1999 DODGE NEON engine oil
[x] Cancel search: engine oilPage 195 of 1200
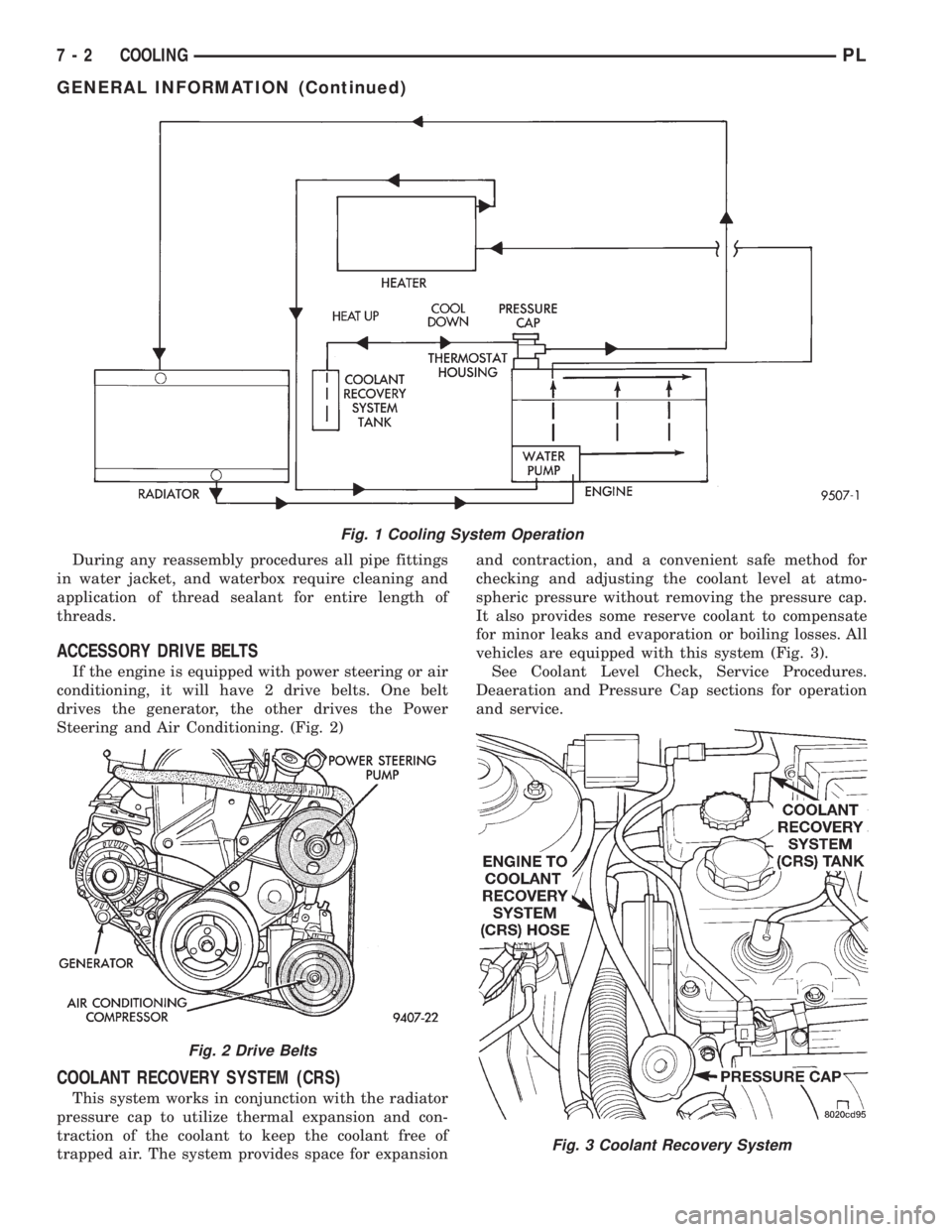
During any reassembly procedures all pipe fittings
in water jacket, and waterbox require cleaning and
application of thread sealant for entire length of
threads.
