1997 SSANGYONG KORANDO engine oil
[x] Cancel search: engine oilPage 1107 of 2053
AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION 5A-13
SSANGYONG MY2002
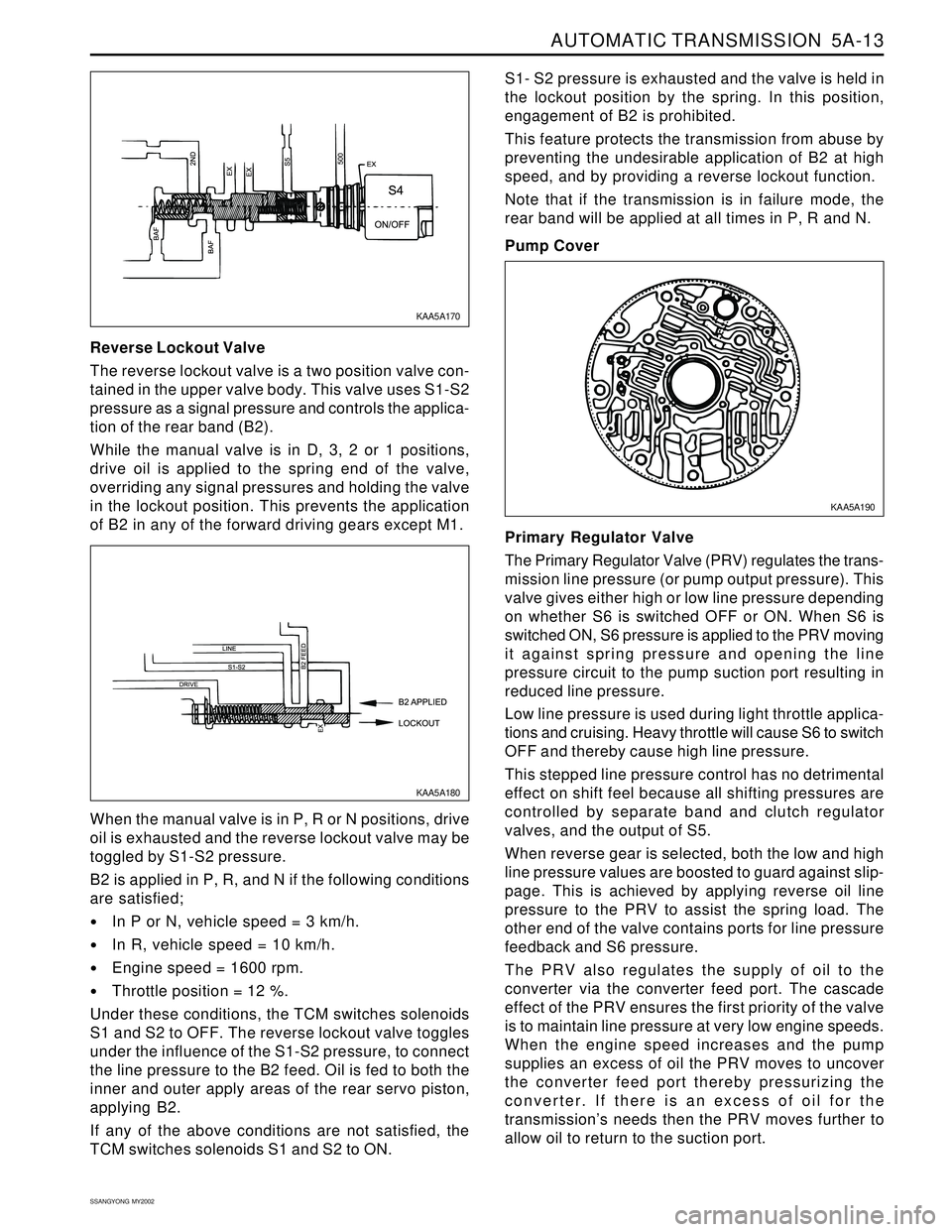
Reverse Lockout Valve
The reverse lockout valve is a two position valve con-
tained in the upper valve body. This valve uses S1-S2
pressure as a signal pressure and controls the applica-
tion of the rear band (B2).
While the manual valve is in D, 3, 2 or 1 positions,
drive oil is applied to the spring end of the valve,
overriding any signal pressures and holding the valve
in the lockout position. This prevents the application
of B2 in any of the forward driving gears except M1.S1- S2 pressure is exhausted and the valve is held in
the lockout position by the spring. In this position,
engagement of B2 is prohibited.
This feature protects the transmission from abuse by
preventing the undesirable application of B2 at high
speed, and by providing a reverse lockout function.
Note that if the transmission is in failure mode, the
rear band will be applied at all times in P, R and N.
Pump Cover
When the manual valve is in P, R or N positions, drive
oil is exhausted and the reverse lockout valve may be
toggled by S1-S2 pressure.
B2 is applied in P, R, and N if the following conditions
are satisfied;
In P or N, vehicle speed = 3 km/h.
In R, vehicle speed = 10 km/h.
Engine speed = 1600 rpm.
Throttle position = 12 %.
Under these conditions, the TCM switches solenoids
S1 and S2 to OFF. The reverse lockout valve toggles
under the influence of the S1-S2 pressure, to connect
the line pressure to the B2 feed. Oil is fed to both the
inner and outer apply areas of the rear servo piston,
applying B2.
