2001 CHRYSLER VOYAGER maintenance schedule
[x] Cancel search: maintenance schedulePage 1513 of 4284

²Inspect air filter element.
²Replace fuel filter/water separator element. (2)
²Check alignment.
140 000 km (86 000 Miles)
²Change engine oil. (1)
²Replace engine oil filter.
²Replace air filter element.
150 000 km (93 000 Miles)
²Change engine oil. (1)
²Replace engine oil filter.
²Inspect air filter element.
²Replace fuel filter/water separator element. (2)
²Check alignment.
160 000 km (100 000 Miles)
²Change engine oil. (1)
²Replace engine oil filter.
²Replace air filter element.
²Flush and replace engine coolant. (3)
²Change oil every 12 months regardless of mile-
age.
²The fuel filter/water separator element should
be replaced once a year if the vehicle is driven less
than 20 000 km annually or if power loss from fuel
starvation is detected.
²
Flush and replace engine coolant every 60 months
even if the vehicle is driven less than 160 000 km.
²Change manual transaxle fluid.
HOISTING
STANDARD PROCEDURE - HOISTING
Refer to Owner's Manual provided with vehicle for
proper emergency jacking procedures.
WARNING: THE HOISTING AND JACK LIFTING
POINTS PROVIDED ARE FOR A COMPLETE VEHI-
CLE. WHEN THE ENGINE OR REAR SUSPENSION
IS REMOVED FROM A VEHICLE, THE CENTER OF
GRAVITY IS ALTERED MAKING SOME HOISTING
CONDITIONS UNSTABLE. PROPERLY SUPPORT OR
SECURE VEHICLE TO HOISTING DEVICE WHEN
THESE CONDITIONS EXIST.
CAUTION: Do not position hoisting device on any
suspension component, including the front suspen-
sion crossmember, the rear leaf springs, and the
rear axle. Do not hoist on the front and rear
bumpers, the lower liftgate crossmember, the lower
radiator crossmember, the down standing flanges
on the sill or the front engine mount.
FOR PROPER HOIST PLACEMENT REFER
TO (Fig. 7).The hoisting points are identified by S.A.E.
inverted triangle hoisting symbols (Fig. 7). The front
hoisting points are at the bottom of the font rail
below the hoisting symbol approximately 250mm
behind the front suspension crossmember. When
using outboard lift hoists, verify that the hoist lift
pads have been properly adjusted to eliminate con-
tact between the hoist arm and the down standing
flange on the sill. The rear hoisting points are the
leaf spring front mounting brackets. The hoist pad
must be positioned to pick up the flanges on the
bracket, not the leaf spring.
When servicing the leaf springs or the leaf spring
mounting brackets, special provisions are required to
support the rear of the vehicle. Position the rear
hoist pads under the horizontal surface on the bot-
tom of the sill, inboard adjacent to the flange and
centered fore/aft between the jacking indicator tabs
on the lower flange.DO NOT HOIST ON THE
FLANGE.Place a soft pad between the hoist and the
painted surface on the sill to avoid scratching the fin-
ish.
Fig. 7 HOISTING AND JACKING POINTS
1 - Drive On Lift
2 - Frame Contact Lift (Single Post)
Chassis Lift (Non-Axle Dual Post)
Outboard Lift (Dual Post)
Floor Jack
3 - S.A.E. Hoisting Symbols
RGLUBRICATION & MAINTENANCE - RG - 2.5 L TURBO DIESEL0a-7
MAINTENANCE SCHEDULES (Continued)
Page 1752 of 4284

A refractometer will test the amount of glycol in a
coolant mixture by measuring the amount a beam of
light bends as it passes through the fluid.
Some coolant manufactures use other types of gly-
cols into their coolant formulations. Propylene glycol
is the most common new coolant. However, propylene
glycol based coolants do not provide the same freez-
ing protection and corrosion protection and is not rec-
ommended.
CAUTION: Do not mix types of coolantÐcorrosion
protection will be severely reduced.
