2001 DODGE RAM weight
[x] Cancel search: weightPage 71 of 2889

SPECIAL TOOLS
SUSPENSION-REAR
BUSHINGS
REMOVAL
(1) Remove the spring from the vehicle.
(2) Position the spring eye in a press.
(3) Press the bushing out with an appropriate size
driver.
INSTALLATION
(1) Press new bushing into the spring eye with an
appropriate size driver. The bushing should be cen-
tered in the spring eye.
(2) Install the spring on the vehicle.
JOUNCE BUMPER
DESCRIPTION
The jounce bumpers are bolted to the frame rail
above the axle.
OPERATION
The jounce bumpers are used to limit the spring
and axle travel.
SHOCK
DESCRIPTION
The top of the shock absorbers are bolted to the
body crossmember. The bottom of the shocks are
bolted to the axle bracket.
OPERATION
The shocks dampen the jounce and rebound as the
vehicle travels over various road conditions.
REMOVAL
(1) Raise vehicle and support axle.
(2) Remove the bolt and flag nut from the frame
crossmember bracket (Fig. 1) .
(3) Remove the bolt and nut from the axle bracket.(4) Remove the rear shock absorber from the vehi-
cle.
INSTALLATION
(1) Position the shock absorber in the brackets.
(2) Install the bolts through the brackets and the
shock. Install the flag nut on the top bolt and nut on
lower bolt.
(3) Tighten the upper and lower bolt/nuts Tighten
to 136 N.m (100 ft. lbs.)
(4) Remove the support and lower the vehicle.
SPRING
DESCRIPTION
The rear suspension system uses a multi-leaf
springs and a solid drive axle. The forward end of the
springs are mounted to the body rail hangers
through rubber bushings. The rearward end of the
springs are attached to the body by the use of shack-
les. The spring and shackles use rubber bushings.
OPERATION
The springs control ride quality and maintain vehi-
cle ride height. The shackles allow the springs to
change their length as the vehicle moves over various
road conditions.
REMOVAL
(1) Raise the vehicle and support the axle to
remove all weight from the springs.
Puller C-3894-A
Fig. 1 Shock Absorber
1 - FLAG NUT
2 - AXLE
3 - SHOCK
2 - 28 REARBR/BE
REAR (Continued)
Page 72 of 2889
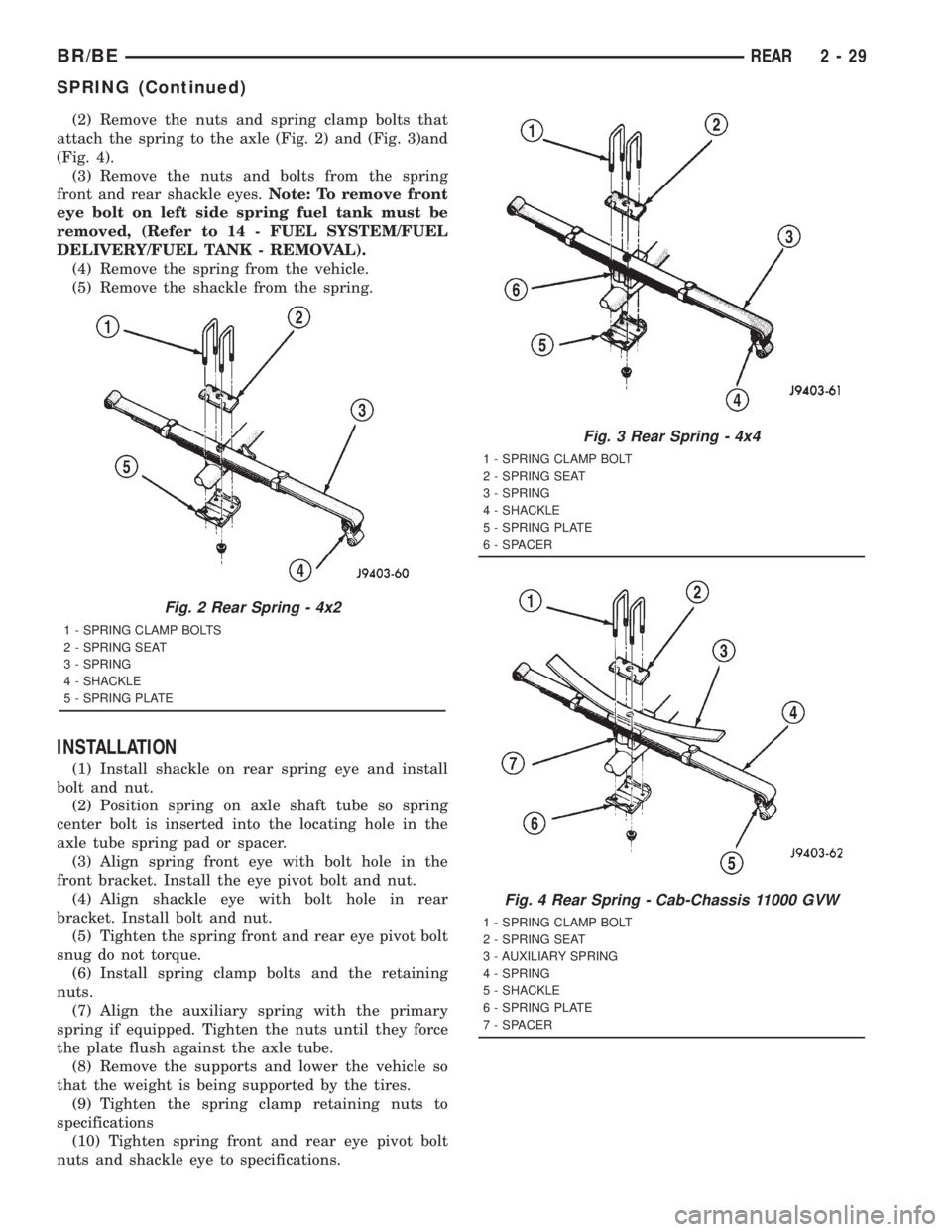
(2) Remove the nuts and spring clamp bolts that
attach the spring to the axle (Fig. 2) and (Fig. 3)and
(Fig. 4).
(3) Remove the nuts and bolts from the spring
front and rear shackle eyes.Note: To remove front
eye bolt on left side spring fuel tank must be
removed, (Refer to 14 - FUEL SYSTEM/FUEL
DELIVERY/FUEL TANK - REMOVAL).
(4) Remove the spring from the vehicle.
(5) Remove the shackle from the spring.
INSTALLATION
(1) Install shackle on rear spring eye and install
bolt and nut.
(2) Position spring on axle shaft tube so spring