ACCESSORY DRIVE BELTS
If the engine is equipped with power steering or air
conditioning, it will have 2 drive belts. One belt
drives the generator, the other drives the Power
Steering and Air Conditioning. (Fig. 2)
COOLANT RECOVERY SYSTEM (CRS)
This system works in conjunction with the radiator
pressure cap to utilize thermal expansion and con-
traction of the coolant to keep the coolant free of
trapped air. The system provides space for expansionand contraction, and a convenient safe method for
checking and adjusting the coolant level at atmo-
spheric pressure without removing the pressure cap.
It also provides some reserve coolant to compensate
for minor leaks and evaporation or boiling losses. All
vehicles are equipped with this system (Fig. 3).
See Coolant Level Check, Service Procedures.
Deaeration and Pressure Cap sections for operation
and service.
Fig. 1 Cooling System Operation
Fig. 2 Drive Belts
Fig. 3 Coolant Recovery System
7 - 2 COOLINGPL
GENERAL INFORMATION (Continued)
Page 196 of 1200

ENGINE THERMOSTAT
The engine thermostat is located on the front of
the engine (radiator side) in the thermostat housing/
engine outlet connector. The thermostat has an air
bleed (vent) located in the flange and a O-ring for
sealing incorporate on it. There is a relief in the ther-
mostat housing/outlet connector for the O-ring.
WATER PUMP
The water pump has a diecast aluminum body and
housing with a stamped steel impeller. The water
pump bolts directly to the block (Fig. 4). Cylinder
block to water pump sealing is provided by a rubber
O-ring. The water pump is driven by the timing belt.
Refer to Group 9, Engine section for component
removal to access the water pump.
NOTE: The water pump on all models can be
replaced without discharging the air conditioning
system.
COOLANT
The cooling system is designed around the coolant.
The coolant must accept heat from engine block
metal and in the cylinder head area near the exhaust
valves. Then coolant carries this heat to the radiator
where the tube/fin assemblies of these components
can give off the heat to the air.
MopartAntifreeze or the equivalent is recom-
mended for optimum cooling performance and corro-
sion protection when mixed to a freeze point of -37É C
(-35É F).
COOLANT REPLACEMENT
Refer to Group 0, Lubrication and Maintenance for
schedule.
COOLING SYSTEM PRESSURE CAP
The cooling system is equipped with a pressure cap
that releases pressure at some point within a range
of 97-124 kPa (14-18 psi) (Fig. 5).
The system will operate at higher than atmo-
spheric pressure, which raises the coolant boiling
point, allowing increased radiator cooling capacity.
AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION OIL COOLER
Oil coolers are internal oil to coolant type, mounted
in the radiator lower tank (Fig. 6). Rubber oil lines
feed the oil cooler and the automatic transmission.
Use only approved transmission oil cooler hose. Since
these are molded to fit space available, molded hoses
are recommended. Tighten Oil Cooler Hose Clamps
to 2 N´m (18 in. lbs.).
RADIATOR
The radiator is a down-flow type (vertical tubes)
with design features that provide greater strength,
as well as sufficient heat transfer capabilities to keep
the engine satisfactorily cooled (Fig. 6).
ENGINE BLOCK HEATER
The engine block heater is available as an optional
accessory. The heater, operated by ordinary house
current (110 Volt A.C.) through a power cord and con-
nector behind the radiator grille, provides easier
engine starting and faster warm-up when vehicle is
operated in areas having extremely low tempera-
tures.
Fig. 4 Water Pump
Fig. 5 Cooling System Pressure Cap
PLCOOLING 7 - 3
GENERAL INFORMATION (Continued)
Page 197 of 1200

DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
ENGINE THERMOSTAT
The engine cooling thermostats are wax pellet
driven, reverse poppet choke type. They are designed
to provide the fastest warm up possible by prevent-
ing leakage through them and to guarantee a mini-
mum engine operating temperature of 88 to 93ÉC
(192 to 199ÉF). They also automatically reach wide
open so they do not restrict flow to the radiator as
temperature of the coolant rises in hot weather to
around 104ÉC (220ÉF). Above this temperature the
coolant temperature is controlled by the radiator, fan,
and ambient temperature, not the thermostat.
