1999 TOYOTA CAMRY relay
[x] Cancel search: relayPage 4234 of 4592

Pins used in the system circuit.
Occupied positions, but not
applicable to the system circuit.
Unoccupied positions.
The pins shown are only for the highest grade, or only include those in the specification.
Junction Connector
Short Terminal Same ColorJunction connector (code: J1 to J40) in this manual include a short
terminal which is connected to a number of wire harnesses. Always
perform inspection with the short terminal installed. (When
installing the wire harnesses, the harnesses can be connected to
any position within the short terminal grouping. Accordingly, in
other vehicles, the same position in the short terminal may be
connected to a wire harness from a different part.)
Wire harness sharing the same short terminal grouping have the
same color.
HINT :
B
[O]: Explains the system outline.
[P]: Indicates values or explains the function for reference during troubleshooting.
[Q]: Indicates the reference page showing the position on the vehicle of the parts in the system circuit.
Example : Part ºL4º (Light Failure Sensor) is on page 36 of the manual.
*The letter in the code is from the first letter of the part, and the number indicates its order in parts
starting with that letter.
Example : L 4
� �Parts is 4th in order
Light Failure Sensor
[R]: Indicates the reference page showing the position on the vehicle of Relay Block Connectors in the system circuit.
Example : Connector º1º is described on page 18 of this manual and is installed on the left side of the instrument
panel.
[S]: Indicates the reference page showing the position on the vehicle of J/B and Wire Harness in the system circuit.
Example : Connector º3Cº connects the Instrument Panel Wire and J/B No.3. It is described on page 22 of this
manual, and is installed on the instrument panel left side.
[T]: Indicates the reference page describing the wiring harness and wiring harness connector (the female wiring
harness is shown first, followed by the male wiring harness).
Example : Connector ºIE1º connects the floor wire (female) and Instrument panel wire (male). It is described on
page 42 of this manual, and is installed on the left side kick panel.