center bolt is inserted into the locating hole in the
axle tube spring pad or spacer.
(3) Align spring front eye with bolt hole in the
front bracket. Install the eye pivot bolt and nut.
(4) Align shackle eye with bolt hole in rear
bracket. Install bolt and nut.
(5) Tighten the spring front and rear eye pivot bolt
snug do not torque.
(6) Install spring clamp bolts and the retaining
nuts.
(7) Align the auxiliary spring with the primary
spring if equipped. Tighten the nuts until they force
the plate flush against the axle tube.
(8) Remove the supports and lower the vehicle so
that the weight is being supported by the tires.
(9) Tighten the spring clamp retaining nuts to
specifications
(10) Tighten spring front and rear eye pivot bolt
nuts and shackle eye to specifications.
Fig. 2 Rear Spring - 4x2
1 - SPRING CLAMP BOLTS
2 - SPRING SEAT
3 - SPRING
4 - SHACKLE
5 - SPRING PLATE
Fig. 3 Rear Spring - 4x4
1 - SPRING CLAMP BOLT
2 - SPRING SEAT
3 - SPRING
4 - SHACKLE
5 - SPRING PLATE
6 - SPACER
Fig. 4 Rear Spring - Cab-Chassis 11000 GVW
1 - SPRING CLAMP BOLT
2 - SPRING SEAT
3 - AUXILIARY SPRING
4 - SPRING
5 - SHACKLE
6 - SPRING PLATE
7 - SPACER
BR/BEREAR 2 - 29
SPRING (Continued)
Page 74 of 2889

DIFFERENTIAL & DRIVELINE
TABLE OF CONTENTS
page page
PROPELLER SHAFT.......................1
FRONT AXLE - 216FBI....................12
FRONT AXLE - 248FBI....................45
REAR AXLE-91/4.......................77REAR AXLE - 248RBI....................109
REAR AXLE - 267RBI....................140
REAR AXLE - 286RBI....................169
PROPELLER SHAFT
TABLE OF CONTENTS
page page
PROPELLER SHAFT
DESCRIPTION............................1
OPERATION.............................1
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING..................3
PROPELLER SHAFT.....................3
STANDARD PROCEDURE...................5
SPECIFICATIONS.........................8
SPECIAL TOOLS..........................8
PROPELLER SHAFT - FRONT
REMOVAL...............................8
INSTALLATION............................8PROPELLER SHAFT - REAR
REMOVAL...............................9
INSTALLATION............................9
CENTER BEARING
DESCRIPTION...........................10
OPERATION.............................10
REMOVAL..............................10
INSTALLATION...........................10
ADJUSTMENTS..........................10
SINGLE CARDAN UNIVERSAL JOINTS
DISASSEMBLY...........................11
PROPELLER SHAFT
DESCRIPTION
A propeller shaft (Fig. 1), (Fig. 2), (Fig. 3), and
(Fig. 4) is a shaft which connects the transmission/
transfer case to the axle differential. This is the link
through which the engine power is transmitted to the
axle.
