2001 DODGE RAM lock
[x] Cancel search: lockPage 2779 of 2889

(1) On gasoline engine models:
(a) Insert the two lower condenser locators into
the isolators in the holes of the lower crossmember.
(b) Tilt the condenser up towards the engine
compartment far enough to align the upper mount-
ing bracket holes with the holes in the upper radi-
ator crossmember.
(c) Install the two screws that secure the con-
denser upper mounting brackets to the outside of
the upper radiator crossmember. Tighten the
mounting screws to 10.5 N´m (95 in. lbs.).
(2) On diesel engine models:
(a) Install the driver side condenser mounting
brackets over the two studs on the charge air
cooler.
(b) Install the two screws that secure the brack-
ets on the passenger side end of the condenser to
the charge air cooler. Tighten the mounting screws
to 10.5 N´m (95 in. lbs.).
(c) Install the two nuts that secure the driver
side end of the condenser to the studs on the
charge air cooler. Tighten the mounting nuts to
10.5 N´m (95 in. lbs.).
(3) Remove the plugs or tape from the refrigerant
line fittings on the liquid line and the condenser out-
let. Connect the liquid line to the condenser outlet.
(Refer to 24 - HEATING & AIR CONDITIONING/
PLUMBING - STANDARD PROCEDURE - A/C LINE
COUPLERS)
(4) Install a new gasket and the discharge line
block fitting over the stud on the condenser inlet.
Tighten the mounting nut to 20 N´m (180 in. lbs.).
(5) Check that all of the condenser and radiator
air seals are in their proper locations.(6) Connect the battery negative cable.
(7) Evacuate the refrigerant system. (Refer to 24 -
HEATING & AIR CONDITIONING/PLUMBING -
STANDARD PROCEDURE - REFRIGERANT SYS-
TEM EVACUATE)
(8) Charge the refrigerant system. (Refer to 24 -
HEATING & AIR CONDITIONING/PLUMBING -
STANDARD PROCEDURE - REFRIGERANT SYS-
TEM CHARGE)
NOTE: If the condenser is replaced, add 30 millili-
ters (1 fluid ounce) of refrigerant oil to the refriger-
ant system. Use only refrigerant oil of the type
recommended for the compressor in the vehicle.
(Refer to 24 - HEATING & AIR CONDITIONING/
PLUMBING/REFRIGERANT OIL - DESCRIPTION)
SUCTION AND DISCHARGE
LINE
REMOVAL
WARNING: REVIEW THE WARNINGS AND CAU-
TIONS IN THE FRONT OF THIS SECTION BEFORE
PERFORMING THE FOLLOWING OPERATION.
(Refer to 24 - HEATING & AIR CONDITIONING/
PLUMBING - WARNING) (Refer to 24 - HEATING &
AIR CONDITIONING/PLUMBING - CAUTION)
(1) Disconnect and isolate the battery negative
cable.
(2) Recover the refrigerant from the refrigerant
system. (Refer to 24 - HEATING & AIR CONDI-
TIONING/PLUMBING - STANDARD PROCEDURE -
REFRIGERANT RECOVERY)
(3) Unplug the wire harness connector from the a/c
high pressure switch.
(4) Disconnect the suction line refrigerant line cou-
pler at the accumulator. (Refer to 24 - HEATING &
AIR CONDITIONING/PLUMBING - STANDARD
PROCEDURE - A/C LINE COUPLER) Install plugs
in, or tape over all of the opened refrigerant line fit-
tings.
(5) Remove the nut that secures the block fitting
to the stud on the condenser inlet and disconnect the
discharge line from the condenser. Install plugs in, or
tape over all of the opened refrigerant line fittings.
(6) On models with a gasoline engine, remove the
nut that secures the refrigerant line support bracket
to the stud on the compressor mounting bracket.
(7) Remove the bolt that secures the refrigerant
line manifold to the compressor (Fig. 8) or (Fig. 9).
Install plugs in, or tape over all of the opened refrig-
erant line fittings.
