1999 DODGE NEON sensor
[x] Cancel search: sensorPage 888 of 1200

(7) Attach the other end of the jumper wire to
relay terminal 86. This activates the relay. The ohm-
meter should now show continuity between relay ter-
minals 87 and 30. The ohmmeter should not show
continuity between relay terminals 87A and 30.
(8) Disconnect jumper wires.
(9) Replace the relay if it did not pass the continu-
ity and resistance tests. If the relay passed the tests,
it operates properly. Check the remainder of the ASD
and fuel pump relay circuits. Refer to group 8W, Wir-
ing Diagrams.
CAMSHAFT AND CRANKSHAFT POSITION SENSOR
Refer to Group 8D, Ignition for Diagnosis and Test-
ing of Camshaft and Crankshaft Sensors.
ENGINE COOLANT TEMPERATURE SENSOR
(1) With the key off, disconnect wire harness con-
nector from coolant temperature sensor (Fig. 79) or
(Fig. 80).(2) Connect a high input impedance (digital) volt-
ohmmeter to terminals A and B (Fig. 81). The ohm-
meter should read as follows:
²Engine/Sensor at normal operating temperature
around 200ÉF should read approximately 700 to
1,000 ohms.
²Engine/Sensor at room temperature around 70ÉF
ohmmeter should read approximately 7,000 to 13,000
ohms.
(3) T
est the resistance of the wire harness between
the PCM 60-way connector terminal 28 and the sensor
harness connector. Also check for continuity between
PCM 60-way connector terminal 51 and the sensor har-
ness connector. Refer to Group 8W, Wiring diagrams for
circuit information. If the resistance is greater than 1
ohm, repair the wire harness as necessary.
HEATED OXYGEN SENSOR
Use an ohmmeter to test the heating element of
the oxygen sensors. Disconnect the electrical connec-
tor from each oxygen sensor. The white wires in the
sensor connector are the power and ground circuits
for the heater. Connect the ohmmeter test leads to
terminals of the white wires in the heated oxygen
sensor connector. Replace the heated oxygen sensor if
the resistance is not between 4 and 7 ohms.
IDLE AIR CONTROL (IAC) MOTOR TEST
To preform a complete test of IAC motor and its
circuitry, refer to DRB scan tool and the appropriate
Powertrain Diagnostics Procedures manual.
KNOCK SENSOR
The engine knock sensor is affected by a number of
factors. A few of these are: ignition timing, cylinder
pressure, fuel octane, etc. The knock sensor generates
an AC voltage whose amplitude increases with the
increase of engine knock. The knock sensor can be
tested with a digital voltmeter. The RMS voltage starts
Fig. 79 Engine Coolant Temperature Sensor
LocationÐSOHC
Fig. 80 Engine Coolant Temperature Sensor
LocationÐDOHC
Fig. 81 Engine Coolant Temperature Sensor
PLFUEL SYSTEM 14 - 47
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING (Continued)
Page 889 of 1200

at about 20mVac (at about 700 rpm) and increases to
approximately 600 mVac (5000 rpm). If the output falls
outside of this range a DTC will be set.
MANIFOLD ABSOLUTE PRESSURE (MAP) SENSOR
To perform a complete test of the MAP sensor and
its circuitry, refer to the DRB scan tool and appropri-
ate Powertrain Diagnostics Procedures manual. To
test the MAP sensor only, refer to the following:
CAUTION: When testing the MAP sensor, be sure
that the harness wires are not damaged by the test
meter probes.
(1) Test the MAP sensor output voltage at the
MAP sensor connector between terminals 1 and 4
(Fig. 82). With the ignition switch ON and the engine
not running, output voltage should be 4 to 5 volts.
The voltage should drop to 1.5 to 2.1 volts with a hot,
neutral idle speed condition. If OK, go to next step. If
not OK, go to step 3.
(2) Test PCM terminal 36 for the same voltage
described in the previous step to verify wire harness
condition. Repair as required.
(3) Test the MAP sensor ground circuit at sensor
connector terminal 1 and PCM terminal 43. If OK, go
to next step. If not OK, repair as required.
