1997 SSANGYONG KORANDO ignition switch
[x] Cancel search: ignition switchPage 926 of 2053

SSAMGYONG MY2002
4A-6 HYDRAULIC BRAKES
Action
1. Turn the ignition ON.
2. Apply the parking brake.
Does the BRAKE warning lamp turn on?
Check fuse F30.
Is fuse F30 blown?
Check for a short circuit and repair it, if necessary.
Replace fuse F30.
1. Turn the ignition ON.
2. Check the voltage at F30.
Is the voltage equal to the specified value?
Repair the power supply to fuse F30.
Is the repair complete?
1. Disconnect terminal A1 of the instrument cluster.
2. Turn the ignition ON.
3. Use a voltmeter to check the voltage at terminal A1.
Is the voltage equal to the specified value?
Repair the open circuit between terminal A1 of the
instrument cluster and fuse F30.
Is the repair complete?
1. Reconnect terminal A1 of the instrument cluster.
Turn the ignition ON.
2. Use a voltmeter to backprobe terminal D10 of the
instrument cluster.
Is the voltage equal to the specified value?
1. Remove the BRAKE warning lamp from its socket.
2. Test the Brake warning lamp.
Is the BRAKEwarning lamp OK?
Replace the instrument cluster.
Is the repair complete?
Replace the BRAKE warning lamp.
Is the repair complete?
1. Disconnect terminal C10 of the STICS.
2. Connect a jumper wire between terminal C10 and
ground.
3. Turn the ignition ON.
Is the BRAKE warning lamp on?
Replace the STICS.
Is the repair complete?
1. Disconnect the STICS connector.
2. Connect a jump wire between terminal C19 and
ground.
3. Turn the ignition ON.
Is the BRAKE warning lamp on?
Replace the brake warning lamp switch.
Is the repair complete?
Repair the open circuit between the brake warning
lamp switch and terminal C19 of the STICS
BRAKE LAMP WARNING CIRCUIT (Cont’d)
Yes
Go To Step 31
Go To Step 17
System OK
Go To Step 20
System OK
Go To Step 22
System OK
Go To Step 26
Go To Step 24
System OK
System OK
Go To Step 27
System OK
Go To Step 29
System OK
System OKNO
Go To Step 16
Go To Step 18
-
Go To Step 19
-
Go To Step 21
-
Go To Step 23
Go To Step 25
-
-
Go To Step 28
-
Go To Step 30
-
-Step
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30Value
-
-
-
11 - 14 v
-
11 - 14 v
-
11 - 14 v
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
Page 989 of 2053

ABS AND TCS 4F-5
SSANGYONG MY2002
EBD (ELECTRONIC BRAKE
FORCE DISTRIBUTION) SYSTEM
System Description
As an add-on logic to the ABS base algorithm, EBD
works in a range in which the intervention thresholds
for ABS control are not reached yet.
EBD ensures that the rear wheels are sensitively
monitored for slip with respect to the front axle. If slip
is detected, the inlet valves for the rear wheels are
switched to pressure hold to prevent a further increase
in pressure at the rear-wheel breaks, thus electronically
reproducing a pressure-reduction function at the rear-
wheel brakes.
ABS features an enhanced algorithm which includes
control of the brake force distribution between the front
and rear axles. This is called Electronic Brake
Distribution. In an unloading car condition the brake
efficiency is comparable to the conventional system
but for a fully loaden vehicle the efficiency of the EBD
system is higher due to the better use of rear axle
braking capability.
The Benefits of EBD
Elimination of conventional proportioning valve EBD
utilizes the existing rear axle wheel speed sensor
to monitor rear wheel slip.
Based on many variables in algorithm a pressure
hold, increase and/or decrease pulsetrain may be
triggered at the rear wheels insuring vehicle
stability.
Vehicle approaches the ideal brake force
distribution (front to rear).
Constant brake force distribution during vehicle
lifetime.
EBD function is monitored via ABS safety logic
(conventional proportioning valves are not
monitorable).
