1999 DODGE NEON sensor
[x] Cancel search: sensorPage 727 of 1200

MAIN/ROD BEARINGS
A diagonal hole in each bulkhead feeds oil to each
main bearing. Drilled passages within the crankshaft
route oil from main bearing journals to connecting
rod journals.
CAMSHAFT/HYDRAULIC LASH ADJUSTERS
A vertical hole at the number five bulkhead routes
pressurized oil through a restrictor up into the cylin-
der head. The rocker shafts route oil to the rocker
arms/hydraulic lash adjuster assemblies.
SPLASH LUBRICATION
Oil returning to the pan from pressurized compo-
nents supplies lubrication to the valve stems. Cylin-
der bores and wrist pins are splash lubricated from
directed slots on the connecting rod thrust collars.
ENGINE COMPONENTS
CYLINDER BLOCK AND BEDPLATE ASSEM-
B LY:A partial open deck is used for cooling and
weight reduction with water pump molded into the
block. Nominal wall thickness is 4 mm. The bedplate
incorporates main bearing caps. Rear seal retainer is
integral with the block.
CRANKSHAFT:A nodular cast iron crankshaft is
used. The engine has 5 main bearings, with number
3 flanged to control thrust. The 52 mm diameter
main and 48 mm diameter crank pin journals (all)
have undercut fillet radiuses that are deep rolled for
added strength. To optimize bearing loading 8 coun-
terweights are used. Hydrodynamic seals provide end
sealing, where the crankshaft exits the block.
Anaerobic gasket material is used for parting line
sealing. A sintered iron timing belt sprocket is
mounted on the crankshaft nose. This sprocket trans-
mits crankshaft movement, via timing belt to the
camshaft sprocket providing timed valve actuation.
PISTONS:The SOHC EngineDOES NOThave
provision for a free wheeling valve train. Non free
wheeling valve train means, in the event of a broken
timing belt Pistons will contact the Valves. All
engines use pressed-in piston pins to attach forged
powdered metal connecting rods. The connecting rods
are a cracked cap design and are not repairable. Hex
head cap screw are used to provide alignment and
durability in the assembly. Pistons And Connecting
rods are serviced as an assembly.
PISTON RINGS:The piston rings include a
molybdenum faced top ring for reliable compression
sealing and a taper faced intermediate ring for addi-
tional cylinder pressure control. Oil Control Ring
Package consist of 2 steel rails and a expander
spacer.
CYLINDER HEADÐSOHC:It features a Single
Over Head Camshaft, four-valves per cylinder cross
flow design. The valves are arranged in two inlinebanks, with the two intake per cylinder facing
toward the radiator. The exhaust valves facing
toward the dash panel. Rocker arm shafts mount
directly to the cylinder head. It incorporates powder
metal valve guides and seats. The hollow rocker arm
shafts supplies oil to the hydraulic lash adjusters,
camshaft and valve mechanisms.
CAMSHAFTÐSOHC:The nodular iron camshaft
has five bearing journals and 3 cam lobes per cylin-
der. Provision for cam position sensor on the cam at
the rear of cylinder head which also acts as thrust
plate. A hydrodynamic oil seal is used for oil control
at the front of the camshaft.
VALVESÐSOHC:Four valves per cylinder are
actuated by roller rocker arms/hydraulic lash adjust-
ers assemblies which pivot on rocker arm shafts. All
valves have 6 mm diameter chrome plated valve
stems. The valve train has 33 mm (1.299 inch) diam-
eter intake valves and 28 mm (1.10 inch) diameter
exhaust valves. Viton rubber valve stem seals are
integral with spring seats. Valve springs, spring
retainers, and locks are conventional design.
INTAKE MANIFOLD:The intake manifold is a
molded plastic composition, attached to the cylinder
head with ten fasteners. This long branch design
enhances low and mid-range torque.
EXHAUST MANIFOLD:The exhaust manifold is
made of nodular cast iron for strength and high tem-
peratures. Exhaust gasses exit through a machined,
articulated joint connection to the exhaust pipe.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
CHECKING ENGINE OIL PRESSURE
(1) Remove oil pressure switch and install gauge
assembly C-3292 with adaptor.
(2) Run engine until thermostat opens.
CAUTION: If oil pressure is 0 at idle, Do Not per-
form the 3000 RPM test in the next step.
(3) Oil Pressure:Curb Idle25 kPa (4 psi) mini-
mum3000 RPM170-550 kPa (25-80 psi).
