2000 NISSAN PATROL sensor
[x] Cancel search: sensorPage 238 of 1033

Special Service Tool
Tool number
Tool nameDescription
KV10109300
Puller holder
NT628a = 68 mm (2.68 in)
b = 8 mm (0.31 in) dia.
Supplemental Restraint System (SRS) ªAIR
BAGº and ªSEAT BELT PRE-TENSIONERº
The Supplemental Restraint System such as ªAIR BAGº and ªSEAT BELT PRE-TENSIONERº used along
with a seat belt, helps to reduce the risk or severity of injury to the driver and front passenger for certain
types of collision. The SRS system composition which is available to NISSAN MODEL Y61 is as follows (The
composition varies according to the destination and optional equipment.):
+For a frontal collision
The Supplemental Restraint System consists of driver air bag module (located in the center of the
steering wheel), front passenger air bag module (located on the instrument panel on passenger side),
seat belt pre-tensioners, a diagnosis sensor unit, warning lamp, wiring harness and spiral cable.
+For a side collision
The Supplemental Restraint System consists of front side air bag module (located in the outer side of
front seat), satellite sensor, diagnosis sensor unit (one of components of air bags for a frontal collision),
wiring harness, warning lamp (one of components of air bags for a frontal collision).
Information necessary to service the system safely is included in theRS sectionof this Service Manual.
WARNING:
+To avoid rendering the SRS inoperative, which could increase the risk of personal injury or death
