2001 CHRYSLER VOYAGER lock
[x] Cancel search: lockPage 2887 of 4284

PLASTIC RETAINER RING TYPE FITTING
This type of fitting can be identified by the use of a
full-round plastic retainer ring (Fig. 25) usually black
in color.
CAUTION: The interior components (O-rings, spac-
ers, retainers) of this type of quick-connect fitting
are not serviced separately. Do not attempt to repair
damaged fittings or fuel lines/tubes. If repair is nec-
essary, replace the complete fuel tube assembly.
WARNING: THE FUEL SYSTEM IS UNDER A CON-
STANT PRESSURE (EVEN WITH THE ENGINE OFF).
BEFORE SERVICING ANY FUEL SYSTEM HOSES,
FITTINGS OR LINES, THE FUEL SYSTEM PRES-
SURE MUST BE RELEASED. REFER TO THE FUEL
SYSTEM PRESSURE RELEASE PROCEDURE IN
THIS GROUP.DISCONNECTION/CONNECTION
(1) Perform fuel pressure release procedure. Refer
to Fuel Pressure Release Procedure in this section.
(2) Disconnect negative battery cable from battery
or auxiliary jumper terminal.
(3) Clean fitting of any foreign material before dis-
assembly.
(4) To release fuel system component from quick-
connect fitting, firmly push fitting towards compo-
nent being serviced while firmly pushing plastic
retainer ring into fitting (Fig. 25). With plastic ring
depressed, pull fitting from component.The plastic
retainer ring must be pressed squarely into fit-
ting body. If this retainer is cocked during
removal, it may be difficult to disconnect fit-
ting. Use an open-end wrench on shoulder of
plastic retainer ring to aid in disconnection.
(5) After disconnection, plastic retainer ring will
remain with quick-connect fitting connector body.
(6) Inspect fitting connector body, plastic retainer
ring and fuel system component for damage. Replace
as necessary.
(7) Prior to connecting quick-connect fitting to
component being serviced, check condition of fitting
and component. Clean parts with a lint-free cloth.
Lubricate with clean engine oil.
(8) Insert quick-connect fitting into component
being serviced until a click is felt.
(9) Verify a locked condition by firmly pulling on
fuel tube and fitting (15-30 lbs.).
(10) Connect negative battery cable to battery or
auxiliary jumper terminal.
(11) Use the DRB IIItscan tool ASD Fuel System
Test to pressurize the fuel system. Check for leaks.
ROLLOVER VALVE
DESCRIPTION
All vehicles have rollover valve(s) on top of the fuel
tank.
OPERATION
The valves prevent fuel flow through the fuel tank
vent valve hoses should the vehicle rollover.
The rollover valves on the fuel tank are not ser-
viceable.
Fig. 25 Plastic Retainer Ring Type Fitting
1 - FUEL TUBE
2 - QUICK CONNECT FITTING
3 - PUSH
4 - PLASTIC RETAINER
5 - PUSH
6 - PUSH
7 - PUSH
8 - PUSH
RSFUEL DELIVERY14-15
QUICK CONNECT FITTING (Continued)
Page 2896 of 4284

(3) Disconnect the speed control vacuum harness
from servo.
(4) Remove the speed control servo and bracket
and reposition. Disconnect the electrical connector.
(5) Disconnect the electrical connector from crank-
shaft sensor.
(6) Remove the mounting bolt.
(7) Remove sensor.
INSTALLATION - 2.4L
(1) Install the crankshaft sensor.
(2) Install crankshaft sensor bolt and tighten.
(3) Connect the electrical connector (Fig. 5).
(4) Lower vehicle.
(5) Connect the negative battery cable.
INSTALLATION - 3.3/3.8L
(1) Install the crankshaft sensor.
(2) Install the mounting bolt and tighten.
(3) Connect the electrical connector to crankshaft
sensor. Make sure locking tab is in position.
(4) Connect the electrical connector to the speed
control servo.
(5) Install the speed control servo and bracket.
(6) Connect the speed control vacuum harness to
servo.
(7) Install the battery tray, refer to the Battery
section for more information.
(8) Install battery, refer to the Battery section for
more information.
