1997 MERCEDES-BENZ ML320 engine
[x] Cancel search: enginePage 3324 of 4133
AUTOMATIC AIR CONDITIONING (AAC), FUNCTION - GF83.40-P-0001GI
MODEL 163 as of 1.9.01 with CODE (580a) Automatic air conditioning
Function
The automatic air conditioning (AAC) is equipped with an electronically regulated cooling, heating and
ventilating system and can be summed up by the following list of subfunctions.
Ventilation
The ventilation ensures that there is a sufficient supply of air within the passenger compartment.
Ventilation is achieved with the support of the blower during normal operation, when vehicle is standing
or to increase the air flow. The air is distributed in the passenger compartment using air distribution flaps.
Automatic air conditioning temperature control
The desired temperature is reached or held constant by cooling or heating the air. Precise temperature
control can be achieved by reading in the various temperature sensors.
Residual engine heat utilization
Electromagnetic clutch, location/purpose/
design/function GF83.55-P-
2101GH
In-car temperature sensor, location/purpose/ functionwith intake jet nozzle up to
30.11.99GF83.57-P-
2115GH
In-car temperature sensor with ventilation blower,
location/purpose/functionas of 1.12.99GF83.57-P-
2107GH
Ice-up protection temperature sensor, location/
purpose/function GF83.57-P-
2113GH
Blending air flap actuator, location/purpose/ function GF83.57-P-
2112GC
Outside temperature sensor, location/purpose/ functionas of 1.12.99GF83.57-P-
2110GH
Electric heater booster, location/purpose/
design/functionEngines 612.963 and 628.963GF83.70-P-
4054GH
Temperature regulator microswitch, location/
purpose/functionEngine 612.963GF83.70-P-
4055GH
Extended activity module, location/purpose GF54.21-P-
4106GH
Extended activity module, location/purpose/ designas of 1.12.99GF54.21-P-
4107GK
CDI control module, location/purpose/functionEngine 612.963GF07.16-P-
3102IA
2001 Mercedes-Benz ML320
1998-2005 HVAC Climate Control - 163 Chassis
me
Saturday, October 02, 2010 3:23:16 PMPage 80 © 2006 Mitchell Repair Information Company, LLC.
Page 3325 of 4133

The residual engine heat utilization system allows the vehicle to be heated even when the ignition is
switched OFF. To do so the system utilizes the residual heat from the engine and guides it via the
blower into the passenger compartment. The heating water circulation pump ensures that the
coolant is properly circulated.
Automatic air conditioning push-button control module
The automatic air conditioning can be operated by the driver using various tip switches. Apart from this
the push-
button control module reads in different sensor signals, processes them and controls components
in the automatic air conditioning.
Rear ventilation control panel
The operator can intervene in the automatic regulation of the rear ventilation through the automatic air
conditioning by using the rear ventilation control panel and adjust it accordingly to suit needs at any
given time. With the aid of the air distribution switch and blower switch the operator can accommodate
his/her own wishes. The correspondingly altered function is then no longer regulated by the automatic air
conditioning.
By pressing the automatic control button the manually initiated settings can be reset and thus regulated
again by the automatic air conditioning.
Regulation of the air quantity and air distribution ensues thus solely by way of the automatic air
conditioning push-button control module.
Heater circuit
Coolant is heated by the engine. Subsequently, the heated coolant is then routed through the heat exchanger,
where the heat is dissipated to the air in the passenger compartment. The heater return line, in which the heating
water circulation pump is located, takes the coolant back to the coolant pump.
The heating water circulation pump ensures that the coolant is properly circulated.
The coolant flows through the heat exchanger permanently.
Depending upon the desired in-car temperature, regulation is conducted over the blending air flaps, which are
operated by the blending air flap actuator motor.
Heater operation with heater booster in vehicles with OM 612.963
In vehicles equipped with direct-injection diesel engines, an electrical heater booster is additionally installed in
the evaporator housing downstream of the heat exchanger, in order to compensate the heater output deficit
which occurs in the case of certain operating conditions.
The 3 heating elements in the heater booster are supplied with current, as a result of which they are heated and
start to glow. As a result of the structural conditions, it is ensured that the drawn in fresh air flows directly past
the electric heater booster, and is therefore heated.
