1995 JEEP YJ length
[x] Cancel search: lengthPage 1344 of 2158

VALVE COMPONENT REPLACEÐCYLINDER HEAD
NOT REMOVED
ROCKER ARMS AND PUSH RODS
This procedure can be done with the engine in or
out of the vehicle.
REMOVAL
(1) Remove the engine cylinder head cover.
(2) Remove the capscrews at each bridge and pivot
assembly (Fig. 2). Alternately loosen the capscrews
one turn at a time to avoid damaging the bridges.
(3) Check for rocker arm bridges which are causing
misalignment of the rocker arm to valve tip area.
(4) Remove the bridges, pivots and corresponding
pairs of rocker arms (Fig. 2). Place them on a bench
in the same order as removed.
(5) Remove the push rods and place them on a
bench in the same order as removed.
CLEANING
Clean all the components with cleaning solvent.
Use compressed air to blow out the oil passages in
the rocker arms and push rods.
INSPECTION
Inspect the pivot surface area of each rocker arm.
Replace any that are scuffed, pitted, cracked or ex-
cessively worn.
Inspect the valve stem tip contact surface of each
rocker arm and replace any rocker arm that is deeply
pitted.
Inspect each push rod end for excessive wear and
replace as required. If any push rod is excessivelyworn because of lack of oil, replace it and inspect the
corresponding hydraulic tappet for excessive wear.
Inspect the push rods for straightness by rolling
them on a flat surface or by shining a light between
the push rod and the flat surface.
A wear pattern along the length of the push rod is
not normal. Inspect the engine cylinder head for ob-
struction if this condition exists.
INSTALLATION
(1) Lubricate the ball ends of the push rods with
Mopar Engine Oil Supplement, or equivalent and in-
stall push rods in their original locations. Ensure
that the bottom end of each push rod is centered in
the tappet plunger cap seat.
(2) Using Mopar Engine Oil Supplement, or equiv-
alent, lubricate the area of the rocker arm that the
pivot contacts. Install rocker arms, pivots and bridge
above each cylinder in their originally position.
(3) Loosely install the capscrews through each
bridge.
(4) At each bridge, tighten the capscrews alter-
nately, one turn at a time, to avoid damaging the
bridge. Tighten the capscrews to 28 Nzm (21 ft. lbs.)
torque.
(5) Install the engine cylinder head cover.
VALVE STEM SEAL AND SPRING REPLACEMENT
This procedure can be done with the engine cylin-
der head installed on the block.
REMOVAL
Each valve spring is held in place by a retainer and
a set of conical valve locks. The locks can be removed
only by compressing the valve spring.
(1) Remove the engine cylinder head cover.
(2) Remove capscrews, bridge and pivot assemblies
and rocker arms for access to each valve spring to be
removed.
(3) Remove push rods. Retain the push rods,
bridges, pivots and rocker arms in the same order
and position as removed.
(4) Inspect the springs and retainer for cracks and
possible signs of weakening.
(5) Remove the spark plug(s) adjacent to the cylin-
der(s) below the valve springs to be removed.
(6) Connect an air hose to the adapter and apply
air pressure slowly. Maintain at least 621 kPa (90
psi) of air pressure in the cylinder to hold the valves
against their seats. For vehicles equipped with an air
conditioner, use a flexible air adaptor when servicing
the No.1 cylinder.
(7) Tap the retainer or tip with a rawhide hammer
to loosen the lock from the retainer. Use Valve Spring
Compressor Tool MD-998772A to compress the spring
and remove the locks (Fig. 3).
(8) Remove valve spring and retainer (Fig. 3).
Fig. 2 Rocker Arm Assembly
J4.0L ENGINE 9 - 65
Page 1349 of 2158

(2) After refacing, a margin of at least 0.787 mm
(0.031 inch) must remain (Fig. 8). If the margin is
less than 0.787 mm (0.031 inch), the valve must be
replaced.
VALVE SEAT REFACING
(1) Install a pilot of the correct size in the valve
guide bore. Reface the valve seat to the specified an-
gle with a good dressing stone. Remove only enough
metal to provide a smooth finish.
(2) Use tapered stones to obtain the specified seat
width when required.
