1999 DODGE NEON Water pump
[x] Cancel search: Water pumpPage 109 of 1200

FRONT DISC BRAKE SHOES
WARNING: ALTHOUGH FACTORY INSTALLED
BRAKELININGS ARE MADE FROM ASBESTOS
FREE MATERIALS, SOME AFTER MARKET BRAKE-
LINING MAY CONTAIN ASBESTOS. THIS SHOULD
BE TAKEN INTO ACCOUNT WHEN SERVICING A
VEHICLE'S BRAKE SYSTEM, WHEN AFTERMARKET
BRAKELININGS MAY HAVE BEEN INSTALLED ON
THE VEHICLE. ALWAYS WEAR A RESPIRATOR
WHEN CLEANING BRAKE COMPONENTS AS
ASBESTOS CAN CAUSE SERIOUS BODILY HARM
SUCH AS ASBESTOSIS AND OR CANCER. NEVER
CLEAN BRAKE COMPONENTS BY USING COM-
PRESSED AIR, USE ONLY A VACUUM CLEANER
SPECIFICALLY DESIGNED FOR THE REMOVAL OF
BRAKE DUST. IF A VACUUM CLEANER IS NOT
AVAILABLE, CLEAN BRAKE PARTS USING ONLY
WATER DAMPENED SHOP TOWELS. DO NOT CRE-
ATE BRAKELINING DUST BY SANDING BRAKE LIN-
INGS WHEN SERVICING A VEHICLE. DISPOSE OF
ALL DUST AND DIRT SUSPECTED OF CONTAINING
ASBESTOS FIBERS USING ONLY SEALED AIR-
TIGHT BAGS OR CONTAINERS. FOLLOW ALL REC-
OMMENDED SAFETY PRACTICES PRESCRIBED BY
THE OCCUPATIONAL SAFETY AND HEALTH ADMIN-
ISTRATION (OSHA) AND THE ENVIRONMENTAL
PROTECTION AGENCY (EPA), FOR HANDLING AND
DISPOSAL OF PRODUCTS CONTAINING ASBES-
TOS.
During service procedures, grease or any other for-
eign material must be kept off caliper assembly, sur-
faces of braking rotor and external surfaces of hub.
Handling of the brake rotor and caliper should be
done in such a way as to avoid deformation of the
rotor and scratching or nicking of the brake linings.
If inspection reveals that the square sectioned cal-
iper piston seal is worn or damaged, it should be
replaced immediately.
During removal and installation of a wheel and
tire, use care not to strike the caliper.
NOTE: Before vehicle is moved after any brake
service work, pump the brake pedal several times
to insure the vehicle has a firm brake pedal.
NOTE: Starting with the 1998 model year, different
lining material is used on the disc brake shoes
depending on the type of brake system the vehicle
is equipped with. Vehicles equipped with standard
front disc and rear drum brakes use a new lining
material on the front disc brake shoes. Vehicles that
are equipped with optional 4 wheel disc brakes use
a new lining material on both the front and rear disc
brake shoes. When new brake shoes are installed,be sure brake shoes for the correct model year and
type of brake system the vehicle is equipped with
are used.
REMOVE
(1) Raise vehicle on jackstands or centered on a
hoist. See Hoisting in the Lubrication and Mainte-
nance section of this manual.
(2) Remove the front wheel and tire assemblies
from vehicle.
(3) Remove the 2 guide pin bolts (Fig. 60) mount-
ing the caliper to the steering knuckle.
(4) Remove brake caliper from steering knuckle, by
first rotating free end of caliper away from steering
knuckle. Then slide opposite end of caliper out from
under machined abutment on steering knuckle (Fig.
61).
(5) Support caliper firmly to prevent weight of cal-
iper from damaging the flexible brake hose (Fig. 62).
Fig. 60 Caliper Guide Pin Bolts
Fig. 61 Removing Caliper From Steering Knuckle
5 - 28 BRAKESPL
REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION (Continued)
Page 113 of 1200

(4) Carefully lower caliper and brake shoe assem-
blies over braking disc (rotor) reversing the required
removal procedure (Fig. 71). Make sure that the cal-
iper guide pin bolts, bushings and sleeves are clear of
the adapter bosses.
CAUTION: Extreme caution should be taken not to
cross thread the caliper guide pin bolts when they
are installed.
(5) Install caliper assembly guide pin bolts into
adapter and tighten (Fig. 70). Then torque both guide
pin bolts to 22 N´m (192 in. lbs.).
(6) Install the wheel and tire assembly.