STANDARD PROCEDURE - COOLANT SERVICE
For engine coolant recommended service schedule,
(Refer to LUBRICATION & MAINTENANCE/MAIN-
TENANCE SCHEDULES - DESCRIPTION).
COOLANT RECOVERY
CONTAINER
DESCRIPTION
The coolant recovery/reserve system container is
mounted in the engine compartment (Fig. 2). The
container is made of plastic.
OPERATION
The coolant recovery system works with the radia-
tor pressure cap to use thermal expansion and con-
traction of the coolant to keep the coolant free of
trapped air. Provides a convenient and safe method
for checking coolant level and adjusting level at
atmospheric pressure without removing the radiator
pressure cap. It also provides some reserve coolant to
cover deaeration, evaporation, or boiling losses.
Fig. 1 Temperature Gauge Indications
7 - 18 ENGINERS
COOLANT (Continued)
Page 1789 of 4284

100 Percent Ethylene-GlycolÐShould Not Be Used in
Chrysler Vehicles
Use of 100 percent ethylene-glycol will cause for-
mation of additive deposits in the system, as the cor-
rosion inhibitive additives in ethylene-glycol require
the presence of water to dissolve. The deposits act as
insulation, causing temperatures to rise to as high as
149 deg. C (300 deg. F). This temperature is hot
enough to melt plastic and soften solder. The
increased temperature can result in engine detona-
tion. In addition, 100 percent ethylene-glycol freezes
at -22 deg. C (-8 deg. F ).
Propylene-glycol FormulationsÐShould Not Be Used in
Chrysler Vehicles
Propylene-glycol formulations do not meet
Chrysler coolant specifications.It's overall effec-
tive temperature range is smaller than that of ethyl-
ene-glycol. The freeze point of 50/50 propylene-glycol
and water is -32 deg. C (-26 deg. F). 5 deg. C higher
than ethylene-glycol's freeze point. The boiling point
(protection against summer boil-over) of propylene-
glycol is 125 deg. C (257 deg.F)at96.5 kPa (14 psi),
compared to 128 deg. C (263 deg. F) for ethylene-gly-
col. Use of propylene-glycol can result in boil-over or
freeze-up in Chrysler vehicles, which are designed for
ethylene-glycol. Propylene glycol also has poorer heat
transfer characteristics than ethylene glycol. This
can increase cylinder head temperatures under cer-
tain conditions.
Propylene-glycol/Ethylene-glycol MixturesÐShould Not Be
Used in Chrysler Vehicles
Propylene-glycol/ethylene-glycol Mixtures can
cause the destabilization of various corrosion inhibi-
tors, causing damage to the various cooling system
components. Also, once ethylene-glycol and propy-
lene-glycol based coolants are mixed in the vehicle,
conventional methods of determining freeze point will
not be accurate. Both the refractive index and spe-
cific gravity differ between ethylene glycol and propy-
lene glycol.
CAUTION: Richer antifreeze mixtures cannot be
measured with normal field equipment and can
cause problems associated with 100 percent ethyl-
ene-glycol.DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - COOLANT
CONCENTRATION TESTING
Coolant concentration should be checked when any
additional coolant was added to system or after a
coolant drain, flush and refill. The coolant mixture
offers optimum engine cooling and protection against
corrosion when mixed to a freeze point of -37ÉC
(-34ÉF) to -59ÉC (-50ÉF). The use of a hydrometer or a
refractometer can be used to test coolant concentra-
tion.
A hydrometer will test the amount of glycol in a
mixture by measuring the specific gravity of the mix-
ture. The higher the concentration of ethylene glycol,
the larger the number of balls that will float, and
higher the freeze protection (up to a maximum of
60% by volume glycol).
A refractometer will test the amount of glycol in a
coolant mixture by measuring the amount a beam of
light bends as it passes through the fluid.
Some coolant manufactures use other types of gly-
cols into their coolant formulations. Propylene glycol
is the most common new coolant. However, propylene
glycol based coolants do not provide the same freez-
ing protection and corrosion protection and is not rec-
ommended.
