2001 CHRYSLER VOYAGER lock
[x] Cancel search: lockPage 3736 of 4284
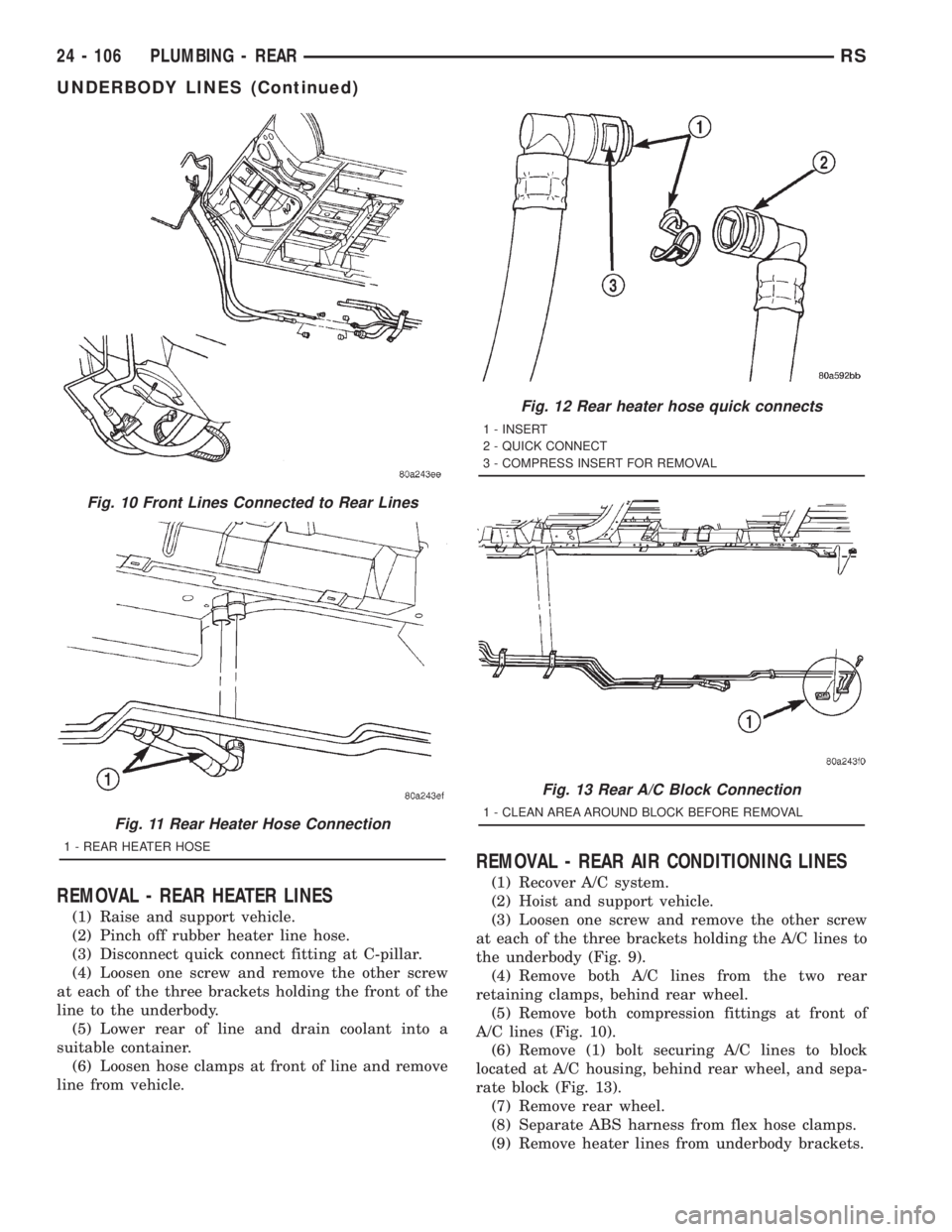
REMOVAL - REAR HEATER LINES
(1) Raise and support vehicle.
(2) Pinch off rubber heater line hose.
(3) Disconnect quick connect fitting at C-pillar.