(7) Tighten the wheel mounting stud nuts in
proper sequence until all nuts are torqued to half
specification. Then repeat the tightening sequence to
the full specified torque of 135 N´m (100 ft. lbs.).
(8) Remove jackstands or lower hoist.Before
moving vehicle, pump the brake pedal several
times to insure the vehicle has a firm brake
pedal.
(9) Road test the vehicle and make several stops to
wear off any foreign material on the brakes and to
seat the brake pads.
REAR DISC BRAKE SHOES
WARNING: ALTHOUGH FACTORY INSTALLED
BRAKELININGS ARE MADE FROM ASBESTOS
FREE MATERIALS, SOME AFTER MARKET BRAKE-
LINING MAY CONTAIN ASBESTOS. THIS SHOULD
BE TAKEN INTO ACCOUNT WHEN SERVICING A
VEHICLE'S BRAKE SYSTEM, WHEN AFTERMARKET
BRAKELININGS MAY HAVE BEEN INSTALLED ON
THE VEHICLE. ALWAYS WEAR A RESPIRATOR
WHEN CLEANING BRAKE COMPONENTS AS
ASBESTOS CAN CAUSE SERIOUS BODILY HARM
SUCH AS ASBESTOSIS AND OR CANCER. NEVER
CLEAN BRAKE COMPONENTS BY USING COM-
PRESSED AIR, USE ONLY A VACUUM CLEANER
SPECIFICALLY DESIGNED FOR THE REMOVAL OF
BRAKE DUST. IF A VACUUM CLEANER IS NOT
AVAILABLE, CLEAN BRAKE PARTS USING ONLY
WATER DAMPENED SHOP TOWELS. DO NOT CRE-
ATE BRAKELINING DUST BY SANDING BRAKE LIN-
INGS WHEN SERVICING A VEHICLE. DISPOSE OF
ALL DUST AND DIRT SUSPECTED OF CONTAINING
ASBESTOS FIBERS USING ONLY SEALED AIR-
TIGHT BAGS OR CONTAINERS. FOLLOW ALL REC-
OMMENDED SAFETY PRACTICES PRESCRIBED BY
THE OCCUPATIONAL SAFETY AND HEALTH ADMIN-
ISTRATION (OSHA) AND THE ENVIRONMENTAL
PROTECTION AGENCY (EPA), FOR HANDLING AND
DISPOSAL OF PRODUCTS CONTAINING ASBES-
TOS.During service procedures, grease or any other for-
eign material must be kept off caliper assembly, sur-
faces of braking rotor and external surfaces of hub.
Handling of the braking rotor and caliper should
be done in such a way as to avoid deformation of the
rotor and scratching or nicking of the brake linings.
If inspection reveals that the square sectioned cal-
iper piston seal is worn or damaged, it should be
replaced immediately.
During removal and installation of a wheel and
tire assembly, use care not to strike the caliper.
NOTE: Before vehicle is moved after any brake
service work, pump the brake pedal several times
to insure the vehicle has a firm brake pedal.
NOTE: Starting with the 1998 model year, different
lining material is used on the rear disc brake shoes.
Vehicles equipped with optional 4 wheel disc
brakes use a new lining material on the rear disc
brake shoes than prior model year vehicles
equipped with this brake system. When new brake
shoes are installed, be sure brake shoes for the
correct model year and type of brake system the
vehicle is equipped with are used.REMOVE
(1) Raise vehicle on jackstands or centered on a
hoist. See Hoisting in the Lubrication and Mainte-
nance section of this manual.
(2) Remove rear wheel and tire assemblies from
vehicle.
(3) Remove the 2 caliper assembly to adapter
guide pin bolts (Fig. 74).
(4) Remove caliper assembly from adapter and
rotor by first rotating top of caliper assembly away
Fig. 74 Caliper Assembly Guide Pin Bolts
5 - 32 BRAKESPL
REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION (Continued)
Page 163 of 1200

CAUTION: Certain components of the ABS System
are not intended to be serviced individually.
Attempting to remove or disconnect certain system
components may result in improper system opera-
tion. Only those components with approved
removal and installation procedures in this manual
should be serviced.
CAUTION: Brake fluid will damage painted sur-
faces. If brake fluid is spilled on any painted sur-
faces, wash off with water immediately.
CAUTION: When performing any service procedure
on a vehicle equipped with ABS do not apply a 12
volt power source to the ground circuit of the pump
motor in the HCU. Doing this will damage the pump
motor and will require replacement of the entire
HCU.
