2001 DODGE RAM sensor
[x] Cancel search: sensorPage 1453 of 2889

(3) Install the injection pump (Refer to 14 - FUEL
SYSTEM/FUEL DELIVERY/FUEL INJECTION
PUMP - INSTALLATION).
(4) Install the camshaft (Refer to 9 - ENGINE/EN-
GINE BLOCK/CAMSHAFT & BEARINGS (IN
BLOCK) - INSTALLATION). Align the crankshaft,
camshaft, and injection pump gear marks as shown
in (Fig. 178).
(5) If a new housing is installed, the camshaft
position sensor must be transferred to the new hous-
ing.
(6) Obtain a seal pilot/installation tool from a
crankshaft front seal service kit and install the pilot
into the crankshaft front oil seal.
(7) Apply a bead of MopartSilicone Rubber Adhe-
sive Sealant or equivalent to the gear housing cover.
Be sure to surround all through holes.
(8) Using the seal pilot to align the cover (Fig.
179), install the cover to the housing and install the
bolts. Tighten the bolts to 24 N´m (18 ft. lbs.) torque.
(9) Remove the seal pilot.
(10) Raise the vehicle.
(11) Trim any excess gear housing gasket to make
it flush with the oil pan rail.
(12) Using a new gasket, install the oil pan and
suction tube (Refer to 9 - ENGINE/LUBRICATION/
OIL PAN - INSTALLATION).
(13) Install the crankshaft damper (Fig. 175)
(Refer to 9 - ENGINE/ENGINE BLOCK/VIBRATION
DAMPER - INSTALLATION).
(14) Lower vehicle.
(15) Install the fan support/hub assembly (Fig.
174) and tighten bolts to 24 N´m (18 ft. lbs.) torque.(16) Install the accessory drive belt (Refer to 7 -
COOLING/ACCESSORY DRIVE/DRIVE BELTS -
INSTALLATION).
(17) Install the cooling fan and shroud together
(Refer to 7 - COOLING/ENGINE/RADIATOR FAN -
INSTALLATION).
(18) Install the windshield washer reservoir to the
fan shroud and connect the washer pump supply
hose and electrical connection.
(19) Install the coolant recovery bottle to the fan
shroud and connect the hose to the radiator filler
neck.
(20) Install the radiator upper hose and clamps.
(21) Add engine oil.
(22) Add coolant (Refer to 7 - COOLING - STAN-
DARD PROCEDURE).
(23) Connect the battery cables.
(24) Start engine and inspect for leaks.
GEAR HOUSING COVER
REMOVAL
(1) Disconnect both battery negative cables.
(2) Raise vehicle on hoist.
(3) Partially drain engine coolant into container
suitable for re-use (Refer to 7 - COOLING - STAN-
DARD PROCEDURE).
(4) Lower vehicle.
(5) Remove radiator upper hose.
(6) Disconnect coolant recovery bottle hose from
radiator filler neck and lift bottle off of fan shroud.
(7) Disconnect windshield washer pump supply
hose and electrical connections and lift washer bottle
off of fan shroud.
(8) Remove viscous fan/drive assembly (Refer to 7 -
COOLING/ENGINE/RADIATOR FAN - REMOVAL).
Fig. 178 Camshaft/Crankshaft Gear Alignment
Fig. 179 Installing Cover with Seal Pilot
1 - SEAL PILOT
9 - 306 ENGINE 5.9L DIESELBR/BE
GEAR HOUSING (Continued)
Page 1459 of 2889

DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - GAS ENGINE
EXHAUST SYSTEM DIAGNOSIS CHART
CONDITION POSSIBLE CAUSE CORRECTION
EXCESSIVE EXHAUST NOISE OR
LEAKING EXHAUST GASES1. Leaks at pipe joints. 1. Tighten clamps/bolts at leaking
joints.
2. Rusted or blown out muffler. 2. Replace muffler. Inspect exhaust
system.
3. Broken or rusted out exhaust
pipe.3. Replace exhaust pipe.
4. Exhaust pipe leaking at manifold
flange.4. Tighten/replace flange attaching
nuts/bolts.
5. Exhaust manifold cracked or
broken.5. Replace exhaust manifold.
6. Leak between exhaust manifold
and cylinder head.6. Tighten exhaust manifold to
cylinder head bolts.
