2001 CHRYSLER VOYAGER load capacity
[x] Cancel search: load capacityPage 3374 of 4284
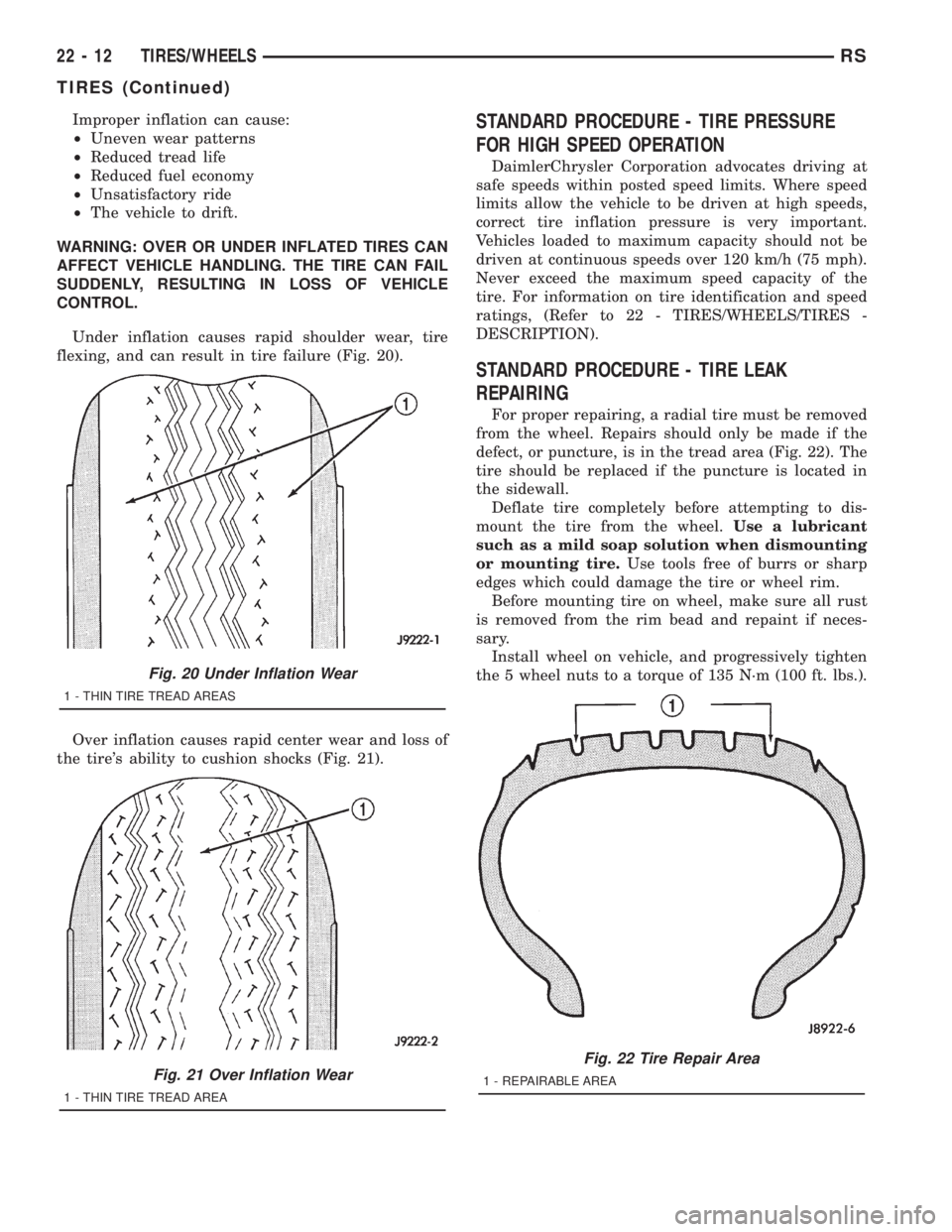
Improper inflation can cause:
²Uneven wear patterns
²Reduced tread life
²Reduced fuel economy
²Unsatisfactory ride
²The vehicle to drift.
WARNING: OVER OR UNDER INFLATED TIRES CAN
AFFECT VEHICLE HANDLING. THE TIRE CAN FAIL
SUDDENLY, RESULTING IN LOSS OF VEHICLE
CONTROL.