The following are general cautions which should be
observed when servicing the ABS system and/or
other vehicle systems. Failure to observe these pre-
cautions may result in ABS System component dam-
age.
If welding work is to be performed on the vehicle,
using an electric arc welder, the CAB connector
should be disconnected during the welding operation.
The CAB 25 way connector connector should never
be connected or disconnected with the ignition switch
in the ON position.
Many components of the ABS System are not ser-
viceable and must be replaced as an assembly. Do not
disassemble any component which is not designed to
be serviced.
ABS HYDRAULIC CONTROL UNIT
REMOVE
(1) Disconnect negative (ground) cable from the
battery and isolate cable.
(2) Remove the power distribution center (PDC)
(Fig. 17) from the battery thermogaurd. PDC is
removed by unlatching the two retaining clips hold-
ing it to the thermogaurd and then pulling it straight
up off of the thermogaurd.
(3) Remove vacuum supply hose from speed control
servo (Fig. 18).
(4) Remove the 2 bolts (Fig. 18) mounting the
bracket for the speed control servo to the body.
(5) Remove the wiring harness connector (Fig. 19)
from the speed control servo. Then remove the rout-
ing clip for the speed control servo wiring harness
from the speed control servo mounting bracket.
(6) Lay the speed control servo, with the speed
control cable attached, on top of the engine.(7) Disconnect wiring harness connector from the
brake fluid level sensor on master cylinder reservoir.
Fig. 17 PDC Attachment To Thermogaurd
Fig. 18 Speed Control Servo Bracket Mounting
Fig. 19 Wiring Harness Connection To Speed
Control Servo
5 - 82 BRAKESPL
REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION (Continued)
Page 194 of 1200

COOLING
CONTENTS
page page
GENERAL INFORMATION
ACCESSORY DRIVE BELTS................ 2
AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION OIL COOLER.... 3
COOLANT RECOVERY SYSTEM (CRS)....... 2
COOLANT.............................. 3
COOLING SYSTEM PRESSURE CAP......... 3
COOLING SYSTEM....................... 1
ENGINE BLOCK HEATER.................. 3
ENGINE THERMOSTAT.................... 3
RADIATOR............................. 3
WATER PUMP.......................... 3
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
COOLANT PERFORMANCE................. 4
COOLING SYSTEM PRESSURE CAP......... 5
ENGINE BLOCK HEATER.................. 5
ENGINE THERMOSTAT.................... 4
RADIATOR HOSES AND CLAMPS........... 5
WATER PUMP.......................... 6
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
ACCESSORY DRIVEBELT DIAGNOSIS....... 13
COOLING SYSTEM DIAGNOSIS............. 7
COOLING SYSTEM FLOW CHECK.......... 14
DEAERATION.......................... 15
ELECTRIC FAN MOTOR TEST.............. 14
ENGINE THERMOSTAT TESTING........... 13
LOW COOLANT LEVEL AERATION.......... 15
PRESSURE CAP TO FILLER NECK SEAL
PRESSURE RELIEF CHECK.............. 15
PRESSURE TESTING COOLING SYSTEM
PRESSURE CAP...................... 15
RADIATOR FAN CONTROL................ 14
TEMPERATURE GAUGE INDICATION........ 16
TESTING COOLING SYSTEM FOR LEAKS.... 14WATER PUMP DIAGNOSIS............... 14
SERVICE PROCEDURES
COOLANT LEVEL CHECKÐROUTINE........ 16
COOLANT LEVELÐSERVICING............ 16
COOLANTÐADDING ADDITIONAL......... 16
COOLING SYSTEMÐDRAINING............ 16
COOLING SYSTEMÐREFILLING........... 17
REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION
ACCESSORY DRIVE BELTS............... 21
ENGINE BLOCK HEATER................. 21
ENGINE THERMOSTAT................... 18
RADIATOR DRAINCOCK.................. 20
RADIATOR FANS AND MOTOR............ 20
RADIATOR............................ 19
WATER PUMP INLET TUBE............... 18
WATER PUMP......................... 17
CLEANING AND INSPECTION
ACCESSORY DRIVE BELT INSPECTION...... 22
CHEMICAL CLEANING................... 23
CLEANING COOLING SYSTEM............. 22
COOLING SYSTEM CAP.................. 22
RADIATOR FLUSHING................... 23
REVERSE FLUSHING.................... 23
WATER PUMP......................... 21
ADJUSTMENTS
BELT TENSION GAUGE METHOD........... 24
PROPER BELT TENSION................. 23
SPECIFICATIONS
COOLING SYSTEM CAPACITY............. 24
TORQUE.............................. 24
SPECIAL TOOLS
COOLING............................. 24
GENERAL INFORMATION
COOLING SYSTEM
The cooling system consists of an engine cooling
module, thermostat, coolant, and a water pump to
circulate the coolant. The engine cooling module may
consist of a radiator, electric fan motor, fan, shroud,
coolant reserve system, transmission oil cooler, hoses,
clamps, air condition condenser and transmission oil lines.