“Keep alive” function.Service Precautions
Observe the following general precautions during any
ABS/TCS service. Failure to adhere to these
precautions may result in ABS/TCS system damage.
1. Disconnect the EBCM harness connector before
performing the electric welding procedures.
2. Carefully note the routing of the ABS/TCS wiring
and wring components during removal. The ABS/
TCS components are extremely sensitive to EMI
(eletromagnetic interference). Proper mounting is
critical during component service.
3. Disconnect the EBCM connector with the ignition
OFF.
4. Do not hang the suspension components from the
wheel speed sensor cables. The cables may be
damaged.
5. Do not use petroleum based fluids in the master
cylinder. Do not use any containers previously used
for petroleum based fluids. Petroleum causes
swelling and distortion of the rubber components
in the hydraulic brake system, resulting in water
entering the system and lowering the fluid boiling
point.
KAA4F020
Page 999 of 2053

SSANGYONG MY2002
4F-16 ABS AND TCS
1. Install the scan tool.
2. Turn ignition switch to ON.
3. Select the Data List mode.
Is the scan tool receiving data from the electronic
brake control module (EBCM)?
Check the display.
Are there any current DTCs displayed?
1. Turn the ignition to LOCK for 10 seconds.
2. Turn the ignition to ON and observe the ABS
indicator.
Does the indicator light for 2 seconds and then go off?
Check the ABS indicator.
Did the ABS indicator turn on and stay on?
Check whether the vehicle is equipped with traction
control.
Is the vehicle equipped with traction control?
1. Turn the ignition to LOCK for 10 seconds.
2. Turn the ignition to ON and observe the TCS
indicator.
Does the indicator light for 2 seconds and then go off?
1. Turn the ignition to LOCK.
2. Disconnect the EBCM harness connector.
3. Turn the ignition to ON.
4. Use a digital voltmeter (DVM) to measure the
voltage from ground to terminal 1 and 50 of the
EBCM harness connector.
Is the voltage equal to the specified value?
1. Turn the ignition to LOCK.
2. Use a DVM to measure the resistance from the EBCM
