1998 OPEL FRONTERA ECO mode
[x] Cancel search: ECO modePage 1392 of 6000
6E–275 ENGINE DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS
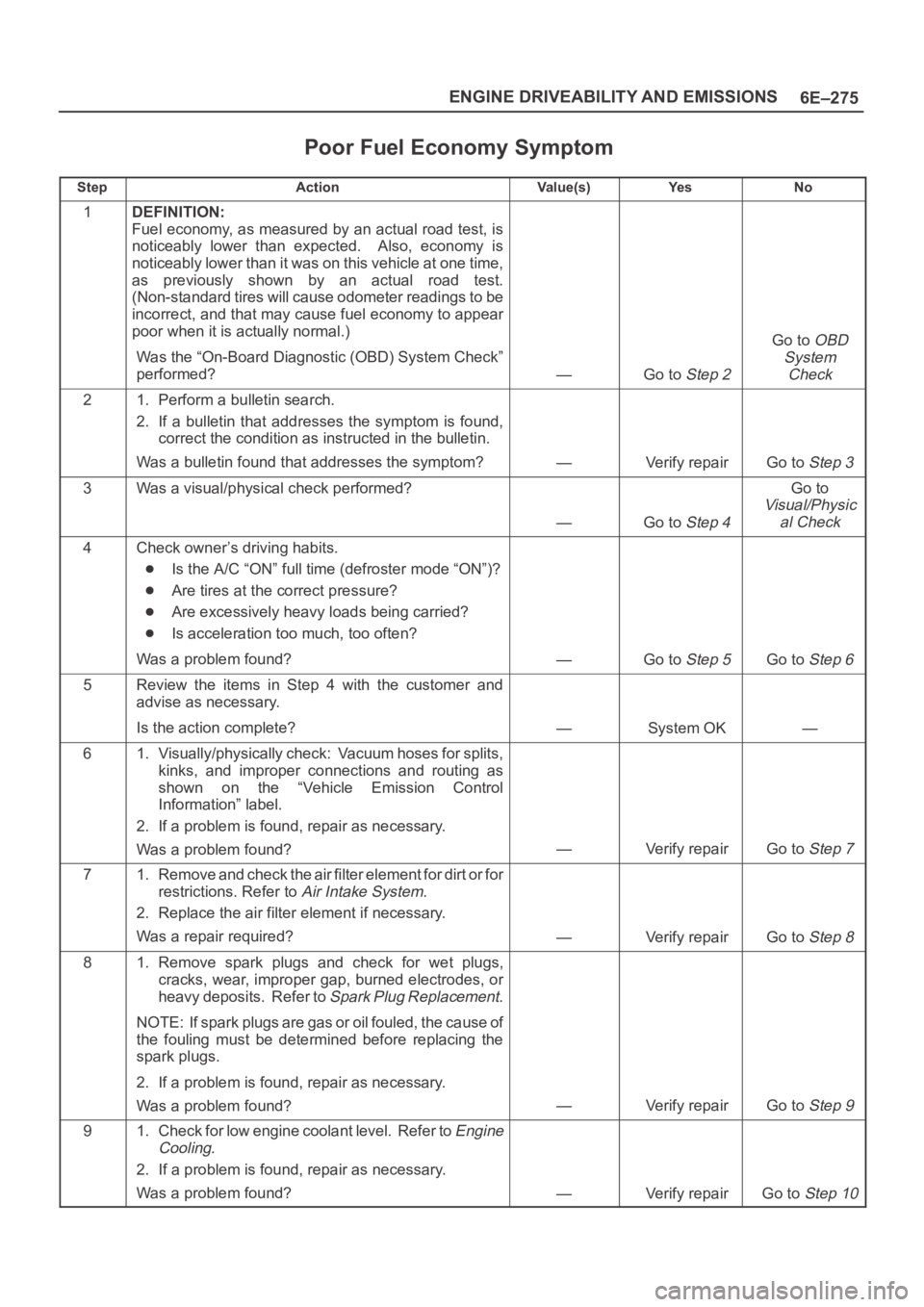
Poor Fuel Economy Symptom
StepActionVa l u e ( s )Ye sNo
1DEFINITION:
Fuel economy, as measured by an actual road test, is
noticeably lower than expected. Also, economy is
noticeably lower than it was on this vehicle at one time,
as previously shown by an actual road test.
(Non-standard tires will cause odometer readings to be
incorrect, and that may cause fuel economy to appear
poor when it is actually normal.)
