2001 DODGE RAM checking oil
[x] Cancel search: checking oilPage 1288 of 2889

INSPECTION
Measure valve stems for wear. If wear exceeds
0.051 mm (0.002 in.), replace the valve.
Measure valve stem guide clearance as follows:
(1) Install Valve Guide Sleeve Tool C-3973 over
valve stem and install valve (Fig. 14). The special
sleeve places the valve at the correct height for
checking with a dial indicator.
(2) Attach dial indicator Tool C-3339 to cylinder
head and set it at right angles to valve stem being
measured (Fig. 15).
(3) Move valve to and from the indicator. The total
dial indicator reading should not exceed 0.432 mm
(0.017 in.). Ream the guides for valves with oversize
stems if dial indicator reading is excessive or if the
stems are scuffed or scored.
INSTALLATION
(1) Clean valves thoroughly. Discard burned,
warped and cracked valves.
(2) Remove carbon and varnish deposits from
inside of valve guides with a reliable guide cleaner.
(3) Measure valve stems for wear. If wear exceeds
0.051 mm (0.002 inch), replace the valve.
(4) Coat valve stems with lubrication oil and insert
them in cylinder head.
(5) If valves or seats are reground, check valve
stem height. If valve is too long, replace cylinder
head.
(6) Install new seals on all valve guides. Install
valve springs and valve retainers.
(7) Compress valve springs with Valve Spring
Compressor Tool MD-998772A and adapter 6716A,
install locks and release tool. If valves and/or seats
are ground, measure the installed height of springs.
Make sure the measurement is taken from bottom of
spring seat in cylinder head to the bottom surface of
