1998 OPEL FRONTERA ESP
[x] Cancel search: ESPPage 5000 of 6000

6E–343 ENGINE DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS
constant measuring and adjusting of the air/fuel ratio, the
fuel injection system is called a “closed loop” system.
The PCM monitors signals from several sensors in order
to determine the fuel needs of the engine. Fuel is
delivered under one of several conditions called “modes.”
All modes are controlled by the PCM.
Fuel Pressure Regulator
The fuel pressure regulator is a diaphragm-operated
relief valve mounted on the fuel rail with fuel pump
pressure on one side and manifold pressure on the other
side. The fuel pressure regulator maintains the fuel
pressure available to the injector at three times
barometric pressure adjusted for engine load. It may be
serviced separate.
If the pressure is too low, poor performance and a DTC
P0131, DTC P0151,DTC P0171 or DTC P1171 will be the
result. If the pressure is too high, excessive odor and/or a
DTC P0132, DTC P0152,DTC P0172 or DTC P0175 will
be the result. Refer to
Fuel System Diagnosis for
information on diagnosing fuel pressure conditions.
0011
Fuel Pump Electrical Circuit
When the key is first turned “ON,” the PCM energizes the
fuel pump relay for two seconds to build up the fuel
pressure quickly. If the engine is not started within two
seconds, the PCM shuts the fuel pump off and waits until
the engine is cranked. When the engine is cranked and
the 58 X crankshaft position signal has been detected by
the PCM, the PCM supplies 12 volts to the fuel pump relay
to energize the electric in-tank fuel pump.
An inoperative fuel pump will cause a “no-start” condition.
A fuel pump which does not provide enough pressure will
result in poor performance.
Fuel Rail
The fuel rail is mounted to the top of the engine and
distributes fuel to the individual injectors. Fuel is
delivered to the fuel inlet tube of the fuel rail by the fuel
lines. The fuel goes through the fuel rail to the fuel
pressure regulator. The fuel pressure regulator maintainsa constant fuel pressure at the injectors. Remaining fuel
is then returned to the fuel tank.
055RW009
Idle Air Control (IAC) Valve
The purpose of the idle air control (IAC) valve is to control
engine idle speed, while preventing stalls due to changes
in engine load. The IAC valve, mounted in the throttle
body, controls bypass air around the throttle plate. By
moving the conical valve (pintle) in (to decrease air flow)
or out (to increase air flow), a controlled amount of air can
move around the throttle plate. If the RPM is too low, the
PCM will retract the IAC pintle, resulting in more air
moving past the throttle plate to increase the RPM. If the
RPM is too high, the PCM will extend the IAC pintle,
allowing less air to move past the throttle plate,
decreasing the RPM.
The IAC pintle valve moves in small steps called counts.
During idle, the proper position of the IAC pintle is
calculated by the PCM based on battery voltage, coolant
temperature, engine load, and engine RPM. If the RPM
drops below a specified value, and the throttle plate is
closed, the PCM senses a near-stall condition. The PCM
will then calculate a new IAC pintle valve position to
prevent stalls.
If the IAC valve is disconnected and reconnected with the
engine running, the idle RPM will be wrong. In this case,
the IAC must be reset. The IAC resets when the key is
cycled “ON” then “OFF.” When servicing the IAC, it
should only be disconnected or connected with the
ignition “OFF.”
The position of the IAC pintle valve affects engine start-up
and the idle characteristics of the vehicle. If the IAC pintle
is fully open, too much air will be allowed into the manifold.
This results in high idle speed, along with possible hard
starting and a lean air/fuel ratio. DTC P0507 or DTC
P1509 may set. If the IAC pintle is stuck closed, too little
air will be allowed in the manifold. This results in a low idle
speed, along with possible hard starting and a rich air/fuel
ratio. DTC P0506 or DTC P1508 may set. If the IAC
pintle is stuck part-way open, the idle may be high or low
and will not respond to changes in the engine load.
Page 5004 of 6000

6E–347 ENGINE DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS
the secondary ignition circuit to flow through the spark
plug to the ground.
