2001 CHRYSLER VOYAGER battery replacement
[x] Cancel search: battery replacementPage 1877 of 4284

SPECIAL TOOLS
SPECIAL TOOLS
BATTERY TEMPERATURE
SENSOR
DESCRIPTION
The PCM incorporates a Battery Temperature Sen-
sor (BTS) on its circuit board.
OPERATION
The PCM uses the temperature of the battery area
to control the charge rate. This temperature data,
along with data from monitored line voltage, is used
by the PCM to vary the battery charging rate. The
system voltage is higher at cold temperatures and is
gradually reduced as temperature around the battery
increases.
The function of the battery temperature sensor
(BTS) is to enable control of the generator output
based upon ambient battery temperature. As battery
temperature increases, the charging rate should
decrease. As battery temperature decreases, the
charging rate should increase. The sensor functions
similar to the ECT sensor with one major difference,
the ambient sensor does not have a dual temperature
range program. The PCM maintains the optimal out-
put of the generator by monitoring battery voltage
and controlling battery voltage to a range of
13.5-14.7 volts based on battery temperature.
The battery temperature sensor is also used for
OBD II diagnostics. Certain faults and OBD II mon-
itors are either enabled or disabled depending upon
the battery temperature sensor input (example: dis-
able purge and EGR, enable LDP). Most OBD II
monitors are disabled below 20ÉF.
REMOVAL
The battery temperature sensor is not a serviced
separately. If replacement is necessary, the PCM
must be replaced.
GENERATOR
DESCRIPTION
The generator is belt-driven by the engine. It is
serviced only as a complete assembly. The generator
produces DC voltage at the B+ terminal. If the gen-
erator is failed, the generator assembly subcompo-
nents (generator and decoupler pulley) must be
inspected for individual failure and replaced accord-
ingly.
OPERATION
As the energized rotor begins to rotate within the
generator, the spinning magnetic field induces a cur-
rent into the windings of the stator coil. Once the
generator begins producing sufficient current, it also
provides the current needed to energize the rotor.
The Y type stator winding connections deliver the
induced AC current to 3 positive and 3 negative
diodes for rectification. From the diodes, rectified DC
current is delivered to the vehicles electrical system
through the generator, battery, and ground terminals.
Noise emitting from the generator may be caused
by:
²Worn, loose or defective bearings
²Loose or defective drive pulley (2.4L) or decou-
pler (3.3/3.8L)
²Incorrect, worn, damaged or misadjusted drive
belt
²Loose mounting bolts
²Misaligned drive pulley
²Defective stator or diode
²Damaged internal fins
REMOVAL - 2.4L
(1) Release hood latch and open hood.
(2) Disconnect battery negative cable.
(3) Disconnect the Inlet Air Temperature sensor.
(4) Remove the Air Box, refer to the Engine/Air
Cleaner for more information.
(5) Remove the EVAP Purge solenoid from its
bracket and reposition.
(6) Disconnect the push-in field wire connector
from back of generator.
(7) Remove nut holding B+ wire terminal to back
of generator.
(8) Separate B+ terminal from generator.
(9) Remove accessory drive belt, refer to the Cool-
ing System section for proper procedures.
(10) Remove the generator.
Fig. 1 GENERATOR DECOUPLER 8433
RSCHARGING8F-23
Page 1880 of 4284

INSTALLATION
(1) Install the Generator Decoupler to the genera-
tor shaft.
(2) Use Special Tool #8433 (Fig. 6) to tighten the
Generator Decoupler. Refer to the torque chart for
the proper torque.
(3) Install the Air Box, refer to the Engine section
for more information.
(4) Raise vehicle and support.
(5) Install accessory drive belt, refer to the Cooling
System section for proper procedures (Fig. 5).
(6) Install the right front lower splash shield.
(7) Lower vehicle.
(8) Connect battery negative cable.
VOLTAGE REGULATOR
DESCRIPTION
The Electronic Voltage Regulator (EVR) is not a
separate component. It is actually a voltage regulat-
ing circuit located within the Powertrain Control
Module (PCM). The EVR is not serviced separately. If
replacement is necessary, the PCM must be replaced.