ENGINE SPEED SENSOR
DESCRIPTION
The PCM receives a signal from the TCM and the
transaxle output speed sensor over the bus communi-
cation line.
OPERATION
The Transmission Control Module (TCM) supplies
the road speed and distance traveled inputs to the
PCM. From these inputs and the throttle position
sensor input, the PCM determines when a decelera-
tion condition occurs.
Fig. 3 Crankshaft Position Sensor
1 - CRANKSHAFT POSITION SENSOR
Fig. 4 Timing Slots
1 - TORQUE CONVERTER DRIVE PLATE
2 - SLOTS
Fig. 5 CRANKSHAFT SENSOR 2.4L
1 - CRANKSHAFT POSITION SENSOR
14 - 24 FUEL INJECTIONRS
CRANKSHAFT POSITION SENSOR (Continued)
Page 2898 of 4284

(1) Disconnect injector wiring connector from injec-
tor.
(2) Position fuel rail assembly so that the fuel
injectors are easily accessible (Fig. 9).
(3) Rotate injector and pull injector out of fuel rail.
The clip will stay on the injector.
(4) Check injector O-ring for damage. If O-ring is
damaged, it must be replaced. If injector is reused, a
protective cap must be installed on the injector tip to
prevent damage. Replace the injector clip if it is dam-
aged.
(5) Repeat for remaining injectors.
REMOVAL - 3.3/3.8L
(1) Disconnect the negative battery cable.
(2) Remove the Intake Manifold, (Refer to 9 -
ENGINE/MANIFOLDS/INTAKE MANIFOLD -
REMOVAL)
(3) Disconnect injector wiring connector from injec-
tor.
(4) Position fuel rail assembly so that the fuel
injectors are easily accessible (Fig. 9).
(5) Rotate injector and pull injector out of fuel rail.
The clip will stay on the injector.
(6)
Check injector O-ring for damage. If O-ring is
damaged, it must be replaced. If injector is reused, a
protective cap must be installed on the injector tip to
prevent damage. Replace the injector clip if it is dam-
aged.
(7) Repeat for remaining injectors.
INSTALLATION - 2.4L
The fuel rail must be removed first. Refer to Fuel
Injector Rail Removal in this section.
(1) Before installing an injector the rubber O-ring
must be lubricated with a drop of clean engine oil to
aid in installation.
(2) Install injector clip by sliding open end into the
top slot of the injector. The edge of the receiver cup
will slide into the side slots of clip.
(3) Install injector top end into fuel rail receiver
cap. Be careful not to damage O-ring during installa-
tion (Fig. 10).
(4) Repeat steps for remaining injectors.
(5) Connect fuel injector wiring.
INSTALLATION - 3.3/3.8L
(1) Before installing an injector the rubber O-ring
must be lubricated with a drop of clean engine oil to
aid in installation.
(2) Install injector clip by sliding open end into the
top slot of the injector. The edge of the receiver cup
will slide into the side slots of clip (Fig. 9).
(3) Install injector top end into fuel rail receiver
cap. Be careful not to damage O-ring during installa-
tion (Fig. 9).
(4) Repeat steps for remaining injectors.
(5) Install fuel rail, refer to Fuel Rail in the Fuel
Delivery section.
(6) Connect fuel injector wiring.
(7) Install the Intake Manifold, (Refer to 9 -
ENGINE/MANIFOLDS/INTAKE MANIFOLD -
INSTALLATION)
(8) Connect the negative battery cable.
Fig. 9 FUEL INJECTOR AND RAIL TYPICAL
1 - FUEL RAIL ASSEMBLY
2 - FUEL INJECTOR
3 - FUEL RAIL RECEIVER
Fig. 10 SERVICING FUEL INJECTOR TYPICAL
1 - FUEL INJECTOR
2 - LOCKING SLOT
3 - FUEL RAIL RECEIVER CUP
14 - 26 FUEL INJECTIONRS
FUEL INJECTOR (Continued)
Page 2909 of 4284

FUEL SYSTEM
TABLE OF CONTENTS
page page
FUEL SYSTEM 2.5L TURBO DIESEL
DESCRIPTION............................1
WARNING...............................1
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING..................1
AIR IN FUEL SYSTEM....................1
FUEL SUPPLY RESTRICTIONS.............1STANDARD PROCEDURE...................2
WATER DRAINING AT FUEL FILTER.........2
CLEANING FUEL SYSTEM PARTS...........2
SPECIFICATIONS.........................2
FUEL DELIVERY..........................3
FUEL INJECTION........................10
FUEL SYSTEM 2.5L TURBO
DIESEL
DESCRIPTION - DIESEL FUEL DELIVERY
SYSTEM
The fuel system on the 2.5L Common Rail Diesel
Engine uses a fuel injection pump and an Electronic
Control Module (ECM).
