1996 CHRYSLER VOYAGER belt
[x] Cancel search: beltPage 1168 of 1938

(4) Install drive belt Refer to Group 7, Cooling
System for installation procedure.
(5) Install inner splash shield and wheel.
(6) Lower vehicle and connect negative cable to
battery.
CRANKSHAFT OIL SEALÐREAR
REMOVAL
(1) Insert a 3/16 flat bladed pry tool between the
dust lip and the metal case of the crankshaft seal.
Angle the pry tool (Fig. 69) through the dust lip
against metal case of the seal. Pry out seal.
CAUTION: Do not permit the pry tool blade to con-
tact crankshaft seal surface. Contact of the pry toolblade against crankshaft edge (chamfer) is permit-
ted.
INSTALLATION
CAUTION: If burr or scratch is present on the
crankshaft edge (chamfer), cleanup with 400 grit
sand paper to prevent seal damage during installa-
tion of new seal.
(1) Place Special Tool 6926-1 magnetic pilot tool on
crankshaft (Fig. 70).
(2) Lightly coat seal O.D. with MopartStud N'
Bearing Mount Adhesive or equivalent.
(3) Place seal over Special Tool 6926-1 Pilot. Using
Special Tool 6926-2 Installer with C-4171 Handle,
drive seal into the retainer housing (Fig. 70).
REAR CRANKSHAFT SEAL RETAINER
When retainer removal is required, remove
retainer and clean engine block and retainer of old
gasket. Make sure surfaces are clean and free of oil.
Fig. 66 Front Crankshaft Oil SealÐRemoval
Fig. 67 Crankshaft Oil SealÐInstallation
Fig. 68 Crankshaft DamperÐInstallation
Fig. 69 Rear Crankshaft Oil SealÐRemoval
9 - 118 3.3/3.8L ENGINENS
REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION (Continued)
Page 1179 of 1938

ENGINE
CONTENTS
page page
2.0L SOHC ENGINE...................... 12.5L VM DIESEL....................... 40
2.0L SOHC ENGINE
INDEX
page page
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
ENGINE COMPONENTS.................. 3
ENGINE IDENTIFICATION................. 1
ENGINE LUBRICATION SYSTEM............ 2
GENERAL SPECIFICATION................ 2
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
CHECKING ENGINE OIL PRESSURE........ 3
SERVICE PROCEDURES
CRANKSHAFT END PLAY................. 6
CYLINDER BORE AND PISTON SIZING....... 4
FITTING CONNECTING RODS.............. 5
FITTING CRANKSHAFT BEARINGS.......... 6
FITTING PISTON RINGS.................. 4
REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION
CAMSHAFT OIL SEAL................... 12
CAMSHAFT............................ 7
CRANKSHAFT OIL SEALÐREAR........... 20
CRANKSHAFT......................... 21
CYLINDER HEAD COVER................. 6
CYLINDER HEAD....................... 10
FRONT CRANKSHAFT OIL SEAL........... 18
OILFILTER ........................... 24
OIL FILTER ADAPTER................... 24OILPAN .............................. 17
OIL PUMP............................ 25
PISTON AND CONNECTING ROD.......... 25
ROCKER ARM/HYDRAULIC LASH ADJUSTER . . 8
SPARK PLUG TUBE...................... 7
TIMING BELT COVER................... 11
TIMING BELT SYSTEM.................. 13
VALVE SEALS AND SPRINGS IN VEHICLE . . . 10
VIBRATION DAMPER.................... 28
DISASSEMBLY AND ASSEMBLY
OIL PUMP............................ 29
VALVE SERVICE WITH THE CYLINDER HEAD
REMOVED.......................... 29
CLEANING AND INSPECTION
CYLINDER BLOCK AND BORE............ 34
CYLINDER HEAD AND CAMSHAFT
JOURNALS.......................... 32
OIL PUMP............................ 32
SPECIFICATIONS
ENGINE 2.0L SOHC..................... 34
TORQUE CHART 2.0L SOHC.............. 36
SPECIAL TOOLS
ENGINE 2.0L SOHC..................... 36
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
ENGINE IDENTIFICATION
The engine identification number is located on the
left rear of the cylinder block behind starter (Fig. 1).