2001 Mercedes-Benz ML320
1998-2005 HVAC Climate Control - 163 Chassis
me
Saturday, October 02, 2010 3:23:16 PMPage 81 © 2006 Mitchell Repair Information Company, LLC.
Page 3326 of 4133
Refrigerant circuit
The refrigerant compressor serves to compresses the gaseous refrigerant which heats up during the process, is
then routed into the condenser and thus cooled down. After purification in the fluid reservoir the liquid
refrigerant is injected into the evaporator. The refrigerant is vaporized and cools down. The refrigerant
compressor intakes the refrigerant again which has turned gaseous through the heat absorption process.
TABLE OF CONTENTS, AUTOMATIC AIR CONDITIONING (AAC) FUNCTION DESCRIPTION - GF83.40-P-0999GI
MODEL 163 as of 1.9.01 with CODE (580a) Automatic air conditioning
Ventilation, function GF83.10-P-2000GI
Heater circuit function GF83.20-P-2003GH
Automatic air conditioning push-button control module, function GF83.40-P-2000GI
Rear ventilation control panel, function GF83.40-P-2007GI
Refrigerant circuit function GF83.40-P-2001GI
Temperature control, function GF83.57-P-2000GI
Heater booster (ZUH), function GF83.70-P-0005GH
Residual engine heat utilization system, function GF83.75-P-2000GI
Automatic air conditioning (AAC), function GF83.40-P-
0001GI
Ventilation system function GF83.10-P-
2000GI
Heater circuit function GF83.20-P-
2003GH
Automatic air conditioning push-button control module, function GF83.40-P-
2000GI
Rear ventilation control panel, function GF83.40-P-
2007GI
Refrigerant circuit function GF83.40-P-
2001GI
Temperature control, function GF83.57-P-
2000GI
Heater booster (ZUH), function Engine
612.963GF83.70-P-
0005GH
Start heater operation, function Engine
612.963GF83.70-P-
2000GH
End heater operation, function Engine
612.963GF83.70-P-
2002GH