[U]: Indicates the reference page showing the position of the ground points on the vehicle.
Example : Ground point ºBOº is described on page 50 of this manual and is installed on the back panel center.
[V]: Indicates the reference page showing the position of the splice points on the vehicle.
Example : Splice point ºI5º is on the Cowl Wire Harness and is described on page 44 of this manual.
[W]: Indicates connector to be connected to a part (the numeral indicates the pin No.) Explanation of pin use.
[X]: Connector Color
Connectors not indicated are milky white in color.
Page 4235 of 4592

B HOW TO USE THIS MANUAL
The ground points circuit diagram shows the connections from all major parts to the respective ground points. When
troubleshooting a faulty ground point, checking the system circuits which use a common ground may help you identify
the problem ground quickly. The relationship between ground points (
EA, IB and IC shown below) can also be
checked this way.
���� ���� ���� ���� ���� ���� ���� ���� ���� ���� ���� ���� ���� ���� ���� ���� ���� ���� ����
I GROUND POINT
FAN MAIN RELAY
FAN MAIN RELAY
A/C FAN RELAY NO.2
A/C FAN RELAY NO.3
RADIATOR FAN MOTOR
RETRACT CONTROL
RELAY
RETRACT MOTOR RH
RETRACT MOTOR LH
FRONT TURN SIGNAL
LIGHT RH
PARKING LIGHT RH
FRONT TURN SIGNAL
LIGHT LH
PARKING LIGHT LH
DOOR LOCK CONTROL
SW RH
DOOR KEY LOCK
SW RH
DOOR LOCK MOTOR
RH
BLOWER RESISTOR
A/C AMPLIFIER
RADIO AND PLAYER
HEATER RELAY
AUTO ANTENNA
MOTOR
BLOWER SW
PARKING BRAKE SW
COMBINATION METER
HORN SW [COMB. SW]
TURN SIGNAL FLASHER
DOOR KEY LOCK SW LH
DOOR LOCK MOTOR LH
FUEL CONTROL SW
WOOFER AMPLIFIER
COMBINATION METER
COMBINATION METER
FUEL SENDER
CIGARETTE LIGHTER
O/D MAIN SW
CLOCK
5
5
5
5
4
4
4
4
4BA15
IB18
EA2 10
3E5
3E
6 3G
13 3F
3 3D
1 3B
7
ID115
IC33
IA12
E 3
A
A AW±B
W±BW±B W±B
W±B W±B
W±B
W±B
W±B
W±B
W±B
W±B
W±B
W±B
W±B W±BW±B W±B W±B W±B
W±B W±B
W±BW±B
W±B
W±B
W±B W±B
W±B
BR
W±B
BR BRW±BW±B
W±B
W±B
W±B
W±B
W±B
W±B
W±B
W±B
W±B W±B
W±B
W±B
W±B
W±B
BR W±B
BR BR
BR W±B W±BW±B
W±BW±BBR W±B (4A±GZE)
W±B A A A
I 6
I 6
I 2
I 2
I 2
B 5I 5
I 5
I 5
B 5
B 5
B 5
I 5
I 5
I 3I 3
E 3
E 3
E 3
E 2
E 4
E 5
E 4
E 5
E 6E 4
E 4
B 4
EAI 4
B 4
B 4
I 4I 8
IBIC
3C7
4
JUNCTION
CONNECTOR J 1
4
DOOR LOCK CONTROL
RELAY
ELECTRICAL IDLE-UP