(4) Loosen one screw and remove the other screw
at each of the three brackets holding the front of the
line to the underbody.
(5) Lower rear of line and drain coolant into a
suitable container.
(6) Loosen hose clamps at front of line and remove
line from vehicle.
REMOVAL - REAR AIR CONDITIONING LINES
(1) Recover A/C system.
(2) Hoist and support vehicle.
(3) Loosen one screw and remove the other screw
at each of the three brackets holding the A/C lines to
the underbody (Fig. 9).
(4) Remove both A/C lines from the two rear
retaining clamps, behind rear wheel.
(5) Remove both compression fittings at front of
A/C lines (Fig. 10).
(6) Remove (1) bolt securing A/C lines to block
located at A/C housing, behind rear wheel, and sepa-
rate block (Fig. 13).
(7) Remove rear wheel.
(8) Separate ABS harness from flex hose clamps.
(9) Remove heater lines from underbody brackets.
Fig. 10 Front Lines Connected to Rear Lines
Fig. 11 Rear Heater Hose Connection
1 - REAR HEATER HOSE
Fig. 12 Rear heater hose quick connects
1 - INSERT
2 - QUICK CONNECT
3 - COMPRESS INSERT FOR REMOVAL
Fig. 13 Rear A/C Block Connection
1 - CLEAN AREA AROUND BLOCK BEFORE REMOVAL
24 - 106 PLUMBING - REARRS
UNDERBODY LINES (Continued)
Page 3737 of 4284

(10) Pinch off rubber heater line hoses at front of
vehicle.
(11) Loosen hose clamps at front of heater lines
and allow them to hang from vehicle.
(12) Remove rear A/C lines from vehicle.
(13) Remove nylon wedge holding lines into rear
block (Fig. 14).INSTALLATION - REAR HEATER LINES
(1) Install line into underbody straps.
(2) Install line into front hose and install hose
clamp.
(3) Connect quick fitting at rear of line.
(4) Lower vehicle.
(5) Fill cooling system (Refer to 7 - COOLING -
STANDARD PROCEDURE).
INSTALLATION - REAR AIR CONDITIONING
LINES
(1) Before installation, replace all O-rings and gas-
kets. Coat all sealing surfaces with approved wax-
free refrigerant oil.
(2) Install A/C line into rear block with nylon
wedge.
(3) Install A/C lines into five underbody brackets.
(4) Connect forward compression fittings.
(5) Install bolt at sealing block to rear A/C hous-
ing.
(6) Install ABS harness into clips.
(7) Install heater hoses into underbody brackets.
(8) Install lines into front hoses and install hose
clamps.
(9) Lower vehicle.
(10) Evacuate and recharge system.
(11) Fill cooling system (Refer to 7 - COOLING -
STANDARD PROCEDURE).
Fig. 14 UNDERBODY LINE WEDGES
1 - O-RING
2 - DISCHARGE LINE
3 - NYLON WEDGE
4 - SEALING BLOCK
5 - VISE
6 - SUCTION LINE
RSPLUMBING - REAR24 - 107
UNDERBODY LINES (Continued)
Page 3758 of 4284

LEAK DETECTION PUMP MONITOR
The leak detection assembly incorporates two pri-
mary functions: it must detect a leak in the evapora-
tive system and seal the evaporative system so the
leak detection test can be run.
The primary components within the assembly are:
A three port solenoid that activates both of the func-
tions listed above; a pump which contains a switch,
two check valves and a spring/diaphragm, a canister
vent valve (CVV) seal which contains a spring loaded
vent seal valve.
Immediately after a cold start, between predeter-
mined temperature thresholds limits, the three port
solenoid is briefly energized. This initializes the
pump by drawing air into the pump cavity and also
closes the vent seal. During non test conditions the
vent seal is held open by the pump diaphragm
assembly which pushes it open at the full travel posi-
tion. The vent seal will remain closed while the
pump is cycling due to the reed switch triggering of
the three port solenoid that prevents the diaphragm
assembly from reaching full travel. After the brief
initialization period, the solenoid is de-energized
allowing atmospheric pressure to enter the pump
cavity, thus permitting the spring to drive the dia-
phragm which forces air out of the pump cavity and
into the vent system. When the solenoid is energized
and de energized, the cycle is repeated creating flow
in typical diaphragm pump fashion. The pump is con-
trolled in 2 modes:
Pump Mode:The pump is cycled at a fixed rate to
achieve a rapid pressure build in order to shorten the
overall test length.