CAUTION: Do not mix types of coolantÐcorrosion
protection will be severely reduced.
STANDARD PROCEDURE - COOLANT SERVICE
For engine coolant recommended service schedule,
(Refer to LUBRICATION & MAINTENANCE/MAIN-
TENANCE SCHEDULES - DESCRIPTION).
STANDARD PROCEDURE - ADDING
ADDITIONAL COOLANT
The pressure/vent cap should not be removed
from the coolant recovery pressure container.
When additional coolant is needed to maintain this
level, it should be added to the coolant recovery pres-
sure container (Fig. 1). Use only 50/50 mix of ethyl-
ene glycol type antifreeze and distilled water. For the
recommeded antifreeze/coolant type (Refer to LUBRI-
CATION & MAINTENANCE/FLUID TYPES -
DESCRIPTION).
CAUTION: Do not use well water, or suspect water
supply in cooling system. A 50/50 ethylene glycol
and distilled water mix is recommended. For the
recommeded antifreeze/coolant type (Refer to
LUBRICATION & MAINTENANCE/FLUID TYPES -
DESCRIPTION).
RGENGINE7a-15
COOLANT (Continued)
Page 1856 of 4284

BATTERY SYSTEM
DESCRIPTION
A single 12-volt battery system is standard factory-
installed equipment on this model. All of the compo-
nents of the battery system are located within the
engine compartment of the vehicle. The service infor-
mation for the battery system in this vehicle covers
the following related components, which are covered
in further detail elsewhere in this service manual:
²Battery- The storage battery provides a reli-
able means of storing a renewable source of electrical
energy within the vehicle.
²Battery Cable- The battery cables connect the
battery terminal posts to the vehicle electrical sys-
tem.
²Battery Holddown- The battery holddown
hardware secures the battery in the battery tray in
the engine compartment.
²Battery Thermoguard- The battery thermo-
guard insulates the battery to protect it from engine
compartment temperature extremes.
²Battery Tray- The battery tray provides a
secure mounting location in the vehicle for the bat-
tery and an anchor point for the battery holddown
hardware.
For battery system maintenance schedules and
jump starting procedures, see the owner's manual in
the vehicle glove box. Optionally, refer to Lubrication
and Maintanance for the recommended battery main-
tenance schedules and for the proper battery jump
starting procedures. While battery charging can be
considered a maintenance procedure, the battery
charging procedures and related information are
located in the standard procedures section of this ser-
vice manual. This was done because the battery must
be fully-charged before any battery system diagnosis
or testing procedures can be performed. Refer to
Standard procedures for the proper battery charging
procedures.
OPERATION
The battery system is designed to provide a safe,
efficient, reliable and mobile means of delivering and
storing electrical energy. This electrical energy is
required to operate the engine starting system, as
well as to operate many of the other vehicle acces-sory systems for limited durations while the engine
and/or the charging system are not operating. The
battery system is also designed to provide a reserve
of electrical energy to supplement the charging sys-
tem for short durations while the engine is running
and the electrical current demands of the vehicle
exceed the output of the charging system. In addition
to delivering, and storing electrical energy for the
vehicle, the battery system serves as a capacitor and
voltage stabilizer for the vehicle electrical system. It
absorbs most abnormal or transient voltages caused
by the switching of any of the electrical components
or circuits in the vehicle.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - BATTERY SYSTEM
The battery, starting, and charging systems in the
vehicle operate with one another and must be tested
as a single complete system. In order for the engine
to start and the battery to charge properly, all of the
components that are used in these systems must per-
form within specifications. It is important that the
battery, starting, and charging systems be thoroughly
tested and inspected any time a battery needs to be
charged or replaced. The cause of abnormal battery
discharge, overcharging or early battery failure must
be diagnosed and corrected before a battery is
replaced and before a vehicle is returned to service.
The service information for these systems has been
separated within this service manual to make it eas-
ier to locate the specific information you are seeking.
However, when attempting to diagnose any of these
systems, it is important that you keep their interde-
pendency in mind.