7. Catalytic converter rusted or
blown out.7. Replace catalytic converter assy.
8. Restriction in exhaust system. 8. Remove restriction, if possible.
Replace restricted part if necessary.
caution:
When servicing and replacing exhaust system components, disconnect the oxygen sensor connector(s).
Allowing the exhaust to hang by the oxygen sensor wires will damage the harness and/or sensor.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - DIESEL ENGINE
EXHAUST SYSTEM DIAGNOSIS CHART
CONDITION POSSIBLE CAUSE CORRECTION
EXCESSIVE EXHAUST NOISE OR
LEAKING EXHAUST GASES1. Leaks at pipe joints. 1. Tighten clamps/bolts at leaking
joints.
2. Rusted or blown out muffler. 2. Replace muffler. Inspect exhaust
system.
3. Broken or rusted out exhaust
pipe.3. Replace exhaust pipe.
4. Exhaust pipe leaking at manifold
flange.4. Tighten/replace flange attaching
nuts/bolts.
5. Exhaust manifold cracked or
broken.5. Replace exhaust manifold.
6. Leak between exhaust manifold
and cylinder head.6. Tighten exhaust manifold to
cylinder head bolts.
7. Turbocharger mounting flange
cracked.7. Remove turbocharger and
inspect. (Refer to 11 - EXHAUST
SYSTEM/TURBOCHARGER
SYSTEM/TURBOCHARGER -
REMOVAL).
8. Restriction in exhaust system. 8. Remove restriction, if possible.
Replace restricted part if necessary.
11 - 4 EXHAUST SYSTEMBR/BE
EXHAUST SYSTEM (Continued)
Page 1488 of 2889

FUEL SYSTEM
TABLE OF CONTENTS
page page
FUEL DELIVERY - GASOLINE................1
FUEL INJECTION - GASOLINE..............28FUEL DELIVERY - DIESEL.................54
FUEL INJECTION - DIESEL.................87
FUEL DELIVERY - GASOLINE
TABLE OF CONTENTS
page page
FUEL DELIVERY - GASOLINE
DESCRIPTION............................2
OPERATION.............................2
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING..................2
FUEL PRESSURE LEAK DOWN TEST........2
STANDARD PROCEDURE...................3
FUEL SYSTEM PRESSURE RELEASE
PROCEDURE...........................3
SPECIFICATIONS.........................4
SPECIAL TOOLS..........................4
FUEL FILTER/PRESSURE REGULATOR
DESCRIPTION............................5
OPERATION.............................5
REMOVAL...............................5
INSTALLATION............................6
FUEL LEVEL SENDING UNIT / SENSOR
DESCRIPTION............................7
OPERATION.............................7
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING..................8
FUEL GAUGE SENDING UNIT..............8
REMOVAL...............................8
INSTALLATION............................9
FUEL LINES
DESCRIPTION............................9
FUEL PUMP
DESCRIPTION............................9
OPERATION.............................9
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING..................9
FUEL PUMP CAPACITY TEST..............9FUEL PUMP PRESSURE TEST............10
FUEL PUMP AMPERAGE TEST............10
FUEL PUMP MODULE
DESCRIPTION...........................12
OPERATION.............................13
REMOVAL..............................13
INSTALLATION...........................13
FUEL RAIL
DESCRIPTION...........................15
OPERATION.............................15
REMOVAL..............................16
INSTALLATION...........................18
FUEL TANK
DESCRIPTION...........................19
OPERATION.............................19
REMOVAL..............................19
INSTALLATION...........................20
INLET FILTER
REMOVAL..............................22
INSTALLATION...........................22
QUICK CONNECT FITTING
DESCRIPTION...........................22
STANDARD PROCEDURE..................22
QUICK-CONNECT FITTINGS..............22
ROLLOVER VALVE
DESCRIPTION...........................25
REMOVAL..............................26
INSTALLATION...........................27
BR/BEFUEL SYSTEM 14 - 1
Page 1489 of 2889

FUEL DELIVERY - GASOLINE
DESCRIPTION - FUEL DELIVERY SYSTEM
The fuel delivery system consists of:
²the fuel pump module containing the electric
fuel pump, fuel filter/fuel pressure regulator, rollover
valve (certain modules), fuel gauge sending unit (fuel
level sensor) and a separate fuel filter located at bot-
tom of pump module
²fuel tubes/lines/hoses
²quick-connect fittings
²fuel injector rail
²fuel injectors
²fuel tank
²fuel tank filler/vent tube assembly
²fuel tank filler tube cap
²accelerator pedal
²throttle cable
OPERATION - FUEL DELIVERY SYSTEM
Fuel is returned through the fuel pump module
and back into the fuel tank through the fuel filter/
fuel pressure regulator. A separate fuel return line
from the engine to the tank is not used with any gas-
oline powered engine.
