1998 JAGUAR X308 module
[x] Cancel search: modulePage 1262 of 2490

Contains th
e hydraulic system pump.
Contains
th
e fluid temperature sensor.
The epicyclic geartrain:
Provi des fi
ve forward gears and Reverse.
Has
h
ydraulically actuated, multi-disk clutches, to select the required gear ratios.
Feature
s clutch-to-clutch operation to permit
gear shifts for uninterrupted power flow.
The electro-hydraulic control unit:
Is lo c
ated in the lower part of
the unit, within the fluid pan.
Is controlled
by the TCM (transmissio
n control module), and the manual selector valve which is cable operated.
Re
gulates the flow of fluid to the ge
artrain clutches via three solenoid-operated valv es and the manual selector
valve.
Has fi ve pressure
regulators for controll
ing fluid pressures within the system.
Is con
nected to the TCM via a 16-way connector mounted on
the left-hand side of the transmission casing. Refer to
Connector Pins Identification, Section 307-01A.
The hydraulic system pump:
Is l o
cated at the front of the transmission casing.
Is dri
v
en from the impeller hub,
pressurising the fluid whenever the engine is running.
Supplie
s fluid under pressure to the torq
ue converter, geartrain, electro-hydr aulic control unit and the lubrication
circuit.
D r
aws fluid from the fluid pa
n below the transmission casing, through a filter.
The rear extension housing:
Is bolt
ed to the rear of the transmission casing.
Provides the rear engine / transmi
ssion mo
unting point; refer to section 303-01.
Carrie
s the transmission output shaft oil seal.
Filled-for-l
i
fe Fluid System
The
transm
ission is 'filled for life' and
does not require fluid changes, except where extreme driving conditions prevail.
Routine level checking is not required and a dipstick is not pr ovided. A level / filler plug is fitted for level checking and
replenishment, following service actions; see 303-01 General Procedures.
Transmission Torque Converter
Page 1263 of 2490
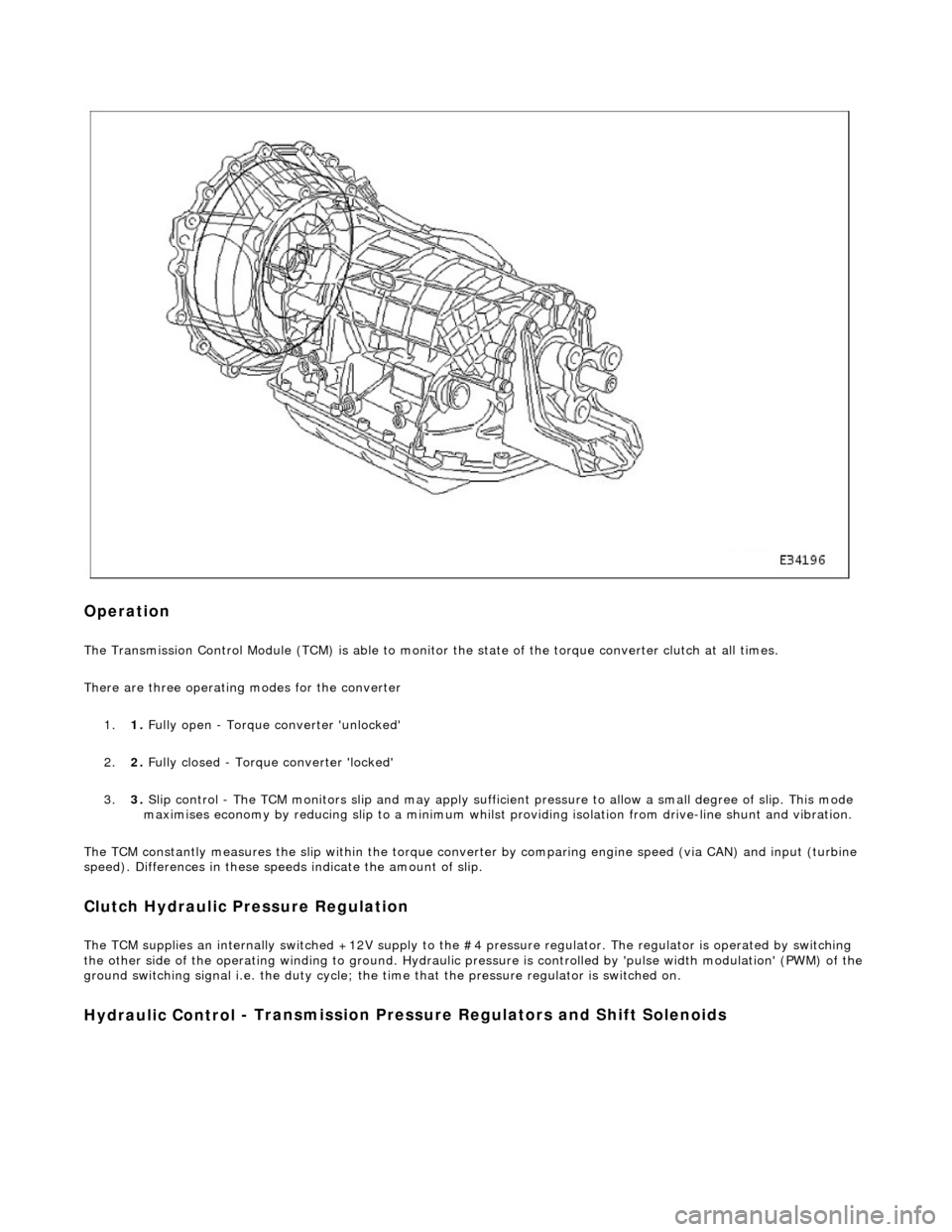
Op
eration
The T
ransmission Control Module (TCM) is
able to monitor the state of the torque converter clut ch at all times.
There are three operating modes for the converter
1. 1. Fully open - Torque converter 'unlocked'
2. 2. Fully closed - Torque converter 'locked'
3. 3. Slip control - The TCM monitors slip and may apply sufficie nt pressure to allow a small degree of slip. This mode
maximises economy by reducing slip to a minimum whilst providing isolation from drive-line shunt and vibration.
The TCM constantly measures the slip within the torque conver ter by comparing engine speed (via CAN) and input (turbine
speed). Differences in these speeds indicate the amount of slip.