spring retainer. If spacers are installed, measure
from the top of spacer. If height is greater than 42.86
mm (1-11/16 inches), install a 1.587 mm (1/16 inch)
spacer in head counterbore. This should bring spring
height back to normal 41.27 to 42.86 mm (1-5/8 to
1-11/16 inch).
(8) Install cylinder head (Refer to 9 - ENGINE/
CYLINDER HEAD - INSTALLATION).
Fig. 13 Testing Valve Spring for Compressed
Length
1 - TORQUE WRENCH
2 - VALVE SPRING TESTER
Fig. 14 Positioning Valve with Tool C-3973
1 - VALVE
2 - SPACER TOOL
Fig. 15 Measuring Valve Guide Wear
1 - VALVE
2 - SPECIAL TOOL C-3339
BR/BEENGINE 5.9L 9 - 141
INTAKE/EXHAUST VALVES & SEATS (Continued)
Page 1310 of 2889
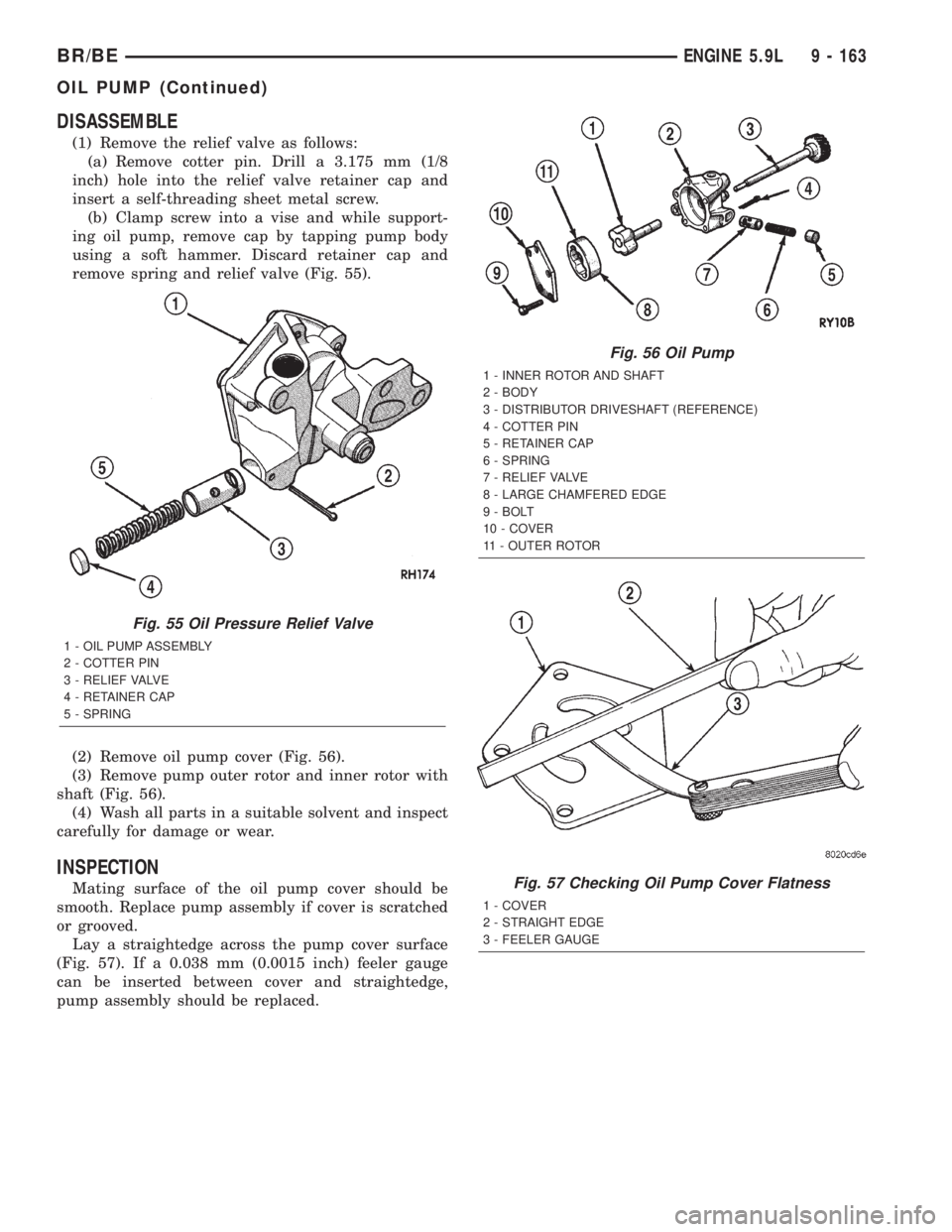
DISASSEMBLE
(1) Remove the relief valve as follows:
(a) Remove cotter pin. Drill a 3.175 mm (1/8
inch) hole into the relief valve retainer cap and
insert a self-threading sheet metal screw.
(b) Clamp screw into a vise and while support-
ing oil pump, remove cap by tapping pump body
using a soft hammer. Discard retainer cap and
remove spring and relief valve (Fig. 55).
(2) Remove oil pump cover (Fig. 56).
(3) Remove pump outer rotor and inner rotor with
shaft (Fig. 56).
(4) Wash all parts in a suitable solvent and inspect
carefully for damage or wear.
INSPECTION
Mating surface of the oil pump cover should be
smooth. Replace pump assembly if cover is scratched
or grooved.
Lay a straightedge across the pump cover surface
(Fig. 57). If a 0.038 mm (0.0015 inch) feeler gauge
can be inserted between cover and straightedge,
pump assembly should be replaced.
