2000 TOYOTA CAMRY headlights
[x] Cancel search: headlightsPage 946 of 4770

'99camry U
232
ÐHeadlights
1. Open the hood. Unplug the connec-
tor. Remove the rubber cover.
If the connector is tight, wiggle it.2. Release the bulb retaining spring
and remove the bulb. Install a new
bulb and the bulb retaining spring.
To install a bulb, align the tabs of the
bulb with the cutouts of the mounting
hole.3. Install the rubber cover with the
ºTOPº mark upward, and snuggle on
the boss. Insert the connector. Then
install the plastic cover.
Make sure the rubber cover fits snugly on
the connector and the headlight body.
Aiming is not necessary after replacing
the bulb. When aiming adjustment is nec-
essary, contact your Toyota dealer.
Page 1001 of 4770

'99camry U
205
Tire surface and wheel nuts
Check the tires carefully for cuts, damage
or excessive wear. See Chapter 7±2 for
additional information. When checking the
tires, make sure no nuts are missing, and
check the nuts for looseness. Tighten
them if necessary.
Tire rotation
Rotate the tires every 12000 km (7500
miles). See Chapter 7±2 for additional in-
formation.
Fluid leaks
Check underneath for leaking fuel, oil, wa-
ter or other fluid after the vehicle has
been parked for a while. If you smell fuel
fumes or notice any leak, have the cause
found and corrected immediately.
Doors and engine hood
Check that all doors including trunk lid
operate smoothly and all latches lock se-
curely. Make sure the engine hood sec-
ondary latch secures the hood from open-
ing when the primary latch is released.
INSIDE THE VEHICLE
Items listed below should be checked
regularly, e.g. while performing periodic
services, cleaning the vehicle, etc.Lights
Make sure the headlights, stop lights, tail
lights, turn signal lights, and other lights
are all working. Check headlight aim.
Service reminder indicators and warning
buzzers
Check that all service reminder indicators
and warning buzzers function properly.
Steering wheel
Be alert for changes in steering condition,
such as hard steering or strange noise.
Seats
Check that all front seat controls such as
seat adjusters, seatback recliner, etc. op-
erate smoothly and that all latches lock
securely in any position. Check that the
head restraints move up and down
smoothly and that the locks hold securely
in any latched position. For folding±down
rear seatbacks, check that the latches
lock securely.
Seat belts
Check that the seat belt system such as
buckles, retractors and anchors operate
properly and smoothly. Make sure that the
belt webbings not cut, frayed, worn or
damaged.Accelerator pedal
Check the pedal for smooth operation and
uneven pedal effort or catching.
Clutch pedal
Check the pedal for smooth operation.
Brake pedal
Check the pedal for smooth operation and
that the pedal has the proper clearance.
Check the brake booster function.
Brakes
At a safe place, check that the brakes do
not pull to one side when applied.
Parking brake
Check that the lever has the proper travel
and that, on a safe incline, your vehicle
is held securely with only the parking
brake applied.
Automatic transmission ºParkº mecha-
nism
Check the lock release button of the se-
lector lever for proper and smooth opera-
tion. On a safe incline, check that your
vehicle is held securely with the selector
lever in ºPº position and all brakes re-
leased.