Was the “On-Board Diagnostic (OBD) System Check”
performed?
—Go to Step 2
Go to OBD
System
Check
21. Perform a bulletin search.
2. If a bulletin that addresses the symptom is found,
correct the condition as instructed in the bulletin.
Was a bulletin found that addresses the symptom?
—Verify repairGo to Step 3
3Was a visual/physical check performed?
—Go to Step 4
Go to
Visual/Physic
al Check
4Check owner’s driving habits.
Is the A/C “ON” full time (defroster mode “ON”)?
Are tires at the correct pressure?
Are excessively heavy loads being carried?
Is acceleration too much, too often?
Was a problem found?
—Go to Step 5Go to Step 6
5Review the items in Step 4 with the customer and
advise as necessary.
Is the action complete?
—System OK—
61. Visually/physically check: Vacuum hoses for splits,
kinks, and improper connections and routing as
shown on the “Vehicle Emission Control
Information” label.
2. If a problem is found, repair as necessary.
Was a problem found?
—Verify repairGo to Step 7
71. Remove and check the air filter element for dirt or for
restrictions. Refer to
Air Intake System.
2. Replace the air filter element if necessary.
Was a repair required?
—Verify repairGo to Step 8
81. Remove spark plugs and check for wet plugs,
cracks, wear, improper gap, burned electrodes, or
heavy deposits. Refer to
Spark Plug Replacement.
NOTE: If spark plugs are gas or oil fouled, the cause of
the fouling must be determined before replacing the
spark plugs.
2. If a problem is found, repair as necessary.
Was a problem found?
—Verify repairGo to Step 9
91. Check for low engine coolant level. Refer to Engine
Cooling
.
2. If a problem is found, repair as necessary.
Was a problem found?
—Verify repairGo to Step 10
Page 1456 of 6000

6E–339 ENGINE DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS
0005
PCM Components
The PCM is designed to maintain exhaust emission levels
to government mandated standards while providing
excellent driveability and fuel efficiency. The PCM
monitors numerous engine and vehicle functions via
electronic sensors such as the throttle position (TP)
sensor, heated oxygen sensor (HO2S), and vehicle
speed sensor (VSS). The PCM also controls certain
engine operations through the following:
Fuel injector control
Ignition control module
Knock sensor
Automatic transmission shift functions
Cruise control
A/C clutch control
PCM Voltage Description
The PCM supplies a buffered voltage to various switches
and sensors. It can do this because resistance in the
PCM is so high in value that a test light may not illuminate
when connected to the circuit. An ordinary shop
voltmeter may not give an accurate reading because the
voltmeter input impedance is too low. Use a 10-megohm
input impedance digital voltmeter (such as J 39200) to
assure accurate voltage readings.
The input/output devices in the PCM include
analog-to-digital converters, signal buffers, counters,
and special drivers. The PCM controls most components
with electronic switches which complete a ground circuit
when turned “ON.” These switches are arranged in
groups of 4 and 7, called either a surface-mounted quad
driver module (QDM), which can independently control up
to 4 output terminals, or QDMs which can independently
control up to 7 outputs. Not all outputs are always used.
PCM Input/Outputs
Inputs – Operating Conditions Read
Air Conditioning “ON” or “OFF”
Engine Coolant Temperature
Crankshaft Position
Exhaust Oxygen Content
Electronic Ignition
Manifold Absolute Pressure
Battery Voltage
Throttle Position
Vehicle Speed
Fuel Pump Voltage
Power Steering Pressure
Intake Air Temperature
Mass Air Flow
Engine Knock
Camshaft Position
Outputs – Systems Controlled
Exhaust Gas Recirculation (EGR)
Ignition Control
Fuel Control
Idle Air Control
Electric Fuel Pump
Air Conditioning
Diagnostics
– Malfunction Indicator Lamp (Service Engine Soon
lamp)
– Data Link Connector (DLC)
– Data Output
Transmission Control Module
Alternator Gain Control
PCM Service Precautions
The PCM is designed to withstand normal current draws
associated with vehicle operation. Avoid overloading any
circuit. When testing for opens and shorts, do not ground
or apply voltage to any of the PCM’s circuits unless
instructed to do so. These circuits should only be tested
Tech-2. The PCM should remain connected to the PCM
or to a recommended breakout box.
Reprogramming The PCM
The Trooper allow reprogramming of the PCM without
removing it from the vehicle . This provides a flexible and
cost-effective method of making changes in software
calibrations.