OPERATION
The amount of DC current produced by the gener-
ator is controlled by EVR circuitry contained within
the PCM. This circuitry is connected in series with
the generators second rotor field terminal and its
ground.
Voltage is regulated by cycling the ground path to
control the strength of the rotor magnetic field. The
EVR circuitry monitors system line voltage (B+) and
battery temperature or inlet air temperature sensor
(refer to Battery Temperature Sensor or Inlet Air
Temperature Sensor for more information). It then
determines a target charging voltage. If sensed bat-
tery voltage is 325 mv or lower than the target volt-
age, the PCM grounds the field winding until sensed
battery volage is 325 mv above target voltage. A cir-
cuit in the PCM cycles the ground side of the gener-
ator field up to 250 times per second (250Hz), but
has the capability to ground the field control wire
100% of the time (full field) to achieve the target
voltage. If the charging rate cannot be monitored
(limp-in), a duty cycle of 25% is used by the PCM in
order to have some generator output. Also refer to
Charging System Operation for additional informa-
tion.
REMOVAL
The electronic voltage regulator is not a serviced
separately. If replacement is necessary, the PCM
must be replaced.
Fig. 6 SPECIAL TOOL 8433 AND DECOUPLER
8F - 26 CHARGINGRS
GENERATOR DECOUPLER PULLEY (Continued)
Page 1899 of 4284

WINDSHIELD GRID
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - SYSTEM TEST
Electrically heated rear window defogger or the
heated windshield wiper deicer operation can be
checked on the vehicle in the following manner:
(1) Turn the ignition switch to the ON position.
(2) Using a ammeter on the battery, turn the rear
defogger control switch to the ON position, a distinct
increase in amperage draw should be noted.
(3) The rear window defogger or the heated wind-
shield wiper deicer operation can be checked by feel-
ing the glass. A distinct difference in temperature
between the grid lines and adjacent clear glass can
be detected in 3 to 4 minutes of operation.
(4) Using a DC voltmeter (Fig. 4) contact terminal
B with the negative lead, and terminal A with the
positive lead. The voltmeter should read 10-14 volts.
(5) Indicator light illumination means that there is
power available at the switch only and does not nec-
essarily verify system operation.
(6) If turning the defogger switch ON, no distinct
current draw on the ammeter the problem should be
isolated in the following manner:
²Confirm that ignition switch is ON.
²Ensure that the heated rear window or the
heated windshield wiper deicer feed pigtail is con-
nected to the wiring harness and that the ground
pigtail is in fact grounded.
²Ensure that the proper fuse in the PDC is OK.
(7) When the above steps have been completed and
the system is still inoperative it may be necessary to
connect a DRBIII scan tool and refer to the Diagnos-
tic Service Manual, you may also check for the fol-
lowing being defective:
²HVAC control assembly
²Rear window defogger relay in the IPM.
²Check for loose connector or a wire pushed out
of connector.
²Rear window or the windshield grid lines (all
grid lines would have to be broken, or one of the feed
pigtails not connected to the bus bar, for no ammeter
deflection).
(8) If turning the switch ON produces severe volt-
meter deflection, the circuit should be closely checked
for a shorting condition.
(9) If the system operation has been verified but
indicator LED does not light, replace the HVAC con-
trol assembly.
(10) For detailed wiring information, refer to the
appropriate section for Wiring Diagrams.
STANDARD PROCEDURE - GRID LINE AND
TERMINAL REPAIR
WARNING:
REPAIR KIT MAY CAUSE SKIN OR EYE IRRITATION.
CONTAINS EPOXY RESIN AND AMINE TYPE HARD-
ENER, HARMFUL IF SWALLOWED. AVOID CON-
TACT WITH SKIN AND EYES. FOR SKIN, WASH
AFFECTED AREAS WITH SOAP AND WATER. DO
NOT TAKE INTERNALLY. IF TAKEN INTERNALLY,
INDUCE VOMITING; CALL A PHYSICIAN IMMEDI-
ATELY. IF IN CONTACT WITH EYES, FLUSH WITH
PLENTY OF WATER. USE WITH ADEQUATE VENTI-
LATION. DO NOT USE NEAR FIRE OR FLAME. CON-
TENTS CONTAINS 3% FLAMMABLE SOLVENTS.