Fig. 55 Oil Pressure Relief Valve
1 - OIL PUMP ASSEMBLY
2 - COTTER PIN
3 - RELIEF VALVE
4 - RETAINER CAP
5 - SPRING
Fig. 56 Oil Pump
1 - INNER ROTOR AND SHAFT
2 - BODY
3 - DISTRIBUTOR DRIVESHAFT (REFERENCE)
4 - COTTER PIN
5 - RETAINER CAP
6 - SPRING
7 - RELIEF VALVE
8 - LARGE CHAMFERED EDGE
9 - BOLT
10 - COVER
11 - OUTER ROTOR
Fig. 57 Checking Oil Pump Cover Flatness
1 - COVER
2 - STRAIGHT EDGE
3 - FEELER GAUGE
BR/BEENGINE 5.9L 9 - 163
OIL PUMP (Continued)
Page 1367 of 2889

(5) Inspect oil pump for wear (Refer to 9 -
ENGINE/LUBRICATION/OIL PUMP - INSPEC-
TION).
CLEANING
Wash all parts in a suitable solvent and inspect
carefully for damage or wear.
INSPECTION
Mating surface of the oil pump cover should be
smooth. Replace pump cover if scratched or grooved.
Lay a straightedge across the pump cover surface
(Fig. 61). If a 0.076 mm (0.003 inch) feeler gauge can
be inserted between cover and straightedge, cover
should be replaced.
Measure thickness (Fig. 62) (Fig. 63) and diameter
of rotors. If either rotor thickness measures 14.956
mm (0.5876 inch) or less, or if the diameter is 82.45
mm (3.246 inches) or less, replace rotor set.
Slide outer rotor into timing chain cover pump
body. Press rotor to the side with your fingers and
measure clearance between rotor and pump body
(Fig. 64). If clearance is 0.19 mm (0.007 inch) or
more, and outer rotor is within specifications, replace
timing chain cover.
Install inner rotor into timing chain cover pump
body (Fig. 65). Inner rotor should be positioned with
chamfer up or toward engine when cover is installed.
This allows easy installation over crankshaft. If
Fig. 60 Oil Pump
1 - OUTER ROTOR
2 - INNER ROTOR
3 - OIL PUMP COVER
4 - TIMING CHAIN COVER
Fig. 61 Checking Oil Pump Cover Flatness
1 - FEELER GAUGE
2 - STRAIGHT EDGE
3 - OIL PUMP COVER
Fig. 62 Measuring Outer Rotor Thickness
Fig. 63 Measuring Inner Rotor Thickness
9 - 220 ENGINE 8.0LBR/BE
OIL PUMP (Continued)
Page 1442 of 2889

DIAGNOSIS AND TESTINGÐENGINE OIL
PRESSURE
(1) Remove the engine oil pressure sensor and
install Oil Pressure Line and Gauge Tool C-3292 with
a suitable adapter.
(2) Start engine and warm to operating tempera-
ture.
(3) Record engine oil pressure and compare with
engine oil pressure chart.
CAUTION: If engine oil pressure is zero at idle, DO
NOT RUN THE ENGINE.
Engine Oil Pressure (MIN)
At Idle 103.4 kPa (15 psi)
At 2000 rpm 310.2 kPa (45 psi)
If minimum engine oil pressure is below these
ranges, (Refer to 9 - ENGINE - DIAGNOSIS AND
TESTING).
(4) Remove oil pressure gauge and install the oil
pressure sensor. Tighten the sensor to 16 N´m (144
in. lbs.) torque.
OIL
STANDARD PROCEDURE-ENGINE OIL LEVEL
CAUTION: Do not overfill crankcase with engine oil,
oil foaming and oil pressure loss can result.
To ensure proper lubrication of an engine, the
engine oil must be maintained at an acceptable level.
The acceptable oil level is in the SAFE RANGE on
the engine oil dipstick (Fig. 150).
Unless the engine has exhibited loss of oil pres-
sure, run the engine for about five minutes before
checking oil level. Checking engine oil level of a cold
engine is not accurate.
(1) Position vehicle on level surface.
(2) With engine OFF, allow approximately ten min-
utes for oil to settle to bottom of crankcase, remove
engine oil dipstick.
(3) Wipe dipstick clean.(4)
Replace dipstick and verify it is seated in the
tube.
(5) Remove dipstick, with handle held above the
tip, take oil level reading.