The service programming system (SPS) will not allow
incorrect software programming or incorrect calibration
changes.
Refer to the UBS 98model year Immobilizer Workshop
Manual.
Throttle Position (TP) Sensor
The throttle position (TP) sensor is a potentiometer
connected to the throttle shaft on the throttle body. The
PCM monitors the voltage on the signal line and
calculates throttle position. As the throttle valve angle is
changed (accelerator pedal moved), the TP sensor signal
also changes. At a closed throttle position, the output of
Page 1458 of 6000

6E–341 ENGINE DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS
this is done, if the problem still exists, it may be diagnosed
in the normal manner.
Electrostatic Discharge Damage
Electronic components used in the PCM are often
designed to carry very low voltage. Electronic
components are susceptible to damage caused by
electrostatic discharge. Less than 100 volts of static
electricity can cause damage to some electronic
components. By comparison, it takes as much as 4000
volts for a person to feel even the zap of a static
discharge.
TS23793
There are several ways for a person to become statically
charged. The most common methods of charging are by
friction and induction.
An example of charging by friction is a person sliding
across a vehicle seat.
Charge by induction occurs when a person with well
insulated shoes stands near a highly charged object
and momentary touches ground. Charges of the
same polarity are drained off leaving the person
highly charged with the opposite polarity. Static
charges can cause damage, therefore it is important
to use care when handling and testing electronic
components.
NOTE: To prevent possible electrostatic discharge
damage, follow these guidelines:
Do not touch the PCM connector pins or soldered
components on the PCM circuit board.
Do not touch the knock sensor module component
leads.
Do not open the replacement part package until the
part is ready to be installed.
Before removing the part from the package, ground
the package to a known good ground on the vehicle.
If the part has been handled while sliding across the
seat, while sitting down from a standing position, or
while walking a distance, touch a known good ground
before installing the part.
Upshift Lamp
Refer to Manual Transmission.
General Description (Air Induction)
Air Induction System
The air induction system filters contaminants from the
outside air, and directs the progress of the air as it is
drawn into the engine. A remote-mounted air cleaner
prevents dirt and debris in the air from entering the
engine. The air duct assembly routes filtered air to the
throttle body. Air enters the engine by to following steps:
1. Through the throttle body.
2. Into the common chamber.
3. Through the cylinder head intake ports.
4. Into the cylinders.
055RV010
General Description (Fuel Metering)
Acceleration Mode
The PCM provides extra fuel when it detects a rapid
increase in the throttle position and the air flow.
Accelerator Controls
The accelerator control system is a cable-type system
with specific linkage adjustments.
Refer to
Cable Adjustment.
Battery Voltage Correction Mode
When battery voltage is low, the PCM will compensate for
the weak spark by increasing the following:
The amount of fuel delivered.
The idle RPM.
Ignition dwell time.
CMP Signal
The PCM uses this signal to determine the position of the
number 1 piston during its power stroke, allowing the
Page 1459 of 6000

6E–342
ENGINE DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS
PCM to calculate true sequential multiport fuel injection
(SFI). Loss of this signal will set a DTC P0341. If the CMP
signal is lost while the engine is running, the fuel injection
system will shift to a calculated sequential fuel injection
based on the last fuel injection pulse, and the engine will
continue to run. The engine can be restarted and will run
in the calculated sequential mode as long as the fault is
present, with a 1-in-6 chance of being correct.
Clear Flood Mode
Clear a flooded engine by pushing the accelerator pedal
down all the way. The PCM then de-energizes the fuel
injectors. The PCM holds the fuel injectors de-energized
as long as the throttle remains above 80% and the engine
speed is below 800 RPM. If the throttle position becomes
less than 80%, the PCM again begins to pulse the
injectors “ON” and “OFF,” allowing fuel into the cylinders.
Deceleration Mode
The PCM reduces the amount of fuel injected when it
detects a decrease in the throttle position and the air flow.
When deceleration is very fast, the PCM may cut off fuel
completely for short periods.
Engine Speed/Vehicle Speed/Fuel Disable
Mode
The PCM monitors engine speed. It turns off the fuel
injectors when the engine speed increase above 6400
RPM. The fuel injectors are turned back on when engine
speed decreases below 6150 RPM.
Fuel Cutoff Mode
No fuel is delivered by the fuel injectors when the ignition
is “OFF.” This prevents engine run-on. In addition, the
PCM suspends fuel delivery if no reference pulses are
detected (engine not running) to prevent engine flooding.