Regulate heater operation, function Engine
612.963GF83.70-P-
2004GH
Cancel heater operation, function Engine GF83.70-P-
2001 Mercedes-Benz ML320
1998-2005 HVAC Climate Control - 163 Chassis
me
Saturday, October 02, 2010 3:23:16 PMPage 82 © 2006 Mitchell Repair Information Company, LLC.
Page 3327 of 4133
AUTOMATIC AIR CONDITIONING PUSH-BUTTON CONTROL MODULE, FUNCTION - GF83.40-P-2000GI
MODEL 163 as of 1.9.01 with CODE (580a) Automatic air conditioning
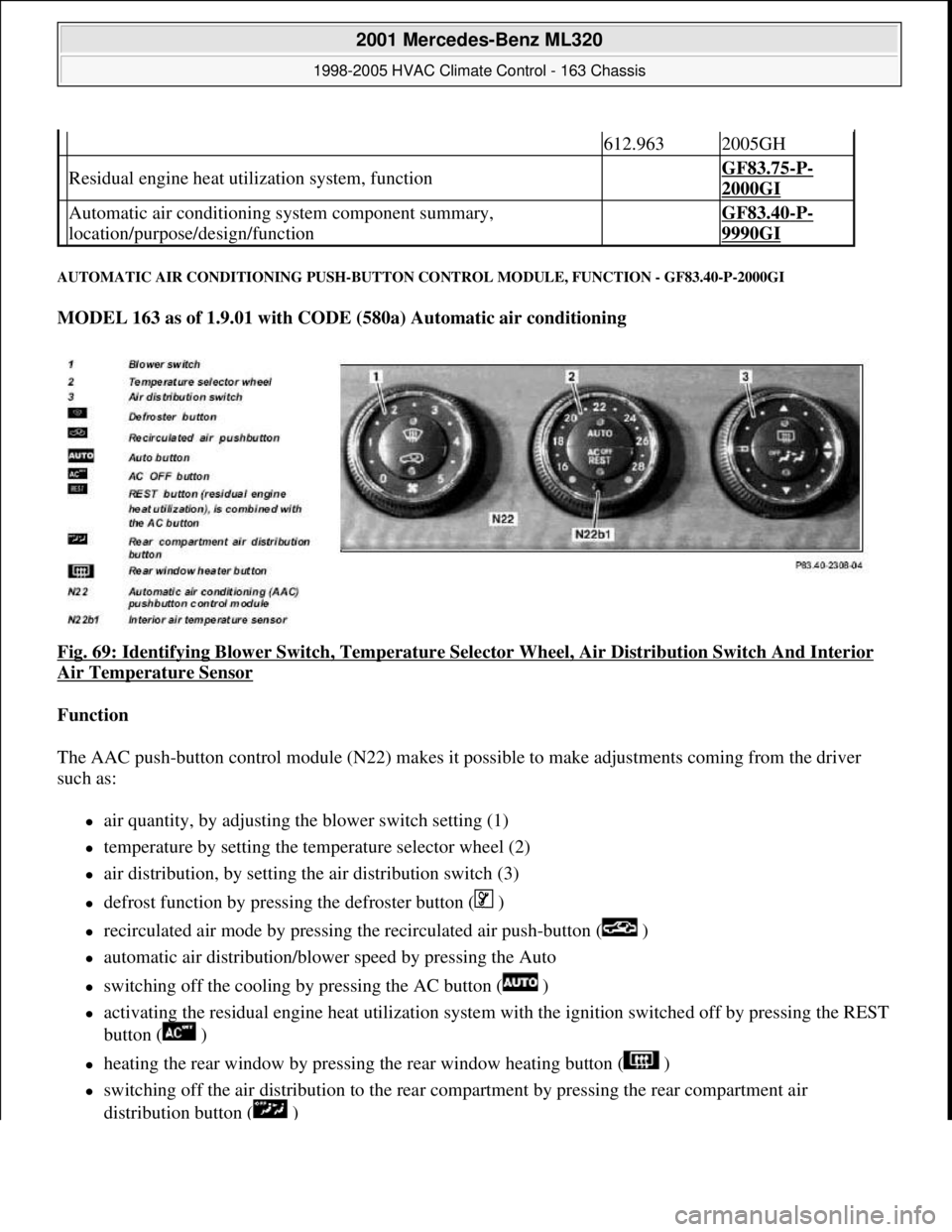
Fig. 69: Identifying Blower Switch , Temperature Selector Wheel, Air Di stribution Switch And Interior
Air Temperature Sensor
Function
The AAC push-button control module (N 22) makes it possible to make adjustments coming from the driver
such as:
air quantity, by adjusting the blower switch setting (1)
temperature by setting the temp erature selector wheel (2)
air distribution, by setting the air distribution switch (3)
defrost function by pressing the defroster button ( )
recirculated air mode by pressing th e recirculated air push-button ( )
automatic air distribution/blower speed by pressing the Auto
switching off the cooling by pressing the AC button ( )
activating the residual engine heat ut ilization system with the ignition switched of f by pressing the REST
button ( )
heating the rear window by pressing the rear window heating button ( )
switching off the air distribution to the rear compartment by pressing the rear compartment air
distribution button ( )
612.9632005GH
Residual engine heat util ization system, function GF83.75-P-
2000GI
Automatic air conditioning sy stem component summary,
location/purpose/design/function GF83.40-P-
9990GI
2001 Mercedes-Benz ML320
1998-2005 HVAC Climate Control - 163 Chassis
me
Saturday, October 02, 2010 3:23:16 PMPage 83 © 2006 Mitchell Repair Information Company, LLC.