Page 1165 of 4770
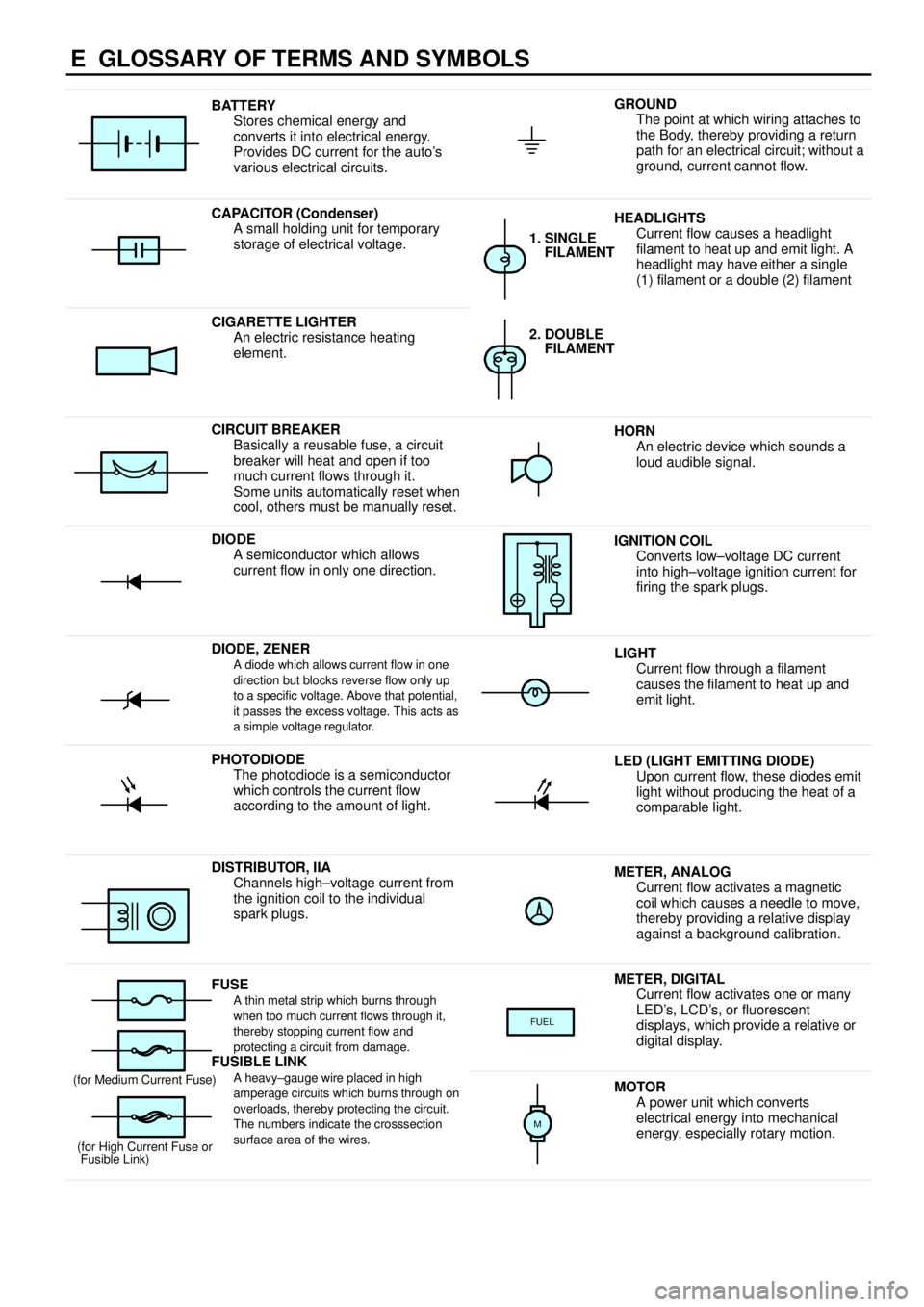
E GLOSSARY OF TERMS AND SYMBOLS
BATTERY
Stores chemical energy and
converts it into electrical energy.
Provides DC current for the auto's
various electrical circuits.GROUND
The point at which wiring attaches to
the Body, thereby providing a return
path for an electrical circuit; without a
ground, current cannot flow.
CAPACITOR (Condenser)
A small holding unit for temporary
storage of electrical voltage.HEADLIGHTS
Current flow causes a headlight
filament to heat up and emit light. A
headlight may have either a single
(1) filament or a double (2) filament
1. SINGLE
FILAMENT
CIGARETTE LIGHTER
An electric resistance heating
element.2. DOUBLE
FILAMENT
CIRCUIT BREAKER
Basically a reusable fuse, a circuit
breaker will heat and open if too
much current flows through it.
Some units automatically reset when
cool, others must be manually reset.HORN
An electric device which sounds a
loud audible signal.
DIODE
A semiconductor which allows
current flow in only one direction.IGNITION COIL
Converts low±voltage DC current
into high±voltage ignition current for
firing the spark plugs.
DIODE, ZENERA diode which allows current flow in one
direction but blocks reverse flow only up
to a specific voltage. Above that potential,
it passes the excess voltage. This acts as
a simple voltage regulator.LIGHT
Current flow through a filament
causes the filament to heat up and
emit light.
PHOTODIODE
The photodiode is a semiconductor
which controls the current flow
according to the amount of light.LED (LIGHT EMITTING DIODE)
Upon current flow, these diodes emit
light without producing the heat of a
comparable light.
DISTRIBUTOR, IIA
Channels high±voltage current from
the ignition coil to the individual
spark plugs.METER, ANALOG
Current flow activates a magnetic
coil which causes a needle to move,
thereby providing a relative display
against a background calibration.