harness connector, terminals 28 and 29 to ground.
Is the resistance equal to the specified value?
Repair the open in the circuit that failed.
Is the repair complete?
Use a DVM to measure the resistance between
terminal 46 of the EBCM harness connector and
terminal 8 of the data link connector (DLC).
Is the resistance below the specified value?
Replace the ABS unit.
Is the repair complete?
Repair the open or high resistance in circuit BrG
between terminal 11 of the EBCM harness connector
and terminal 13 of the DLC.
Is the repair complete?
Perform the road test described above.
Are any DTCs set? Step
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
Diagnostic Circuit Check
Action Yes
Go to Step 2
Refer to the
applicable DTC
table
Go to Step 5
Go to “ABS
Indicator Lamp
Illuminated
Constantly”
Go to Step 6
Go to Step 13
Go to Step 8
Go to Step 10
System OK
Go to Step 11
System OK
Go to Step 1
Go to the table
for the DTCNo
Go to Step 7
Go to Step 3
Go to Step 4
Go to
“ABS Indicator
Lamp Inopera-
tive
Go to Step 13
Go to “Traction
Control System
Indicator Lamp
Inoperative”
Go to “Power
Supply to
Control Mod-
ule, No DTCs
Stored
Go to Step 9
-
Go to Step 12
-
-
System OK Value(s)
-
-
-
-
-
-
11 - 14 v
≈ 0 Ω
-
2 Ω
-
-
-
Page 1001 of 2053
SSANGYONG MY2002
4F-18 ABS AND TCS
ABS INDICATOR LAMP INOPERATIVE
KAA4F120
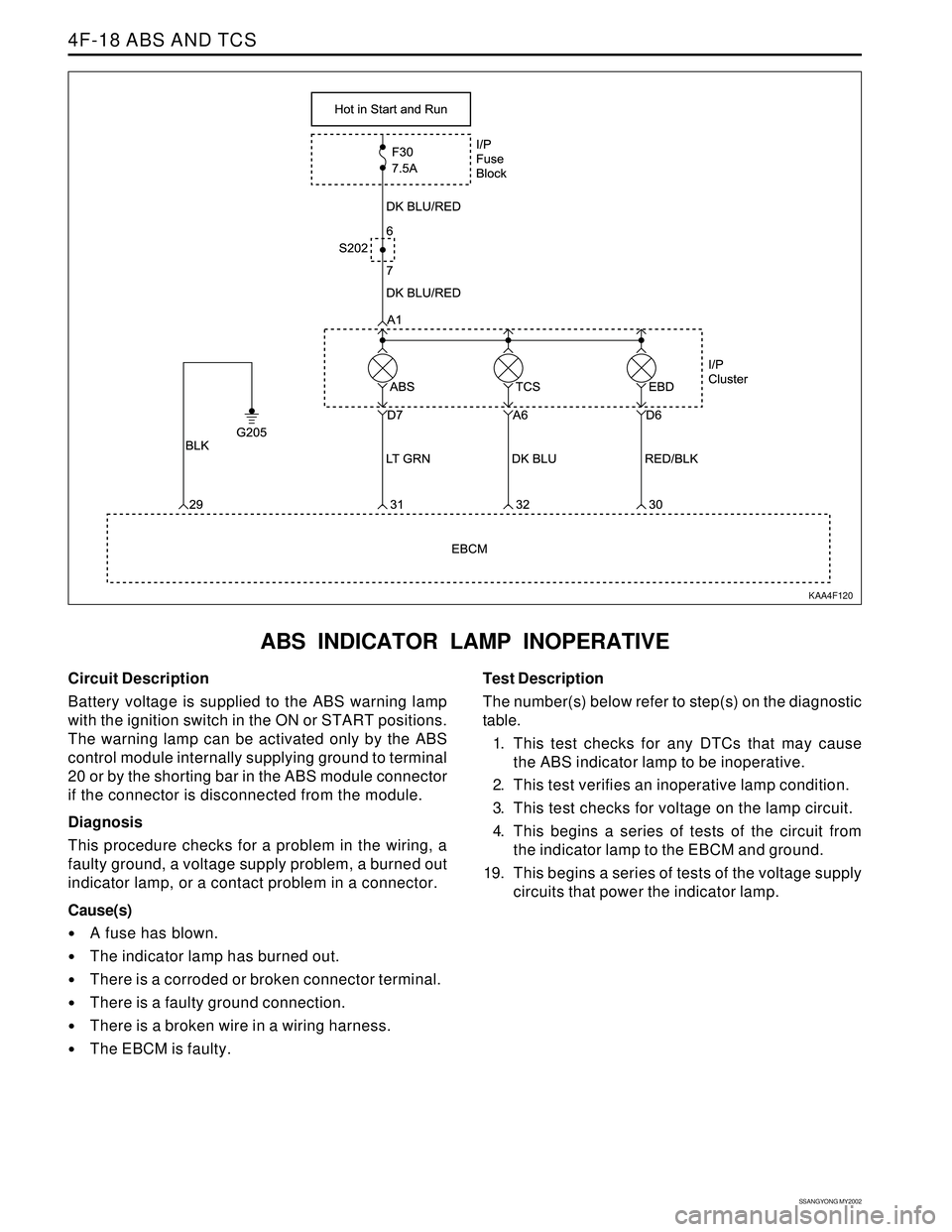
Circuit Description
Battery voltage is supplied to the ABS warning lamp
with the ignition switch in the ON or START positions.
The warning lamp can be activated only by the ABS
control module internally supplying ground to terminal
20 or by the shorting bar in the ABS module connector
if the connector is disconnected from the module.
Diagnosis
This procedure checks for a problem in the wiring, a
faulty ground, a voltage supply problem, a burned out
indicator lamp, or a contact problem in a connector.
Cause(s)
A fuse has blown.
The indicator lamp has burned out.
There is a corroded or broken connector terminal.
There is a faulty ground connection.
There is a broken wire in a wiring harness.