If any of the above conditions are not satisfied, the
TCM switches solenoids S1 and S2 to ON.Primary Regulator Valve
The Primary Regulator Valve (PRV) regulates the trans-
mission line pressure (or pump output pressure). This
valve gives either high or low line pressure depending
on whether S6 is switched OFF or ON. When S6 is
switched ON, S6 pressure is applied to the PRV moving
it against spring pressure and opening the line
pressure circuit to the pump suction port resulting in
reduced line pressure.
Low line pressure is used during light throttle applica-
tions and cruising. Heavy throttle will cause S6 to switch
OFF and thereby cause high line pressure.
This stepped line pressure control has no detrimental
effect on shift feel because all shifting pressures are
controlled by separate band and clutch regulator
valves, and the output of S5.
When reverse gear is selected, both the low and high
line pressure values are boosted to guard against slip-
page. This is achieved by applying reverse oil line
pressure to the PRV to assist the spring load. The
other end of the valve contains ports for line pressure
feedback and S6 pressure.
The PRV also regulates the supply of oil to the
converter via the converter feed port. The cascade
effect of the PRV ensures the first priority of the valve
is to maintain line pressure at very low engine speeds.
When the engine speed increases and the pump
supplies an excess of oil the PRV moves to uncover
the converter feed port thereby pressurizing the
converter. If there is an excess of oil for the
transmission’s needs then the PRV moves further to
allow oil to return to the suction port.
KAA5A170
KAA5A180KAA5A190
Page 1119 of 2053
AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION 5A-25
SSANGYONG MY2002
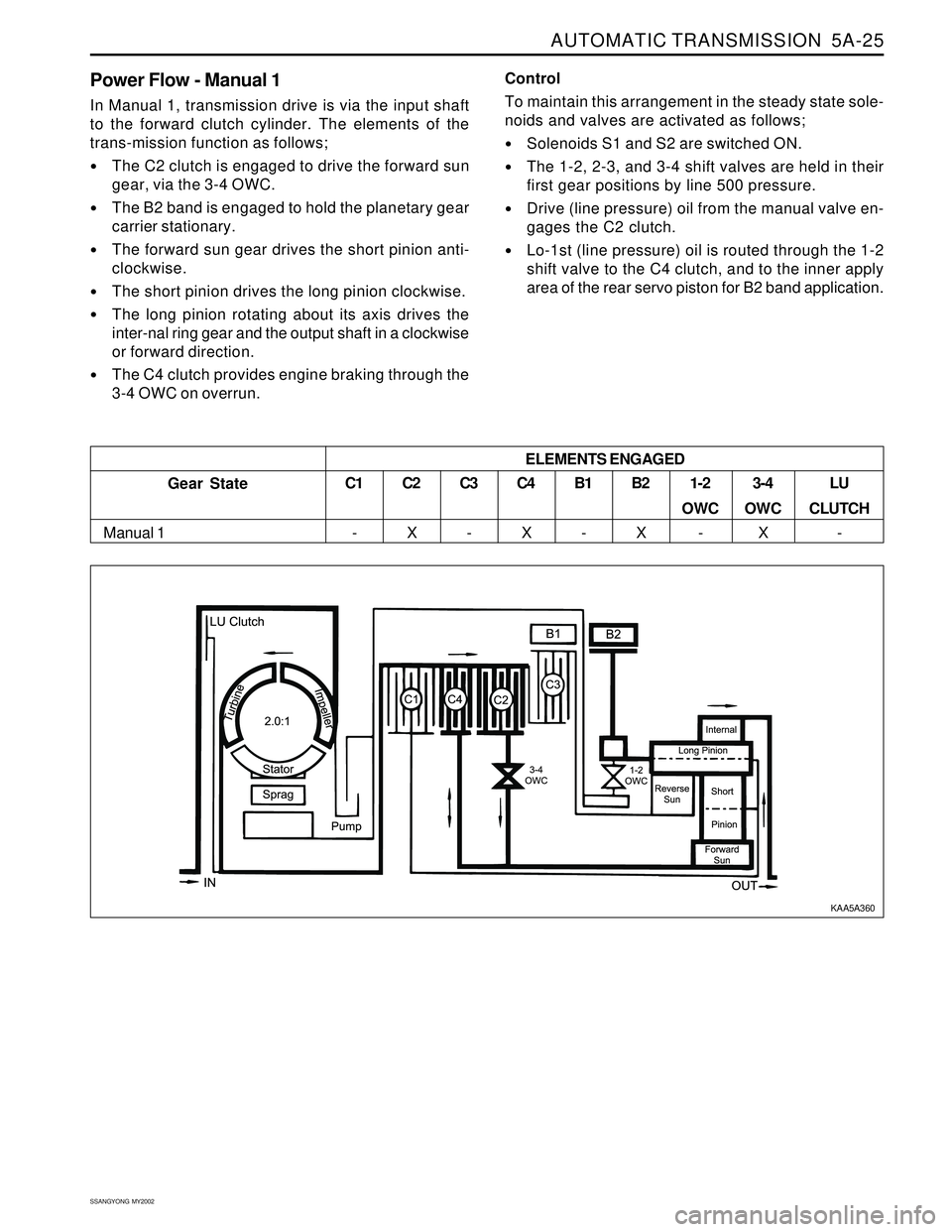
Power Flow - Manual 1
In Manual 1, transmission drive is via the input shaft
to the forward clutch cylinder. The elements of the
trans-mission function as follows;
The C2 clutch is engaged to drive the forward sun
gear, via the 3-4 OWC.
The B2 band is engaged to hold the planetary gear
carrier stationary.
The forward sun gear drives the short pinion anti-
clockwise.
The short pinion drives the long pinion clockwise.