(3) Control valve seat runout to a maximum of
0.0635 mm (0.0025 in.) (Fig. 9).
VALVE STEM OIL SEAL REPLACEMENT
Valve stem oil seals are installed on each valve
stem to prevent rocker arm lubricating oil from en-
tering the combustion chamber through the valve
guide bores. One seal is marked INT (intake valve)
and the other is marked EXH (exhaust valve).
Replace the oil seals whenever valve service is per-
formed or if the seals have deteriorated.
VALVE GUIDES
The valve guides are an integral part of the engine
cylinder head and are not replaceable.
When the valve stem guide clearance is excessive,
the valve guide bores must be reamed oversize. Ser-
vice valves with oversize stems are available in 0.076
mm (0.003 inch) and 0.381 mm (0.015 inch) incre-
ments.
Corresponding oversize valve stem seals are also
available and must be used with valves having 0.381
mm (0.015 inch) oversize stems.
If the valve guides are reamed oversize, the
valve seats must be ground to ensure that the
valve seat is concentric to the valve guide.
VALVE STEM-TO-GUIDE CLEARANCE
MEASUREMENT
Valve stem-to-guide clearance may be measured by
either of the following two methods.
PREFERRED METHOD:
(1) Remove the valve from the head.
(2) Clean the valve stem guide bore with solvent
and a bristle brush.
(3) Insert a telescoping gauge into the valve stem
guide bore approximately 9.525 mm (.375 inch) from
the valve spring side of the head (Fig. 10).
(4) Remove and measure telescoping gauge with a
micrometer.
(5) Repeat the measurement with contacts length-
wise to engine cylinder head.
(6) Compare the crosswise to lengthwise measure-
ments to determine out-of-roundness. If the measure-
Fig. 10 Measurement of Valve Guide Bore Diameter
Fig. 8 Valve Facing Margin
Fig. 9 Measurement of Valve Seat Runout
9 - 70 4.0L ENGINEJ
Page 1358 of 2158

LUBRICATION SYSTEM
A gearÐtype positive displacement pump is
mounted at the underside of the block opposite the
No. 4 main bearing. The pump draws oil through the
screen and inlet tube from the sump at the rear of
the oil pan. The oil is driven between the drive and
idler gears and pump body, then forced through the
outlet to the block. An oil gallery in the block chan-
nels the oil to the inlet side of the full flow oil filter.
After passing through the filter element, the oil
passes from the center outlet of the filter through an
oil gallery that channels the oil up to the main gal-
lery which extends the entire length of the block.
Galleries extend downward from the main oil gal-
lery to the upper shell of each main bearing. The
crankshaft is drilled internally to pass oil from the
main bearing journals (except number 4 main bear-
ing journal) to the connecting rod journals. Each con-
necting rod bearing cap has a small squirt hole, oilpasses through the squirt hole and is thrown off as
the rod rotates. This oil throwoff lubricates the cam-
shaft lobes, distributor drive gear, cylinder walls, and
piston pins.
The hydraulic valve tappets receive oil directly
from the main oil gallery. Oil is provided to the cam-
shaft bearing through galleries. The front camshaft
bearing journal passes oil through the camshaft
sprocket to the timing chain. Oil drains back to the
oil pan under the number one main bearing cap.
The oil supply for the rocker arms and bridged
pivot assemblies is provided by the hydraulic valve
tappets which pass oil through hollow push rods to a
hole in the corresponding rocker arm. Oil from the
rocker arm lubricates the valve train components,
then passes down through the push rod guide holes
in the cylinder head past the valve tappet area, and
returns to the oil pan.