(4) If oil pressure is 0 at idle. Shut off engine,
check for pressure relief valve stuck open, a clogged
oil pick-up screen or a damaged oil pick-up tube
O-ring.
SERVICE PROCEDURES
CYLINDER BORE AND PISTON SIZING
The cylinder walls should be checked for out-of-
round and taper with Tool C-119 (Fig. 3). The cylin-
der bore out-of-round is 0.050 mm (.002 inch)
maximum and cylinder bore taper is 0.051 mm (0.002
9 - 14 2.0L SOHC ENGINEPL
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION (Continued)
Page 735 of 1200

(4) Apply MopartStud and Bearing Mount or
equivalent to a new tube approximately 1 mm from
theendina3mmwide area.
(5) Install sealer end of tube into the cylinder
head. Then carefully install the tube using a hard-
wood block and mallet until the tube is seated into
the bottom of the bore.
(6) Install cylinder head cover. Refer to procedure
outlined in this section.
SPARK PLUG TUBE SEALS
The spark plug tube seals are located in the cylin-
der head cover (Fig. 20). These seals are pressed into
the cylinder head cover to seal the outside perimeter
of the spark plug tubes. If these seals show signs of
hardness and/or cracking they should be replaced.
CAMSHAFT
NOTE: TO REMOVE CAMSHAFT THE CYLINDER
HEAD MUST BE REMOVED.
REMOVAL
(1) Perform fuel system pressure release procedure
before attempting any repairs.Refer to Group 14,
Fuel System
(2) Remove the cylinder head cover. Refer to proce-
dure outlined in this section.
(3) Mark rocker arm shaft assemblies so that they
are installed in their original positions.
(4) Remove rocker arm shaft bolts. Refer to proce-
dure outlined in this section.
(5) Remove timing belt, timing belt tensioner, and
camshaft sprocket. Refer to procedures outlined in
this section.
(6) Remove rear timing belt cover.
(7) Remove cylinder head. Refer to procedure out-
lined in this section.
(8) Remove camshaft sensor and camshaft target
magnet.
(9) Remove camshaft from the rear of cylinder
head.
INSPECT CYLINDER HEAD FOR THE FOLLOWING:
NOTE:
²Check oil feed holes for blockage.
²Inspect cylinder head camshaft bearings for
wear, Refer to Cylinder Head, Inspection and Clean-
ing.
²Check camshaft bearing journals for scratches
and worn areas. If light scratches are present, they
may be removed with 400 grit sand paper. If deep
scratches are present, replace the camshaft and
check the cylinder head for damage. Replace the
cylinder head if worn or damaged. Check the lobes
for pitting and wear. If the lobes show signs of
wear, check the corresponding rocker arm roller for
wear or damage. Replace rocker arm/hydraulic lash
adjuster if worn or damaged. If lobes show signs of
pitting on the nose, flank or base circle; replace the
camshaft.
INSTALLATION
(1) Lubricate the camshaft journals with oil and
install camshaftwithoutrocker arm assemblies
installed.
(2) Install camshaft target magnet into the end of
the camshaft. Tighten mounting screw to 3.4 N´m (30
in. lbs.).
(3) Install camshaft position sensor and tighten
mounting screws to 9 N´m (80 in. lbs.).
(4) Measure camshaft end play using the following
procedure:
²Mount dial indicator C-3339 or equivalent, to a
stationary point on cylinder head (Fig. 21).
²Using a suitable tool, move camshaft to rear-
ward limits of travel.
