2001 CHRYSLER VOYAGER fuel filter
[x] Cancel search: fuel filterPage 2756 of 4284
OIL
STANDARD PROCEDURE - ENGINE OIL AND
FILTER CHANGE
Change engine oil at mileage and time intervals
described in the Maintenance Schedule. (Refer to
LUBRICATION & MAINTENANCE/MAINTE-
NANCE SCHEDULES - DESCRIPTION)
WARNING: NEW OR USED ENGINE OIL CAN BE
IRRITATING TO THE SKIN. AVOID PROLONGED OR
REPEATED SKIN CONTACT WITH ENGINE OIL.
CONTAMINANTS IN USED ENGINE OIL, CAUSED BY
INTERNAL COMBUSTION, CAN BE HAZARDOUS TO
YOUR HEALTH. THOROUGHLY WASH EXPOSED
SKIN WITH SOAP AND WATER. DO NOT WASH
SKIN WITH GASOLINE, DIESEL FUEL, THINNER, OR
SOLVENTS, HEALTH PROBLEMS CAN RESULT. DO
NOT POLLUTE, DISPOSE OF USED ENGINE OIL
PROPERLY. CONTACT YOUR DEALER OR GOVERN-
MENT AGENCY FOR LOCATION OF COLLECTION
CENTER IN YOUR AREA.
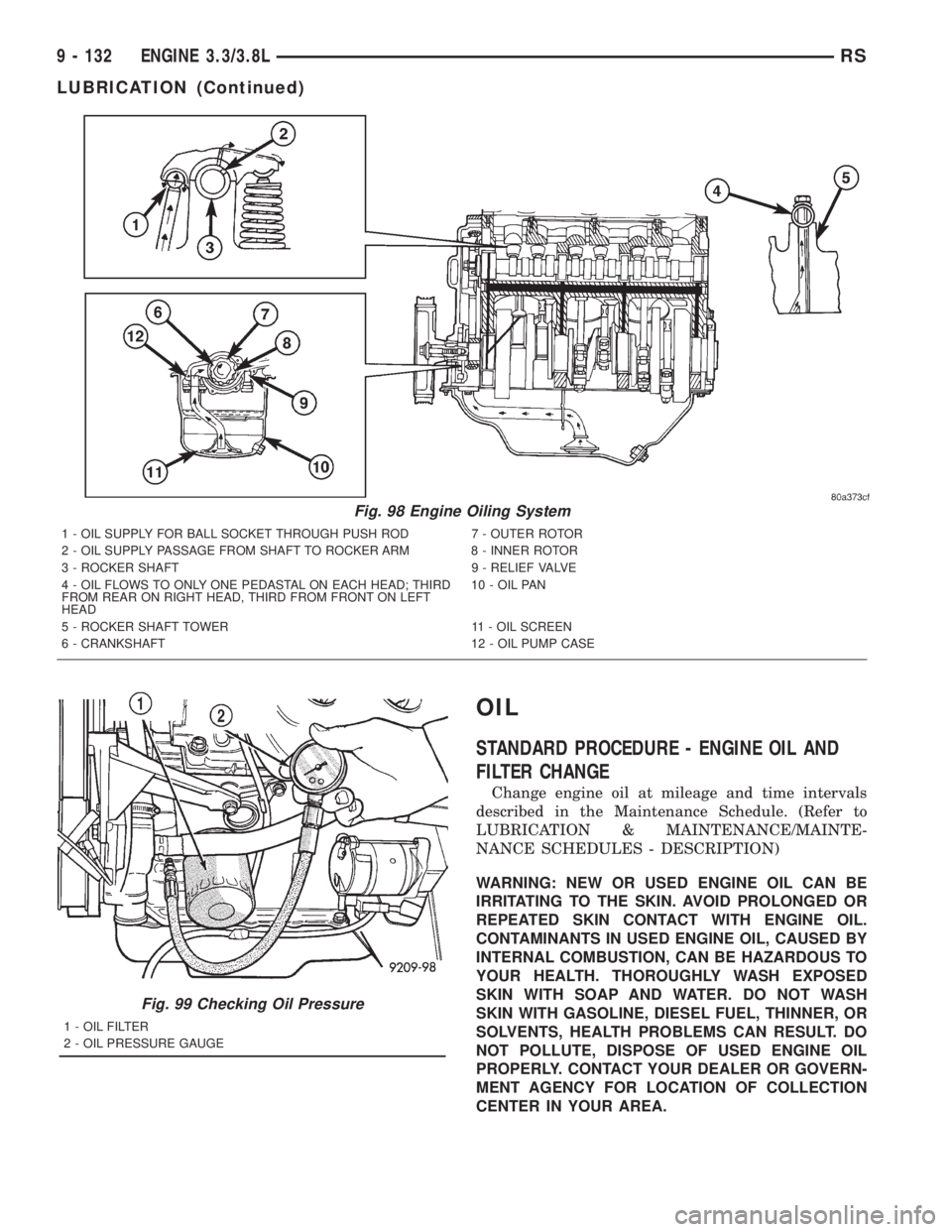
Fig. 98 Engine Oiling System
1 - OIL SUPPLY FOR BALL SOCKET THROUGH PUSH ROD 7 - OUTER ROTOR
2 - OIL SUPPLY PASSAGE FROM SHAFT TO ROCKER ARM 8 - INNER ROTOR
3 - ROCKER SHAFT 9 - RELIEF VALVE
4 - OIL FLOWS TO ONLY ONE PEDASTAL ON EACH HEAD; THIRD
FROM REAR ON RIGHT HEAD, THIRD FROM FRONT ON LEFT
HEAD10 - OIL PAN
5 - ROCKER SHAFT TOWER 11 - OIL SCREEN
6 - CRANKSHAFT 12 - OIL PUMP CASE
Fig. 99 Checking Oil Pressure
1 - OIL FILTER
2 - OIL PRESSURE GAUGE
9 - 132 ENGINE 3.3/3.8LRS
LUBRICATION (Continued)
Page 2784 of 4284

OIL FILTER
DESCRIPTION...........................52
REMOVAL..............................53
