2001 CHRYSLER VOYAGER lock
[x] Cancel search: lockPage 3081 of 4284
(2) Verify gearshift lever is in PARK (P) and con-
nect solenoid connector (Fig. 219).
(3) Install steering column lower shroud.
(4) Install knee bolster (Fig. 220).
(5) Install instrument panel lower silencer (Fig.
221).
(6) Connect battery negative cable.
(7) Verify proper shift interlock system operation.
(Refer to 21 - TRANSMISSION/TRANSAXLE/AUTO-MATIC - 31TH/SHIFT INTERLOCK SOLENOID -
OPERATION)
SOLENOID - TCC
DESCRIPTION
The torque converter clutch (TCC) solenoid is fas-
tened to the transaxle valve body, and its connector
protrudes through the transaxle case (Fig. 222).
OPERATION
The torque converter clutch solenoid is responsible
for controlling application of the torque converter
clutch. It is controlled by the Powertrain Control
Module (PCM), which determines when conditions
are acceptable for torque converter lock-up.
Fig. 219 BTSI Solenoid Connector
1 - BTSI SOLENOID
2 - SOLENOID CONNECTOR
Fig. 220 Knee Bolster
1 - KNEE BOLSTER
Fig. 221 Instrument Panel Lower Silencer
1 - INSTRUMENT PANEL LOWER SILENCER
Fig. 222 Torque Converter Clutch Solenoid
1 - TCC SOLENOID WIRING CONNECTOR
RSAUTOMATIC - 31TH21 - 117
SHIFT INTERLOCK SOLENOID (Continued)
Page 3084 of 4284

THROTTLE VALVE LINKAGE ADJUSTMENT
The throttle valve linkage adjustment is very
important to proper transaxle operation. This adjust-
ment positions a valve which controls shift speed,
shift quality, and part throttle downshift sensitivity.
If the setting is too short, early shifts and slippage
between shifts may occur. If the setting is too long,
shifts may be delayed and part throttle downshifts
may be very sensitive.
LINKAGE ADJUSTMENT PROCEDURE
(1) Perform transaxle throttle valve linkage
adjustment while engine is at normal operating tem-
perature.
(2) Using small screwdriver, disengage adjustment
lock at transaxle.
(3) Rotate lever at transaxle all the way to the left
side of vehicle against stop.
(4) Slide cable adjuster until cable core end
touches clip at throttle valve lever.
(5) Press adjuster lock (Fig. 228) to retain setting.
TORQUE CONVERTER
DESCRIPTION
The torque converter (Fig. 229) is a hydraulic
device that couples the engine crankshaft to the
transmission. The torque converter consists of an
outer shell with an internal turbine, a stator, an
overrunning clutch, an impeller and an electronically
applied converter clutch. The converter clutch pro-
vides reduced engine speed and greater fuel economy
when engaged. Clutch engagement also provides
reduced transmission fluid temperatures. The con-
verter clutch engages in third gear. The torque con-
verter hub drives the transmission oil (fluid) pump.
The torque converter is a sealed, welded unit that
is not repairable and is serviced as an assembly.
CAUTION: The torque converter must be replaced if
a transmission failure resulted in large amounts of
metal or fiber contamination in the fluid. If the fluid
is contaminated, flush the fluid cooler and lines.