Fuel Injector
The sequential multiport fuel injection (SFI) fuel injector is
a solenoid-operated device controlled by the PCM. The
PCM energizes the solenoid, which opens a valve to allow
fuel delivery.
The fuel is injected under pressure in a conical spray
pattern at the opening of the intake valve. Excess fuel not
used by the injectors passes through the fuel pressure
regulator before being returned to the fuel tank.
A fuel injector which is stuck partly open will cause a loss
of fuel pressure after engine shut down, causing long
crank times.
0003
Fuel Metering System Components
The fuel metering system is made up of the following
parts:
The fuel injectors.
The throttle body.
The fuel rail.
The fuel pressure regulator.
The PCM.
The crankshaft position (CKP) sensor.
The camshaft position (CMP) sensor.
The idle air control (IAC) valve.
The fuel pump.
The fuel pump relay.
Basic System Operation
The fuel metering system starts with the fuel in the fuel
tank. An electric fuel pump, located in the fuel tank,
pumps fuel to the fuel rail through an in-line fuel filter. The
pump is designed to provide fuel at a pressure above the
pressure needed by the injectors. A fuel pressure
regulator in the fuel rail keeps fuel available to the fuel
injectors at a constant pressure. A return line delivers
unused fuel back to the fuel tank. Refer to
Section 6C f o r
further information on the fuel tank, line filter, and fuel
pipes.
Fuel Metering System Purpose
The basic function of the air/fuel metering system is to
control the air/fuel delivery to the engine. Fuel is delivered
to the engine by individual fuel injectors mounted in the
intake manifold near each intake valve.
The main control sensor is the heated oxygen sensor
(HO2S) located in the exhaust system. The HO2S tells
the PCM how much oxygen is in the exhaust gas. The
PCM changes the air/fuel ratio to the engine by controlling
the amount of time that fuel injector is “ON.” The best
mixture to minimize exhaust emissions is 14.7 parts of air
to 1 part of gasoline by weight, which allows the catalytic
converter to operate most efficiently. Because of the
Page 1460 of 6000

6E–343 ENGINE DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS
constant measuring and adjusting of the air/fuel ratio, the
fuel injection system is called a “closed loop” system.
The PCM monitors signals from several sensors in order
to determine the fuel needs of the engine. Fuel is
delivered under one of several conditions called “modes.”
All modes are controlled by the PCM.
Fuel Pressure Regulator
The fuel pressure regulator is a diaphragm-operated
relief valve mounted on the fuel rail with fuel pump
pressure on one side and manifold pressure on the other
side. The fuel pressure regulator maintains the fuel
pressure available to the injector at three times
barometric pressure adjusted for engine load. It may be
serviced separate.
If the pressure is too low, poor performance and a DTC
P0131, DTC P0151,DTC P0171 or DTC P1171 will be the
result. If the pressure is too high, excessive odor and/or a
DTC P0132, DTC P0152,DTC P0172 or DTC P0175 will
be the result. Refer to
Fuel System Diagnosis for
information on diagnosing fuel pressure conditions.
0011
Fuel Pump Electrical Circuit
When the key is first turned “ON,” the PCM energizes the
fuel pump relay for two seconds to build up the fuel
pressure quickly. If the engine is not started within two
seconds, the PCM shuts the fuel pump off and waits until
the engine is cranked. When the engine is cranked and
the 58 X crankshaft position signal has been detected by
the PCM, the PCM supplies 12 volts to the fuel pump relay
to energize the electric in-tank fuel pump.
An inoperative fuel pump will cause a “no-start” condition.
A fuel pump which does not provide enough pressure will
result in poor performance.
Fuel Rail
The fuel rail is mounted to the top of the engine and
distributes fuel to the individual injectors. Fuel is
delivered to the fuel inlet tube of the fuel rail by the fuel
lines. The fuel goes through the fuel rail to the fuel
pressure regulator. The fuel pressure regulator maintainsa constant fuel pressure at the injectors. Remaining fuel
is then returned to the fuel tank.
055RW009
Idle Air Control (IAC) Valve
The purpose of the idle air control (IAC) valve is to control
engine idle speed, while preventing stalls due to changes
in engine load. The IAC valve, mounted in the throttle
body, controls bypass air around the throttle plate. By
moving the conical valve (pintle) in (to decrease air flow)
or out (to increase air flow), a controlled amount of air can
move around the throttle plate. If the RPM is too low, the
PCM will retract the IAC pintle, resulting in more air
moving past the throttle plate to increase the RPM. If the
RPM is too high, the PCM will extend the IAC pintle,
allowing less air to move past the throttle plate,
decreasing the RPM.