CUT RELAY (M/T)FRONT SIDE MARKER
LIGHT RH
FRONT SIDE MARKER
LIGHT LH
BRAKE FLUID LEVEL
WARNING SW
UNLOCK WARNING
SW WIPER AND WASHER
SW [COMB. SW] LIGHT CONTROL SW
[COMB. SW] HEATER CONTROL
ASSEMBLY
HEATER SERVO
MOTOR AMPLIFIER
DIMMER SW
[COMB. SW]
CRUISE CONTROL
MIRROR SW
REAR WINDOW
DEFOGGER SW
POWER WINDOW
MASTER SW
POWER WINDOW
CONTROL RELAY
DOOR LOCK CONTROL
SW
REMOTE CONTROL
MIRROR SW
* The system shown here is an EXAMPLE ONLY. It is different to the actual circuit shown in the SYSTEM CIRCUITS SECTION.
Page 4236 of 4592
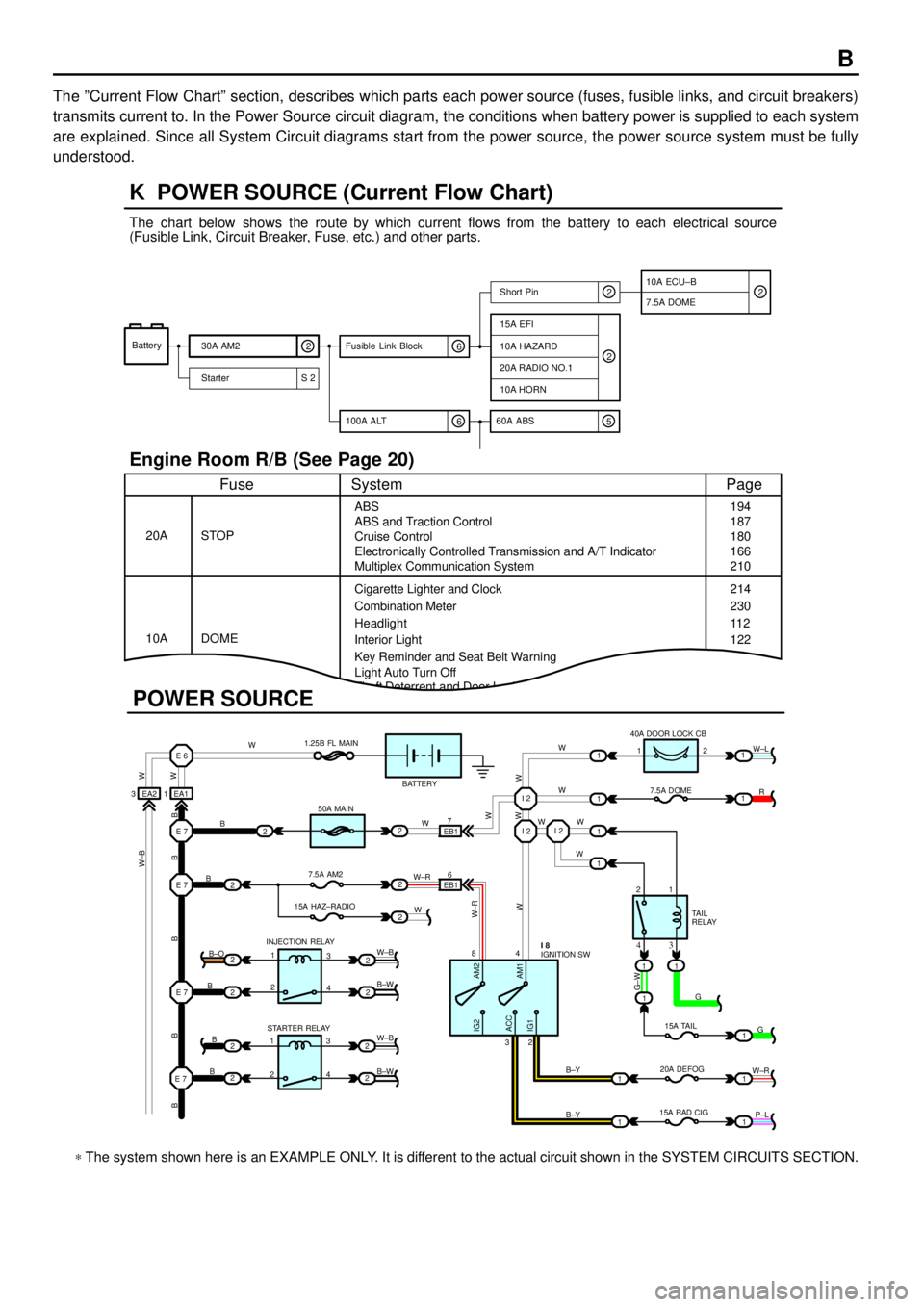
B
The ºCurrent Flow Chartº section, describes which parts each power source (fuses, fusible links, and circuit breakers)
transmits current to. In the Power Source circuit diagram, the conditions when battery power is supplied to each system
are explained. Since all System Circuit diagrams start from the power source, the power source system must be fully
understood.
Theft Deterrent and Door Lock Control
K POWER SOURCE (Current Flow Chart)
11
1
EA1 1EA2 3
7
EB16
E 6
E 7I 2I 2
I 2
E 7
E 7
E 7
2
1
1
2
2
2
2
2
B
B
W W
B B B B BW±B
B
B
B B±O
B±W
W±B
B±W STARTER RELAY INJECTION RELAY15A HAZ±RADIO7.5A AM250A MAIN 1.25B FL MAIN
BATTERY
WWW
W W W
R W±L
W
W
G±W
G
15A TAIL
20A DEFOG
15A RAD CIGTA I L
RELAY 7.5A DOME 40A DOOR LOCK CB
2 1
1 2
4 8
2 3
3 4
G
W±R
P±L B±Y
B±Y
W±R
AM2 IG2
ACC
IG1AM1W W
W±R
W W
W±B
21
1
1
1
1
2
2
2
2
3
4
3
4 1
2
1
22
1
11
1
IGNITION SW I 8
Battery
30A AM2
2
Starter S 220A RADIO NO.1
10A HORN
15A EFI
7.5A DOMEShort Pin
10A HAZARD
The chart below shows the route by which current flows from the battery to each electrical source
(Fusible Link, Circuit Breaker, Fuse, etc.) and other parts.
Engine Room R/B (See Page 20)
ABS
ABS and Traction Control
Cruise Control
Electronically Controlled Transmission and A/T Indicator
Multiplex Communication System
Cigarette Lighter and Clock
Key Reminder and Seat Belt Warning STOP
Fuse Page
194
214
11 2
System
DOME 20A
10ACombination Meter
Headlight
Interior Light
2
2
6 100A ALT
EB1
POWER SOURCE
Light Auto Turn Off187
180
166
210
230
122
10A ECU±B
5 60A ABS
2
6 Fusible Link Block2
* The system shown here is an EXAMPLE ONLY. It is different to the actual circuit shown in the SYSTEM CIRCUITS SECTION.