Under inflation causes rapid shoulder wear, tire
flexing, and can result in tire failure (Fig. 20).
Over inflation causes rapid center wear and loss of
the tire's ability to cushion shocks (Fig. 21).STANDARD PROCEDURE - TIRE PRESSURE
FOR HIGH SPEED OPERATION
DaimlerChrysler Corporation advocates driving at
safe speeds within posted speed limits. Where speed
limits allow the vehicle to be driven at high speeds,
correct tire inflation pressure is very important.
Vehicles loaded to maximum capacity should not be
driven at continuous speeds over 120 km/h (75 mph).
Never exceed the maximum speed capacity of the
tire. For information on tire identification and speed
ratings, (Refer to 22 - TIRES/WHEELS/TIRES -
DESCRIPTION).
STANDARD PROCEDURE - TIRE LEAK
REPAIRING
For proper repairing, a radial tire must be removed
from the wheel. Repairs should only be made if the
defect, or puncture, is in the tread area (Fig. 22). The
tire should be replaced if the puncture is located in
the sidewall.
Deflate tire completely before attempting to dis-
mount the tire from the wheel.Use a lubricant
such as a mild soap solution when dismounting
or mounting tire.Use tools free of burrs or sharp
edges which could damage the tire or wheel rim.
Before mounting tire on wheel, make sure all rust
is removed from the rim bead and repaint if neces-
sary.
Install wheel on vehicle, and progressively tighten
the 5 wheel nuts to a torque of 135 N´m (100 ft. lbs.).
Fig. 20 Under Inflation Wear
1 - THIN TIRE TREAD AREAS
Fig. 21 Over Inflation Wear
1 - THIN TIRE TREAD AREA
Fig. 22 Tire Repair Area
1 - REPAIRABLE AREA
22 - 12 TIRES/WHEELSRS
TIRES (Continued)
Page 3375 of 4284

CLEANING - TIRES
Before delivery of a vehicle, remove the protective
coating on the tires with white sidewalls or raised
white letters. To remove the protective coating, apply
warm water and let it soak for a few minutes. After-
wards, scrub the coating away with a soft bristle
brush. Steam cleaning may also be used to remove
the coating.
CAUTION: DO NOT use gasoline, mineral oil, oil-
based solvent or a wire brush for cleaning.
WHEELS
DESCRIPTION - WHEEL
Original equipment wheels are designed for proper
operation at all loads up to the specified maximum
vehicle capacity.
All models use either steel or aluminum drop-cen-
ter wheels. Every wheel has raised sections between
the rim flanges and rim drop well called safety
humps (Fig. 23). Initial inflation of the tires forces
the bead over these raised sections. In case of air
loss, the safety humps hold the tire in position on the
wheel until the vehicle can be brought to a safe stop.
Cast aluminum wheels require special balance
weights to fit on the flange of the rim (Fig. 24).
When wheel alignment is necessary on a vehicle
with cast aluminum wheels, special wheel clamps are
required to avoid damage to the wheel's finish.The wheel studs and nuts are designed for specific
wheel applications and must be replaced with equiv-
alent parts.
All aluminum wheels have wheel mounting (lug)
nuts with an enlarged nose. This enlarged nose is
necessary to ensure proper retention of the wheels.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - WHEEL
INSPECTION
Inspect wheels for:
²Excessive runout
²Dents, cracks or irregular bends
²Damaged wheel stud (lug) holes
²Air Leaks
NOTE: Do not attempt to repair a wheel by hammer-
ing, heating or welding.
If a wheel is damaged, an original equipment
replacement wheel should be used. When obtaining
replacement wheels, they should be equivalent in
load carrying capacity. The diameter, width, offset,
pilot hole and bolt circle of the wheel should be the
same as the original wheel.
WARNING: FAILURE TO USE EQUIVALENT
REPLACEMENT WHEELS MAY ADVERSELY
AFFECT THE SAFETY AND HANDLING OF THE
VEHICLE.
WARNING: REPLACEMENT WITH USED WHEELS IS
NOT RECOMMENDED. THE SERVICE HISTORY OF
THE WHEEL MAY HAVE INCLUDED SEVERE TREAT-
MENT OR VERY HIGH MILEAGE. THE RIM COULD
FAIL WITHOUT WARNING.