INSTALLATION...........................53
OIL JET
DESCRIPTION...........................53
REMOVAL..............................53
INSTALLATION...........................53
INTAKE MANIFOLD
DESCRIPTION...........................54
REMOVAL..............................54
INSTALLATION...........................54
VALVE TIMING
STANDARD PROCEDURE..................54
LOCKING ENGINE 90É AFTER TDC.........54
BALANCE SHAFT
DESCRIPTION...........................55OPERATION.............................56
REMOVAL..............................56
INSTALLATION...........................57
TIMING BELT / CHAIN COVER(S)
REMOVAL..............................57
INSTALLATION...........................58
TIMING BELT IDLER PULLEY
REMOVAL..............................59
INSTALLATION...........................60
TIMING BELT/CHAIN TENSIONER
REMOVAL..............................60
INSTALLATION...........................60
ADJUSTMENTS..........................61
TIMING BELT/CHAIN AND SPROCKETS
REMOVAL..............................62
INSTALLATION...........................63
ENGINE 2.5L TURBO DIESEL
DESCRIPTION - 2.5L COMMON RAIL DIESEL
ENGINE
This 2.5 Liter (2500cc) four-cylinder ªcommon railº
direct injection engine is an in-line overhead valve
diesel engine. This engine utilizes a cast iron cylin-
der block and an aluminum cylinder head. The
engine is turbocharged and intercooled. The engine
also has four valves per cylinder and dual overhead
camshafts (Fig. 1).