FUSEA thin metal strip which burns through
when too much current flows through it,
thereby stopping current flow and
protecting a circuit from damage.
FUSIBLE LINK
METER, DIGITAL
Current flow activates one or many
LED's, LCD's, or fluorescent
displays, which provide a relative or
digital display.
FUEL
FUSIBLE LINK
A heavy±gauge wire placed in high
amperage circuits which burns through on
overloads, thereby protecting the circuit.
The numbers indicate the crosssection
surface area of the wires.(for Medium Current Fuse)
(for High Current Fuse or
Fusible Link)MOTOR
A power unit which converts
electrical energy into mechanical
energy, especially rotary motion.
M
Page 1235 of 4770

ENGINE CONTROL (5S±FE)
This system utilizes an engine control module and maintains overall control of the engine, transmission and so on. An outline
of the engine control is explained here.
1. INPUT SIGNALS
(1) Engine coolant temp. signal circuit
The engine coolant temp. sensor detects the engine coolant temp. and has a built±in thermistor with a resistance which
varies according to the engine coolant temp. thus the engine coolant temp. is input in the form of a control signal into
TERMINAL THW of the engine control module.
(2) Intake air temp. signal circuit
The intake air temp. sensor detects the intake air temp., which is input as a control signal into TERMINAL THA of the
engine control module.
(3) Oxygen sensor signal circuit
The oxygen density in the exhaust gases is detected and input as a control signal into TERMINAL OX1 (except
California) and OX2 of the engine control module.
(4) RPM signal circuit
Camshaft position and crankshaft position are detected by the camshaft position sensor and crankshaft position sensor.
Camshaft position is input as a control signal to TERMINAL G+ of the engine control module, and engine RPM is input
into TERMINAL NE+.
(5) Throttle signal circuit
The throttle position sensor detects the throttle valve opening angle, which is input as a control signal into TERMINAL
VTA of the engine control module.
(6) Vehicle speed signal circuit
The vehicle speed sensor, installed inside the transmission, detects the vehicle speed and inputs a control signal into
TERMINAL SPD of the engine control module.
(7) Park/Neutral position SW signal circuit (A/T)
The Park/Neutral position SW detects whether the shift position are in neutral, parking or not, and inputs a control signal
into TERMINAL STA of the engine control module.
(8) A/C SW signal circuit
The A/C amplifier function is built in the engine control module. The A/C SW signal inputs into the TERMINAL A/C SW of
the engine control module.
(9) Battery signal circuit
Voltage is constantly applied to TERMINAL BATT of the engine control module. When the ignition SW is turned on, the
voltage for engine control module start±up power supply is applied to TERMINAL +B of engine control module via EFI
relay.
(10) Intake air volume signal circuit
Intake air volume is detected by the manifold absolute pressure sensor (for manifold pressure) and is input as a control
signal into TERMINAL PIN of the engine control module.
(11) Starter signal circuit
To confirm whether the engine is cranking, the voltage applied to the starter motor during cranking is detected and the
signal is input into TERMINAL NSW of the engine control module as a control signal.
(12) Engine knock signal circuit
Engine knocking is detected by knock sensor 1 and the signal is input into TERMINAL KNK as a control signal.
(13) Electrical load signal circuit
The signal when systems such as the rear window defogger, headlights, etc. Which cause a high electrical burden are
on is input to TERMINAL ELS as a control signal.
(14) Air fuel ratio signal circuit (California)
The air fuel ratio is detected and input as a control signal into TERMINAL AF+ of the engine control module.
SYSTEM OUTLINE
Page 1251 of 4770

HEADLIGHT (w/ DAYTIME RUNNING LIGHT)
The current from the FL MAIN is always flowing from the MAIN fuse to HEAD relay (Coil side) to TERMINAL H±LP of the
daytime running light relay (Main), from DOME fuse to TERMINAL +B of the daytime running light relay (Main) and from the
ALT fuse to Taillight relay (Coil side) to TERMINAL TAIL (TMMK Made) of the daytime running light relay (Main).
When the ignition SW is turned on, the current flowing through the GAUGE fuse flows to TERMINAL IG of the daytime
running light relay (Main).