(6) Add oil only if level is below the SAFE RANGE
area on the dipstick.
(7) Replace dipstick
STANDARD PROCEDURE-ENGINE OIL SERVICE
WARNING: HOT OIL CAN CAUSE PERSONAL
INJURY.
NOTE: Change engine oil and filter at intervals
specified in the owner's manual.
(1) Operate the engine until the water tempera-
ture reaches 60ÉC (140ÉF). Shut the engine off.
(2) Use a container that can hold at least 14 liters
(15 quarts) to hold the used oil. Remove the oil drain
plug and drain the used engine oil into the container.
(3) Always check the condition of the used oil. This
can give you an indication of engine problems that
might exist.
²Thin, black oil indicates fuel dilution.
1 - ROCKER ARM
2 - ROCKER SHAFT
3 - PEDESTAL
4 - FROM MAIN OIL RIFLE
5 - TO VALVE TRAIN
6 - MAIN OIL RIFLE
7 - FROM MAIN OIL RIFLE
8 - TO CAMSHAFT9 - TO PISTON COOLING NOZZLE
10 - FROM OIL COOLER
11 - CRANKSHAFT MAIN JOURNAL
12 - ROD JOURNAL
13 - TO ROD BEARING
14 - MAIN OIL RIFLE
Fig. 150 Oil Level Indicator (Dipstick)
1 - ADD OIL MARK
2 - O-RING
3 - SAFE RANGE
BR/BEENGINE 5.9L DIESEL 9 - 295
LUBRICATION (Continued)
Page 1555 of 2889

(1) Remove hose clamp and crankcase vent hose at
crankcase breather (Fig. 17). Remove crankcase
breather from gear cover. Breather threads into
cover.
(2) Remove injection pump nut and washer (Fig.
18). Locate keyway behind washer.
(3) Be sure keyway aligning fuel injection pump
shaft to injection pump gear is in proper position and
pump gear has not slipped on pump shaft.
The following steps will require removing timing
gear cover to gain access to timing gears. Refer to
Group 9, Engines for procedures.
(4) Use a T-type puller to separate injection pump
gear from pump shaft.
(5) Be sure keyway has been installed with arrow
pointed torearof pump (Fig. 19).
(6)Pump timing has been calibrated to pump
keyway. Be sure 3±digit number on pump key-
way (Fig. 19) matches 3±digit number on fuel
injection pump data plate. Plate is located on
side of injection pump (Fig. 20). Twenty±one dif-
ferent calibrated keyways/pumps are available.
(7) Verify timing marks on crank, cam and pump
are aligned (Fig. 21).
(8) Perform necessary gear alignment/repairs as
needed.
(9) Install crankcase breather to gear cover. Install
hose clamp and crankcase vent hose to breather (Fig.
17).
(10) After repairs are completed, erase DTC using
DRB Scan Tool.
REMOVAL
CAUTION: Refer to Cleaning Fuel System Parts.
(1) Disconnect both negative battery cables at both
batteries. Cover and isolate ends of cables.
(2) Thoroughly clean fuel lines at cylinder head
and injection pump ends. Thoroughly clean fuel injec-
tion pump and supply/return lines at side of pump.
(3) Disconnect 9±way electrical connector at Fuel
Pump Control Module (FPCM) (Fig. 22).
(4) Remove fuel return line at side of injection
pump by removing overflow valve (Fig. 23). Place rag
beneath overflow valve to catch excess fuel.
(5) Remove fuel supply line at side of injection
pump by removing banjo bolt (Fig. 23). Also remove
same line at top of fuel filter housing (banjo bolt).
(6) Remove all high-pressure fuel lines, intake air
tube, accelerator pedal position sensor, air intake
housing, engine oil dipstick tube, wiring clips, electri-
cal cables at intake heaters and engine lifting
bracket. Refer to High-Pressure Fuel Line Removal/
Installation. All of these items are covered in this
procedure.