The fuel delivery system consists of the:
²Accelerator pedal
²Air cleaner housing/element
²Fuel filter/water separator
²Fuel heater
²Fuel heater relay
²Fuel transfer (lift) pump
²Fuel injection pump
²Fuel injectors
²Fuel tank
²Fuel tank filler/vent tube assembly
²Fuel tank filler tube cap
²Fuel tank module containing the rollover valve
and a fuel gauge sending unit (fuel level sensor).
²Fuel tubes/lines/hoses
²High-pressure fuel injector lines
²Low-pressure fuel supply lines
²Low-pressure fuel return line
²Overflow valve
²Quick-connect fittings
²Water draining
WARNING - HIGH FUEL SYSTEM PRESSURE
WARNING: THE INJECTION PUMP SUPPLIES HIGH-
PRESSURE FUEL TO EACH INDIVIDUAL INJECTOR
THROUGH HIGH-PRESSURE LINES. FUEL UNDER
THIS AMOUNT OF PRESSURE CAN PENETRATE
SKIN AND CAUSE PERSONAL INJURY. WEAR
SAFETY GOGGLES AND ADEQUATE PROTECTIVE
CLOTHING. AVOID CONTACT WITH FUEL SPRAY
WHEN BLEEDING HIGH-PRESSURE FUEL LINES.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - AIR IN FUEL
SYSTEM
Air will enter the fuel system whenever fuel supply
lines, separator filters, injection pump, high-pressure
lines or injectors are removed or disconnected. Air
trapped in the fuel system can result in hard start-
ing, a rough running engine, engine misfire, low
power, excessive smoke and fuel knock. After service
is performed, air must be bled from the system
before starting the engine.
Inspect the fuel system from the fuel transfer
pump to the injectors for loose connections. Leaking
fuel is an indicator of loose connections or defective
seals. Air can also enter the fuel system between the
fuel tank and the transfer pump. Inspect the fuel
tank and fuel lines for damage that might allow air
into the system.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - FUEL SUPPLY
RESTRICTIONS
LOW-PRESSURE LINES
Fuel supply line restrictions or a defective fuel
transfer pump can cause starting problems and pre-
vent engine from accelerating. The starting problems
include; low power and/or white fog like exhaust.
Test all fuel supply lines for restrictions or block-
age. Flush or replace as necessary. Bleed fuel system
of air once a fuel supply line has been replaced. Refer
to Air Bleed Procedure for procedures.
To test for fuel line restrictions, a vacuum restric-
tion test may be performed. Refer to Fuel Transfer
Pump Pressure Test.
HIGH-PRESSURE LINES
Restricted (kinked or bent) high-pressure lines can
cause starting problems, poor engine performance,
engine mis-fire and white smoke from exhaust.
Examine all high-pressure lines for any damage.
Each radius on each high-pressure line must be
smooth and free of any bends or kinks.
RGFUEL SYSTEM14a-1
Page 2922 of 4284

(3) Disconnect intake air temperature electrical
connector.
(4) Remove intake air temperature sensor retain-
ing screws and sensor (Fig. 6).
INSTALLATION
(1) Install intake air temperature sensor and
retaining bolts (Fig. 6). Torque to 5.4 N´m.
(2) Connect intake air temperature sensor.
(3) Install engine cover and retaining bolts (Refer
to 9 - ENGINE COVER - INSTALLATION).
CRANKSHAFT POSITION
SENSOR
DESCRIPTION
The crankshaft position sensor is mounted in the
right rear of the engine block below the turbocharger
(Fig. 7). This sensor is used to detect engine speed.