Test Mode:The solenoid is energized with a fixed
duration pulse. Subsequent fixed pulses occur when
the diaphragm reaches the Switch closure point.
The spring in the pump is set so that the system
will achieve an equalized pressure of about 7.5º H20.
The cycle rate of pump strokes is quite rapid as the
system begins to pump up to this pressure. As the
pressure increases, the cycle rate starts to drop off. If
there is no leak in the system, the pump would even-
tually stop pumping at the equalized pressure. If
there is a leak, it will continue to pump at a rate rep-
resentative of the flow characteristic of the size of the
leak. From this information we can determine if the
leak is larger than the required detection limit (cur-
rently set at .020º orifice by CARB). If a leak is
revealed during the leak test portion of the test, the
test is terminated at the end of the test mode and no
further system checks will be performed.
After passing the leak detection phase of the test,
system pressure is maintained by turning on the
LDP's solenoid until the purge system is activated.
Purge activation in effect creates a leak. The cycle
rate is again interrogated and when it increases dueto the flow through the purge system, the leak check
portion of the diagnostic is complete.
The canister vent valve will unseal the system
after completion of the test sequence as the pump
diaphragm assembly moves to the full travel position.
Evaporative system functionality will be verified by
using the stricter evap purge flow monitor. At an
appropriate warm idle the LDP will be energized to
seal the canister vent. The purge flow will be clocked
up from some small value in an attempt to see a
shift in the 02 control system. If fuel vapor, indicated
by a shift in the 02 control, is present the test is
passed. If not, it is assumed that the purge system is
not functioning in some respect. The LDP is again
turned off and the test is ended.
DESCRIPTION - HIGH AND LOW LIMITS
The PCM compares input signal voltages from each
input device with established high and low limits for
the device. If the input voltage is not within limits
and other criteria are met, the PCM stores a diagnos-
tic trouble code in memory. Other diagnostic trouble
code criteria might include engine RPM limits or
input voltages from other sensors or switches that
must be present before verifying a diagnostic trouble
code condition.
OPERATION - SYSTEM
The Powertrain Control Module (PCM) monitors
many different circuits in the fuel injection, ignition,
emission and engine systems. If the PCM senses a
problem with a monitored circuit often enough to
indicate an actual problem, it stores a Diagnostic
Trouble Code (DTC) in the PCM's memory. If the
code applies to a non-emissions related component or
system, and the problem is repaired or ceases to
exist, the PCM cancels the code after 40 warmup
cycles. Diagnostic trouble codes that affect vehicle
emissions illuminate the Malfunction Indicator Lamp
(MIL). Refer to Malfunction Indicator Lamp in this
section.
Certain criteria must be met before the PCM
stores a DTC in memory. The criteria may be a spe-
cific range of engine RPM, engine temperature,
and/or input voltage to the PCM.
The PCM might not store a DTC for a monitored
circuit even though a malfunction has occurred. This
may happen because one of the DTC criteria for the
circuit has not been met.For example, assume the
diagnostic trouble code criteria requires the PCM to
monitor the circuit only when the engine operates
between 750 and 2000 RPM. Suppose the sensor's
output circuit shorts to ground when engine operates
above 2400 RPM (resulting in 0 volt input to the
PCM). Because the condition happens at an engine
25 - 8 EMISSIONS CONTROLRS
EMISSIONS CONTROL (Continued)
Page 3763 of 4284

LEAK DETECTION PUMP
DESCRIPTION
The leak detection pump is a device used to detect
a leak in the evaporative system.
The primary components within the leak detection
pump assembly are: a three-port leak detection sole-
noid valve, a pump assembly that includes a spring
loaded diaphragm, a reed switch which is used to
monitor the pump diaphragm movement (position),
two check valves, and a spring loaded vent seal
valve.