DESCRIPTION SPECIFICATION
Displacement 2.5L (2499 cc)
Bore 92.00
Stroke 94.00
Compression Ratio 17.5:1
Vacuum at Idle 685.8 mm/Hg (27.0
In/Hg)
Belt Tension Automatic Belt Tensioner
Thermostat Opening 80ÉC 2ÉC
Generator Rating Denso 12V-95A
DESCRIPTION SPECIFICATION
Cooling System Capacity 13.8 Liters W/O Auxiliary
Heater
16.6 Liters With Auxiliary
Heater
Engine Oil Capacity 5.22L W/Filter Change
Timing System Belt Driven Camshafts In
Cylinder Head Cover
Air Intake Dry Filter
Fuel Feed Vane Pump Incorporated
In Injection Pump
Fuel System Direct Fuel Injection
Combustion Cycle 4 Stroke
Cooling System Water Cooling
Injection Pump Rotary Pump and
Electronically Managed
Lubrication Pressure Lubricated By
Rotary Pump
Engine Rotation Clockwise Viewed From
Front Cover
9a - 2 ENGINE 2.5L TURBO DIESELRG
Page 2873 of 4284

FUEL SYSTEM
TABLE OF CONTENTS
page page
FUEL DELIVERY..........................1FUEL INJECTION........................16
FUEL DELIVERY
TABLE OF CONTENTS
page page
FUEL DELIVERY
DESCRIPTION............................1
OPERATION.............................2
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING..................2
FUEL DELIVERY SYSTEM.................2
STANDARD PROCEDURE...................2
FUEL PRESS RELEASE...................2
STANDARD PROCEDURE.................2
SPECIFICATIONS.........................2
SPECIAL TOOLS..........................3
FUEL FILTER
REMOVAL...............................4
INSTALLATION............................4
FUEL LEVEL SENDING UNIT / SENSOR
DESCRIPTION............................4
OPERATION.............................4
REMOVAL...............................4
INSTALLATION............................5
FUEL LINES
DESCRIPTION............................6
STANDARD PROCEDURE...................6
HOSES & CLAMP........................6
FUEL PRESSURE REGULATOR
OPERATION.............................6
REMOVAL...............................7
INSTALLATION............................7
FUEL PUMP
DESCRIPTION............................7OPERATION.............................7
FUEL PUMP MODULE
DESCRIPTION............................7
OPERATION.............................7
REMOVAL...............................8
INSTALLATION............................8
FUEL RAIL
REMOVAL...............................9
INSTALLATION............................9
FUEL TANK
DESCRIPTION...........................10
OPERATION.............................10
REMOVAL..............................10
INSTALLATION...........................11
FUEL TANK FILLER TUBE
REMOVAL..............................12
INSTALLATION...........................12
INLET FILTER
REMOVAL..............................13
INSTALLATION...........................13
QUICK CONNECT FITTING
STANDARD PROCEDURE..................13
QUICK CONNECT FITTING...............13
ROLLOVER VALVE
DESCRIPTION...........................15
OPERATION.............................15
FUEL DELIVERY
DESCRIPTION
The front wheel drive car uses a plastic fuel tank
located rear center of the vehicle.
The Fuel Delivery System consists of: the following
items:²Electric fuel pump module
²Fuel filter
²Tubes/lines/hoses
²Fuel injectors
The in-tank fuel pump module contains the fuel
pump. The pump is serviced as part of the fuel pump
module. Refer to Fuel Pump Module.
RSFUEL SYSTEM14-1
Page 2874 of 4284

The fuel filter is replaceable, it is mounted on the
outside and on top of the fuel tank. Refer to the
Maintenance Schedules in the Introduction section of
this manual for recommended fuel filter replacement
intervals.
FFV REPLACEMENT PARTS
Many components in a Flexible Fuel Vehicle (FFV)
are designed to be compatible with ethanol. Always
be sure that the vehicle is serviced with correct etha-
nol compatible parts.
CAUTION: Replacing fuel system components with
non-ethanol compatible components can damage
your vehicle and may void the warranty.
OPERATION
The fuel system is provided fuel pressure by an in-
tank pump module. The PCM controls the operation
of the fuel system by providing battery voltage to the
fuel pump through the fuel pump relay. The PCM
requires only three inputs and a good ground to oper-
ate the fuel pump relay. The three inputs are:
²Ignition voltage
²Crankshaft Position (CKP) sensor
²Camshaft Position (CMP) sensor
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - FUEL DELIVERY
SYSTEM
(Refer to Appropriate Diagnositic Information)
STANDARD PROCEDURE - FUEL SYSTEM
PRESSURE RELEASE PROCEDURE
(1) Remove Fuel Pump relay from Power Distribu-
tion Center (PDC). For location of relay, refer to label
on underside of PDC cover.(2) Start and run engine until it stalls.
(3) Attempt restarting engine until it will no
longer run.
(4) Turn ignition key to OFF position.
(5) Place a rag or towel below fuel line quick-con-
nect fitting at fuel rail.
(6) Return fuel pump relay to PDC.
(7) One or more Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTC's)
may have been stored in PCM memory due to fuel
pump relay removal. The DRB IIItscan tool must be
used to erase a DTC.