(7) Remove hose clamp at crankcase vent hose
(Fig. 24) and remove hose from canister.
(8) Remove (unscrew) canister (Fig. 24) from gear
cover.
Fig. 21 Checking Fuel Injection Pump Gear Timing
1 - PUMP SHAFT
2 - KEYWAY
3 - PUMP GEAR
4 - CAM GEAR
5 - CRANKSHAFT GEAR
Fig. 22 FPCM 9±Way Connector
1 - FPCM ELECTRICAL CONNECTOR
2 - HIGH-PRESSURE FUEL LINES
3 - FITTINGS
4 - FUEL INJECTION PUMP
5 - FPCM
14 - 68 FUEL DELIVERY - DIESELBR/BE
FUEL INJECTION PUMP (Continued)
Page 1624 of 2889

PUMP
TABLE OF CONTENTS
page page
PUMP
DESCRIPTION...........................31
OPERATION.............................31
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING.................31
PUMP LEAKAGE.......................31
STANDARD PROCEDURE..................31
POWER STEERING PUMP - INITIAL
OPERATION...........................31
FLUSHING POWER STEERING SYSTEM.....32
REMOVAL..............................33
INSTALLATION...........................35SPECIAL TOOLS.........................36
PULLEY
REMOVAL..............................36
INSTALLATION...........................36
HOSES - PRESSURE
DESCRIPTION...........................37
OPERATION.............................37
HOSES - RETURN
DESCRIPTION...........................37
OPERATION.............................37
PUMP
DESCRIPTION
The P-Series pump is used on these vehicles (Fig.
1). The pump shaft has a pressed-on pulley that is
belt driven by the crankshaft pulley on gasoline
engines. The pump is driven off the back of the vac-
uum pump on the diesel engine.
Trailer tow option vehicles are equipped with a
power steering pump oil cooler. The oil cooler is
mounted to the front crossmember.
NOTE: Power steering pumps are not interchange-
able with pumps installed on other vehicles.
OPERATION
Hydraulic pressure is provided by the pump for the
power steering gear. The power steering pump is a
constant flow rate and displacement, vane-type
pump. The pump is connected to the steering gear
via the pressure hose and the return hose. On vehi-
cles equipped with a hydraulic booster, the pump
supplies the hydraulic pressure for the booster.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - PUMP LEAKAGE
(1) Possible pump leakage areas. (Fig. 2).
STANDARD PROCEDURE - POWER STEERING
PUMP - INITIAL OPERATION
WARNING: THE FLUID LEVEL SHOULD BE
CHECKED WITH ENGINE OFF TO PREVENT INJURY
FROM MOVING COMPONENTS.
CAUTION: Use MOPAR Power Steering Fluid or
equivalent. Do not use automatic transmission fluid
and do not overfill.
Wipe filler cap clean, then check the fluid level.
The dipstick should indicateCOLDwhen the fluid is
at normal temperature.
(1) Turn steering wheel all the way to the left
(2) Fill the pump fluid reservoir to the proper level
and let the fluid settle for at least two (2) minutes.
(3) Raise the front wheels off the ground.
(4) Slowly turn the steering wheel lock-to-lock 20
times with the engine off while checking the fluid
level.