OPERATION
The crankshaft position sensor is a magnetic
pickup type sensor that generates an ac signal. The
sensor contains a permanent magent and a coil of
wire. The sensor generates an ac signal each time a
notch in the reluctor wheel on the crankshaft passesacross the permanent magnet. The ECM calculates
engine speed based on the frequency of the ac signal.
The ECM supplies the sensor ground.
MASS AIR FLOW (MAF)
SENSOR
DESCRIPTION
The Mass Air Flow (MAF) Sensor is mounted
inline in the air intake between the air filter and the
turbocharger (Fig. 8).
Fig. 6 BOOST PRESSURE SENSOR/INTAKE AIR
TEMPERATURE SENSOR LOCATION
1 - FUEL RAIL
2 - FUEL PRESSURE SENSOR
3 - INTAKE AIR TEMPERATURE/BOOST PRESSURE SENSOR
4 - CYLINDER HEAD COVER/INTAKE MANIFOLD
Fig. 7 CRANKSHAFT POSITION SENSOR
1 - CRANKSHAFT POSITION SENSOR
2 - CRANKSHAFT POSITION SENSOR ELECTRICAL
CONNECTOR
Fig. 8 MASS AIR FLOW (MAF) SENSOR
14a - 14 FUEL INJECTIONRG
INTAKE AIR TEMPERATURE SENSOR (Continued)
Page 2928 of 4284
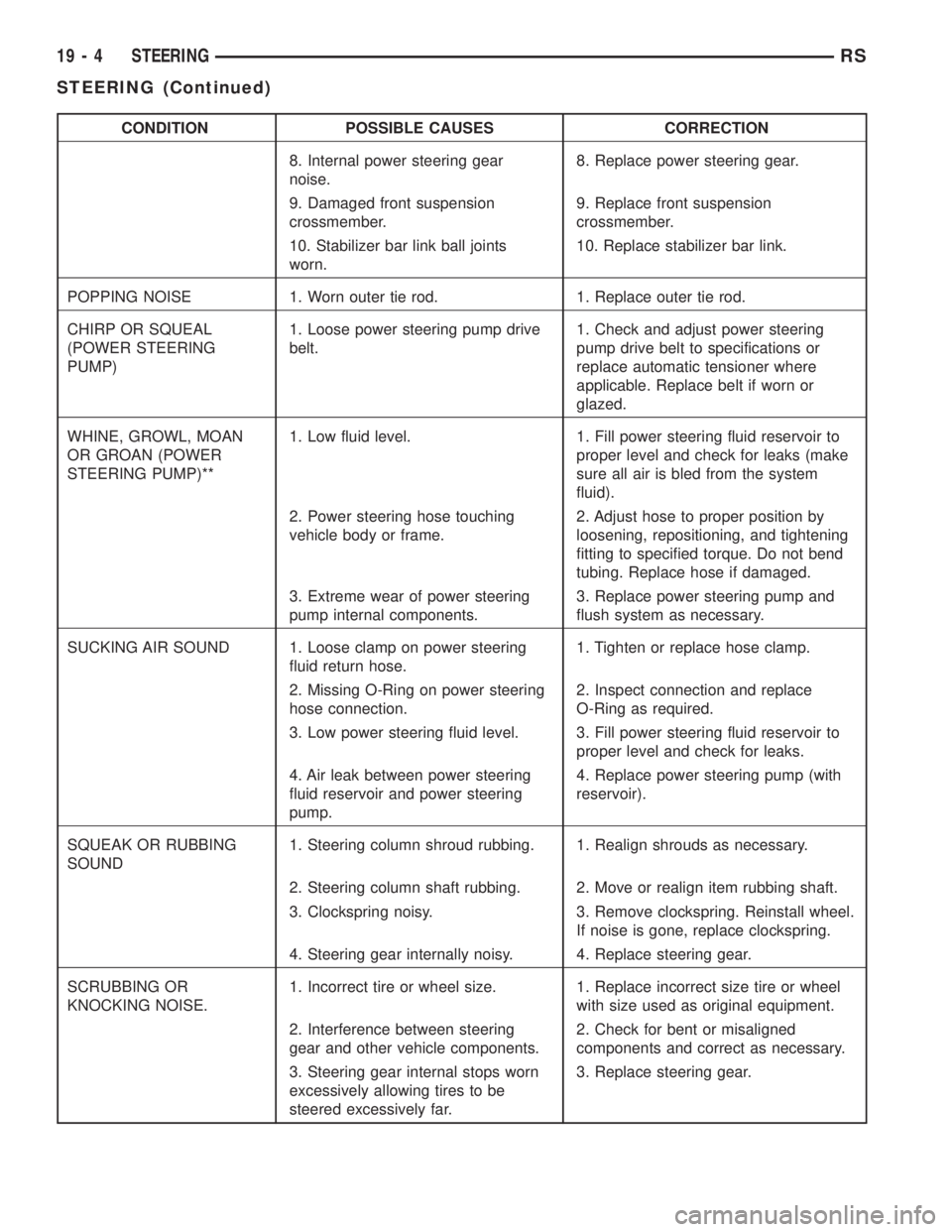
CONDITION POSSIBLE CAUSES CORRECTION
8. Internal power steering gear
noise.8. Replace power steering gear.