Page 3329 of 4133
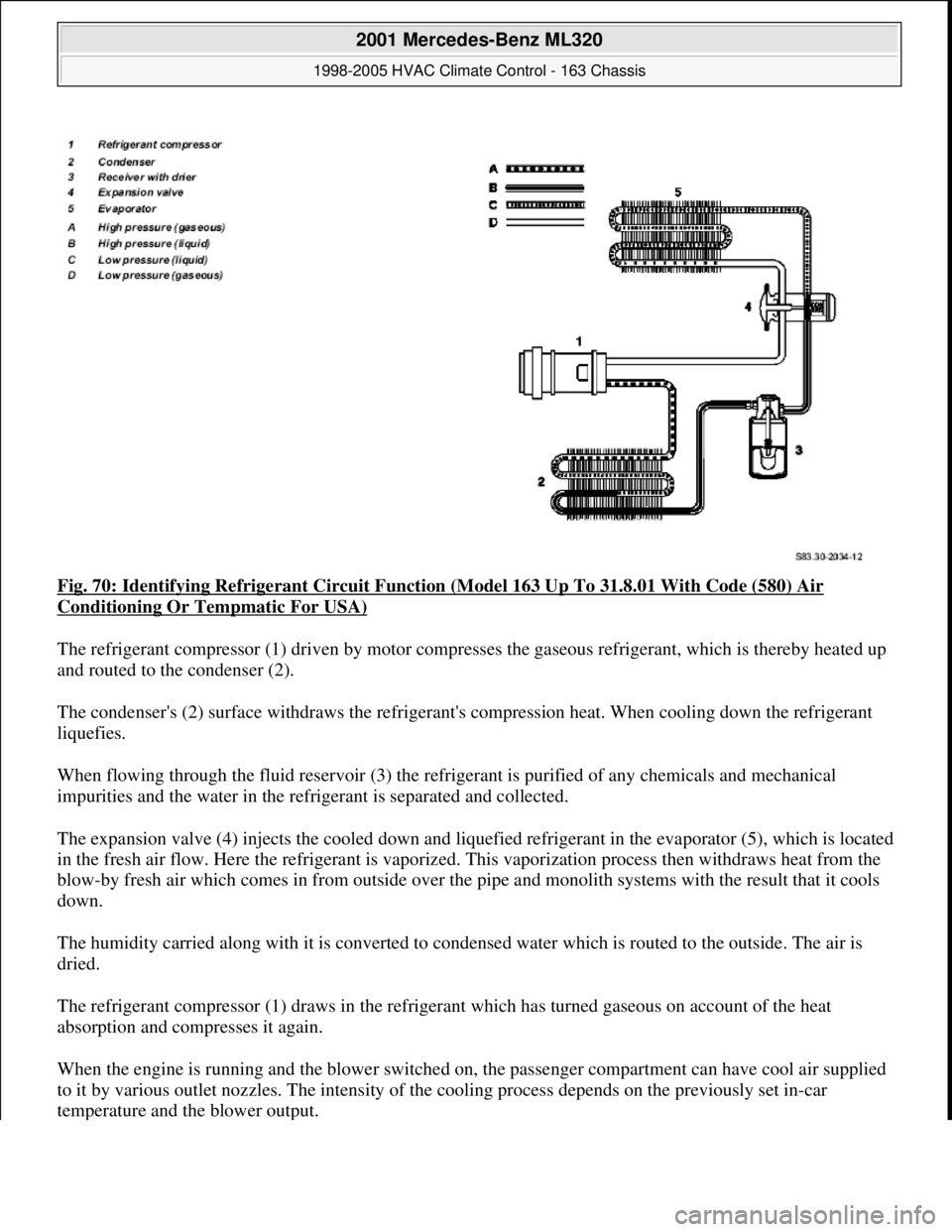
Fig. 70: Identifying Refrigerant Circuit Function (Model 163 Up To 31.8.01 With Code (580) Air
Conditioning Or Tempmatic For USA)
The refrigerant compressor (1) driven by motor compresses the gaseous refrigerant, which is thereby heated up
and routed to the condenser (2).
The condenser's (2) surface withdraws the refrigerant's compression heat. When cooling down the refrigerant
liquefies.
When flowing through the fluid reservoir (3) the refrigerant is purified of any chemicals and mechanical
impurities and the water in the refrigerant is separated and collected.
The expansion valve (4) injects the cooled down and liquefied refrigerant in the evaporator (5), which is located
in the fresh air flow. Here the refrigerant is vaporized. This vaporization process then withdraws heat from the
blow-by fresh air which comes in from outside over the pipe and monolith systems with the result that it cools
down.
The humidity carried along with it is converted to condensed water which is routed to the outside. The air is
dried.
The refrigerant compressor (1) draws in the refrigerant which has turned gaseous on account of the heat
absorption and compresses it again.
When the engine is running and the blower switched on, the passenger compartment can have cool air supplied
to it by various outlet nozzles. The intensity of the cooling process depends on the previously set in-car
temperature and the blower output.