KEEP OUT OF REACH OF CHILDREN.
The repair for the front windshield or the rear win-
dow grids are the same.
The repair of grid lines and replacement of the ter-
minal is possible using the MopartRepair Package
or equivalent.
(1) Clean area surrounding grid line or terminal
by gently rubbing area with steel wool.
(2) Wipe area with clean cloth soaked in alcohol or
similar solvent. It is necessary that all contaminants
be removed from repair area.
Fig. 4 Grid Line Test
1 - VOLTMETER
2 - TERMINAL B
3 - FEED WIRE
4 - MID-POINT C (TYPICAL)
5 - HEATED REAR WINDOW GRIDS
6 - GROUND WIRE
7 - TERMINAL A
RSHEATED GLASS8G-3
Page 1927 of 4284

INSTRUMENT CLUSTER
TABLE OF CONTENTS
page page
INSTRUMENT CLUSTER
DESCRIPTION............................1
OPERATION.............................1
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING..................1
INSTRUMENT CLUSTER..................1
REMOVAL..............................11
INSTALLATION...........................11
CLUSTER LENS
REMOVAL..............................12INSTALLATION...........................12
MECHANICAL TRANSMISSION RANGE
INDICATOR
REMOVAL..............................12
INSTALLATION...........................12
RED BRAKE WARNING INDICATOR
DESCRIPTION...........................12
OPERATION.............................12
INSTRUMENT CLUSTER
DESCRIPTION
The instrumentation gauges are contained in a
subdial assembly within the instrument cluster. The
individual gauges are not serviceable. If one of the
cluster gauges becomes faulty, the entire cluster
would require replacement.
The mechanical instrument cluster with a tachom-
eter is equipped with a electronic vacuum fluorescent
transmission range indicator (PRND3L), odometer,
and trip odometer display.
The mechanical instrument cluster without a
tachometer is equipped with a cable operated trans-
mission range indicator (PRND21) and a vacuum
flourescent odometer display.
The instrument cluster is equipped with the follow-
ing warning lamps.
²Lift Gate Ajar
²Low Fuel Level
²Low Windshield Washer Fluid Level
²Cruise
²Battery Voltage
²Fasten Seat Belt
²Door Ajar
²Headlamp Out
²Coolant Temperature
²Anti-Lock Brake
²Brake
²Airbag
²Traction Control
²Autostick
OPERATION
Refer to the vehicle Owner's Manual for operation
instructions and conditions for the Instrument Clus-
ter Gauges.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - SELF-
DIAGNOSTICS
The instrument clusters are equipped with a self
diagnostic test feature to help identify electronic
problems. Prior to any test, perform the Self-Diag-
nostic Test. The self diagnostic system displays
instrument cluster stored fault codes in the odometer
display, sweeps the gauges to the calibration points,
and bulb checks the warning indicators. When the
key is in the ON position with the engine not run-
ning, the MIL will remain illuminated for regulatory
purposes.
To activate the Self-Diagnostic program:
(1) With the ignition switch in the OFF position,
depress the TRIP ODOMETER RESET button.
(2) Continue to hold the TRIP ODOMETER
RESET button untilSofand a number (software ver-
sion number (i.e.Sof 3.2) appears in the odometer
window (about five seconds) then release the button.
If a fault code is present, the cluster will display it in
the odometer display. When all fault codes have been
displayed, the cluster will displayªendºin the odom-
eter display. Refer to the table to determine what
each trouble code means.
RSINSTRUMENT CLUSTER8J-1
Page 1959 of 4284
(4) Disconnect wire harness from switch.
(5) Pull bulb from switch.
INSTALLATION
(1) Push bulb into switch.
(2) Connect wire harness to switch.
(3) Push switch into instrument panel.
(4) Close glove box door.