J4.0L ENGINE 9 - 79
Page 1421 of 2158

MULTI-PORT FUEL INJECTION (MFI)ÐCOMPONENT DESCRIPTION/SYSTEM
OPERATION
INDEX
page page
Air Cleaner.............................. 29
Air Conditioning (A/C) Clutch RelayÐPCM Output . 26
Air Conditioning (A/C) ControlsÐPCM Input...... 21
Auto Shutdown (ASD) RelayÐPCM Output...... 26
Automatic Shutdown (ASD) SenseÐPCM Input . . . 21
Battery VoltageÐPCM Input................. 21
Brake SwitchÐPCM Input................... 22
Camshaft Position SensorÐPCM Input......... 22
Crankshaft Position SensorÐPCM Input........ 22
Data Link ConnectorÐPCM Input............. 22
Data Link ConnectorÐPCM Output............ 27
EMR LampÐPCM Output................... 27
Engine Coolant Temperature SensorÐPCM Input . 23
Extended Idle SwitchÐPCM Input............. 23
Fuel InjectorsÐPCM Output................. 27
Fuel Pressure Regulator.................... 33
Fuel Pump RelayÐPCM Output.............. 27
Fuel Rail................................ 33
General Information....................... 19
Generator FieldÐPCM Output................ 27
Generator LampÐPCM Output............... 27
Idle Air Control (IAC) MotorÐPCM Output....... 27
Ignition Circuit SenseÐPCM Input............. 23
Ignition CoilÐPCM Output................... 28Intake Manifold Air Temperature SensorÐ
PCM Input............................. 22
Malfunction Indicator LampÐPCM Output....... 28
Manifold Absolute Pressure (MAP) SensorÐPCM
Input................................. 23
Open Loop/Closed Loop Modes of Operation..... 30
Oxygen (O2S) SensorÐPCM Input............ 24
Park/Neutral SwitchÐPCM Input.............. 24
Power Ground........................... 24
Power Steering Pressure SwitchÐPCM Input.... 24
Powertrain Control Module (PCM)............. 20
Radiator Fan RelayÐPCM Output............. 28
SCI ReceiveÐPCM Input................... 24
SCI TransmitÐPCM Output.................. 29
Sensor ReturnÐPCM Input.................. 25
Shift IndicatorÐPCM Output................. 29
Speed ControlÐPCM Input.................. 25
Speed ControlÐPCM Output................. 29
TachometerÐPCM Output................... 29
Throttle Body............................ 33
Throttle Position Sensor (TPS)ÐPCM Input...... 25
Torque Converter Clutch RelayÐPCM Output.... 29
Vehicle Speed SensorÐPCM Input............ 25
GENERAL INFORMATION
All 2.5L 4-cylinder and 4.0L 6-cylinder engines are
equipped with sequential Multi-Port Fuel Injection
(MFI). The MFI system provides precise air/fuel ra-
tios for all driving conditions.
The Powertrain Control Module (PCM) operates
the fuel system. The PCM was formerly referred to
as the SBEC or engine controller. The PCM is a pre-
programmed, dual microprocessor digital computer. It
regulates ignition timing, air-fuel ratio, emission con-
trol devices, charging system, speed control, air con-
ditioning compressor clutch engagement and idle
speed. The PCM can adapt its programming to meet
changing operating conditions.
Powertrain Control Module (PCM) Inputsrep-
resent the instantaneous engine operating conditions.
Air-fuel mixture and ignition timing calibrations for
various driving and atmospheric conditions are pre-
programmed into the PCM. The PCM monitors and
analyzes various inputs. It then computes engine fuel
and ignition timing requirements based on these in-
puts. Fuel delivery control and ignition timing will
then be adjusted accordingly.
Other inputs to the PCM are provided by the brake
light switch, air conditioning select switch and the
speed control switches. All inputs to the PCM are
converted into signals.
Electrically operated fuel injectors spray fuel inprecise metered amounts into the intake port directly
above the intake valve. The injectors are fired in a
specific sequence by the PCM. The PCM maintains
an air/fuel ratio of 14.7 to 1 by constantly adjusting
injector pulse width. Injector pulse width is the
length of time that the injector opens and sprays fuel
into the chamber. The PCM adjusts injector pulse
width by opening and closing the ground path to the
injector.
Manifold absolute pressure (air density) and engine
rpm (speed) are the primary inputs that determine
fuel injector pulse width. The PCM also monitors
other inputs when adjusting air-fuel ratio.
