1997 SSANGYONG KORANDO manual transmission
[x] Cancel search: manual transmissionPage 643 of 2053

1B3 -- 94 OM600 ENGINE MECHANICAL
D AEW OO M Y_2000
OM662LA OM661LA
DManual transmission flywheel
DAutomatic transmission flywheel
Page 644 of 2053

OM600 ENGINE MECHANICAL 1B3 -- 95
D AEW OO M Y_2000
Tools Required
602 589 00 40 00 Engine Lock
Removal & Installation Procedure
1. Install the engine lock.
Engine Lock 602 589 02 40 00
2. Remove the 12-- sided stretch bolts (4).
Installation Notice
Tightening Torque45 N∙m (33 lb-ft) + 90_
Notice
If the length ’L’ of bolts exceeds 22.5mm, replace
the bolts.
3. Remove the flywheel (3), if equipped with manual
transmission.
Installation Notice
Correctly align the position of dowel pin (2).
Page 803 of 2053

1F3 -- 46 OM600 ENGINE CONTROLS
D AEW OO M Y_2000
Removal Procedure
1. Position then no.1 cylinder at 15_ATDC.
Notice
Do not rotate the engine in opposition direction of
engine rotation.
2. Remove the connecting rod (9).
3. Disconnect the vacuum lines (13, 14).
4. Remove the accelerator control damper (10).
(Manual transmission vehicle)
5. Remove the suction line (16) and pressure line (4).
6. Remove the banjo bolt (1) and then remove the seal
(2) and fuel line (3).
7. Remove the plastic clip (8) on the injection line.
8. Disconnect the injection lines (15) from the injection
pump (25).
9. Remove the banjo bolt (1) and then remove the seal
(7) and return line (5).
Page 807 of 2053

1F3 -- 50 OM600 ENGINE CONTROLS
D AEW OO M Y_2000
11. Assemble the plastic clip (8).
12. Connect the vacuum line (13, 14).
13. Connect the connecting rod (9).
14. Connect the accelerator control damper (10).
(Manual transmission vehicle)
15. Install the chain tensioner.
16. Install the vacuum pump.
17. Check the start of delivery.
18. Adjust the idle speed.
Page 1095 of 2053

SECTION 5A
AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION
CAUTION: Disconnect the negative battery cable before removing or installing any electrical unit or when a
tool or equipment could easily come in contact with exposed electrical terminals. Disconnecting this cable
will help prevent personal injury and damage to the vehicle. The ignition must also be in LOCK unless
otherwise noted.
TABLE OF CONTENTS
Description and Operation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5A-2
BTRA M74 4WD Automatic Transmission . . . . . . 5A-2
Operators Interfaces . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5A-2
Control Systems . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5A-3
Electronic Control System . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5A-3
Hydraulic Control System . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5A-9
Hydraulic Control Circuit . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5A-10
Power Train System . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5A-14
Power Flows . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5A-18
Park and Neutral . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5A-20
Reverse . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5A-22
Manual 1 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5A-24
Drive 1 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5A-26
Drive 2 and Manual 2 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5A-28
Drive 3 and Manual 3 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5A-30
Drive 3 Lock Up and Manual 3 Lock Up . . . . . . 5A-32
Drive 4 (Overdrive) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5A-34
Drive 4 Lock Up . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5A-36
Diagnostic Information and Procedures . . . . . 5A-38
Diagnosis . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5A-38
Basic Knowledge Required . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5A-38
Functional Check Procedure . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5A-38
Transmission Fluid Level Service Procedure . . . 5A-38
Fluid Leak Diagnosis and Repair . . . . . . . . . . . 5A-39
Electrical / Garage Shift Test . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5A-40
Road Test Procedure . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5A-40
Electronic Adjustments . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5A-40
Symptom Diagnosis . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5A-41
Drive Faults . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5A-41
Faulty Shift Pattern . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5A-42Shift Quality Faults . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5A-44
After Teardown Faults . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5A-46
Trouble Code Diagnosis - Gasoline Vehicle . . 5A-48
TCM Diagnostic System Overview . . . . . . . . . . 5A-48
Clearing Trouble Codes . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5A-48
Diagnostic Trouble Codes . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5A-48
Trouble Code Diagnosis - Diesel Vehicle . . . . . 5A-50
TCM Diagnostic System Overview . . . . . . . . . . 5A-50
Clearing Trouble Codes . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5A-50
Diagnostic Trouble Codes . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5A-50
Repair Instructions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5A-157
On-Vehicle Service . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5A-157
Transmission . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5A-157
Unit Repair . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5A-160
Rebuild Warnings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5A-160
Disassembly Procedure . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5A-161
Assembly Procedure . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5A-171
Front and Rear Band Adjustment . . . . . . . . . . . 5A-199
Gear Shift Control Lever . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5A-202
Kickdown Switch . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5A-202
Specifications . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5A-203
General Specification . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5A-203
Fastener Tightening Specifications . . . . . . . . . . 5A-205
Schematic and Routing Diagrams . . . . . . . . . . 5A-206
TCM Wiring Diagrams (Gasoline Engine) . . . . . 5A-206
TCM Wiring Diagrams (Diesel Engine) . . . . . . . 5A-208
Connector End View . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5A-210
Special Tools and Equipment . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5A-211
Special Tools Table . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5A-211
Page 1097 of 2053
AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION 5A-3
SSANGYONG MY2002
N - Neutral allows the engine to be started and oper-
ated while driving the vehicle. The inhibitor switch
allows the engine to be started. There is no power
transferred through the transmission in Neutral. But
the final drive is not locked by the parking pawl, so
thewheels are free to rotate.