in the event of a collision which would result in air bag inflation, all maintenance should be per-
formed by an authorized NISSAN dealer.
+Improper maintenance, including incorrect removal and installation of the SRS, can lead to per-
sonal injury caused by unintentional activation of the system. For removal of Spiral Cable and
Air Bag Module, see the RS section.
+Do not use electrical test equipment on any circuit related to the SRS unless instructed to in this
Service Manual. Spiral cable and wiring harnesses covered with yellow insulation tape either just
before the harness connectors or for the complete harness are related to the SRS.
PRECAUTIONS AND PREPARATIONZD30DDTi
EC-1005
Page 239 of 1033
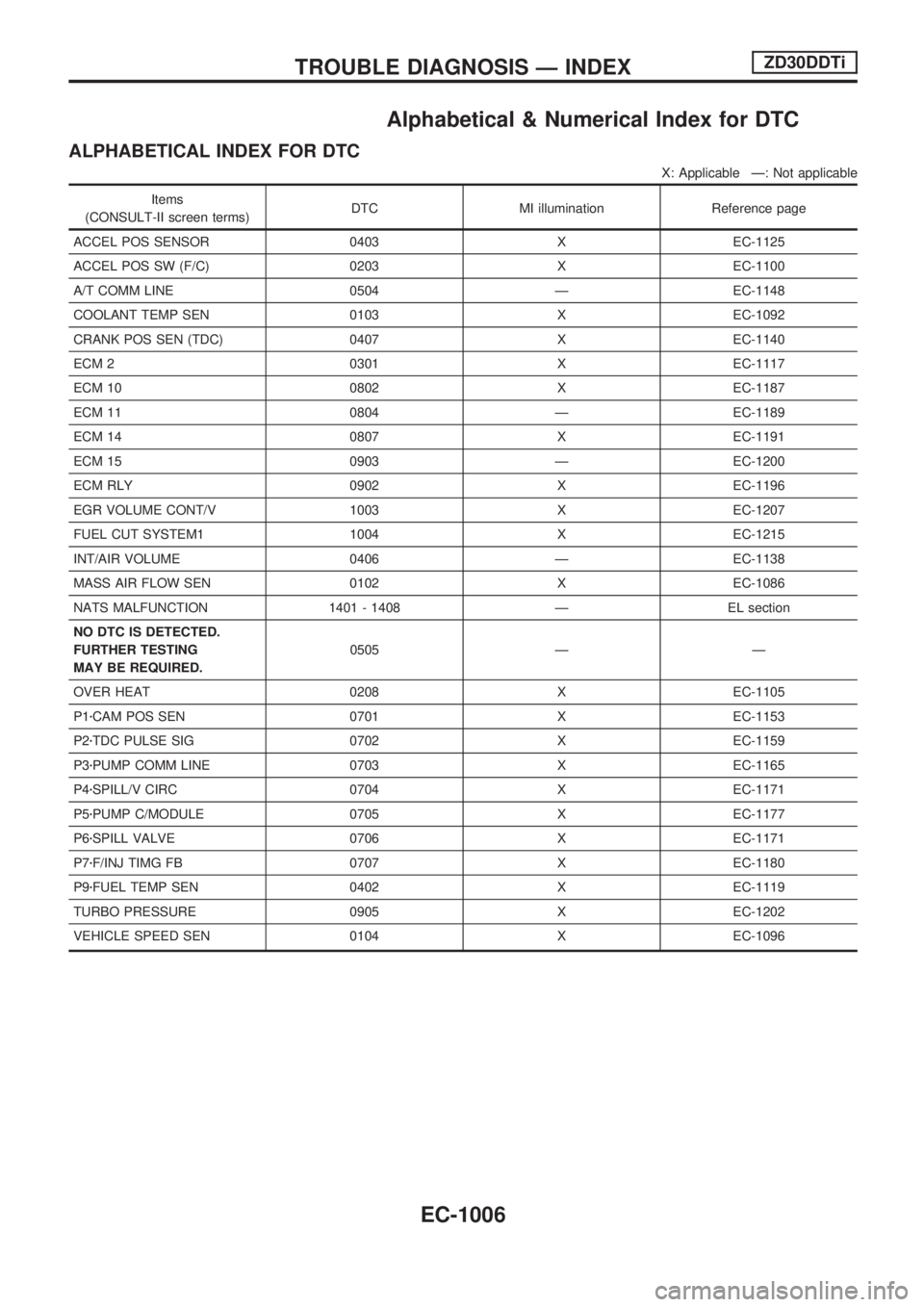
Alphabetical & Numerical Index for DTC
ALPHABETICAL INDEX FOR DTC
X: Applicable Ð: Not applicable
Items
(CONSULT-II screen terms)DTC MI illumination Reference page
ACCEL POS SENSOR 0403 X EC-1125
ACCEL POS SW (F/C) 0203 X EC-1100
A/T COMM LINE 0504 Ð EC-1148
COOLANT TEMP SEN 0103 X EC-1092
CRANK POS SEN (TDC) 0407 X EC-1140
ECM 2 0301 X EC-1117
ECM 10 0802 X EC-1187
ECM 11 0804 Ð EC-1189
ECM 14 0807 X EC-1191
ECM 15 0903 Ð EC-1200
ECM RLY 0902 X EC-1196
EGR VOLUME CONT/V 1003 X EC-1207
FUEL CUT SYSTEM1 1004 X EC-1215
INT/AIR VOLUME 0406 Ð EC-1138
MASS AIR FLOW SEN 0102 X EC-1086
NATS MALFUNCTION 1401 - 1408 Ð EL section
NO DTC IS DETECTED.
FURTHER TESTING
MAY BE REQUIRED.0505 Ð Ð
OVER HEAT 0208 X EC-1105
P1zCAM POS SEN 0701 X EC-1153
P2zTDC PULSE SIG 0702 X EC-1159