The long pinion rotating about its axis drives the
inter-nal ring gear and the output shaft in a clockwise
or forward direction.
The C4 clutch provides engine braking through the
3-4 OWC on overrun.Control
To maintain this arrangement in the steady state sole-
noids and valves are activated as follows;
Solenoids S1 and S2 are switched ON.
The 1-2, 2-3, and 3-4 shift valves are held in their
first gear positions by line 500 pressure.
Drive (line pressure) oil from the manual valve en-
gages the C2 clutch.
Lo-1st (line pressure) oil is routed through the 1-2
shift valve to the C4 clutch, and to the inner apply
area of the rear servo piston for B2 band application.
ELEMENTS ENGAGED
Gear State
Manual 1C1
-C2
XC3
-C4
XB1
-B2
X1-2
OWC
-3-4
OWC
XLU
CLUTCH
-
KAA5A360
Page 1121 of 2053
AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION 5A-27
SSANGYONG MY2002
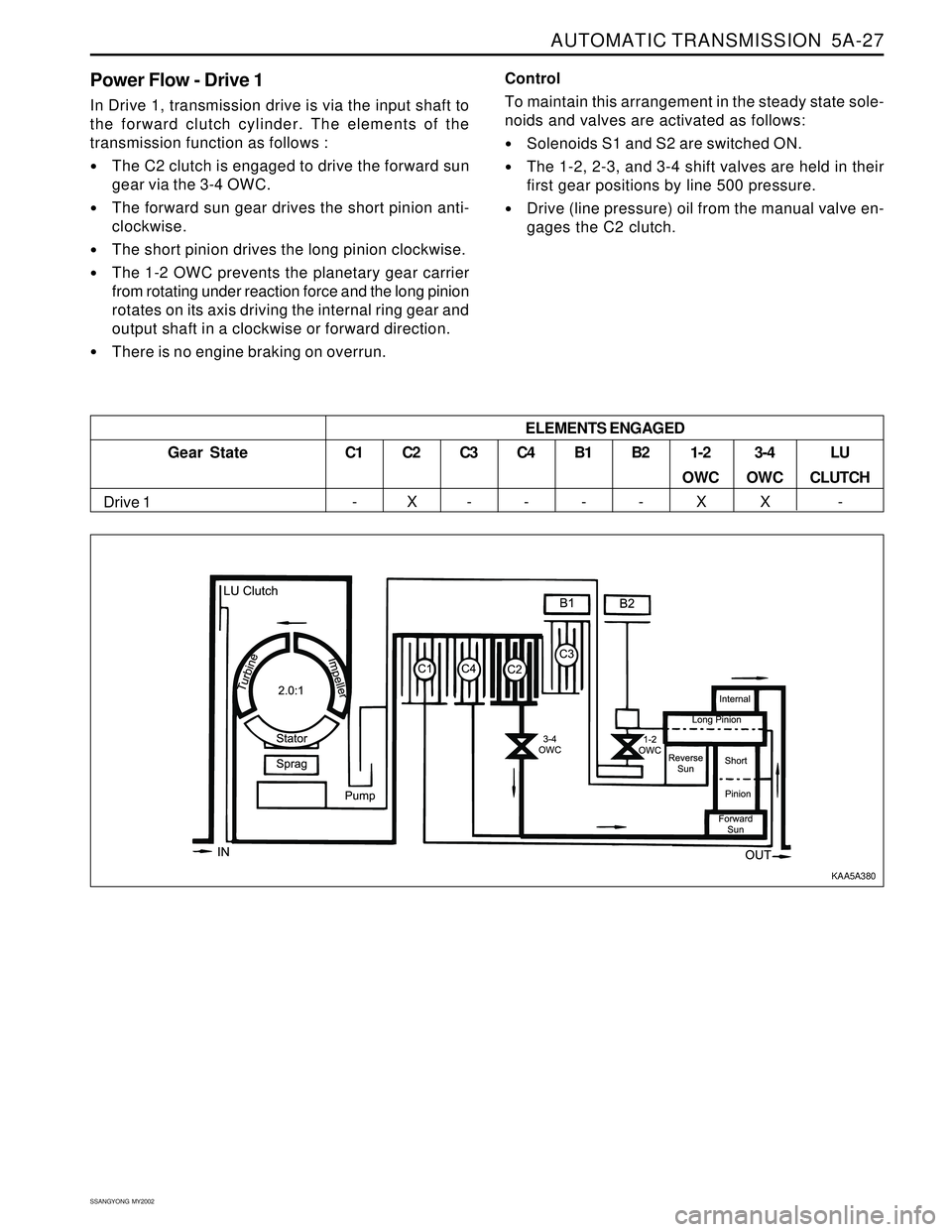
Power Flow - Drive 1
In Drive 1, transmission drive is via the input shaft to
the forward clutch cylinder. The elements of the
transmission function as follows :
The C2 clutch is engaged to drive the forward sun
gear via the 3-4 OWC.
The forward sun gear drives the short pinion anti-
clockwise.
The short pinion drives the long pinion clockwise.
The 1-2 OWC prevents the planetary gear carrier
from rotating under reaction force and the long pinion
rotates on its axis driving the internal ring gear and
output shaft in a clockwise or forward direction.
There is no engine braking on overrun.Control
To maintain this arrangement in the steady state sole-
noids and valves are activated as follows:
Solenoids S1 and S2 are switched ON.
The 1-2, 2-3, and 3-4 shift valves are held in their
first gear positions by line 500 pressure.
Drive (line pressure) oil from the manual valve en-
gages the C2 clutch.