9. Damaged front suspension
crossmember.9. Replace front suspension
crossmember.
10. Stabilizer bar link ball joints
worn.10. Replace stabilizer bar link.
POPPING NOISE 1. Worn outer tie rod. 1. Replace outer tie rod.
CHIRP OR SQUEAL
(POWER STEERING
PUMP)1. Loose power steering pump drive
belt.1. Check and adjust power steering
pump drive belt to specifications or
replace automatic tensioner where
applicable. Replace belt if worn or
glazed.
WHINE, GROWL, MOAN
OR GROAN (POWER
STEERING PUMP)**1. Low fluid level. 1. Fill power steering fluid reservoir to
proper level and check for leaks (make
sure all air is bled from the system
fluid).
2. Power steering hose touching
vehicle body or frame.2. Adjust hose to proper position by
loosening, repositioning, and tightening
fitting to specified torque. Do not bend
tubing. Replace hose if damaged.
3. Extreme wear of power steering
pump internal components.3. Replace power steering pump and
flush system as necessary.
SUCKING AIR SOUND 1. Loose clamp on power steering
fluid return hose.1. Tighten or replace hose clamp.
2. Missing O-Ring on power steering
hose connection.2. Inspect connection and replace
O-Ring as required.
3. Low power steering fluid level. 3. Fill power steering fluid reservoir to
proper level and check for leaks.
4. Air leak between power steering
fluid reservoir and power steering
pump.4. Replace power steering pump (with
reservoir).
SQUEAK OR RUBBING
SOUND1. Steering column shroud rubbing. 1. Realign shrouds as necessary.
2. Steering column shaft rubbing. 2. Move or realign item rubbing shaft.
3. Clockspring noisy. 3. Remove clockspring. Reinstall wheel.
If noise is gone, replace clockspring.
4. Steering gear internally noisy. 4. Replace steering gear.
SCRUBBING OR
KNOCKING NOISE.1. Incorrect tire or wheel size. 1. Replace incorrect size tire or wheel
with size used as original equipment.
2. Interference between steering
gear and other vehicle components.2. Check for bent or misaligned
components and correct as necessary.
3. Steering gear internal stops worn
excessively allowing tires to be
steered excessively far.3. Replace steering gear.
19 - 4 STEERINGRS
STEERING (Continued)
Page 2932 of 4284
NOTE: ** To evaluate this condition, it may be nec-
essary to disconnect the coupling at the base of the
steering column. Turn the steering wheel and feel or
listen for internal rubbing in steering column. To
avoid damaging the column clockspring, note the
following. Before disconnecting coupling, place
tires in the straight-ahead position and center steer-
ing wheel. Once disconnected, DO NOT rotatesteering wheel more than one revolution in either
direction and place steering wheel in original loca-
tion before reconnecting coupling. If this position is
lost, the steering column clockspring must be
recentered following the procedure found within the
procedure for steering column installation in the
steering column section.