Fig. 23 Safety Rim
1 - TIRE
2 - WELL
3 - SAFETY HUMPS
4 - FLANGE
Fig. 24 Styled Aluminum Wheel Weight
1 - TIRE
2 - WHEEL
3 - STYLED WHEEL WEIGHT
RSTIRES/WHEELS22-13
TIRES (Continued)
Page 3651 of 4284

(11) On models with the 3.3L and 3.8L engines
only, loosely install the three screws and one nut that
secure the compressor to the engine. Tighten each of
the fasteners using the following sequence to 54 N´m
(40 ft. lbs.).
²The upper screw at the rear of the compressor.
²The lower screw at the rear of the compressor.
²The lower screw at the front of the compressor.
²The upper nut at the front of the compressor.
(12) On models with the 3.3L and 3.8L engines
only, engage the retainer on the engine wire harness
compressor clutch coil take out with the bracket on
the top of the compressor.
(13) Reconnect the engine wire harness connector
for the compressor clutch coil to the coil pigtail wire
connector on the top of the compressor.
(14) Reinstall the serpentine accessory drive belt
onto the front of the engine. (Refer to 7 - COOLING/
ACCESSORY DRIVE/DRIVE BELTS - 2.4L -
INSTALLATION) or (Refer to 7 - COOLING/ACCES-
SORY DRIVE/DRIVE BELTS - 3.3L/3.8L - INSTAL-
LATION).
(15) Lower the vehicle.
(16) Reconnect the battery negative cable.
(17) If a new clutch plate and/or clutch pulley are
being installed, the new clutch components must be
burnished. (Refer to 24 - HEATING & AIR CONDI-
TIONING/CONTROLS - FRONT/COMPRESSOR
CLUTCH - STANDARD PROCEDURE - COMPRES-
SOR CLUTCH BREAK-IN).
COMPRESSOR CLUTCH COIL
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - COMPRESSOR
CLUTCH COIL
The air conditioning compressor clutch coil electri-
cal circuit is controlled by the Powertrain Control
Module (PCM) through the compressor clutch relay,
which is located in the Intelligent Power Module
(IPM) in the engine compartment near the battery.
Begin testing of a suspected compressor clutch coil
problem by performing the preliminary checks.
PRELIMINARY CHECKS
(1) If the compressor clutch will not engage, verify
the refrigerant charge level. (Refer to 24 - HEATING
& AIR CONDITIONING/PLUMBING - FRONT/RE-
FRIGERANT - DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING -
REFRIGERANT CHARGE LEVEL). If the refriger-
ant charge level is OK, go to Step 2. If the refriger-
ant charge level is not OK, adjust the refrigerant
charge as required.
(2) If the a/c compressor clutch still will not
engage, disconnect the headlamp and dash wire har-
ness connector for the A/C pressure transducer andcheck for battery current at the connector with the
engine running and the heater-A/C control set to the
A/C mode. If OK, go to TESTS . If not OK, use a
DRBIIItscan tool to perform further diagnosis. Refer
to the appropriate diagnostic information.
TESTS
(1) Verify the battery state of charge. (Refer to 8 -
ELECTRICAL/BATTERY SYSTEM/BATTERY -
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING).
(2) Connect an ammeter (0 to 10 ampere scale
selected) in series with the clutch coil feed terminal.
Connect a voltmeter (0 to 20 volt scale selected) to
measure voltage across the battery and the clutch
coil.
(3) With the heater-A/C control in the A/C mode
and the blower at low speed, start the engine and
allow it to run at a normal idle speed.
(4) The compressor clutch should engage immedi-
ately, and the clutch coil voltage should be within
two volts of the battery voltage. If the coil voltage is
not within two volts of battery voltage, test the
clutch coil feed circuit for excessive voltage drop. If
the compressor clutch does not engage, use a
DRBIIItscan tool to perform further diagnosis. Refer
to the appropriate diagnostic information.
(5) With the ambient temperature at 21É C (70É F),
the compressor clutch coil is acceptable if the current
draw is 2.0 to 3.7 amperes at 11.5 to 12.5 volts at the
clutch coil. If the voltage is more than 12.5 volts, add
electrical loads by turning on electrical accessories
until the voltage reads below 12.5 volts.
(a) If the compressor clutch coil current reading
is zero, the coil is open and must be replaced.
(b) If the compressor clutch coil current reading
is four amperes or more, the coil is shorted and
must be replaced.