Gear State
Drive 1C1
-
C2
XC3
-C4
-B1
-B2
-1-2
OWC
X3-4
OWC
XLU
CLUTCH
- ELEMENTS ENGAGED
KAA5A380
Page 1123 of 2053
AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION 5A-29
SSANGYONG MY2002
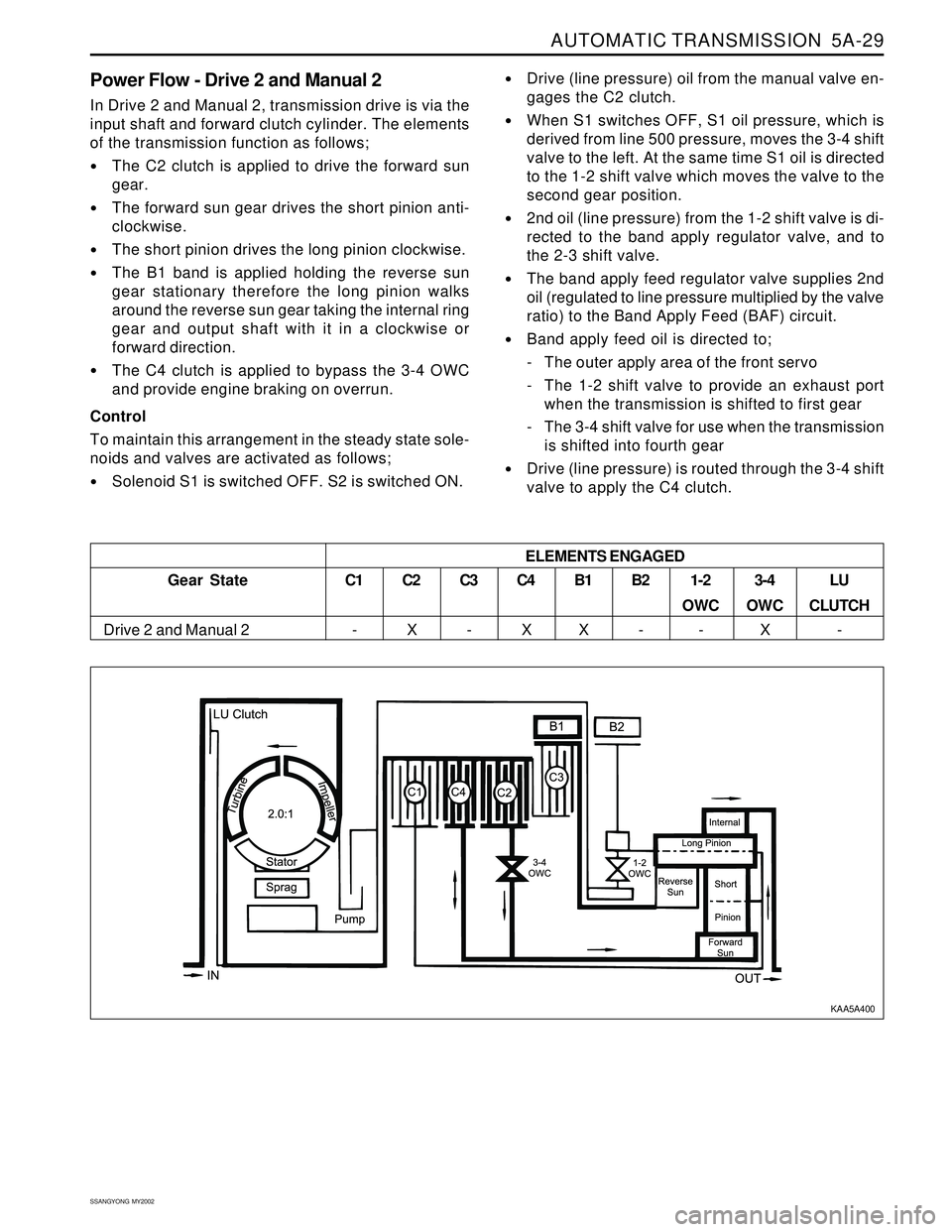
Power Flow - Drive 2 and Manual 2
In Drive 2 and Manual 2, transmission drive is via the
input shaft and forward clutch cylinder. The elements
of the transmission function as follows;
The C2 clutch is applied to drive the forward sun
gear.
The forward sun gear drives the short pinion anti-
clockwise.
The short pinion drives the long pinion clockwise.
The B1 band is applied holding the reverse sun
gear stationary therefore the long pinion walks
around the reverse sun gear taking the internal ring
gear and output shaft with it in a clockwise or
forward direction.
The C4 clutch is applied to bypass the 3-4 OWC
and provide engine braking on overrun.
Control
To maintain this arrangement in the steady state sole-
noids and valves are activated as follows;
Solenoid S1 is switched OFF. S2 is switched ON.
Drive (line pressure) oil from the manual valve en-
gages the C2 clutch.
When S1 switches OFF, S1 oil pressure, which is
derived from line 500 pressure, moves the 3-4 shift
valve to the left. At the same time S1 oil is directed
to the 1-2 shift valve which moves the valve to the
second gear position.
2nd oil (line pressure) from the 1-2 shift valve is di-
rected to the band apply regulator valve, and to
the 2-3 shift valve.
The band apply feed regulator valve supplies 2nd
oil (regulated to line pressure multiplied by the valve
ratio) to the Band Apply Feed (BAF) circuit.