Inputs That Effect Fuel Injector Pulse Width:
²Exhaust gas oxygen content
²Engine coolant temperature
²Manifold absolute pressure (MAP)
²Engine speed
²Throttle position
²Battery voltage
²Air conditioning selection
²Transmission gear selection (automatic transmis-
sions only)
²Speed control
The powertrain control module (PCM) adjusts igni-
tion timing by controlling ignition coil operation. The
ignition coil receives battery voltage when the igni-
tion key is in the run or starter position. The PCM
JFUEL SYSTEM COMPONENT DESCRIPTION/SYSTEM OPERATION 14 - 19
Page 1470 of 2158
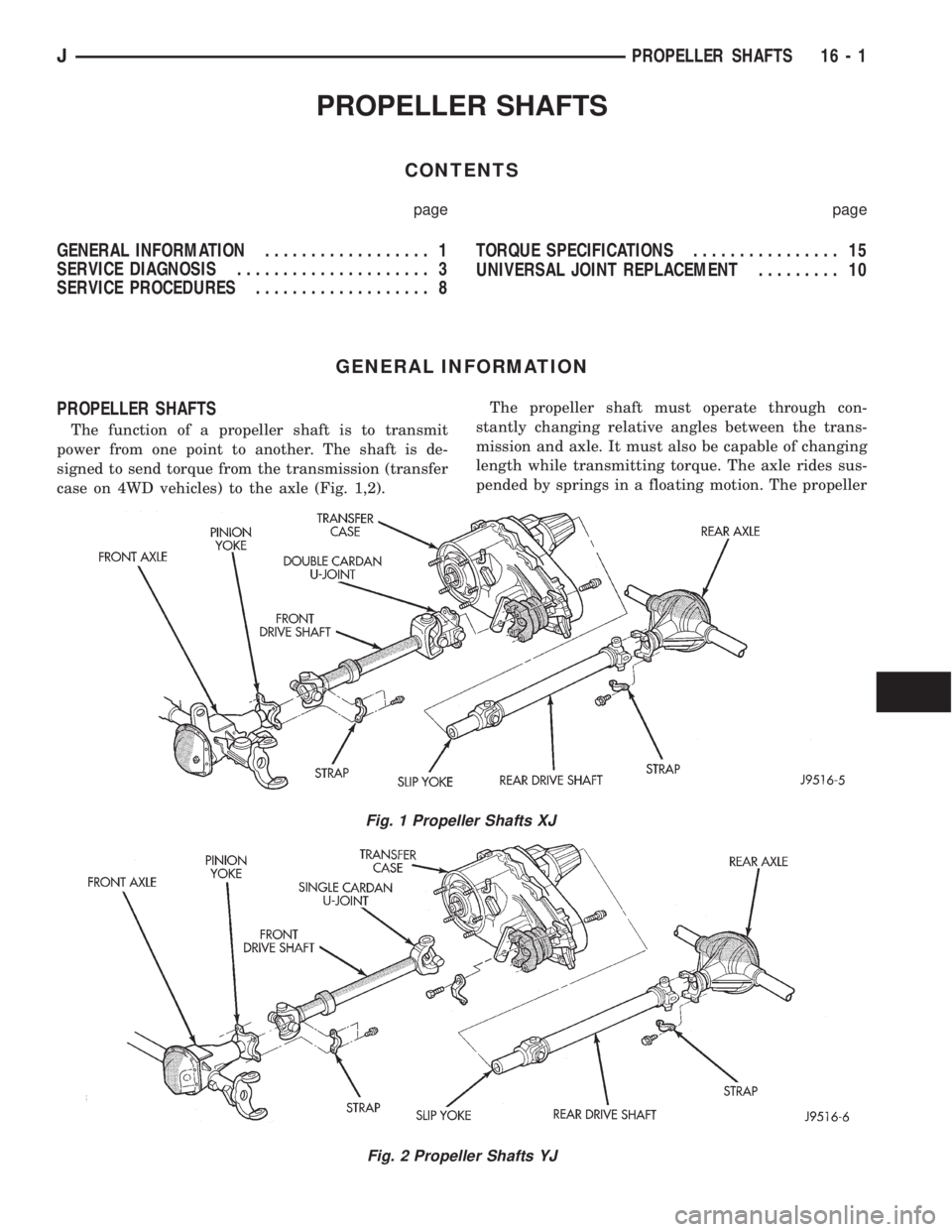
PROPELLER SHAFTS
CONTENTS
page page
GENERAL INFORMATION.................. 1
SERVICE DIAGNOSIS..................... 3
SERVICE PROCEDURES................... 8TORQUE SPECIFICATIONS................ 15