Fig. 228 Throttle Valve Cable Adjustment Lock
1 - ADJUSTER LOCK
Fig. 229 Torque Converter Assembly
1 - TURBINE
2 - IMPELLER
3 - HUB
4-STATOR
5 - CONVERTER CLUTCH DISC
6 - DRIVE PLATE
21 - 120 AUTOMATIC - 31THRS
THROTTLE VALVE CABLE (Continued)
Page 3086 of 4284
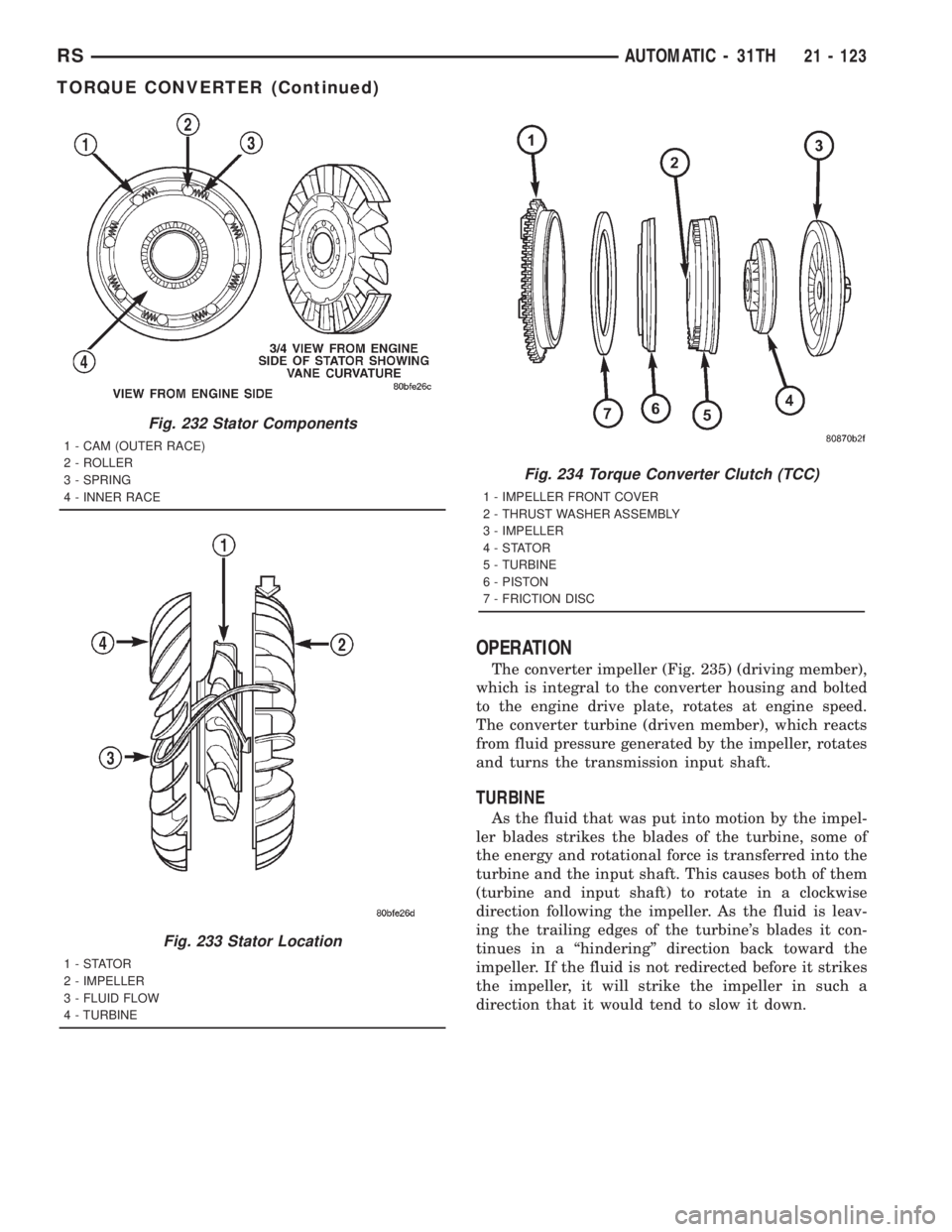
STATOR
The stator assembly (Fig. 232) is mounted on a sta-
tionary shaft which is an integral part of the oil
pump. The stator is located between the impeller and
turbine within the torque converter case (Fig. 233).
The stator contains an over-running clutch, which
allows the stator to rotate only in a clockwise direc-
tion. When the stator is locked against the over-run-
ning clutch, the torque multiplication feature of the
torque converter is operational.
TORQUE CONVERTER CLUTCH (TCC)
The TCC (Fig. 234) was installed to improve the
efficiency of the torque converter that is lost to the
slippage of the fluid coupling. Although the fluid cou-
pling provides smooth, shock±free power transfer, it
is natural for all fluid couplings to slip. If the impel-
ler and turbine were mechanically locked together, a
zero slippage condition could be obtained. A hydraulic
piston was added to the turbine, and a friction mate-
rial was added to the inside of the front cover to pro-
vide this mechanical lock-up.