COMPRESSOR CLUTCH RELAY
DESCRIPTION
The compressor clutch relay (Fig. 18) is a Interna-
tional Standards Organization (ISO) micro-relay.
Relays conforming to the ISO specifications have
common physical dimensions, current capacities, ter-
minal patterns, and terminal functions. The ISO
micro-relay terminal functions are the same as a con-
ventional ISO relay. However, the ISO micro-relay
terminal pattern (or footprint) is different, the cur-
rent capacity is lower, and the physical dimensions
are smaller than those of the conventional ISO relay.
The compressor clutch relay is located in the Intelli-
gent Power Module (IPM), which is in the engine
compartment near the battery. See the fuse and relay
layout map molded into the inner surface of the IPM
RSCONTROLS - FRONT24-21
COMPRESSOR CLUTCH (Continued)
Page 3805 of 4284

important to block the wheels on front-wheel drive
vehicles; the parking brake does not hold the drive
wheels.
When servicing a vehicle, always wear eye pro-
tection, and remove any metal jewelry such as
watchbands or bracelets that might make an inad-
vertent electrical contact.
When diagnosing a powertrain system problem,
it is important to follow approved procedures where
applicable. These procedures can be found in ser-
vice manual procedures. Following these proce-
dures is very important to the safety of individuals
performing diagnostic tests.
4.2.2 VEHICLE PREPARATION FOR
TESTING
Make sure the vehicle being tested has a fully
charged battery. If it does not, false diagnostic codes
or error messages may occur.
4.2.3 SERVICING SUB ASSEMBLIES
Some components of the powertrain system are
intended to be serviced in assembly only. Attempt-
ing to remove or repair certain system sub-
components may result in personal injury and/or
improper system operation. Only those components
with approved repair and installation procedures in
the service manual should be serviced.
4.2.4 DRBIIITSAFETY INFORMATION
WARNING: EXCEEDING THE LIMITS OF THE
DRB MULTIMETER IS DANGEROUS. IT CAN
EXPOSE YOU TO SERIOUS INJURY.
CAREFULLY READ AND UNDERSTAND THE
CAUTIONS AND THE SPECIFICATION
LIMITS.
Follow the vehicle manufacturer 's service specifi-
cations at all times.
²Do not use the DRB if it has been damaged.
²Do not use the test leads if the insulation is
damaged or if metal is exposed.
²To avoid electrical shock, do not touch the test
leads, tips, or the circuit being tested.
²Choose the proper range and function for the
measurement. Do not try voltage or current mea-
surements that may exceed the rated capacity.
²Do not exceed the limits shown in the table below:
FUNCTION INPUT LIMIT
Volts 0 - 500 peak volts AC
0 - 500 volts DC
Ohms (resistance)* 0 - 1.12 megohms
FUNCTION INPUT LIMIT
Frequency Measured
Frequency Generated0-10kHz
Temperature -58 - 1100ÉF
-50 - 600ÉC
* Ohms cannot be measured if voltage is present.
Ohms can be measured only in a non-powered
circuit.
²Voltage between any terminal and ground must
not exceed 500v DC or 500v peak AC.
²Use caution when measuring voltage above 25v
DC or 25v AC.
²The circuit being tested must be protected by a
10A fuse or circuit breaker.
²Use the low current shunt to measure circuits up
to 10A. Use the high current clamp to measure
circuits exceeding 10A.
²When testing for the presence of voltage or cur-
rent, make sure the meter is functioning cor-
rectly. Take a reading of a known voltage or
current before accepting a zero reading.
²When measuring current, connect the meter in
series with the load.
²Disconnect the live test lead before disconnecting
the common test lead.
²When using the meter function, keep the DRBIIIt
away from spark plug or coil wires to avoid mea-
suring error from outside interference.
4.3 WARNINGS AND CAUTIONS
4.3.1 ROAD TEST WARNINGS
Some complaints will require a test drive as part
of the repair verification procedure. The purpose of
the test drive is to try to duplicate the diagnostic
code or symptom condition.
CAUTION: BEFORE ROAD TESTING A
VEHICLE, BE SURE THAT ALL
COMPONENTS ARE REASSEMBLED.
