2001 CHRYSLER VOYAGER tow
[x] Cancel search: towPage 3079 of 4284
A conventional mechanical interlock system is also
used. This system manually prohibits shifter move-
ment when the ignition switch is in the LOCK or
ACC positions. Solenoid operation is not required in
these key positions. When the ignition key is in the
OFF position, the gearshift lever is unrestricted, and
able to move into any gear position (during towing,
dead battery, etc.).
For intended BTSI system operation, refer to the
following chart:
ACTION EXPECTED RESPONSE
1. Turn key to the9OFF9
position.1. Shifter CAN be shifted
out of park.
2. Turn key to the
9ON/RUN9position.2. Shifter CANNOT be
shifted out of park.
3. Turn key to the
9ON/RUN9position and
depress the brake pedal.3. Shifter CAN be shifted
out of park.
4. Leave shifter in any
gear and try to return key
to the9LOCK9or9ACC9
position.4. Key cannot be
returned to the9LOCK9or
9ACC9position.
5. Return shifter to
9PARK9and try to remove
the key.5. Key can be removed
(after returning to9LOCK9
position).
6. With the key removed,
try to shift out of9PARK9.6. Shifter cannot be
shifted out of9PARK9.
NOTE: Any failure to meet these expected
responses requires system adjustment or repair.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - BRAKE/
TRANSMISSION SHIFT INTERLOCK SOLENOID
For intended BTSI system operation, refer to the
following chart:
ACTION EXPECTED RESPONSE
1. Turn key to the9OFF9
position.1. Shifter CAN be shifted
out of park.
2. Turn key to the
9ON/RUN9position.2. Shifter CANNOT be
shifted out of park.
3. Turn key to the
9ON/RUN9position and
depress the brake pedal.3. Shifter CAN be shifted
out of park.
4. Leave shifter in any
gear and try to return key