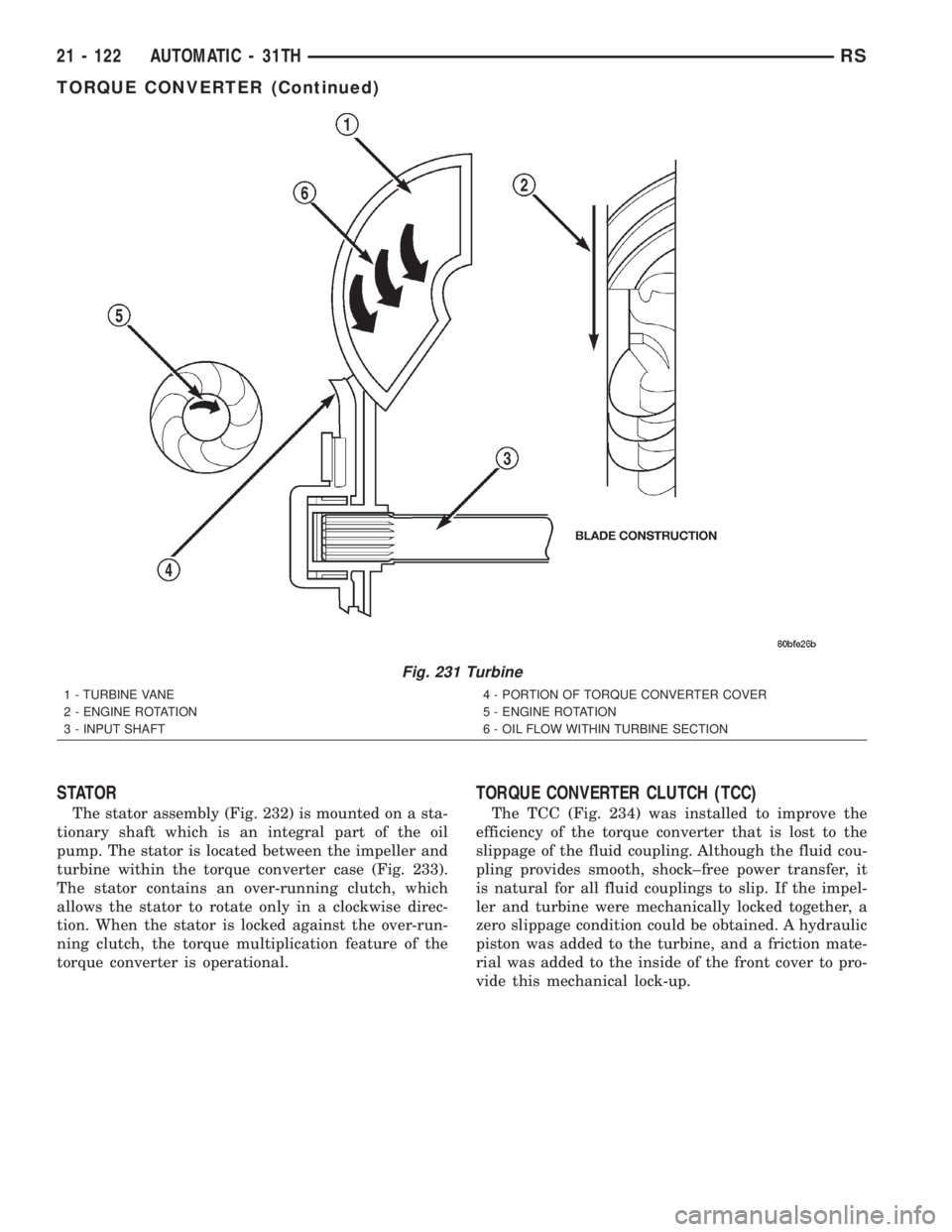
Fig. 231 Turbine
1 - TURBINE VANE
2 - ENGINE ROTATION
3 - INPUT SHAFT4 - PORTION OF TORQUE CONVERTER COVER
5 - ENGINE ROTATION
6 - OIL FLOW WITHIN TURBINE SECTION
21 - 122 AUTOMATIC - 31THRS
TORQUE CONVERTER (Continued)
Page 3087 of 4284
OPERATION
The converter impeller (Fig. 235) (driving member),
which is integral to the converter housing and bolted
to the engine drive plate, rotates at engine speed.
The converter turbine (driven member), which reacts
from fluid pressure generated by the impeller, rotates
and turns the transmission input shaft.