Clutch Hydraulic Pressure Regulation
The T
CM supplies an internally switched +1
2V supply to the #4 pressure regulator. The regulator is operated by switching
the other side of the operating winding to ground. Hydraulic pressure is controlled by 'pulse width modulation' (PWM) of the
ground switching signal i.e. the duty cycle; the time that the pressure regulator is switched on.
Hydraulic Control
- Transmission Pre
ssure Regulators an d Shift Solenoids
Page 1268 of 2490
Input speed is monitored by the TCM with a rationality check being made against output speed. A fault will be flagged if the
indicated input speed exceeds 7400 rpm. Additionally, a failure judgement will be made if the indicated input speed is <160
rpm with engine speed >608 rpm and output speed >224 rpm
The procedure is similar for the output sp eed diagnostic. A fault (non OBDII) will be flagged if the indicated input speed
exceeds 6712 rpm. Additionally a failure judgement will be ma de if the indicated output speed is <160 rpm and the average
road wheel speed exceeds 100 rpm.
Under normal circumstance s after the output speed diagnost ic fault code has been set, the TCM uses rear wheel speed
information to compute its calculations, this has no effect on transmission operation. However, should a second fault occur,
in the ABS system, thus making rear wheel speed information unavailable, an additional fault code will be logged.
Control Systems
Introduction
Gear selection is achieved by controlling the flow of transmission fluid to internal multi-disc clutches.
The three solenoid valves direct the transmission fluid flow to the selected clutches and the pressure regulators control the
fluid pressure to each component. One pr essure regulator serves as a master pressure control for the entire system and a
second is used exclusively for torque converter clutch lock-up operation.
The TCM controls the internal components thus determining gear selection and shift pattern.
In the event of an electronic system fault the basic function s Park, Reverse Neutral and Drive Fourth are retained by the
hydraulic system.
Transmission Control Module (TCM)
The TCM is located in the same housing as th e ECM and is accessed in the same manner.
The TCM performs several 'self check' procedur es to ensure correct operation. It is possible due to the nature of these faults
that the module will fail to communicate with other nodes. However, condemnation of the TCM should not take place until
any CAN or power supply related problems have been resolved.
There are three self check procedures for the TCM. 1. 1. Check on ROM by calculatin
g a checksum and comparing this with a known stored value.