The propeller shaft is designed and built with the
yoke lugs in line with each other which is called zero
phasing. This design produces the smoothest running
condition, an out-of-phase shaft can cause a vibra-
tion.
Tubular propeller shafts are balanced by the man-
ufacturer with weights spot welded to the tube.
Use the exact replacement parts when installing
the propeller shafts. The use of the correct replace-
ment parts helps to ensure safe operation. All fasten-
ers must be torqued to the specified values for safe
operation.Also make alignment reference marks (Fig. 5)on
the propeller shaft yoke and axle, or transmission,
yoke prior to servicing. This helps to eliminate possi-
ble vibration.
CAUTION: Do not allow the propeller shaft to drop
or hang from any propeller shaft joint during
removal. Attach the propeller shaft to the vehicle
underside with wire to prevent damage to the joints.
OPERATION
The propeller shaft must operate through con-
stantly changing relative angles between the trans-
mission and axle. It must also be capable of changing
length while transmitting torque. The axle rides sus-
pended by springs in a floating motion. The propeller
shaft must be able to change operating angles when
going over various road surfaces. This is accom-
plished through universal joints, which permit the
propeller shaft to operate at different angles. The slip
joints (or yokes) permit contraction or expansion.
BR/BEDIFFERENTIAL & DRIVELINE 3 - 1
Page 77 of 2889

DRIVELINE VIBRATION
Drive Condition Possible Cause Correction
Propeller Shaft Noise 1) Undercoating or other foreign
material on shaft.1) Clean exterior of shaft and wash
with solvent.
2) Loose U-joint clamp screws. 2) Install new clamps and screws
and tighten to proper torque.
3) Loose or bent U-joint yoke or
excessive runout.3) Install new yoke.
4) Incorrect driveline angularity. 4) Measure and correct driveline
angles.
5) Rear spring center bolt not in
seat.5) Loosen spring u-bolts and seat
center bolt.
6) Worn U-joint bearings. 6) Install new U-joint.
7) Propeller shaft damaged or out
of balance.7) Installl new propeller shaft.
8) Broken rear spring. 8) Install new rear spring.
9) Excessive runout or unbalanced
condition.9) Re-index propeller shaft, test,
and evaluate.
10) Excessive drive pinion gear
shaft runout.10) Re-index propeller shaft and
evaluate.
11) Excessive axle yoke deflection. 11) Inspect and replace yoke if
necessary.
12) Excessive transfer case runout. 12) Inspect and repair as necessary.
Universal Joint Noise 1) Loose U-joint clamp screws. 1) Install new clamps and screws
and tighten to proper torque.
2) Lack of lubrication. 2) Replace as U-joints as
necessary.
BALANCE
NOTE: Removing and re-indexing the propeller
shaft 180É relative to the yoke may eliminate some
vibrations.
If propeller shaft is suspected of being unbalanced,
it can be verified with the following procedure:
(1) Raise the vehicle.
(2) Clean all the foreign material from the propel-
ler shaft and the universal joints.
(3) Inspect the propeller shaft for missing balance
weights, broken welds, and bent areas.If the pro-
peller shaft is bent, it must be replaced.
(4) Inspect the universal joints to ensure that they
are not worn, are properly installed, and are cor-
rectly aligned with the shaft.