TURBINE
As the fluid that was put into motion by the impel-
ler blades strikes the blades of the turbine, some of
the energy and rotational force is transferred into the
turbine and the input shaft. This causes both of them
(turbine and input shaft) to rotate in a clockwise
direction following the impeller. As the fluid is leav-
ing the trailing edges of the turbine's blades it con-
tinues in a ªhinderingº direction back toward the
impeller. If the fluid is not redirected before it strikes
the impeller, it will strike the impeller in such a
direction that it would tend to slow it down.
Fig. 232 Stator Components
1 - CAM (OUTER RACE)
2 - ROLLER
3 - SPRING
4 - INNER RACE
Fig. 233 Stator Location
1-STATOR
2 - IMPELLER
3 - FLUID FLOW
4 - TURBINE
Fig. 234 Torque Converter Clutch (TCC)
1 - IMPELLER FRONT COVER
2 - THRUST WASHER ASSEMBLY
3 - IMPELLER
4-STATOR
5 - TURBINE
6 - PISTON
7 - FRICTION DISC
RSAUTOMATIC - 31TH21 - 123
TORQUE CONVERTER (Continued)
Page 3088 of 4284
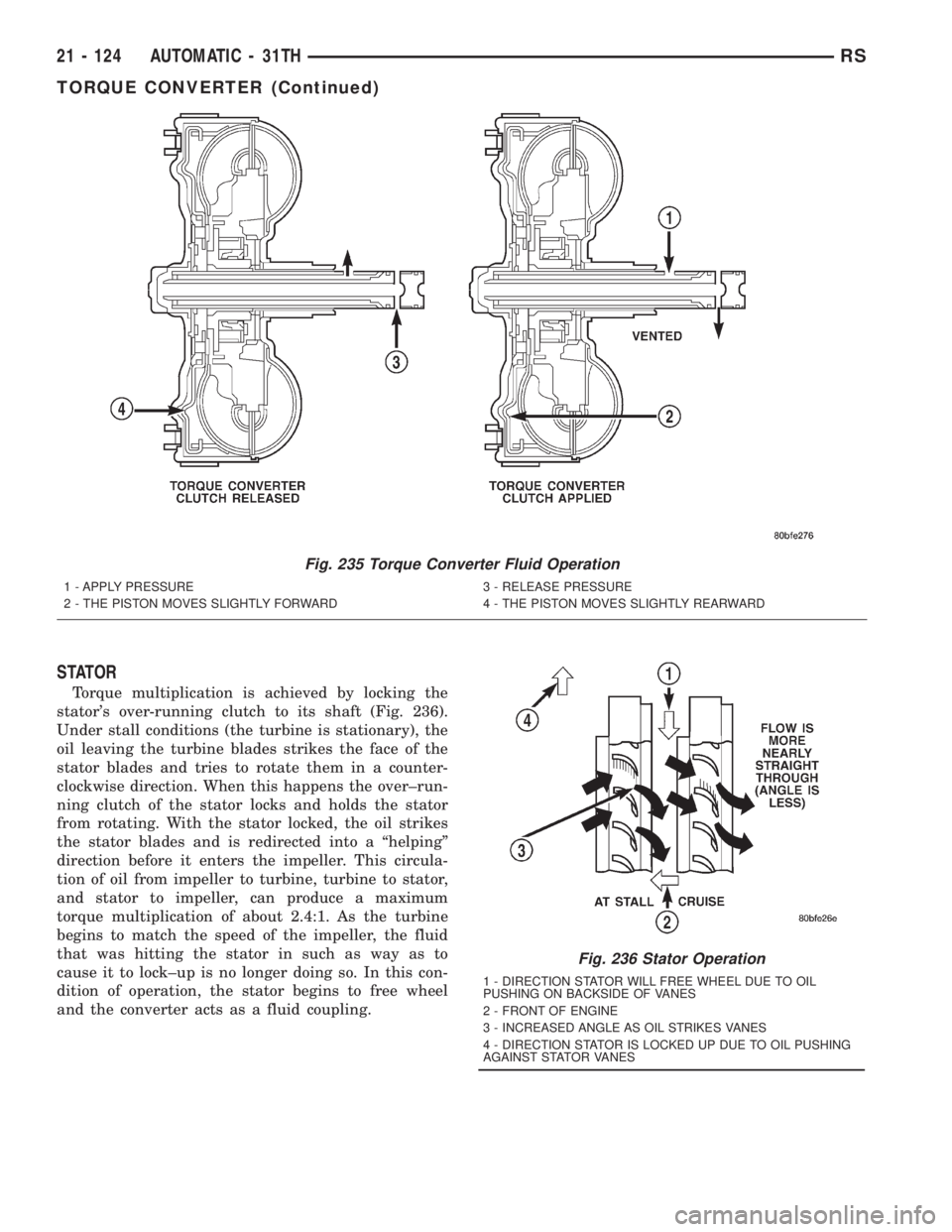
STATOR
Torque multiplication is achieved by locking the
stator's over-running clutch to its shaft (Fig. 236).