The fuel tank assembly consists of: the fuel tank,
fuel pump module assembly, fuel pump module lock-
nut/gasket and rollover valve(s) (refer to 25, Emis-
sion Control System for rollover valve information).
A fuel filler/vent tube assembly using a pressure/
vacuum, 1/4 turn fuel filler cap is used. The fuel
filler tube contains a flap door located below the fuel
fill cap.
Also to be considered part of the fuel system is the
evaporation control system. This is designed to
reduce the emission of fuel vapors into the atmo-
sphere. The description and function of the Evapora-
tive Control System is found in 25, Emission Control
Systems.
Both fuel filters (at bottom of fuel pump module
and within fuel pressure regulator) are designed for
extended service. They do not require normal sched-
uled maintenance. Filters should only be replaced if
a diagnostic procedure indicates to do so.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - FUEL PRESSURE
LEAK DOWN TEST
Use this test in conjunction with the Fuel Pump
Pressure Test and Fuel Pump Capacity Test.
Check Valve Operation:The electric fuel pump
outlet contains a one-way check valve to prevent fuel
flow back into the tank and to maintain fuel supply
line pressure (engine warm) when pump is not oper-
ational. It is also used to keep the fuel supply line
full of gasoline when pump is not operational. Afterthe vehicle has cooled down, fuel pressure may drop
to 0 psi (cold fluid contracts), but liquid gasoline will