(5) Reconnect the battery negative cable.
LIFTGATE LAMP
REMOVAL
(1) Disconnect and isolate the battery negative
cable.
(2) Using a flat bladed tool, pry lamp from trim
panel (Fig. 3).
(3) Disconnect wire harness connector from lamp.
(4) Pry off lens and remove bulb.
INSTALLATION
(1) Install bulb and snap lens into place.
(2) Reconnect wire harness connector to lamp.
(3) Position lamp onto trim panel and snap into
place.
(4) Reconnect battery negative cable.
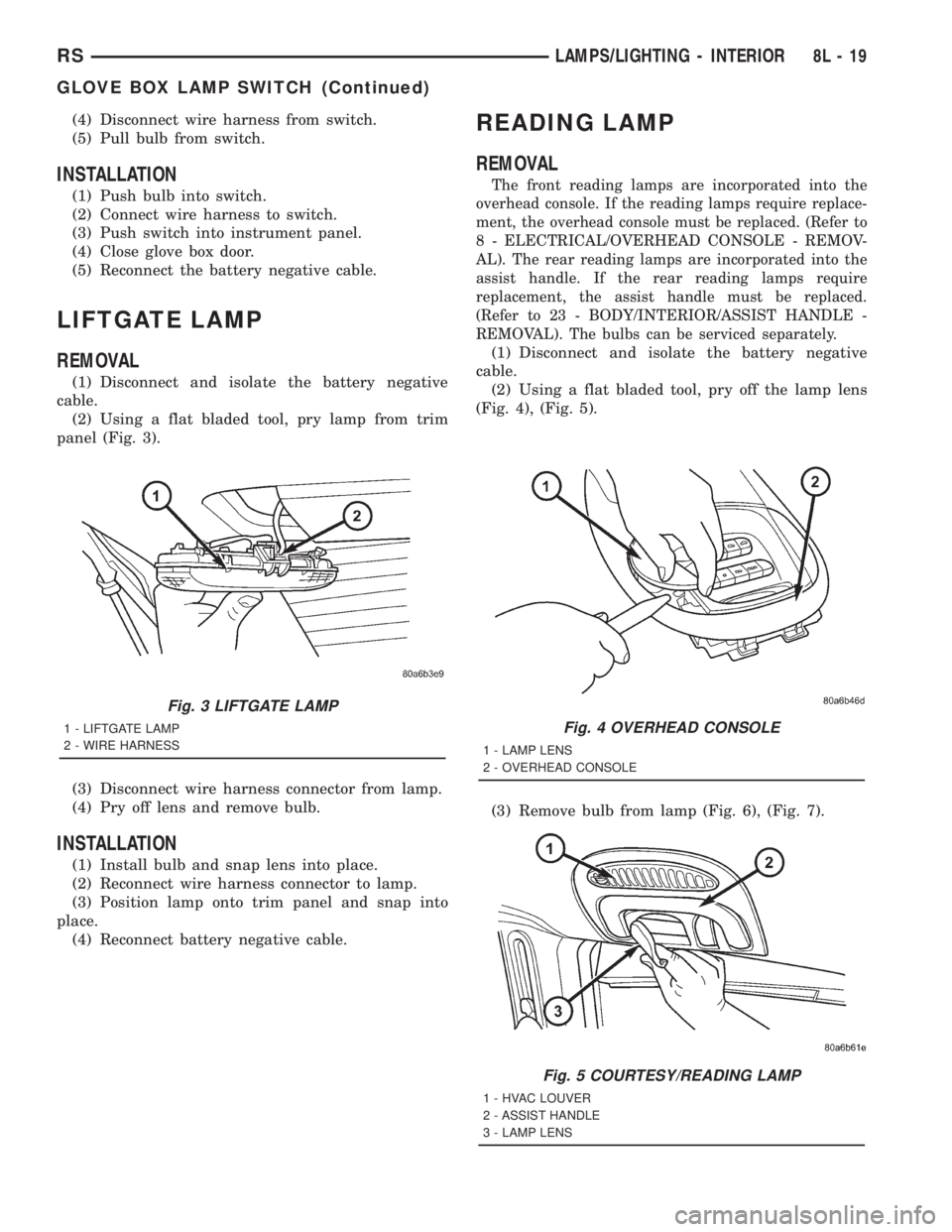
READING LAMP
REMOVAL
The front reading lamps are incorporated into the
overhead console. If the reading lamps require replace-
ment, the overhead console must be replaced. (Refer to
8 - ELECTRICAL/OVERHEAD CONSOLE - REMOV-
AL). The rear reading lamps are incorporated into the
assist handle. If the rear reading lamps require
replacement, the assist handle must be replaced.