The diagnostic procedures used for the battery,
starting, and charging systems include the most
basic conventional diagnostic methods, to the more
sophisticated On-Board Diagnostics (OBD) built into
the Powertrain Control Module (PCM). Use of an
induction-type milliampere ammeter, a volt/ohmme-
ter, a battery charger, a carbon pile rheostat (load
tester) and a 12-volt test lamp may be required. All
OBD-sensed systems are monitored by the PCM.
Each monitored circuit is assigned a Diagnostic Trou-
ble Code (DTC). The PCM will store a DTC in elec-
tronic memory for any failure it detects. Refer to
Charging System for the proper charging system on-
board diagnostic test procedures.
8F - 2 BATTERY SYSTEMRS
Page 1859 of 4284
²A faulty or incorrect starting system component.
Refer to Starting System for the proper starting sys-
tem diagnosis and testing procedures.
²A faulty or incorrect battery. Refer to Standard
Procedures for the proper battery diagnosis and test-
ing procedures. Refer to Battery System Specifica-
tions for the proper specifications.
CLEANING
The following information details the recommended
cleaning procedures for the battery and related com-
ponents. In addition to the maintenance schedules
found in this service manual and the owner's man-
ual, it is recommended that these procedures be per-
formed any time the battery or related components
must be removed for vehicle service.
(1) Clean the battery cable terminal clamps of all
corrosion. Remove any corrosion using a wire brush
or a post and terminal cleaning tool, and a sodium
bicarbonate (baking soda) and warm water cleaning
solution (Fig. 1).
(2) Clean the battery tray and battery holddown
hardware of all corrosion. Remove any corrosion
using a wire brush and a sodium bicarbonate (baking
soda) and warm water cleaning solution. Paint any
exposed bare metal.
(3) If the removed battery is to be reinstalled,
clean the outside of the battery case and the top
cover with a sodium bicarbonate (baking soda) and
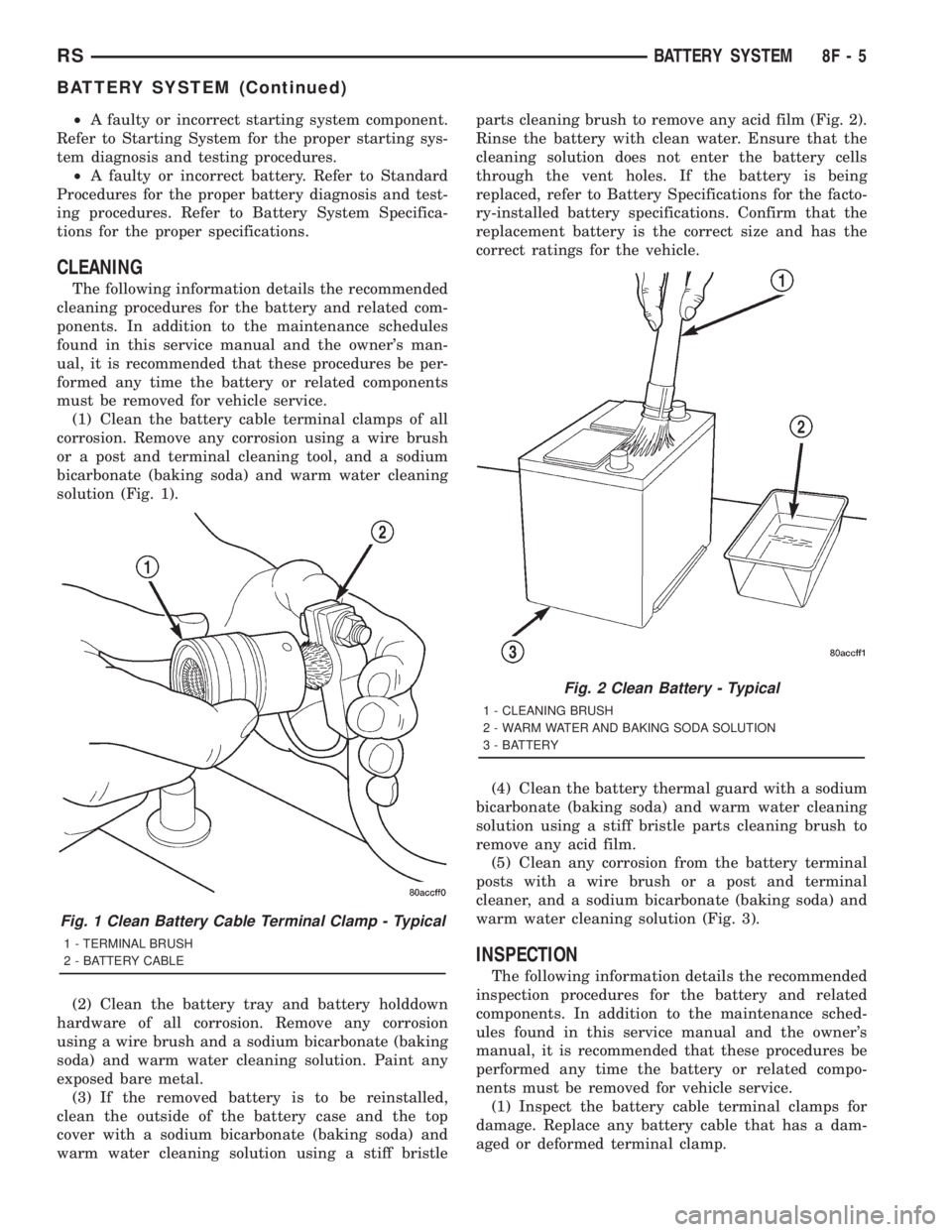
warm water cleaning solution using a stiff bristleparts cleaning brush to remove any acid film (Fig. 2).