UNIVERSAL JOINT REPLACEMENT......... 10
GENERAL INFORMATION
PROPELLER SHAFTS
The function of a propeller shaft is to transmit
power from one point to another. The shaft is de-
signed to send torque from the transmission (transfer
case on 4WD vehicles) to the axle (Fig. 1,2).The propeller shaft must operate through con-
stantly changing relative angles between the trans-
mission and axle. It must also be capable of changing
length while transmitting torque. The axle rides sus-
pended by springs in a floating motion. The propeller
Fig. 1 Propeller Shafts XJ
Fig. 2 Propeller Shafts YJ
JPROPELLER SHAFTS 16 - 1
Page 1539 of 2158
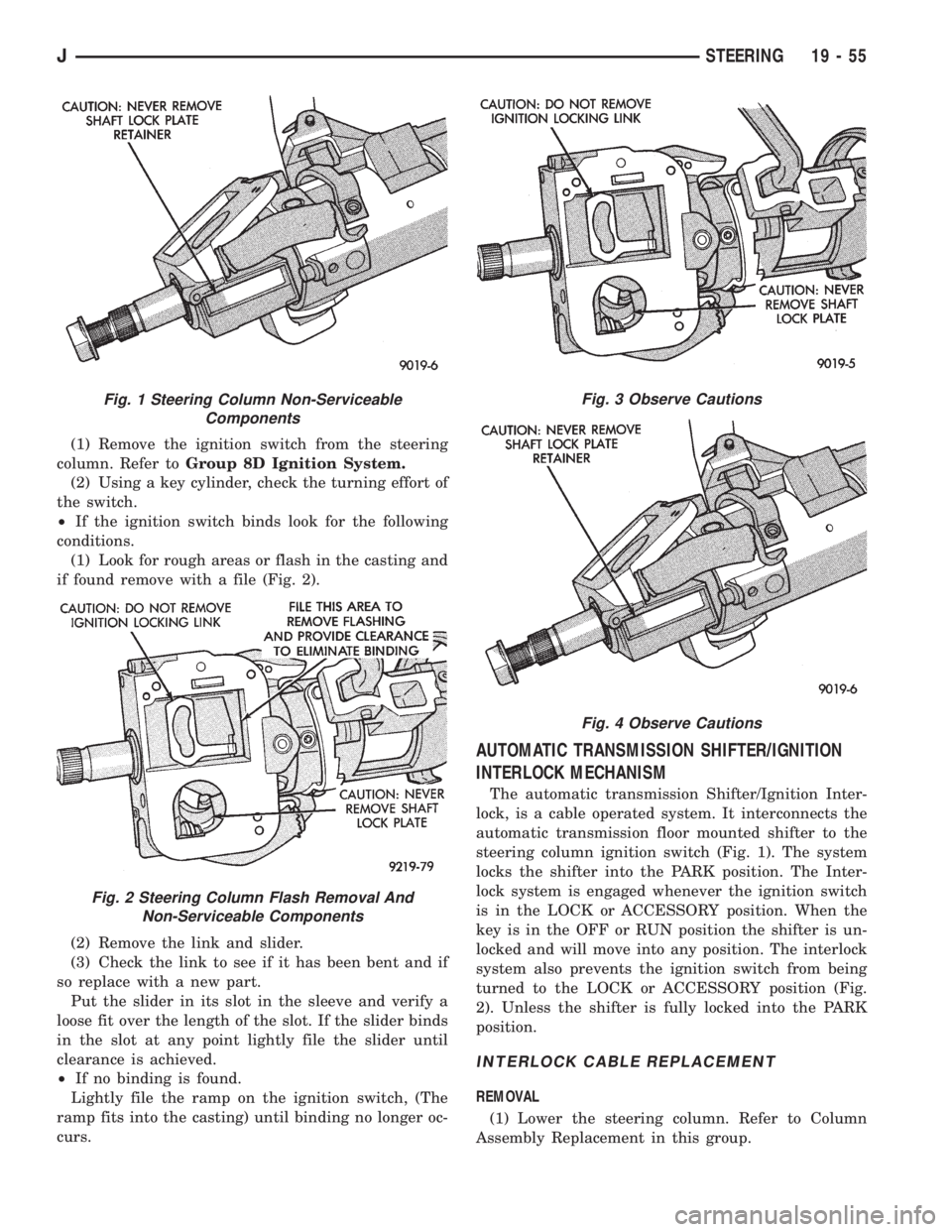
(1) Remove the ignition switch from the steering
column. Refer toGroup 8D Ignition System.