STANDARD PROCEDURE - DRAINING FUEL
TANK
(1) Release fuel system pressure, refer to the Fuel
System Release Procedure in this section.
(2) Insert a 1/4 inch siphon (max. O. D. 5/16) hose
from a portable fuel siphoning tank through the fuel
filler neck opening into the fuel tank. Hose most
have a 30 degree angle cut on the end to bypass the
check valve in the end of the filler neck. Refer to the
siphoning tank's Manufacturing Instructions.
(3) Drain fuel from fuel tank into siphoning tank.
SPECIFICATIONS
FUEL SYSTEM PRESSURE
400 kpa634 kpa (58 psi65 psi)
TORQUE
DESCRIPTION N´m Ft. Lbs. In. Lbs.
Fuel Rail 2.4L 22 200
Fuel Rail 3.3/3.8L 11.8 105
Fuel Tank Strap 54 40
Fuel Tank T Strap 28.2 250
Fuel Filter Bolt 4.5 40
14 - 2 FUEL DELIVERYRS
FUEL DELIVERY (Continued)
Page 2876 of 4284

FUEL FILTER
REMOVAL
(1) Release fuel pressure, refer to the Fuel release
procedure in this section.
(2) Disconnect the negative battery cable.
(3) Raise vehicle and support.
(4) Support the fuel tank with a transmission jack.
(5) Remove fuel line from the front of the tank.
(6) Remove ground strap
(7) Remove the inboard side of the fuel tank straps
and front T strap fastner.
(8) Lower the tank about 6 inches (Fig. 1).
(9) Remove fuel lines from the fuel pump module.
(10) Remove fuel filter from tank.
INSTALLATION
(1) Install fuel filter to tank. Tighten bolt to 4.5
N´m (40 in. lbs.)
(2) Install fuel lines to the fuel pump module (Fig.
1).
(3) Raise tank into position.
(4) Install the fuel tank straps.Tighten bolt for
main straps to 54 N´m (40 ft. lbs.) and the T strap
bolt to 28.2 N´m (250 in. lbs.)
(5) Install the ground strap
(6) Connect the fuel line at the front of the tank.
(7) Lower vehicle.
(8) Connect the negative battery cable.
(9) Pressurize the fuel system with the DRBIIIt
and check for leaks.
FUEL LEVEL SENDING UNIT /
SENSOR
DESCRIPTION
The fuel gauge level sending unit is attached to the
side of fuel pump module. The level sensor is a vari-
able resistor.
OPERATION
Its resistance changes with the amount of fuel in
the tank. The float arm attached to the sensor moves
as the fuel level changes.
The fuel level input is used as an input for OBD II.
If the fuel level is below 15% of total tank capacity
several monitors are disabled. There are diagnostics
for the level circuit open and shorted.
REMOVAL
Remove fuel pump module. Refer to Fuel Pump
Module in this section.
(1) Depress retaining tab and remove the fuel
pump/level sensor connector from theBOTTOMof
the fuel pump module electrical connector (Fig. 2).
NOTE: The pump module harness on TOP of flange
is not serviceable or removable.
Fig. 1 FUEL FILTER
Fig. 2 Fuel Pump/Level Sensor Electrical Connector
1 - ELECTRICAL CONNECTOR
2 - RETAINING TAB
14 - 4 FUEL DELIVERYRS
Page 2882 of 4284

(3) Put the tip of each injector into their ports.
Push the assembly into place until the injectors are
seated in the ports.
(4) Install the fuel rail mounting bolts. Tighten
bolts to 22 N´m (200 in. lbs.) torque.
(5) Remove covering on lower intake manifold and
clean surface.
(6) Install the Upper Intake Manifold, refer to
Engine/Manifolds/Upper Intake for more information.
(7) Install fuel hose quick connector fitting to chas-
sis tubes.Refer to Fuel Hoses, Clamps and
Quick Connect Fittings in this Section.Push the
fitting onto the chassis tube until it clicks into place.
Pull on the fitting to ensure complete insertion.
(8) Connect negative cable to battery.
(9) Use the DRBIIItscan tool to pressurize the
fuel system. Check for leaks.
FUEL TANK
DESCRIPTION
The fuel tank is constructed of a plastic material.