Rinse the battery with clean water. Ensure that the
cleaning solution does not enter the battery cells
through the vent holes. If the battery is being
replaced, refer to Battery Specifications for the facto-
ry-installed battery specifications. Confirm that the
replacement battery is the correct size and has the
correct ratings for the vehicle.
(4) Clean the battery thermal guard with a sodium
bicarbonate (baking soda) and warm water cleaning
solution using a stiff bristle parts cleaning brush to
remove any acid film.
(5) Clean any corrosion from the battery terminal
posts with a wire brush or a post and terminal
cleaner, and a sodium bicarbonate (baking soda) and
warm water cleaning solution (Fig. 3).
INSPECTION
The following information details the recommended
inspection procedures for the battery and related
components. In addition to the maintenance sched-
ules found in this service manual and the owner's
manual, it is recommended that these procedures be
performed any time the battery or related compo-
nents must be removed for vehicle service.
(1) Inspect the battery cable terminal clamps for
damage. Replace any battery cable that has a dam-
aged or deformed terminal clamp.
Fig. 1 Clean Battery Cable Terminal Clamp - Typical
1 - TERMINAL BRUSH
2 - BATTERY CABLE
Fig. 2 Clean Battery - Typical
1 - CLEANING BRUSH
2 - WARM WATER AND BAKING SODA SOLUTION
3 - BATTERY
RSBATTERY SYSTEM8F-5
BATTERY SYSTEM (Continued)
Page 1924 of 4284

INSTALLATION - 2.4L
The knock sensor threads into the side of the cyl-
inder block in front of the starter (Fig. 13).
(1) Install knock sensor. Tighten knock sensor to
10 N´m (7 ft. lbs.) torque.Over or under tighten-
ing effects knock sensor performance, possibly
causing improper spark control.
(2) Attach electrical connector to knock sensor.
INSTALLATION - 3.8L
The knock sensor threads into the side of the cyl-
inder block in the rear.
(1) Install knock sensor. Tighten knock sensor to
10 N´m (7 ft. lbs.) torque.Over or under tighten-
ing effects knock sensor performance, possibly
causing improper spark control.
(2) Attach electrical connector to knock sensor.