TS24047
Ignition Control PCM Output
The PCM provides a zero volt (actually about 100 mV to
200 mV) or a 5-volt output signal to the ignition control (IC)
module. Each spark plug has its own primary and
secondary coil module (”coil-at-plug”) located at the spark
plug itself. When the ignition coil receives the 5-volt signal
from the PCM, it provides a ground path for the B+ supply
to the primary side of the coil-at -plug module. This
energizes the primary coil and creates a magnetic field in
the coil-at-plug module. When the PCM shuts off the
5-volt signal to the ignition control module, the ground
path for the primary coil is broken. The magnetic field
collapses and induces a high voltage secondary impulse
which fires the spark plug and ignites the air/fuel mixture.
The circuit between the PCM and the ignition coil is
monitored for open circuits, shorts to voltage, and shorts
to ground. If the PCM detects one of these events, it will
set one of the following DTCs:
P0351: Ignition coil Fault on Cylinder #1
P0352: Ignition coil Fault on Cylinder #2
P0353: Ignition coil Fault on Cylinder #3
P0354: Ignition coil Fault on Cylinder #4
P0355: Ignition coil Fault on Cylinder #5
P0356: Ignition coil Fault on Cylinder #6
Knock Sensor (KS) PCM Input
The knock sensor (KS) system is comprised of a knock
sensor and the PCM. The PCM monitors the KS signals
to determine when engine detonation occurs. When a
knock sensor detects detonation, the PCM retards the
spark timing to reduce detonation. Timing may also be
retarded because of excessive mechanical engine or
transmission noise.
Powertrain Control Module (PCM)
The PCM is responsible for maintaining proper spark and
fuel injection timing for all driving conditions. To provideoptimum driveability and emissions, the PCM monitors
the input signals from the following components in order
to calculate spark timing:
Engine coolant temperature (ECT) sensor.
Intake air temperature (IAT) sensor.
Mass air flow (MAF) sensor.
PRNDL input from transmission range switch.
Throttle position (TP) sensor.
Vehicle speed sensor (VSS) .
Crankshaft position (CKP) sensor.
Spark Plug
Although worn or dirty spark plugs may give satisfactory
operation at idling speed, they frequency fail at higher
engine speeds. Faulty spark plugs may cause poor fuel
economy, power loss, loss of speed, hard starting and
generally poor engine performance. Follow the
scheduled maintenance service recommendations to
ensure satisfactory spark plug performance. Refer to
Maintenance and Lubrication.
Normal spark plug operation will result in brown to
grayish-tan deposits appearing on the insulator portion of
the spark plug. A small amount of red-brown, yellow, and
white powdery material may also be present on the
insulator tip around the center electrode. These deposits
are normal combustion by-products of fuels and
lubricating oils with additives. Some electrode wear will
also occur. Engines which are not running properly are
often referred to as “misfiring.” This means the ignition
spark is not igniting the air/fuel mixture at the proper time.
While other ignition and fuel system causes must also be
considered, possible causes include ignition system
conditions which allow the spark voltage to reach ground
in some other manner than by jumping across the air gap
at the tip of the spark plug, leaving the air/fuel mixture
unburned. Misfiring may also occur when the tip of the
spark plug becomes overheated and ignites the mixture
before the spark jumps. This is referred to as
“pre-ignition.”
Spark plugs may also misfire due to fouling, excessive
gap, or a cracked or broken insulator. If misfiring occurs
before the recommended replacement interval, locate
and correct the cause.
Carbon fouling of the spark plug is indicated by dry, black
carbon (soot) deposits on the portion of the spark plug in
the cylinder. Excessive idling and slow speeds under
light engine loads can keep the spark plug temperatures
so low that these deposits are not burned off. Very rich
fuel mixtures or poor ignition system output may also be
the cause. Refer to DTC P0172.
Oil fouling of the spark plug is indicated by wet oily
deposits on the portion of the spark plug in the cylinder,
usually with little electrode wear. This may be caused by
oil during break-in of new or newly overhauled engines.
Deposit fouling of the spark plug occurs when the normal
red-brown, yellow or white deposits of combustion by
products become sufficient to cause misfiring. In some
c a s e s , t h e s e d e p o s i t s m a y m e l t a n d f o r m a s h i n y g l a z e o n
the insulator around the center electrode. If the fouling is
found in only one or two cylinders, valve stem clearances
or intake valve seals may be allowing excess lubricating
Page 5007 of 6000

6E–350
ENGINE DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS
to the intake manifold through an orifice with a PCM
controlled pintle. During operation, the PCM controls
pintle position by monitoring the pintle position feedback
signal. The feedback signal can be monitored with Tech 2
as “Actual EGR Pos.” “Actual EGR Pos.” should always
be near the commanded EGR position (”Desired EGR
Pos.”). If a problem with the EGR system will not allow the
PCM to control the pintle position properly, DTC P1406
will set. The PCM also tests for EGR flow. If incorrect flow
is detected, DTC P0401 will set. If DTCs P0401 and/or
P1406 are set, refer to the DTC charts.