Page 4237 of 4592
![TOYOTA CAMRY 1999 Service Repair Manual To Ignition SW
IG Terminal
Fuse
Voltmeter SW 1
Relay
SW 2Solenoid[A]
[B]
[C]
Ohmmeter
SW
Ohmmeter
Diode
Digital Type Analog Type
C TROUBLESHOOTING
VOLTAGE CHECK
(a)Establish conditions in which volta TOYOTA CAMRY 1999 Service Repair Manual To Ignition SW
IG Terminal
Fuse
Voltmeter SW 1
Relay
SW 2Solenoid[A]
[B]
[C]
Ohmmeter
SW
Ohmmeter
Diode
Digital Type Analog Type
C TROUBLESHOOTING
VOLTAGE CHECK
(a)Establish conditions in which volta](/manual-img/14/57448/w960_57448-4236.png)
To Ignition SW
IG Terminal
Fuse
Voltmeter SW 1
Relay
SW 2Solenoid[A]
[B]
[C]
Ohmmeter
SW
Ohmmeter
Diode
Digital Type Analog Type
C TROUBLESHOOTING
VOLTAGE CHECK
(a)Establish conditions in which voltage is present at the check
point.
Example:
[A] ± Ignition SW on
[B] ± Ignition SW and SW 1 on
[C] ± Ignition SW, SW 1 and Relay on (SW 2 off)
(b)Using a voltmeter, connect the negative lead to a good ground
point or negative battery terminal, and the positive lead to the
connector or component terminal.
This check can be done with a test light instead of a voltmeter.
CONTINUITY AND RESISTANCE CHECK
(a)Disconnect the battery terminal or wire so there is no voltage
between the check points.
(b)Contact the two leads of an ohmmeter to each of the check
points.
If the circuit has diodes, reverse the two leads and check
again.
When contacting the negative lead to the diode positive side
and the positive lead to the negative side, there should be
continuity.
When contacting the two leads in reverse, there should be no
continuity.
(c)Use a volt/ohmmeter with high impedance (10 kW/V
minimum) for troubleshooting of the electrical circuit.
Page 4238 of 4592
![TOYOTA CAMRY 1999 Service Repair Manual To Ignition SW
IG Terminal
Test Light
Relay Light
SW 2 SolenoidDisconnectShort [A]
Disconnect
DisconnectSW 1Fuse Case
Short [B]
Short [C]
Pull Up
Press Down Press DownPull Up
C
FINDING A SHORT CIRCUIT TOYOTA CAMRY 1999 Service Repair Manual To Ignition SW
IG Terminal
Test Light
Relay Light
SW 2 SolenoidDisconnectShort [A]
Disconnect
DisconnectSW 1Fuse Case
Short [B]
Short [C]
Pull Up
Press Down Press DownPull Up
C
FINDING A SHORT CIRCUIT](/manual-img/14/57448/w960_57448-4237.png)
To Ignition SW
IG Terminal
Test Light
Relay Light
SW 2 SolenoidDisconnectShort [A]
Disconnect
DisconnectSW 1Fuse Case
Short [B]
Short [C]
Pull Up
Press Down Press DownPull Up
C
FINDING A SHORT CIRCUIT
(a)Remove the blown fuse and disconnect all loads of the fuse.
(b)Connect a test light in place of the fuse.
(c)Establish conditions in which the test light comes on.
Example:
[A] ± Ignition SW on
[B] ± Ignition SW and SW 1 on
[C] ± Ignition SW, SW 1 and Relay on (Connect the
Relay) and SW 2 off (or Disconnect SW 2)
(d)Disconnect and reconnect the connectors while watching the
test light.
The short lies between the connector where the test light
stays lit and the connector where the light goes out.