to the9LOCK9or9ACC9
position.4. Key cannot be
returned to the9LOCK9or
9ACC9position.
5. Return shifter to
9PARK9and try to remove
the key.5. Key can be removed
(after returning to9LOCK9
position).
6. With the key removed,
try to shift out of9PARK9.6. Shifter cannot be
shifted out of9PARK9.
NOTE: Any failure to meet these expected
responses requires system repair. Refer to the
appropriate Diagnostic Information.
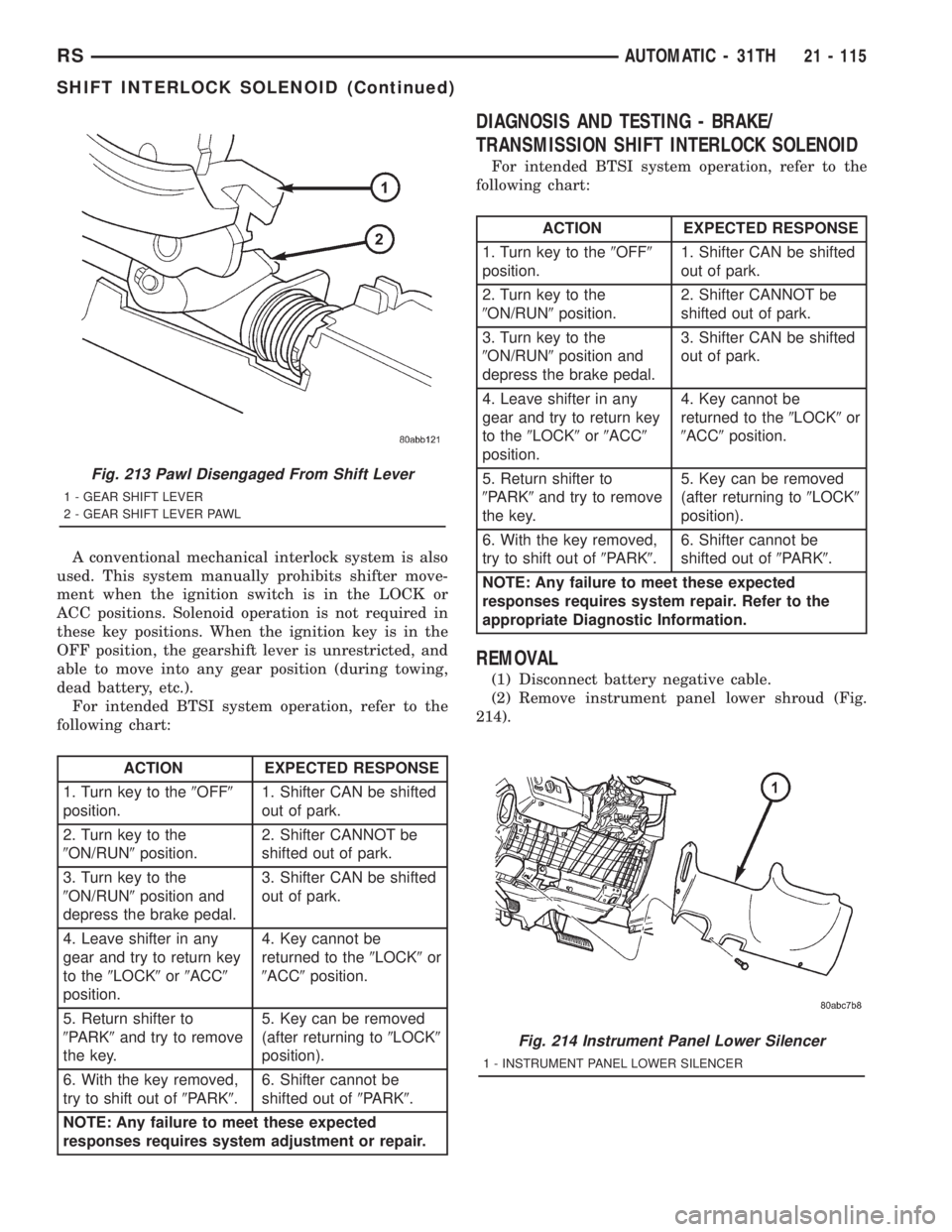
REMOVAL
(1) Disconnect battery negative cable.
(2) Remove instrument panel lower shroud (Fig.
214).
Fig. 213 Pawl Disengaged From Shift Lever
1 - GEAR SHIFT LEVER
2 - GEAR SHIFT LEVER PAWL
Fig. 214 Instrument Panel Lower Silencer
1 - INSTRUMENT PANEL LOWER SILENCER
RSAUTOMATIC - 31TH21 - 115
SHIFT INTERLOCK SOLENOID (Continued)
Page 3087 of 4284
OPERATION
The converter impeller (Fig. 235) (driving member),
which is integral to the converter housing and bolted
to the engine drive plate, rotates at engine speed.
The converter turbine (driven member), which reacts
from fluid pressure generated by the impeller, rotates
and turns the transmission input shaft.
TURBINE
As the fluid that was put into motion by the impel-
ler blades strikes the blades of the turbine, some of
the energy and rotational force is transferred into the
turbine and the input shaft. This causes both of them
(turbine and input shaft) to rotate in a clockwise
direction following the impeller. As the fluid is leav-
ing the trailing edges of the turbine's blades it con-
tinues in a ªhinderingº direction back toward the
impeller. If the fluid is not redirected before it strikes
the impeller, it will strike the impeller in such a
direction that it would tend to slow it down.