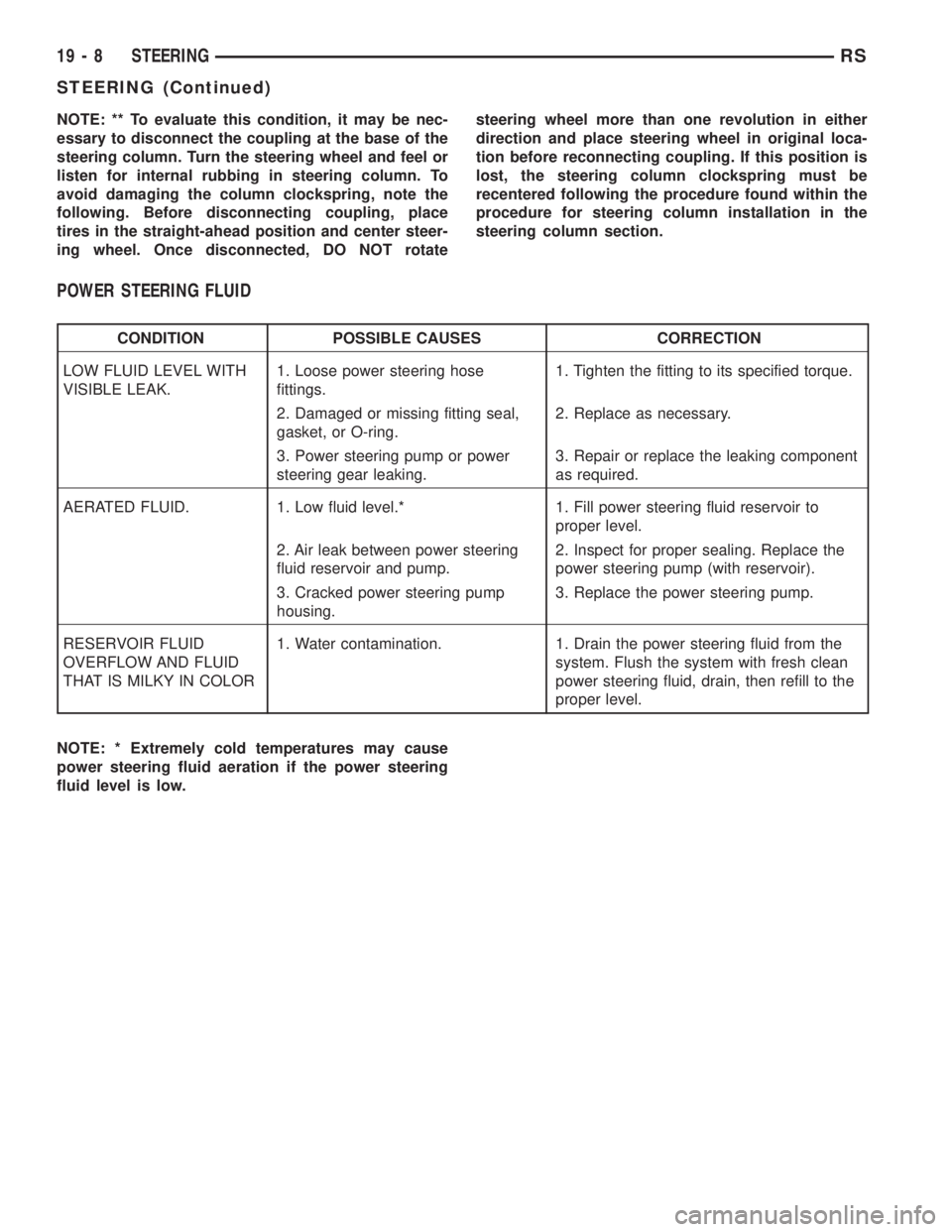
POWER STEERING FLUID
CONDITION POSSIBLE CAUSES CORRECTION
LOW FLUID LEVEL WITH
VISIBLE LEAK.1. Loose power steering hose
fittings.1. Tighten the fitting to its specified torque.
2. Damaged or missing fitting seal,
gasket, or O-ring.2. Replace as necessary.
3. Power steering pump or power
steering gear leaking.3. Repair or replace the leaking component
as required.
