2000 DODGE NEON warning
[x] Cancel search: warningPage 218 of 1285
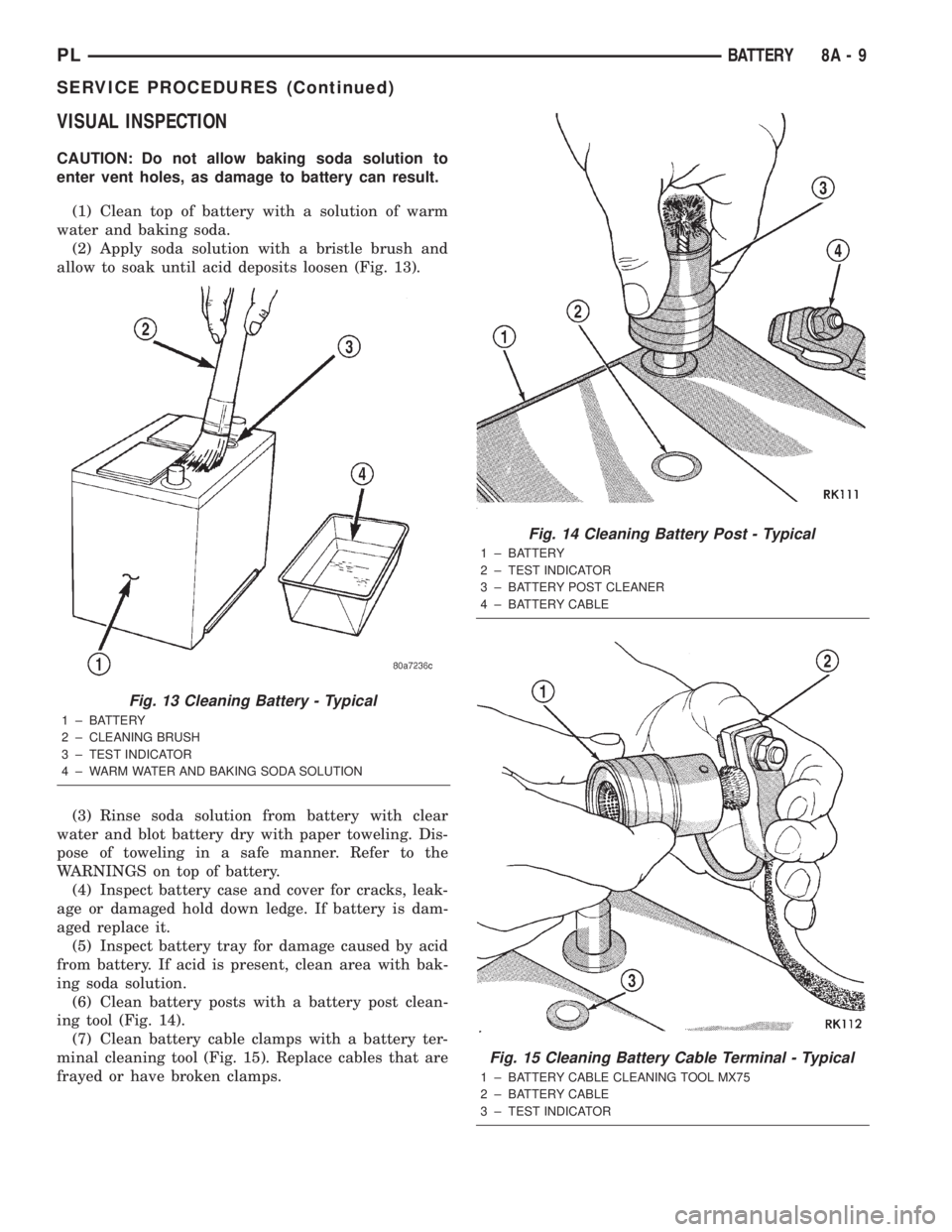
VISUAL INSPECTION
CAUTION: Do not allow baking soda solution to
enter vent holes, as damage to battery can result.