The linear EGR valve is usually activated under the
following conditions:
Warm engine operation.
Above-idle speed.
Too much EGR flow at idle, cruise or cold operation may
cause any of the following conditions to occur:
Engine stalls after a cold start.
Engine stalls at idle after deceleration.
Vehicle surges during cruise.
Rough idle.
Too little or no EGR flow may allow combustion
temperatures to get too high. This could cause:
Spark knock (detonation).
Engine overheating.
Emission test failure.
DTC P0401 (EGR flow test).
Poor fuel economy.
0017
EGR Pintle Position Sensor
The PCM monitors the EGR valve pintle position input to
endure that the valve responds properly to commands
from the PCM and to detect a fault if the pintle position
sensor and control circuits are open or shorted. If the
PCM detects a pintle position signal voltage outside the
normal range of the pintle position sensor, or a signal
voltage that is not within a tolerance considered
acceptable for proper EGR system operation, the PCM
will set DTC P1406.
General Description (Positive
Crankcase Ventilation (PCV) System)
Crankcase Ventilation System Purpose
The crankcase ventilation system is use to consume
crankcase vapors in the combustion process instead of
venting them to the atmosphere. Fresh air from the
throttle body is supplied to the crankcase and mixed with
blow-by gases. This mixture is then passed through the
positive crankcase ventilation (PCV) valve into the
common chamber.
Crankcase Ventilation System Operation
The primary control is through the positive crankcase
v e n t i l a t i o n ( P C V ) v a l v e . T h e PCV valve meters the flow at
a rate that depends on the intake vacuum. The PCV valve
restricts the flow when the inlet vacuum is highest. In
addition, the PCV valve can seal the common chamber
off in case of sudden high pressure in the crankcase.
028RV002
While the engine is running, exhaust fuses and small
amounts of the fuel/air mixture escape past the piston
Page 5275 of 6000
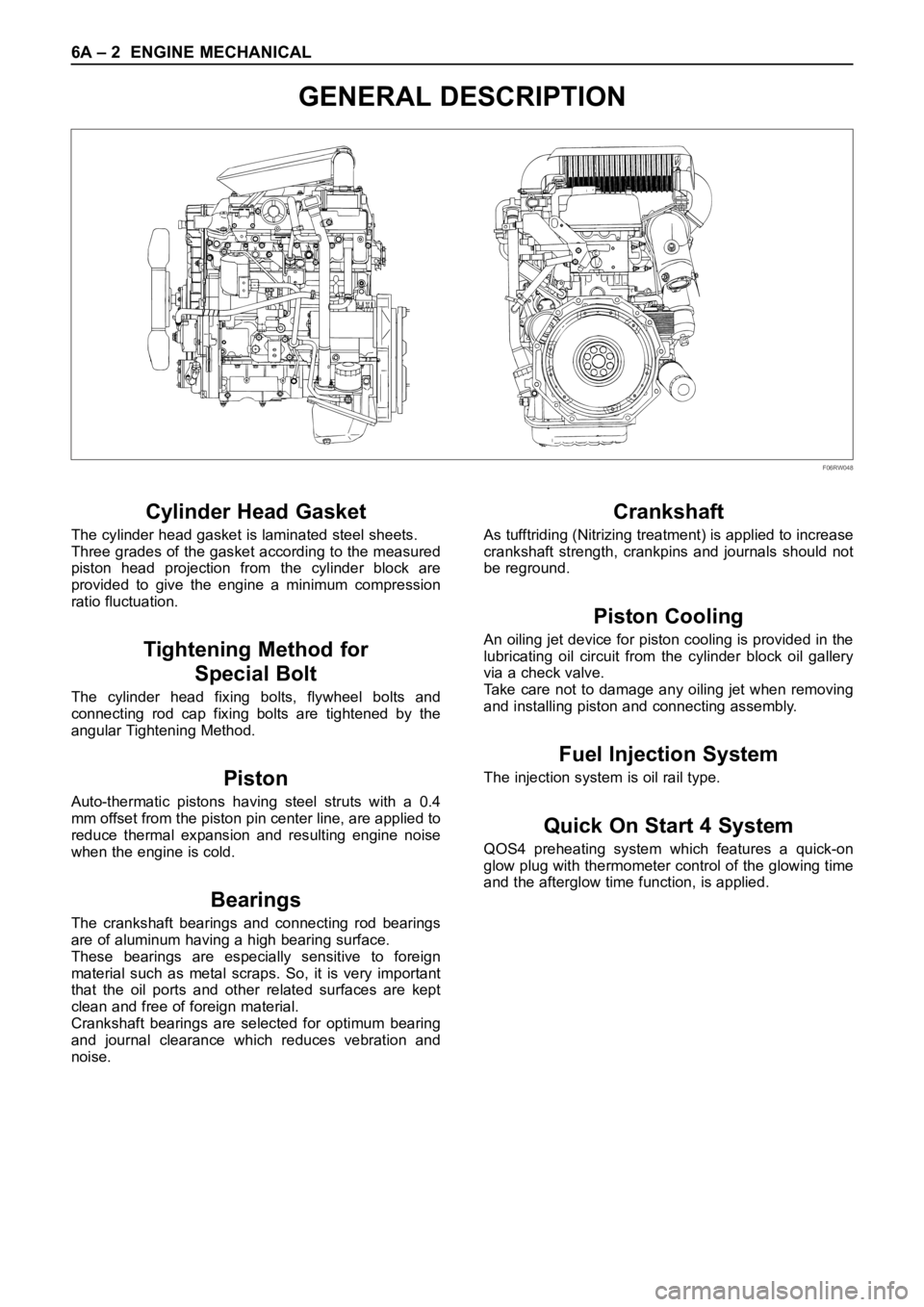
6A – 2 ENGINE MECHANICAL
GENERAL DESCRIPTION