Its primary purpose is to maintain engine temper-
ature in a range that will provide satisfactory engine
performance and emission levels under all expected
driving conditions. It also provides hot water (cool-
ant) for heater performance. It does this by transfer-
ring heat from engine metal and automatic
transmission oil cooler (if equipped) to coolant, mov-
ing this heated coolant to the heater core and radia-
tor, and then transferring this heat to the ambient
air.
COOLANT PERFORMANCE
Performance is measurable. For heat transfer pure
water excels (Formula = 1 btu per minute for each
degree of temperature rise for each pound of water).
This formula is altered when necessary additives to
control boiling, freezing, and corrosion are added as
follows:
²Pure Water (1 btu) boils at 100ÉC (212ÉF) and
freezes at 0ÉC (32ÉF).
²100 Percent Glycol (.7 btu) can cause a hot
engine and detonation and will raise the freeze point
to 22ÉC (-8ÉF).
²50/50 Glycol and Water (.82 btu) is the recom-
mended combination that provides a freeze point of
-37ÉC(-35ÉF). The radiator, water pump, engine water
jacket, radiator pressure cap, thermostat, tempera-
ture gauge, sending unit and heater are all designed
for 50/50 glycol.
Where required, a 56 percent glycol and 44 percent
water mixture will provide a freeze point of -59ÉC
(-50ÉF).
CAUTION: Richer mixtures cannot be measured
with field equipment which can lead to problems
associated with 100 percent glycol.
Fig. 6 Cooling Modules
7 - 4 COOLINGPL
GENERAL INFORMATION (Continued)
Page 198 of 1200

SELECTION AND ADDITIVES
The use of aluminum cylinder heads, intake mani-
folds DOHC, and water pumps requires special corro-
sion protection. MopartAntifreeze or the equivalent
is recommended for best engine cooling without cor-
rosion. When mixed only to a freeze point of -37ÉC
(-35ÉF) to -59ÉC (-50ÉF). If it looses color or becomes
contaminated, drain, flush, and replace with fresh
properly mixed solution.
COOLING SYSTEM PRESSURE CAP
The cooling system is equipped with a pressure cap
that releases built up pressure, maintaining a range
of 97-124 kPa (14-18 psi).
The cooling system will operate at higher than
atmospheric pressure. The higher pressure raises the
coolant boiling point thus, allowing increased radia-
tor cooling capacity.
There is a vent valve in the center of the cap that
allows a small coolant flow from the coolant reserve
system (CRS) tank. This valve is spring loaded in the
closed position. However it must be free to open dur-
ing system cool-down.If the valve is stuck shut,
the radiator hoses will collapse on cool-down.
Clean the vent valve (Fig. 7) to ensure proper
sealing function.
There is a gasket in the cap that seals to the top of
the filler neck so that vacuum is maintained to draw
coolant back into the system from the coolant reserve
system (CRS) tank.
RADIATOR HOSES AND CLAMPS
WARNING: IF VEHICLE HAS BEEN RUN
RECENTLY, WAIT 15 MINUTES BEFORE WORKING
ON VEHICLE. RELIEVE PRESSURE BY PLACING A
SHOP TOWEL OVER THE CAP AND WITHOUT
PUSHING DOWN ROTATE IT COUNTERCLOCKWISE
TO THE FIRST STOP. ALLOW FLUIDS TO ESCAPE
THROUGH THE OVERFLOW TUBE AND WHEN THE
SYSTEM STOPS PUSHING OUT COOLANT AND
STEAM AND THE PRESSURE DROPS CONTINUE
SERVICE.
WARNING: CONSTANT TENSION HOSE CLAMPS
ARE USED ON MOST COOLING SYSTEM HOSES.
WHEN REMOVING OR INSTALLING, USE ONLY
TOOLS DESIGNED FOR SERVICING THIS TYPE OF
CLAM. ALWAYS WEAR SAFETY GLASSES WHEN
SERVICING CONSTANT TENSION CLAMPS.