(1) Clean top of battery with a solution of warm
water and baking soda.
(2) Apply soda solution with a bristle brush and
allow to soak until acid deposits loosen (Fig. 13).
(3) Rinse soda solution from battery with clear
water and blot battery dry with paper toweling. Dis-
pose of toweling in a safe manner. Refer to the
WARNINGS on top of battery.
(4) Inspect battery case and cover for cracks, leak-
age or damaged hold down ledge. If battery is dam-
aged replace it.
(5) Inspect battery tray for damage caused by acid
from battery. If acid is present, clean area with bak-
ing soda solution.
(6) Clean battery posts with a battery post clean-
ing tool (Fig. 14).
(7) Clean battery cable clamps with a battery ter-
minal cleaning tool (Fig. 15). Replace cables that are
frayed or have broken clamps.
Fig. 13 Cleaning Battery - Typical
1 ± BATTERY
2 ± CLEANING BRUSH
3 ± TEST INDICATOR
4 ± WARM WATER AND BAKING SODA SOLUTION
Fig. 14 Cleaning Battery Post - Typical
1 ± BATTERY
2 ± TEST INDICATOR
3 ± BATTERY POST CLEANER
4 ± BATTERY CABLE
Fig. 15 Cleaning Battery Cable Terminal - Typical
1 ± BATTERY CABLE CLEANING TOOL MX75
2 ± BATTERY CABLE
3 ± TEST INDICATOR
PLBATTERY 8A - 9
SERVICE PROCEDURES (Continued)
Page 219 of 1285
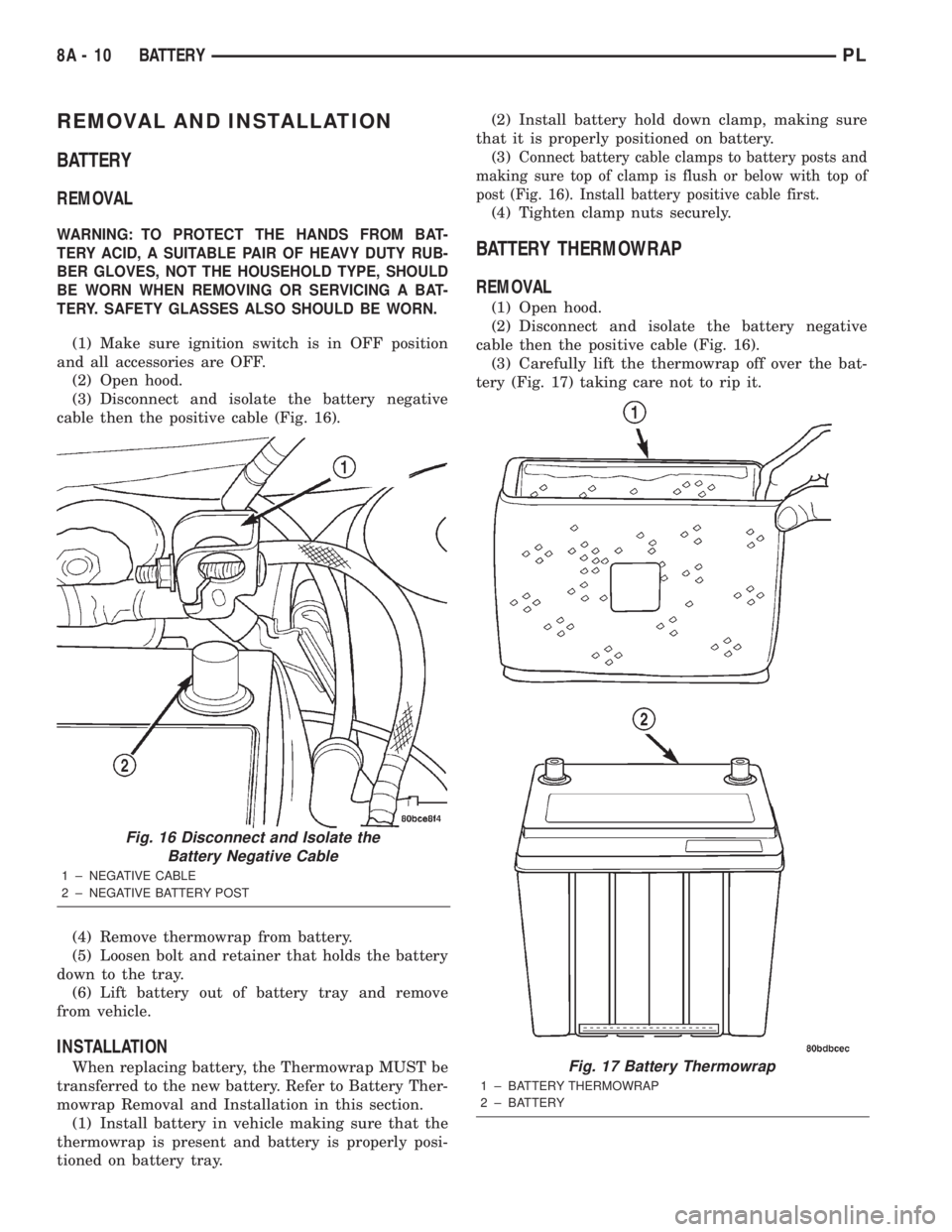
REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION
BATTERY
REMOVAL
WARNING: TO PROTECT THE HANDS FROM BAT-
TERY ACID, A SUITABLE PAIR OF HEAVY DUTY RUB-
BER GLOVES, NOT THE HOUSEHOLD TYPE, SHOULD
BE WORN WHEN REMOVING OR SERVICING A BAT-
TERY. SAFETY GLASSES ALSO SHOULD BE WORN.
(1) Make sure ignition switch is in OFF position
and all accessories are OFF.
(2) Open hood.
(3) Disconnect and isolate the battery negative