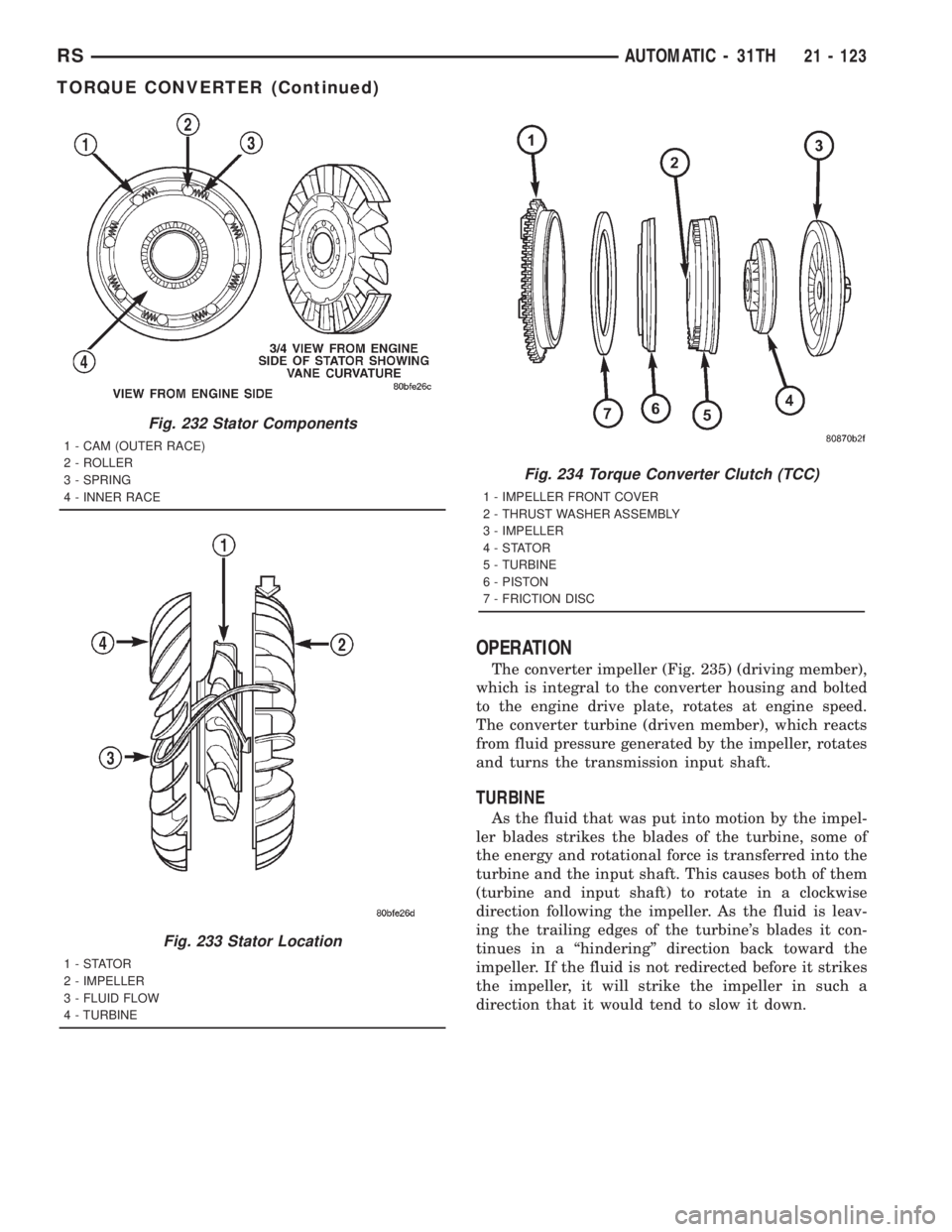
Fig. 232 Stator Components
1 - CAM (OUTER RACE)
2 - ROLLER
3 - SPRING
4 - INNER RACE
Fig. 233 Stator Location
1-STATOR
2 - IMPELLER
3 - FLUID FLOW
4 - TURBINE
Fig. 234 Torque Converter Clutch (TCC)
1 - IMPELLER FRONT COVER
2 - THRUST WASHER ASSEMBLY
3 - IMPELLER
4-STATOR
5 - TURBINE
6 - PISTON
7 - FRICTION DISC
RSAUTOMATIC - 31TH21 - 123
TORQUE CONVERTER (Continued)
Page 3115 of 4284
CLEANING
Clean the valve body components in a parts clean-
ing solution only. Do not use gasoline, kerosene, or
any type of caustic solution. Dry the parts with com-
pressed air. Make sure all passages are clean and
free from obstructions.
NOTE: Do not use rags or shop towels to wipe off
valve body components. Lint from these materials
will adhere to the valve body components. Lint will
interfere with valve operation and may clog filters
and fluid passages.