CAUTION: A number or letter is stamped into the
tongue of constant tension clamps. If replacement
is necessary, use only a original equipment clamp
with matching number or letter.The hose clamps are removed by using Special Tool
6094 or equivalent constant tension clamp pliers
(Fig. 8) to compress hose clamp.
A hardened, cracked, swollen or restricted hose
should be replaced. Do not damage radiator inlet and
outlet when loosening hoses.
Radiator hoses should be routed without any kinks
and indexed as designed. The use of molded hoses is
recommended.
Spring type hose clamps are used in all applica-
tions. If replacement is necessary replace with the
original Mopartequipment spring type clamp.
ENGINE BLOCK HEATER
The heater is mounted in a core hole (in place of a
core hole plug) in the engine block, with the heating
element immersed in coolant.The power cord
must be secured in its retainer clips, and not
positioned so it could contact linkages or
exhaust manifolds and become damaged.
If unit does not operate, trouble can be in either
the power cord or the heater element. Test power
cord for continuity with a 110-volt voltmeter or 110-
volt test light; test heater element continuity with an
ohmmeter or 12-volt test light.
Fig. 7 Cooling System Pressure Cap
PLCOOLING 7 - 5
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION (Continued)
Page 200 of 1200

DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
COOLING SYSTEM DIAGNOSIS
CONDITION POSSIBLE CAUSE CORRECTION
TEMPERATURE GAUGE READS
LOW1. Has a Diagnostic Trouble Code
(DTC) been set indicating a stuck
open engine thermostat?1. Refer to On Board Diagnostic in
Group 25. Replace thermostat if
necessary. If a (DTC) has not been
set, the problem may be with the
temperature gauge.
2. Is the temperature gauge (if
equipped) connected to the
temperature gauge coolant sensor
on the engine?2. Check the connector at the
engine coolant sensor. Refer to
Group 8E. Repair as necessary.
3. Is the temperature gauge (if
equipped) operating OK?3. Check Gauge operation. Refer to
Group 8E. Repair as necessary.
4. Coolant level low during cold
ambient temperature, accompanied
by poor heater performance.4. Check coolant level in the coolant
overflow/reserve tank and the
radiator. Inspect the system for
leaks. Repair as necessary. Refer to
WARNINGS outlined in this section
before removing pressure cap.
TEMPERATURE GAUGE READS
HIGH OR ENGINE COOLANT
WARNING LAMP ILLUMINATES.
COOLANT MAY OR MAY NOT BE
LOST FROM SYSTEM.1. Trailer being towed, a steep hill
being climbed, vehicle being
operated in slow moving traffic, or
engine idling during high ambient
(outside) temperatures with air
conditioning on. High altitudes
Could aggravate these conditions.1. This may be a temporary
condition and repair is not
necessary. Turn off the air
conditioning and drive the vehicle
without any of the previous
conditions. Observe the temperature
gauge the gauge should return to
the normal range. If the gauge does
not return to the normal range,
determine the cause of the
overheating and repair. Refer to
POSSIBLE CAUSES in this section.
2. Is temperature gauge (if
equipped) reading correctly?2. Check gauge. Refer to Group 8E.
Repair as necessary.
3. Is temperature warning lamp (if
equipped) illuminating
unnecessarily?3. Check warning lamp operation.
Refer to Group 8E. Repair as
necessary.
4. Coolant low in overflow/reserve
tank and radiator?4. Check for coolant leaks and
repair as necessary. Refer to
checking cooling system for leaks in
this group.
5. Pressure cap not installed tightly.
If cap is loose, boiling point of
coolant will be lowered. Also refer
to the following step 6.5. Tighten cap.
6. Poor seals at radiator cap. 6. (a) Check condition of cap and
cap seals. Refer to Radiator cap
Inspection. Replace cap if
necessary.
6. (b) Check condition of filler neck.
If neck is bent or damaged, replace
neck.
PLCOOLING 7 - 7
Page 208 of 1200

There may be internal leaks, which can be deter-
mined by removing the oil dipstick. If water globules
appear intermixed with the oil, it indicates an inter-
nal leak in the engine. If there is an internal leak,
the engine must be disassembled for repair.