Fig. 1 P-SeriesÐPump
1 - RESERVOIR CAP AND DIPSTICK
2 - RESERVOIR
BR/BEPUMP 19 - 31
Page 1638 of 2889

The driver selects a particular gear by moving the
shift lever to the desired gear position. This move-
ment moves the internal transmission shift compo-
nents to begin the shift sequence. As the shift lever
moves the selected shift rail, the shift fork attached
to that rail begins to move. The fork is positioned in
a groove in the outer circumference of the synchro-
nizer sleeve. As the shift fork moves the synchronizer
sleeve, the synchronizer begins to speed-up or slow
down the selected gear (depending on whether we are
up-shifting or down-shifting). The synchronizer does
this by having the synchronizer hub splined to the
mainshaft, or the countershaft in some cases, and
moving the blocker ring into contact with the gear's
friction cone. As the blocker ring and friction cone
come together, the gear speed is brought up or down
to the speed of the synchronizer. As the two speeds
match, the splines on the inside of the synchronizer
sleeve become aligned with the teeth on the blocker
ring and the friction cone and eventually will slide
over the teeth, locking the gear to the mainshaft, or
countershaft, through the synchronizer.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - MANUAL
TRANSMISSION
LOW LUBRICANT LEVEL
A low transmission lubricant level is generally the
result of a leak, inadequate lubricant fill or an incor-
rect lubricant level check.
Leaks can occur at the mating surfaces of the gear
case, adaptor or extension housing, or from the front/
rear seals. A suspected leak could also be the result
of an overfill condition.
Leaks at the rear of the extension or adapter hous-
ing will be from the housing oil seals. Leaks at com-
ponent mating surfaces will probably be the result of
inadequate sealer, gaps in the sealer, incorrect bolt
tightening or use of a non-recommended sealer.
A leak at the front of the transmission will be from
either the front bearing retainer or retainer seal.
Lubricant may be seen dripping from the clutch
housing after extended operation. If the leak is
severe, it may also contaminate the clutch disc caus-
ing the disc to slip, grab and or chatter.
A correct lubricant level check can only be made
when the vehicle is level. Also allow the lubricant to
settle for a minute or so before checking. These rec-
ommendations will ensure an accurate check and
avoid an underfill or overfill condition. Always check
the lubricant level after any addition of fluid to avoid
an incorrect lubricant level condition.
HARD SHIFTING
Hard shifting is usually caused by a low lubricant
level, improper or contaminated lubricants. The con-sequence of using non-recommended lubricants is
noise, excessive wear, internal bind and hard shift-
ing. Substantial lubricant leaks can result in gear,
shift rail, synchro, and bearing damage. If a leak
goes undetected for an extended period, the first indi-
cations of component damage are usually hard shift-
ing and noise.
Component damage, incorrect clutch adjustment or
damaged clutch pressure plate or disc are additional
probable causes of increased shift effort. Incorrect
adjustment or a worn/damaged pressure plate or disc
can cause incorrect release. If clutch problem is
advanced, gear clash during shifts can result. Worn
or damaged synchro rings can cause gear clash when
shifting into any forward gear. In some new or
rebuilt transmissions, new synchro rings may tend to
stick slightly causing hard or noisy shifts. In most
cases this condition will decline as the rings wear-in.
TRANSMISSION NOISE
Most manual transmissions make some noise dur-
ing normal operation. Rotating gears generate a mild
whine that is audible, but generally only at extreme
speeds.
Severe highly audible transmission noise is gener-
ally the initial indicator of a lubricant problem.
Insufficient, improper or contaminated lubricant will
promote rapid wear of gears, synchros, shift rails,
forks and bearings. The overheating caused by a
lubricant problem, can also lead to gear breakage.
REMOVAL
(1) Disconnect battery negative cable.
(2) Shift transmission into Neutral.
(3) Remove shift boot bezel screws and slide boot
upward on shift lever extension.
(4) Remove shift lever extension from the shift
tower and lever assembly.
(5) Remove bolts attaching shift tower and lever
assembly to rear case. Then remove shift tower and
lever assembly.
(6) Raise vehicle on hoist.
(7) Remove crankshaft position sensor. Retain sen-
sor attaching bolts.
(8) Remove skid plate, if equipped.
(9) Drain transmission lubricant if transmission
will be disassembled for service.
(10) Mark propeller shaft/shafts and yoke/yokes for
installation reference and remove propeller shaft/
shafts.
(11) Disengage harness from clips on transmission
housing.
(12) Support engine with adjustable jack stand
and wood block.