(e)Find the exact location of the short by lightly shaking the
problem wire along the body.
CAUTION:
(a) Do not open the cover or the case of the ECU unless
absolutely necessary. (If the IC terminals are touched,
the IC may be destroyed by static electricity.)
(b) When replacing the internal mechanism (ECU part) of
the digital meter, be careful that no part of your body or
clothing comes in contact with the terminals of leads
from the IC, etc. of the replacement part (spare part).
DISCONNECTION OF MALE AND FEMALE
CONNECTORS
To pull apart the connectors, pull on the connector itself, not
the wire harness.
HINT : C h e c k t o s e e w h a t k i n d o f connector you are
disconnecting before pulling apart.
Page 4242 of 4592

* The titles given inside the components are the names of the terminals (terminal codes) and are not treated as being
abbreviations.
ABBREVIATIONS D
ABBREVIATIONS
The following abbreviations are used in this manual.
ABS = Anti±Lock Brake System
A/C = Air Conditioning
ACIS = Acoustic Control Induction System
A/T = Automatic Transaxle
COMB. = Combination
ECU = Electronic Control Unit
EGR = Exhaust Gas Recirculation
ESA = Electronic Spark Advance
EVAP = Evaporative Emission
FL = Fusible Link
J/B = Junction Block
LH = Left±Hand
M/T = Manual Transaxle
O/D = Overdrive
R/B = Relay Block
RH = Right±Hand
SFI = Sequential Multiport Fuel Injection
SRS = Supplemental Restraint System
SW = Switch
TEMP. = Temperature
VSV = Vacuum Switching Valve
w/ = With
w/o = Without
Page 4244 of 4592
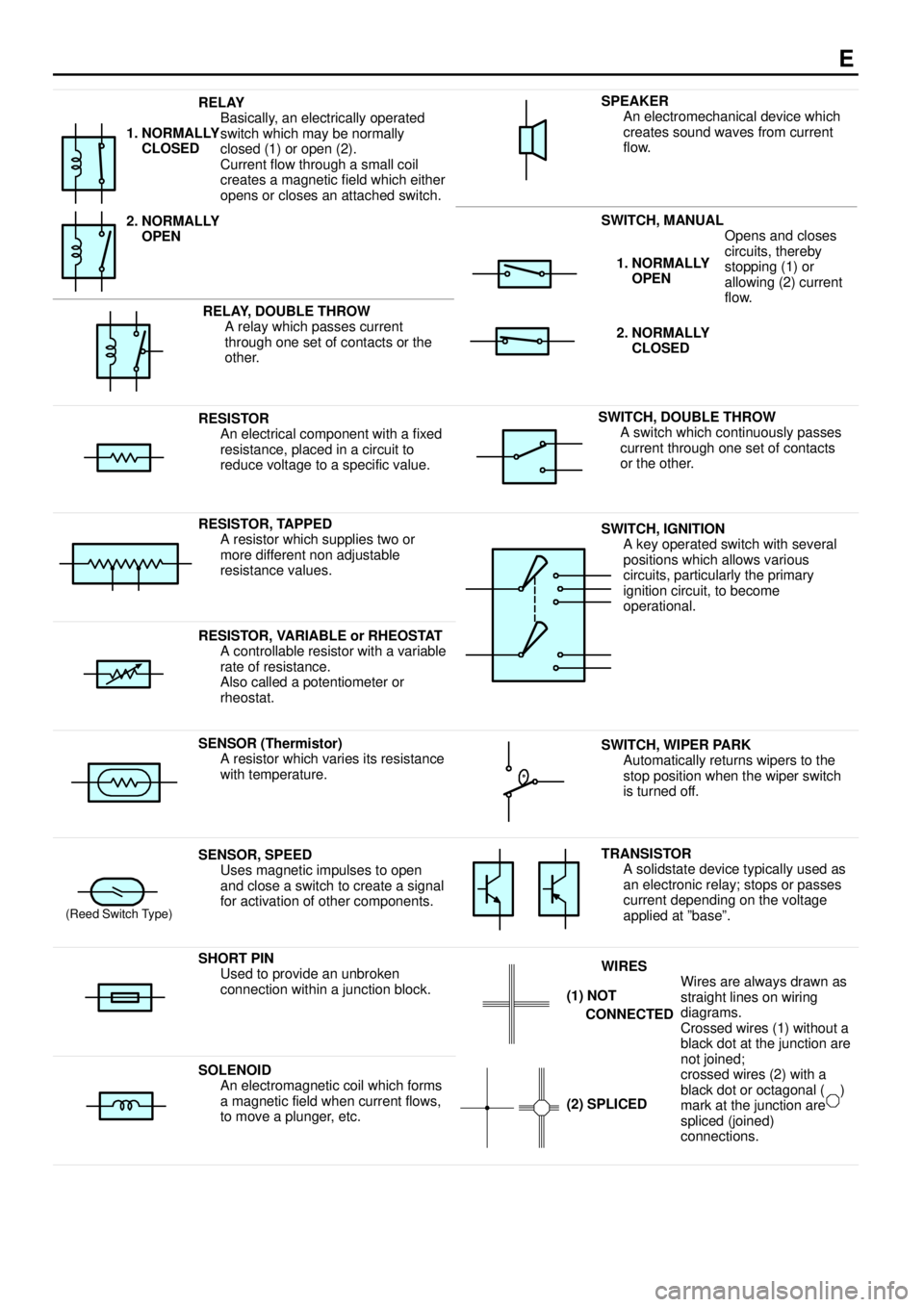
E
RELAY
Basically, an electrically operated
switch which may be normally
closed (1) or open (2).
Current flow through a small coil
creates a magnetic field which either
opens or closes an attached switch.
1. NORMALLY
CLOSED
2. NORMALLY
OPEN
SWITCH, MANUAL
Opens and closes
iitth b
SPEAKER
An electromechanical device which
creates sound waves from current
flow.
RELAY, DOUBLE THROW
A relay which passes current