The EBCM is faulty.Test Description
The number(s) below refer to step(s) on the diagnostic
table.
1. This test checks for any DTCs that may cause
the ABS indicator lamp to be inoperative.
2. This test verifies an inoperative lamp condition.
3. This test checks for voltage on the lamp circuit.
4. This begins a series of tests of the circuit from
the indicator lamp to the EBCM and ground.
19. This begins a series of tests of the voltage supply
circuits that power the indicator lamp.
Page 1002 of 2053
ABS AND TCS 4F-19
SSANGYONG MY2002
Step
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
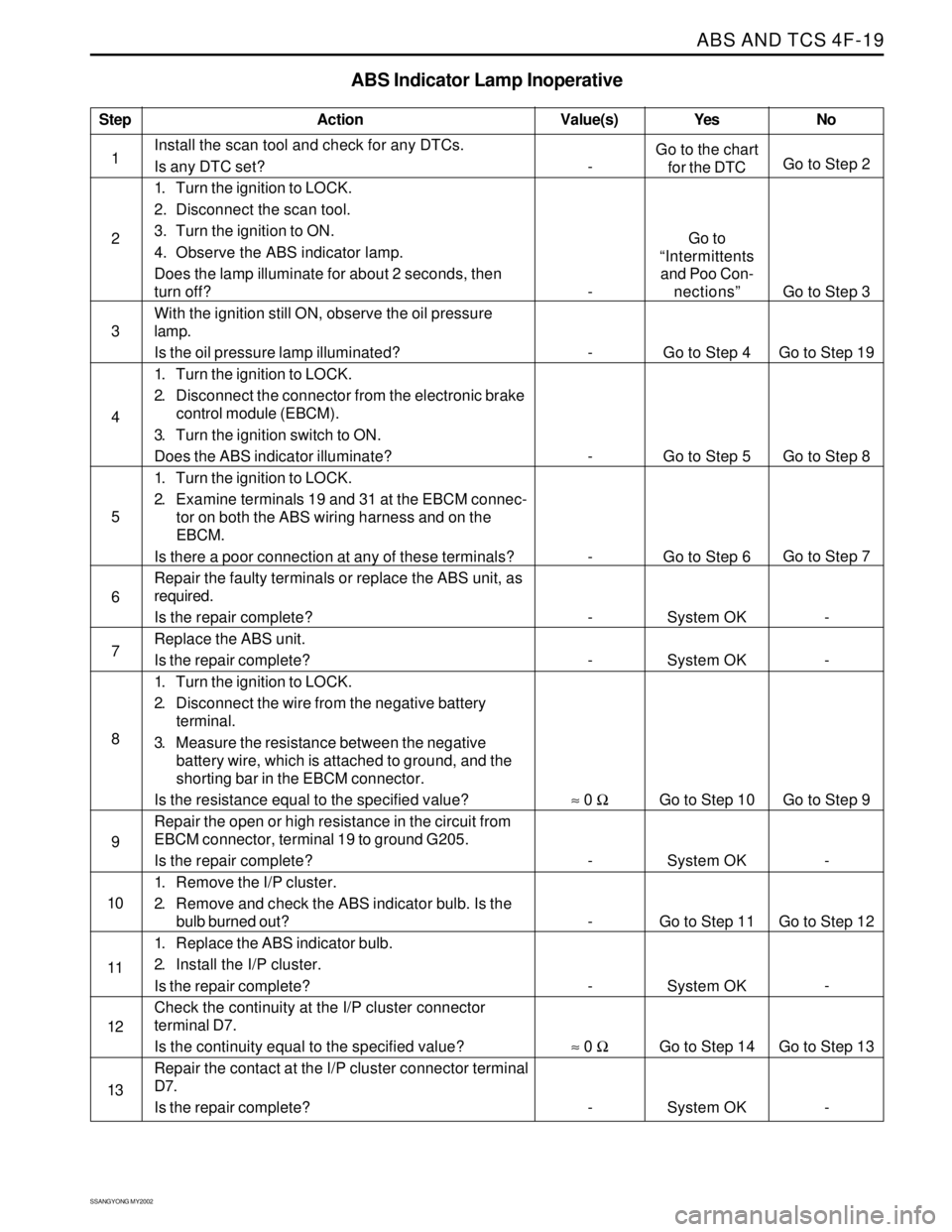
ABS Indicator Lamp Inoperative
Action Yes
Go to the chart
for the DTC
Go to
“Intermittents
and Poo Con-
nections”
Go to Step 4
Go to Step 5
Go to Step 6
System OK
System OK
Go to Step 10
System OK
Go to Step 11
System OK
Go to Step 14
System OKNo
Go to Step 2
Go to Step 3
Go to Step 19
Go to Step 8
Go to Step 7
-
-
Go to Step 9
-
Go to Step 12
-
Go to Step 13
- Value(s)
Install the scan tool and check for any DTCs.