Its main functions are for fuel storage and for place-
ment of the fuel pump module. The tank is made
from High density Polyethylene (HDPE) material.If
equipped with ORVR (Onboard Refueling Vapor
Recovery) it has been added to the fuel tank to con-
trol refueling vapor emissions.
OPERATION
All models pass a full 360 degree rollover test
without fuel leakage. To accomplish this, fuel and
vapor flow controls are required for all fuel tank con-
nections.
All models are equipped with either one or two
rollover valves mounted into the top of the fuel tank
(or pump module).
An evaporation control system is connected to the
rollover valve(s)/control valves(Refer to 25 - EMIS-
SIONS CONTROL/EVAPORATIVE EMISSIONS/
ORVR - OPERATION) to reduce emissions of fuel
vapors into the atmosphere. When fuel evaporates
from the fuel tank, vapors pass through vent hoses or
tubes to a charcoal canister where they are tempo-
rarily held. When the engine is running, the vapors
are drawn into the intake manifold. In addition, fuel
vapors produced during vehicle refueling are allowed
to pass through the vent hoses/tubes to the charcoal
canister(s) for temporary storage (prior to being
drawn into the intake manifold). All models areequipped with a self-diagnosing system using a Leak
Detection Pump (LDP). Refer to the Emission Control
System for additional information.
INLET CHECK VALVE
All vehicles have an inlet check valve on the inside
of the fuel tank at the filler inlet
The valve prevents fuel from splashing back on
customer during vehicle refueling. The valve is a
non-serviceable item.
REMOVAL
(1) Remove fuel filler cap and perform Fuel Sys-
tem Pressure Release procedure.
(2) Disconnect negative cable from battery.
(3) Insert fuel siphon hose into fuel filler neck and
push it into the tank.
(4) Drain fuel tank dry into holding tank or a
properly labeledGASOLINEsafety container.
(5) Raise vehicle on hoist and support.
(6) Use a transmission jack to support fuel tank.
Remove bolts from fuel tank straps.
(7) Lower tank slightly.
Fig. 15 Fuel Tank
1 - ROLLOVER VALVE
2 - FUEL FILLER INLET
3 - ROLLOVER VALVE
4 - GROUND STRAP
5 - FUEL FILTER
6 - FUEL PUMP MODULE
14 - 10 FUEL DELIVERYRS
FUEL RAIL (Continued)
Page 2885 of 4284

INLET FILTER
REMOVAL
(1) Remove fuel pump module. Refer to Fuel Pump
Module Removal in this section.
(2) Using a thin straight blade screwdriver, pry
back the locking tabs on fuel pump reservoir and
remove the strainer (Fig. 22).
(3) Remove strainer O-ring from the fuel pump
reservoir body.
(4) Remove any contaminants in the fuel tank by
washing the inside of the fuel tank.
INSTALLATION
(1) Lubricate the strainer O-ring with clean engine
oil.
(2) Insert strainer O-ring into outlet of strainer so
that it sits evenly on the step inside the outlet.
(3) Push strainer onto the inlet of the fuel pump
reservoir body. Make sure the locking tabs on the
reservoir body lock over the locking tangs on the
strainer.
(4) Install fuel pump module. Refer to Fuel Pump
Module Installation in this section.
QUICK CONNECT FITTING
STANDARD PROCEDURES - QUICK-CONNECT
FITTINGS
REMOVAL
When disconnecting a quick-connect fitting, the
retainer will remain on the fuel tube nipple.WARNING: RELEASE FUEL SYSTEM PRESSURE
BEFORE DISCONNECTING A QUICK-CONNECT FIT-
TINGS. REFER TO THE FUEL PRESSURE RELEASE
PROCEDURE.
(1) Perform Fuel Pressure Release Procedure.
Refer to the Fuel Pressure Release Procedure in this
section.
(2) Disconnect negative cable from battery or aux-
iliary jumper terminal.
(3) Squeeze retainer tabs together and pull fuel
tube/quick-connect fitting assembly off of fuel tube
nipple. The retainer will remain on fuel tube.
INSTALLATION
CAUTION: Never install a quick-connect fitting with-
out the retainer being either on the fuel tube or
already in the quick-connect fitting. In either case,
ensure the retainer locks securely into the quick-
connect fitting by firmly pulling on fuel tube and fit-
ting to ensure it is secured.
(1) Using a clean lint free cloth, clean the fuel tube
nipple and retainer.