P3zPUMP COMM LINE 0703 X EC-1165
P4zSPILL/V CIRC 0704 X EC-1171
P5zPUMP C/MODULE 0705 X EC-1177
P6zSPILL VALVE 0706 X EC-1171
P7zF/INJ TIMG FB 0707 X EC-1180
P9zFUEL TEMP SEN 0402 X EC-1119
TURBO PRESSURE 0905 X EC-1202
VEHICLE SPEED SEN 0104 X EC-1096
TROUBLE DIAGNOSIS Ð INDEXZD30DDTi
EC-1006
Page 240 of 1033
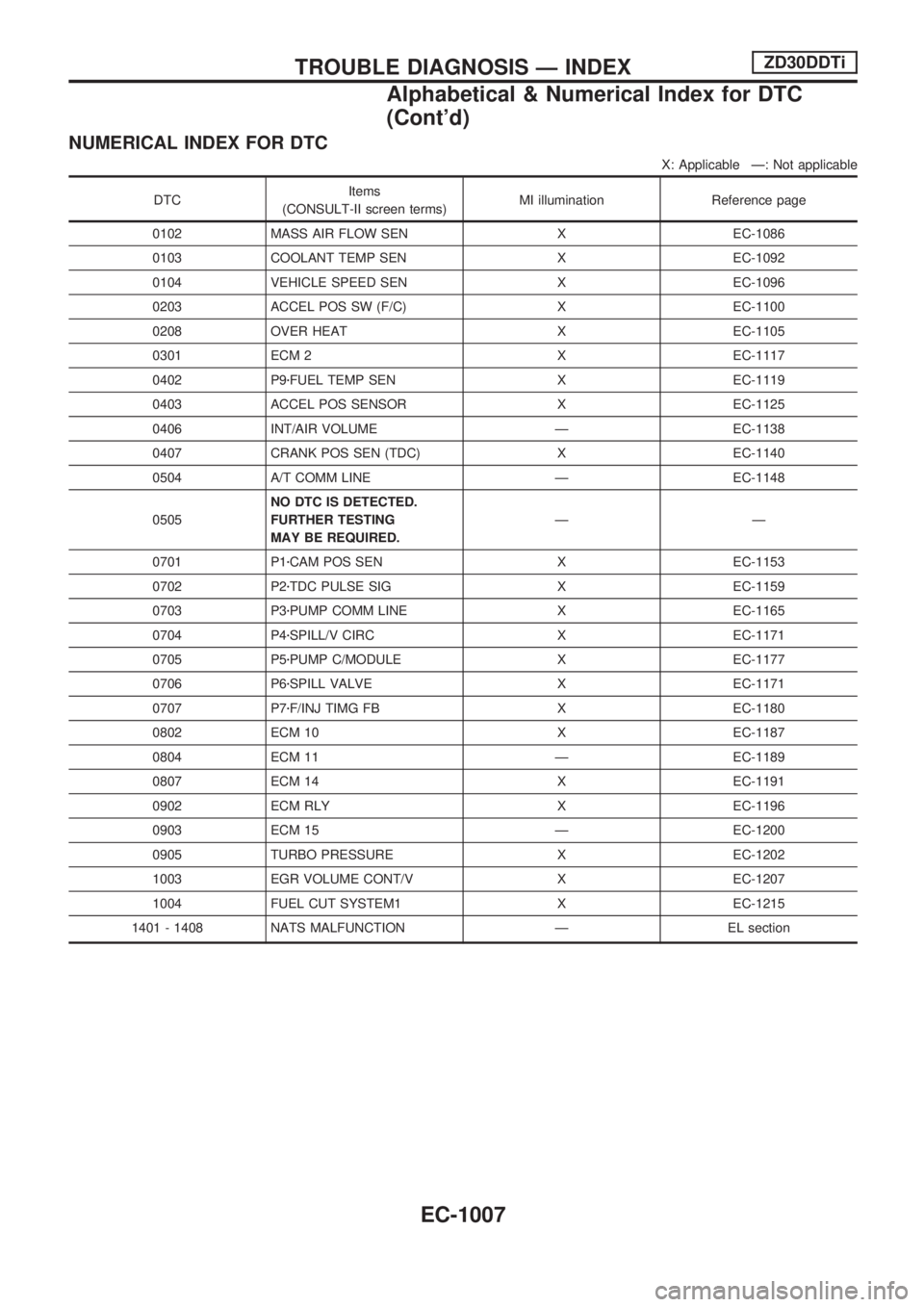
NUMERICAL INDEX FOR DTC
X: Applicable Ð: Not applicable
DTCItems
(CONSULT-II screen terms)MI illumination Reference page
0102 MASS AIR FLOW SEN X EC-1086
0103 COOLANT TEMP SEN X EC-1092
0104 VEHICLE SPEED SEN X EC-1096
0203 ACCEL POS SW (F/C) X EC-1100
0208 OVER HEAT X EC-1105
0301 ECM 2 X EC-1117
0402 P9zFUEL TEMP SEN X EC-1119
0403 ACCEL POS SENSOR X EC-1125
0406 INT/AIR VOLUME Ð EC-1138
0407 CRANK POS SEN (TDC) X EC-1140
0504 A/T COMM LINE Ð EC-1148
0505NO DTC IS DETECTED.
FURTHER TESTING
MAY BE REQUIRED.ÐÐ
0701 P1zCAM POS SEN X EC-1153
0702 P2zTDC PULSE SIG X EC-1159
0703 P3zPUMP COMM LINE X EC-1165
0704 P4zSPILL/V CIRC X EC-1171
0705 P5zPUMP C/MODULE X EC-1177
0706 P6zSPILL VALVE X EC-1171
0707 P7zF/INJ TIMG FB X EC-1180
0802 ECM 10 X EC-1187
0804 ECM 11 Ð EC-1189
0807 ECM 14 X EC-1191
0902 ECM RLY X EC-1196
0903 ECM 15 Ð EC-1200
0905 TURBO PRESSURE X EC-1202
1003 EGR VOLUME CONT/V X EC-1207
1004 FUEL CUT SYSTEM1 X EC-1215
1401 - 1408 NATS MALFUNCTION Ð EL section
TROUBLE DIAGNOSIS Ð INDEXZD30DDTi
Alphabetical & Numerical Index for DTC
(Cont'd)
EC-1007
Page 243 of 1033

+Do not disconnect pump harness connector with engine
running.