cable then the positive cable (Fig. 16).
(4) Remove thermowrap from battery.
(5) Loosen bolt and retainer that holds the battery
down to the tray.
(6) Lift battery out of battery tray and remove
from vehicle.
INSTALLATION
When replacing battery, the Thermowrap MUST be
transferred to the new battery. Refer to Battery Ther-
mowrap Removal and Installation in this section.
(1) Install battery in vehicle making sure that the
thermowrap is present and battery is properly posi-
tioned on battery tray.(2) Install battery hold down clamp, making sure
that it is properly positioned on battery.
(3)
Connect battery cable clamps to battery posts and
making sure top of clamp is flush or below with top of
post (Fig. 16). Install battery positive cable first.
(4) Tighten clamp nuts securely.
BATTERY THERMOWRAP
REMOVAL
(1) Open hood.
(2) Disconnect and isolate the battery negative
cable then the positive cable (Fig. 16).
(3) Carefully lift the thermowrap off over the bat-
tery (Fig. 17) taking care not to rip it.
Fig. 16 Disconnect and Isolate the
Battery Negative Cable
1 ± NEGATIVE CABLE
2 ± NEGATIVE BATTERY POST
Fig. 17 Battery Thermowrap
1 ± BATTERY THERMOWRAP
2 ± BATTERY
8A - 10 BATTERYPL
Page 223 of 1285

DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
CONTROL CIRCUIT
The starter control circuit has:
²Starter solenoid
²Starter relay
²Park/Neutral Starting and Back-Up Lamp
Switch with automatic transmissions
²Clutch Interlock/Upstop Switch with manual
transmissions
²Ignition switch
²Battery
²All related wiring and connections
²Double Start Override algorithm located in the
PCM
CAUTION: Before performing any starter tests, the
ignition and fuel systems must be disabled.