D - Overdrive range is used for all normal driving
conditions. 4th gear (overdrive gear) reduces the
fuel consumption and the engine noise. Engine
braking is applied with reduced throttle.
First to second (1 → 2), first to third (1 → 3), second
to third (2 → 3), second to fourth (2 → 4), third to
fourth (3 → 4), fourth to third (4 → 3), fourth to
second (4 → 2), third to second (3 → 2), third to
first (3 → 1) and second to first (2 → 1) shifts are
all available as a function of vehicle speed, throttle
position and the time change rate of the throttle
position.
Downshifts are available for safe passing by
depress-ing the accelerator. Lockup clutch may be
enabled in 3rd and 4th gears depending on vehicle
type.
3 - Manual 3 provides three gear ratios (first through
third) and prevents the transmission from operating
in 4th gear. 3rd gear is used when driving on long
hill roads or in heavy city traffic. Downshifts are
available by depressing the accelerator.
2 - Manual 2 provides two gear ratios (first and
second). It is used to provide more power when
climbing hills or engine braking when driving down
a steep hill or starting off on slippery roads.
1 - Manual 1 is used to provide the maximum engine
braking when driving down the severe gradients.When NORMAL mode is selected upshifts will occur
to maximize fuel economy. When POWER mode is se-
lected, upshifts will occur to give maximum
performance and the POWER mode indicator light is
switched ON.
When WINTER mode is selected, starting in second
gear is facilitated, the WINTER mode indicator light is
switched ON and the POWER mode indicator light is
switched OFF.
Indicator Light
The indicator light is located on the instrument panel.
Auto shift indicator light comes ON when the ignition
switch ON and shows the gear shift control lever
position.
POWER mode indicator light comes ON when the
POWER mode is selected and when the kickdown
switch is depressed.
WINTER mode indicator light comes ON when the
WINTER mode is selected.
CONTROL SYSTEMS
BTRA M74 4WD automatic transmission consists of
two control systems. One is the electronic control
system that monitors vehicle parameters and adjusts
the transmission performance. Another is the hydraulic
control system that implements the commands of the
electronic control system commands.
ELECTRONIC CONTROL SYSTEM
The electronic control system comprises of sensors, a
TCM and seven solenoids. The TCM reads the inputs
and activates the outputs according to values stored
in Read Only Memory (ROM).
The TCM controls the hydraulic control system. This
control is via the hydraulic valve body, which contains
seven electromagnetic solenoids. Six of the seven
solenoids are used to control the line pressure, operate
the shift valves and the torque converter lock-up clutch,
and to turn ON and OFF the two regulator valves that
control the shift feel.
The seventh solenoid is the proportional or Variable
Pressure Solenoid (VPS) which works with the two regu-
lator valves to control shift feel.
Transmission Control Module (TCM)
The TCM is an in-vehicle micro-processor based trans-
mission management system. It is mounted under the
driver’s side front seat in the vehicle cabin.
The TCM contains:
Processing logic circuits which include a central mi-
croprocessor controller and a back-up memory
system.
Input circuits.