Fig. 7 CONDENSER REMOVE/INSTALL - DIESEL
ENGINE
1 - CHARGE AIR COOLER
2 - NUT
3 - CONDENSER
4 - SCREW
24 - 50 PLUMBINGBR/BE
A/C CONDENSER (Continued)
Page 2780 of 2889
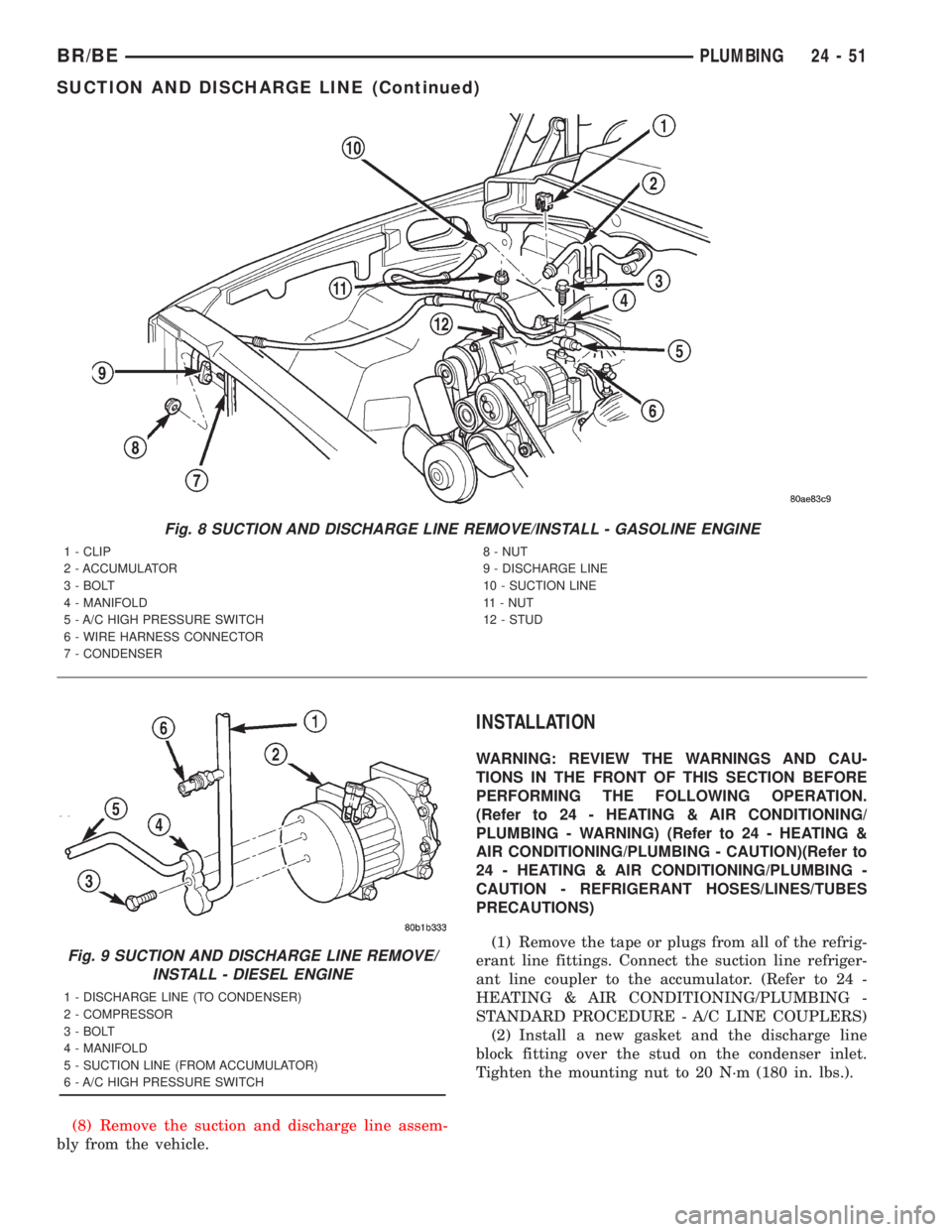
(8) Remove the suction and discharge line assem-
bly from the vehicle.