²To disable ignition and fuel systems, disconnect
the Automatic Shutdown Relay (ASD). The ASD relay
is located in the in the Power Distribution Center
(PDC). Refer to the PDC cover for the proper relay
location.
STARTER SOLENOID
WARNING: CHECK TO ENSURE THAT THE TRANS-
MISSION IS IN THE PARK POSITION WITH THE
PARKING BRAKE APPLIED
(1) Verify battery condition. Battery must be in
good condition with a full charge before performing
any starter tests. Refer to Battery Tests.
(2) Perform Starter Solenoid test BEFORE per-
forming the starter relay test.
(3) Raise the vehicle.
(4) Perform a visual inspection of the starter/
starter solenoid for corrosion, loose connections or
faulty wiring.
(5) Lower the vehicle.
(6) Locate and remove the starter relay from the
Power Distribution Center (PDC). Refer to the PDC
label for relay identification and location.
(7) Connect a starter switch or a jumper wire
between the remote battery positive post and termi-
nal 87 of the starter relay connector.
(a) If engine cranks, starter motor and starter
solenoid is good. Go to the Starter Relay Test.(b) If engine does not crank or solenoid chatters,
check wiring and connectors from starter relay to
starter solenoid for loose or corroded connections.
Check for corroded connections at starter termi-
nals.
(c) Repeat test. If engine still fails to crank prop-
erly, trouble is within starter or starter mounted
solenoid, and replace starter.
STARTER RELAY
WARNING: CHECK TO ENSURE THAT THE TRANS-
MISSION IS IN THE PARK POSITION WITH THE
PARKING BRAKE APPLIED.
RELAY TEST
The starter relay is located in the Power Distribu-
tion Center (PDC) in the engine compartment. Refer
to the PDC label for relay identification and location.
Use the Starter Relay Pin Call-Out table and (Fig. 3)
for relay testing.
Remove the starter relay from the PDC as
described in this group to perform the following tests:
(1) A relay in the de-energized position should
have continuity between terminals 87A and 30, and
no continuity between terminals 87 and 30. If OK, go
to Step 2. If not OK, replace the faulty relay.
(2) Resistance between terminals 85 and 86 (elec-
tromagnet) should be 7565 ohms. If OK, go to Step
3. If not OK, replace the faulty relay.
(3) Connect a battery B+ lead to terminals 86 and
a ground lead to terminal 85 to energize the relay.
The relay should click. Test for continuity between
terminals 30 and 87, and no continuity between ter-
minals 87A and 30. If OK, refer to Relay Circuit Test
procedure. If not OK, replace the faulty relay.
Fig. 3 Starter Relay
8B - 2 STARTING SYSTEMSPL
Page 227 of 1285

STARTING SYSTEM
For circuit descriptions and diagrams, refer to
8W-21, Starting System in Group 8W-Wiring Dia-
grams.
WARNING: ON VEHICLES EQUIPPED WITH AIR-
BAGS, REFER TO GROUP 8M - PASSIVE
RESTRAINT SYSTEMS BEFORE ATTEMPTING
STEERING WHEEL, STEERING COLUMN, OR
INSTRUMENT PANEL COMPONENT DIAGNOSIS OR
SERVICE. FAILURE TO TAKE THE PROPER PRE-
CAUTIONS COULD RESULT IN ACCIDENTAL AIR-
BAG DEPLOYMENT AND POSSIBLE PERSONAL
INJURY.
INSPECTION
Before removing any unit from the starting system
for repair or diagnosis, perform the following inspec-
tions:
²Battery- Visually inspect the battery for indi-
cations of physical damage and loose or corroded
cable connections. Determine the state-of-charge and
cranking capacity of the battery. Charge or replace
the battery, if required. Refer to Group 8A-Battery
for more information.²Ignition Switch- Visually inspect the ignition
switch for indications of physical damage and loose
or corroded wire harness connections.