OPERATION - LDP
Immediately after a cold start, when the engine
temperature is between 40ÉF and 86ÉF, the 3 port
solenoid is briefly energized. This initializes the
pump by drawing air into the pump cavity and also
closes the vent seal. During non-test test conditions,
the vent seal is held open by the pump diaphragm
assembly which pushes it open at the full travel posi-
tion. The vent seal will remain closed while the
pump is cycling. This is due to the operation of the 3
port solenoid which prevents the diaphragm assem-
bly from reaching full travel. After the brief initial-
ization period, the solenoid is de-energized, allowing
atmospheric pressure to enter the pump cavity. This
permits the spring to drive the diaphragm which
forces air out of the pump cavity and into the vent
system. When the solenoid is energized and de-ener-
gized, the cycle is repeated creating flow in typical
diaphragm pump fashion. The pump is controlled in
2 modes:
PUMP MODE:The pump is cycled at a fixed rate
to achieve a rapid pressure build in order to shorten
the overall test time.
TEST MODE:The solenoid is energized with a
fixed duration pulse. Subsequent fixed pulses occur
when the diaphragm reaches the switch closure
point.
The spring in the pump is set so that the system
will achieve an equalized pressure of about 7.5 inches
of water.
When the pump starts, the cycle rate is quite high.
As the system becomes pressurized, pump rate drops.
If there is no leak, the pump will quit. If there is a
leak, the test is terminated at the end of the test
mode.
If there is no leak, the purge monitor is run. If the
cycle rate increases due to the flow through the
purge system, the test is passed and the diagnostic is
complete.
The canister vent valve will unseal the system
after completion of the test sequence as the pump
diaphragm assembly moves to the full travel position.
OPERATION - LDP SWITCH
The leak detection pump LDP assembly incorpo-
rates two primary functions: it detects a leak in the
evaporative system, and it seals the evaporative sys-
tem so that the required leak detection monitor test
can be run.
The three-port LDP solenoid valve is used to
expose either engine vacuum or atmospheric pressure
to the top side of the leak detection pump diaphragm.
When the LDP solenoid valve is denergized its port
(opening) to engine vacuum is blocked off. This
allows ambient air (atmospheric pressure) to enter
the top of the pump diaphragm. The spring load on
the diaphragm will push the diaphragm down, as
long as there is no pressure present in the rest of the
evaporative system. If there is sufficient evaporative
system pressure present, then the pump diaphragm
will stay in the9up9position. If the evaporative sys-
tem pressure decays, then the pump diaphragm will
eventually fall. The rate of this decent is dependent
upon the size of the evaporative system leak (Large
or small).
When the LDP solenoid valve is energized the port
(opening) to atmosphere is blocked off. At the same
time, the port to engine vacuum is opened. Engine
vacuum replaces atmospheric pressure. When engine
vacuum is sufficient, it over comes the spring pres-
sure load on the pump diaphragm and causes the
diaphragm to rise to its9up9position. The reed
switch will change state depending upon the position
of the pump diaphragm.
If the diaphragm is in the9up9position the reed
switch will be in its9open9state. This means that the
12 volt signal sense to the PCM is interrupted. Zero
volts is detected by the PCM. If the pump diaphragm
is in the9down9position the reed switch will be in its
9closed9state. 12 volts is sent to the PCM via the
switch sense circuit.
The check valves are one-way valves. The first
check valve is used to draw outside air into the lower
chamber of the LDP (the space that is below the
pump diaphragm). The second check valve is used to
vent this outside air, which has become pressurized
from the fall of the pump diaphragm, into the evap-
orative system.
The spring loaded vent seal valve, inside the LDP
is used to seal off the evaporative system. When the
pump diaphragm is in the9up9position the spring
pushes the vent seal valve closed. The vent seal valve
opens only when the pump diaphragm is in its9full
down9position. When the pump assembly is in its
pump mode the pump diaphragm is not allowed to
descend (fall) so far as to allow the vent seal valve to
open. This allows the leak detection pump to develop
the required pressure within the evaporative system
for system leak testing.