Fig. 19 Servicing Spark Plug Tubes
Fig. 20 Spark Plug Tube Seals
9 - 22 2.0L SOHC ENGINEPL
REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION (Continued)
Page 738 of 1200
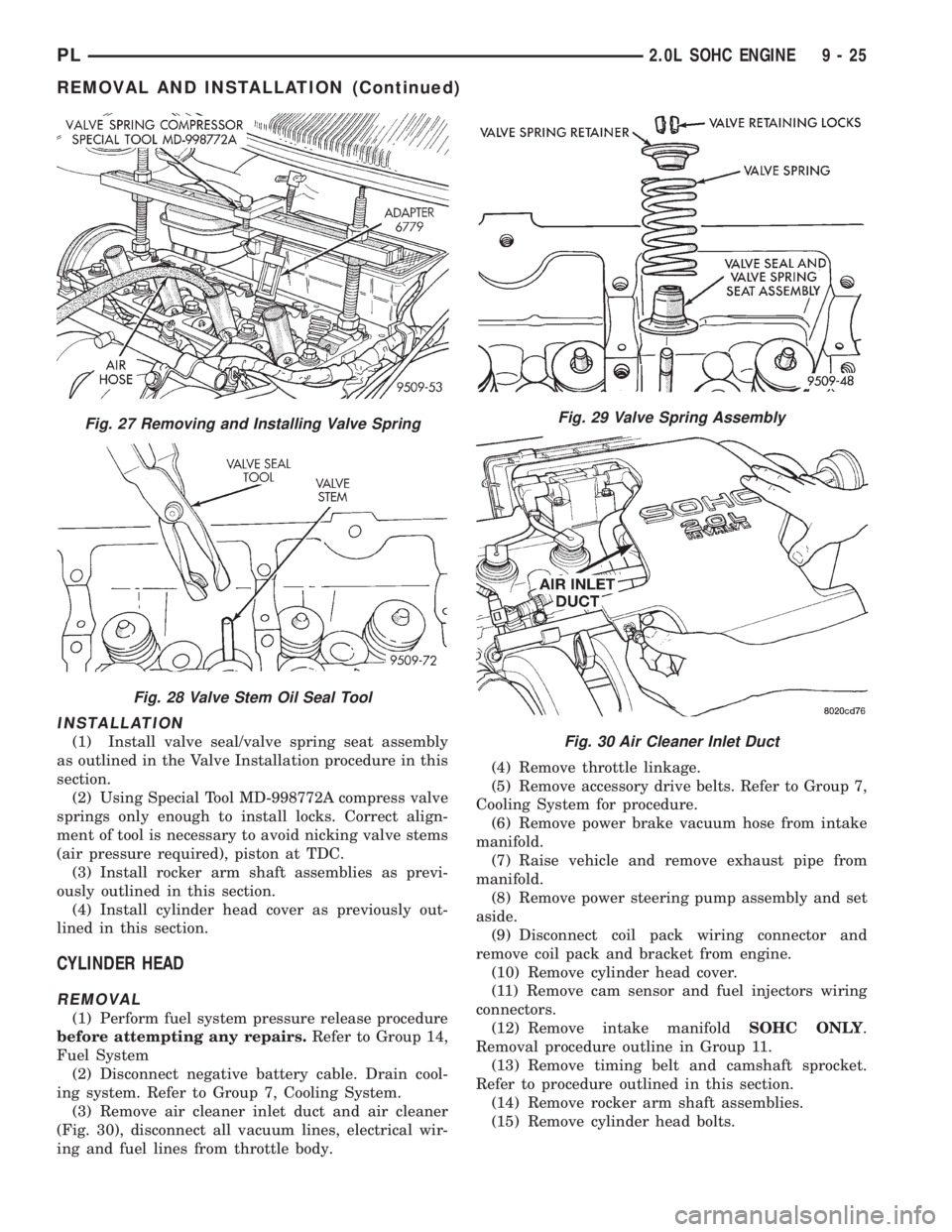
INSTALLATION
(1) Install valve seal/valve spring seat assembly
as outlined in the Valve Installation procedure in this
section.
(2) Using Special Tool MD-998772A compress valve
springs only enough to install locks. Correct align-
ment of tool is necessary to avoid nicking valve stems
(air pressure required), piston at TDC.
(3) Install rocker arm shaft assemblies as previ-
ously outlined in this section.
(4) Install cylinder head cover as previously out-
lined in this section.
CYLINDER HEAD
REMOVAL
(1) Perform fuel system pressure release procedure
before attempting any repairs.Refer to Group 14,
Fuel System
(2) Disconnect negative battery cable. Drain cool-
ing system. Refer to Group 7, Cooling System.
(3) Remove air cleaner inlet duct and air cleaner
(Fig. 30), disconnect all vacuum lines, electrical wir-
ing and fuel lines from throttle body.(4) Remove throttle linkage.
(5) Remove accessory drive belts. Refer to Group 7,
Cooling System for procedure.
(6) Remove power brake vacuum hose from intake
manifold.
(7) Raise vehicle and remove exhaust pipe from
manifold.
(8) Remove power steering pump assembly and set
aside.
(9) Disconnect coil pack wiring connector and
remove coil pack and bracket from engine.
(10) Remove cylinder head cover.
(11) Remove cam sensor and fuel injectors wiring
connectors.