(Refer to 23 - BODY/INTERIOR/ASSIST HANDLE -
REMOVAL). The bulbs can be serviced separately.
(1) Disconnect and isolate the battery negative
cable.
(2) Using a flat bladed tool, pry off the lamp lens
(Fig. 4), (Fig. 5).
(3) Remove bulb from lamp (Fig. 6), (Fig. 7).
Fig. 3 LIFTGATE LAMP
1 - LIFTGATE LAMP
2 - WIRE HARNESSFig. 4 OVERHEAD CONSOLE
1 - LAMP LENS
2 - OVERHEAD CONSOLE
Fig. 5 COURTESY/READING LAMP
1 - HVAC LOUVER
2 - ASSIST HANDLE
3 - LAMP LENS
RSLAMPS/LIGHTING - INTERIOR8L-19
GLOVE BOX LAMP SWITCH (Continued)
Page 1972 of 4284

more faulty electronic modules in the vehicle, or from
a faulty PCI data bus. The use of a DRB IIItscan
tool and the proper Diagnostic Procedures manual
are required for further diagnosis.
NOTE: If the compass functions, but accuracy is
suspect, it may be necessary to perform a variation
adjustment. This procedure allows the compass
unit to accommodate variations in the earth's mag-
netic field strength, based on geographic location.
Refer to Compass Variation Adjustment in the Ser-
vice Procedures section of this group.
NOTE: If the compass reading displays dashes, and
only ªCALº appears in the display, demagnetizing
may be necessary to remove excessive residual
magnetic fields from the vehicle. Refer to Compass
Demagnetizing in the Service Procedures section of
this group.
STANDARD PROCEDURE - READING/
COURTESY LAMP REPLACEMENT
(1) Open hood, disconnect and isolate the negative
battery cable remote terminal from the remote bat-
tery post.
(2) Remove the reading/courtesy lamp lens. Using
a trim stick, gently pry the forward edge of the read-
ing/courtesy lamp lens outward.
(3) Remove the reading/courtesy lamp socket from
the overhead console. Rotate the reading/courtesy
lamp socket one quarter turn counter clockwise.
(4) Remove the lamp and socket assembly.
(5) Reverse the above procedure to install.
STANDARD PROCEDURE - COMPASS
CALIBRATION
CAUTION: Do not place any external magnets, such
as magnetic roof mount antennas, in the vicinity of
the compass. Do not use magnetic tools when ser-
vicing the overhead console.
The electronic compass unit features a self-cali-
brating design, which simplifies the calibration pro-
cedure. This feature automatically updates the
compass calibration while the vehicle is being driven.
This allows the compass unit to compensate for small
changes in the residual magnetism that the vehicle
may acquire during normal use. If the compass read-
ings appear to be erratic or out of calibration, per-
form the following calibration procedure. Also, new
service replacement Electronic Modules (EVIC,
CMTC, CT) must have their compass calibrated
using this procedure. Do not attempt to calibrate the
compass near large metal objects such as other vehi-cles, large buildings, or bridges; or, near overhead or
underground power lines.
NOTE: Whenever the compass is calibrated manu-
ally, the variance number must also be reset. Refer
to Compass Variation Adjustment in this group.
Calibrate the compass manually as follows:
(1) Turn the ignition switch to the On position. If
the compass/thermometer data is not currently being
displayed, momentarily depress and release the C/T
push button to reach the compass/thermometer dis-
play.