RSEVAPORATIVE EMISSIONS25-13
Page 3764 of 4284

A pressure build up within the evaporative system
may cause pressure on the lower side of the LDP dia-
phragm. This will cause the LDP diaphragm to
remain in its9up9position (stuck in the up position).
This condition can occur even when the solenoid
valve is deenergized. This condition can be caused by
previous cycling (pumping) of the LDP by the techni-
cian (dealer test). Another way that this condition is
created is immediately following the running of the
vehicle evaporative system monitor. In this case, the
PCM has not yet opened the proportional purge sole-
noid in order to vent the pressure that has been built
up in the evaporative system to the engine combus-
tion system. The technician will need to vent the
evaporative system pressure via the vehicle fuel filler
cap and its fuel filler secondary seal (if so equipped
in the fuel filler neck). This will allow the technician
to cycle the LDP and to watch switch state changes.
After passing the leak detection phase of the test,
system pressure is maintained until the purge sys-
tem is activated, in effect creating a leak. If the dia-
phragm falls (as is expected), causing the reed switch
to change state, then the diagnostic test is completed.
When one of the evaporative system leak monitors
begins its various tests, a test is performed to deter-
mine that no part of the evaporative system is
blocked. In this test, the LDP is cycled (pumped) a
calibrated (few) number of times. Pressure should not
build up in the evaporative system. If pressure is
present, then LDP diaphragm is forced to stay in its
9up9position. The reed switch now stays open and
the PCM senses this open (incorrect) state. The evap-
orative system monitor will fail the test because of a
detected obstruction within the system.
Possible causes:
²Open or shorted LDP switch sense circuit
²Leak Detection Pump switch failure
²Open fused ignition switch output
²Restricted, disconnected, or blocked manifold
vacuum source
²Obstruction of hoses or lines
²PCM failure
REMOVAL
(1) Disconnect the negative battery cable.
(2) Raise and support the vehicle.
(3) Remove 3 hoses (Fig. 4).
(4) Remove the electrical connector (Fig. 5) .
(5) Remove the 3 screws and remove LDP pump.
INSTALLATION
(1) Install LDP.
(2) Install the 3 screws and tighten (Fig. 5).
(3) Install the electrical connector.
(4) Install the 3 hoses (Fig. 4).(5) Lower vehicle.
(6) Connect the negative battery cable.
Fig. 4 LDP LOCATION
Fig. 5 LDP REMOVAL/INSTALLATION
25 - 14 EVAPORATIVE EMISSIONSRS
LEAK DETECTION PUMP (Continued)
Page 3767 of 4284

PCV VALVE
DESCRIPTION
The PCV valve contains a spring loaded plunger.
The plunger meters the amount of crankcase vapors
routed into the combustion chamber based on intake
manifold vacuum.
OPERATION
When the engine is not operating or during an
engine backfire, the spring forces the plunger back
against the seat. This prevents vapors from flowing
through the valve (Fig. 8).
When the engine is at idle or cruising, high mani-
fold vacuum is present. At these times manifold vac-
uum is able to completely compress the spring and
pull the plunger to the top of the valve (Fig. 9). In
this position there is minimal vapor flow through the
valve.During periods of moderate intake manifold vac-
uum the plunger is only pulled part way back from
the inlet. This results in maximum vapor flow
through the valve (Fig. 10).
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - PCV SYSTEM
INSPECTION
WARNING: APPLY PARKING BRAKE AND/OR
BLOCK WHEELS BEFORE PERFORMING ANY TEST
OR ADJUSTMENT WITH THE ENGINE OPERATING.
(1) With engine idling, remove the hose from the
PCV valve. If the valve is not plugged, a hissing
noise will be heard as air passes through the valve. A
strong vacuum should also be felt when a finger is
placed over the valve inlet.
(2) Install hose on PCV valve. Remove the
make-up air hose from the air plenum at the rear of
the engine. Hold a piece of stiff paper (parts tag)
loosely over the end of the make-up air hose.