Cylinder Head Gasket
The cylinder head gasket is laminated steel sheets.
Three grades of the gasket according to the measured
piston head projection from the cylinder block are
provided to give the engine a minimum compression
ratio fluctuation.
Tightening Method for
Special Bolt
The cylinder head fixing bolts, flywheel bolts and
connecting rod cap fixing bolts are tightened by the
angular Tightening Method.
Piston
Auto-thermatic pistons having steel struts with a 0.4
mm offset from the piston pin center line, are applied to
reduce thermal expansion and resulting engine noise
when the engine is cold.
Bearings
The crankshaft bearings and connecting rod bearings
are of aluminum having a high bearing surface.
These bearings are especially sensitive to foreign
material such as metal scraps. So, it is very important
that the oil ports and other related surfaces are kept
clean and free of foreign material.
Crankshaft bearings are selected for optimum bearing
and journal clearance which reduces vebration and
noise.
Crankshaft
As tufftriding (Nitrizing treatment) is applied to increase
crankshaft strength, crankpins and journals should not
be reground.
Piston Cooling
An oiling jet device for piston cooling is provided in the
lubricating oil circuit from the cylinder block oil gallery
via a check valve.
Take care not to damage any oiling jet when removing
and installing piston and connecting assembly.
Fuel Injection System
The injection system is oil rail type.
Quick On Start 4 System
QOS4 preheating system which features a quick-on
glow plug with thermometer control of the glowing time
and the afterglow time function, is applied.
F06RW048
Page 5311 of 6000
6A – 38 ENGINE MECHANICAL
1. Cylinder head bolts for damaged threads or
stretching and damaged heads caused by improper
use of tools.
CAUTION: Suspected bolts must be replaced.
2. Cylinder head for cracks, especially between valve
seats and in the exhaust ports.
3. Cylinder head deck for corrosion, sand particles in
head and porosity.
CAUTION: Do not attempt to weld the cylinder
head. Replace it.