Page 1269 of 2490

2.2. Check on non-volatile diagnostic memory by wr iting a test pattern and then reading it back.
3. 3. Internal 'watchdog' hardware to check whether the TCM has crashed.
Transmission Control Module Supply Voltage
The TCM monitors battery and igni tion switched supply voltages.
A permanent supply is used to maintain a battery backed 'memor y'. Should this supply be cut, due to battery disconnection
perhaps, the 'adaptive shift' valu es will be lost. This will result in a small reduction in shift quality for a period until th e
adaptions are 're-learned'
The TCM will adopt 'limp home' mode as a result of the supply voltage being >16V or <7V with an engine speed >1600
rpm.
Should the ignition supply be >7V but <9V the TCM will hold the gear that it has currently selected. If after 2.5 seconds,
with the engine speed >1600 rpm, the voltage remains at this level, 'limp home' mode will be adopted. The 2.5 second
delay is built in to prevent reaction to a momentary voltage fluctuation.
Operation
CAUTION: Disconnection of the TCM and / or the vehicle batt ery will cause system adaptions to be lost; this may be
apparent by shift quality degradation. Fo llowing reconnection, a period of 'varied' driving will reinstate adaptions and thus
normal operation. Please ensure that the customer is made aware that the adaption period is variable and may occur after
handover, as the transmission re-learns the prevailing driving style.
• NOTE: Should the TCM fail, please ensure that the control housing cooling fan is operating correctly. Failure of the cooling
fan MUST be rectified before renewing the TCM and details of a fan fa ilure should accompany the returned TCM.
The TCM processes information received in both analogue and digital form, such as:
Transmission input speed Transmission output speed Throttle position Pedal demand Gear selector position Engine torque Engine speed Transmission oil temperature Mode switch
This information is then used by the TC M to control shift energy management and decide which shift program to implement
and which gear to select.
The TCM uses the various sensors and inpu ts to monitor the correct operation of the system an d is programmed to take
default action and inform the operator when a fault occurs.
Safety Functions
The safety functions are designed to safeguard against inappr opriate actions by the operator as well as against system
malfunctions. The system prevents reve rse gear from being engaged at high forward speeds and prevents manual
downshifting at excessive engine speeds; these functions are not operational in mechanical limp-home mode.
The TCM constantly monitors the transmissi on for faults. In the event of a problem the TCM will adopt a 'limp home' mode
in which only P R N D - (selector in D but only fourth gear is enabled) are available. The operator will be made aware of
certain faults by an in strument panel warning.
The electrical and diagnostic system has been designed such that system integrity is protected at all times, the safety
concept being based on th e following three points:
Page 1271 of 2490

Controller Area Network (CAN)
The TCM is an integral part of the CAN system which facilitates the interchange of real-time data between control modules
and sensors. Please see section 303- 14 for a full description of CAN.
OBDII Interface
Data concerning OBDII related transmission failures is stored in the ECM for access via the J1962 socket.
System Functions
Range Selection
The selector lever is connected to the transmission via a bowden cable, which operates the transmission selector shaft
between all positions except Drive to 4 .
The TCM detects the gear selected by means of a rotary position switch fitted to the transmission selector shaft. A separate
Drive to 4 switch is located within the 'J' gate' assembly.
Movement of the selector lever between Park, Reverse, Neutral and Drive manually directs th e flow of transmission oil; the
TCM having control of the forward gears selected while the lever is in the Drive position.
Shift Point Selection
The gearshift points are selected, by the TCM, as a function of the output speed, engine load, selector position and shift
program selected. The operator has control over the shift points via the selector lever, throttle pedal movement, kickdown
function and mode switch.
'J' Gate Layout
Mode Switch
This switch allows the driver to select one of two base shift maps; Normal and Sport modes, the switch being illuminated
when Sport is selected.
Special Shift Programs
These specific condition shift maps are available to enhance the operation of the vehicle under specific driving conditions.
and are listed below in order of priority / title and operating condition.