(4) Test MAP sensor supply voltage between sen-
sor connector terminals 3 and 1 with the key ON.
The voltage should be approximately 5 volts (6.5V).
Five volts (6.5V) should also be at terminal 61 of the
PCM. If OK, replace MAP sensor. If not OK, repair or
replace the wire harness as required.
THROTTLE POSITION SENSOR
To perform a complete test of the this sensor and
its circuitry, refer to the DRB scan tool and appropri-
ate Powertrain Diagnostics Procedures manual. To
test the throttle position sensor only, refer to the fol-
lowing:
The Throttle Position Sensor (TPS) can be tested
with a digital voltmeter (DVM). The center terminal
of the sensor is the output terminal. One of the other
terminals is a 5 volt supply and the remaining ter-
minal is ground.
Connect the DVM between the center and sensor
ground terminal. Refer to Group 8W - Wiring Dia-
grams for correct pinout.
With the ignition switch in the ON position, check
the output voltage at the center terminal wire of the
connector. Check the output voltage at idle and at
Wide-Open-Throttle (WOT). At idle, TPS output volt-
age should be approximately 0.38 volts to 1.2 volts.
At wide open throttle, TPS output voltage should be
approximately 3.1 volts to 4.4 volts. The output volt-
age should gradually increase as the throttle plate
moves slowly from idle to WOT.
Check for spread terminals at the sensor and PCM
connections before replacing the TPS.
THROTTLE BODY MINIMUM AIR FLOW
(1) Turn ignition key to Off.
(2) Disconnect the PCV valve hose from the intake
manifold nipple (Fig. 83). Cap the PCV vacuum nip-
ple.
(3) Disconnect purge hose from the nipple on the
throttle body (Fig. 84).
(4) Use a piece of hose to attach Air Metering Ori-
fice 6457 (0.125 in. orifice) to the purge nipple on the
throttle body (Fig. 85).
(5) Ensure that all accessories are off.
Fig. 82 MAP Sensor Connector
Fig. 83 PCV Vacuum Nipple
14 - 48 FUEL SYSTEMPL
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING (Continued)
Page 890 of 1200

(6) Connect the DRB scan tool to the data link
connector inside the passenger compartment.
(7) Run engine in Park or Neutral until the cooling
fan has cycled on and off at least once (180ÉF).
(8) Using the DRB scan tool, access Minimum Air-
flow Idle Speed.
(9) The following will then occur:
²Idle air control motor will fully close
²Idle spark advance will become fixed
²PCM will go open loop enriched
²DRB scan tool displays engine RPM
(10) If idle RPM is within the range shown in the
Idle Specification chart, throttle body minimum air-
flow is set correctly.
IDLE SPECIFICATION Ð2.0L ENGINEOdometer Reading Idle RPM
Below 1000 Miles.................550±1300 RPM
Above 1000 Miles.................600±1300 Miles
(11) If idle RPM is above specifications, use the
DRB scan tool to check idle air control motor opera-
tion. If idle air control motor is OK, replace throttle
body. If idle air flow is below specification, shut off
the engine and clean the throttle body as follows:
WARNING: CLEAN THROTTLE BODY IN A WELL
VENTILATED AREA. WEAR RUBBER OR BUTYL
GLOVES, DO NOT LET MOPAR PARTS CLEANER
COME IN CONTACT WITH EYES OR SKIN. AVOID
INGESTING THE CLEANER. WASH THOROUGHLY
AFTER USING CLEANER.
(a) Remove the throttle body from engine.
(b) While holding the throttle open, spray the
entire throttle body bore and the manifold side of
the throttle plate with Mopar Parts Cleaner.Only
use Mopar Parts Cleaner to clean the throttle
body.
(c) Using a soft scuff pad, clean the top and bot-
tom of throttle body bore and the edges and mani-
fold side of the throttle blade.The edges of the
throttle blade and portions of the throttle
bore that are closest to the throttle blade
when closed, must be free of deposits.