Is any DTC set?
1. Turn the ignition to LOCK.
2. Disconnect the scan tool.
3. Turn the ignition to ON.
4. Observe the ABS indicator lamp.
Does the lamp illuminate for about 2 seconds, then
turn off?
With the ignition still ON, observe the oil pressure
lamp.
Is the oil pressure lamp illuminated?
1. Turn the ignition to LOCK.
2. Disconnect the connector from the electronic brake
control module (EBCM).
3. Turn the ignition switch to ON.
Does the ABS indicator illuminate?
1. Turn the ignition to LOCK.
2. Examine terminals 19 and 31 at the EBCM connec-
tor on both the ABS wiring harness and on the
EBCM.
Is there a poor connection at any of these terminals?
Repair the faulty terminals or replace the ABS unit, as
required.
Is the repair complete?
Replace the ABS unit.
Is the repair complete?
1. Turn the ignition to LOCK.
2. Disconnect the wire from the negative battery
terminal.
3. Measure the resistance between the negative
battery wire, which is attached to ground, and the
shorting bar in the EBCM connector.
Is the resistance equal to the specified value?
Repair the open or high resistance in the circuit from
EBCM connector, terminal 19 to ground G205.
Is the repair complete?
1. Remove the I/P cluster.
2. Remove and check the ABS indicator bulb. Is the
bulb burned out?
1. Replace the ABS indicator bulb.
2. Install the I/P cluster.
Is the repair complete?
Check the continuity at the I/P cluster connector
terminal D7.
Is the continuity equal to the specified value?