INSTALLATION
WARNING: REVIEW THE WARNINGS AND CAU-
TIONS IN THE FRONT OF THIS SECTION BEFORE
PERFORMING THE FOLLOWING OPERATION.
(Refer to 24 - HEATING & AIR CONDITIONING/
PLUMBING - WARNING) (Refer to 24 - HEATING &
AIR CONDITIONING/PLUMBING - CAUTION)(Refer to
24 - HEATING & AIR CONDITIONING/PLUMBING -
CAUTION - REFRIGERANT HOSES/LINES/TUBES
PRECAUTIONS)
(1) Remove the tape or plugs from all of the refrig-
erant line fittings. Connect the suction line refriger-
ant line coupler to the accumulator. (Refer to 24 -
HEATING & AIR CONDITIONING/PLUMBING -
STANDARD PROCEDURE - A/C LINE COUPLERS)
(2) Install a new gasket and the discharge line
block fitting over the stud on the condenser inlet.
Tighten the mounting nut to 20 N´m (180 in. lbs.).
Fig. 8 SUCTION AND DISCHARGE LINE REMOVE/INSTALL - GASOLINE ENGINE
1 - CLIP
2 - ACCUMULATOR
3 - BOLT
4 - MANIFOLD
5 - A/C HIGH PRESSURE SWITCH
6 - WIRE HARNESS CONNECTOR
7 - CONDENSER8 - NUT
9 - DISCHARGE LINE
10 - SUCTION LINE
11 - NUT
12 - STUD
Fig. 9 SUCTION AND DISCHARGE LINE REMOVE/
INSTALL - DIESEL ENGINE
1 - DISCHARGE LINE (TO CONDENSER)
2 - COMPRESSOR
3 - BOLT
4 - MANIFOLD
5 - SUCTION LINE (FROM ACCUMULATOR)
6 - A/C HIGH PRESSURE SWITCH
BR/BEPLUMBING 24 - 51
SUCTION AND DISCHARGE LINE (Continued)
Page 2782 of 2889

compressor is engaged and circulating refrigerant
through the evaporator coil tubes.
OPERATION
Refrigerant enters the evaporator from the fixed
orifice tube as a low-temperature, low-pressure liq-
uid. As air flows over the fins of the evaporator, the
humidity in the air condenses on the fins, and the
heat from the air is absorbed by the refrigerant. Heat
absorption causes the refrigerant to boil and vapor-
ize. The refrigerant becomes a low-pressure gas when
it leaves the evaporator.
The evaporator coil cannot be repaired and, if
faulty or damaged, it must be replaced.
REMOVAL
WARNING: REVIEW THE WARNINGS AND CAU-
TIONS IN THE FRONT OF THIS SECTION BEFORE
PERFORMING THE FOLLOWING OPERATION.
(Refer to 24 - HEATING & AIR CONDITIONING/
PLUMBING - WARNING) (Refer to 24 - HEATING &
AIR CONDITIONING/PLUMBING - CAUTION)
(1) Remove the HVAC housing from the vehicle,
and disassemble the housing halves. (Refer to 24 -
HEATING & AIR CONDITIONING/DISTRIBUTION/
HVAC HOUSING - REMOVAL) (Refer to 24 - HEAT-
ING & AIR CONDITIONING/DISTRIBUTION/HVAC
HOUSING - DISASSEMBLY)
(2) Lift the a/c evaporator out of the HVAC hous-
ing (Fig. 11).
INSTALLATION
WARNING: REVIEW THE WARNINGS AND CAU-
TIONS IN THE FRONT OF THIS SECTION BEFORE
PERFORMING THE FOLLOWING OPERATION.