(d) Use compressed air to dry the throttle body.
(e) Inspect throttle body for foreign material.
(f) Install throttle body on manifold.
(g) Repeat steps 1 through 14. If the minimum
air flow is still not within specifications, the prob-
lem is not caused by the throttle body.
(12) Shut off engine.
(13) Remove Air Metering Orifice 6457. Install
purge hose.
(14) Remove cap from PCV valve. Connect hose to
PCV valve.
(15) Remove DRB scan tool.
VEHICLE SPEED SENSOR
To perform a complete test of the sensor and its
circuitry, refer to the DRB scan tool and appropriate
Powertrain Diagnostics Procedures Manual.
Fig. 84 Purge Hose
Fig. 85 Orifice 6457 Attached to Purge Nipple
PLFUEL SYSTEM 14 - 49
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING (Continued)
Page 893 of 1200

(9) Rotate throttle lever forward to the wide open
position and slide kickdown cable connector onto nail
head.
(10) Install throttle cable cover. Tighten bolt to 5.6
N´m (50 ins. lbs.).
THROTTLE POSITION SENSOR (TPS)
The throttle position sensor attaches to the side of
the throttle body (Fig. 93).
REMOVAL
(1) Disconnect EVAP purge hose from throttle
body.
(2) Disconnect electrical connector from idle air
control motor and throttle position sensor.
(3) Remove throttle body. Refer to Throttle Body in
this section.
(4) Remove throttle position sensor mounting
screws.
(5) Remove throttle position sensor.
INSTALLATION
(1) The throttle shaft end of the throttle body
slides into a socket in the TPS (Fig. 94). The socket
has two tabs inside it. The throttle shaft rests
against the tabs. When indexed correctly, the TPS
can rotate clockwise a few degrees to line up the
mounting screw holes with the screw holes in the
throttle body. The TPS has slight tension when
rotated into position. If it is difficult to rotate the
TPS into position, install the sensor with the throttle
shaft on the other side of the tabs in the socket.
Tighten mounting screws to 2 N´m (17 in. lbs.)
torque.
(2) After installing the TPS, the throttle plate
should be closed. If the throttle plate is open, install
the sensor on the other side of the tabs in the socket.
(3) Install throttle body. Refer to Throttle Body in
this section.(4) Attach electrical connectors to idle air control
motor and throttle position sensor.
(5) Install EVAP purge hose to throttle body nip-
ple.
IDLE AIR CONTROL MOTOR
When servicing throttle body components, always
reassemble components with new O-rings and seals
where applicable. Never use lubricants on O-rings or
seals, damage may result. If assembly of component
is difficult, use water to aid assembly. Use care when
removing hoses to prevent damage to hose or hose
nipple.
REMOVAL
(1) Disconnect negative cable from battery.
(2) Remove throttle body. Refer to Throttle Body in
this section.
(3) Remove electrical connector from idle air con-
trol motor and throttle position sensor.
(4) Remove the EVAP purge hose from the throttle
body.
(5) Remove idle air control motor mounting screws
(Fig. 95).
(6) Remove motor from throttle body. Ensure the
O-ring is removed with the motor.
INSTALLATION
(1) The new idle air control motor has a new
O-ring installed on it. If pintle measures more than 1
inch (25 mm) it must be retracted. Use the DRB Idle
Air Control Motor Open/Close Test to retract the
pintle (battery must be connected.)
(2) Carefully place idle air control motor into
throttle body.
(3) Install mounting screws. Tighten screws to 2
N´m (17 in. lbs.) torque.
(4) Connect electrical connector to idle air control
motor and throttle position sensor.
Fig. 93 Throttle Position Sensor and Idle Air Control
Motor
Fig. 94 Throttle Position Sensor Installation
14 - 52 FUEL SYSTEMPL
REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION (Continued)
Page 894 of 1200

(5) Install throttle body. Refer to Throttle Body in
this section.
(6) Connect the EVAP purge hose to the throttle
body nipple.
(7) Connect negative cable to battery.