Fig. 1 Engine Identification SOHC
NS/GSENGINE 9 - 1
Page 1181 of 1938

SPLASH LUBRICATION
Oil returning to the pan from pressurized compo-
nents supplies lubrication to the valve stems. Cylin-
der bores and wrist pins are splash lubricated from
directed slots on the connecting rod thrust collars.
ENGINE COMPONENTS
CYLINDER BLOCK AND BEDPLATE ASSEM-
B LY:A partial open deck is used for cooling and
weight reduction with water pump molded into the
block. Nominal wall thickness is 4 mm. The bedplate
incorporates main bearing caps. Rear seal retainer is
integral with the block.
CRANKSHAFT:A nodular cast iron crankshaft is
used. The engine has 5 main bearings, with number
3 flanged to control thrust. The 52 mm diameter
main and 48 mm diameter crank pin journals (all)
have undercut fillet radiuses that are deep rolled for
added strength. To optimize bearing loading 8 coun-
terweights are used. Hydrodynamic seals provide end
sealing, where the crankshaft exits the block.
Anaerobic gasket material is used for parting line
sealing. A sintered iron timing belt sprocket is
mounted on the crankshaft nose. This sprocket trans-
mits crankshaft movement, via timing belt to the
camshaft sprocket providing timed valve actuation.
PISTONS:The SOHC EngineDOES NOThave
provision for a free wheeling valve train. Non free
wheeling valve train means, in the event of a broken
timing belt Pistons will contact the Valves. All
engines use pressed-in piston pins to attach forged
powdered metal connecting rods. The connecting rods
are a cracked cap design and are not repairable. Hexhead cap screw are used to provide alignment and
durability in the assembly. Pistons And Connecting
rods are serviced as an assembly.
PISTON RINGS:The piston rings include a
molybdenum faced top ring for reliable compression
sealing and a taper faced intermediate ring for addi-
tional cylinder pressure control. Oil Control Ring
Package consist of 2 steel rails and a expander
spacer.
CYLINDER HEADÐSOHC:It features a Single
Over Head Camshaft, four-valves per cylinder cross
flow design. The valves are arranged in two inline
banks, with the two intake per cylinder facing
toward the radiator. The exhaust valves facing
toward the dash panel. Rocker arm shafts mount
directly to the cylinder head. It incorporates powder
metal valve guides and seats. The hollow rocker arm
shafts supplies oil to the hydraulic lash adjusters,
camshaft and valve mechanisms.
CAMSHAFTÐSOHC:The nodular iron camshaft
has five bearing journals and 3 cam lobes per cylin-
der. Provision for cam position sensor on the cam at
the rear of cylinder head which also acts as thrust
plate. A hydrodynamic oil seal is used for oil control
at the front of the camshaft.
VALVESÐSOHC:Four valves per cylinder are
actuated by roller rocker arms/hydraulic lash adjust-
ers assemblies which pivot on rocker arm shafts. All
valves have 6 mm diameter chrome plated valve
stems. The valve train has 33 mm (1.299 inch) diam-
eter intake valves and 28 mm (1.10 inch) diameter
exhaust valves. Viton rubber valve stem seals are
integral with spring seats. Valve springs, spring
retainers, and locks are conventional design.
INTAKE MANIFOLD:The intake manifold is a
molded plastic composition, attached to the cylinder
head with ten fasteners. This long branch design
enhances low and mid-range torque.
EXHAUST MANIFOLD:The exhaust manifold is
made of nodular cast iron for strength and high tem-
peratures. Exhaust gasses exit through a machined,
articulated joint connection to the exhaust pipe.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
CHECKING ENGINE OIL PRESSURE
(1) Remove oil pressure switch and install gauge
assembly C-3292 with adaptor.
(2) Run engine until thermostat opens.
CAUTION: If oil pressure is 0 at idle, Do Not per-
form the 3000 RPM test in the next step.
(3) Oil Pressure:Curb Idle25 kPa (4 psi) mini-
mum3000 RPM170-550 kPa (25-80 psi).
Fig. 2 Engine Lubrication SystemÐ SOHC
NS/GSENGINE 9 - 3
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION (Continued)
Page 1184 of 1938

FITTING CRANKSHAFT BEARINGS
Refer to Measuring Main Bearing Clearance in
Standard Service Procedures. Refer to Crankshaft
Specification Chart for specifications.