Under stall conditions (the turbine is stationary), the
oil leaving the turbine blades strikes the face of the
stator blades and tries to rotate them in a counter-
clockwise direction. When this happens the over±run-
ning clutch of the stator locks and holds the stator
from rotating. With the stator locked, the oil strikes
the stator blades and is redirected into a ªhelpingº
direction before it enters the impeller. This circula-
tion of oil from impeller to turbine, turbine to stator,
and stator to impeller, can produce a maximum
torque multiplication of about 2.4:1. As the turbine
begins to match the speed of the impeller, the fluid
that was hitting the stator in such as way as to
cause it to lock±up is no longer doing so. In this con-
dition of operation, the stator begins to free wheel
and the converter acts as a fluid coupling.
Fig. 235 Torque Converter Fluid Operation
1 - APPLY PRESSURE
2 - THE PISTON MOVES SLIGHTLY FORWARD3 - RELEASE PRESSURE
4 - THE PISTON MOVES SLIGHTLY REARWARD
Fig. 236 Stator Operation
1 - DIRECTION STATOR WILL FREE WHEEL DUE TO OIL
PUSHING ON BACKSIDE OF VANES
2 - FRONT OF ENGINE
3 - INCREASED ANGLE AS OIL STRIKES VANES
4 - DIRECTION STATOR IS LOCKED UP DUE TO OIL PUSHING
AGAINST STATOR VANES
21 - 124 AUTOMATIC - 31THRS
TORQUE CONVERTER (Continued)
Page 3095 of 4284

(7) Install output shaft gear onto shaft. Use Tool
L-4439 to get gear started (Fig. 258).
(8) Install Tool L-4434 and C-4658. Install washer
and nut (Fig. 259).
(9) Torque output shaft retaining nut to 271 N´m
(200 ft. lbs.) (Fig. 260).
(10) Set up Tool L-4432 and C-4658 as shown in
(Fig. 261). Install dial indicator and measure output
shaft end play.
(11) Using an in. lb. torque wrench, measure out-
put shaft bearing turning torque (Fig. 262).
(12) Install stirrup and strap. Install bolts but do
not tighten.
NOTE: Once the stirrup assembly is positioned
onto the output gear, it is necessary to ªclockº the
stirrup against the flats of the output gear retaining
nut.(13) Rotate stirrup clockwise against flats of gear
retaining nut (Fig. 263).
(14) Torque stirrup and strap bolts to 23 N´m (200
in. lbs..) (Fig. 264).
(15) Bend tabs of strap up against ªflatsºof retain-
ing bolts to prevent bolts from backing out of gear in
the event they come loose.
(16) Install transfer shaft and gear. (Refer to 21 -
TRANSMISSION/TRANSAXLE/AUTOMATIC -
31TH/TRANSFER SYSTEM - INSTALLATION)
(17) Assemble transaxle geartrain. (Refer to 21 -
TRANSMISSION/TRANSAXLE/AUTOMATIC - 31TH
- ASSEMBLY)
Fig. 257 Output Shaft and (Select) Shims in Position
1 - BEARING CUP
2 - (SELECT) SHIM
3 - OUTPUT SHAFT ASSEMBLY
Fig. 258 Start Output Shaft Gear onto Output Shaft
1 - OUTPUT SHAFT GEAR
2 - OUTPUT SHAFT
3 - SPECIAL TOOL L-4439
Fig. 259 Holding Output Shaft Gear
1 - OUTPUT SHAFT
2 - SCREW (2)
3 - SPECIAL TOOL L-4434 AND C-4658
4 - WASHER
5 - NUT
Fig. 260 Tighten Output Shaft Retaining Nut
1 - OUTPUT SHAFT GEAR
2 - SPECIAL TOOL L-4434 AND C-4658
3 - SCREW (2)
RSAUTOMATIC - 31TH21 - 131
TRANSFER SYSTEM - OUTPUT SHAFT/GEAR/BEARING (Continued)
Page 3096 of 4284

ADJUSTMENT - OUTPUT SHAFT BEARING
(1) With output shaft gear removed, install a 13.65
mm (0.537 inch) and a 1.34 mm (0.053 inch) gauging
shims on the planetary rear annulus gear hub using
grease to hold the shims in place. The 13.65 mm
shim has a larger inside diameter and must be
installed over the output shaft first. The 1.34 mm
shim pilots on the output shaft.