through one set of contacts or the
other.
circuits, thereby
stopping (1) or
allowing (2) current
flow.1. NORMALLY
OPEN
2. NORMALLY
CLOSED
RESISTOR
An electrical component with a fixed
resistance, placed in a circuit to
reduce voltage to a specific value.SWITCH, DOUBLE THROW
A switch which continuously passes
current through one set of contacts
or the other.
RESISTOR, TAPPED
A resistor which supplies two or
more different non adjustable
resistance values.SWITCH, IGNITION
A key operated switch with several
positions which allows various
circuits, particularly the primary
ignition circuit, to become
operational.
RESISTOR, VARIABLE or RHEOSTAT
A controllable resistor with a variable
rate of resistance.
Also called a potentiometer or
rheostat.
SENSOR (Thermistor)
A resistor which varies its resistance
with temperature.SWITCH, WIPER PARK
Automatically returns wipers to the
stop position when the wiper switch
is turned off.
(Reed Switch Type)
SENSOR, SPEED
Uses magnetic impulses to open
and close a switch to create a signal
for activation of other components.TRANSISTOR
A solidstate device typically used as
an electronic relay; stops or passes
current depending on the voltage
applied at ºbaseº.
SHORT PIN
Used to provide an unbroken
connection within a junction block.WIRES
Wires are always drawn as
straight lines on wiring
diagrams.
Crossed wires (1) without a
black dot at the junction are
tj i d
(1) NOT
CONNECTED
SOLENOID
An electromagnetic coil which forms
a magnetic field when current flows,
to move a plunger, etc.
j
not joined;
crossed wires (2) with a
black dot or octagonal ( )
mark at the junction are
spliced (joined)
connections.
(2) SPLICED
Page 4245 of 4592
![TOYOTA CAMRY 1999 Service Repair Manual F RELAY LOCATIONS
[Engine Compartment]
[Body] TOYOTA CAMRY 1999 Service Repair Manual F RELAY LOCATIONS
[Engine Compartment]
[Body]](/manual-img/14/57448/w960_57448-4244.png)
F RELAY LOCATIONS
[Engine Compartment]
[Body]