2001 Mercedes-Benz ML320
1998-2005 HVAC Climate Control - 163 Chassis
me
Saturday, October 02, 2010 3:23:16 PMPage 85 © 2006 Mitchell Repair Information Company, LLC.
Page 3330 of 4133
REFRIGERANT CIRCUIT, FUNCTION - GF83.40-P-2001GI
MODEL 163 as of 1.9.01 with code (580a) Automatic air conditioning
Auxiliary fan, location/task/function Engines 111.977, 112.942GF83.40-P-
2162GH
Electric fan motor/air conditioning,
location/task/function Engines 113.942/981 and
612.963GF83.40-P-
2151GH
Condenser position/task/function GF83.40-P-
2152GC
Evaporator, location/purpose/design/function GF83.40-P-
2121GC
Fluid reservoir (TAC), location/task/function GF83.30-P-
2120GC
Expansion valve, location/task/design/function GF83.40-P-
2123GC
Refrigerant pressure sensor, location/task/ function GF83.40-P-
2156GH
Refrigerant compressor, location/task/design/
function GF83.55-P-
2100GH
Air conditioning control module, location/task/
function GF83.30-P-
2102GH
All-activity module, location/task/design/ function GF54.21-P-
4110GH
Extended-activity module, position/task GF54.21-P-
4106GH
Extended-activity module, location/task/designas of 1.12.99GF54.21-P-
4107GK
CDI control module, location/task/function Engine 612.963GF07.16-P-
3102IA
2001 Mercedes-Benz ML320
1998-2005 HVAC Climate Control - 163 Chassis
me
Saturday, October 02, 2010 3:23:16 PMPage 86 © 2006 Mitchell Repair Information Company, LLC.
Page 3331 of 4133
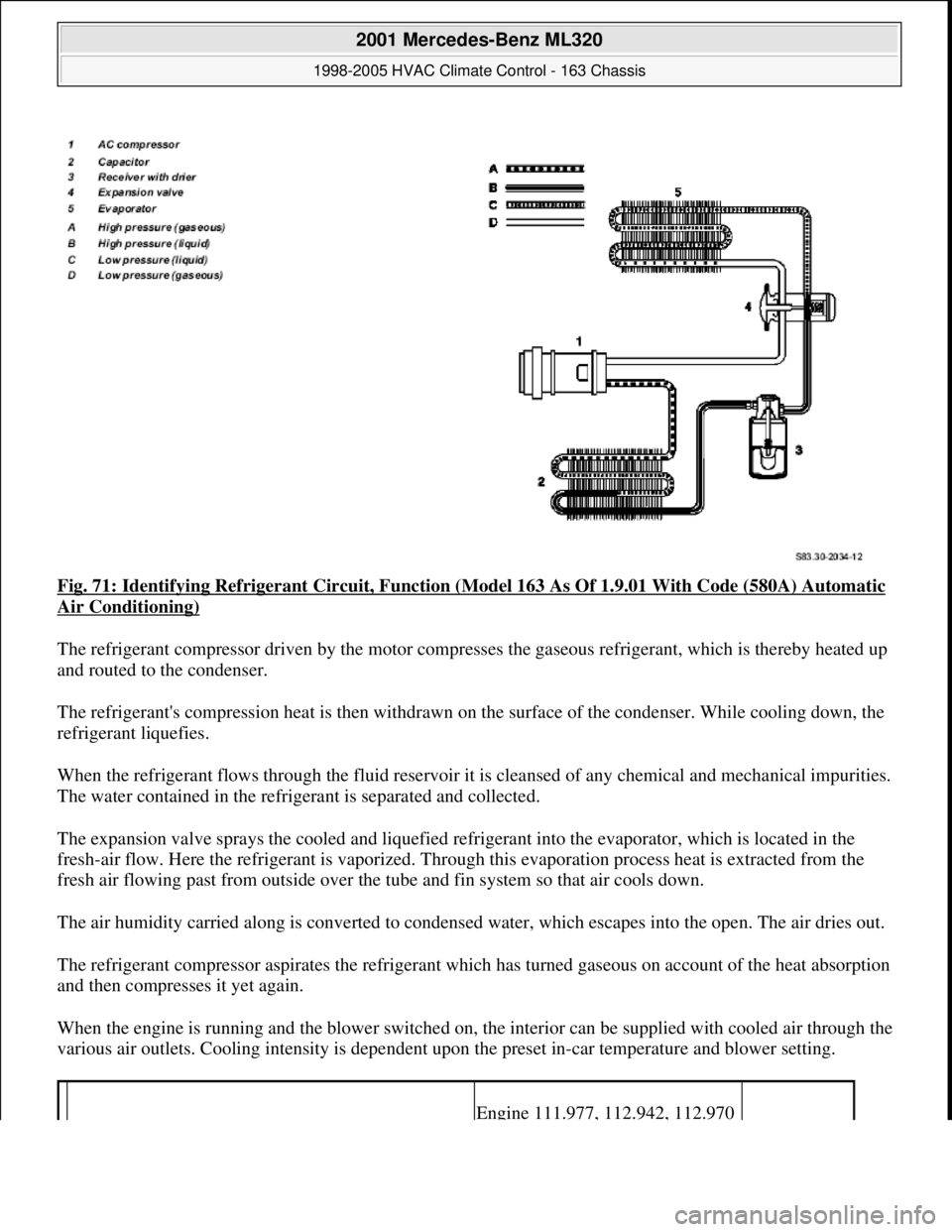
Fig. 71: Identifying Refrigerant Circuit, Function (Model 163 As Of 1.9.01 With Code (580A) Automatic
Air Conditioning)
The refrigerant compressor driven by the motor compresses the gaseous refrigerant, which is thereby heated up
and routed to the condenser.
The refrigerant's compression heat is then withdrawn on the surface of the condenser. While cooling down, the
refrigerant liquefies.
When the refrigerant flows through the fluid reservoir it is cleansed of any chemical and mechanical impurities.
The water contained in the refrigerant is separated and collected.
The expansion valve sprays the cooled and liquefied refrigerant into the evaporator, which is located in the