1. 1. Traction: When traction intervention is active
2. 2. Hot mode: Extreme engine / transmission temperatures
Page 1357 of 2490
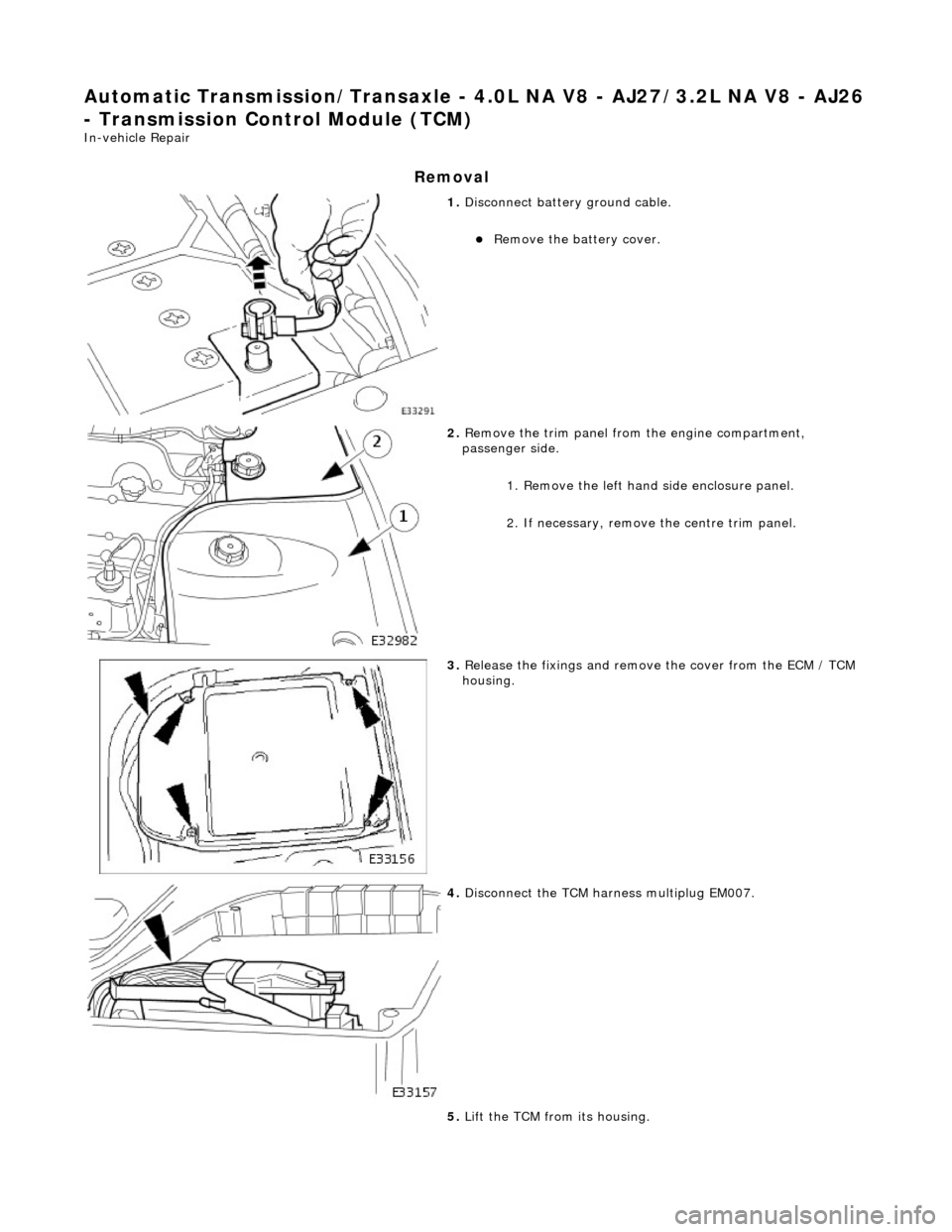
Automatic Transmission/Transaxle - 4.0L NA V8 - AJ27/3.2L NA V8 - AJ26
- Transmission Control Module (TCM)
In-vehicle Repair
Removal
1. Disconnect battery ground cable.
Remove the battery cover.
2. Remove the trim panel from the engine compartment,
passenger side.
1. Remove the left hand side enclosure panel.
2. If necessary, remove the centre trim panel.
3. Release the fixings and remove the cover from the ECM / TCM
housing.
4. Disconnect the TCM harness multiplug EM007.
5. Lift the TCM from its housing.
Page 1391 of 2490
In the event of a system fault, the TCM will adopt 'limp home' mode.
Electrical control
Refer to Section 307-01B.