Band apply feed oil is directed to;
- The outer apply area of the front servo
- The 1-2 shift valve to provide an exhaust port
when the transmission is shifted to first gear
- The 3-4 shift valve for use when the transmission
is shifted into fourth gear
Drive (line pressure) is routed through the 3-4 shift
valve to apply the C4 clutch.
Gear State
Drive 2 and Manual 2ELEMENTS ENGAGEDC1
-C2
XC3
-C4
XB1
XB2
-1-2
OWC
-3-4
OWC
XLU
CLUTCH
-
KAA5A400
Page 1125 of 2053
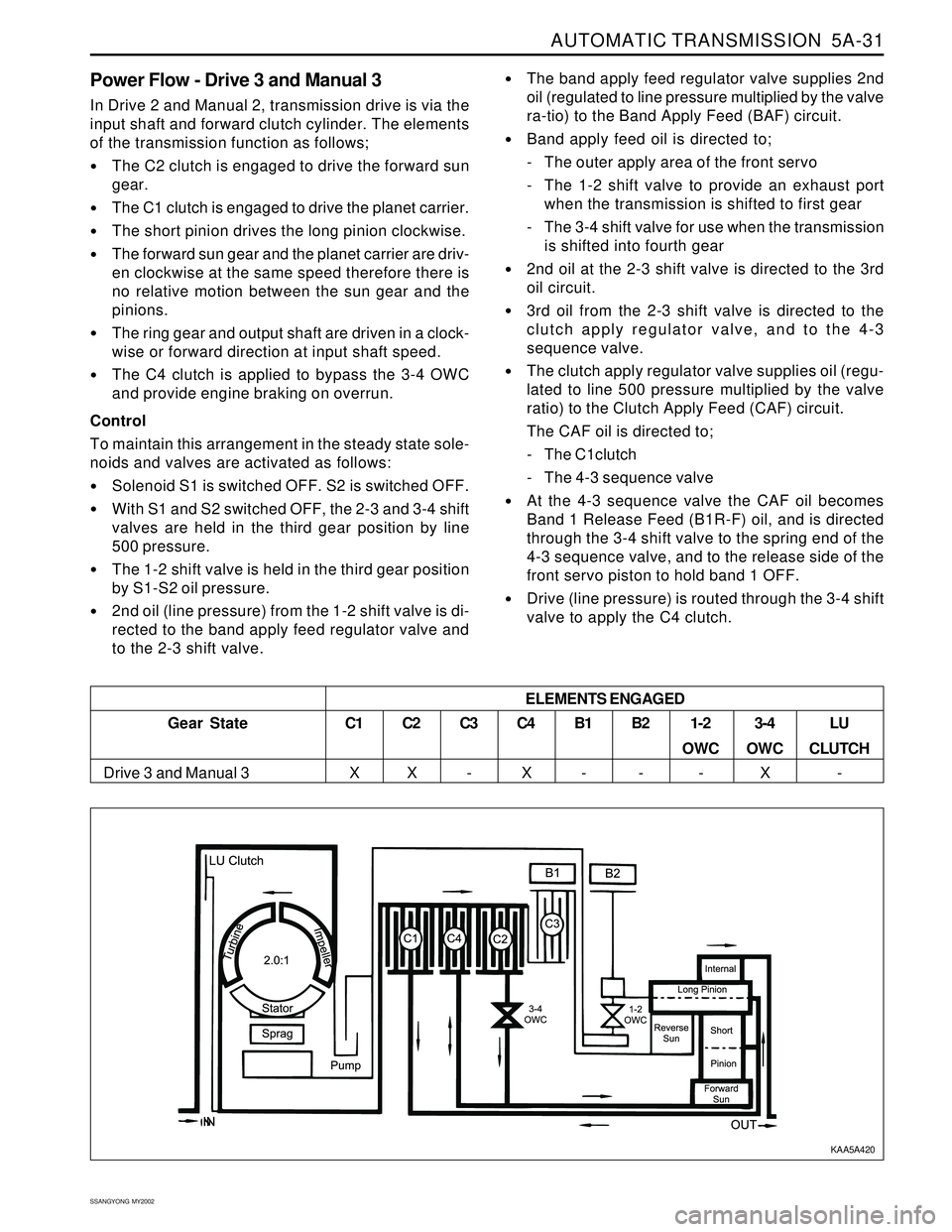
AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION 5A-31
SSANGYONG MY2002
Power Flow - Drive 3 and Manual 3
In Drive 2 and Manual 2, transmission drive is via the
input shaft and forward clutch cylinder. The elements
of the transmission function as follows;
The C2 clutch is engaged to drive the forward sun
gear.
The C1 clutch is engaged to drive the planet carrier.
The short pinion drives the long pinion clockwise.
The forward sun gear and the planet carrier are driv-
en clockwise at the same speed therefore there is
no relative motion between the sun gear and the
pinions.
The ring gear and output shaft are driven in a clock-
wise or forward direction at input shaft speed.
The C4 clutch is applied to bypass the 3-4 OWC
and provide engine braking on overrun.
Control
To maintain this arrangement in the steady state sole-
noids and valves are activated as follows:
Solenoid S1 is switched OFF. S2 is switched OFF.
With S1 and S2 switched OFF, the 2-3 and 3-4 shift
valves are held in the third gear position by line
500 pressure.
The 1-2 shift valve is held in the third gear position
by S1-S2 oil pressure.
2nd oil (line pressure) from the 1-2 shift valve is di-
rected to the band apply feed regulator valve and
to the 2-3 shift valve.
The band apply feed regulator valve supplies 2nd
oil (regulated to line pressure multiplied by the valve
ra-tio) to the Band Apply Feed (BAF) circuit.