Minor distortion of a valve body mating surface
may be corrected by smoothing the surface with cro-
cus cloth. The cloth should be in sheet form and be
positioned on a surface plate, sheet of plate glass, or
equally flat surface. However, if distortion is severeor any surfaces are heavily scored, the valve body
will have to be replaced.
CAUTION: Many of the valve body valves and plugs
are made of coated aluminum. Aluminum compo-
nents can be identified by the dark color of the spe-
cial coating applied to the surface (or by testing
with a magnet). DO NOT polish or sand aluminum
valves or plugs with any type of material, or under
any circumstances. This practice might damage the
special coating and cause the valves and plugs to
stick and bind.
Aluminum valves and plugs should not be sanded
or polished under any circumstances. However, minor
burrs or scratches on steel valves and plugs can be
removed with crocus cloth but do not round off the
valve or plug edges. Squareness of these edges is
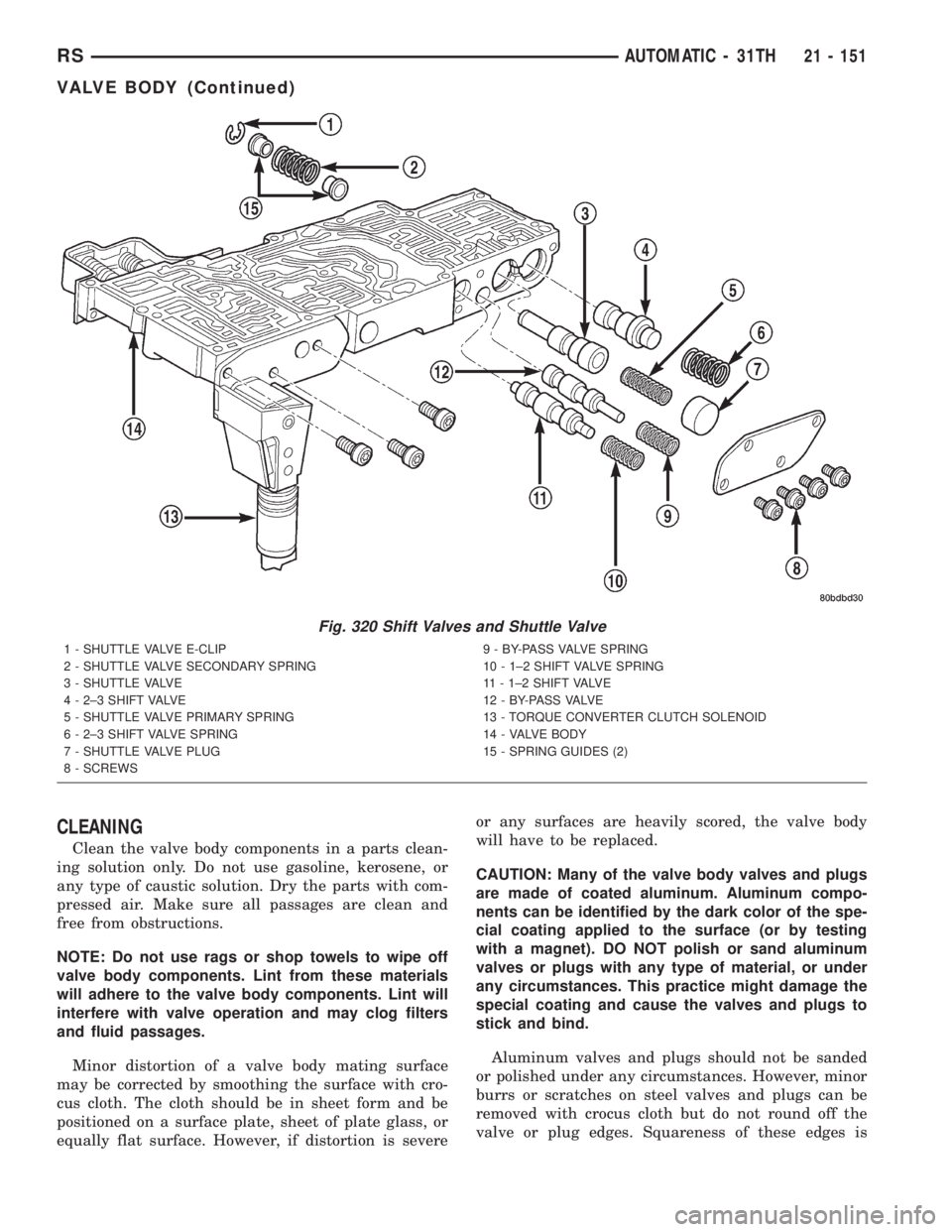
Fig. 320 Shift Valves and Shuttle Valve
1 - SHUTTLE VALVE E-CLIP
2 - SHUTTLE VALVE SECONDARY SPRING
3 - SHUTTLE VALVE
4 - 2±3 SHIFT VALVE
5 - SHUTTLE VALVE PRIMARY SPRING
6 - 2±3 SHIFT VALVE SPRING
7 - SHUTTLE VALVE PLUG