(5) Check the universal joint clamp screws torque.
(6) Remove the wheels and tires. Install the wheel
lug nuts to retain the brake drums or rotors.
(7) Mark and number the shaft six inches from the
yoke end at four positions 90É apart.(8) Run and accelerate the vehicle until vibration
occurs. Note the intensity and speed the vibration
occurred. Stop the engine.
(9) Install a screw clamp at position 1 (Fig. 6).
(10) Start the engine and re-check for vibration. If
there is little or no change in vibration, move the
clamp to one of the other three positions. Repeat the
vibration test.
(11) If there is no difference in vibration at the
other positions, the source of the vibration may not
be propeller shaft.
(12) If the vibration decreased, install a second
clamp (Fig. 7) and repeat the test.
(13) If the additional clamp causes an additional
vibration, separate the clamps (1/2 inch above and
below the mark). Repeat the vibration test (Fig. 8).
(14) Increase distance between the clamp screws
and repeat the test until the amount of vibration is
at the lowest level. Bend the slack end of the clamps
so the screws will not loosen.
3 - 4 PROPELLER SHAFTBR/BE
PROPELLER SHAFT (Continued)
Page 87 of 2889

cle turns. A worn pinion mate shaft can also cause a
snapping or a knocking noise.
BEARING NOISE
The axle shaft, differential and pinion bearings can
all produce noise when worn or damaged. Bearing
noise can be either a whining, or a growling sound.
Pinion bearings have a constant-pitch noise. This
noise changes only with vehicle speed. Pinion bearing
noise will be higher pitched because it rotates at a
faster rate. Drive the vehicle and load the differen-
tial. If bearing noise occurs, the rear pinion bearing
is the source of the noise. If the bearing noise is
heard during a coast, the front pinion bearing is the
source.
Worn or damaged differential bearings usually pro-
duce a low pitch noise. Differential bearing noise is
similar to pinion bearing noise. The pitch of differen-
tial bearing noise is also constant and varies only
with vehicle speed.
Axle shaft bearings produce noise and vibration
when worn or damaged. The noise generally changes
when the bearings are loaded. Road test the vehicle.
Turn the vehicle sharply to the left and to the right.
This will load the bearings and change the noise
level. Where axle bearing damage is slight, the noise
is usually not noticeable at speeds above 30 mph.
LOW SPEED KNOCK
Low speed knock is generally caused by a worn
U-joint or by worn side-gear thrust washers. A worn
pinion shaft bore will also cause low speed knock.
VIBRATION
Vibration at the rear of the vehicle is usually
caused by:
²Damaged drive shaft.²Missing drive shaft balance weight(s).
²Worn or out of balance wheels.
²Loose wheel lug nuts.
²Worn U-joint(s).
²Loose/broken springs.
²Damaged axle shaft bearing(s).
²Loose pinion gear nut.
²Excessive pinion yoke run out.
²Bent axle shaft(s).
Check for loose or damaged front end components
or engine/transmission mounts. These components
can contribute to what appears to be a rear end
vibration. Do not overlook engine accessories, brack-
ets and drive belts.
All driveline components should be examined
before starting any repair.
(Refer to 22 - TIRES/WHEELS - DIAGNOSIS AND
TESTING)
DRIVELINE SNAP
A snap or clunk noise when the vehicle is shifted
into gear (or the clutch engaged) can be caused by:
²High engine idle speed.
²Transmission shift operation.
²Loose engine/transmission/transfer case mounts.
²Worn U-joints.
²Loose spring mounts.
²Loose pinion gear nut and yoke.
²Excessive ring gear backlash.
²Excessive side gear to case clearance.
The source of a snap or a clunk noise can be deter-
mined with the assistance of a helper. Raise the vehi-
cle on a hoist with the wheels free to rotate. Instruct
the helper to shift the transmission into gear. Listen
for the noise, a mechanics stethoscope is helpful in
isolating the source of a noise.