remain in fuel supply line between the check valve
and fuel injectors.Fuel pressure that has
dropped to 0 psi on a cooled down vehicle
(engine off) is a normal condition.When the elec-
tric fuel pump is activated, fuel pressure should
immediately(1±2 seconds) rise to specification.
Abnormally long periods of cranking to restart a
hotengine that has been shut down for a short
period of time may be caused by:
²Fuel pressure bleeding past a fuel injector(s).
²Fuel pressure bleeding past the check valve in
the fuel pump module.
(1) Disconnect the fuel inlet line at fuel rail. Refer
to Fuel Tubes/Lines/Hoses and Clamps for proce-
dures. On some engines, air cleaner housing removal
may be necessary before fuel line disconnection.
(2) Obtain correct Fuel Line Pressure Test Adapter
Tool Hose. Tool number 6539 is used for 5/16º fuel
lines and tool number 6631 is used for 3/8º fuel lines.
(3) Connect correct Fuel Line Pressure Test
Adapter Tool Hose between disconnected fuel line
and fuel rail (Fig. 1).
Fig. 1 Connecting Adapter ToolÐTypical
1 - VEHICLE FUEL LINE
2 - TEST PORT ªTº
3 - SPECIAL TOOL 6923, 6631, 6541 OR 6539
4 - FUEL PRESSURE TEST GAUGE
5 - FUEL LINE CONNECTION AT RAIL
6 - FUEL RAIL
14 - 2 FUEL DELIVERY - GASOLINEBR/BE
Page 1491 of 2889
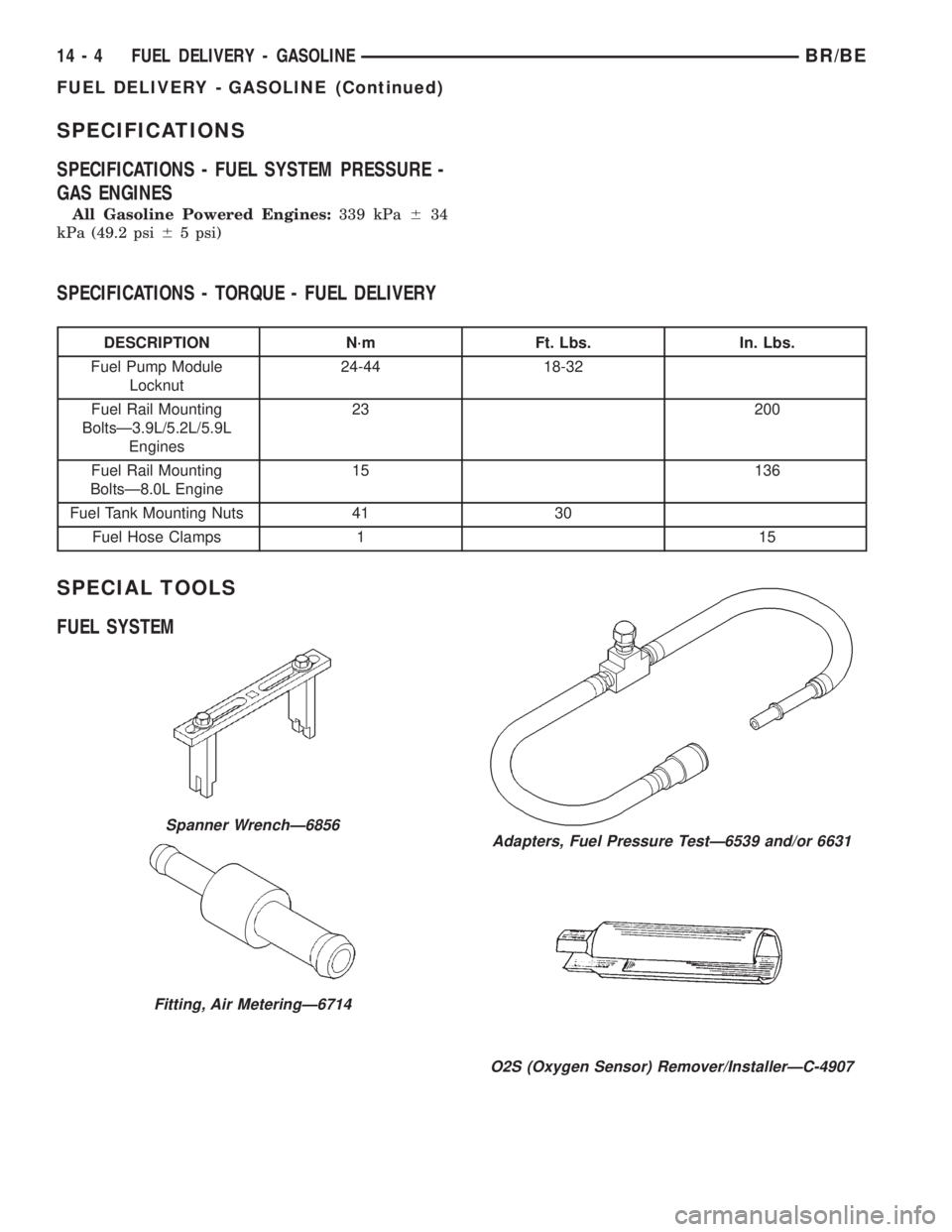
SPECIFICATIONS
SPECIFICATIONS - FUEL SYSTEM PRESSURE -
GAS ENGINES
All Gasoline Powered Engines:339 kPa634
kPa (49.2 psi65 psi)
SPECIFICATIONS - TORQUE - FUEL DELIVERY
DESCRIPTION N´m Ft. Lbs. In. Lbs.