(Refer to 24 - HEATING & AIR CONDITIONING/
PLUMBING - WARNING) (Refer to 24 - HEATING &
AIR CONDITIONING/PLUMBING - CAUTION)(Refer to
24 - HEATING & AIR CONDITIONING/PLUMBING -
CAUTION - REFRIGERANT HOSES/LINES/TUBES
PRECAUTIONS)
(1) Insert the evaporator coil into the bottom of the
HVAC housing.
(2) Reassemble and reinstall the HVAC housing in
the vehicle. (Refer to 24 - HEATING & AIR CONDI-
TIONING/DISTRIBUTION/HVAC HOUSING -
ASSEMBLY) (Refer to 24 - HEATING & AIR CON-
DITIONING/DISTRIBUTION/HVAC HOUSING -
INSTALLATION)
NOTE: If the evaporator is replaced, add 60 millili-
ters (2 fluid ounces) of refrigerant oil to the refrig-
erant system.
A/C ORIFICE TUBE
DESCRIPTION
The fixed orifice tube is installed in the liquid line
between the outlet of the condenser and the inlet of
the evaporator. The fixed orifice tube is only serviced
as an integral part of the liquid line.
OPERATION
The inlet end of the fixed orifice tube has a nylon
mesh filter screen, which filters the refrigerant and
helps to reduce the potential for blockage of the
metering orifice by refrigerant system contaminants
(Fig. 12). The outlet end of the tube has a nylon
mesh diffuser screen. The O-rings on the plastic body
of the fixed orifice tube seal the tube to the inside of
the liquid line and prevent the refrigerant from
bypassing the fixed metering orifice.
The fixed orifice tube is used to meter the flow of
liquid refrigerant into the evaporator coil. The high-
pressure liquid refrigerant from the condenser
expands into a low-pressure liquid as it passes
through the metering orifice and diffuser screen of
the fixed orifice tube.
The fixed orifice tube cannot be repaired and, if
faulty or plugged, the liquid line assembly must be
replaced.
Fig. 11 A/C EVAPORATOR LOCATION IN HVAC
HOUSING (UPSIDE DOWN)
1 - EVAPORATOR LOCATION
2 - BOTTOM HALF OF HVAC HOUSING
3 - TOP HALF OF HVAC HOUSING
BR/BEPLUMBING 24 - 53
A/C EVAPORATOR (Continued)
Page 2788 of 2889

EMISSIONS CONTROL
TABLE OF CONTENTS
page page
EMISSIONS CONTROL
DESCRIPTION............................1
OPERATION.............................18AIR INJECTION..........................25
EVAPORATIVE EMISSIONS.................31
EMISSIONS CONTROL
DESCRIPTION - DIESEL
Two different modules are used for powertrain con-
trol with the diesel engine. The Powertrain Control
Module (PCM) is used primarily for charging system,
transmission, A/C compressor clutch operation and
speed control functions. The Engine Control Module
(ECM) is used to control thefuel and emissions
systems.The PCM is located in the right/rear of
engine compartment (Fig. 1). The ECM is bolted to
the left side of the engine cylinder block (Fig. 2).
DESCRIPTION - STATE DISPLAY TEST MODE
The switch inputs to the Powertrain Control Mod-
ule (PCM) have two recognized states; HIGH and
LOW. For this reason, the PCM cannot recognize the
difference between a selected switch position versus
an open circuit, a short circuit, or a defective switch.
If the State Display screen shows the change from
HIGH to LOW or LOW to HIGH, assume the entire
switch circuit to the PCM functions properly. Connectthe DRB scan tool to the data link connector and
access the state display screen. Then access either
State Display Inputs and Outputs or State Display
Sensors.
DESCRIPTION - CIRCUIT ACTUATION TEST
MODE
The Circuit Actuation Test Mode checks for proper
operation of output circuits or devices the Powertrain
Control Module (PCM) may not internally recognize.
The PCM attempts to activate these outputs and
allow an observer to verify proper operation. Most of
the tests provide an audible or visual indication of
device operation (click of relay contacts, fuel spray,
etc.). Except for intermittent conditions, if a device
functions properly during testing, assume the device,
its associated wiring, and driver circuit work cor-
rectly. Connect the DRB scan tool to the data link
connector and access the Actuators screen.