CRANKSHAFT END PLAY
DIAL INDICATOR METHOD
(1) Mount a dial indicator to front of engine, locat-
ing probe on nose of crankshaft (Fig. 9).
(2) Move crankshaft all the way to the rear of its
travel.(3) Zero the dial indicator.
(4) Move crankshaft all the way to the front and
read the dial indicator. Refer to Crankshaft Specifi-
cation Chart for specifications.
FEELER GAGE METHOD
(1) Move crankshaft all the way to the rear of its
travel using a lever inserted between a main bearing
cap and a crankshaft cheek, using care not to dam-
age any bearing surface. Donotloosen main bearing
cap.
(2) Use a feeler gauge between number three
thrust bearing and machined crankshaft surface to
determine end play.
REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION
CYLINDER HEAD COVER
REMOVAL
(1) Remove ignition coil pack (Fig. 10).
(2) Remove the cylinder head cover bolts.
(3) Remove cylinder head cover from cylinder
head.
INSTALLATION
Before installation, clean cylinder head and cover
mating surfaces. Make certain the cylinder head
cover mating surface is flat.
(1) Install new valve cover gasket.
CAUTION: Do not allow oil or solvents to contact
the timing belt as they can deteriorate the rubber
and cause tooth skipping.
(2) Install cover assembly to head and tighten fas-
teners to 12 N´m (105 in. lbs.).
(3) Install ignition coil pack. Tighten fasteners to
23 N´m (200 in. lbs.).
CONNECTING ROD SPECIFICATION CHART
Connecting Rod Bearing Oil Clearance
New Part: 0.026 - 0.059 mm (0.001 - 0.0023 in.)
Wear Limit: 0.075 mm (0.003 in.)
Connecting Rod Side Clearance
New Part: 0.13 - 0.38 mm (0.005 - 0.015 in.)
Wear Limit: 0.40 mm (0.016 in.)
CRANKSHAFT SPECIFICATION CHART
Crankshaft End-PlayNew Part: 0.09 - 0.24 mm (0.0035 - 0.0094 in.)
Wear Limit: 0.37 mm (0.015 in.)
Main Bearing ClearanceNew Part: 0.022 - 0.062 mm (0.0008 - 0.0024 in.)
Connecting Rod Bearing ClearanceNew Part: 0.026 - 0.059 mm (0.001 - 0.0023 in.)
Wear Limit: 0.075 mm (0.003 in.)
Main Bearing Journal DiameterStandard: 52.00060.008 mm (2.047260.0003 in.)
1st Undersize: 51.98360.008 mm
(2.046660.0003 in.)
Connecting Rod Journal DiameterStandard: 48.00060.008 mm (1.889760.0003 in.)
1st Undersize: 47.98360.008 mm
(1.889160.0003 in.)
Fig. 9 Checking Crankshaft End PlayÐ Dial
Indicator
9 - 6 ENGINENS/GS
SERVICE PROCEDURES (Continued)
Page 1185 of 1938

SPARK PLUG TUBE
(1) Remove valve cover. Refer to procedure out-
lined in this section.
(2) Using locking pliers remove the tube from the
cylinder head (Fig. 11). Discard old tube.
(3) Clean area around spark plug with Mopart
parts cleaner or equivalent.
(4) Apply MopartStud and Bearing Mount or
equivalent to a new tube approximately 1 mm from
theendina3mmwide area.
(5) Install sealer end of tube into the cylinder
head. Then carefully install the tube using a hard-
wood block and mallet until the tube is seated into
the bottom of the bore.
(6) Install valve cover. Refer to procedure outlined
in this section.
SPARK PLUG TUBE SEALS
The spark plug tube seals are located in the cylin-
der head cover (Fig. 12). These seals are pressed into
the cylinder head cover to seal the outside perimeterof the spark plug tubes. If these seals show signs of
hardness and/or cracking they should be replaced.
CAMSHAFT
NOTE: TO REMOVE CAMSHAFT THE CYLINDER
HEAD MUST BE REMOVED.