(3) On All Wheel Drive vehicles install the PTU
(Power Transfer Unit) for the rear wheels, refer to
the Transmission section for more information.
(4) Lower vehicle.
(5) Connect the negative cable.
SPARK PLUG
DESCRIPTION - STANDARD 2.4L
All engines use resistor spark plugs. They have
resistance values ranging from 6,000 to 20,000 ohms
when checked with at least a 1000 volt spark plug
tester.
Do not use an ohm meter to check the resis-
tance of the spark plugs. This will give an inac-
curate reading.
Refer to the Specifications section for gap and type
of spark plug.
DESCRIPTION - PLATINUM 3.3/3.8L
These engines utilize platinum spark plugs. Refer
to the maintenance schedule.
All engines use resistor spark plugs. They have
resistance values ranging from 6,000 to 20,000 ohms
when checked with at least a 1000 volt spark plug
tester.
Do not use an ohm meter to check the resis-
tance of the spark plugs. This will give an inac-
curate reading.
The spark plugs are double platinum and have a
recommended service life of 100,000 miles for normal
driving conditions per schedule A in this manual. The
spark plugs have a recommended service life of
75,000 miles for severe driving conditions per sched-
ule B in this manual. A thin platinum pad is welded
to both electrode ends as show in (Fig. 14). Extreme
care must be used to prevent spark plug cross
threading, mis-gaping and ceramic insulator damage
during plug removal and installation.
Fig. 13 Knock Sensor
1 - GENERATOR
2 - INTAKE MANIFOLD
3 - KNOCK SENSOR
4-STARTER
Fig. 14 Platinum Pads
1 - APPLY ANTI-SEIZE COMPOUND HERE ONLY
2 - PLATINUM SPARK SURFACE
8I - 8 IGNITION CONTROLRS
KNOCK SENSOR (Continued)
Page 2675 of 4284

(3) Start engine and record oil pressure. Refer to
Specifications for correct oil pressure requirements.
(Refer to 9 - ENGINE - SPECIFICATIONS)
CAUTION: If oil pressure is 0 at idle, do not perform
the 3000 RPM test
(4) If oil pressure is 0 at idle. Shut off engine,
check for pressure relief valve stuck open, a clogged
oil pick-up screen or a damaged oil pick-up tube
O-ring.
(5) After test is complete, remove test gauge and
fitting.
(6) Install oil pressure switch and connector. (Refer
to 9 - ENGINE/LUBRICATION/OIL PRESSURE
SENSOR/SWITCH - INSTALLATION)
OIL
ENGINE OIL LEVEL CHECK
The best time to check engine oil level is after it
has sat overnight, or if the engine has been running,
allow the engine to be shut off for at least 5 minutes
before checking oil level.
Checking the oil while the vehicle is on level
ground will improve the accuracy of the oil level
reading. Remove dipstick and observe oil level. Add
oil only when the level is at or below the ADD mark
(Fig. 88).
STANDARD PROCEDURE - ENGINE OIL AND
FILTER CHANGE
Change engine oil at mileage and time intervals
described in the Maintenance Schedule. (Refer to
LUBRICATION & MAINTENANCE/MAINTE-
NANCE SCHEDULES - DESCRIPTION)
WARNING: NEW OR USED ENGINE OIL CAN BE
IRRITATING TO THE SKIN. AVOID PROLONGED OR
REPEATED SKIN CONTACT WITH ENGINE OIL.
CONTAMINANTS IN USED ENGINE OIL, CAUSED BY
INTERNAL COMBUSTION, CAN BE HAZARDOUS TO
YOUR HEALTH. THOROUGHLY WASH EXPOSED
SKIN WITH SOAP AND WATER. DO NOT WASH
SKIN WITH GASOLINE, DIESEL FUEL, THINNER, OR
SOLVENTS, HEALTH PROBLEMS CAN RESULT. DONOT POLLUTE, DISPOSE OF USED ENGINE OIL
PROPERLY. CONTACT YOUR DEALER OR GOVERN-
MENT AGENCY FOR LOCATION OF COLLECTION
CENTER IN YOUR AREA.