Fig. 1 Powertrain Control Module (PCM) Location
1 - PCM MOUNTING BOLTS (3)
2 - POWERTRAIN CONTROL MODULE (PCM)
3 - (3) 32±WAY CONNECTORS
Fig. 2 Engine Control Module (ECM) Location
1 - ENGINE CONTROL MODULE (ECM)
2 - HEX HEADED BOLT
3 - FUEL TRANSFER PUMP
4 - MOUNTING BOLTS (3)
5 - 50±WAY CONNECTOR
BR/BEEMISSIONS CONTROL 25 - 1
Page 2796 of 2889

(M)Malfunction Indicator Lamp (MIL) illuminated during engine operation if this DTC was recorded
(depending if required by CARB and/or EPA). MIL is displayed as an engine icon on instrument panel.
(G)Generator lamp illuminated
Generic Scan
Tool P-CodeDRB Scan Tool Display Brief Description of DTC
P0713 Trans Temp Sensor Voltage Too
HighTransmission fluid temperature sensor input above
acceptable voltage. Was MIL code 37.
P0713 (M) Trans Temp Sensor Voltage Too
HighVoltage greater than 3.76 volts (4-speed auto. trans.
only).
P0720 (M) Low Output SPD Sensor RPM,
Above 15 MPHThe relationship between the Output Shaft Speed Sensor
and vehicle speed is not within acceptable limits.
P0720 (M) Low Output Spd Sensor RPM Above
15 mphOutput shaft speed is less than 60 rpm with vehicle speed
above 15 mph (4-speed auto. trans. only).
P0740 (M) Torq Con Clu, No RPM Drop at
LockupRelationship between engine and vehicle speeds
indicated failure of torque convertor clutch lock-up system
(TCC/PTU solenoid)
P0743 (M) Torque Converter Clutch Solenoid/
Trans Relay CircuitsAn open or shorted condition detected in the torque
converter clutch (part throttle unlock) solenoid control
circuit. Shift solenoid C electrical fault - Aisin transmission
P0743 (M) Torque Converter Clutch Solenoid/
Trans Relay CircuitsAn open or shorted condition detected in the torque
converter part throttle unlock solenoid control circuit (3 or
4-speed auto. trans. only).
P0748 (M) Governor Pressur Sol Control/Trans
Relay CircuitsAn open or shorted condition detected in the Governor
Pressure Solenoid circuit or Trans Relay Circuit in JTEC
RE transmissions.
P0748 (M) Governor Pressure Sol Control/Trans
Relay CircuitsAn open or shorted condition detected in the governor
pressure solenoid or relay circuits (4-speed auto. trans.
only).
P0751 (M) O/D Switch Pressed (Lo) More Than
5 MinutesOverdrive override switch input is in a prolonged
depressed state.
P0751 (M) O/D Switch Pressed (LO) More Than
5 MinOverdrive Off switch input too low for more than 5
minutes (4-speed auto. trans. only).
P0753 (M) Trans 3-4 Shift Sol/Trans Relay
CircuitsAn open or shorted condition detected in the overdrive
solenoid control circuit or Trans Relay Circuit in JTEC RE
transmissions. Was MIL code 45.
P0753 (M) Trans 3-4 Shift Sol/Trans Relay
CircuitsAn open or shorted condition detected in the transmission
2-4 shift solenoid circuit (4-speed auto. trans. only).
P0756 AW4 Shift Sol B (2-3) Functional
FailureShift solenoid B (2-3) functional fault - Aisin transmission
P0783 (M) 3-4 Shift Sol, No RPM Drop at
LockupThe overdrive solenoid is unable to engage the gear
change from 3rd gear to the overdrive gear.
P0801 Reverse Gear Lockout Circuit Open
or ShortAn open or shorted condition detected in the transmission
reverse gear lock-out solenoid control circuit.