3 - 14 FRONT AXLE - 216FBIBR/BE
FRONT AXLE - 216FBI (Continued)
Page 88 of 2889
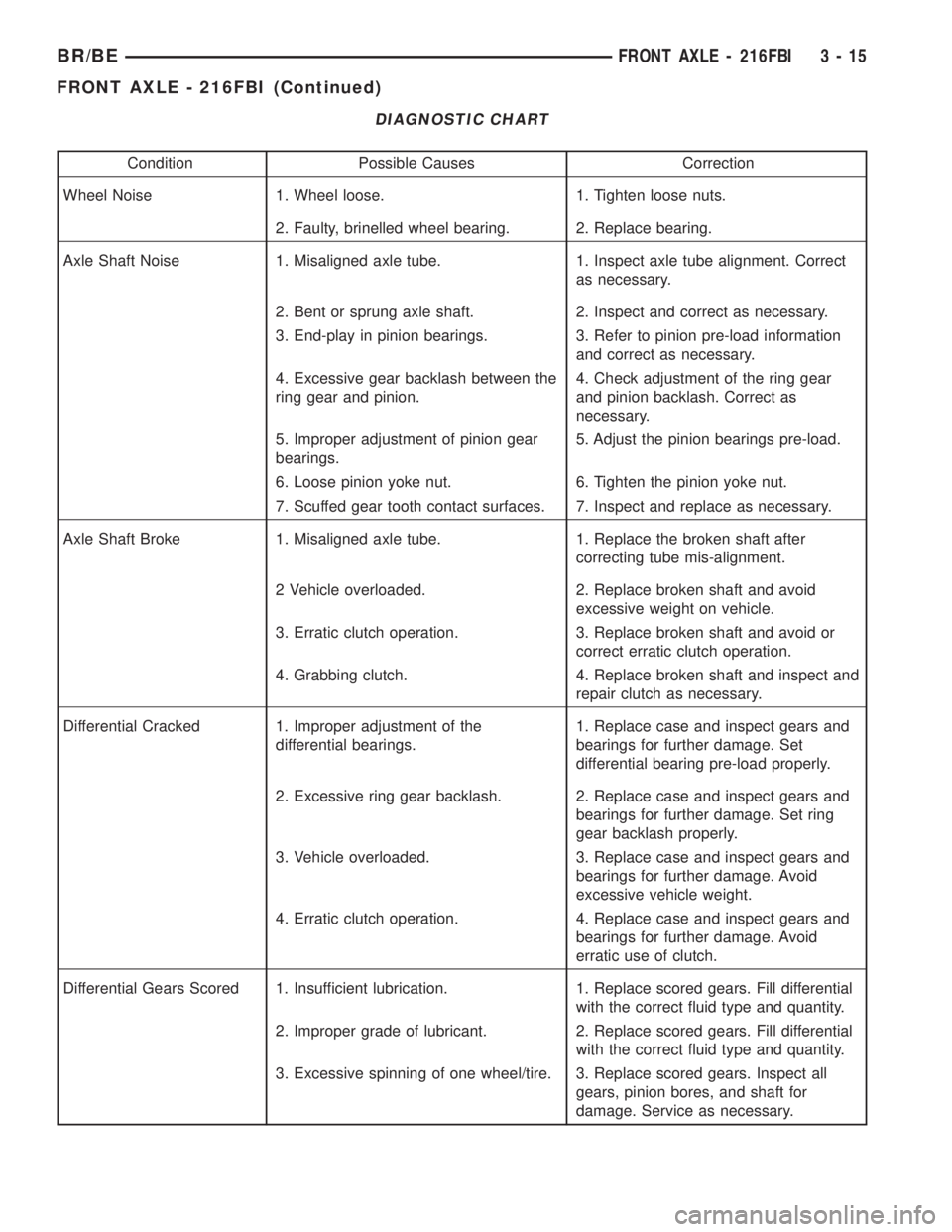
DIAGNOSTIC CHART
Condition Possible Causes Correction
Wheel Noise 1. Wheel loose. 1. Tighten loose nuts.
2. Faulty, brinelled wheel bearing. 2. Replace bearing.
Axle Shaft Noise 1. Misaligned axle tube. 1. Inspect axle tube alignment. Correct
as necessary.
2. Bent or sprung axle shaft. 2. Inspect and correct as necessary.
3. End-play in pinion bearings. 3. Refer to pinion pre-load information
and correct as necessary.
4. Excessive gear backlash between the
ring gear and pinion.4. Check adjustment of the ring gear
and pinion backlash. Correct as
necessary.
5. Improper adjustment of pinion gear
bearings.5. Adjust the pinion bearings pre-load.