Run engine until achieving normal operating tem-
perature.
(1) Position the vehicle on a level surface and turn
engine off.
(2) Hoist and support vehicle on safety stands.
Refer to Hoisting and Jacking Recommendations.
(Refer to LUBRICATION & MAINTENANCE/HOIST-
ING - STANDARD PROCEDURE)
(3) Remove oil fill cap.
(4) Place a suitable drain pan under crankcase
drain.
(5) Remove drain plug from crankcase and allow
oil to drain into pan. Inspect drain plug threads for
stretching or other damage. Replace drain plug and
gasket if damaged.
(6) Remove oil filter. (Refer to 9 - ENGINE/LUBRI-
CATION/OIL FILTER - REMOVAL)
(7) Install and tighten drain plug in crankcase.
(8) Install new oil filter. (Refer to 9 - ENGINE/LU-
BRICATION/OIL FILTER - INSTALLATION)
(9) Lower vehicle and fill crankcase with specified
type and amount of engine oil. (Refer to LUBRICA-
TION & MAINTENANCE/FLUID TYPES -
DESCRIPTION)
(10) Install oil fill cap.
(11) Start engine and inspect for leaks.
(12) Stop engine and inspect oil level.
NOTE: Care should be exercised when disposing
used engine oil after it has been drained from a
vehicle engine. Refer to the WARNING listed above.
OIL FILTER
DESCRIPTION
The engine oil filter (Fig. 89) is a high quality full-
flow, disposable type. Replace the oil filter with a
Mopartor the equivalent.
REMOVAL
(1) Raise vehicle on hoist.
(2) Position an oil collecting container under oil fil-
ter location.
CAUTION: When servicing the oil filter avoid
deforming the filter can by installing the remove/in-
stall tool band strap against the can to base lock
seam. The lock seam joining the can to the base is
reinforced by the base plate.
Fig. 88 Oil Level
1 - ENGINE OIL LEVEL DIPSTICK
RSENGINE 2.4L9-51
LUBRICATION (Continued)
Page 2756 of 4284
OIL
STANDARD PROCEDURE - ENGINE OIL AND
FILTER CHANGE
Change engine oil at mileage and time intervals
described in the Maintenance Schedule. (Refer to
LUBRICATION & MAINTENANCE/MAINTE-
NANCE SCHEDULES - DESCRIPTION)
WARNING: NEW OR USED ENGINE OIL CAN BE
IRRITATING TO THE SKIN. AVOID PROLONGED OR
REPEATED SKIN CONTACT WITH ENGINE OIL.
CONTAMINANTS IN USED ENGINE OIL, CAUSED BY
INTERNAL COMBUSTION, CAN BE HAZARDOUS TO
YOUR HEALTH. THOROUGHLY WASH EXPOSED
SKIN WITH SOAP AND WATER. DO NOT WASH
SKIN WITH GASOLINE, DIESEL FUEL, THINNER, OR
SOLVENTS, HEALTH PROBLEMS CAN RESULT. DO
NOT POLLUTE, DISPOSE OF USED ENGINE OIL
PROPERLY. CONTACT YOUR DEALER OR GOVERN-
MENT AGENCY FOR LOCATION OF COLLECTION
CENTER IN YOUR AREA.