P0830 Clutch Depressed Switch Circuit Problem detected in clutch switch circuit.
P0833 Clutch Released Switch Circuit Problem detected in clutch switch circuit.
P1110 Decrease Engine Performance Due
To High Intake Air TemperatureIntake manifold air temperature is above the engine
protection limit. Engine power will be derated.
P1180 Decreased Engine Performance Due
To High Injection Pump Fuel TempFuel temperature is above the engine protection limit.
Engine power will be derated.
BR/BEEMISSIONS CONTROL 25 - 9
EMISSIONS CONTROL (Continued)
Page 2801 of 2889

(M)Malfunction Indicator Lamp (MIL) illuminated during engine operation if this DTC was recorded
(depending if required by CARB and/or EPA). MIL is displayed as an engine icon on instrument panel.
(G)Generator lamp illuminated
Generic Scan
Tool P-CodeDRB Scan Tool Display Brief Description of DTC
P1691 Fuel Injection Pump Controller
Calibration ErrorInternal fuel injection pump failure. Low power, engine
derated, or engine stops.
P1692 DTC Set In ECM A9Companion DTC9was set in both the ECM and PCM.
P1693 (M) DTC Detected in Companion Module A fault has been generated in the companion engine
control module.
P1693 (M) DTC Detected in PCM/ECM or DTC
Detected in ECMA9Companion DTC9was set in both the ECM and PCM.
P1694 Fault In Companion Module No CCD/J1850 messages received from the powertrain
control module-Aisin transmission
P1694 (M) No CCD Messages received from
ECMBus communication failure to PCM.
P1695 No CCD/J1850 Message From Body
Control ModuleNo CCD/J1850 messages received from the body control
module.
P1696 PCM Failure EEPROM Write Denied Unsuccessful attempt to write to an EEPROM location by
the control module.
P1697 PCM Failure SRI Mile Not Stored Unsuccessful attempt to update Service Reminder
Indicator (SRI or EMR) mileage in the control module
EEPROM.
P1698 No CCD/J1850 Message From TCM No CCD/J1850 messages received from the electronic
transmission control module (EATX) or the Aisin
transmission controller.
P1698 No CCD Messages received from
PCMBus communication failure to PCM. A9Companion DTC9
was set in both the ECM and PCM.
P1719 Skip Shift Solenoid Circuit An open or shorted condition detected in the transmission
2-3 gear lock-out solenoid control circuit.
P1740 TCC or OD Sol Perf A rationality error has been detected in either the TCC
solenoid or overdrive solenoid systems.
P1740 (M) TCC OR O/D Solenoid Performance Problem detected in transmission convertor clutch and/or
overdrive circuits (diesel engine with 4-speed auto. trans.
only).
P1756 (M) GOV Press Not Equal to Target @
15-20 PSIThe requested pressure and the actual pressure are not
within a tolerance band for the Governor Control System
which is used to regulate governor pressure to control
shifts for 1st, 2nd, and 3rd gear. (Mid Pressure
Malfunction)
P1756 (M) Governor Pressure Not Equal to
Target @ 15-20 PSIGovernor sensor input not between 10 and 25 psi when
requested (4-speed auto. trans. only).
P1757 GOV Press Not Equal to Target @
15-20 PSIThe requested pressure and the actual pressure are not
within a tolerance band for the Governor Control System
which is used to regulate governor pressure to control
shifts for 1st, 2nd, and 3rd gear (Zero Pressure
Malfunction)
P1757 (M) Governor Pressure Above 3 PSI In
Gear With 0 MPHGovernor pressure greater than 3 psi when requested to
be 0 psi (4-speed auto. trans. only).
25 - 14 EMISSIONS CONTROLBR/BE
EMISSIONS CONTROL (Continued)
Page 2804 of 2889

After passing the leak detection phase of the test,
system pressure is maintained by turning on the
LDP's solenoid until the purge system is activated.