(12) Remove intake manifoldSOHC ONLY.
Removal procedure outline in Group 11.
(13) Remove timing belt and camshaft sprocket.
Refer to procedure outlined in this section.
(14) Remove rocker arm shaft assemblies.
(15) Remove cylinder head bolts.
Fig. 27 Removing and Installing Valve Spring
Fig. 28 Valve Stem Oil Seal Tool
Fig. 29 Valve Spring Assembly
Fig. 30 Air Cleaner Inlet Duct
PL2.0L SOHC ENGINE 9 - 25
REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION (Continued)
Page 767 of 1200

Valve Margin
Intake......1.15 ± 1.48 mm (0.0452 ± 0.0582 in.)
Exhaust.....1.475 ± 1.805 mm (0.058 ± 0.071 in.)
Valve Length (Overall)
Intake.....114.69 ± 115.19 mm (4.515 ± 4.535 in.)
Exhaust . . .109.59 ± 110.09 mm (4.603 ± 4.623 in.)
Valve Stem Tip Height
Intake........45.01 ± 46.07 mm (1.77 ± 1.81 in.)
Exhaust.......43.51 ± 44.57 mm (1.71 ± 1.75 in.)
Stem Diameter
Intake......5.934 ± 5.952 mm (0.234 ± 0.234 in.)
Exhaust.....5.906 ± 5.924 mm (0.233 ± 0.233 in.)
Stem to Guide Clearance
Intake. . . .0.048 ± 0.066 mm (0.0018 ± 0.0025 in.)
Exhaust . .0.0736 ± 0.094 mm (0.0029 ± 0.0037 in.)
Max. Allowable Intake......0.076 mm (0.003 in.)
Max. Allowable Exhaust.....0.101 mm (0.004 in.)
Valve Springs
Free Length (Approx.).......44.4 mm (1.747 in.)
Nominal Force (Valve closed) . .91 N´m @ 39.8 mm
(67 ft. lbs. @ 1.57 in.)
Nominal Force (Valve open). . .239 N´m @ 32.6 mm
(176 lbs. @ 1.28 in.)
Installed Height...........40.18 mm (1.580 in.)
* SERVICE AS AN ASSEMBLY WITH ROCKER
ARM.
** ALL READINGS IN CRANKSHAFT DEGREES,
AT 0.5 mm (0.019 in.) OF VALVE LIFT.
TORQUE CHART 2.0L SOHC
DESCRIPTION TORQUE
Camshaft Sensor Pick Up
Bolts....................9.6 N´m (85 in. lbs.)
Camshaft Sprocket
Bolt.....................115N´m(85ft.lbs.)
Connecting Rod Cap
Bolts..........27N´m(20ft.lbs.) Plus 1/4 Turn
CollarÐOil Pan to Transaxle
Step 1: Collar to Oil Pan Bolts . .3 N´m (30 in. lbs.)
Step 2: Collar to Transaxle Bolts.108 N´m (80 ft. lbs.)
Step 3: Collar to Oil Pan Bolts .54 N´m (40 ft. lbs.)
Crankshaft Main Bearing Cap/Bedplate
M8 Bedplate Bolts...........30N´m(22ft.lbs.)
M11 Main Cap Bolts.........81N´m(60ft.lbs.)
Crankshaft Damper
Bolt....................142 N´m (105 ft. lbs.)
Cylinder Head
Bolts........Refer To Cylinder Head Installation
Cylinder Head Cover
Bolts....................12N´m(105 in. lbs.)
Drive Plate to Flywheel
Bolts.....................95N´m(70ft.lbs.)
Engine Mount BracketÐRight
Bolts.....................61N´m(45ft.lbs.)DESCRIPTION TORQUE
Engine Mounting
Bolts........Refer to Engine Mount Installation
Exhaust Manifold to Cylinder Head
Bolts....................23N´m(200 in. lbs.)
Exhaust Manifold Heat Shield
Bolts....................12N´m(105 in. lbs.)
Front Mount Torque Bracket
Bolts.....................33N´m(24ft.lbs.)
Front Powertrain Bending Strut
Long Bolts................101 N´m (75 ft. lbs.)
Short Bolt.................61N´m(45ft.lbs.)
Intake Manifold
Bolts....................12N´m(105 in. lbs.)
Oil Filter Adapter
Fastener..................80N´m(60ft.lbs.)
Oil Filter..................20N´m(15ft.lbs.)