8 - SCREWS9 - BY-PASS VALVE SPRING
10 - 1±2 SHIFT VALVE SPRING
11 - 1±2 SHIFT VALVE
1 2 - B Y- PA S S VA LV E
13 - TORQUE CONVERTER CLUTCH SOLENOID
14 - VALVE BODY
15 - SPRING GUIDES (2)
RSAUTOMATIC - 31TH21 - 151
VALVE BODY (Continued)
Page 3169 of 4284

(55) Install cooler bypass valve with o-ring end
towards rear of case (Fig. 148).
(56) Install oil pump gasket (Fig. 149).(57) Install oil pump assembly (Fig. 150).
(58) Install oil pump-to-case bolts and torque to 27
N´m (20 ft. lbs.) (Fig. 151).
Fig. 148 Install Cooler Bypass Valve
1 - COOLER BYPASS VALVE
Fig. 149 Install Oil Pump Gasket
1 - PUMP GASKET
Fig. 150 Install Oil Pump
1 - OIL PUMP
2 - GASKET
Fig. 151 Install Pump-to-Case Bolts
1 - PUMP ATTACHING BOLTS
2 - PUMP HOUSING
RSAUTOMATIC - 41TE21 - 205
AUTOMATIC - 41TE (Continued)
Page 3229 of 4284
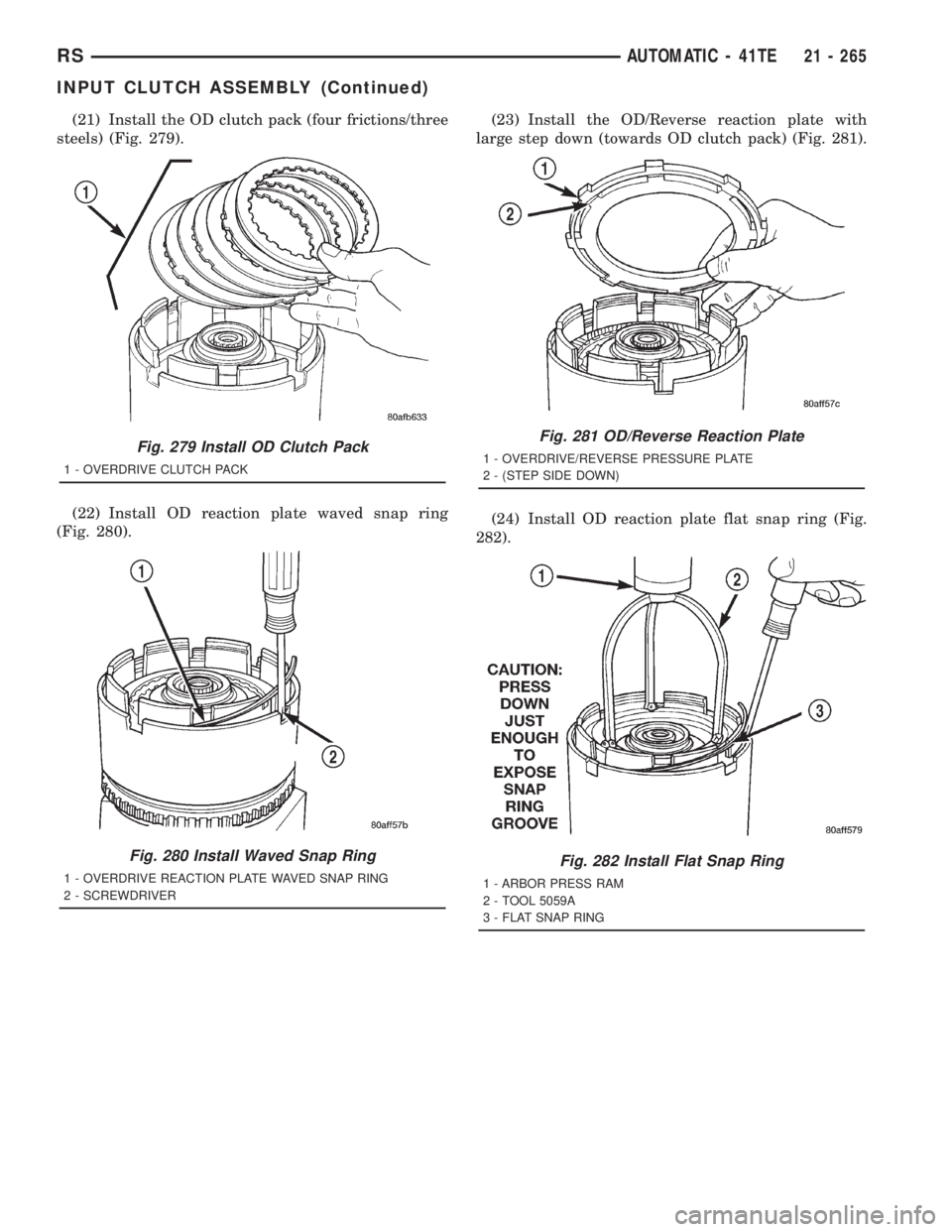
(21) Install the OD clutch pack (four frictions/three
steels) (Fig. 279).
(22) Install OD reaction plate waved snap ring
(Fig. 280).(23) Install the OD/Reverse reaction plate with
large step down (towards OD clutch pack) (Fig. 281).
(24) Install OD reaction plate flat snap ring (Fig.
282).
Fig. 279 Install OD Clutch Pack
1 - OVERDRIVE CLUTCH PACK
Fig. 280 Install Waved Snap Ring
1 - OVERDRIVE REACTION PLATE WAVED SNAP RING