²When the Engine is cold: The thermostat is
closed; the cooling system has no flow through the
radiator. The coolant flows through the engine,
heater system and bypass.
²When the Engine is warm: Thermostat is open;
the cooling system has flow through radiator, engine,
heater system and bypass.
Coolant flow circuit for the 2.0L engine is shown in
(Fig. 1).
PLCOOLING 7 - 1
Page 196 of 1200

ENGINE THERMOSTAT
The engine thermostat is located on the front of
the engine (radiator side) in the thermostat housing/
engine outlet connector. The thermostat has an air
bleed (vent) located in the flange and a O-ring for
sealing incorporate on it. There is a relief in the ther-
mostat housing/outlet connector for the O-ring.
WATER PUMP
The water pump has a diecast aluminum body and
housing with a stamped steel impeller. The water
pump bolts directly to the block (Fig. 4). Cylinder
block to water pump sealing is provided by a rubber
O-ring. The water pump is driven by the timing belt.
Refer to Group 9, Engine section for component
removal to access the water pump.
NOTE: The water pump on all models can be
replaced without discharging the air conditioning
system.
COOLANT
The cooling system is designed around the coolant.
The coolant must accept heat from engine block
metal and in the cylinder head area near the exhaust
valves. Then coolant carries this heat to the radiator
where the tube/fin assemblies of these components
can give off the heat to the air.
MopartAntifreeze or the equivalent is recom-
mended for optimum cooling performance and corro-
sion protection when mixed to a freeze point of -37É C
(-35É F).
COOLANT REPLACEMENT
Refer to Group 0, Lubrication and Maintenance for
schedule.
COOLING SYSTEM PRESSURE CAP
The cooling system is equipped with a pressure cap
that releases pressure at some point within a range
of 97-124 kPa (14-18 psi) (Fig. 5).
The system will operate at higher than atmo-
spheric pressure, which raises the coolant boiling
point, allowing increased radiator cooling capacity.
AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION OIL COOLER
Oil coolers are internal oil to coolant type, mounted
in the radiator lower tank (Fig. 6). Rubber oil lines
feed the oil cooler and the automatic transmission.
Use only approved transmission oil cooler hose. Since
these are molded to fit space available, molded hoses
are recommended. Tighten Oil Cooler Hose Clamps
to 2 N´m (18 in. lbs.).
RADIATOR
The radiator is a down-flow type (vertical tubes)
with design features that provide greater strength,
as well as sufficient heat transfer capabilities to keep
the engine satisfactorily cooled (Fig. 6).
ENGINE BLOCK HEATER
The engine block heater is available as an optional
accessory. The heater, operated by ordinary house
current (110 Volt A.C.) through a power cord and con-
nector behind the radiator grille, provides easier
engine starting and faster warm-up when vehicle is
operated in areas having extremely low tempera-
tures.
Fig. 4 Water Pump
Fig. 5 Cooling System Pressure Cap
PLCOOLING 7 - 3
GENERAL INFORMATION (Continued)
Page 197 of 1200

DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
ENGINE THERMOSTAT
The engine cooling thermostats are wax pellet
driven, reverse poppet choke type. They are designed
to provide the fastest warm up possible by prevent-
ing leakage through them and to guarantee a mini-
mum engine operating temperature of 88 to 93ÉC
(192 to 199ÉF). They also automatically reach wide
open so they do not restrict flow to the radiator as
temperature of the coolant rises in hot weather to
around 104ÉC (220ÉF). Above this temperature the
coolant temperature is controlled by the radiator, fan,
and ambient temperature, not the thermostat.
Its primary purpose is to maintain engine temper-
ature in a range that will provide satisfactory engine
performance and emission levels under all expected
driving conditions. It also provides hot water (cool-
ant) for heater performance. It does this by transfer-
ring heat from engine metal and automatic
transmission oil cooler (if equipped) to coolant, mov-
ing this heated coolant to the heater core and radia-
tor, and then transferring this heat to the ambient
air.