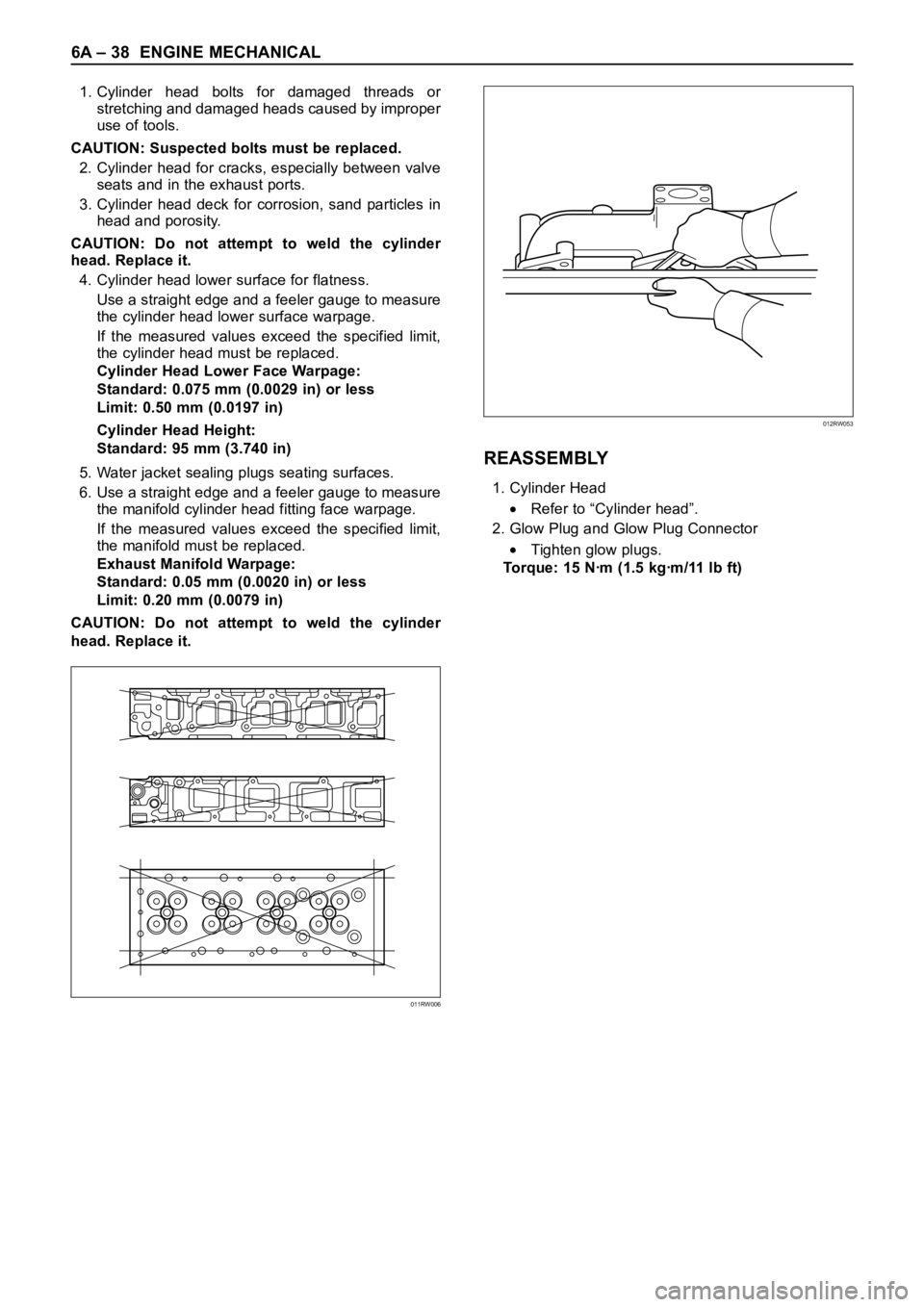
4. Cylinder head lower surface for flatness.
Use a straight edge and a feeler gauge to measure
the cylinder head lower surface warpage.
If the measured values exceed the specified limit,
the cylinder head must be replaced.
Cylinder Head Lower Face Warpage:
Standard: 0.075 mm (0.0029 in) or less
Limit: 0.50 mm (0.0197 in)
Cylinder Head Height:
Standard: 95 mm (3.740 in)
5. Water jacket sealing plugs seating surfaces.
6. Use a straight edge and a feeler gauge to measure
the manifold cylinder head fitting face warpage.
If the measured values exceed the specified limit,
the manifold must be replaced.
Exhaust Manifold Warpage:
Standard: 0.05 mm (0.0020 in) or less
Limit: 0.20 mm (0.0079 in)
CAUTION: Do not attempt to weld the cylinder
head. Replace it.