1. DAYTIME RUNNING LIGHT OPERATION
When the engine is started, voltage generated at TERMINAL L of the generator is applied to TERMINAL CHG± of the
daytime running light relay (Main). If the parking brake lever is pulled up (Parking brake SW on) at this time, the relay is not
activated so the daytime running light system does not operate. If the parking brake lever is then released (Parking brake
SW off), a signal is input to TERMINAL PKB of the relay.
This activates the daytime running light relay (Main) and the HEAD relay is turned to on, so the current flows from the MAIN
fuse to the HEAD relay (Point side) to TERMINAL 1 of the DIM relay to TERMINAL 4 to H±LP LH (LWR), H±LP RH (LWR)
fuses to TERMINAL 1 of the headlights to TERMINAL 3 to TERMINAL 1 of the daytime running light resistor to TERMINAL 2
to GROUND, causing the headlights to light up (Headlights light up dimmer than normal brightness.). Once the daytime
running light system operates and the headlights light up, the headlights remain on even if the parking brake lever is pulled
up (Parking brake SW on).
If the engine stalls and the ignition SW remains on, the headlights remain light up even through current is no longer output
from TERMINAL L of the generator. If the ignition SW is then turned off, the headlights go off.
If the engine is started with the parking brake lever released (Parking brake SW off), the daytime running light system
operates and headlights light up when the engine starts.
2. HEADLIGHT OPERATION
When the light control SW is switched to HEAD position and the dimmer SW is set to LOW position, causing the daytime
running light relay (Main) and the HEAD relay to turn on, so the current flows from the MAIN fuse to HEAD relay (Point side)
to DRL NO.2 fuse to TERMINAL 3 of the DRL NO.4 relay to TERMINAL 4 to TERMINAL H±ON of the daytime running light
relay (Main) to TERMINAL H to TERMINAL 3 of the integration relay to TERMINAL 4 to TERMINAL 13 of the light control
SW to TERMINAL 16 to GROUND, activating the DRL. NO.4 relay. The current to HEAD relay (Point side) then flows to
TERMINAL 1 of the DIM relay to TERMINAL 4 to H±LP LH (LWR), H±LP RH (LWR) fuses to TERMINAL 1 of the headlights
to TERMINAL 3 to TERMINAL 1 of the DRL NO.4 relay to TERMINAL 2 to GROUND, causing the headlights to light up at
normal intensity.
When the light control SW is switched to HEAD position and the dimmer SW is set to HIGH position, the signal from the
dimmer SW is input to the daytime running light relay (Main). This activates the daytime running light relay (Main) and the
HEAD relay is turned on, so the current flows from the MAIN fuse to HEAD relay (Point side) to TERMINAL 1 of the DIM
relay to TERMINAL 3 to TERMINAL DIM of the daytime running light relay (Main), activating the DIM relay. This causes
current to flow from TERMINAL 1 of the DIM relay to TERMINAL 2 to HEAD LH (UPR), HEAD RH (UPR) fuses to TERMINAL
2 of the headlights to TERMINAL 3 to TERMINAL 1 of the DRL NO.4 relay to TERMINAL 2 to GROUND, causing the
headlights to light up at high beam and the high beam indicator light to light up.
When the dimmer SW is switched to FLASH position, the signal from the dimmer SW is input to the daytime running light
relay (Main). This activates the daytime running light relay (Main) and the HEAD relay is turned on, so the current flows from
the MAIN fuse to HEAD relay (Point side) to DRL NO.2 fuse to TERMINAL 3 of the DRL NO.4 relay to TERMINAL 4 to
TERMINAL H±ON of the daytime running light relay (Main) to TERMINAL H to TERMINAL 8 of the dimmer SW to
TERMINAL 16 to GROUND, activating the DRL NO.4 relay. At the same time, the current flows from the TERMINAL 1 of the
DIM relay to TERMINAL 3 to TERMINAL DIM of the daytime running light relay (Main), activating the DIM relay, and also
flows from the HEAD LH (UPR), HEAD RH (UPR) fuses to TERMINAL 2 of the headlights to TERMINAL 3 to TERMINAL 1 of
the DRL NO.4 relay to TERMINAL 2 to GROUND, causing the headlights to light up at high beam and the high beam
indicator light to light up.