(2) Install output shaft gear and bearing assembly,
torque to 271 N´m (200 ft. lbs.).
(3) To measure bearing end play:
(4) Attach Tool L-4432 to the output shaft gear.(5) Mount a steel ball with grease into the end of
the output shaft.
(6) Push and pull the gear while rotating back and
forth to insure seating of the bearing rollers.
(7) Using a dial indicator, mounted to the trans-
axle case, measure output shaft end play.
(8) Once bearing end play has been determined,
refer to the output shaft bearing shim chart.
(9) The 12.65 mm (0.498 inch), 13.15 mm (0.518
inch) or 13.65 mm (0.537 inch) shims are always
installed first.These shims have lubrication slots
which are necessary for proper bearing lubrica-
tion.
Fig. 261 Checking Output Shaft End Play
1 - SPECIAL TOOL L-4432 AND C-4658
2 - SCREW (2)
3 - OUTPUT SHAFT GEAR
4 - STEEL BALL (GREASE IN PLACE)
5 - SPECIAL TOOL L-4438
6 - DIAL INDICATOR
Fig. 262 Checking Bearing Turning Torque
1 - OUTPUT SHAFT GEAR
2 - TORQUE WRENCH
Fig. 263 Turn Stirrup Clockwise Against Flats of
Retaining Nut
1 - TURN STIRRUP CLOCKWISE
2 - STRAP
Fig. 264 Tighten Strap Retaining Nuts
1 - STRAP
2 - OUTPUT GEAR
3 - STIRRUP
21 - 132 AUTOMATIC - 31THRS
TRANSFER SYSTEM - OUTPUT SHAFT/GEAR/BEARING (Continued)
Page 3105 of 4284

(14) Using Tool L-4434 and adapter C-4658 (Fig.
293), torque transfer shaft gear retaining nut to 271
N´m (200 ft. lbs.).
(15) Measure transfer shaft end play. Set up Tool
L-4432 and C-4658 as shown in (Fig. 294). Measure
end play with dial indicator.
(16) Position stirrup and strap on transfer gear.
(17) Install bolts but do not tighten.
(18) Rotate stirrup clockwise until it contacts
transfer gear retaining nut flat.(19) Torque stirrup and strap-to-transfer gear bolts
to 23 N´m (200 in. lbs.).
(20) Bend tabs of strap up against ªflatsº of retain-
ing bolts.
(21) Install a bead of Moparž Silicone Rubber
Adhesive Sealant to transfer gear cover (Fig. 295).
Immediately install to transaxle case.
(22) Install and torque transfer gear cover-to-case
bolts (Fig. 296) to 19 N´m (165 in. lbs.) .
Fig. 293 Tighten Transfer Shaft Gear Retaining Nut
to 271 N´m (200 ft. lbs.)
1 - TRANSFER SHAFT GEAR
2 - TORQUE WRENCH
3 - SPECIAL TOOL L-4434 AND ADAPTER C-4658
Fig. 294 Measuring Transfer Shaft End-Play
1 - SPECIAL TOOL L-4432 AND C-4658
2 - TRANSFER SHAFT GEAR
3 - STEEL BALL (USE GREASE TO HOLD IN PLACE)
4 - DIAL INDICATOR
5 - SCREW (2)
Fig. 295 Install Rear Cover
1 - OUTPUT SHAFT GEAR
2 - USE MOPAR SILICONE RUBBER ADHESIVE SEALER
3 - REAR COVER
4 - TRANSFER SHAFT GEAR
Fig. 296 Rear Cover Bolts
1 - REAR COVER
2 - REAR COVER BOLTS (10)
RSAUTOMATIC - 31TH21 - 141
TRANSFER SYSTEM - TRANSFER SHAFT/GEAR/BEARING (Continued)