COOLANT PERFORMANCE
Performance is measurable. For heat transfer pure
water excels (Formula = 1 btu per minute for each
degree of temperature rise for each pound of water).
This formula is altered when necessary additives to
control boiling, freezing, and corrosion are added as
follows:
²Pure Water (1 btu) boils at 100ÉC (212ÉF) and
freezes at 0ÉC (32ÉF).
²100 Percent Glycol (.7 btu) can cause a hot
engine and detonation and will raise the freeze point
to 22ÉC (-8ÉF).
²50/50 Glycol and Water (.82 btu) is the recom-
mended combination that provides a freeze point of
-37ÉC(-35ÉF). The radiator, water pump, engine water
jacket, radiator pressure cap, thermostat, tempera-
ture gauge, sending unit and heater are all designed
for 50/50 glycol.
Where required, a 56 percent glycol and 44 percent
water mixture will provide a freeze point of -59ÉC
(-50ÉF).
CAUTION: Richer mixtures cannot be measured
with field equipment which can lead to problems
associated with 100 percent glycol.
Fig. 6 Cooling Modules
7 - 4 COOLINGPL
GENERAL INFORMATION (Continued)
Page 198 of 1200

SELECTION AND ADDITIVES
The use of aluminum cylinder heads, intake mani-
folds DOHC, and water pumps requires special corro-
sion protection. MopartAntifreeze or the equivalent
is recommended for best engine cooling without cor-
rosion. When mixed only to a freeze point of -37ÉC
(-35ÉF) to -59ÉC (-50ÉF). If it looses color or becomes
contaminated, drain, flush, and replace with fresh
properly mixed solution.
COOLING SYSTEM PRESSURE CAP
The cooling system is equipped with a pressure cap
that releases built up pressure, maintaining a range
of 97-124 kPa (14-18 psi).
The cooling system will operate at higher than
atmospheric pressure. The higher pressure raises the
coolant boiling point thus, allowing increased radia-
tor cooling capacity.
There is a vent valve in the center of the cap that
allows a small coolant flow from the coolant reserve
system (CRS) tank. This valve is spring loaded in the
closed position. However it must be free to open dur-
ing system cool-down.If the valve is stuck shut,
the radiator hoses will collapse on cool-down.
Clean the vent valve (Fig. 7) to ensure proper
sealing function.
There is a gasket in the cap that seals to the top of
the filler neck so that vacuum is maintained to draw
coolant back into the system from the coolant reserve
system (CRS) tank.
RADIATOR HOSES AND CLAMPS
WARNING: IF VEHICLE HAS BEEN RUN
RECENTLY, WAIT 15 MINUTES BEFORE WORKING
ON VEHICLE. RELIEVE PRESSURE BY PLACING A
SHOP TOWEL OVER THE CAP AND WITHOUT
PUSHING DOWN ROTATE IT COUNTERCLOCKWISE
TO THE FIRST STOP. ALLOW FLUIDS TO ESCAPE
THROUGH THE OVERFLOW TUBE AND WHEN THE
SYSTEM STOPS PUSHING OUT COOLANT AND
STEAM AND THE PRESSURE DROPS CONTINUE
SERVICE.
WARNING: CONSTANT TENSION HOSE CLAMPS
ARE USED ON MOST COOLING SYSTEM HOSES.
WHEN REMOVING OR INSTALLING, USE ONLY
TOOLS DESIGNED FOR SERVICING THIS TYPE OF
CLAM. ALWAYS WEAR SAFETY GLASSES WHEN
SERVICING CONSTANT TENSION CLAMPS.