+Do not disassemble electronic fuel injection pump.
If NG, take proper action.
+Do not disassemble injection nozzle.
If NG, replace injection nozzle.
+Even a slight leak in the air intake system can cause
serious problems.
+Do not shock or jar the crankshaft position sensor
(TDC).
+Do not depress accelerator pedal when starting.
+Immediately after starting, do not rev up engine unnec-
essarily.
+Do not rev up engine just prior to shutdown.
+When installing C.B. ham radio or a mobile phone, be
sure to observe the following as it may adversely affect
electronic control systems depending on its installation
location.
1) Keep the antenna as far as possible away from the ECM.
2) Keep the antenna feeder line more than 20 cm (7.9 in)
away from the harness of electronic controls.
Do not let them run parallel for a long distance.
3) Adjust the antenna and feeder line so that the standing-
wave ratio can be kept smaller.
4) Be sure to ground the radio to vehicle body.
SEF437Y
SEF709Y
SEF708Y
PRECAUTIONSZD30DDTi
Precautions (Cont'd)
EC-1010
Page 251 of 1033
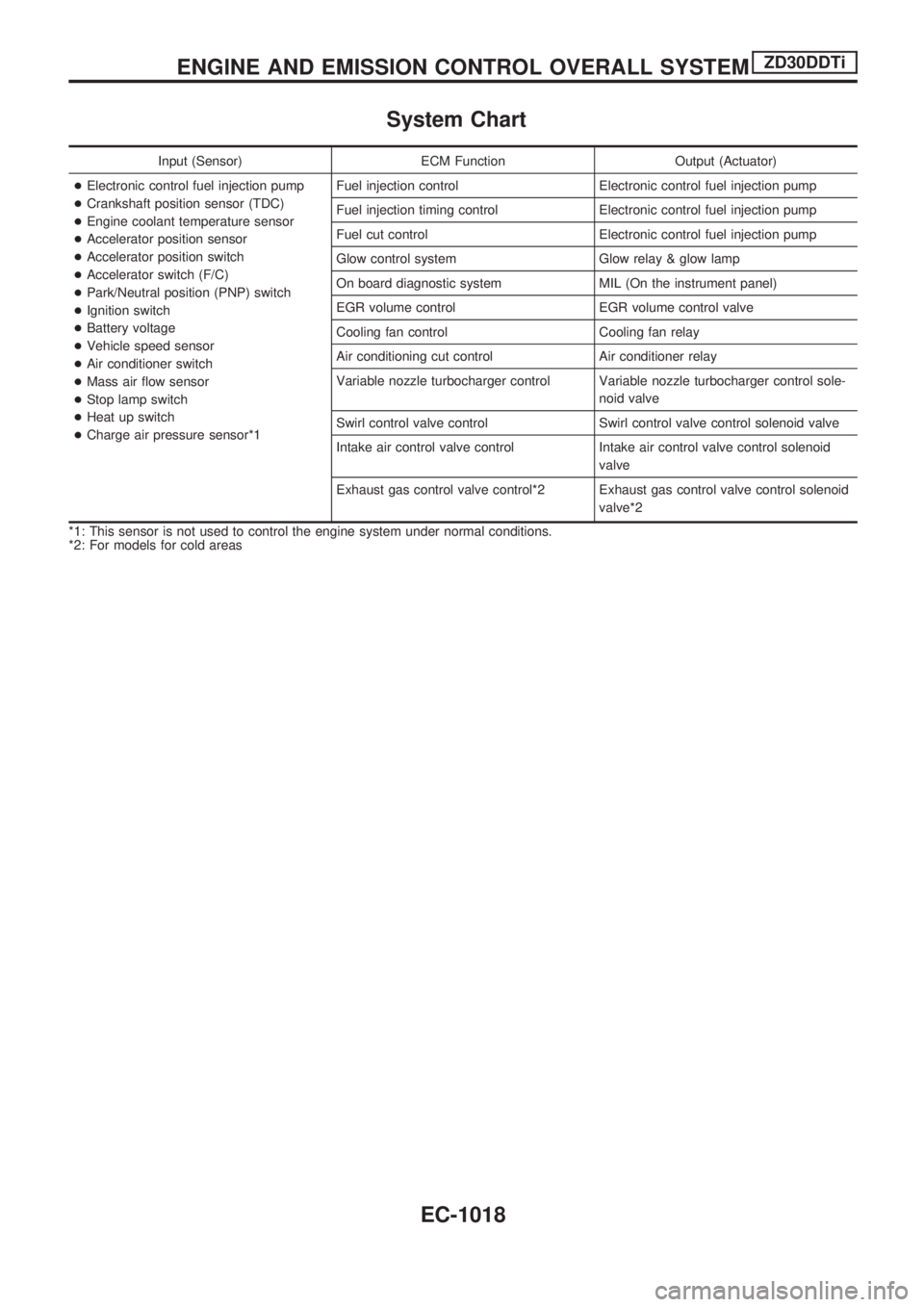
System Chart
Input (Sensor) ECM Function Output (Actuator)
+Electronic control fuel injection pump
+Crankshaft position sensor (TDC)
+Engine coolant temperature sensor
+Accelerator position sensor
+Accelerator position switch
+Accelerator switch (F/C)
+Park/Neutral position (PNP) switch
+Ignition switch
+Battery voltage
+Vehicle speed sensor
+Air conditioner switch
+Mass air flow sensor
+Stop lamp switch
+Heat up switch
+Charge air pressure sensor*1Fuel injection control Electronic control fuel injection pump
Fuel injection timing control Electronic control fuel injection pump
Fuel cut control Electronic control fuel injection pump
Glow control system Glow relay & glow lamp
On board diagnostic system MIL (On the instrument panel)
EGR volume control EGR volume control valve
Cooling fan control Cooling fan relay
Air conditioning cut control Air conditioner relay
Variable nozzle turbocharger control Variable nozzle turbocharger control sole-
noid valve
Swirl control valve control Swirl control valve control solenoid valve
Intake air control valve control Intake air control valve control solenoid
valve
Exhaust gas control valve control*2 Exhaust gas control valve control solenoid
valve*2
*1: This sensor is not used to control the engine system under normal conditions.
*2: For models for cold areas
ENGINE AND EMISSION CONTROL OVERALL SYSTEMZD30DDTi