Transmission Control Components
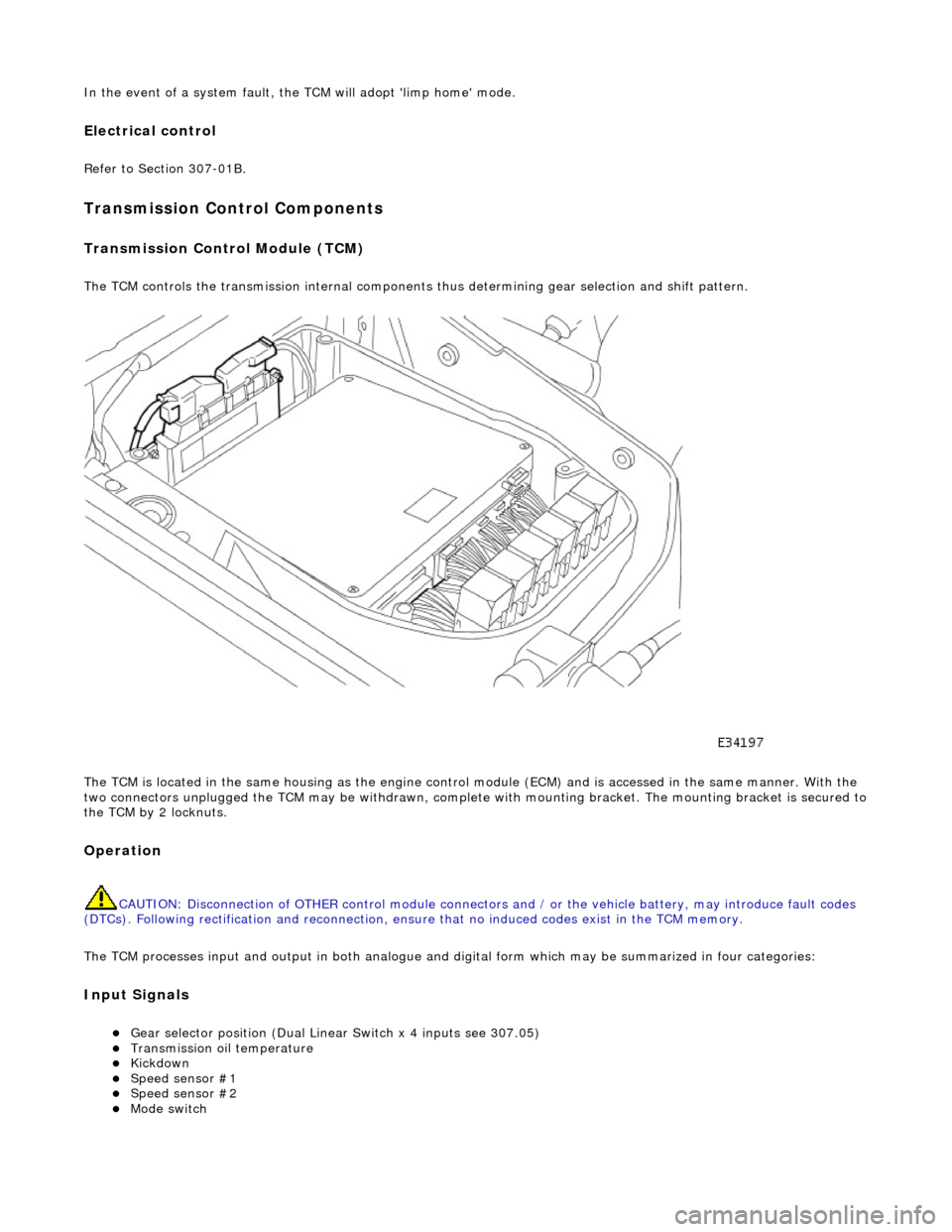
Transmission Control Module (TCM)
The TCM controls the transmission internal components thus determining gear selection and shift pattern.
The TCM is located in the same housing as the engine control module (ECM) and is accessed in the same manner. With the
two connectors unplugged the TCM may be withdrawn, complete with mounting bracket. The mounting bracket is secured to
the TCM by 2 locknuts.
Operation
CAUTION: Disconnection of OTHER contro l module connectors and / or the vehicle battery, may introduce fault codes
(DTCs). Following rectification and reconnection, ensu re that no induced codes exist in the TCM memory.
The TCM processes input and output in both analogue and di gital form which may be summarized in four categories:
Input Signals
Gear selector position (Dual Linear Switch x 4 inputs see 307.05) Transmission oil temperature Kickdown Speed sensor #1 Speed sensor #2 Mode switch
Page 1395 of 2490
and/or increased performance as appropriate.