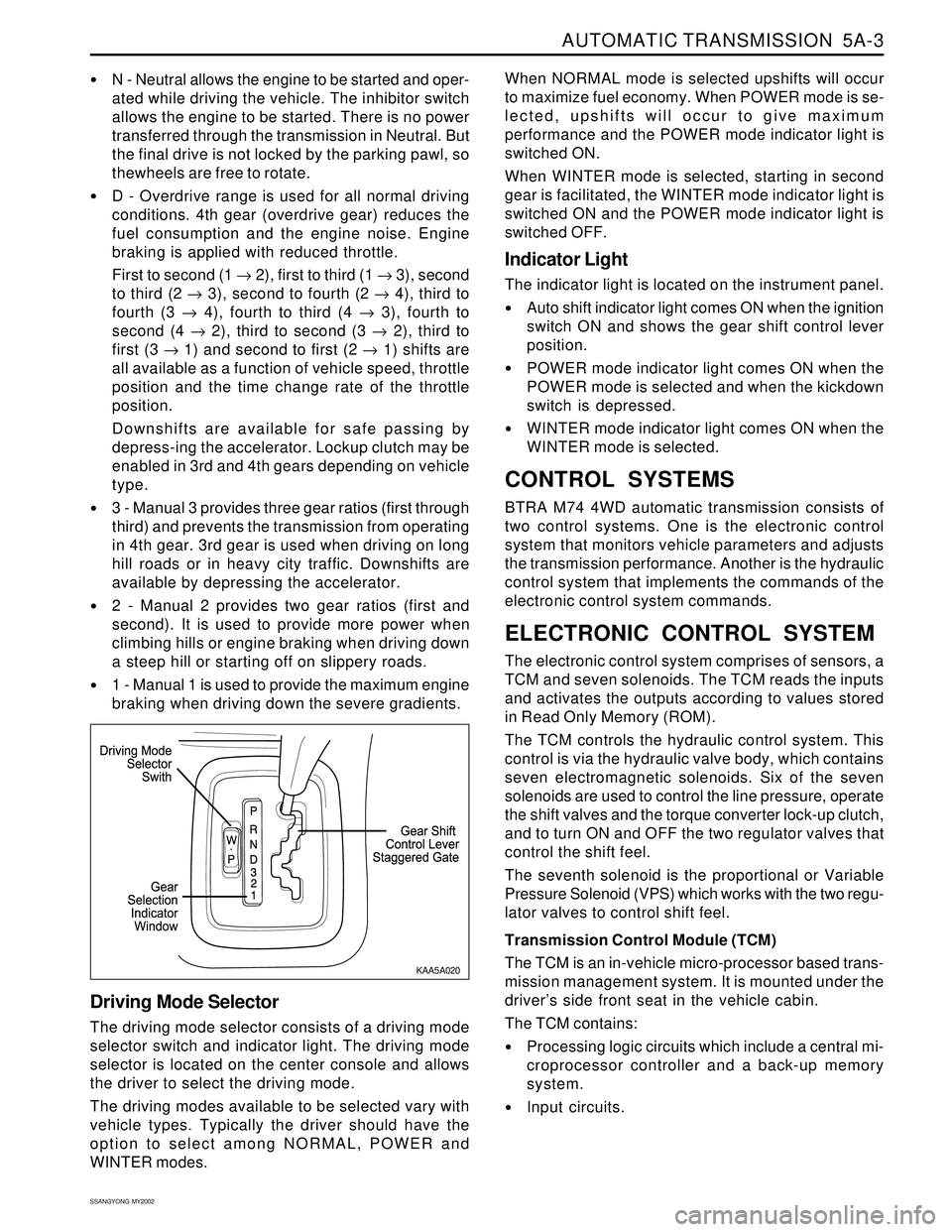
Driving Mode Selector
The driving mode selector consists of a driving mode
selector switch and indicator light. The driving mode
selector is located on the center console and allows
the driver to select the driving mode.
The driving modes available to be selected vary with
vehicle types. Typically the driver should have the
option to select among NORMAL, POWER and
WINTER modes.
KAA5A020
Page 1100 of 2053
5A-6 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION
SSANGYONG MY2002
Solenoids
The TCM controls seven solenoids. Solenoids 1 to 6
(S1 to S6) are mounted in the valve body, while
Solenoid 7 (S7) is mounted in the pump cover.
Solenoid 1 and 2: S1 and S2 are normally open ON/
OFF solenoids that set the selected gear. These
solenoids determine static gear position by
operating the shift valves. Note that S1 and S2
solenoids also send signal pressure to allow or
prohibit rear band engagement.
Solenoid 3 and 4: S3 and S4 are normally open ON/
OFF solenoids that combine to control shift quality
and sequencing. S3 switches the clutch regulator
valve OFF or ON. S4 switches the front band regula-
tor valve OFF or ON. S5 also provides the signal
pressure for the converter clutch regulator valve.