AERATED FLUID. 1. Low fluid level.* 1. Fill power steering fluid reservoir to
proper level.
2. Air leak between power steering
fluid reservoir and pump.2. Inspect for proper sealing. Replace the
power steering pump (with reservoir).
3. Cracked power steering pump
housing.3. Replace the power steering pump.
RESERVOIR FLUID
OVERFLOW AND FLUID
THAT IS MILKY IN COLOR1. Water contamination. 1. Drain the power steering fluid from the
system. Flush the system with fresh clean
power steering fluid, drain, then refill to the
proper level.
NOTE: * Extremely cold temperatures may cause
power steering fluid aeration if the power steering
fluid level is low.
19 - 8 STEERINGRS
STEERING (Continued)
Page 2934 of 4284

COLUMN
TABLE OF CONTENTS
page page
COLUMN
DESCRIPTION...........................10
WARNING..............................10
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING.................12
STEERING COLUMN....................12
REMOVAL..............................12
INSTALLATION...........................13
SPECIFICATIONS........................14
KEY/LOCK CYLINDER
DESCRIPTION...........................14OPERATION.............................14
REMOVAL..............................14
INSTALLATION...........................14
GEAR SHIFT LEVER
REMOVAL..............................15
INSTALLATION...........................15
SHROUD
REMOVAL..............................16
INSTALLATION...........................16
COLUMN
DESCRIPTION - STEERING COLUMN
The steering column has been designed to be ser-
viced as a complete assembly (Fig. 1), except for the
components listed here. They are the key cylinder,
ignition switch, lock cylinder housing, multi-function
switch, clockspring, halo lamp, speed control
switches, driver airbag, trim shrouds, steering wheel
and steering column intermediate shaft. These
replaceable components of the steering column can be
serviced without requiring removal of the steering
column from the vehicle.
SERVICE WARNINGS AND CAUTIONS
(Refer to 8 - ELECTRICAL/RESTRAINTS - WARN-
ING)
WARNING: BEFORE BEGINNING ANY SERVICE
PROCEDURES THAT INVOLVES REMOVING THE
AIR BAG. REMOVE AND ISOLATE THE NEGATIVE
(-) BATTERY CABLE (GROUND) FROM THE VEHI-
CLE BATTERY. THIS IS THE ONLY SURE WAY TO
DISABLE THE AIR BAG SYSTEM. FAILURE TO DO
THIS COULD RESULT IN ACCIDENTAL AIR BAG
DEPLOYMENT AND POSSIBLE PERSONAL INJURY.
WARNING: THE AIR BAG SYSTEM IS A SENSITIVE,
COMPLEX ELECTRO-MECHANICAL UNIT. BEFORE
ATTEMPTING TO DIAGNOSE, REMOVE OR INSTALL
THE AIR BAG SYSTEM COMPONENTS YOU MUST
FIRST DISCONNECT AND ISOLATE THE BATTERY
NEGATIVE (GROUND) CABLE. THEN WAIT TWO
MINUTES FOR THE SYSTEM CAPACITOR TO DIS-
CHARGE. FAILURE TO DO SO COULD RESULT INACCIDENTAL DEPLOYMENT OF THE AIR BAG AND
POSSIBLE PERSONAL INJURY. THE FASTENERS,
SCREWS, AND BOLTS, ORIGINALLY USED FOR
THE AIR BAG COMPONENTS, HAVE SPECIAL
COATINGS AND ARE SPECIFICALLY DESIGNED
FOR THE AIR BAG SYSTEM. THEY MUST NEVER
BE REPLACED WITH ANY SUBSTITUTES. ANYTIME
A NEW FASTENER IS NEEDED, REPLACE WITH
THE CORRECT FASTENERS PROVIDED IN THE
SERVICE PACKAGE OR FASTENERS LISTED IN
THE PARTS BOOKS.Fig. 1 STEERING COLUMN
1 - STEERING COLUMN
2 - B.T.S.I.
3 - TURN SIGNAL LEVER
4 - KEY CYLINDER
5 - SHIFT LEVER
6 - MOUNTING HOLES
7 - COUPLING
19 - 10 COLUMNRS