REASSEMBLY
1. Cylinder Head
Refer to “Cylinder head”.
2. Glow Plug and Glow Plug Connector
Tighten glow plugs.
Torque: 15 Nꞏm (1.5 kgꞏm/11 lb ft)
011RW006
012RW053
Page 5455 of 6000

6E–26
4JX1–TC ENGINE DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS
Output Components:
Output components are diagnosed for proper response to
control module commands. Components where
functional monitoring is not feasible will be monitored for
circuit continuity and out-of-range values if applicable.
Output components to be monitored include, but are not
limited to, the following circuit:
EGR VSV
EGR EVRV
Electronic Transmission controls
Injector
Intake throttle
Glow plug
MIL control
Refer to ECM and Sensors in General Descriptions.
Passive and Active Diagnostic Tests
A passive test is a diagnostic test which simply monitors a
vehicle system or component. Conversely, an active test,
actually takes some sort of action when performing
diagnostic functions, often in response to a failed passive
test.
Intrusive Diagnostic Tests
This is any on-board test run by the Diagnostic
Management System which may have an effect on
vehicle performance or emission levels.
Warm-Up Cycle
A warm-up cycle means that engine at temperature must
reach a minimum of 70
C (160F) and rise at least 22C
(40
F) over the course of a trip.
Freeze Frame
Freeze Frame is an element of the Diagnostic
Management System which stores various vehicle
information at the moment an emissions-related fault is
stored in memory and when the MIL is commanded on.
These data can help to identify the cause of a fault. Refer
to
Storing And Erasing Freeze Fame Data for more
detailed information.
Failure Records
Failure Records data is an enhancement of the OBD
Freeze Frame feature. Failure Records store the same
vehicle information as does Freeze Frame, but it will store
that information for any fault which is stored in on-board
memory, while Freeze Frame stores information only for
emission-related faults that command the MIL on.
Common OBD Terms
Diagnostic
When used as a noun, the word diagnostic refers to any
on-board test run by the vehicle’s Diagnostic
Management System. A diagnostic is simply a test run on
a system or component to determine if the system or
component is operating according to specification. There
are many diagnostics, shown in the following list:
EGR
engine speed
vehicle speed
ECT
MAP
VSV
IAT
ITP
AP
FT (Fuel Temp)
RP (Rail Pressure)
OT (Oil Temp)
EGR EVRV
Idle SW
Brake SW
The Diagnostic Executive
The Diagnostic Executive is a unique segment of
software which is designed to coordinate and prioritize
the diagnostic procedures as well as define the protocol
for recording and displaying their results. The main
responsibilities of the Diagnostic Executive are listed as
follows:
Commanding the MIL (“Check Engine” lamp) on and
off
DTC logging and clearing
Freeze Frame data for the first emission related DTC
recorded
Current status information on each diagnostic
Diagnostic Information
The diagnostic charts and functional checks are designed
to locate a faulty circuit or component through a process
of logical decisions. The charts are prepared with the
requirement that the vehicle functioned correctly at the
time of assembly and that there are not multiple faults
present.
There is a continuous self-diagnosis on certain control
functions. This diagnostic capability is complemented by
the diagnostic procedures contained in this manual. The
language of communicating the source of the malfunction
is a system of diagnostic trouble codes. When a
malfunction is detected by the control module, a
diagnostic trouble code is set and the Malfunction
Indicator Lamp (MIL) (“Check Engine” lamp) is
illuminated.
Malfunction Indicator Lamp (MIL)
The Malfunction Indicator Lamp (MIL) looks the same as
the MIL you are already familiar with “Check Engine”
lamp.
Basically, the MIL is turned on when the ECM detects a
DTC that will impact the vehicle emissions.
When the MIL remains “ON” while the engine is
running, or when a malfunction is suspected due to a
driveability or emissions problem, a Powertrain
On-Board Diagnostic (OBD) System Check must be
performed. The procedures for these checks are
given in On-Board Diagnostic (OBD) System Check.
These checks will expose faults which may not be
detected if other diagnostics are performed first.