MAP/IAT SENSORÐSOHC
The MAP/IAT sensor attaches to the intake mani-
fold plenum (Fig. 96).
REMOVAL
(1) Disconnect the electrical connector from the
MAP/IAT sensor.
(2) Remove sensor mounting screws.
(3) Remove sensor.
INSTALLATION
(1) Insert sensor into intake manifold while mak-
ing sure not to damage O-ring seal.
(2) Tighten mounting screws to 2 N´m (20 in. lbs)
torque for plastic manifold and 3 N´m (30 in. lbs.) for
aluminum manifold.
(3) Attach electrical connector to sensor.
MAP/IAT SENSORÐDOHC
The MAP/IAT sensor attaches to the intake mani-
fold plenum (Fig. 98).
REMOVAL
(1) Remove air inlet duct wing nut and duct from
intake manifold (Fig. 97).
(2) Disconnect the electrical connector from the
MAP/IAT sensor.
(3) Remove sensor mounting screws.
(4) Remove sensor.
INSTALLATION
(1) Insert sensor into intake manifold while mak-
ing sure not to damage O-ring seals.(2) Tighten mounting screws to 2 N´m (20 in. lbs)
torque foe a plastic manifold and 3 N´m (30 in. lbs)
for a aluminum manifold.
(3) Attach electrical connector to sensor.
(4) Install air inlet duct wing nut and duct from
intake manifold, insure that the duct does not inter-
fer with ignition cables.
DUTY CYCLE EVAP PURGE SOLENOID VALVE
The solenoid attaches to a bracket near the front
engine mount (Fig. 99). The solenoid will not operate
unless it is installed correctly.
REMOVAL
(1) Disconnect electrical connector from solenoid.
(2) Disconnect vacuum tubes from solenoid.
Fig. 95 Servicing Idle Air Control MotorFig. 96 MAP/IAT SensorÐSOHC
Fig. 97 Air Inlet DuctÐDOHC
PLFUEL SYSTEM 14 - 53
REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION (Continued)
Page 895 of 1200

(3) Remove solenoid from bracket.
INSTALLATION
The top of the solenoid has TOP printed on it. The
solenoid will not operate unless it is installed cor-
rectly.
(1) Install solenoid on bracket.
(2) Connect vacuum tube to solenoid.
(3) Connect electrical connector to solenoid.
POWERTRAIN CONTROL MODULE (PCM)
The PCM attaches to the inner fender panel next
to the washer fluid bottle on the passenger side (Fig.
100).
REMOVAL
(1) Disconnect negative cable from battery.
(2) Disconnect positive cable from battery.
(3) Remove washer bottle neck.
(4) Squeeze tabs on PDC while pulling PDC up to
remove it from bracket. Lay PDC aside to gain access
to PCM bracket screws.
(5) Remove screws attaching PCM to body.
(6) Lift PCM up and disconnect the 2 40-way con-
nector.
(7) Remove PCM.
INSTALLATION
(1) Attach the 2 40-way connector to PCM.
(2) Install PCM. Tighten mounting screws to 9
N´m (80 in. lbs.) torque.
(3) Install PDC by pushing down into brackets.
(4) Install washer bottle neck.
(5) Connect positive cable to battery.
(6) Connect negative cable to battery.
CRANKSHAFT POSITION SENSOR
For removal/installation procedures refer to group
8D - Ignition System, Service Procedures.
CAMSHAFT POSITION SENSOR
For removal/installation procedures refer to group
8D - Ignition System, Service Procedures.
UPSTREAM HEATED OXYGEN SENSOR
REMOVAL
(1) Raise and support vehicle.
(2) Unplug sensor connector.
(3) Remove sensor using an oxygen sensor crow
foot wrench such as Snap-On tool YA8875 or equiva-
lent (Fig. 101).
(4) A
fter removing the sensor, the exhaust manifold
threads must be cleaned with an 18 mm X 1.5 + 6E tap.