The IAC pintle valve moves in small steps called counts.
During idle, the proper position of the IAC pintle is
calculated by the PCM based on battery voltage, coolant
temperature, engine load, and engine RPM. If the RPM
drops below a specified value, and the throttle plate is
closed, the PCM senses a near-stall condition. The PCM
will then calculate a new IAC pintle valve position to
prevent stalls.
If the IAC valve is disconnected and reconnected with the
engine running, the idle RPM will be wrong. In this case,
the IAC must be reset. The IAC resets when the key is
cycled “ON” then “OFF.” When servicing the IAC, it
should only be disconnected or connected with the
ignition “OFF.”
The position of the IAC pintle valve affects engine start-up
and the idle characteristics of the vehicle. If the IAC pintle
is fully open, too much air will be allowed into the manifold.
This results in high idle speed, along with possible hard
starting and a lean air/fuel ratio. DTC P0507 or DTC
P1509 may set. If the IAC pintle is stuck closed, too little
air will be allowed in the manifold. This results in a low idle
speed, along with possible hard starting and a rich air/fuel
ratio. DTC P0506 or DTC P1508 may set. If the IAC
pintle is stuck part-way open, the idle may be high or low
and will not respond to changes in the engine load.
Page 1461 of 6000

6E–344
ENGINE DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS
0006
Run Mode
The run mode has the following two conditions:
Open loop
Closed loop
When the engine is first started the system is in “open
loop” operation. In “open loop,” the PCM ignores the
signal from the heated oxygen sensor (HO2S). It
calculates the air/fuel ratio based on inputs from the TP,
ECT, and MAF sensors.
The system remains in “open loop” until the following
conditions are met:
The HO2S has a varying voltage output showing that
it is hot enough to operate properly (this depends on
temperature).
The ECT has reached a specified temperature.
A specific amount of time has elapsed since starting
the engine.
Engine speed has been greater than a specified RPM
since start-up.
The specific values for the above conditions vary with
different engines and are stored in the programmable
read only memory (PROM). When these conditions are
met, the system enters “closed loop” operation. In
“closed loop,” the PCM calculates the air/fuel ratio
(injector on-time) based on the signal from the HO2S.
This allows the air/fuel ratio to stay very close to 14.7:1.
Starting Mode
When the ignition is first turned “ON,” the PCM energizes
the fuel pump relay for two seconds to allow the fuel pump
to build up pressure. The PCM then checks the engine
coolant temperature (ECT) sensor and the throttle
position (TP) sensor to determine the proper air/fuel ratio
for starting.
The PCM controls the amount of fuel delivered in the
starting mode by adjusting how long the fuel injectors are
energized by pulsing the injectors for very short times.
Throttle Body Unit
The throttle body has a throttle plate to control the amount
of air delivered to the engine. The TP sensor and IAC
valve are also mounted on the throttle body. Vacuum
ports located behind the throttle plate provide the vacuum
signals needed by various components.
Engine coolant is directed through a coolant cavity in the
throttle body to warm the throttle valve and to prevent
icing.
0019
General Description (Electronic
Ignition System)
Camshaft Position (CMP) Sensor
As the camshaft sprocket turns, a magnet in the sprocket
activates the Hall-effect switch in the CMP sensor. When
the Hall-effect switch is activated, it grounds the signal
line to the PCM, pulling the camshaft position sensor
signal circuit’s applied voltage low. This is a CMP signal.
The CMP signals is created as piston #1 is approximately
25
after top dead counter on the power stroke. If the
correct CMP signal is not received by the PCM, DTC
P0341 will be set.
Page 1466 of 6000

6E–349 ENGINE DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS
Damage during re-gapping can happen if the gapping
tool is pushed against the center electrode or the
insulator around it, causing the insulator to crack.
When re-gapping a spark plug, make the adjustment
by bending only the ground side terminal, keeping the
tool clear of other parts.
”Heat shock” breakage in the lower insulator tip
generally occurs during several engine operating
conditions (high speeds or heavy loading) and may be
caused by over-advanced timing or low grade fuels.
Heat shock refers to a rapid increase in the tip
temperature that causes the insulator material to
crack.