(3)
After allowing approximately one minute for
crankcase pressure to reduce, the paper should draw up
against the hose with noticeable force. If the engine
does not draw the paper against the grommet after
installing a new valve, replace the PCV valve hose.
(4)Turn the engine off. Remove the PCV valve from
intake manifold. The valve should rattle when shaken.
(5) Replace the PCV valve and retest the system if
it does not operate as described in the preceding
tests.Do not attempt to clean the old PCV valve.
If the valve rattles, apply a light coating of Loctitet
Pipe Sealant With Teflon to the threads. Thread the
PCV valve into the manifold plenum and tighten to 7
N´m (60 in. lbs.) torque.
Fig. 7 PCV VALVE 2.4L
1 - PCV Valve
Fig. 8 Engine Off or Engine Backfire No Vapor Flow
Fig. 9 High Intake Manifold Vacuum Minimal Vapor
Flow
Fig. 10 Moderate Intake Manifold Vacuum Maximum
Vapor Flow
RSEVAPORATIVE EMISSIONS25-17
Page 3779 of 4284

EXHAUST GAS RECIRCULATION
TABLE OF CONTENTS
page page
EXHAUST GAS RECIRCULATION
DESCRIPTION............................3
OPERATION.............................3
VA LV E
DESCRIPTION............................3
OPERATION.............................4REMOVAL...............................4
INSTALLATION............................4
VALVE COOLER
DESCRIPTION............................4
REMOVAL...............................4
INSTALLATION............................5
EXHAUST GAS
RECIRCULATION
DESCRIPTION
The EGR system reduces oxides of nitrogen (NOx)
in the engine exhaust. This is accomplished by allow-
ing a predetermined amount of hot exhaust gas to
recirculate and dilute the incoming fuel/air mixture.
A malfunctioning EGR system can cause engine
stumble, sags, or hesitation, rough idle, engine stall-
ing and poor driveability.
OPERATION
The system consists of:
²An EGR valve assembly. The valve is located on
the rear of the engine above the exhaust manfiold.
²An EGR solenoid.The EGR solenoid controls the
ªon timeº of the EGR valve.
²The ECM operates the EGR solenoid. The ECM
is located inside the vehicle under the instrument
panel.
²An EGR tube connects a passage in the EGR
valve to the rear of the exhaust manifold.
²The vacuum pump supplies vacuum for the EGR
solenoid and the EGR valve. This pump also supplies
vacuum for operation of the power brake boosterb
and the heating and air conditioning system. The
pump is located internally in the front of the engine
block and is driven by the crankshaft gear.
²Vacuum lines and hoses connect the various
components.
When the ECM supplies a variable ground signal
to the EGR solenoid, EGR system operation starts to
occur. The ECM will monitor and determine when tosupply and remove this variable ground signal. This
will depend on inputs from the engine coolant tem-
perature, throttle position and engine speed sensors.
When the variable ground signal is supplied to the
EGR solenoid, vacuum from the vacuum pump will
be allowed to pass through the EGR solenoid and on
to the EGR valve with a connecting hose.
Exhaust gas recirculation will begin in this order
when:
²The ECM determines that EGR system opera-
tion is necessary.
²The engine is running to operate the vacuum
pump.
²A variable ground signal is supplied to the EGR
solenoid.
²Variable vacuum passes through the EGR sole-
noid to the EGR valve.
²The inlet seat (poppet valve) at the bottom of
the EGR valve opens to dilute and recirculate
exhaust gas back into the intake manifold.
The EGR system will be shut down by the ECM
after 60 seconds of continuous engine idling to
improve idle quality.