DTC Types
Characteristic of Code
Page 5456 of 6000

6E–27 4JX1–TC ENGINE DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS
Non-Emissions related
Dose not request illumination of any lamp
Stores a History DTC on the first trip with a fail
Stores Fail Record when test fails
Updates the Fail Record each time the diagnostic test
fails
Storing and Erasing Freeze Frame Data and Failure
Records
The data captured is called Freeze Frame data. The
Freeze Frame data is very similar to a single record of
operating conditions. Whenever the MIL is illuminated,
the corresponding record of operating conditions is
recorded to the Freeze Frame buffer.
Data from these faults take precedence over data
associated with any other fault. The Freeze Frame data
will not be erased unless the associated history DTC is
cleared.
Each time a diagnostic test reports a failure, the current
engine operating conditions are recorded in the
Failure
Records
buffer. A subsequent failure will update the
recorded operating conditions. The following operating
conditions for the diagnostic test which failed
typically
include the following parameters:
Engine Speed
Engine Load
Engine Coolant Temperature
Vehicle Speed
Intake Throttle Position
MAP
Injector Base Pulse Width
Loop Status
Data Link Connector (DLC)
The provision for communication with the contorl module
is the Data Link Connector (DLC). It is located at behind
the lower front instrument panel. The DLC is used to
connect to a Tech 2. Some common uses of the Tech 2
are listed below:
Identifying stored Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs).
Clearing DTCs.
Performing out put control tests.
Reading serial data.
060RW046
Verifying Vehicle Repair
Verification of vehicle repair will be more comprehensive
for vehicles with OBD system diagnostic. Following a
repair, the technician should perform the following steps:
1. Review and record the Fail Records and/or Freeze
Frame data for the DTC which has been diagnosed.
2. Clear DTC(s).
3. Operate the vehicle within conditions noted in the Fail
Records and/or Freeze Frame data.
4. Monitor the DTC status information for the specific
DTC which has been diagnosed until the diagnostic
test associated with that DTC runs.
Following these steps are very important in verifying
repairs on OBD systems. Failure to follow these steps
could result in unnecessary repairs.
Reading Flash Diagnostic Trouble Codes
The provision for communicating with the Engine Control
Module (ECM) is the Data Link Connector (DLC). The
DLC is located in the front console box. It is used in the
assembly plant to receive information in checking that the
engine is operating properly before it leaves the plant.
The diagnostic trouble code(s) (DTCs) stored in the