REMOVAL
(1) Perform fuel system pressure release procedure
before attempting any repairs.Refer to Group 14,
Fuel System
(2) Remove the cylinder head cover. Refer to proce-
dure outlined in this section.
(3) Mark rocker arm shaft assemblies so that they
are installed in their original positions.
(4) Remove rocker arm shaft bolts. Refer to proce-
dure outlined in this section.
(5) Remove timing belt, timing belt tensioner, and
camshaft sprocket. Refer to timing belt service out-
lined in this section.
(6) Remove inner timing belt cover.
(7) Remove cylinder head. Refer to procedure out-
lined in this section.
(8) Remove camshaft sensor and camshaft target
magnet.
(9) Remove camshaft from the rear of cylinder
head.
INSPECT CYLINDER HEAD FOR THE FOLLOWING:
NOTE:
²Check oil feed holes for blockage.
²Inspect cylinder head camshaft bearings for
wear, Refer to Cylinder Head, Inspection and Clean-
ing.
²Check camshaft bearing journals for scratches
and worn areas. If light scratches are present, they
may be removed with 400 grit sand paper. If deep
Fig. 10 Ingition Coil Pack
Fig. 11 Servicing Spark Plug Tubes
Fig. 12 Spark Plug Tube Seals
NS/GSENGINE 9 - 7
REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION (Continued)
Page 1186 of 1938

scratches are present, replace the camshaft and
check the cylinder head for damage. Replace the
cylinder head if worn or damaged. Check the lobes
for pitting and wear. If the lobes show signs of
wear, check the corresponding rocker arm roller for
wear or damage. Replace rocker arm/hydraulic lash
adjuster if worn or damaged. If lobes show signs of
pitting on the nose, flank or base circle; replace the
camshaft.
INSTALLATION
(1) Lubricate the camshaft journals with oil and
install camshaftwithoutrocker arm assemblies
installed.
(2) Install camshaft target magnet into the end of
the camshaft. Tighten mounting screw to 3.4 N´m (30
in. lbs.).
(3) Install camshaft position sensor and tighten
mounting screws to 9 N´m (80 in. lbs.).
(4) Measure camshaft end play using the following
procedure:
²Mount dial indicator C-3339 or equivalent, to a
stationary point on cylinder head (Fig. 13).
²Using a suitable tool, move camshaft to rear-
ward limits of travel.
²Zero the dial indicator.
²Move camshaft forward to limits of travel and
read dial indicator.
²End play travel: 0.13 - 0.33 mm (0.005 - 0.013
in.).
(5) Install front camshaft seal. Camshaft must be
installed before the camshaft seal is installed. Refer
to procedure outlined in this section.
(6) Install cylinder head. Refer to procedure out-
lined in this section.
(7) Install camshaft sprocket and tighten to 115
N´m (85 ft. lbs.).
(8) Install inner timing belt cover.(9) Install timing belt tensioner and timing belt.
Refer to procedures outlined in this section.
(10) Install rocker arm assemblies in correct order
as removed. Tighten the rocker arm assemblies in
sequence shown in (Fig. 14) to 28 N´m (250 in. lbs.).
(11) Install cylinder head cover and tighten fasten-
ers to 12 N´m (105 in. lbs.).
(12) Install ignition coil pack and ignition cables.
(13) Perform camshaft and crankshaft timing
relearn procedure as follows:
²Connect the DRB scan tool to the data link
(diagnostic) connector. This connector is located in
the passenger compartment; at the lower edge of
instrument panel; near the steering column.
²Turn the ignition switch on and access the ªmis-
cellaneousº screen.
²Select ªre-learn cam/crankº option and follow
directions on DRB screen.
ROCKER ARM/HYDRAULIC LASH ADJUSTER
REMOVAL
(1) Remove valve cover using procedure outlined in
this section.
(2) Identify the rocker arm shaft assemblies before
removal.
(3) Loosen the attaching fasteners. Remove rocker
arm shaft assemblies from cylinder head.
(4) Identify the rocker arms spacers and retainers
for reassembly. Disassemble the rocker arm assem-
blies by removing the attaching bolts from the shaft
(Fig. 15).
(5) Slide the rocker arms and spacers off the shaft.
Keep the spacers and rocker arms in the same loca-
tion for reassembly.