EC-1018
Page 252 of 1033
Fuel Injection Control System
DESCRIPTION
System description
Three types of fuel injection control are provided to accommodate engine operating conditions; normal
control, idle control and start control. The ECM determines the appropriate fuel injection control. Under each
control, the amount of fuel injected is compensated to improve engine performance.
Pulse signals are exchanged between ECM and electronic control fuel injection pump (control unit is built-
in). The fuel injection pump control unit performs duty control on the spill valve (built into the fuel injection
pump) according to the input signals to compensate the amount of fuel injected to the preset value.
Start control
Input/output signal chart
Sensor Input Signal to ECM ECM Function Actuator
Engine coolant temperature sensor Engine coolant temperature
Fuel injection con-
trol (start control)Electronic control fuel injec-
tion pump Crankshaft position sensor (TDC) Engine speed
Ignition switch Start signal
When the ECM receives a start signal from the ignition switch,
the ECM adapts the fuel injection system for the start control.
The amount of fuel injected at engine starting is a preset program
value in the ECM. The program is determined by the engine
speed and engine coolant temperature.
For better startability under cool engine conditions, the lower the
coolant temperature becomes, the greater the amount of fuel
injected. The ECM ends the start control when the engine speed
reaches the specific value, and shifts the control to the normal
or idle control.
Idle control
Input/output signal chart
Sensor Input Signal to ECM ECM Function Actuator
Engine coolant temperature sensor Engine coolant temperature
Fuel injection con-
trol (Idle control)Electronic control fuel injec-
tion pump Crankshaft position sensor (TDC) Engine speed
Park/Neutral position (PNP) switch Gear position
Battery Battery voltage
Accelerator position switch Idle position
Vehicle speed sensor Vehicle speed
Air conditioner switch Air conditioner signal
Heat up switch Heat up switch signal
When the ECM determines that the engine speed is at idle, the fuel injection system is adapted for the idle
control. The ECM regulates the amount of fuel injected corresponding to changes in load applied to the
engine to keep engine speed constant. The ECM also provides the system with a fast idle control in response
to the engine coolant temperature and heat up switch signal.