²Clutch Interlock/Upstop Switch- Visually
inspect the clutch interlock/upstop switch for indica-
tions of physical damage and loose or corroded wire
harness connections.
²Park/Neutral Starting and Back-Up Lamp
Switch- Visually inspect the park/neutral starting
and back-up lamp switch for indications of physical
damage and loose or corroded wire harness connec-
tions.
²Starter Relay- Visually inspect the starter
relay for indications of physical damage and loose or
corroded wire harness connections.
²Starter Motor- Visually inspect the starter
motorfor indications of physical damage and loose or
corroded wire harness connections.
²Starter Solenoid- Visually inspect the starter
solenoid for indications of physical damage and loose
or corroded wire harness connections.
²Wiring- Visually inspect the wire harness for
damage. Repair or replace any faulty wiring, as
required.
8B - 6 STARTING SYSTEMSPL
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING (Continued)
Page 237 of 1285

Loose cable connections will corrode, increase resis-
tance and permit water to enter the coil towers.
These conditions can cause ignition malfunction.
Plastic clips in various locations protect the cables
from damage. When the cables are replaced the clips
must be used to prevent damage to the cables, and
should be rotated about 30É below the horizontal.
ELECTRONIC IGNITION COILS
DESCRIPTION
The coil pack consists of 2 coils molded together.
The coil pack is mounted on the valve cover (Fig. 2).
OPERATION
WARNING: THE DIRECT IGNITION SYSTEM GEN-
ERATES APPROXIMATELY 40,000 VOLTS. PER-
SONAL INJURY COULD RESULT FROM CONTACT
WITH THIS SYSTEM.
High tension leads route to each cylinder from the
coil. The coil fires two spark plugs every power
stroke. One plug is the cylinder under compression,
the other cylinder fires on the exhaust stroke. Coil