(2) Prior to connecting the fitting to the fuel tube,
coat the fuel tube nipple with clean 30 weight engine
oil.
(3) Push the quick-connect fitting over the fuel
tube until theretainer seats and a click is heard.
(4) The plastic quick-connect fitting has windows
in the sides of the casing. When the fitting com-
pletely attaches to the fuel tube, the retainer locking
ears and the fuel tube shoulder are visible in the
windows. If they are not visible, the retainer was not
properly installed (Fig. 23).Do not rely upon the
audible click to confirm a secure connection.
Fig. 22 Inlet
1 - TABS
2 - INLET STRAINER
Fig. 23 Plastic Quick-Connect Fitting/Fuel Tube
Connection
1 - WINDOW
2-TAB(2)
3 - EAR
4 - SHOULDER (ON TUBE)
RSFUEL DELIVERY14-13
Page 2906 of 4284

OPERATION
Filtered air from the air cleaner enters the intake
manifold through the throttle body. The throttle body
contains an air control passage controlled by an Idle
Air Control (IAC) motor. The air control passage is
used to supply air for idle conditions. A throttle valve
(plate) is used to supply air for above idle conditions.
Certain sensors are attached to the throttle body.
The accelerator pedal cable, speed control cable and
transmission control cable (when equipped) are con-
nected to the throttle body linkage arm.
A (factory adjusted) set screw is used to mechani-
cally limit the position of the throttle body throttle
plate.Never attempt to adjust the engine idle
speed using this screw.All idle speed functions are
controlled by the PCM.
REMOVAL
(1) Disconnect negative cable from battery cable.
(2) Remove air inlet to throttle body hose clamp.
(3) Remove throttle and the speed control (if
equipped) cables from lever and bracket.
(4) Disconnect electrical connectors from the idle
air control motor and throttle position sensor (TPS)
(Fig. 23) or (Fig. 24).
(5) Remove throttle body to intake manifold
attaching bolts.
(6) Remove throttle body and gasket.
INSTALLATION
(1) Install a new gasket.
(2) Install throttle body.
(3) Tighten throttle body mounting bolts. The 2.4L
to 28.2 N´m (250650 in. lbs.) torque, The 3.3/3.8L to
11.6 N´m (105620 in. lbs.) torque.
(4) Connect electrical connectors to the idle air
control motor and throttle position sensor (TPS) (Fig.
23) or (Fig. 24).
(5) Install air inlet to throttle body hose clamp and
tighten.
(6) Connect negative cable to battery cable.
THROTTLE CONTROL CABLE
REMOVAL
(1) Working from the engine compartment, hold
the throttle body throttle lever in the wide open posi-
tion.
(2) Remove the throttle cable from the throttle
body cam.
(3) From inside the vehicle, hold up the pedal and
remove the cable retainer and throttle cable from the
upper end of the pedal shaft.
(4) Remove retainer clip from throttle cable and
grommet at dash panel.(5) From the engine compartment, pull the throttle
cable out of the dash panel grommet. The grommet
should remain in the dash panel.
(6) Remove the throttle cable from throttle bracket
by carefully compressing both retaining ears simulta-
neously. Then gently pull the throttle cable from
throttle bracket.
INSTALLATION
(1) From the engine compartment, push the hous-
ing end fitting into the dash panel grommet.
(2) Install the cable housing (throttle body end)
into the cable mounting bracket on the engine.
(3) From inside the vehicle, hold up the pedal and
install throttle cable and cable retainer in the upper
end of the pedal shaft.
(4) At the dash panel, install the cable retainer
clip between the end of the throttle cable fitting and
grommet
(5) From the engine compartment, rotate the
throttle lever wide open and install the throttle
cable.
THROTTLE POSITION SENSOR
DESCRIPTION
The throttle position sensor mounts to the side of
the throttle body (Fig. 25) or (Fig. 26).The sensor
connects to the throttle blade shaft. The TPS is a
variable resistor that provides the Powertrain Con-
trol Module (PCM) with an input signal (voltage).
Fig. 25 Throttle Position SensorÐ2.4L Engine
1 - IAC MOTOR
2 - TP SENSOR
3 - IAT SENSOR
14 - 34 FUEL INJECTIONRS
THROTTLE BODY (Continued)