Purge activation in effect creates a leak. The cycle
rate is again interrogated and when it increases due
to the flow through the purge system, the leak check
portion of the diagnostic is complete.
The canister vent valve will unseal the system
after completion of the test sequence as the pump
diaphragm assembly moves to the full travel position.
Evaporative system functionality will be verified by
using the stricter evap purge flow monitor. At an
appropriate warm idle the LDP will be energized to
seal the canister vent. The purge flow will be clocked
up from some small value in an attempt to see a
shift in the 02 control system. If fuel vapor, indicated
by a shift in the 02 control, is present the test is
passed. If not, it is assumed that the purge system is
not functioning in some respect. The LDP is again
turned off and the test is ended.
MISFIRE MONITOR
Excessive engine misfire results in increased cata-
lyst temperature and causes an increase in HC emis-
sions. Severe misfires could cause catalyst damage.
To prevent catalytic convertor damage, the PCM
monitors engine misfire.
The Powertrain Control Module (PCM) monitors
for misfire during most engine operating conditions
(positive torque) by looking at changes in the crank-
shaft speed. If a misfire occurs the speed of the
crankshaft will vary more than normal.
FUEL SYSTEM MONITOR
To comply with clean air regulations, vehicles are
equipped with catalytic converters. These converters
reduce the emission of hydrocarbons, oxides of nitro-
gen and carbon monoxide. The catalyst works best
when the Air Fuel (A/F) ratio is at or near the opti-
mum of 14.7 to 1.
The PCM is programmed to maintain the optimum
air/fuel ratio of 14.7 to 1. This is done by making
short term corrections in the fuel injector pulse width
based on the O2S sensor output. The programmed
memory acts as a self calibration tool that the engine
controller uses to compensate for variations in engine
specifications, sensor tolerances and engine fatigue
over the life span of the engine. By monitoring the
actual fuel-air ratio with the O2S sensor (short term)
and multiplying that with the program long-term
(adaptive) memory and comparing that to the limit,
it can be determined whether it will pass an emis-
sions test. If a malfunction occurs such that the PCM
cannot maintain the optimum A/F ratio, then the
MIL will be illuminated.
CATALYST MONITOR
To comply with clean air regulations, vehicles are
equipped with catalytic converters. These converters
reduce the emission of hydrocarbons, oxides of nitro-
gen and carbon monoxide.
Normal vehicle miles or engine misfire can cause a
catalyst to decay. A meltdown of the ceramic core can
cause a reduction of the exhaust passage. This can
increase vehicle emissions and deteriorate engine
performance, driveability and fuel economy.
The catalyst monitor uses dual oxygen sensors
(O2S's) to monitor the efficiency of the converter. The
dual O2S's sensor strategy is based on the fact that
as a catalyst deteriorates, its oxygen storage capacity
and its efficiency are both reduced. By monitoring
the oxygen storage capacity of a catalyst, its effi-
ciency can be indirectly calculated. The upstream
O2S is used to detect the amount of oxygen in the
exhaust gas before the gas enters the catalytic con-
verter. The PCM calculates the A/F mixture from the
output of the O2S. A low voltage indicates high oxy-
gen content (lean mixture). A high voltage indicates a
low content of oxygen (rich mixture).
When the upstream O2S detects a lean condition,
there is an abundance of oxygen in the exhaust gas.
A functioning converter would store this oxygen so it
can use it for the oxidation of HC and CO. As the
converter absorbs the oxygen, there will be a lack of
oxygen downstream of the converter. The output of
the downstream O2S will indicate limited activity in
this condition.
As the converter loses the ability to store oxygen,
the condition can be detected from the behavior of
the downstream O2S. When the efficiency drops, no
chemical reaction takes place. This means the con-
centration of oxygen will be the same downstream as
upstream. The output voltage of the downstream
O2S copies the voltage of the upstream sensor. The
only difference is a time lag (seen by the PCM)
between the switching of the O2S's.