Fig. 13 Camshaft End Play
Fig. 14 Rocker Arm Shaft Tightening Sequence
9 - 8 ENGINENS/GS
REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION (Continued)
Page 1187 of 1938

NOTE: Inspect the rocker arm for scoring, wear on
the roller or damage to the rocker arm (Fig. 16)
Replace if necessary. Check the location where the
rocker arms mount to the shafts for wear or dam-
age. Replace if damaged or worn. The rocker arm
shaft is hollow and is used as a lubrication oil duct.
Check oil holes for clogging with small wire, clean
as required. Lubricate the rocker arms and spacers.
Install onto shafts in their original position (Fig. 15).
INSTALLATION
CAUTION: Set crankshaft to 3 notches before TDC
before installing rocker arm shafts. Refer to Timing
Belt System and Camshaft Seal Service of this sec-
tion for procedure.
(1) Install rocker arm/hydraulic lash adjuster
assembly making sure that adjusters are at leastpartially full of oil. This is indicated by little or no
plunger travel when the lash adjuster is depressed. If
there is excessive plunger travel. Place the rocker
arm assembly into clean engine oil and pump the
plunger until the lash adjuster travel is taken up. If
travel is not reduced, replace the assembly. Hydraulic
lash adjuster and rocker arm are serviced as an
assembly.
(2) Install rocker arm and shaft assemblies with
NOTCH in the rocker arm shafts pointing up and
toward the timing belt side of the engine (Fig. 17).
Install the retainers in their original positions on the
exhaust and intake shafts (Fig. 15).
CAUTION: When installing the intake rocker arm
shaft assembly be sure that the plastic spacers do
not interfere with the spark plug tubes. If the spac-
ers do interfere rotate until they are at the proper
angle. To avoid damaging the spark plug tubes, do
not attempt rotating the spacers by forcing down
the shaft assembly.
(3) Tighten bolts to 28 N´m (250 in. lbs.) in
sequence shown in (Fig. 18).
Fig. 15 Rocker Arm Shaft Assemblies
Fig. 16 Rocker Arm Assemblies
Fig. 17 Rocker Arm Shaft Notches
Fig. 18 Rocker Arm Shaft Tightening Sequence
NS/GSENGINE 9 - 9
REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION (Continued)
Page 1188 of 1938
HYDRAULIC LASH ADJUSTER NOISE
