye, particularly at the suspected area
of oil leak. If the oil leak is found and identified,
repair per service manual instructions.
(4) If dye is not observed, drive the vehicle at var-
ious speeds for approximately 24km (15 miles), and
repeat previous step.
(5) If the oil leak source is not positively identified
at this time, proceed with the air leak detection test
method as follows:
(6) Disconnect the breather cap to air cleaner hose
at the breather cap end. Cap or plug breather cap
nipple.
(7) Remove the PCV valve from the cylinder head
cover. Cap or plug the PCV valve grommet.
(8) Attach an air hose with pressure gauge and
regulator to the dipstick tube.
CAUTION: Do not subject the engine assembly to
more than 20.6 kpa (3 PSI) of test pressure.
(9) Gradually apply air pressure from 1 psi to 2.5
psi maximum while applying soapy water at the sus-
pected source. Adjust the regulator to the suitable
test pressure that provide the best bubbles which
will pinpoint the leak source. If the oil leak is
detected and identified, repair per service manual
procedures.
(10) If the leakage occurs at the rear oil seal area,
refer to the section, Inspection for Rear Seal Area
Leak.
(11) If no leaks are detected, turn off the air sup-
ply and remove the air hose and all plugs and caps.
Install the PCV valve and breather cap hose. Proceed
to next step.
(12) Clean the oil off the suspect oil leak area
using a suitable solvent. Drive the vehicle at various
speeds approximately 24 km (15 miles). Inspect the
engine for signs of an oil leak by using a black light.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTINGÐENGINE OIL
PRESSURE
(1) Remove oil pressure sending unit.
(2) Install Oil Pressure Line and Gauge Tool
C-3292. Start engine and record pressure. (Refer to 9
- ENGINE - SPECIFICATIONS).
OIL
STANDARD PROCEDUREÐENGINE OIL
OIL LEVEL INDICATOR (DIPSTICK)
The engine oil level indicator is located at the right
front of the engine, left of the generator on 3.9L
engines (Fig. 50).
CRANKCASE OIL LEVEL INSPECTION
CAUTION: Do not overfill crankcase with engine oil,
oil foaming and oil pressure loss can result.
To ensure proper lubrication of an engine, the
engine oil must be maintained at an acceptable level.
The acceptable levels are indicated between the ADD
and SAFE marks on the engine oil dipstick.
(1) Position vehicle on level surface.
(2) With engine OFF, allow approximately ten min-
utes for oil to settle to bottom of crankcase, remove
engine oil dipstick.
(3) Wipe dipstick clean.
(4) Install dipstick and verify it is seated in the
tube.
Fig. 50 Oil Level Indicator Location
1 - CYLINDER HEAD COVER
2 - ENGINE OIL FILL CAP
3 - DIPSTICK
4 - ENGINE OIL FILTER
5 - FILTER BOSS
9 - 160 ENGINE 5.9LBR/BE
LUBRICATION (Continued)