Fuel Pump Module
Locknut24-44 18-32
Fuel Rail Mounting
BoltsÐ3.9L/5.2L/5.9L
Engines23 200
Fuel Rail Mounting
BoltsÐ8.0L Engine15 136
Fuel Tank Mounting Nuts 41 30
Fuel Hose Clamps 1 15
SPECIAL TOOLS
FUEL SYSTEM
Spanner WrenchÐ6856
Fitting, Air MeteringÐ6714
Adapters, Fuel Pressure TestÐ6539 and/or 6631
O2S (Oxygen Sensor) Remover/InstallerÐC-4907
14 - 4 FUEL DELIVERY - GASOLINEBR/BE
FUEL DELIVERY - GASOLINE (Continued)
Page 1494 of 2889
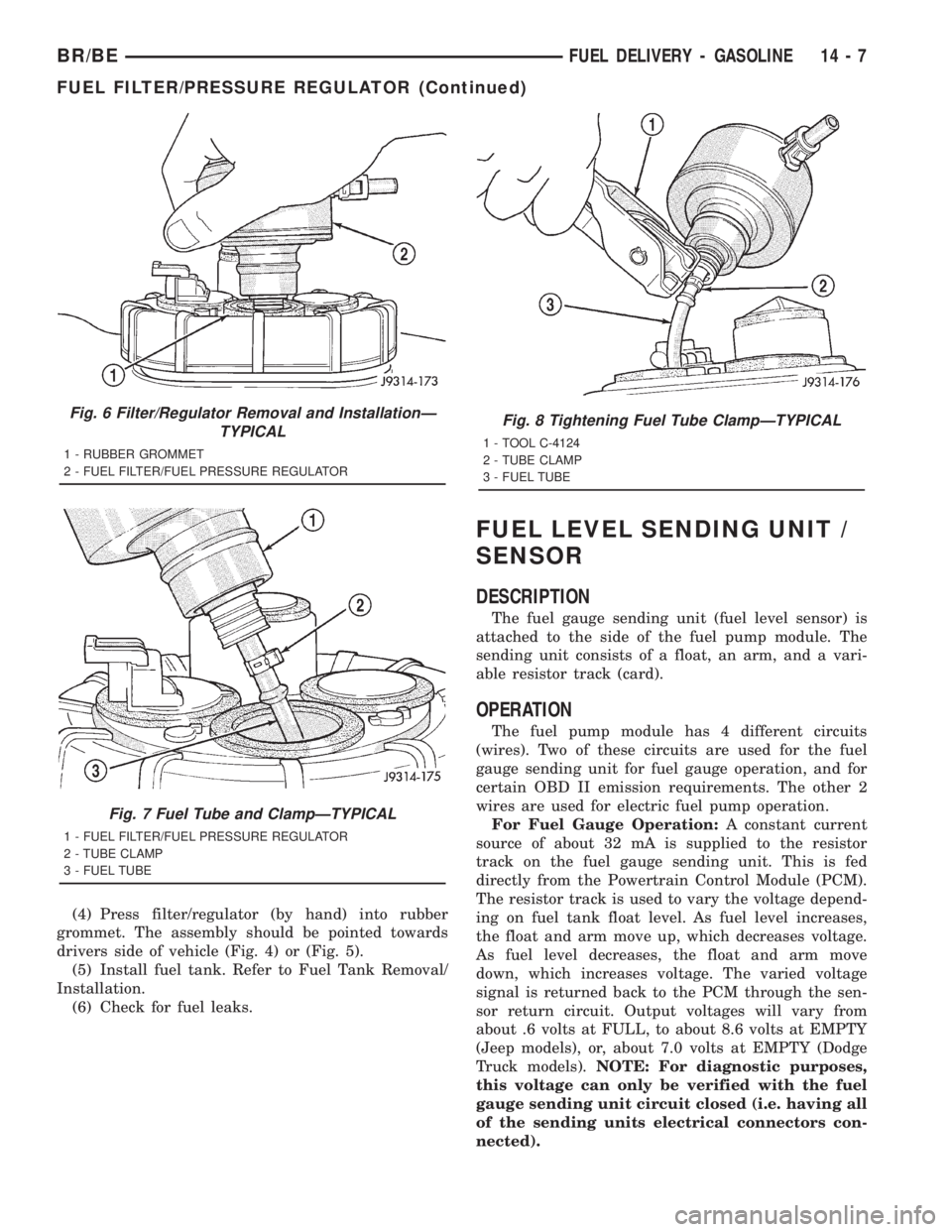
(4) Press filter/regulator (by hand) into rubber
grommet. The assembly should be pointed towards
drivers side of vehicle (Fig. 4) or (Fig. 5).
(5) Install fuel tank. Refer to Fuel Tank Removal/
Installation.
(6) Check for fuel leaks.
FUEL LEVEL SENDING UNIT /
SENSOR
DESCRIPTION
The fuel gauge sending unit (fuel level sensor) is
attached to the side of the fuel pump module. The
sending unit consists of a float, an arm, and a vari-
able resistor track (card).
OPERATION
The fuel pump module has 4 different circuits
(wires). Two of these circuits are used for the fuel
gauge sending unit for fuel gauge operation, and for
certain OBD II emission requirements. The other 2
wires are used for electric fuel pump operation.
For Fuel Gauge Operation:A constant current
source of about 32 mA is supplied to the resistor
track on the fuel gauge sending unit. This is fed
directly from the Powertrain Control Module (PCM).