SYSTEM OUTLINE
Page 1252 of 4770

3. AUTOMATIC LIGHT CONTROL OPERATION
When the daytime running light is operating and the Automatic control sensor detects a decrease in the ambient light (It
continues less than approx. 2500 lux over about 20 seconds, and it is less than 1000 lux.), the automatic light control
operation starts. At the same time, daytime running light relay (Main) is activated, so current flows from the ALT fuse to the
Taillight relay (Coil side) to TERMINAL TAIL of the daytime running light relay (Main), and the DRL NO.2 fuse to the DRL
NO.4 relay (Coil side) to TERMINAL H±ON of the daytime running light relay (Main), activating both the Taillight relay and the
DRL NO.4 relay, so that the taillights and headlights light up.
When the automatic light control sensor detects an increase in the ambient light (It continues more than approx. 1000 lux
over about 20 seconds, and it is more than approx. 2500 lux), the ignition SW is turned to off, the light control SW is turned to
HEAD position, and the automatic light control operation stops.
HEAD RELAY [ENGINE ROOM J/B NO.2]
1±2 : Closed with the light control SW at HEAD position or the dimmer SW at FLASH position
Closed with the engine running and the parking brake lever is released (Parking brake SW off)
TAILLIGHT RELAY [INSTRUMENT PANEL J/B]
5±3 : Closed with the light control SW at TAIL or HEAD position
D6 DAYTIME RUNNING LIGHT RELAY (MAIN)
2±GROUND : Approx. 12 volts with the ignition SW at ON position
5, 7,17±GROUND : Approx. 12 volts with the light control SW at HEAD position or the dimmer SW at FLASH position
Approx. 12 volts with the engine running and the parking brake lever is released
(Parking brake SW off)
6,15±GROUND : Always approx. 12 volts
8±GROUND : Continuity with the parking brake lever pulled up
11±GROUND :13.9±15.1 volts with the engine running at 2000 rpm 25°C (77°F)
12±GROUND : Approx. 12 volts with the high beam light up
13±GROUND : Always continuity
16±GROUND : Continuity with the dimmer SW at HIGH or FLASH position
18±GROUND : Continuity with the brake fluid level not enough
: PARTS LOCATION
CodeSee PageCodeSee PageCodeSee Page
A4030F6C26 (1MZ±FE)J131
B226 (1MZ±FE)F6C28 (5S±FE)J231B228 (5S±FE)F9F26 (1MZ±FE)J431
C9B30F9F28 (5S±FE)J531
C10C30G226 (1MZ±FE)J731
C1330G228 (5S±FE)J1131
D226 (1MZ±FE)H126 (1MZ±FE)J27A31D228 (5S±FE)H128 (5S±FE)J28B31
D630H226 (1MZ±FE)P331
F4A26 (1MZ±FE)H228 (5S±FE)F4A28 (5S±FE)I1730
SERVICE HINTS
Page 1314 of 4770

Door lock control (Lock and unlock) and panic control (Theft alarm and flash) is performed by remote control, without the
ignition key inserted in the door key cylinder, using low±power electrical waves emitted by a transmitter.
1. WIRELESS DOOR LOCK OR UNLOCK NORMAL OPERATION
With the ignition key not inserted into the ignition key cylinder (Unlock warning SW off) and all the doors completely closed,
when the lock or unlock button (Transmitter) is pushed, the wireless door lock ECU receives the electrical waves from the
transmitter, causing it to operate.
As a result, the ECU judges whether the door is locked or unlocked based on the signal from the door lock motor and door
unlock detection SW, and sends a signal to the theft deterrent ECU and integration relay to switch the condition from lock to
unlock or vice versa, causing the door lock motor to operate.
2. VISUAL CONFIRMATION OF LOCK OR UNLOCK
If all doors indicate that they are locked after the lock command, parking lights and taillight will flash once. If any door
indicates that it is open after the unlock command, parking lights and taillights will flash twice.
3. WIRELESS DOOR UNLOCK OPERATION
Pushing the unlock button (Transmitter) once, driver's door is unlocked. Furthermore, pushing the button again within 3
seconds, the other doors are unlocked.
4. AUTOMATIC LOCK OPERATION
With the ignition key not inserted into the ignition key cylinder (Unlock warning SW off) and all the doors completely closed,
after pushing the button (Transmitter) to unlock all the doors, if a door is not opened within 30 seconds, all the doors will be
automatically relocked.
5. WIRELESS CONTROL STOP FUNCTION
If a door is open (Door courtesy SW on), a signal is input from the door courtesy SW to the wireless door lock ECU, stopping
wireless door lock or unlock.
If the ignition key is in the ignition key cylinder (Unlock warning SW on), the unlock warning SW inputs a signal to the
wireless door lock ECU, stopping wireless door lock or unlock.