CAUTION: A number or letter is stamped into the
tongue of constant tension clamps. If replacement
is necessary, use only a original equipment clamp
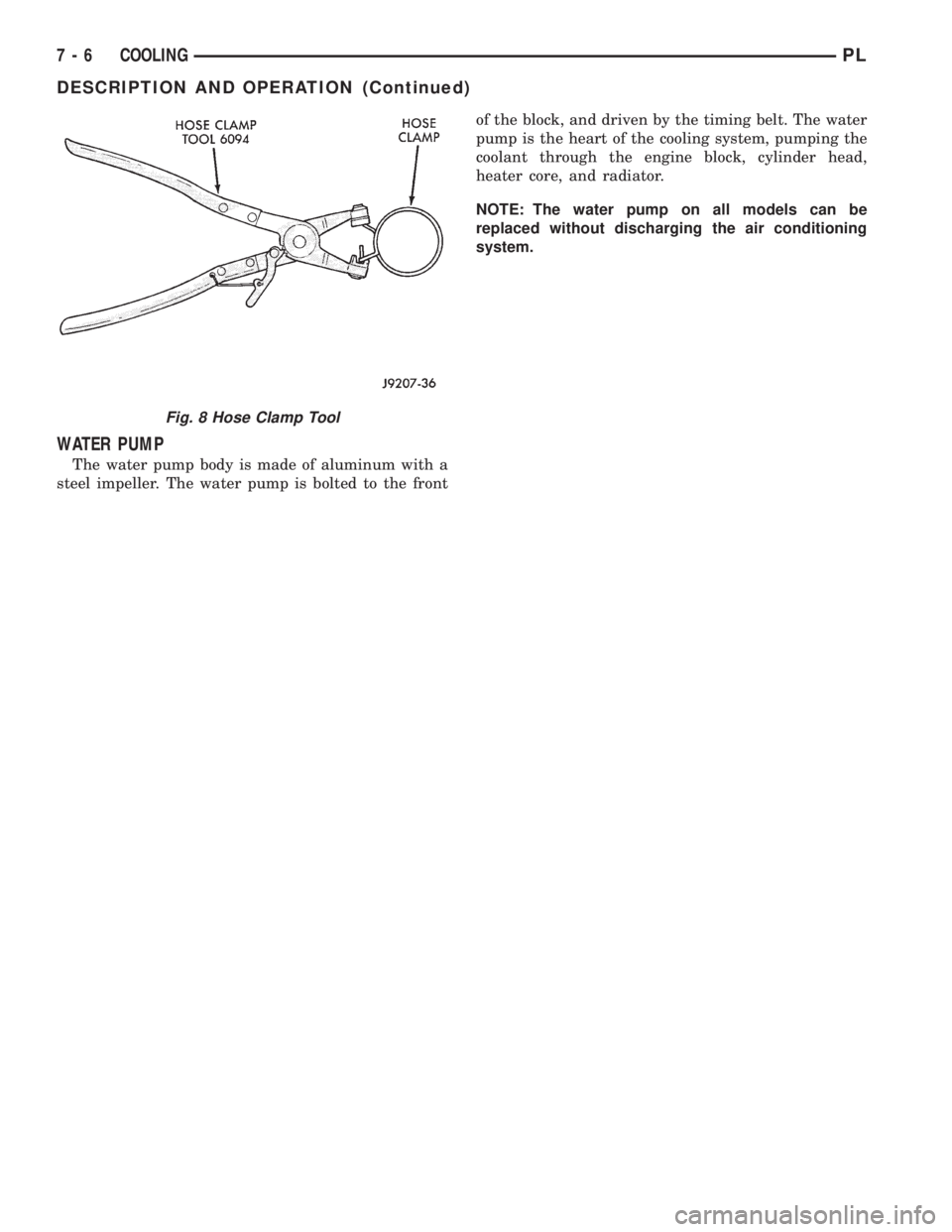
with matching number or letter.The hose clamps are removed by using Special Tool
6094 or equivalent constant tension clamp pliers
(Fig. 8) to compress hose clamp.
A hardened, cracked, swollen or restricted hose
should be replaced. Do not damage radiator inlet and
outlet when loosening hoses.
Radiator hoses should be routed without any kinks
and indexed as designed. The use of molded hoses is
recommended.
Spring type hose clamps are used in all applica-
tions. If replacement is necessary replace with the
original Mopartequipment spring type clamp.
ENGINE BLOCK HEATER
The heater is mounted in a core hole (in place of a
core hole plug) in the engine block, with the heating
element immersed in coolant.The power cord
must be secured in its retainer clips, and not
positioned so it could contact linkages or
exhaust manifolds and become damaged.
If unit does not operate, trouble can be in either
the power cord or the heater element. Test power
cord for continuity with a 110-volt voltmeter or 110-
volt test light; test heater element continuity with an
ohmmeter or 12-volt test light.
Fig. 7 Cooling System Pressure Cap
PLCOOLING 7 - 5
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION (Continued)
Page 199 of 1200
WATER PUMP
The water pump body is made of aluminum with a
steel impeller. The water pump is bolted to the frontof the block, and driven by the timing belt. The water
pump is the heart of the cooling system, pumping the
coolant through the engine block, cylinder head,
heater core, and radiator.
NOTE: The water pump on all models can be
replaced without discharging the air conditioning
system.
Fig. 8 Hose Clamp Tool
7 - 6 COOLINGPL
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION (Continued)