2 - SCREWDRIVER
Fig. 281 OD/Reverse Reaction Plate
1 - OVERDRIVE/REVERSE PRESSURE PLATE
2 - (STEP SIDE DOWN)
Fig. 282 Install Flat Snap Ring
1 - ARBOR PRESS RAM
2 - TOOL 5059A
3 - FLAT SNAP RING
RSAUTOMATIC - 41TE21 - 265
INPUT CLUTCH ASSEMBLY (Continued)
Page 3230 of 4284

(25) Measure OD clutch pack clearance. Set up
dial indicator on top of the OD/Reverse reaction plate
as shown in (Fig. 283).
(26) Zero dial indicator and apply 30 psi (206 kPa)
air pressure to the overdrive clutch hose on Tool
8391. Measure and record OD clutch pack measure-
ment in four (4) places, 90É apart.
(27) Take average of four measurements and com-
pare with OD clutch pack clearance specification.
The overdrive (OD) clutch pack clearance is
1.07-3.25 mm (0.042-0.128 in.).
If not within specifications, the clutch is not
assembled properly. There is no adjustment for the
OD clutch clearance.
(28) Install reverse clutch pack (two frictions/one
steel) (Fig. 284).
(29) Install reverse clutch reaction plate with the
flat side down towards reverse clutch (Fig. 285).
(30) Tap reaction plate down to allow installation
of the reverse clutch snap ring. Install reverse clutch
snap ring (Fig. 286).(31) Pry up reverse reaction plate to seat against
snap ring (Fig. 287).