A tappet-like noise may be produced from several
items. Refer to Lash Adjuster Noise - Diagnosis in
Standard Service Procedures, outlined in this Group.
Lash adjusters are replaced with the rocker
arm as an assembly.
VALVE SEALS AND SPRINGS IN VEHICLE
REMOVAL
(1) Remove rocker arm shafts assemblies as previ-
ously outlined in this section.
(2) Rotate crankshaft until piston is at TDC on
compression.
(3) With air hose attached to adapter tool installed
in spark plug hole, apply 90-120 psi air pressure.
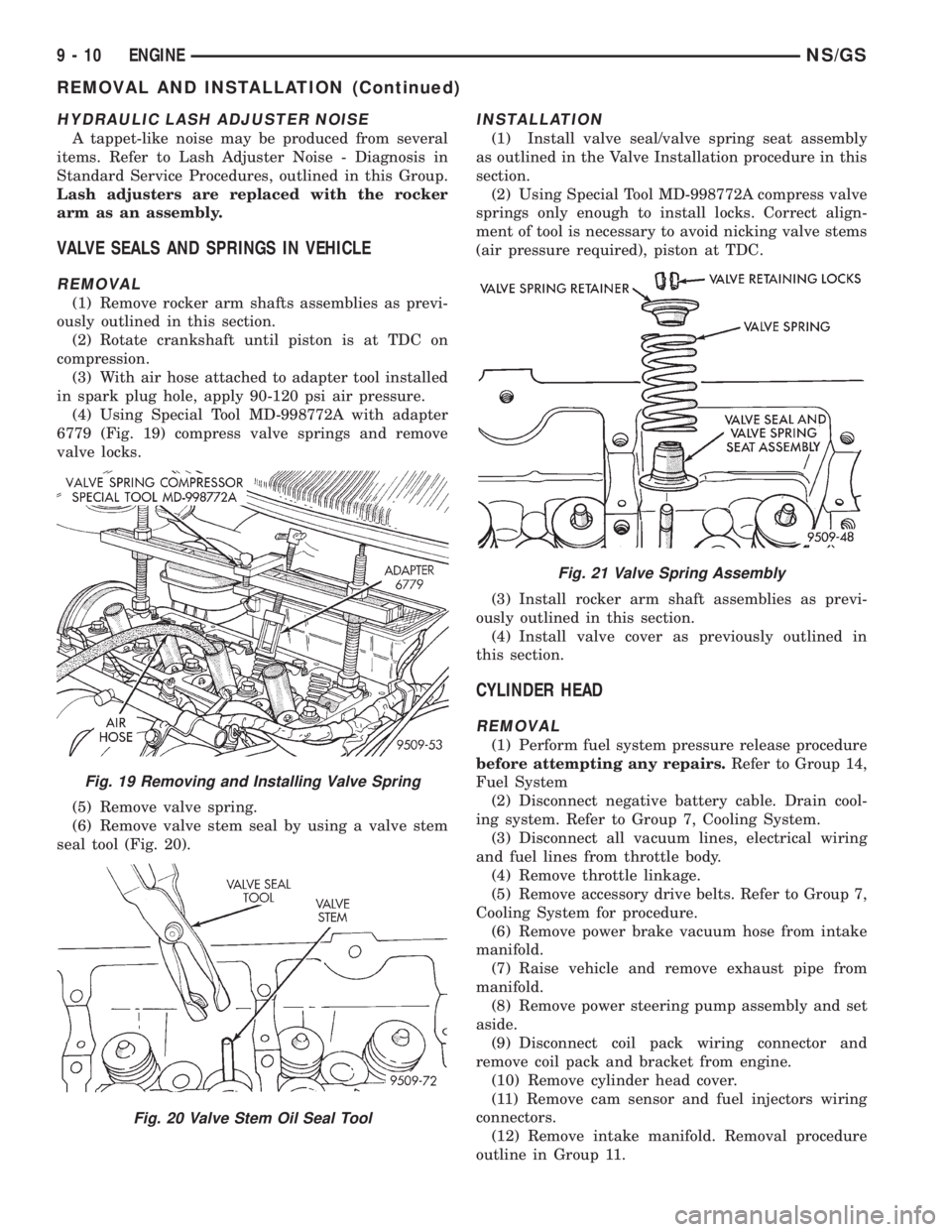
(4) Using Special Tool MD-998772A with adapter
6779 (Fig. 19) compress valve springs and remove
valve locks.
(5) Remove valve spring.
(6) Remove valve stem seal by using a valve stem
seal tool (Fig. 20).
INSTALLATION
(1) Install valve seal/valve spring seat assembly
as outlined in the Valve Installation procedure in this
section.
(2) Using Special Tool MD-998772A compress valve
springs only enough to install locks. Correct align-
ment of tool is necessary to avoid nicking valve stems
(air pressure required), piston at TDC.
(3) Install rocker arm shaft assemblies as previ-
ously outlined in this section.
(4) Install valve cover as previously outlined in
this section.
CYLINDER HEAD
REMOVAL
(1) Perform fuel system pressure release procedure
before attempting any repairs.Refer to Group 14,
Fuel System
(2) Disconnect negative battery cable. Drain cool-
ing system. Refer to Group 7, Cooling System.
(3) Disconnect all vacuum lines, electrical wiring
and fuel lines from throttle body.
(4) Remove throttle linkage.
(5) Remove accessory drive belts. Refer to Group 7,
Cooling System for procedure.
(6) Remove power brake vacuum hose from intake
manifold.
(7) Raise vehicle and remove exhaust pipe from
manifold.
(8) Remove power steering pump assembly and set
aside.
(9) Disconnect coil pack wiring connector and
remove coil pack and bracket from engine.
(10) Remove cylinder head cover.
(11) Remove cam sensor and fuel injectors wiring
connectors.
(12) Remove intake manifold. Removal procedure
outline in Group 11.
Fig. 19 Removing and Installing Valve Spring
Fig. 20 Valve Stem Oil Seal Tool
Fig. 21 Valve Spring Assembly
9 - 10 ENGINENS/GS
REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION (Continued)