Repair the contact at the I/P cluster connector terminal
D7.
Is the repair complete?
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
≈ 0 Ω
-
-
-
≈ 0 Ω
-
Page 1013 of 2053
SSANGYONG MY2002
4F-30 ABS AND TCS
POWER SUPPLY TO CONTROL MODULE, NO DTCS STORED
KAA4F110
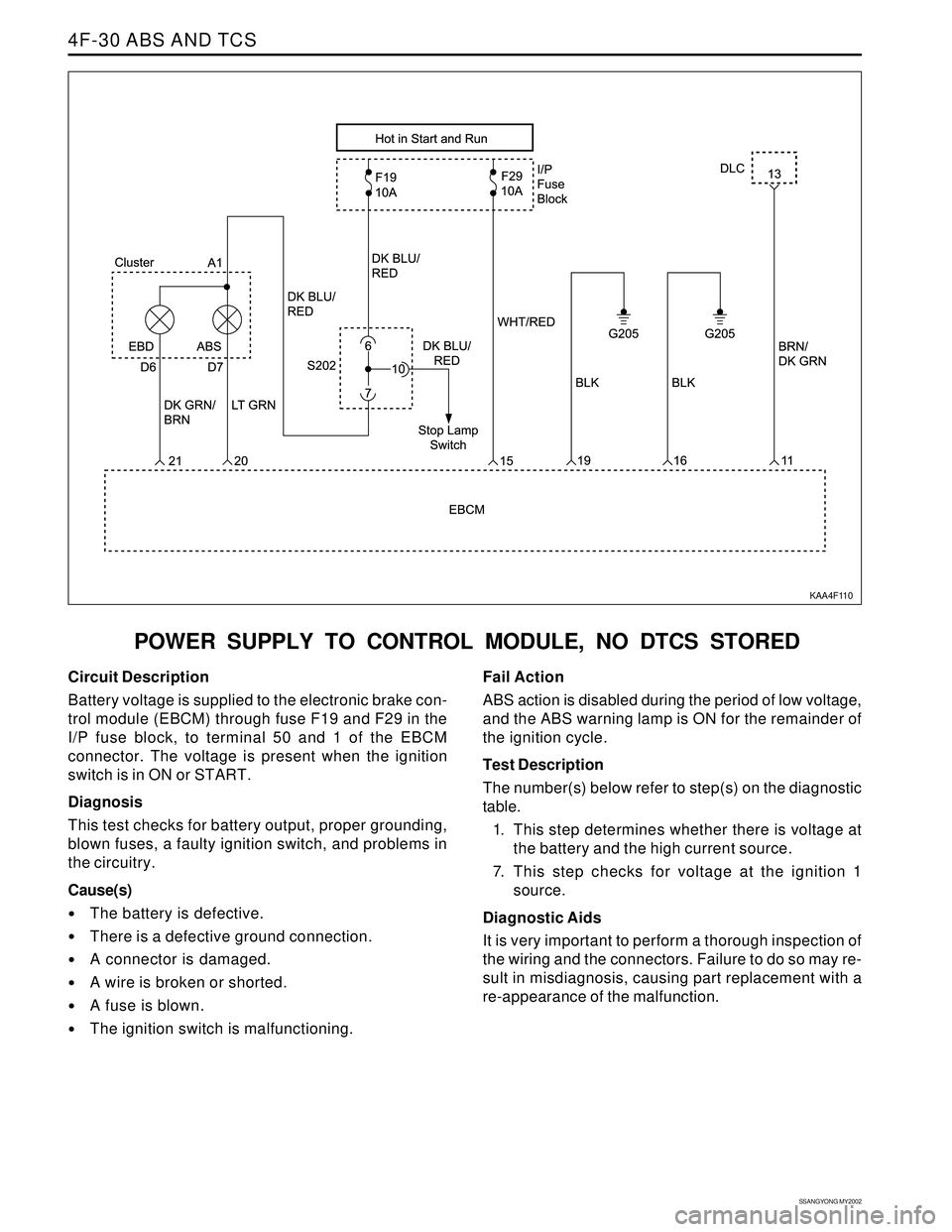
Circuit Description
Battery voltage is supplied to the electronic brake con-
trol module (EBCM) through fuse F19 and F29 in the
I/P fuse block, to terminal 50 and 1 of the EBCM
connector. The voltage is present when the ignition
switch is in ON or START.
Diagnosis
This test checks for battery output, proper grounding,
blown fuses, a faulty ignition switch, and problems in
the circuitry.
Cause(s)
The battery is defective.
There is a defective ground connection.
A connector is damaged.
A wire is broken or shorted.
A fuse is blown.
The ignition switch is malfunctioning.Fail Action
ABS action is disabled during the period of low voltage,
and the ABS warning lamp is ON for the remainder of
the ignition cycle.
Test Description
The number(s) below refer to step(s) on the diagnostic
table.
1. This step determines whether there is voltage at
the battery and the high current source.
7. This step checks for voltage at the ignition 1
source.
Diagnostic Aids
It is very important to perform a thorough inspection of
the wiring and the connectors. Failure to do so may re-
sult in misdiagnosis, causing part replacement with a
re-appearance of the malfunction.