PRESSURE CAP TO FILLER NECK SEAL
PRESSURE RELIEF CHECK
The pressure cap upper gasket (seal) pressure
relief can be checked by removing the overflow hose
at the radiator filler neck nipple (Fig. 10). Attach the
radiator pressure tester to thefiller neck nipple,
and pump air into the system. The pressure cap
upper gasket should relieve pressure at 69-124 kPa
(10-18 psi), and hold pressure at 55 kPa (8 psi) min-
imum.
WARNING: THE WARNING WORDS DO NOT OPEN
HOT ON THE PRESSURE CAP IS A SAFETY PRE-
CAUTION. WHEN HOT, THE COOLING SYSTEM
BUILDS UP PRESSURE. TO PREVENT SCALDING
OR OTHER INJURY, THE PRESSURE CAP SHOULD
NOT BE REMOVED WHILE THE SYSTEM IS HOT
AND/OR UNDER PRESSURE.
There is no need to remove the pressure cap at any
timeexceptfor the following purposes:
²Check and adjust coolant freeze point²Refill system with new coolant
²Conducting service procedures
²Checking for leaks
WARNING: IF VEHICLE HAS BEEN RUN
RECENTLY, WAIT 15 MINUTES BEFORE REMOVING
CAP. PLACE A SHOP TOWEL OVER THE CAP, AND
WITHOUT PUSHING DOWN, ROTATE IT COUNTER-
CLOCKWISE TO THE FIRST STOP. ALLOW FLUIDS
TO ESCAPE THROUGH THE OVERFLOW TUBE.
WHEN THE SYSTEM STOPS PUSHING COOLANT
AND STEAM INTO THE CRS TANK AND PRESSURE
DROPS, PUSH DOWN ON THE CAP AND REMOVE
IT COMPLETELY. SQUEEZING THE RADIATOR
INLET HOSE WITH A SHOP TOWEL (TO CHECK
PRESSURE) BEFORE AND AFTER TURNING TO
THE FIRST STOP IS RECOMMENDED.
PRESSURE TESTING COOLING SYSTEM
PRESSURE CAP
Dip the pressure cap in water; clean off any depos-
its on the vent valve or its seat, and apply the cap to
end of radiator pressure tester (Fig. 11). Working the
plunger, increase the pressure to 104 kPa (15 psi) on
the gauge. If the pressure cap fails to hold pressure
of at least 97 kPa (14 psi), replace the cap.
CAUTION: The radiator pressure tester is very sen-
sitive to small air leaks that will not cause cooling
system problems. A pressure cap that does not
have a history of coolant loss should not be
replaced just because it leaks slowly when tested
with this tool. Add water to the tool. Turn the tool
upside down, and recheck the pressure cap to con-
firm that the cap is faulty.
If the pressure cap tests properly while posi-
tioned the on radiator pressure tester, but will not
hold pressure or vacuum when positioned on the
filler neck, inspect the filler neck and cap top gas-
ket for irregularities that may prevent the cap from
sealing properly.
LOW COOLANT LEVEL AERATION
²Will cause corrosion in the system.
²High reading shown on the temperature gauge.
²Air in the coolant will also cause loss of flow
through the heater.
²Exhaust gas leaks into the coolant can also
cause the above problems.
DEAERATION
Air can only be removed from the system by gath-
ering under the pressure cap. On the next heat up it
will be pushed past the pressure cap into the CRS
tank by thermal expansion of the coolant. It thenFig. 10 Cooling System Pressure Cap
PLCOOLING 7 - 15
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING (Continued)
Page 234 of 1200

(7) Vehicles equipped with A/C:
(a) Using a floor jack or jack stand, raise the
engine and transmission assembly to the original
position.
(b) Install the front engine mount bolt through
the insulator and front crossmember mounting
bracket (Fig. 9).
(c) Tighten bolt to 54 N´m (40 ft. lbs.) torque.
(8) Lower vehicle and connect battery cables.
STARTER RELAY
The relay is located in the Power Distribution Cen-
ter (PDC). Refer to the PDC cover for relay location.