If reusing the original sensor, coat the sensor threads
Fig. 98 MAP/IAT SensorÐDOHC
Fig. 99 Duty Cycle EVAP Purge Solenoid Valve
Fig. 100 Powertrain Control Module
14 - 54 FUEL SYSTEMPL
REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION (Continued)
Page 896 of 1200
with an anti-seize compound such as Loctitet771-64 or
equivalent.
INSTALLATION
New sensors have compound on the threads and do
not require an additional coating.
(1) Install sensor using an oxygen sensor crow foot
wrench such as Snap-On tool YA8875 or equivalent
(Fig. 101). Tighten the sensor to 28 N´m (20 ft. lbs.)
torque.
(2) Plug sensor connector.
(3) Lower vehicle.
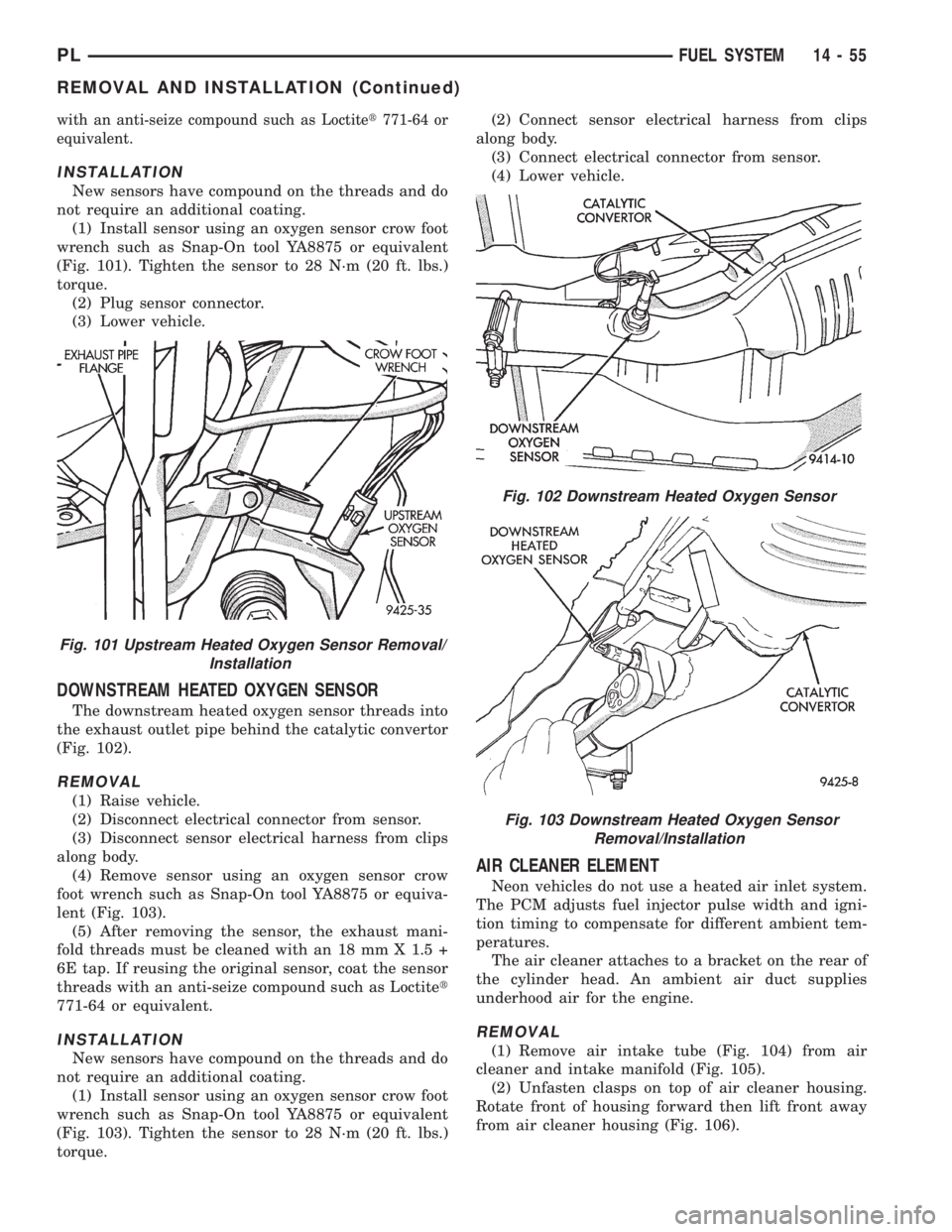
DOWNSTREAM HEATED OXYGEN SENSOR
The downstream heated oxygen sensor threads into
the exhaust outlet pipe behind the catalytic convertor
(Fig. 102).