ECM’s memory can be read either through a hand-held
diagnostic scanner plugged into the DLC or by counting
the number of flashes of the “Check Engine” Malfunction
Indicator Lamp (MIL) when the diagnostic test terminal of
the DLC is grounded. The DLC terminal “6” (diagnostic
request) is pulled “Low” (grounded) by jumpering to DLC
terminal “4”, which is a ground wire.
This will signal the ECM that you want to “flash” DTC(s), if
any are present. Once terminals “4” and “6” have been
connected, the ignition switch must be moved to the “ON”
position, with the engine not running.
The “Check Engine”MIL will indicate a DTC three times if
a DTC is present. If more than one DTC has been stored
Page 5485 of 6000
6E–56
4JX1–TC ENGINE DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS
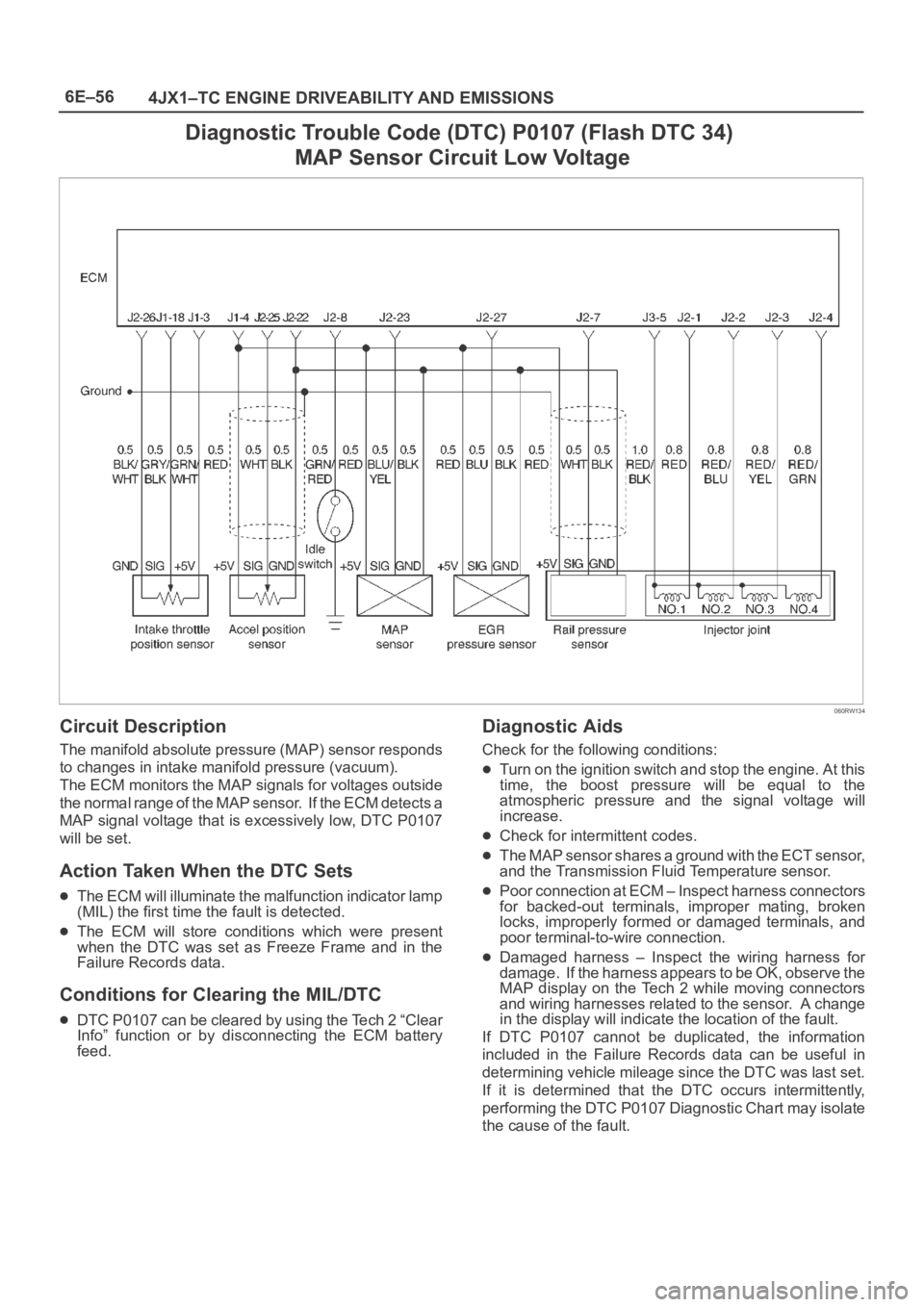
Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) P0107 (Flash DTC 34)
MAP Sensor Circuit Low Voltage
060RW134
Circuit Description
The manifold absolute pressure (MAP) sensor responds
to changes in intake manifold pressure (vacuum).
The ECM monitors the MAP signals for voltages outside
the normal range of the MAP sensor. If the ECM detects a
MAP signal voltage that is excessively low, DTC P0107
will be set.
Action Taken When the DTC Sets
The ECM will illuminate the malfunction indicator lamp
(MIL) the first time the fault is detected.
The ECM will store conditions which were present
when the DTC was set as Freeze Frame and in the
Failure Records data.
Conditions for Clearing the MIL/DTC
DTC P0107 can be cleared by using the Tech 2 “Clear
Info” function or by disconnecting the ECM battery
feed.
Diagnostic Aids
Check for the following conditions:
Turn on the ignition switch and stop the engine. At this
time, the boost pressure will be equal to the
atmospheric pressure and the signal voltage will
increase.
Check for intermittent codes.
The MAP sensor shares a ground with the ECT sensor,
and the Transmission Fluid Temperature sensor.
Poor connection at ECM – Inspect harness connectors
for backed-out terminals, improper mating, broken
locks, improperly formed or damaged terminals, and
poor terminal-to-wire connection.
Damaged harness – Inspect the wiring harness for
damage. If the harness appears to be OK, observe the
MAP display on the Tech 2 while moving connectors
and wiring harnesses related to the sensor. A change
in the display will indicate the location of the fault.
If DTC P0107 cannot be duplicated, the information
included in the Failure Records data can be useful in
determining vehicle mileage since the DTC was last set.
If it is determined that the DTC occurs intermittently,
performing the DTC P0107 Diagnostic Chart may isolate
the cause of the fault.