The resistor track is used to vary the voltage depend-
ing on fuel tank float level. As fuel level increases,
the float and arm move up, which decreases voltage.
As fuel level decreases, the float and arm move
down, which increases voltage. The varied voltage
signal is returned back to the PCM through the sen-
sor return circuit. Output voltages will vary from
about .6 volts at FULL, to about 8.6 volts at EMPTY
(Jeep models), or, about 7.0 volts at EMPTY (Dodge
Truck models).NOTE: For diagnostic purposes,
this voltage can only be verified with the fuel
gauge sending unit circuit closed (i.e. having all
of the sending units electrical connectors con-
nected).
Fig. 6 Filter/Regulator Removal and InstallationÐ
TYPICAL
1 - RUBBER GROMMET
2 - FUEL FILTER/FUEL PRESSURE REGULATOR
Fig. 7 Fuel Tube and ClampÐTYPICAL
1 - FUEL FILTER/FUEL PRESSURE REGULATOR
2 - TUBE CLAMP
3 - FUEL TUBE
Fig. 8 Tightening Fuel Tube ClampÐTYPICAL
1 - TOOL C-4124
2 - TUBE CLAMP
3 - FUEL TUBE
BR/BEFUEL DELIVERY - GASOLINE 14 - 7
FUEL FILTER/PRESSURE REGULATOR (Continued)
Page 1495 of 2889
Both of the electrical circuits between the fuel
gauge sending unit and the PCM are hard-wired (not
multi-plexed). After the voltage signal is sent from
the resistor track, and back to the PCM, the PCM
will interpret the resistance (voltage) data and send
a message across the multi-plex bus circuits to the
instrument panel cluster. Here it is translated into
the appropriate fuel gauge level reading. Refer to
Instrument Panel for additional information.
For OBD II Emission Monitor Requirements:
The PCM will monitor the voltage output sent from
the resistor track on the sending unit to indicate fuel
level. The purpose of this feature is to prevent the
OBD II system from recording/setting false misfire
and fuel system monitor diagnostic trouble codes.
The feature is activated if the fuel level in the tank
is less than approximately 15 percent of its rated
capacity. If equipped with a Leak Detection Pump
(EVAP system monitor), this feature will also be acti-
vated if the fuel level in the tank is more than
approximately 85 percent of its rated capacity.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - FUEL GAUGE
SENDING UNIT
The fuel gauge sending unit contains a variable