Oil Pan
Bolts....................12N´m(105 in. lbs.)
Drain Plug.................27N´m(20ft.lbs.)
Oil Pump Attaching
Bolts....................28N´m(250 in. lbs.)
Oil Pump Cover Fastener. . . .12 N´m (105 in. lbs.)
Oil Pump Pick-up Tube Bolt . .28 N´m (250 in. lbs.)
Oil Pump Relief Valve Cap. . . .41 N´m (30 ft. lbs.)
Rear Torque BracketÐ2.0L Engine
Bolts w/Auto. Transaxle......110N´m(80ft.lbs.)
Bolts w/Manual Transaxle.....61N´m(45ft.lbs.)
Rocker Arm Shaft
Bolts....................28N´m(250 in. lbs.)
Spark Plugs................28N´m(20ft.lbs.)
Thermostat Housing
Bolts....................23N´m(200 in lbs.)
Timing Belt Cover
Bolts M6.................12N´m(105 in. lbs.)
Timing Belt Tensioner AssemblyÐMechanical
Bolts....................28N´m(250 in. lbs.)
Timing Belt TensionerÐHydraulic
Pulley Bolt.................68N´m(50ft.lbs.)
Pivot Bracket Bolt...........31N´m(23ft.lbs.)
Tensioner Bolts.............31N´m(23ft.lbs.)
Water Pump Mounting
Bolts....................12N´m(105 in. lbs.)
9 - 54 2.0L SOHC ENGINEPL
SPECIFICATIONS (Continued)
Page 773 of 1200

incorporates main bearing caps. Rear seal retainer is
integral with the block.
CRANKSHAFTA nodular cast iron crankshaft is
used. The engine has 5 main bearings, with number
3 flanged to control thrust. The 52 mm diameter
main and 48 mm diameter crank pin journals (all)
have undercut fillet radiuses that are deep rolled for
added strength. To optimize bearing loading 8 coun-
terweights are used. Hydrodynamic seals provide end
sealing, where the crankshaft exits the block.
Anaerobic gasket material is used for parting line
sealing. A sintered iron timing belt sprocket is
mounted on the crankshaft nose. This sprocket pro-
vides motive power; via timing belt to the camshaft
sprocket providing timed valve actuation.
PISTONSThe DOHC EngineDO NOThave pro-
vision for a free wheeling valve train. Non free
wheeling valve train means, in the event of a broken
timing belt Pistons will contact the Valves. All
engines use pressed-in piston pins to attach forged
powdered metal connecting rods. The connecting rods
are a cracked cap design and are not repairable. Hex
head cap screw are used to provide alignment and
durability in the assembly.
PISTON RINGSThe piston rings include a
molybdenum faced top ring for reliable compression
sealing and a taper faced intermediate ring for addi-
tional cylinder pressure control. Oil Control Ring
Package contains of 2 steel rails and a expander
spacer.
CYLINDER HEADFeatures a Dual Over Head
Camshaft (DOHC), 4 valves per cylinder cross flow
design. The valves are arranged in two in-line banks,
with the ports of the bank of two intake valves per
cylinder facing toward the radiator side of engine
and ports of the bank of two exhaust valves per cyl-
inder facing toward the dash panel. Incorporates
powder metal valve guides and seats. Integral oil gal-
leys within the cylinder head supplies oil to the
hydraulic lash adjusters, camshaft and valve mecha-
nisms.
CAMSHAFTSThe nodular iron camshafts have
six bearing journals and 2 cam lobes per cylinder.
Flanges at the rear journals control camshaft end
play. Provision for cam position sensor is located on
the intake camshaft at the rear of cylinder head. A
hydrodynamic oil seal is used for oil control at the
front of the camshaft.
VA LV E SFour valves per cylinder are actuated by
roller cam followers which pivot on stationary
hydraulic lash adjusters. All valves have 6 mm diam-
eter chrome plated valve stems. The valve sizes are
34.8 mm (1.370 inch.) diameter intake valves and
30.5 mm (1.20 inch.) diameter exhaust valves. Viton
rubber valve stem seals are integral with the springseats. Valve springs, spring retainers, and locks are
conventional.
INTAKE MANIFOLDThe intake manifold is a
two piece aluminum casting, attached to the cylinder
head with ten fasteners. This long branch fan design
enhances low and mid-speed torque.
EXHAUST MANIFOLDThe exhaust manifold is
made of nodular cast iron for strength and high tem-
peratures. Exhaust gasses exit through a machined,
articulated joint connection to the exhaust pipe.