6. Loose pinion yoke nut. 6. Tighten the pinion yoke nut.
7. Scuffed gear tooth contact surfaces. 7. Inspect and replace as necessary.
Axle Shaft Broke 1. Misaligned axle tube. 1. Replace the broken shaft after
correcting tube mis-alignment.
2 Vehicle overloaded. 2. Replace broken shaft and avoid
excessive weight on vehicle.
3. Erratic clutch operation. 3. Replace broken shaft and avoid or
correct erratic clutch operation.
4. Grabbing clutch. 4. Replace broken shaft and inspect and
repair clutch as necessary.
Differential Cracked 1. Improper adjustment of the
differential bearings.1. Replace case and inspect gears and
bearings for further damage. Set
differential bearing pre-load properly.
2. Excessive ring gear backlash. 2. Replace case and inspect gears and
bearings for further damage. Set ring
gear backlash properly.
3. Vehicle overloaded. 3. Replace case and inspect gears and
bearings for further damage. Avoid
excessive vehicle weight.
4. Erratic clutch operation. 4. Replace case and inspect gears and
bearings for further damage. Avoid
erratic use of clutch.
Differential Gears Scored 1. Insufficient lubrication. 1. Replace scored gears. Fill differential
with the correct fluid type and quantity.
2. Improper grade of lubricant. 2. Replace scored gears. Fill differential
with the correct fluid type and quantity.
3. Excessive spinning of one wheel/tire. 3. Replace scored gears. Inspect all
gears, pinion bores, and shaft for
damage. Service as necessary.
BR/BEFRONT AXLE - 216FBI 3 - 15
FRONT AXLE - 216FBI (Continued)
Page 90 of 2889

(8) Disconnect the stabilizer bar links at the axle
brackets.
(9) Disconnect the shock absorbers from axle
brackets.
(10) Disconnect the track bar from the axle
bracket.
(11) Disconnect the tie rod and drag link from the
steering knuckles.
(12) Position the axle with a suitable lifting device
under the axle assembly.
(13) Secure axle to lifting device.
(14) Mark suspension alignment cams for installa-
tion reference.
(15) Disconnect the upper and lower suspension
arms from the axle bracket.
(16) Lower the axle. The coil springs will drop
with the axle.
(17) Remove the coil springs from the axle bracket.
INSTALLATION
CAUTION: Suspension components with rubber
bushings should be tightened with the weight of the
vehicle on the suspension, at normal height. If
springs are not at their normal ride position, vehicle
ride comfort could be affected and premature bush-
ing wear may occur. Rubber bushings must never
be lubricated.
(1) Support the axle on a suitable lifting device.
(2) Secure axle to lifting device.
(3) Position the axle under the vehicle.
(4) Install the springs, retainer clip and bolts.
(5) Raise the axle and align it with the spring
pads.
(6) Position the upper and lower suspension arms
in the axle brackets. Install bolts, nuts and align the
suspension alignment cams to the reference marks.
Do not tighten at this time.
(7) Connect the track bar to the axle bracket and
install the bolt. Do not tighten at this time.
(8) Install the shock absorber and tighten bolts to
121 N´m (89 ft. lbs.) torque.
(9) Install the stabilizer bar link to the axle
bracket. Tighten the nut to 37 N´m (27 ft. lbs.)
torque.
(10) Install the drag link and tie rod to the steer-
ing knuckles and tighten the nuts to 88 N´m (65 ft.
lbs.) torque.
(11) Install the ABS wheel speed sensors, if
equipped. Refer to group 5, Brakes, for proper proce-
dures.
(12) Install the brake calipers and rotors. Refer to
Group 5, Brakes, for proper procedures.
(13) Connect the vent hose to the tube fitting.
(14) Connect vacuum hose and electrical connector
to disconnect housing.(15) Install front propeller shaft.
(16) Check and add differential lubricant, if neces-
sary. Refer to Lubricant Specifications in this section
for lubricant requirements.
(17) Install the wheel and tire assemblies.
(18) Remove the supports and lower the vehicle.
(19) Tighten the upper suspension arm nuts at
axle to 121 N´m (89 ft. lbs.) torque. Tighten the
upper suspension arm nuts at frame to 84 N´m (62 ft.
lbs.) torque.