SPECIFICATIONS
STARTER
Engine should be up to operating temperature.
Extremely heavy oil or tight engine will increase
starter amperage draw.
TORQUE
DESCRIPTION TORQUE
Starter Mounting Bolts.........54N´m(40ft.lbs.)
Starter Solenoid Battery Nut. . . .10 N´m (90 in. lbs.)
Fig. 11 Wire Connection
Manufacturer BOSCH
Engine Application 2.0L OHC - DOHC
Power rating 0 .95 Kw
Voltage 12 VOLTS
No. of Fields 6
No. of Poles 6
Brushes 4
Drive Planetary Gear Train
Cranking Amperage Draw
test150 - 280 Amps.
PLSTARTING 8B - 7
REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION (Continued)
Page 237 of 1200

A battery temperature sensor located on the front
bumper beam is used to sense battery temperature.
This temperature data, along with data from moni-
tored line voltage, is used by the PCM to vary the
battery charging rate. This is done by cycling the
ground path to control the strength of the rotor mag-
netic field. The PCM then compensates and regulates
generator current output accordingly and to maintain
the proper voltage depending on battery tempera-
ture.
All vehicles are equipped with On-Board Diagnos-
tics (OBD). All OBD-sensed systems, including the
EVR (field control) circuitry, are monitored by the
PCM. Each monitored circuit is assigned a Diagnos-
tic Trouble Code (DTC). The PCM will store a DTC in
electronic memory for any failure it detects. See On-
Board Diagnostic System Test in this group for more
information.
GENERATOR
The generator is belt-driven by the engine. It is
serviced only as a complete assembly. If the genera-
tor fails for any reason, the entire assembly must be
replaced.
As the energized rotor begins to rotate within the
generator, the spinning magnetic field induces a cur-
rent into the windings of the stator coil. Once the
generator begins producing sufficient current, it also
provides the current needed to energize the rotor.
The Y type stator winding connections deliver the
induced AC current to 3 positive and 3 negative
diodes for rectification. From the diodes, rectified DC
current is delivered to the vehicle electrical system
through the generator, battery, and ground terminals.
Noise emitting from the generator may be caused
by:
²Worn, loose or defective bearings
²Loose or defective drive pulley
²Incorrect, worn, damaged or misadjusted drive
belt
²Loose mounting bolts
²Misaligned drive pulley
²Defective stator or diode
BATTERY TEMPERATURE SENSOR
The battery temperature sensor is used to deter-
mine the battery temperature. This temperature
data, along with data from monitored line voltage, is
used by the PCM to vary the battery charging rate.
System voltage will be higher at colder temperatures
and is gradually reduced at warmer temperatures.
The sensor is located on the bottom of the battery
tray (Fig. 1).
ELECTRONIC VOLTAGE REGULATOR
The Electronic Voltage Regulator (EVR) is not a
separate component. It is actually a voltage regulat-
ing circuit located within the Powertrain Control
Module (PCM). The EVR is not serviced separately. If
replacement is necessary, the PCM must be replaced.
Operation:The amount of DC current produced
by the generator is controlled by EVR circuitry con-
tained within the PCM. This circuitry is connected in
series with the generators second rotor field terminal
and its ground.
Voltage is regulated by cycling the ground path to
control the strength of the rotor magnetic field. The
EVR circuitry monitors system line voltage and bat-
tery temperature (refer to Battery Temperature Sen-
sor for more information). It then compensates and
regulates generator current output accordingly. Also
refer to Charging System Operation for additional
information.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
CHARGING SYSTEM
When the ignition switch is turned to the ON posi-
tion, battery potential will register on the voltmeter.
During engine cranking a lower voltage will appear
on the meter. With the engine running, a voltage
reading higher than the first reading (ignition in ON)
should register.
The following are possible symptoms of a charging
system fault:
²The voltmeter does not operate properly
²An undercharged or overcharged battery condi-
tion occurs.
Fig. 1 Battery Temperature Sensor
8C - 2 CHARGING SYSTEMPL
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION (Continued)