Spark plugs with less than the recommended amount of
service can sometimes be cleaned and re-gapped , then
returned to service. However, if there is any doubt about
the serviceability of a spark plug, replace it. Spark plugs
with cracked or broken insulators should always be
replaced.
A/C Clutch Diagnosis
A/C Clutch Circuit Operation
A 12-volt signal is supplied to the A/C request input of the
PCM when the A/C is selected through the A/C control
switch.
The A/C compressor clutch relay is controlled through the
PCM. This allows the PCM to modify the idle air control
position prior to the A/C clutch engagement for better idle
quality. If the engine operating conditions are within their
specified calibrated acceptable ranges, the PCM will
enable the A/C compressor relay. This is done by
providing a ground path for the A/C relay coil within the
PCM. When the A/C compressor relay is enabled,
battery voltage is supplied to the compressor clutch coil.
The PCM will enable the A/C compressor clutch
whenever the engine is running and the A/C has been
requested. The PCM will not enable the A/C compressor
clutch if any of the following conditions are met:
The throttle is greater than 90%.
The engine speed is greater than 6315 RPM.
The ECT is greater than 119C (246F).
The IAT is less than 5C (41F).
The throttle is more than 80% open.
A/C Clutch Circuit Purpose
The A/C compressor operation is controlled by the
powertrain control module (PCM) for the following
reasons:
It improvises idle quality during compressor clutch
engagement.
It improvises wide open throttle (WOT) performance.
It provides A/C compressor protection from operation
with incorrect refrigerant pressures.
The A/C electrical system consists of the following
components:
The A/C control head.
The A/C refrigerant pressure switches.
The A/C compressor clutch.
The A/C compressor clutch relay.
The PCM.
A/C Request Signal
This signal tells the PCM when the A/C mode is selected
at the A/C control head. The PCM uses this to adjust the
idle speed before turning on the A/C clutch. The A/C
compressor will be inoperative if this signal is not
available to the PCM.
Refer to
A/C Clutch Circuit Diagnosis for A/C wiring
diagrams and diagnosis for A/C electrical system.
General Description (Exhaust Gas
Recirculation (EGR) System)
EGR Purpose
The exhaust gas recirculation (EGR) system is use to
reduce emission levels of oxides of nitrogen (NOx). NOx
emission levels are caused by a high combustion
temperature. The EGR system lowers the NOx emission
levels by decreasing the combustion temperature.
057RW002
Linear EGR Valve
The main element of the system is the linear EGR valve.
The EGR valve feeds small amounts of exhaust gas back
into the combustion chamber. The fuel/air mixture will be
diluted and combustion temperatures reduced.
Linear EGR Control
The PCM monitors the EGR actual positron and adjusts
the pintle position accordingly. The uses information from
the following sensors to control the pintle position:
Engine coolant temperature (ECT) sensor.
Throttle position (TP) sensor.
Mass air flow (MAF) sensor.
Linear EGR Valve Operation and Results
of Incorrect Operation
The linear EGR valve is designed to accurately supply
EGR to the engine independent of intake manifold
vacuum. The valve controls EGR flow from the exhaust
Page 1742 of 6000

ENGINE MECHANICAL 6A – 9
SERVICING
Servicing refers to general maintenance procedures to
be performed by qualified service personnel.
MODEL IDENTIFICATION
Engine Serial Number
The engine number is stamped on the rear left hand
side of the cylinder body.
AIR CLEANER
Oil Wetted (Viscous) Type Paper Element.
The air cleaner has an oil wetted paper element. No
servicing is required until the replacement interval is
reached.
Never attempt to clean the element, no matter how dirty
it may appear. The element is designed to provide
normal filtering efficiency until it becomes due for
replacement.
Refer to the Item “Service and Maintenance” in the
Owner’s and Driver’s Manual for general service
information.
LUBRICATING SYSTEM
Main Oil Filter (Cartridge Type Paper Element)
Replacement Procedure
1. Loosen the drain plug to drain the engine oil.
2. Wait a few minutes and then retighten the drain
plug.
3. Loosen the used oil filter (2) by turning it counter-
clockwise with the filter wrench.
4. Clean the oil filer gasket fitting face.
This will allow the new oil filter to seat properly.
5. Apply a light coat of engine oil to the O-ring.
6. Turn the new oil filter until the filter O-ring is fitted
against the sealing face.
7. Use the filter wrench to turn the filter additional one
and 1/4 turns.
Filter Wrench: 5-5540-0203-0
012RW115
012RW062
For Europe1
2
050R200001