(20) Tighten the lower suspension arm nuts at
axle to 84 N´m (62 ft. lbs.) torque. Tighten the lower
suspension arm nuts at frame to 119 N´m (88 ft. lbs.)
torque.
(21) Tighten the track bar bolt at the axle bracket
to 176 N´m (130 ft. lbs.) torque.
(22) Check the front wheel alignment.
ADJUSTMENTS
Ring and pinion gears are supplied as matched
sets only. The identifying numbers for the ring and
pinion gear are etched into the face of each gear (Fig.
4). A plus (+) number, minus (±) number or zero (0) is
etched into the face of the pinion gear. This number
is the amount (in thousandths of an inch) the depth
varies from the standard depth setting of a pinion
etched with a (0). The standard setting from the cen-
ter line of the ring gear to the back face of the pinion
is 109.5 mm (4.312 in.). The standard depth provides
the best gear tooth contact pattern. Refer to Back-
lash and Contact Pattern in this section for addi-
tional information.
Compensation for pinion depth variance is
achieved with a select shim/oil baffle. The shims are
placed between the rear pinion bearing and the pin-
ion gear head (Fig. 5).
Fig. 4 Pinion Gear ID Numbers
1 - PRODUCTION NUMBERS
2 - PINION GEAR DEPTH VARIANCE
3 - GEAR MATCHING NUMBER
BR/BEFRONT AXLE - 216FBI 3 - 17
FRONT AXLE - 216FBI (Continued)
Page 120 of 2889

cle turns. A worn pinion mate shaft can also cause a
snapping or a knocking noise.
BEARING NOISE
The axle shaft, differential and pinion bearings can
all produce noise when worn or damaged. Bearing
noise can be either a whining, or a growling sound.
Pinion bearings have a constant-pitch noise. This
noise changes only with vehicle speed. Pinion bearing
noise will be higher pitched because it rotates at a
faster rate. Drive the vehicle and load the differen-
tial. If bearing noise occurs, the rear pinion bearing
is the source of the noise. If the bearing noise is
heard during a coast, the front pinion bearing is the
source.
Worn or damaged differential bearings usually pro-
duce a low pitch noise. Differential bearing noise is
similar to pinion bearing noise. The pitch of differen-
tial bearing noise is also constant and varies only
with vehicle speed.
Axle shaft bearings produce noise and vibration
when worn or damaged. The noise generally changes
when the bearings are loaded. Road test the vehicle.
Turn the vehicle sharply to the left and to the right.
This will load the bearings and change the noise
level. Where axle bearing damage is slight, the noise
is usually not noticeable at speeds above 30 mph.
LOW SPEED KNOCK
Low speed knock is generally caused by a worn
U-joint or by worn side-gear thrust washers. A worn
pinion shaft bore will also cause low speed knock.
VIBRATION
Vibration at the rear of the vehicle is usually
caused by:
²Damaged drive shaft.²Missing drive shaft balance weight(s).
²Worn or out of balance wheels.
²Loose wheel lug nuts.
²Worn U-joint(s).
²Loose/broken springs.
²Damaged axle shaft bearing(s).
²Loose pinion gear nut.
²Excessive pinion yoke run out.
²Bent axle shaft(s).
Check for loose or damaged front end components
or engine/transmission mounts. These components
can contribute to what appears to be a rear end
vibration. Do not overlook engine accessories, brack-
ets and drive belts.
All driveline components should be examined
before starting any repair.
(Refer to 22 - TIRES/WHEELS - DIAGNOSIS AND
TESTING)
DRIVELINE SNAP
A snap or clunk noise when the vehicle is shifted
into gear (or the clutch engaged) can be caused by:
²High engine idle speed.
²Transmission shift operation.
²Loose engine/transmission/transfer case mounts.
²Worn U-joints.
²Loose spring mounts.
²Loose pinion gear nut and yoke.
²Excessive ring gear backlash.
²Excessive side gear to case clearance.
The source of a snap or a clunk noise can be deter-
mined with the assistance of a helper. Raise the vehi-
cle on a hoist with the wheels free to rotate. Instruct
the helper to shift the transmission into gear. Listen
for the noise, a mechanics stethoscope is helpful in
isolating the source of a noise.
BR/BEFRONT AXLE - 248FBI 3 - 47
FRONT AXLE - 248FBI (Continued)