(13) Drain transmission lubricant if transmission
will be disassembled for service.
BR/BEMANUAL - NV3500 21 - 3
MANUAL - NV3500 (Continued)
Page 1675 of 2889

(5) Fill transmission to bottom edge of fill plug
hole with Mopar Transmission Lubricant.
(6) Install and tighten fill plug to 34 N´m (25 ft.
lbs.).
(7) Check transmission vent. Be sure vent is open
and not restricted.
INSTALLATION
NOTE: If a new transmission is being installed, be
sure to use all components supplied with the new
transmission. For example, if a new shift tower is
supplied with the new transmission, do not re-use
the original shift tower.
Make sure transmission front housing mounting
surface is clean. Before installation apply light coat
of Mopar high temperature bearing grease to contact
surfaces of following components:
²input shaft splines.
²release bearing slide surface of front retainer.
²release bearing bore.
²release fork.
²release fork ball stud.
²propeller shaft slip yoke.
(1) Support and secure transmission to jack with
safety chains.
(2) Raise and align transmission input shaft with
clutch disc, then slide transmission into place.
(3) Install and tighten transmission bolts to 54-61
N´m (40-45 ft. lbs.). Be sure front housing is fully
seated before tightening bolts. Install front dust
cover after all bolts are tightened.
(4) Fill transmission with Mopar lubricant. Correct
fill level is to bottom edge of fill plug hole.
(5) Connect backup lamp switch wires.(6) Connect transmission harnesses to clips on
case.
(7) Install crossmember. Tighten crossmember-to-
frame bolts to 68 N´m (50 ft. lbs.).
(8) Tighten crossmember-to-transmission insulator
nuts to 68 N´m (50 ft. lbs.).
(9) Install slave cylinder. Tighten cylinder nuts to
23 N´m (200 in. lbs.).
(10) Remove jack used to support transmission.
(11) Install strut bolts/nuts, if removed. Also
install oil filter if removal was necessary.
(12) Install and connect exhaust system. Align
exhaust components before tightening clamp and
bracket bolts and nuts. Be sure exhaust components
are clear of all chassis and driveline components.
TWO WHEEL DRIVE
(1) Align and install propeller shaft.
(2) Verify that all linkage components, hoses and
electrical wires have been connected.
(3) Remove any remaining support stands and
lower vehicle.
(4) Install crankshaft position sensor.
(5) Connect battery negative cable.
(6) Install shift tower and lever assembly. Tighten
shift tower bolts to 7-10 N´m (5-7 ft. lbs.).
(7) Install the shift lever extension onto the shift
tower and lever assembly.
(8) Install shift boot and bezel.
FOUR WHEEL DRIVE
(1) Install transfer case. Align and position trans-
fer case with transmission jack or aid of helper.
(2) Install and tighten transfer case attaching nuts
to 47 N´m (35 ft. lbs.).
(3) Install and connect transfer case shift linkage.
(4) Align and install front and rear propeller
shafts.
(5) Verify that all linkage components, hoses and
electrical wires have been connected.
(6) Check transfer case fluid level. Add Mopar
Dexron II, or ATF Plus if necessary. Correct level is
to edge of fill plug hole. Be sure transfer case is level
before checking or adding fluid.
(7) Check and adjust transfer case shift linkage if
necessary.
(8) Install transfer case skid plate, if equipped.
(9) Install crankshaft position sensor.
(10) Remove any remaining support stands and
lower vehicle.
(11) Connect battery negative cable.
(12) Install shift tower and lever assembly. Tighten
shift tower bolts to 7-10 N´m (5-7 ft. lbs.).
(13) Install the shift lever extension onto the shift
tower and lever assembly.
(14) Install shift boot and bezel.
Fig. 122 Shift Tower Bolts
1 - SHIFT TOWER AND LEVER ASSEMBLY
21 - 40 MANUAL - NV3500BR/BE
MANUAL - NV3500 (Continued)