Page 1015 of 2053
SSANGYONG MY2002
4F-32 ABS AND TCS
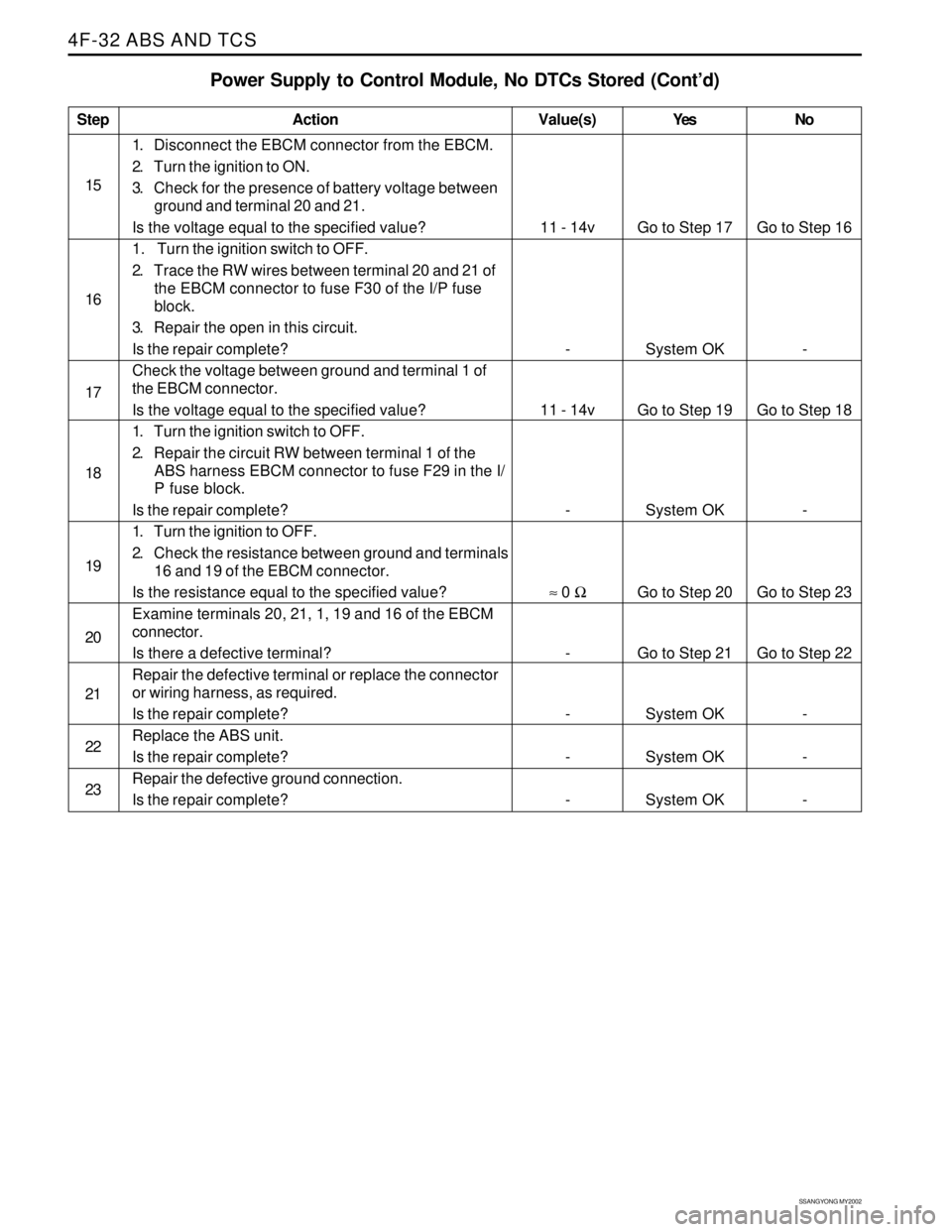
Step
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
Power Supply to Control Module, No DTCs Stored (Cont’d)
Action
Go to Step 17
System OK
Go to Step 19
System OK
Go to Step 20
Go to Step 21
System OK
System OK
System OKGo to Step 16
-
Go to Step 18
-
Go to Step 23
Go to Step 22
-
-
- 11 - 14v
-
11 - 14v
-
≈ 0 Ω
-
-
-
-
1. Disconnect the EBCM connector from the EBCM.
2. Turn the ignition to ON.
3. Check for the presence of battery voltage between
ground and terminal 20 and 21.