(2) On Electronic Vehicle Information Center
(EVIC) and Compass Mini-Trip Computer (CMTC)
equipped vehicles depress the Reset push button and
hold the button down until ªCALº appears in the dis-
play. This takes about ten seconds, and appears
about five seconds after ªVAR = XXº is displayed. On
Compass Temperature Module (CT) equipped vehicles
depress the C/T push button and US/M push button
down until ªCALº appears in the display. This takes
about ten seconds, and appears about five seconds
after ªVAR = XXº is displayed.
(3) Release the push button(s).
(4) Drive the vehicle on a level surface, away from
large metal objects and power lines, through three or
more complete circles at between five and eight kilo-
meters-per-hour (three and five miles-per-hour) in
not less than 48 seconds. The ªCALº message will
disappear from the display to indicate that the com-
pass is now calibrated.
NOTE: If the ªCALº message remains in the display,
either there is excessive magnetism near the com-
pass, or the unit is faulty. Repeat the calibration
procedure one more time.
NOTE: If the wrong direction is still indicated in the
compass display, the area selected for calibration
may be too close to a strong magnetic field. Repeat
the calibration procedure in another location.
STANDARD PROCEDURE - COMPASS
DEMAGNETIZING
A degaussing tool (Special Tool 6029) is used to
demagnetize, or degauss, the overhead console for-
ward mounting screw and the roof panel above the
overhead console. Equivalent units must be rated as
continuous duty for 110/115 volts and 60 Hz. They
must also have a field strength of over 350 gauss at 7
millimeters (0.25 inch) beyond the tip of the probe.
To demagnetize the roof panel and the overhead
console forward mounting screw, proceed as follows:
8M - 4 OVERHEAD CONSOLERS
OVERHEAD CONSOLE (Continued)
Page 1991 of 4284

(6) Verify power liftgate system and full open
switch operation. Cycle the power liftgate through
one complete open and close cycle, this will allow the
power liftgate control module to relearn its cycle with
the new components.
LIFTGATE MOTOR
DESCRIPTION
Vehicles equipped with a power liftgate, utilize a
liftgate gear motor assembly (Fig. 6). The gear motor
assembly consists of a DC motor, hall effect sensor,
engage actuator, full open switch, lift gear, aluminum
housing, drive gears and wire harness. The gears and
motor portion of the assembly provides the power
and torque required to open or close the liftgate
under the worst case conditions. The hall effect sen-
sor is used to provide the liftgate control module with
a speed reading, which is used to monitor the resis-
tance of liftgate travel. This speed reading also
allows the power liftgate control module to detect
obstructions and move the liftgate accordingly. The
engage actuator is used to toggle between power
open/close mode and full manual mode when desired.
The full open switch is used to let the power liftgate
control module know when the liftgate is approach-
ing the full open position.Serviceable components of the power liftgate gear
motor assembly are the complete gear motor assem-
bly, motor and wire harness, lift gear and control rod,
engage actuator, full open switch and the transverse
bracket. Refer to additional information in this group
for more component details.
OPERATION
With the push of a power liftgate command switch
(liftgate closed), the power liftgate control module
will signal the latch assembly to release the door
from its primary closed and latched position to the
released and movable position. The liftgate motor
mounted, engage actuator then engages the liftgate
motor assembly, which moves the liftgate into the
open position. The liftgate motor provides the torque
and power to move the door to its full open or closed
position(Refer to 8 - ELECTRICAL/POWER DOORS -
OPERATION) for additional information.
REMOVAL
The power liftgate motor can be serviced in two
different ways. The first of which is called out here,
the complete gear motor assembly. The second way
includes the motor, aluminum housing, drive gears
and wire harness assembly. To perform this service
procedure, use the following procedure to remove the
gear motor assembly from the vehicle. Then refer to
the other procedures called out this section to trans-
fer the remaining components (engage actuator, full
open switch, transverse bracket and lift gear and
rod) to the replacement motor assembly.
(1) Disconnect and isolate the negative battery
cable.
(2) Remove the left rear D-pillar trim panel from
the vehicle. Refer to the Body section for the proce-
dure.