fresh-air flow. Here the refrigerant is vaporized. Through this evaporation process heat is extracted from the
fresh air flowing past from outside over the tube and fin system so that air cools down.
The air humidity carried along is converted to condensed water, which escapes into the open. The air dries out.
The refrigerant compressor aspirates the refrigerant which has turned gaseous on account of the heat absorption
and then compresses it yet again.
When the engine is running and the blower switched on, the interior can be supplied with cooled air through the
various air outlets. Cooling intensity is dependent upon the preset in-car temperature and blower setting.
Engine 111.977, 112.942, 112.970
2001 Mercedes-Benz ML320
1998-2005 HVAC Climate Control - 163 Chassis
me
Saturday, October 02, 2010 3:23:16 PMPage 87 © 2006 Mitchell Repair Information Company, LLC.
Page 3332 of 4133
REAR VENTILATION CO NTROL PANEL, FUNCTION - GF83.40-P-2007GI
MODEL 163 as of 1.9.01 with CODE (580a) Automatic air conditioning
N72/2s3 Rear ventilation control panel
Auto button
Air distribution button
Blower button
Auxiliary fan, location/purpose/function
with code 580 up to 31.08.01
Engine 112.942, 112.970 with
code 580a as of 01.09.01GF83.40-P-
2162GH
Engine and AC electric su ction fan with integrated
control, location/purpose/function
Engine 113.942 with code 580a up
to 31.08.01
Engine 113.981, 113.965, 612.963,
628.963 with code 580a as of
01.09.01
GF83.40-P-
2172GI
Condenser, location/purpose/function GF83.40-P-
2152GC
Evaporator location/purpose/design/function GF83.40-P-
2121GC
Fluid reservoir, location/purpose/function GF83.40-P-
2153GI
Expansion valve, locati on/purpose/design/ function GF83.40-P-
2123GC
Refrigerant pressure and temperature sensor,
location/purpose/function GF83.40-P-
2171GI
Refrigerant compressor, location/purpose/
design/function GF83.55-P-
2100P
Control valve, location/purpose/function GF83.55-P-
2102P
Belt pulley, location/ purpose/design/function GF83.55-P-
2103P
Pressure relief valve, location/purpose/function GF83.55-P-
2104P
2001 Mercedes-Benz ML320
1998-2005 HVAC Climate Control - 163 Chassis
me
Saturday, October 02, 2010 3:23:16 PMPage 88 © 2006 Mitchell Repair Information Company, LLC.