REMOVAL
(1) Raise vehicle.
(2) Disconnect electrical connector from sensor.
(3) Disconnect sensor electrical harness from clips
along body.
(4) Remove sensor using an oxygen sensor crow
foot wrench such as Snap-On tool YA8875 or equiva-
lent (Fig. 103).
(5) After removing the sensor, the exhaust mani-
fold threads must be cleaned with an 18 mm X 1.5 +
6E tap. If reusing the original sensor, coat the sensor
threads with an anti-seize compound such as Loctitet
771-64 or equivalent.
INSTALLATION
New sensors have compound on the threads and do
not require an additional coating.
(1) Install sensor using an oxygen sensor crow foot
wrench such as Snap-On tool YA8875 or equivalent
(Fig. 103). Tighten the sensor to 28 N´m (20 ft. lbs.)
torque.(2) Connect sensor electrical harness from clips
along body.
(3) Connect electrical connector from sensor.
(4) Lower vehicle.
AIR CLEANER ELEMENT
Neon vehicles do not use a heated air inlet system.
The PCM adjusts fuel injector pulse width and igni-
tion timing to compensate for different ambient tem-
peratures.
The air cleaner attaches to a bracket on the rear of
the cylinder head. An ambient air duct supplies
underhood air for the engine.
REMOVAL
(1) Remove air intake tube (Fig. 104) from air
cleaner and intake manifold (Fig. 105).
(2) Unfasten clasps on top of air cleaner housing.
Rotate front of housing forward then lift front away
from air cleaner housing (Fig. 106).
Fig. 101 Upstream Heated Oxygen Sensor Removal/
Installation
Fig. 102 Downstream Heated Oxygen Sensor
Fig. 103 Downstream Heated Oxygen Sensor
Removal/Installation
PLFUEL SYSTEM 14 - 55
REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION (Continued)
Page 897 of 1200

(3) Remove air cleaner element from front housing
(Fig. 106).
INSTALLATION
(1) Install air cleaner element into front housing.
(2) Rotate front of housing forward then lower into
place and locate tabs in slots. Fasten clasps on top of
air cleaner housing.
(3) Install air intake duct at air cleaner and intake
manifold.
ENGINE COOLANT TEMPERATURE SENSOR
The engine coolant temperature sensor threads
into the rear of the cylinder head (Fig. 107) or (Fig.
108).
REMOVAL
(1) With the engine cold, drain coolant until level
drops below cylinder head. Refer to Group 7, Cooling
System.
(2) Disconnect coolant sensor electrical connector.
(3) Remove coolant sensor.
INSTALLATION
(1) Install coolant sensor. Tighten sensor to 18
N´m (165 in. lbs.) torque.
(2) Attach electrical connector to sensor.
(3) Fill cooling system. Refer to Group 7, Cooling
System.
VEHICLE SPEED SENSOR
The vehicle speed sensor is located in the transmis-
sion extension housing (Fig. 109).
REMOVAL
(1) Disconnect electrical connector from sensor.
(2) Remove the sensor mounting bolt.
(3) Lift the sensor out of the transaxle extension
housing. Ensure the O-ring was removed with the
sensor.
Fig. 104 Air Intake Duct
Fig. 105 Removal/Installation of Air Inlet Duct
Fig. 106 Removal/Installation Air Cleaner Front
Housing and Element
Fig. 107 Engine Coolant Temperature SensorÐ
SOHC
14 - 56 FUEL SYSTEMPL
REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION (Continued)