Serial Communications Interfaces
Controller Area Network (CAN)
The TCM is an integral part of the CAN system which facilita tes the interchange of real-time data between control modules
and sensors; refer to 303-14 fo r a full description of CAN.
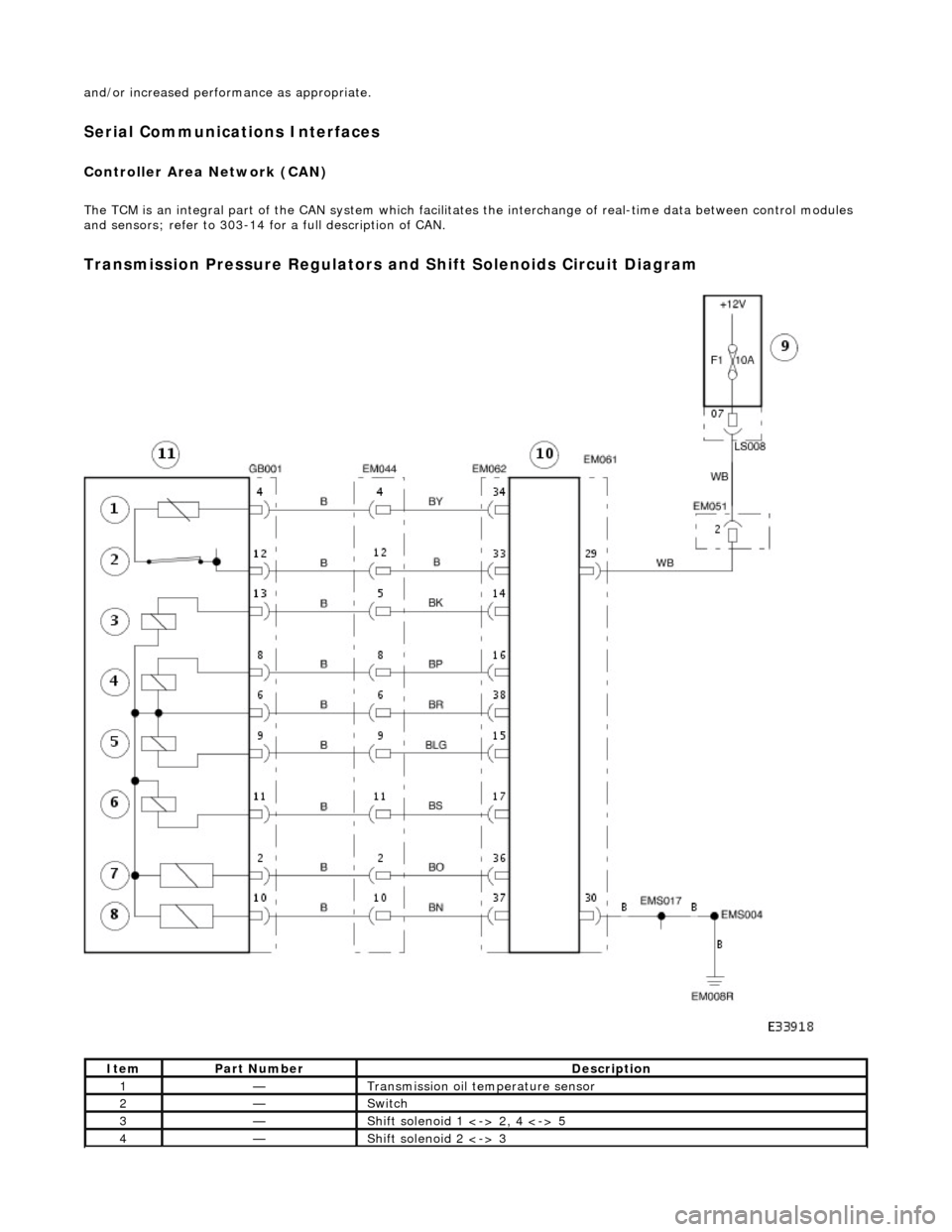
Transmission Pressure Regulators and Shift Solenoids Circuit Diagram
ItemPart NumberDescription
1—Transmission oil temperature sensor
2—Switch
3—Shift solenoid 1 <-> 2, 4 <-> 5
4—Shift solenoid 2 <-> 3