(32) Set up a dial indicator on the reverse clutch
pack as shown in (Fig. 288).
(33) Using moderate pressure, press down and
hold (near indicator) reverse clutch disc with screw-
driver or suitable tool and zero dial indicator (Fig.
289). When releasing pressure, indicator should
advance 0.005-0.010. as clutch pack relaxes.
Fig. 283 Measure OD Clutch Pack Clearance
1 - DIAL INDICATOR
2 - OD/REVERSE REACTION PLATE
Fig. 284 Install Reverse Clutch Pack
1 - REVERSE CLUTCH PLATE
2 - REVERSE CLUTCH DISCS
Fig. 285 Install Reaction Plate
1 - REVERSE CLUTCH REACTION PLATE (FLAT SIDE DOWN)
21 - 266 AUTOMATIC - 41TERS
INPUT CLUTCH ASSEMBLY (Continued)
Page 3237 of 4284

OPERATION
The Brake/Transmission Shift Interlock (BTSI)
Solenoid prevents the transmission shift lever from
being moved out of PARK (P) unless the brake pedal
is applied. The BTSI solenoid is hardwired to and
controlled by the Intelligent Power Module (IPM).
Battery voltage is applied to one side of the solenoid
with the ignition key is in either the ON/RUN or
START positions (Fig. 306). The ground side of the
solenoid is controlled by a driver within the IPM. It
relies on voltage supplied from the stop lamp switch
to the stop lamp sense circuit within the IPM to tell
when the brake pedal is depressed. When the brake
pedal is depressed, the ground circuit opens, de-ener-
gizing the solenoid. When the brake pedal is
released, the ground circuit is closed, energizing the
solenoid.
When the ignition key is in either the ON/RUN or
START positions, the BTSI solenoid is energized, and
the solenoid plunger hook pulls the shift lever pawl
into position, prohibiting the shift lever from moving
out of PARK (P) (Fig. 307). When the brake pedal is
depressed, the ground circuit opens, de-energizing
the solenoid. This moves the gearshift lever pawl out
of the way (Fig. 308), allowing the shift lever to be
moved into any gear position.
A conventional mechanical interlock system is also