SEF648S
ENGINE AND EMISSION BASIC CONTROL SYSTEM
DESCRIPTIONZD30DDTi
EC-1019
Page 253 of 1033

Normal control
Input/output signal chart
Sensor Input Signal to ECM ECM Function Actuator
Crankshaft position sensor (TDC) Engine speed
Fuel injection con-
trol (Normal con-
trol)Electronic control fuel injec-
tion pump Accelerator position sensor Accelerator position
Vehicle speed sensor Vehicle speed
The amount of fuel injected under normal driving conditions is
determined according to sensor signals. The crankshaft position
sensor (TDC) detects engine speed and the accelerator position
sensor detects accelerator position. These sensors send signals
to the ECM.
The fuel injection data, predetermined by correlation between
various engine speeds and accelerator positions, are stored in
the ECM memory, forming a map. The ECM determines the
optimal amount of fuel to be injected using the sensor signals in
comparison with the map.
Maximum amount control
Input/output signal chart
Sensor Input Signal to ECM ECM Function Actuator
Mass air flow sensor Amount of intake air
Fuel injection con-
trol (Maximum
amount control)Electronic control fuel injec-
tion pump Engine coolant temperature sensor Engine coolant temperature
Crankshaft position sensor (TDC) Engine speed
Accelerator position sensor Accelerator position
The maximum injection amount is controlled to an optimum by the engine speed, intake air amount, engine
coolant temperature, and accelerator opening in accordance with the driving conditions.
This prevents the oversupply of the injection amount caused by decreased air density at a high altitude or
during a system failure.
Deceleration control
Input/output signal chart
Sensor Input Signal to ECM ECM Function Actuator
Accelerator switch (F/C) Accelerator positionFuel injection con-
trol (Deceleration
control)Electronic control fuel injec-
tion pump
Crankshaft position sensor (TDC) Engine speed
The ECM sends a fuel cut signal to the electronic control fuel injection pump during deceleration for better
fuel efficiency. The ECM determines the time of deceleration according to signals from the accelerator switch
(F/C) and crankshaft position sensor (TDC).
SEF649S
ENGINE AND EMISSION BASIC CONTROL SYSTEM
DESCRIPTIONZD30DDTi
Fuel Injection Control System (Cont'd)
EC-1020
Page 254 of 1033
Fuel Injection Timing Control System
DESCRIPTION
The target fuel injection timing in accordance with the engine speed and the fuel injection amount are
recorded as a map in the ECM beforehand. The ECM and the injection pump control unit exchange signals
and perform feedback control for optimum injection timing in accordance with the map.
Air Conditioning Cut Control
DESCRIPTION
Input/output signal chart
Sensor Input Signal to ECM ECM Function Actuator
Air conditioner switch Air conditioner ªONº signal
Air conditioner cut
controlAir conditioner relay Accelerator position sensorAccelerator valve opening
angle
Vehicle speed sensor Vehicle speed
Engine coolant temperature sensor Engine coolant temperature
System description
This system improves acceleration when the air conditioner is used.
When the accelerator pedal is fully depressed, the air conditioner is turned off for a few seconds.
When engine coolant temperature becomes excessively high, the air conditioner is turned off. This contin-
ues until the engine coolant temperature returns to normal.
Fuel Cut Control (at no load & high engine
speed)
DESCRIPTION
Input/output signal chart
Sensor Input Signal to ECM ECM Function Actuator
Vehicle speed sensor Vehicle speed
Fuel cut controlElectronic control fuel injec-
tion pump Park/Neutral position (PNP) switch Neutral position
Accelerator position switch or Accelerator
switch (F/C)Accelerator position
Engine coolant temperature sensor Engine coolant temperature
Crankshaft position sensor (TDC) Engine speed
If the engine speed is above 2,700 rpm with no load (for example, in neutral and engine speed over 2,700
rpm) fuel will be cut off after some time. The exact time when the fuel is cut off varies based on engine speed.
Fuel cut will operate until the engine speed reaches 1,500 rpm, then fuel cut is cancelled.
NOTE:
This function is different from deceleration control listed under ªFuel Injection Control Systemº,
EC-1019.
ENGINE AND EMISSION BASIC CONTROL SYSTEM
DESCRIPTIONZD30DDTi
EC-1021