number one fires cylinders 1 and 4. Coil number two
fires cylinders 2 and 3. The PCM determines which
of the coils to charge and fire at the correct time.
The Auto Shutdown (ASD) relay provides battery
voltage to the ignition coil. The PCM provides a
ground contact (circuit) for energizing the coil. When
the PCM breaks the contact, the energy in the coil
primary transfers to the secondary causing thespark. The PCM will de-energize the ASD relay if it
does not receive the crankshaft position sensor and
camshaft position sensor inputs. Refer to Auto Shut-
down (ASD) RelayÐPCM Output, in this section for
relay operation.
AUTOMATIC SHUTDOWN RELAY
DESCRIPTION
The ASD relay is located in the PDC (Fig. 3). The
inside top of the PDC cover has label showing relay
and fuse identification.
Fig. 1 Checking Spark Plug Electrode Gap
1 ± TAPER GAUGE
Fig. 2 Ignition Coil Pack
1 ± IGNITION COILS
2 ± SPARK PLUG CABLE
3 ± SPARK PLUG INSULATOR
Fig. 3 Power Distribution Center (PDC)
8D - 2 IGNITION SYSTEMPL
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION (Continued)
Page 244 of 1285
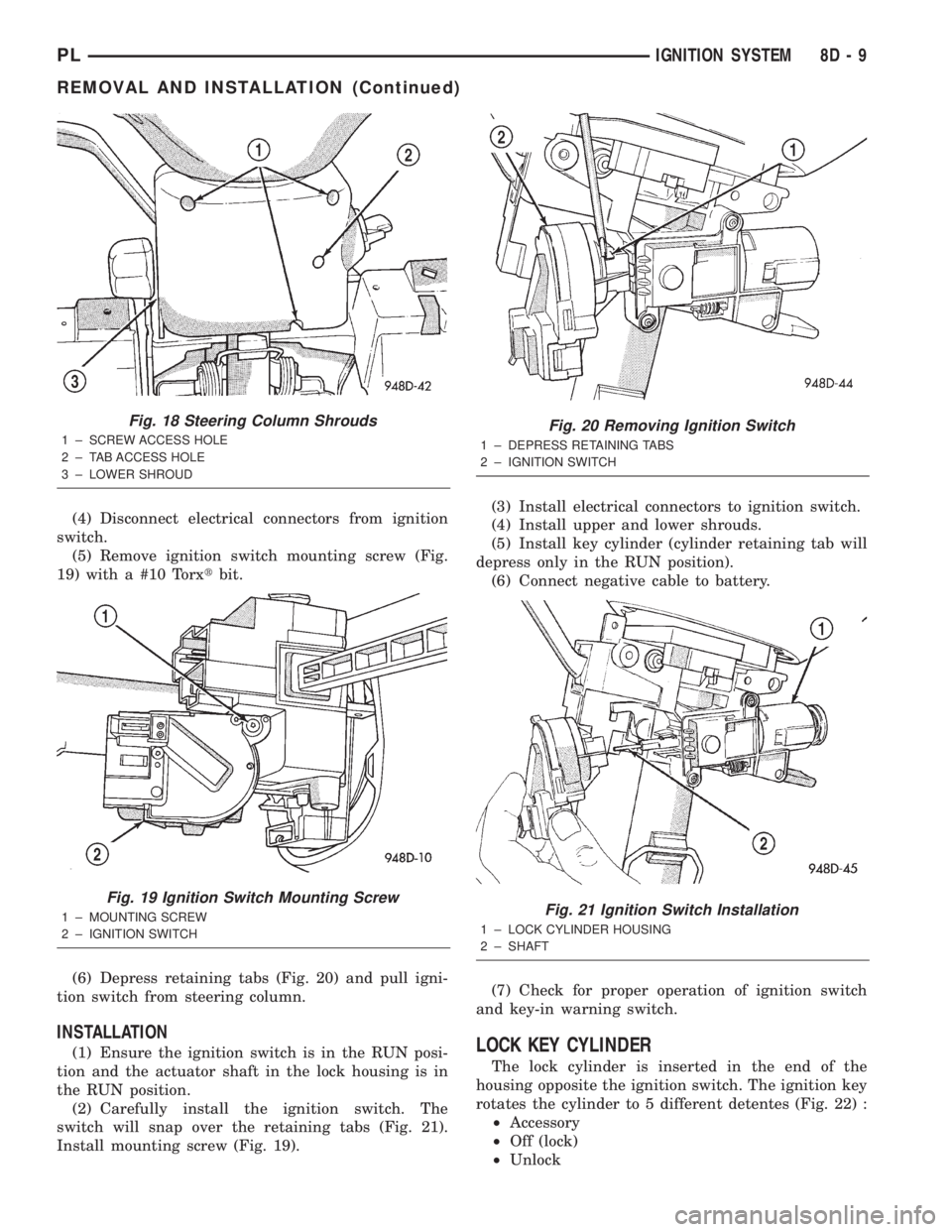
(4) Disconnect electrical connectors from ignition
switch.
(5) Remove ignition switch mounting screw (Fig.
19) with a #10 Torxtbit.
(6) Depress retaining tabs (Fig. 20) and pull igni-
tion switch from steering column.
INSTALLATION
(1) Ensure the ignition switch is in the RUN posi-
tion and the actuator shaft in the lock housing is in
the RUN position.
(2) Carefully install the ignition switch. The
switch will snap over the retaining tabs (Fig. 21).
Install mounting screw (Fig. 19).(3) Install electrical connectors to ignition switch.
(4) Install upper and lower shrouds.
(5) Install key cylinder (cylinder retaining tab will
depress only in the RUN position).
(6) Connect negative cable to battery.