Band apply feed oil is directed to;
- The outer apply area of the front servo
- The 1-2 shift valve to provide an exhaust port
when the transmission is shifted to first gear
- The 3-4 shift valve for use when the transmission
is shifted into fourth gear
2nd oil at the 2-3 shift valve is directed to the 3rd
oil circuit.
3rd oil from the 2-3 shift valve is directed to the
clutch apply regulator valve, and to the 4-3
sequence valve.
The clutch apply regulator valve supplies oil (regu-
lated to line 500 pressure multiplied by the valve
ratio) to the Clutch Apply Feed (CAF) circuit.
The CAF oil is directed to;
- The C1clutch
- The 4-3 sequence valve
At the 4-3 sequence valve the CAF oil becomes
Band 1 Release Feed (B1R-F) oil, and is directed
through the 3-4 shift valve to the spring end of the
4-3 sequence valve, and to the release side of the
front servo piston to hold band 1 OFF.
Drive (line pressure) is routed through the 3-4 shift
valve to apply the C4 clutch.
3-4
OWC
XLU
CLUTCH
- ELEMENTS ENGAGED
Gear State
Drive 3 and Manual 3C1
XC2
XC3
-C4
XB1
-B2
-1-2
OWC
-
KAA5A420
Page 1132 of 2053

5A-38 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION
SSANGYONG MY2002
DIAGNOSIS
BASIC KNOWLEDGE REQUIRED
You must be familliar with some basic electronics to
use this section of the Service Manual. They will help
you to follow diagnostic procedures.
Notice: Lack of the basic knowledge of this transmis-
sion when performing diagnostic procedures could re-
sult in incorrect diagnostic performance or damage to
transmission components. Do not, under any circum-
stances, attempt to diagnose a transmission problem
without this basic knowledge.
Notice: If a wire is probed with a sharp instrument
and not properly sealed afterward, the wire will corrode
and an open circuit will result.
Diagnostic test probes are now available that allow
you to probe individual wires without leaving the wire
open to the environment. These probe devices are
inexpensive and easy to install, and they permanently
seal the wire from corrosion.
Special Tools
You should be able to use a Digital Volt Meter (DVM),
a circuit tester, jumper wires or leads and a line
pressure gauge set. The functional check procedure
is designed to verify the correct operation of electronic
components in the transmission. This will eliminate the
unnecessary removal of transmission components.
FUNCTIONAL CHECK
PROCEDURE
Begin with the Functional Check Procedure which pro-
vides a general outline of how to diagnose automatic
transmission. The following functional check procedure
will indicate the proper path of diagnosing the transmis-
sion by describing the basic checks and then referenc-
ing the locations of the specific checks.
Check the fluid level according to the Fluid Level
Service Procedure.
Check the transmission fluid leak.
Check if the transmission fluid is not burnt by smell.
Notice: The specific fluid used in this transmission
turns brown during normal operation. Brown fluid
does not indicate a transmission fault.
Ensure that the transmission is not in Limp Home
Mode (LHM).
Check the battery terminals and the earth connec-
tions for corrosion or looseness.
Check that the cooler flow is not restricted.
Check all electrical plug connections for tightness.
Use on-board diagnostic tool or a scan tool to see
if any transmission trouble codes have been set.
DIAGNOSTIC INFORMATION AND PROCEDURES
Refer to the appropriate “Diagnostic Trouble Code
(DTC)” information and repair the vehicle as
directed. After repairing the vehicle, perform the
road test and verify that the code has not set again.
Perform the Electrical/Garage Shift Tests.
Perform the Road Test Procedure in this section.
Inspect the oil and check for metal or other contami-
nants in the oil pan.
TRANSMISSION FLUID LEVEL
SERVICE PROCEDURE
This procedure is to be used when checking a concern
with the fluid level in a vehicle. A low fluid level will
result in slipping and loss of drive/ reverse or delay on
engagement of drive/ reverse when the vehicle is cold.
The vehicle is first checked for transmission diagnostic
messages on the scan tool. If the oil level is low, it is
possible to register a vehicle speed signal fault.
The vehicle is to be test driven to determine if there is
an abnormal delay when selecting drive or reverse, or
loss of drive. One symptom of low fluid level is a
momentary loss of drive when driving the vehicle around
a corner. Also when the transmission fluid level is low,
a loss of drive may occur when the transmission fluid
temperature is low.
If there is no loss of drive when the vehicle is driven
warm and a vehicle speed signal fault is registered,
then fluid should be added to the transmission.
When adding or changing transmission fluid use only
Castrol TQ 95 automatic transmission fluid. The use of
incorrect fluid will cause the performance and durability
of the transmission to be severely degraded.
Fluid Level Diagnosis procedure
1. If the vehicle is at operating temperature allow the
vehicle to cool down for two hours, but no greater
than four hours. Or if the vehicle is at cool status,
start the engine and allow the engine to idle for
approximately 5 minutes or, if possible, drive the
vehicle for a few kilometers. This will allow the
transmission to be within the correct temperature
range. Transmission fluid level should be checked
at temperature 50 - 60 °C (82 - 140 °F).
Caution: Removal of the fluid filler plug when
the transmission fluid is hot may cause injury if
fluid drains from the filler hole.
2. With the brake pedal pressed, move the gear shift
control lever through the gear ranges, pausing a
few seconds in each range. Return the gear shift
control lever to P (Park). Turn the engine OFF.
3. Park the vehicle on a hoist, inspection pit or similar
raised level surface. The vehicle must be control
level to obtain a correct fluid level measurement.