COMPONENT REPLACEMENT
If any of the following parts have been changed or
replaced:
²Camshaft
²Camshaft Position Sensor
²Camshaft Position Sensor Target Magnet
²Cylinder Block
²Cylinder Head
²Water Pump
²Powertrain Control Module (PCM)
²Timing Belt and Timing Belt Tensioner
The camshaft and crankshaft timing relearn proce-
dure must be performed. Refer to the component
Removal and Installation procedure outlined in this
Group.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
CHECKING ENGINE OIL PRESSURE
(1) Remove oil pressure switch and install gauge
assembly C-3292 with adaptor.
(2) Run engine until thermostat opens.
CAUTION: If oil pressure is 0 at idle, Do Not per-
form the 3000 RPM test in the next step.
(3) Oil Pressure:Curb Idle25 kPa (4 psi) mini-
mum3000 RPM170-550 kPa (25-80 psi).
(4) If oil pressure is 0 at idle. Shut off engine,
check for pressure relief valve stuck open, a clogged
oil pick-up screen or a damaged oil pick-up tube
O-ring.
SERVICE PROCEDURES
CYLINDER BORE AND PISTON SIZING
The cylinder walls should be checked for out-of-
round and taper with Tool C-119 (Fig. 4). The cylin-
der bore out-of-round is 0.050 mm (.002 inch)
maximum and cylinder bore taper is 0.051 mm (0.002
inch) maximum. If the cylinder walls are badly
scuffed or scored, the cylinder block should be
rebored and honed, and new pistons and rings fitted.
Whatever type of boring equipment is used, boring
and honing operation should be closely coordinated
9 - 60 2.0L DOHC ENGINEPL
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION (Continued)
Page 785 of 1200

REMOVAL
(1) Perform fuel system pressure release procedure
before attempting any repairs.Refer to Group 14,
Fuel System.
(2) Disconnect negative battery cable. Drain cool-
ing system. Refer to Group 7, Cooling System.
(3) Remove air cleaner duct and air cleaner, dis-
connect all vacuum lines, electrical wiring and fuel
line from fuel rail and throttle body.
(4) Remove throttle linkage.
(5) Remove accessory drive belts. Refer to Group 7,
Cooling System for procedure.
(6) Remove power brake vacuum hose from intake
manifold.
(7) Raise vehicle and remove exhaust pipe from
manifold.
(8) Remove power steering pump assembly and set
aside.
(9) Disconnect coil pack wiring connector and
remove coil pack from engine.
(10) Remove cam sensor and fuel injectors wiring
connectors.
(11) Remove timing belt, timing belt tensioner, and
camshaft sprocket. Refer to procedure outlined in
this section.
(12) Remove inner timing belt cover.
(13) Remove cylinder head cover.
(14) Remove camshaft and cam follower assem-
blies. Refer to Camshaft Service for removal proce-
dure outlined in this section.
(15) Remove cylinder head bolts.
CAUTION: Use only a plastic scraper to remove
gasket material on the aluminum head sealing sur-
faces to prevent damage to cylinder head.
CYLINDER HEAD FLATNESS
(1) Cylinder head must be flat within 0.1 mm
(0.004 inch) (Fig. 30).
NOTE: Inspect camshaft bearing journals for scor-
ing.
INSTALLATION
(1) Position new cylinder head gasket onto block.
(2) Before installing the bolts the threads should
be oiled with engine oil. The 4 short bolts 110 mm
(4.330 in.) are to be installed in positions 7, 8, 9, and
10 (Fig. 31).
(3) Tighten the cylinder head bolts in sequence
shown in (Fig. 31). Follow the four step procedure
listed below:
²Step 1: Bolts1±6to34N´m(25ft.lbs.) and
bolts7±10to28N´m(20ft.lbs.)²Step 2: Bolts1±6to68N´m(50ft.lbs.) and
bolts7±10to28N´m(20ft.lbs.)
²Step 3: Bolts1±6to68N´m(50ft.lbs.) and
bolts7±10to28N´m(20ft.lbs.)
²Step 4: Turn all bolts an additional 90É (1/4
turn).Do not use a torque wrench for this step.
(4) Install cam follower assemblies and camshafts.
Refer to procedure outlined in this section.
(5) Install cylinder head cover. Refer to procedure
outlined in this section.
(6) Install inner timing belt cover and camshaft
sprockets.