(7) Check for proper operation of ignition switch
and key-in warning switch.LOCK KEY CYLINDER
The lock cylinder is inserted in the end of the
housing opposite the ignition switch. The ignition key
rotates the cylinder to 5 different detentes (Fig. 22) :
²Accessory
²Off (lock)
²Unlock
Fig. 18 Steering Column Shrouds
1 ± SCREW ACCESS HOLE
2 ± TAB ACCESS HOLE
3 ± LOWER SHROUD
Fig. 19 Ignition Switch Mounting Screw
1 ± MOUNTING SCREW
2 ± IGNITION SWITCH
Fig. 20 Removing Ignition Switch
1 ± DEPRESS RETAINING TABS
2 ± IGNITION SWITCH
Fig. 21 Ignition Switch Installation
1 ± LOCK CYLINDER HOUSING
2 ± SHAFT
PLIGNITION SYSTEM 8D - 9
REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION (Continued)
Page 248 of 1285

INSTRUMENT PANEL SYSTEMS
TABLE OF CONTENTS
page page
GENERAL INFORMATION
INTRODUCTION..........................1
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
HEADLAMP SWITCH......................2
INSTRUMENT CLUSTER....................2
WARNING AND INDICATOR LAMPS..........2
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
AIRBAG WARNING SYSTEM................2
BRAKE SYSTEM WARNING LAMP TEST.......2
INSTRUMENT CLUSTER LAMPS.............2
LOW OIL PRESSURE WARNING LAMP TEST...3
MULTIPLE/INDIVIDUAL GAUGES
INOPERATIVE..........................4
SERVICE PROCEDURES
INSTRUMENT CLUSTER SELF-DIAGNOSTICS...4
REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION
ACCESSORY SWITCH/POWER OUTLET
BEZEL................................4CENTER CONSOLE FLOOD LAMP............5
CIGAR LIGHTER / POWER OUTLET
ASSEMBLY.............................5
GLOVE BOX DOOR/BIN....................6
GLOVE BOX DOOR/BIN....................6
GLOVE BOX SWITCH/LAMP.................6
INSTRUMENT CLUSTER....................6
INSTRUMENT CLUSTER BEZEL..............6
INSTRUMENT CLUSTER LAMPS.............7
INSTRUMENT PANEL ASSEMBLY............7
INSTRUMENT PANEL CENTER BEZEL........10
INSTRUMENT PANEL END CAPS............10
INSTRUMENT PANEL TOP COVER...........10
LOWER INSTRUMENT PANEL COVER........10
LOWER STORAGE BIN....................10
STEERING COLUMN SHROUDS.............11
GENERAL INFORMATION
INTRODUCTION
The purpose of the dash gauges and indicator
lamps is to keep the driver informed about the oper-
ating condition of the vehicle. If an abnormal condi-
tion occurs, the driver is informed by indicator lamp.
The driver can seek service before damage occurs.
Indicator lamps use ON/OFF switch functions for
operation, while gauges use a sending unit or sensor.
The Instrument Panel can be removed as an
assembly after a few part are removed to allow
access to the retaining bolts. There is one self-align-
ing bulkhead connector on the left underside of the
instrument panel replacing most of the main harness
connectors. Once removed, the instrument panel can
be serviced for replacement. Most of the parts of the
instrument panel can be replaced individually with-
out removing the complete instrument panel assem-
bly.
Fig. 1 Instrument Panel
1 ± DEMISTER OUTLET
2 ± INSTRUMENT CLUSTER
3 ± CENTER AIR OUTLET
4 ± INSTRUMENT PANEL SPEAKERS
5 ± GLOVE BOX
6 ± HVAC CONTROL HEAD
7 ± RADIO
8 ± CIGAR LIGHTER/AUXILIARY POWER OUTLET
9 ± TRACTION CONTROL SWITCH
10 ± REAR WINDOW DEFOGGER SWITCH
PLINSTRUMENT PANEL SYSTEMS 8E - 1
Page 249 of 1285

DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
HEADLAMP SWITCH
The headlamp switch is part of the Multi-Function
Switch. Refer to Group 8J, Turn Signal and Flasher
for the Multi-Function Switch Test, Removal and
Installation procedures.