Page 1157 of 2053
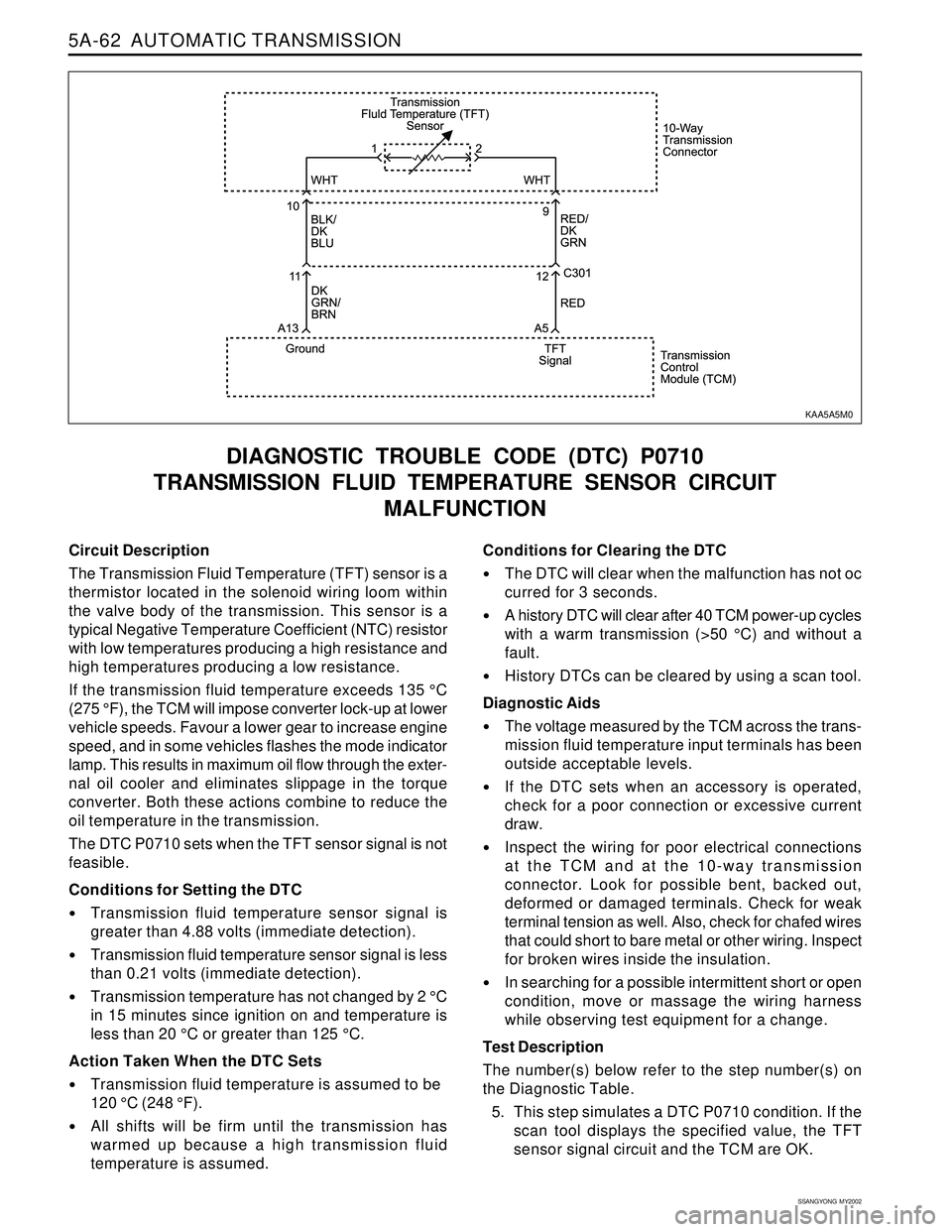
5A-62 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION
SSANGYONG MY2002
Circuit Description
The Transmission Fluid Temperature (TFT) sensor is a
thermistor located in the solenoid wiring loom within
the valve body of the transmission. This sensor is a
typical Negative Temperature Coefficient (NTC) resistor
with low temperatures producing a high resistance and
high temperatures producing a low resistance.
If the transmission fluid temperature exceeds 135 °C
(275 °F), the TCM will impose converter lock-up at lower
vehicle speeds. Favour a lower gear to increase engine
speed, and in some vehicles flashes the mode indicator
lamp. This results in maximum oil flow through the exter-
nal oil cooler and eliminates slippage in the torque
converter. Both these actions combine to reduce the
oil temperature in the transmission.
The DTC P0710 sets when the TFT sensor signal is not
feasible.
Conditions for Setting the DTC
Transmission fluid temperature sensor signal is
greater than 4.88 volts (immediate detection).
Transmission fluid temperature sensor signal is less
than 0.21 volts (immediate detection).
Transmission temperature has not changed by 2 °C
in 15 minutes since ignition on and temperature is
less than 20 °C or greater than 125 °C.
Action Taken When the DTC Sets
Transmission fluid temperature is assumed to be
120 °C (248 °F).
All shifts will be firm until the transmission has
warmed up because a high transmission fluid
temperature is assumed.
DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE (DTC) P0710
TRANSMISSION FLUID TEMPERATURE SENSOR CIRCUIT
MALFUNCTION
Conditions for Clearing the DTC
The DTC will clear when the malfunction has not oc
curred for 3 seconds.
A history DTC will clear after 40 TCM power-up cycles
with a warm transmission (>50 °C) and without a
fault.
History DTCs can be cleared by using a scan tool.