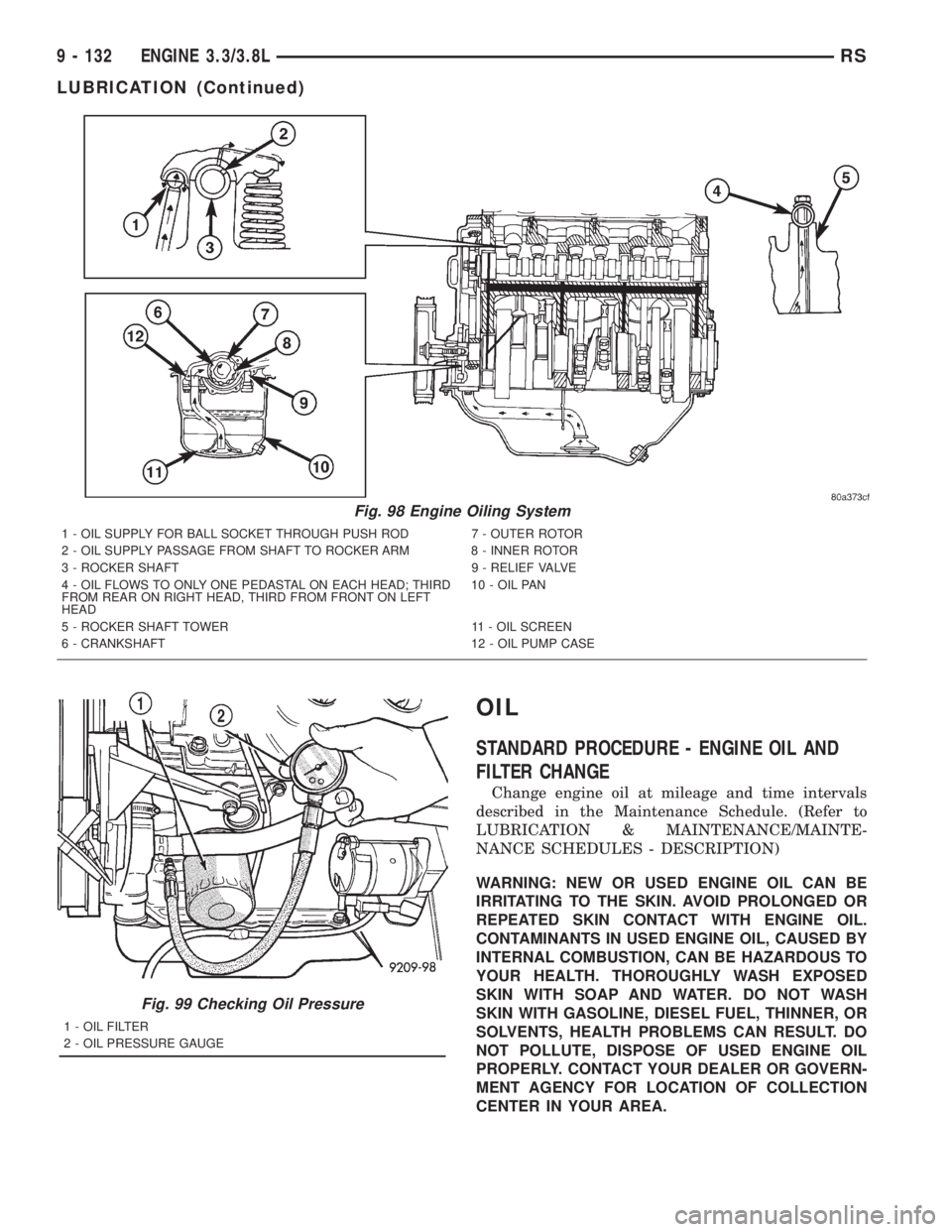
Fig. 98 Engine Oiling System
1 - OIL SUPPLY FOR BALL SOCKET THROUGH PUSH ROD 7 - OUTER ROTOR
2 - OIL SUPPLY PASSAGE FROM SHAFT TO ROCKER ARM 8 - INNER ROTOR
3 - ROCKER SHAFT 9 - RELIEF VALVE
4 - OIL FLOWS TO ONLY ONE PEDASTAL ON EACH HEAD; THIRD
FROM REAR ON RIGHT HEAD, THIRD FROM FRONT ON LEFT
HEAD10 - OIL PAN
5 - ROCKER SHAFT TOWER 11 - OIL SCREEN
6 - CRANKSHAFT 12 - OIL PUMP CASE
Fig. 99 Checking Oil Pressure
1 - OIL FILTER
2 - OIL PRESSURE GAUGE
9 - 132 ENGINE 3.3/3.8LRS
LUBRICATION (Continued)