DURING THE TEST DRIVE, DO NOT TRY TO
READ THE DRBIIITSCREEN WHILE IN
MOTION. DO NOT HANG THE DRBIIITFROM
THE REAR VIEW MIRROR OR OPERATE IT
YOURSELF. HAVE AN ASSISTANT
AVAILABLE TO OPERATE THE DRBIIIT.
4.3.2 VEHICLE DAMAGE CAUTIONS
Before disconnecting any control module, make
sure the ignition is off. Failure to do so could
damage the module.
11
GENERAL INFORMATION
Page 4123 of 4284

information at the time of publication. The right is
reserved to make changes at any time without
notice.
4.2.1 TECHNICIAN SAFETY INFORMATION
WARNING: ENGINES PRODUCE CARBON
MONOXIDE THAT IS ODORLESS, CAUSES
SLOWER REACTION TIMES AND CAN LEAD
TO SERIOUS INJURY. WHEN THE ENGINE IS
OPERATING, KEEP SERVICE AREAS WELL
VENTILATED OR ATTACH THE VEHICLE
EXHAUST SYSTEM TO THE SHOP EXHAUST
REMOVAL SYSTEM.
Some operations in this manual require that
hydraulic tubes, hoses, and fittings, disconnected
for inspection or testing purposes. These systems,
when fully charged contains fluid at high pressure.
Before disconnecting any hydraulic tubes, hoses or
fittings, be sure that the system is fully depressur-
ized.
When servicing a vehicle, always wear eye pro-
tection and remove any metal jewelry such as
watchbands or bracelets that might make an inad-
vertent electrical contact.
When diagnosing a transmission system problem,
it is important to follow approved procedures where
applicable. Following these procedures is very im-
portant to the safety of individuals performing
diagnostic tests.
4.2.2 VEHICLE PREPARATION FOR
TESTING
Make sure the vehicle being tested has a fully
charged battery. If it does not, false diagnostic codes
or error messages may occur. It is extremely impor-
tant that accurate shift lever position data be avail-
able to the TCM. The accuracy of any diagnostic
trouble code found in memory is doubtful unless the
Shift Lever Test, performed on the DRBtScan Tool,
passes.
4.2.3 SERVICING SUB-ASSEMBLIES
Some components of the powertrain system are
intended to be serviced in assembly only. Attempt-
ing to remove or repair certain system subcompo-
nents may result in personal injury and/or im-
proper system operation. Only those components
with approved repair and installation procedures in
the service instructions should be serviced.
4.2.4 DRBIIITSAFETY INSTRUCTIONS
WARNING: EXCEEDING THE LIMITS OF THE
DRBTMULTIMETER IS DANGEROUS. IT CAN
EXPOSE YOU TO SERIOUS OR POSSIBLY
FATAL INJURY. CAREFULLY READ AND
UNDERSTAND THE CAUTIONS AND THE
SPECIFICATION LIMITS.
²Follow the vehicle manufacturer 's service speci-
fications at all times.
²Do not use the DRBtif it has been damaged.
²Do not use the test leads if the insulation is
damaged or if metal is exposed.
²To avoid electrical shock, do not touch the test
leads, tips, or the circuit being tested.
²Choose the proper range and function for the
measurement. Do not try voltage or current mea-
surements that may exceed the rated capacity.
²Do not exceed the limits shown in the table.
FUNCTION INPUT LIMIT
Volts 0 - 500 peak volts AC
0 - 500 volts DC
Ohms (resistance)* 0 - 1.12 megohms
Frequency Measured
Frequency Generated0-10kHz
Temperature -58 - 1100ÉF
-50 - 600ÉC
*Ohms cannot be measured if voltage is present.
Ohms can be measured only in a non-powered
circuit.
²Voltage between any terminal and ground must
not exceed 500v peak AC.
²Use caution when measuring voltage above 25v
DC or 25v AC.
²The circuit being tested must be protected by a
10A fuse or circuit breaker.
²Use the low current shunt to measure circuits up
to 10A. Use the high current clamp to measure
circuits exceeds 10A.
²When testing for the presence of voltage or cur-
rent, make sure the meter is functioning cor-
rectly. Take a reading of a known voltage or
current before attempting a zero reading.
²When measuring current, connect the meter in
series with the load.
²Disconnect the live test lead before disconnecting
the common test lead.
²When using the meter function, keep the DRBt
away from spark plug or coil wires to avoid
measuring error from outside interference.
19
GENERAL INFORMATION