used. This system manually prohibits shifter move-
ment when the ignition switch is in the LOCK or
ACC positions. Solenoid operation is not required in
these key positions. When the ignition key is in the
OFF position, the gearshift lever is unrestricted, and
able to move into any gear position (during towing,
dead battery, etc.).
Fig. 306 Ignition Key/Switch Positions
1 - ACC
2 - LOCK
3 - OFF
4 - ON/RUN
5-START
Fig. 307 Pawl Engaged to Shift Lever
1 - GEAR SHIFT LEVER
2 - GEAR SHIFT LEVER PAWL
Fig. 308 Pawl Disengaged From Shift Lever
1 - GEAR SHIFT LEVER
2 - GEAR SHIFT LEVER PAWL
RSAUTOMATIC - 41TE21 - 273
SHIFT INTERLOCK SOLENOID (Continued)
Page 3248 of 4284
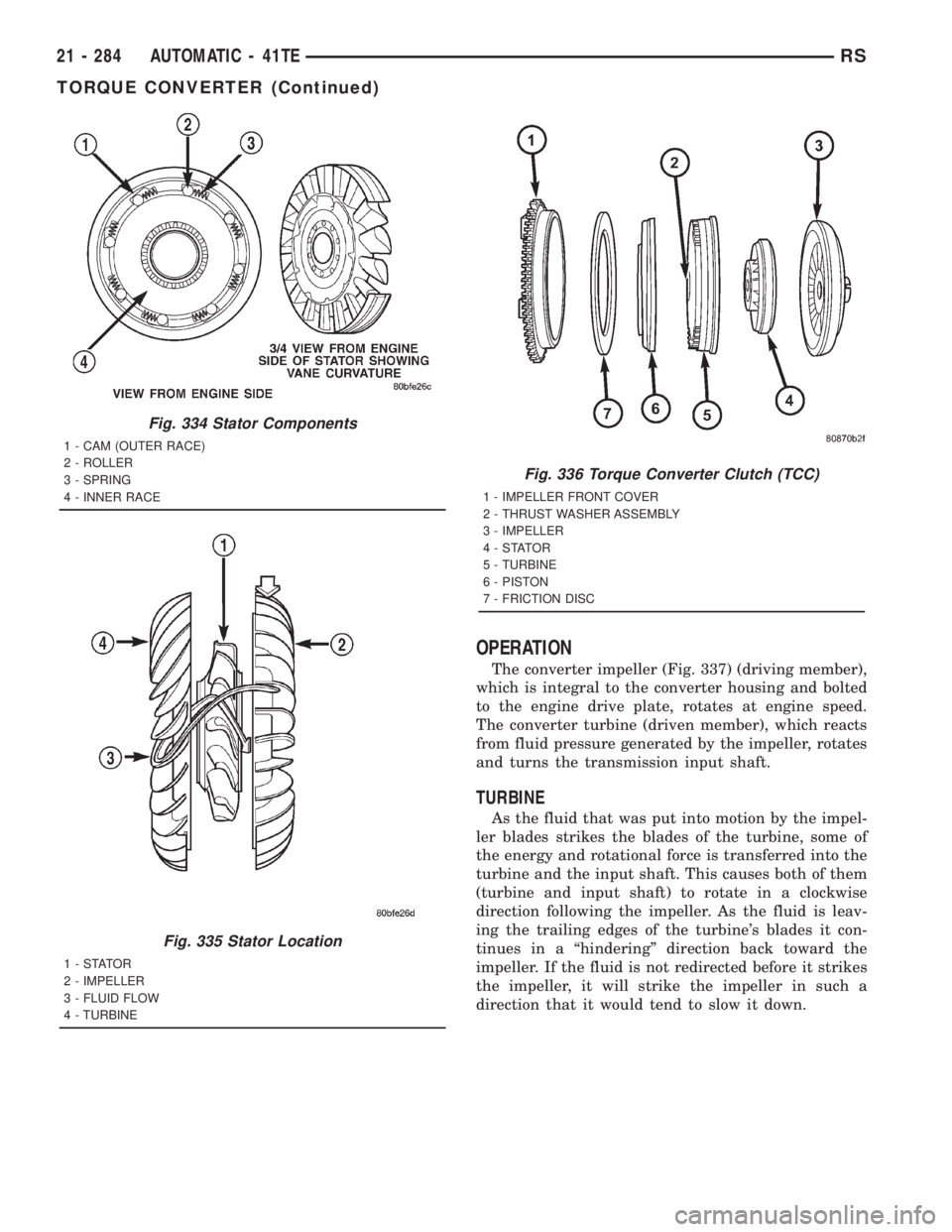
OPERATION
The converter impeller (Fig. 337) (driving member),
which is integral to the converter housing and bolted
to the engine drive plate, rotates at engine speed.
The converter turbine (driven member), which reacts
from fluid pressure generated by the impeller, rotates
and turns the transmission input shaft.
TURBINE
As the fluid that was put into motion by the impel-
ler blades strikes the blades of the turbine, some of
the energy and rotational force is transferred into the
turbine and the input shaft. This causes both of them
(turbine and input shaft) to rotate in a clockwise
direction following the impeller. As the fluid is leav-
ing the trailing edges of the turbine's blades it con-
tinues in a ªhinderingº direction back toward the
impeller. If the fluid is not redirected before it strikes
the impeller, it will strike the impeller in such a
direction that it would tend to slow it down.
Fig. 334 Stator Components
1 - CAM (OUTER RACE)
2 - ROLLER
3 - SPRING
4 - INNER RACE
Fig. 335 Stator Location
1-STATOR
2 - IMPELLER
3 - FLUID FLOW
4 - TURBINE
Fig. 336 Torque Converter Clutch (TCC)
1 - IMPELLER FRONT COVER
2 - THRUST WASHER ASSEMBLY
3 - IMPELLER
4-STATOR
5 - TURBINE
6 - PISTON
7 - FRICTION DISC
21 - 284 AUTOMATIC - 41TERS
TORQUE CONVERTER (Continued)