resistor (track). As the float moves up or down, elec-
trical resistance will change. Refer to 8, Instrument
Panel and Gauges for Fuel Gauge testing. To test the
gauge sending unit only, it must be removed from
vehicle. The unit is part of the fuel pump module.
Refer to Fuel Pump Module Removal/Installation for
procedures. Measure the resistance across the send-
ing unit terminals. With float in up position, resis-
tance should be 20 ohms66 ohms. With float in
down position, resistance should be 220 ohms66
ohms.
REMOVAL
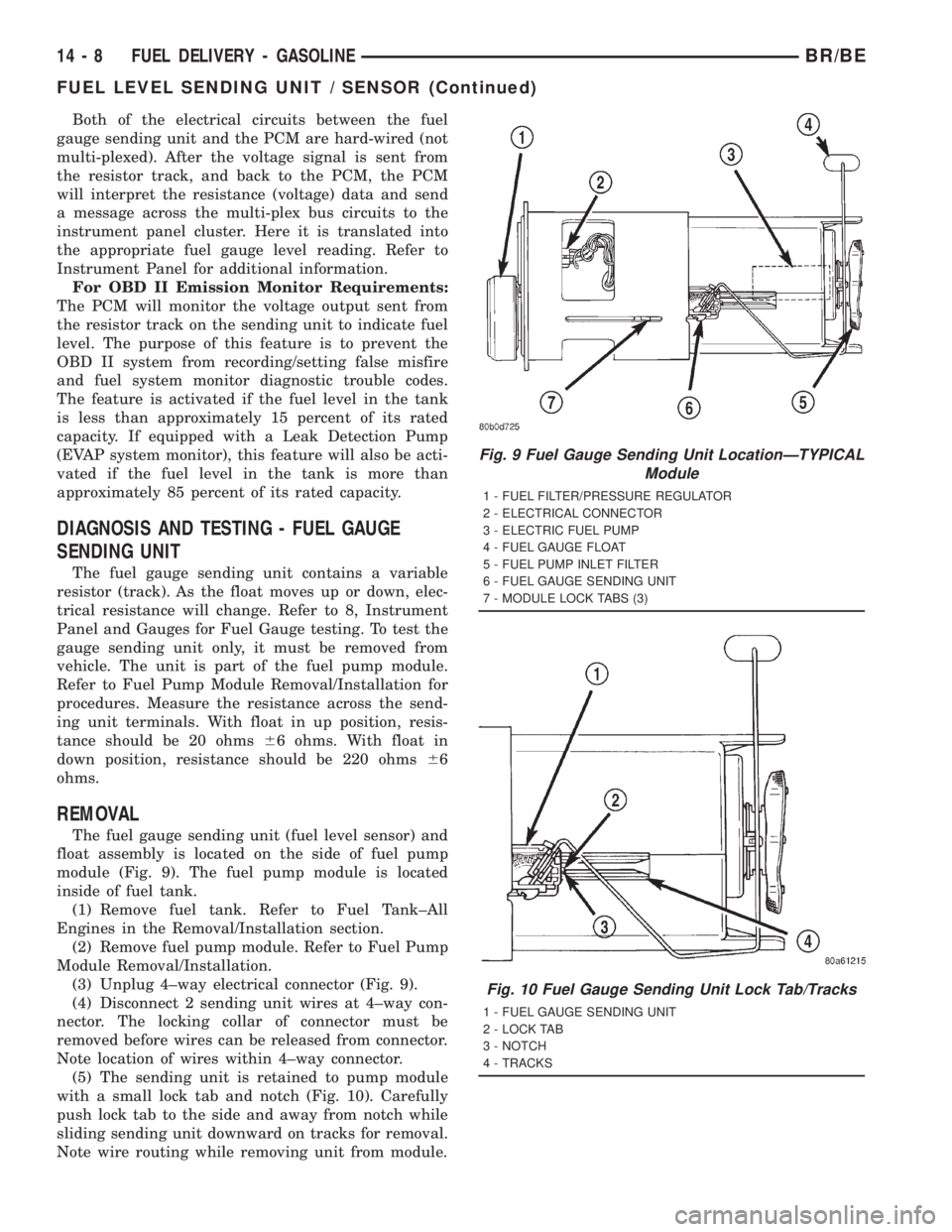
The fuel gauge sending unit (fuel level sensor) and
float assembly is located on the side of fuel pump
module (Fig. 9). The fuel pump module is located
inside of fuel tank.
(1) Remove fuel tank. Refer to Fuel Tank±All
Engines in the Removal/Installation section.
(2) Remove fuel pump module. Refer to Fuel Pump
Module Removal/Installation.
(3) Unplug 4±way electrical connector (Fig. 9).
(4) Disconnect 2 sending unit wires at 4±way con-
nector. The locking collar of connector must be
removed before wires can be released from connector.
Note location of wires within 4±way connector.
(5) The sending unit is retained to pump module
with a small lock tab and notch (Fig. 10). Carefully
push lock tab to the side and away from notch while
sliding sending unit downward on tracks for removal.
Note wire routing while removing unit from module.
Fig. 9 Fuel Gauge Sending Unit LocationÐTYPICAL
Module
1 - FUEL FILTER/PRESSURE REGULATOR
2 - ELECTRICAL CONNECTOR
3 - ELECTRIC FUEL PUMP
4 - FUEL GAUGE FLOAT
5 - FUEL PUMP INLET FILTER
6 - FUEL GAUGE SENDING UNIT
7 - MODULE LOCK TABS (3)
Fig. 10 Fuel Gauge Sending Unit Lock Tab/Tracks
1 - FUEL GAUGE SENDING UNIT
2 - LOCK TAB
3 - NOTCH
4 - TRACKS
14 - 8 FUEL DELIVERY - GASOLINEBR/BE
FUEL LEVEL SENDING UNIT / SENSOR (Continued)
Page 1496 of 2889

INSTALLATION
The fuel gauge sending unit (fuel level sensor) and
float assembly is located on the side of fuel pump
module (Fig. 9). The fuel pump module is located
inside of fuel tank.
(1) Position sending unit into tracks. Note wire
routing.
(2) Push unit on tracks until lock tab snaps into
notch.
(3) Connect 2 sending unit wires into 4±way con-
nector and install locking collar.