(7) Install timing belt tensioner and timing belt.
(8) Connect electrical connectors to cam sensor and
fuel injectors.
(9) Install coil pack and connect electrical connec-
tor.
(10) Install power steering pump.
(11) Connect power brake booster hose to intake
manifold.
(12) Install throttle linkage to throttle body.
(13) Connect all vacuum lines and electrical con-
nectors to throttle body.
Fig. 30 Checking Cylinder Head Flatness
Fig. 31 Cylinder Head Tightening Sequence
9 - 72 2.0L DOHC ENGINEPL
REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION (Continued)
Page 811 of 1200

TORQUE CHART 2.0L DOHC
DESCRIPTION TORQUE
Camshaft Sensor Pick-Up
Bolts....................9.6 N´m (85 in. lbs.)
Camshaft Sprocket
Bolt.....................115N´m(85ft.lbs.)
Connecting Rod Cap
Bolts..........27N´m(20ft.lbs.) Plus 1/4 Turn
CollarÐOil Pan to Transaxle
Step 1: Collar to Oil Pan Bolts . .3 N´m (30 in. lbs.)
Step 2: Collar to Transaxle Bolts.108 N´m (80 ft. lbs.)
Step 3: Collar to Oil Pan Bolts .54 N´m (40 ft. lbs.)
Crankshaft Main Bearing Cap/Bedplate
M8 Bedplate Bolts...........30N´m(22ft.lbs.)
M11 Main Cap Bolts.........81N´m(60ft.lbs.)
Crankshaft Damper
Bolt....................142 N´m (105 ft. lbs.)
Cylinder Head
Bolts........Refer To Cylinder Head Installation
Cylinder Head Cover
Bolts....................12N´m(105 in. lbs.)
Drive Plate to Crankshaft
Bolts.....................95N´m(70ft.lbs.)
Engine Mount Bracket
Bolts.....................41N´m(30ft.lbs.)
Exhaust Manifold to Cylinder Head
Bolts....................23N´m(200 in. lbs.)
Exhaust Manifold Heat Shield
Bolts....................15N´m(130 in. lbs.)
Intake Manifold
Bolts....................28N´m(250 in. lbs.)
Oil Filter Adapter
Fastener..................80N´m(60ft.lbs.)
Oil Filter..................20N´m(15ft.lbs.)
Oil Pan
Bolts....................12N´m(105 in. lbs.)
Drain Plug.................34N´m(25ft.lbs.)
Oil Pump Attaching
Bolts....................28N´m(250 in. lbs.)
Oil Pump Cover Fastener. . . .12 N´m (105 in. lbs.)
Oil Pump Pick-up Tube Bolt . .28 N´m (250 in. lbs.)
Oil Pump Relief Valve Cap. . . .55 N´m (40 ft. lbs.)
Spark Plugs
Plug......................28N´m(20ft.lbs.)
Thermostat Housing
Bolts....................23N´m(200 in lbs.)
Timing Belt Tensioner AssemblyÐMechanical
Bolts....................28N´m(250 in. lbs.)
Timing Belt Tensioner AssemblyÐHydraulic
Bolts....................31N´m(275 in. lbs.)
Timing Belt TensionerÐHydraulic
Bolts....................31N´m(275 in. lbs.)DESCRIPTION TORQUE
Timing Belt Idler Pulley
Bolt........................61N´m(45ft.lbs.)
Timing Belt Cover
Bolts M6.................12N´m(105 in. lbs.)
Water Pump Mounting
Bolts....................12N´m(105 in. lbs.)