Diagnostic Aids
The voltage measured by the TCM across the trans-
mission fluid temperature input terminals has been
outside acceptable levels.
If the DTC sets when an accessory is operated,
check for a poor connection or excessive current
draw.
Inspect the wiring for poor electrical connections
at the TCM and at the 10-way transmission
connector. Look for possible bent, backed out,
deformed or damaged terminals. Check for weak
terminal tension as well. Also, check for chafed wires
that could short to bare metal or other wiring. Inspect
for broken wires inside the insulation.
In searching for a possible intermittent short or open
condition, move or massage the wiring harness
while observing test equipment for a change.
Test Description
The number(s) below refer to the step number(s) on
the Diagnostic Table.
5. This step simulates a DTC P0710 condition. If the
scan tool displays the specified value, the TFT
sensor signal circuit and the TCM are OK.
KAA5A5M0
Page 1255 of 2053
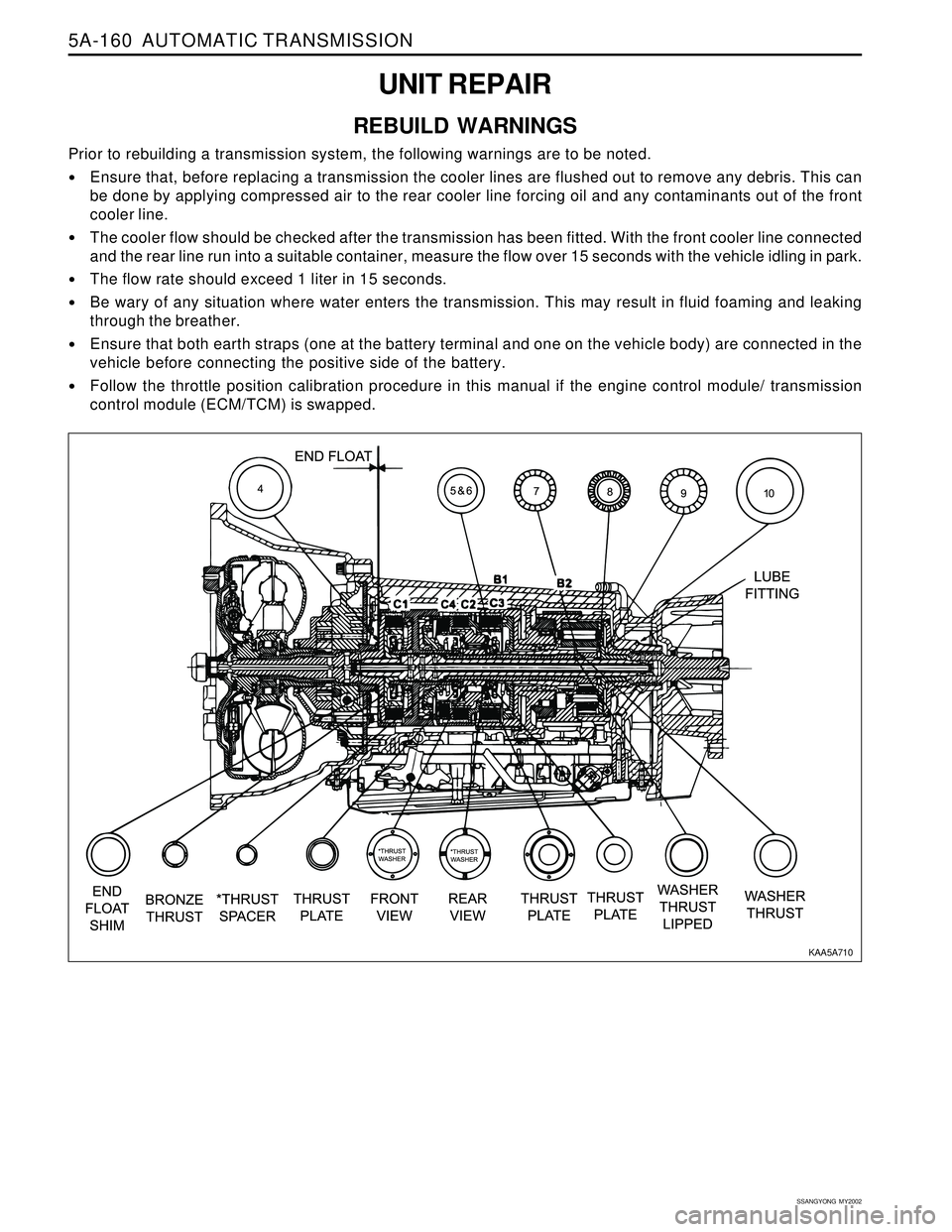
5A-160 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION
SSANGYONG MY2002
UNIT REPAIR
REBUILD WARNINGS
Prior to rebuilding a transmission system, the following warnings are to be noted.
Ensure that, before replacing a transmission the cooler lines are flushed out to remove any debris. This can
be done by applying compressed air to the rear cooler line forcing oil and any contaminants out of the front
cooler line.
The cooler flow should be checked after the transmission has been fitted. With the front cooler line connected
and the rear line run into a suitable container, measure the flow over 15 seconds with the vehicle idling in park.
The flow rate should exceed 1 liter in 15 seconds.
Be wary of any situation where water enters the transmission. This may result in fluid foaming and leaking
through the breather.
Ensure that both earth straps (one at the battery terminal and one on the vehicle body) are connected in the
vehicle before connecting the positive side of the battery.
Follow the throttle position calibration procedure in this manual if the engine control module/ transmission
control module (ECM/TCM) is swapped.
KAA5A710