(4) Connect 4±way electrical connector to module.
(5) Install fuel pump module. Refer to Fuel Pump
Module Removal/Installation.
(6) Install fuel tank. Refer to Fuel Tank±All
Engines in the Removal/Installation section.
FUEL LINES
DESCRIPTION
Also refer to Quick-Connect Fittings.
WARNING: THE FUEL SYSTEM IS UNDER A CON-
STANT PRESSURE (EVEN WITH THE ENGINE OFF).
BEFORE SERVICING ANY FUEL SYSTEM HOSES, FIT-
TINGS OR LINES, THE FUEL SYSTEM PRESSURE
MUST BE RELEASED. REFER TO THE FUEL SYSTEM
PRESSURE RELEASE PROCEDURE IN THIS GROUP.
The lines/tubes/hoses used on fuel injected vehicles
are of a special construction. This is due to the
higher fuel pressures and the possibility of contami-
nated fuel in this system. If it is necessary to replace
these lines/tubes/hoses, only those marked EFM/EFI
may be used.
If equipped:The hose clamps used to secure rub-
ber hoses on fuel injected vehicles are of a special
rolled edge construction. This construction is used to
prevent the edge of the clamp from cutting into the
hose. Only these rolled edge type clamps may be
used in this system. All other types of clamps may
cut into the hoses and cause high-pressure fuel leaks.
Use new original equipment type hose clamps.
FUEL PUMP
DESCRIPTION
The fuel pump is located inside of the fuel pump
module. A 12 volt, permanent magnet, electric motor
powers the fuel pump.
OPERATION
Voltage to operate the electric pump is supplied
through the fuel pump relay.Fuel is drawn in through a filter at the bottom of
the module and pushed through the electric motor
gearset to the pump outlet.
Check Valve Operation:The pump outlet con-
tains a one-way check valve to prevent fuel flow back
into the tank and to maintain fuel supply line pres-
sure (engine warm) when pump is not operational. It
is also used to keep the fuel supply line full of gaso-
line when pump is not operational. After the vehicle
has cooled down, fuel pressure may drop to 0 psi
(cold fluid contracts), but liquid gasoline will remain
in fuel supply line between the check valve and fuel
injectors.Fuel pressure that has dropped to 0
psi on a cooled down vehicle (engine off) is a
normal condition.Refer to the Fuel Pressure Leak
Down Test for more information.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - FUEL PUMP
CAPACITY TEST
Before performing this test, verify fuel pump
pressure. Refer to Fuel Pump Pressure Test.
Use this test in conjunction with the Fuel Pres-
sure Leak Down Test.
(1) Release fuel system pressure. Refer to Fuel
Pressure Release Procedure.
(2) Disconnect fuel supply line at fuel rail. Refer to
Quick-Connect Fittings. Some engines may require
air cleaner housing removal before line disconnection.
(3) Obtain correct Fuel Line Pressure Test Adapter
Tool Hose. Tool number 6539 is used for 5/16º fuel
lines and tool number 6631 is used for 3/8º fuel lines.
(4)
Connect correct Fuel Line Pressure Test Adapter
Tool Hose into disconnected fuel supply line. Insert other
end of Adaptor Tool Hose into a graduated container.
(5) Remove fuel fill cap.
(6) To activate fuel pump and pressurize system,
obtain DRBtscan tool and actuate ASD Fuel System
Test.
(7) A good fuel pump will deliver at least 1/4 liter
of fuel in 7 seconds. Do not operate fuel pump for
longer than 7 seconds with fuel line disconnected as
fuel pump module reservoir may run empty.
(a) If capacity is lower than specification, but
fuel pump can be heard operating through fuel fill
cap opening, check for a kinked/damaged fuel sup-
ply line somewhere between fuel rail and fuel
pump module.
(b) If line is not kinked/damaged, and fuel pres-
sure is OK, but capacity is low, replace fuel filter/
fuel pressure regulator. The filter/regulator may be
serviced separately on certain applications. Refer
to Fuel Filter/Fuel Pressure Regulator Removal/In-
stallation for additional information.
(c) If both fuel pressure and capacity are low,
replace fuel pump module assembly. Refer to Fuel
Pump Module Removal/Installation.
BR/BEFUEL DELIVERY - GASOLINE 14 - 9
FUEL LEVEL SENDING UNIT / SENSOR (Continued)