Is the voltage equal to the specified value?
1. Turn the ignition switch to OFF.
2. Trace the RW wires between terminal 20 and 21 of
the EBCM connector to fuse F30 of the I/P fuse
block.
3. Repair the open in this circuit.
Is the repair complete?
Check the voltage between ground and terminal 1 of
the EBCM connector.
Is the voltage equal to the specified value?
1. Turn the ignition switch to OFF.
2. Repair the circuit RW between terminal 1 of the
ABS harness EBCM connector to fuse F29 in the I/
P fuse block.
Is the repair complete?
1. Turn the ignition to OFF.
2. Check the resistance between ground and terminals
16 and 19 of the EBCM connector.
Is the resistance equal to the specified value?
Examine terminals 20, 21, 1, 19 and 16 of the EBCM
connector.
Is there a defective terminal?
Repair the defective terminal or replace the connector
or wiring harness, as required.
Is the repair complete?
Replace the ABS unit.
Is the repair complete?
Repair the defective ground connection.
Is the repair complete?
Value(s) Yes No
Page 1019 of 2053

SSANGYONG MY2002
4F-36 ABS AND TCS
SELF-DIAGNOSTICS
Important: The electronic brake control module (EBCM)
turns the valve relay off when a diagnostic trouble code
(DTC) is set. The scan tool will indicate that the valve
relay is off when it is used to monitor the data list. This
is normal and should not be considered a mal-function.
The EBCM performs system self-diagnostics and can
detect and often isolate system malfunctions. When it
detects a malfunction, the EBCM sets a DTC that repre
sents the malfunction, turns on the ABS and/or the
TCS indicators in most instances, and may disable the
ABS and/or the TCS functions, as necessary, for the
duration of the ignition cycle.
Once each ignition cycle, the EBCM performs an auto-
matic test when the vehicle reaches 2.75 km/h (1.7
mph). In the course of this test, the system cycles
each valve solenoid and the pump motor, along with
the necessary relays, to check component operation.
If the EBCM detects any malfunctions, it will set a
DTC as described above.
DISPLAYING DTCs
Tools Required
Scan Tool
DTCs can be read through the use of the scan tool.
CLEARING DTCs
Tools Required
Scan Tool
The diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs) in the electronic
brake control module (EBCM) memory are erased in
one of two ways:
Use the scan tool “Clear DTCs” selection.
After 249 DTC-free ignition cycles.
These two methods are detailed below. Be sure to verify
the proper system operation and, the absence of DTCs
when the clearing procedure is completed.The EBCM will not permit DTC clearing until all DTCs
have been displayed. Also, DTCs cannot be cleared
by disconnecting the EBCM, disconnecting the battery
cables, or turning the ignition switch to LOCK.
Scan Tool Method
The scan tool can clear ABS/TCS system DTCs using
the mass storage cartridge.
1. Install the scan tool and the mass storage
cartridge.
2. Select “Fault Memory”.
3. Select “Clear Fault Memory”.
Clearing the fault memory cannot reset a valve relay
which was shut down when the fault was recognized.
Changes are possible only after the fault has been elimi-
nated and the next ignition cycle has begun.
Ignition Cycle Default
A DTC is erased from memory after 249 ignition cycles
without any reappearance of that malfunction.
INTERMITTENTS AND POOR
CONNECTIONS
As with most electronic systems, intermittent malfunc
tions may be difficult to diagnose accurately. The follow-
ing is a method to try to isolate an intermittent
malfunction, especially in wheel speed circuitry.
If an ABS malfunction occurs, the ABS indicator will
illuminate during the ignition cycle in which the
malfunction was detected. If it is an intermittent problem
which seems to have corrected itself (ABS indicator
OFF), a history DTC will be stored. Also stored will be
the history data of the DTC at the time the malfunction
occurred. Use the scan tool modular diagnostic system
to read ABS history data.
Most intermittents are caused by faulty electrical con
nections or wiring, although a sticking relay or solenoid
can occasionally be at fault.