INSTRUMENT CLUSTER
There are two conventional instrument cluster
assemblies available. The clusters electronically drive
the speedometer, odometer, gauges, and tachometer
(if equipped). Refer to (Fig. 2) and (Fig. 3).
The instrument cluster controls the courtesy
lamps, it receives and sends messages to other mod-
ules via the PCI bus circuit, it controls all the instru-
ment illumination and the chime is also an integral
part of the cluster. The front turn signals are wired
through the cluster and then go to the front lamps.
The reason being that the DRL module is built into
the cluster (if equipped).
All gauges in the electronic clusters are the analog
type gauges. When the ignition switch is moved to
the OFF position, the cluster drives each gauge to its
lowest position. The individual gauges are not servi-
cable and require complete replacement of the cluster
if one or more gauges are inoperable.
One button is used to switch the display from trip
to total mileage. Holding the button when the display
is in the trip mode will reset the trip mileage. This
button is also used to put the cluster in self-diagnos-
tic mode. Refer to Service Procedures, Cluster Self-
Diagnostics in this section. Most of the indicators will
come on briefly for a bulb heck when the ignition is
turned from OFF to ON. All of the LED's are replace-
able.
In the event that the instrument cluster looses
communication with all other modules on the PCI
bus, the cluster will display ªnobusº in the VF dis-
play. The VF display also displays ªDoorº, ªCruiseº,
ªTracº, and odometer trip or total.
If the cluster does not detect voltage on the cour-
tesy lamp circuit, the message ªFUSEº will alternate
with the odometer/trip odometer for 30 seconds after
the ignition is turned on and for 15 seconds after the
vehicle is first moved. The lack of voltage can be due
to the M1 Fused B(+) (IOD) fuse being open, a bad or
missing courtesy lamp bulb, or a circuit problem.
WARNING AND INDICATOR LAMPS
The instrument cluster has warning lamps and
indicators for the following systems:
²Airbag
²Anti-lock Brakes (ABS) if equipped
²Brake warning
²Charging System²Front fog lamps (if equipped)
²High beam indicator
²Low fuel (premium cluster only)
²Low oil pressure
²Malfunction indicator (service engine soon) lamp
²Right and left turn signals
²Seat belt warning
²Security system
²Trac-Off (ABS equipped vehicles only)
The instrument cluster has a Vacuum Fluorescent
(VF) display for the following systems:
²Cruise
²Door (ajar)
²Odometer
²Set (cruise)
²Trac
²Trip
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
AIRBAG WARNING SYSTEM
For testing of this system refer to Group 8M, Pas-
sive Restraint Systems.
BRAKE SYSTEM WARNING LAMP TEST
The brake warning lamp illuminates when the
parking brake is applied with ignition switch turned
to the ON position. The same lamp will also illumi-
nate if one of the two service brake systems fail the
when brake pedal is applied.
To test the system:
²As the ignition switch is turned to the start posi-
tion the lamp should light.
²Turn ignition switch to the ON position and
apply the parking brake. The lamp should light.
If lamp fails to light inspect for:
²A burned out lamp
²Loose, corroded or damaged socket
²A damaged circuit board
²A broken or disconnected wire at the switch
²Defective switch
To test the service brake warning system, refer to
Group 5, Brakes, Hydraulic System Control Valves.
INSTRUMENT CLUSTER LAMPS
Every time the vehicle is switched to the START/
RUN position, the cluster goes through a BULB
CHECK. This tests most of the indicator lamps and
Vacuum Fluorescent (VF) displays. If only one lamp
is out, remove the instrument cluster and replace the
defective bulb or Light Emitting Diode (LED). If
some or all of the lamps fail to light, refer to the
proper Body Diagnostics Procedures Manual.
8E - 2 INSTRUMENT PANEL SYSTEMSPL