(3) Disconnect the wire harness connector from the
motor assembly (Fig. 6).
(4) Remove the two bolts from the motor housing
and the one bolt from the transverse mount bracket.
(5) Grab the liftgate motor assembly and lift
upward and out to unhook the motor assembly from
the D-pillar.
(6) Remove the liftgate motor assembly from the
vehicle.
INSTALLATION
(1) Using the motor housing tab, hook the liftgate
motor assembly on the D-pillar.
(2) Install the three motor assembly retaining
bolts. Torque the two rear most bolts first to 9.5 N´m
(85 in. lbs.). Torque the remaining bolt next to the
window actuator to 9.5 N´m (85 in. lbs.).
(3) Connect the liftgate motor assembly electrical
connector.
Fig. 6 POWER LIFTGATE COMPONENTS
1 - POWER LIFTGATE GEAR MOTOR ASSEMBLY
2 - POWER LIFTGATE CONTROL MODULE
3 - ELECTRICAL GROUND LOCATION
RSPOWER LIFTGATE SYSTEM8N-11
FULL OPEN SWITCH (Continued)
Page 2010 of 4284

(8) Disconnect the hold open latch cable from the
latch assembly. Refer to the Body Section of the ser-
vice manual for the procedure.
(9) Disconnect lock actuator link rod from the
latch assembly.
(10) Remove the latch assembly from the vehicle.
INSTALLATION
(1) Position the latch assembly in the vehicle. Be
certain all latch mounted components are installed
on the replacement latch assembly. If not, transfer
components from the old latch to the new latch
assembly.
(2) Connect the lock actuator link rod on the latch
assembly.
(3) Connect the hold open latch cable on the latch
assembly. Refer to the procedure in this section for
detailed instructions.
(4) Connect the inside and outside handle cables
on the latch assembly. Refer to the procedure in the
Body section for detailed instructions.
(5) Connect all electrical connectors leading to the
latch assembly.
(6) With assistance from another person, position
the side door and install the door latch retaining
bolts. Torque to 10 - 12 N´m (100 in. lbs.).
(7) Install the weathershield if necessary. Refer to
the procedure in the Body section for detailed
instructions.
(8) Install the appropriate side door trim panel.
Refer to the procedure in the Body section for
detailed instructions.
(9) Connect the negative battery cable.
SLIDING DOOR MOTOR
DESCRIPTION
Vehicles equipped with a power sliding door utilize
a door motor assembly. The door motor is located in
the center of the side door (Fig. 7) and is comprised
of three parts. The three parts of the door motor
assembly are the motor, gear reduction and clutch
assembly. The door motor assembly provides the
power and torque to move the sliding door from the
open/closed position to full closed/open position, after
the power latching mechanism has released.
Special wellnuts and screws are used in the side
door inner panel to retain the door motor to the door
panel. Refer to Standard Procedures in this section
for additional wellnut information.The door motor is replaced as a complete assembly,
which includes the DC motor, gear reduction and
clutch assemblies. Consult your Mopar parts catalog
for specific part numbers.
OPERATION
With the push of a Power Side Door (PSD) com-
mand switch, the PSD control module will signal the
latch assembly to release the door from its primary
locked position. The drive motor will then take over
to provide the power to open the door to its full open
or closed position. The gear reduction portion of the
motor assembly reduces the speed of the motor from
5800 to 260 rpm and also increases the torque to the
lower drive unit. The clutch portion of the motor
assembly engages the motor to drive the door under
power and disengages it so the door can be moved
easily under manual operation.
Fig. 7 SIDE DOOR COMPONENTS
1 - SLIDING DOOR CONTROL MODULE
2 - MODULE RETAINING SCREW
3 - MODULE ELECTRICAL CONNECTORS
4 - DOOR MOTOR ASSEMBLY
5 - FLEX DRIVE ASSEMBLY
6 - DOOR MOTOR RETAINING FASTENERS
7 - DOOR MOTOR ELECTRICAL CONNECTOR
8N - 30 POWER SLIDING DOOR SYSTEMRS
LATCH (Continued)