VA LV E
DESCRIPTION
The EGR system consists of (Fig. 1):
²EGR valve
²EGR tube
²Vacuum hoses
²EGR cooler
²EGR solenoid
RGEXHAUST GAS RECIRCULATION25a-3
Page 3791 of 4284

TABLE OF CONTENTS - Continued
P0325-KNOCK SENSOR #1 CIRCUIT......................................113
P0340-NO CAM SIGNAL AT PCM.........................................116
P0351-IGNITION COIL #1 PRIMARY CIRCUIT..............................121
P0352-IGNITION COIL #2 PRIMARY CIRCUIT..............................121
P0353-IGNITION COIL #3 PRIMARY CIRCUIT..............................121
P0401 - EGR SYSTEM FAILURE.........................................124
P0403 - EGR SOLENOID CIRCUIT........................................128
P0420-1/1 CATALYTIC CONVERTER EFFICIENCY...........................131
P0441-EVAP PURGE FLOW MONITOR....................................133
P0442-EVAP LEAK MONITOR MEDIUM (.040) LEAK DETECTED...............136
P0455-EVAP LEAK MONITOR LARGE LEAK DETECTED.....................136
P0456 - EVAP LEAK MONITOR SMALL LEAK DETECTED....................136
P0443-EVAP PURGE SOLENOID CIRCUIT.................................139
P0460-FUEL LEVEL UNIT NO CHANGE OVER MILES........................142
P0462-FUEL LEVEL SENDING UNIT VOLTS TOO LOW.......................145
P0463-FUEL LEVEL SENDING UNIT VOLTS TOO HIGH......................145
P0500-NO VEHICLE SPEED SIGNAL (3SP AUTO AND MANUAL
TRANSMISSIONS).....................................................147
P0500-NO VEHICLE SPEED SIGNAL (4SP AUTO TRANS)....................150
P0505-IDLE AIR CONTROL MOTOR CIRCUITS.............................153
P0508 - IAC MOTOR SENSE CIRCUIT LOW................................156
P0509 - IAC MOTOR SENSE CIRCUIT HIGH...............................159
P0700-EATX CONTROLLER DTC PRESENT................................161
P0703-BRAKE SWITCH SENSE CIRCUIT..................................162
P0740-TORQ CONV CLU, NO RPM DROP AT LOCKUP (3SP AUTO TRANS).....165
P0743-TORQUE CONVERTER CLUTCH SOLENOID/TRANS RELAY CIRCUITS
(3SP AUTO TRANS)....................................................168
P0833-CLUTCH RELEASED SWITCH CIRCUIT.............................171
P1192-INLET AIR TEMP SENSOR VOLTAGE LOW...........................174
P1193-INLET AIR TEMP SENSOR VOLTAGE HIGH..........................176
P1195-1/1 O2 SENSOR SLOW DURING CATALYST MONITOR................178
P1281-ENGINE IS COLD TOO LONG......................................180
P1282-FUEL PUMP RELAY CONTROL CIRCUIT.............................181
P1294-TARGET IDLE NOT REACHED (2.4L)................................184
P1294-TARGET IDLE NOT REACHED (3.3L/3.8L)............................187
P1297-NO CHANGE IN MAP FROM START TO RUN.........................189
P1299-VACUUM LEAK FOUND (IAC FULLY SEATED)........................193
P1388-AUTO SHUTDOWN RELAY CONTROL CIRCUIT.......................195
P1389-NO ASD RELAY OUTPUT VOLTAGE AT PCM.........................198
P1391-INTERMITTENT LOSS OF CMP OR CKP.............................201
P1398-MIS-FIRE ADAPTIVE NUMERATOR AT LIMIT.........................205
P1486-EVAP LEAK MONITOR PINCHED HOSE FOUND......................207
P1491-RAD FAN CONTROL RELAY CIRCUIT...............................210
P1494-LEAK DETECT PUMP SW OR MECHANICAL FAULT...................214
P1495-LEAK DETECTION PUMP SOLENOID CIRCUIT.......................216
P1496-5 VOLT SUPPLY, OUTPUT TOO LOW...............................218
P1602-PCM NOT PROGRAMMED........................................221
P1899-P/N SWITCH STUCK IN PARK OR IN GEAR (3SP AUTO TRANS)........222
P1899-P/N SWITCH STUCK IN PARK OR IN GEAR (4SP AUTO TRNAS)........224
*CHECKING ECT SENSOR..............................................226
*CHECKING FUEL DELIVERY............................................227
*CHECKING IAC MOTOR (2.4L)..........................................231
*CHECKING IAT SENSOR...............................................232
iii