SPECIAL TOOLS
2.0L DOHC
Puller 1026
Crankshaft Damper Removal Insert 6827-A
Camshaft Sprocket Remover/Installer C-4687
9 - 98 2.0L DOHC ENGINEPL
SPECIFICATIONS (Continued)
Page 820 of 1200
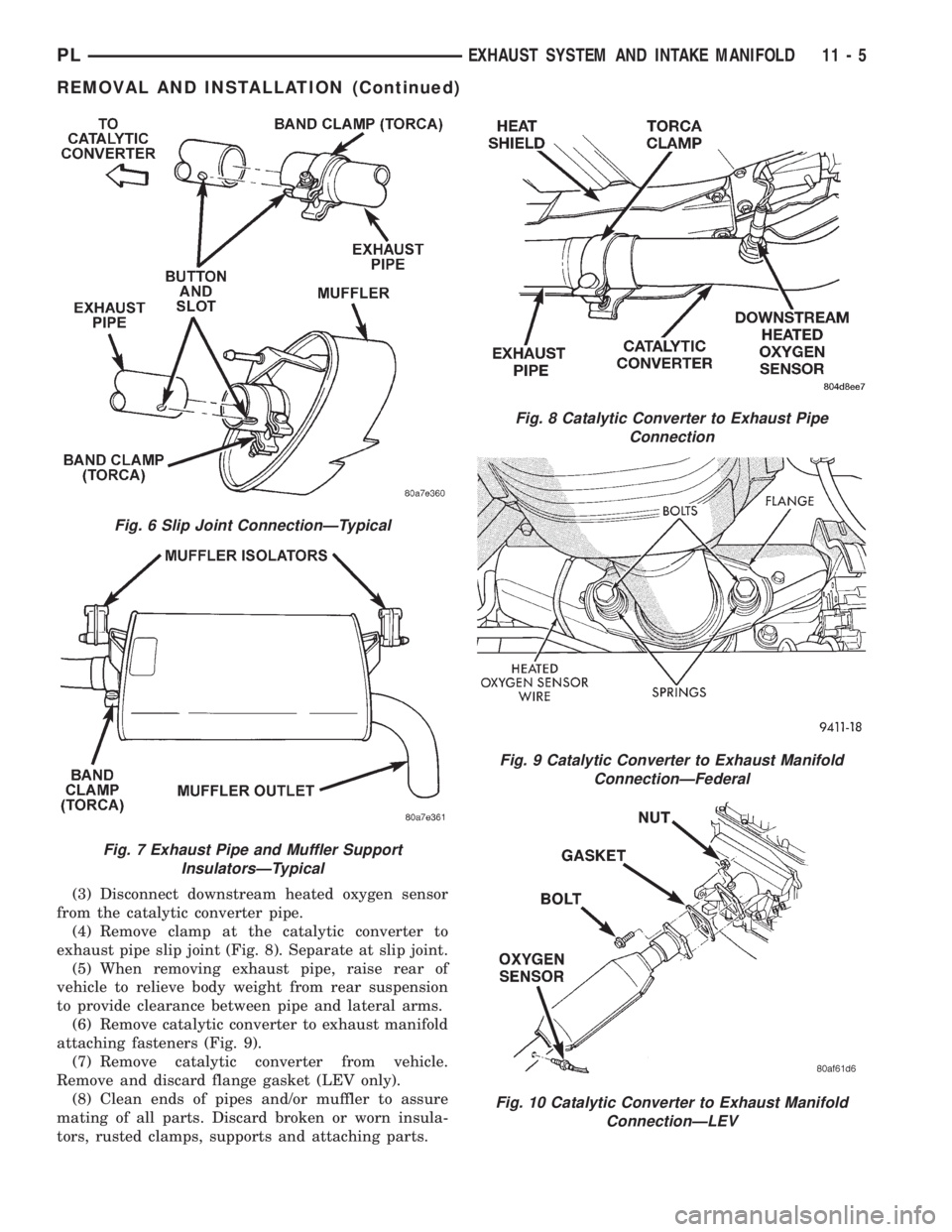
(3) Disconnect downstream heated oxygen sensor
from the catalytic converter pipe.
(4) Remove clamp at the catalytic converter to
exhaust pipe slip joint (Fig. 8). Separate at slip joint.
(5) When removing exhaust pipe, raise rear of
vehicle to relieve body weight from rear suspension
to provide clearance between pipe and lateral arms.
(6) Remove catalytic converter to exhaust manifold
attaching fasteners (Fig. 9).
(7) Remove catalytic converter from vehicle.
Remove and discard flange gasket (LEV only).
(8) Clean ends of pipes and/or muffler to assure
mating of all parts. Discard broken or worn insula-
tors, rusted clamps, supports and attaching parts.
Fig. 6 Slip Joint ConnectionÐTypical
Fig. 7 Exhaust Pipe and Muffler Support
InsulatorsÐTypical
Fig. 8 Catalytic Converter to Exhaust Pipe
Connection
Fig. 9 Catalytic Converter to Exhaust Manifold
ConnectionÐFederal
Fig. 10 Catalytic Converter to Exhaust Manifold
ConnectionÐLEV
PLEXHAUST SYSTEM AND INTAKE MANIFOLD 11 - 5
REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION (Continued)