To monitor the system, the number of lean-to-rich
switches of upstream and downstream O2S's is
counted. The ratio of downstream switches to
upstream switches is used to determine whether the
catalyst is operating properly. An effective catalyst
will have fewer downstream switches than it has
upstream switches i.e., a ratio closer to zero. For a
totally ineffective catalyst, this ratio will be one-to-
one, indicating that no oxidation occurs in the device.
The system must be monitored so that when cata-
lyst efficiency deteriorates and exhaust emissions
increase to over the legal limit, the MIL will be illu-
minated.
BR/BEEMISSIONS CONTROL 25 - 17
EMISSIONS CONTROL (Continued)
Page 2828 of 2889

Items found requiring adjustment and/or repair
should be corrected before delivery of the vehicle.
NOTE: It is the dealer's responsibility to protect
new vehicles from damage and deterioration prior
to retail delivery both before and after new vehicle
preparation.
The information includes the following features:
Inspection points are cross-referenced to the New
Vehicle Preparation Form as follows:
²Titles indicate the general area being inspected
or the types of checks being made (i.e., underhood,
body-exterior, road test, etc.).
²Sub-Titles identify the types of items to be
inspected in that area (i.e., lines/hoses, wiring, etc.).
Procedures follow a logical order to prevent dupli-
cation and wasted effort.
Tips to help you do a better job are found as
NOTES.
RECEIVING
INSPECTION
The following procedures are recommended for
your own protection upon receipt of new vehicles.
When a new car is delivered by the carrier, it should
be inspected to ensure that it is in good condition
and to determine if there is any shortage or transpor-
tation damage.
EXTERIOR
Upon receipt of a new vehicle, check immediately
for:
²Under carriage damage
²Chipped or cracked windshield, broken windows,
and loose or missing moldings and name-plates
²Dents, scrapes, scratches, chips, dirt in paints or
other damage to the body exterior
²Damaged or missing side view mirror(s)
²Missing wheel nuts
²Broken or missing lenses
²Chafing, bruises, cuts, or scrapes on tire side-
walls or tread
²Missing underhood items
²Missing fuel filler cap
²Shipped loose items-license plate bracket, spare
tire, jack and tire wrench, radio antenna, floor mats,
wheel covers, cargo nets, fuses and other items²Ensure that IOD fuse is removed
²Check battery test indicator when easily visible,
or use voltmeter (battery must be at 12.4 volts or
greater). Charge to ensure green dot-visibility, per-
manent damage may occur if battery remains in a
discharged state for any length of time.
INTERIOR
Check interior items such as:
²Rearview mirror
²Accessory control knobs
²Smokers package items
²Keys
²Radio
²Special equipment items listed on shipper
²Owner's Manual and Consumer information Bro-
chures (normally stored in the glove box).
²Cuts, abrasions or stains on interior trim.
NOTE: Remember a careful look at new vehicles
when they are received may prevent problems when
preparing vehicles for delivery to your customers.
MAJOR INSPECTION POINTS
(1) Check operation of hood latch and safety catch-
adjust as required.
(2) Check all fluids for proper level and top off
with the proper fluid as required-engine oil, auto-
matic transmission fluid, brake master cylinder,
clutch master cylinder, power steering, windshield
washer, and cooling system. (Vehicle must be at nor-
mal operating temperature for some of these checks.)
(3) Check brake, clutch, fuel, and power steering
lines and hoses for leaks and clearance from moving
and hot objects-reroute to the proper location and
tighten as required.
(4) Check battery state of charge-recharge if neces-
sary, to ensure green dot is visible or instrument
panel voltmeter indicates 12.4 volts or greater.
(5) Check routing and connections of underhood
wiring, vacuum hoses, refrigerant lines and coolant
hoses for leaks, loose connections and clearance from
moving objects reroute and tighten connections as
required. Install IOD fuse on applicable vehicles.
NOTE: Reset radio, clock, compass, etc., after
installing, if vehicle is being delivered.
BR/BENEW VEHICLE PREPARATION 30 - 3
INTRODUCTION (Continued)