6. DOOR LOCK MOTOR PROTECTIVE FUNCTION
If the door lock or unlock condition does not change after wireless door lock or unlock operation, 2 seconds later, the
integration relay ECU sends current three times to the door lock motor. If the door lock condition still has not changed as a
result, the wireless door lock ECU stops reception and stops door lock and unlock function.
7. REMOTE PANIC OPERATION
Panic will function when doors are locked or unlocked, open or closed. When the panic button (Transmitter) is pushed once,
theft alarm sounds and headlights and taillight flash. Then, the panic or the unlock button (Transmitter) is pushed once more,
sounding and flashing will stop. Panic will not function when ignition key is in ignition key cylinder.
D12, D13, D14, D15 DOOR COURTESY SW FRONT LH, RH, REAR LH, RH
1±GROUND : Continuity with the door open
U1 UNLOCK WARNING SW
2±1 : Continuity with the ignition key in the cylinder
W6 WIRELESS DOOR LOCK ECU
8±GROUND : Always approx. 12 volts
1±GROUND : Always continuity
14±GROUND : Continuity with each of the door open
10±GROUND : Continuity with the ignition key in the cylinder
SYSTEM OUTLINE
SERVICE HINTS
Page 1324 of 4770

Door lock control (Lock and unlock) and panic control (Theft alarm and flash) is performed by remote control, without the
ignition key inserted in the door key cylinder, using low±power electrical waves emitted by a transmitter.
1. WIRELESS DOOR LOCK OR UNLOCK NORMAL OPERATION
With the ignition key not inserted into the ignition key cylinder (Unlock warning SW off) and all the doors completely closed,
when the lock or unlock button (Transmitter) is pushed, the wireless door lock ECU receives the electrical waves from the
transmitter, causing it to operate.
As a result, the ECU judges whether the door is locked or unlocked based on the signal from the door lock motor and door
unlock detection SW, and sends a signal to the theft deterrent ECU and integration relay to switch the condition from lock to
unlock or vice versa, causing the door lock motor to operate.
2. VISUAL CONFIRMATION OF LOCK OR UNLOCK
If all doors indicate that they are locked after the lock command, parking lights and taillight will flash once. If any door
indicates that it is open after the unlock command, parking lights and taillights will flash twice.
3. WIRELESS DOOR UNLOCK OPERATION
Pushing the unlock button (Transmitter) once, driver's door is unlocked. Furthermore, pushing the button again within 3
seconds, the other doors are unlocked.
4. AUTOMATIC LOCK OPERATION
With the ignition key not inserted into the ignition key cylinder (Unlock warning SW off) and all the doors completely closed,
after pushing the button (Transmitter) to unlock all the doors, if a door is not opened within 30 seconds, all the doors will be
automatically relocked.
5. WIRELESS CONTROL STOP FUNCTION
If a door is open (Door courtesy SW on), a signal is input from the door courtesy SW to the wireless door lock ECU, stopping
wireless door lock or unlock.
If the ignition key is in the ignition key cylinder (Unlock warning SW on), the unlock warning SW inputs a signal to the
wireless door lock ECU, stopping wireless door lock or unlock.
6. DOOR LOCK MOTOR PROTECTIVE FUNCTION
If the door lock or unlock condition does not change after wireless door lock or unlock operation, 2 seconds later, the
integration relay ECU sends current three times to the door lock motor. If the door lock condition still has not changed as a
result, the wireless door lock ECU stops reception and stops door lock and unlock function.
7. REMOTE PANIC OPERATION
Panic will function when doors are locked or unlocked, open or closed. When the panic button (Transmitter) is pushed once,
theft alarm sounds and headlights and taillight flash. Then, the panic or the unlock button (Transmitter) is pushed once more,
sounding and flashing will stop. Panic will not function when ignition key is in ignition key cylinder.
D12, D13, D14, D15 DOOR COURTESY SW FRONT LH, RH, REAR LH, RH
1±GROUND : Continuity with the door open
U1 UNLOCK WARNING SW
2±1 : Continuity with the ignition key in the cylinder
W6 WIRELESS DOOR LOCK ECU
8±GROUND : Always approx. 12 volts
1±GROUND : Always continuity
14±GROUND : Continuity with each of the door open
10±GROUND : Continuity with the ignition key in the cylinder
SYSTEM OUTLINE
SERVICE HINTS