Solenoid 5: S5 is a variable pressure solenoid that
ramps the pressure during gear changes. This sole-
noid provides the signal pressure to the clutch and
band regulator, thereby controlling the shift pres-
sures. S5 also provides the signal pressure for the
converter clutch regulator valve.
Solenoid 6: S6 is a normally open ON/OFF solenoid
that sets the high/low level of line pressure. Solenoid
OFF gives high pressure.
Solenoid 7: S7 is a normally open ON/OFF solenoid
that controls the application of the converter clutch.
Solenoid ON activates the clutch.
Solenoid Logic for Static Gear States
Gear S1 S2
1st ON ON
2nd OFF ON
3 r d OFF OFF
4th ON OFF
Reverse OFF OFF
Neutral OFF OFF
Park OFF OFF
Shift Lever Position Resistance (k
Ω ΩΩ Ω
Ω)
Manual 1 1 ~ 1.4
Manual 221.8 ~ 2.2
Manual 3 3 3 ~ 3.4
Drive4.5 ~ 4.9
Neutral6.8 ~ 7.2
Reverse10.8 ~ 11.2
Park18.6 ~ 19
Kickdown Switch
The Kickdown Switch is used to signal the TCM that
the driver has pressed the acclerator to the floor and
requires a kickdown shift. When this switch is used,
the POWER light comes ON and the POWER shift
pattern is used.
Diagnostic Inputs
The diagnostic control input or K-line is used to initiate
the outputting of diagnostic data from the TCM to a
diagnostic test instrument. This input may also be used
to clear the stored fault history data from the TCM’s
retentive memory. Connection to the diagnostic input
of the TCM is via a connector included in the vehicle’s
wiring harness or computer interface.
Battery Voltage Monitoring Input
The battery voltage monitoring input is connected to
the positive side of the battery. This signal is taken
from the main supply to the TCM.
If the battery voltage at the TCM falls below 11.3 V,
the transmission will adopt a low voltage mode of
operating in which shifts into first gear are inhibited.
All other shifts are allowed but may not occur because
of the reduced voltage. This condition normally occurs
only when the battery is in poor condition.
If the battery voltage is greater than 16.5 V, the trans-
mission will adopt limp home mode and all solenoids
are turned OFF.
When system voltage recovers, the TCM will resume
normal operation after a 30 seconds delay period.
TCM Outputs
The outputs from the TCM are supplied to the compo-
nents described below;
Solenoids
Mode Indicator Light Readings for Resistance / Shift Lever Positions
Page 1103 of 2053

AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION 5A-9
SSANGYONG MY2002
The DLC connector is located within the driver’s
compartment, directly below the instrument panel on
the driver’s side.
HYDRAULIC CONTROL SYSTEM
The hydraulic controls are located in the valve body,
pump body and main case.
The valve body contains the following;
Manual valve
Three shift valves
Sequence valve
Solenoid supply pressure regulator valve
Line pressure control valve
Clutch apply feed regulator valve
Band apply feed regulator valve
Solenoid S1 to S6
Reverse lockout valveThe pump cover contains the following;
Primary regulator valve for line pressure
Converter clutch regulator valve
Converter clutch control valve
Solenoid S7
The main case contains the following;
B1R exhaust valve
All upshifts are accomplished by simultaneously
switching on a shift valve(s), switching VPS pressure
to the band and/or clutch regulator valve, and then
sending the VPS a ramped current. The shift is
completed by switching the regulators OFF and at the
same time causing the VPS to reach maximum
pressure.
All downshifts are accomplished by switching VPS pres-
sure to the band and/or clutch regulator valve and send-
ing a ramped current to the VPS. The shift is completed
by simultaneously switching the regulators OFF,
switching the shift valves and at the same time causing
the VPS to return to stand-by pressure.
The primary regulator valve is located in the pump
cover and supplies four line pressures; high and low
for forward gears, and high and low for reverse. This
pressure has no effect on shift quality and merely
provides static clutch capacity during steady state
operation. Low pressure can be obtained by activating
an ON/OFF solenoid with high line pressure being the
default mode.
Torque converter lock-up is initiated by toggling the
converter clutch control valve with an ON/OFF solenoid.
The actual apply and release of the clutch is regulated
by the VPS via the converter clutch regulator valve.
The solenoid supply pressure regulator valve provides
reference pressure for all the solenoids.
KAA5A080