(2) Using a key cylinder, check the turning effort of
the switch.
²If the ignition switch binds look for the following
conditions.
(1) Look for rough areas or flash in the casting and
if found remove with a file (Fig. 2).
(2) Remove the link and slider.
(3) Check the link to see if it has been bent and if
so replace with a new part.
Put the slider in its slot in the sleeve and verify a
loose fit over the length of the slot. If the slider binds
in the slot at any point lightly file the slider until
clearance is achieved.
²If no binding is found.
Lightly file the ramp on the ignition switch, (The
ramp fits into the casting) until binding no longer oc-
curs.
AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION SHIFTER/IGNITION
INTERLOCK MECHANISM
The automatic transmission Shifter/Ignition Inter-
lock, is a cable operated system. It interconnects the
automatic transmission floor mounted shifter to the
steering column ignition switch (Fig. 1). The system
locks the shifter into the PARK position. The Inter-
lock system is engaged whenever the ignition switch
is in the LOCK or ACCESSORY position. When the
key is in the OFF or RUN position the shifter is un-
locked and will move into any position. The interlock
system also prevents the ignition switch from being
turned to the LOCK or ACCESSORY position (Fig.
2). Unless the shifter is fully locked into the PARK
position.
INTERLOCK CABLE REPLACEMENT
REMOVAL
(1) Lower the steering column. Refer to Column
Assembly Replacement in this group.
Fig. 1 Steering Column Non-Serviceable
Components
Fig. 2 Steering Column Flash Removal And
Non-Serviceable Components
Fig. 3 Observe Cautions
Fig. 4 Observe Cautions
JSTEERING 19 - 55
Page 1547 of 2158

(9) Remove the gear selector lever spring from the
lever housing.
The steering column must be removed from
the vehicle to disassemble the remaining steer-
ing column components.
(10) Remove the steering shaft (if not previously
removed).
(11) Remove the spring clip from the steering col-
umn lower bearing retainer. Remove the retainer, the
lower bearing and the adapter (Fig. 12).
(12) Slide out and remove the shift tube.
ASSEMBLY
WARNING: USE ONLY THE ORIGINAL OR EXACT
REPLACEMENT SCREWS, BOLTS AND NUTS TO
ASSEMBLE THE STEERING COLUMN. INCORRECT
SCREW OR BOLT LENGTH COULD PREVENT THE
COLUMN FROM COMPRESSING WITH IMPACT
(FRONT-END COLLISION). ALL FASTENERS USED
FOR ASSEMBLY MUST BE TIGHTENED WITH THE
CORRECT TORQUE. THIS WILL ENSURE THE COL-
UMN WILL BREAKAWAY WITH IMPACT.
CAUTION: Apply chassis lubricant to all the bear-
ing, thrust and friction producing mating surfaces
before assembly.
COLUMN SHIFT ASSEMBLY
(1) Insert the lock sector through the key/lock cyl-
inder hole in the key/lock cylinder housing. Install
the lock sector on the lock sector shaft (Fig. 13). En-
sure that the lock sector turns freely after installa-
tion.
(2) Install the lock rack preload spring. The bowed
side of the spring must contact the lock rack when
the rack is installed.
(3) Assemble the lock bolt and the lock rack (Fig.
14).
(4) Install the assembled lock bolt and lock rack in
the key/lock cylinder housing (Fig. 15). Mate the lock
rack block tooth with the lock sector block tooth.
(5) Install the shift lever detent plate on the key/
lock cylinder housing (Fig. 16).
Fig. 11 Lock Sector Removal
Fig. 12 Lower Bearing, Adapter, Retainer & Clip
Fig. 13 Lock Sector Installation
JSTEERING 19 - 63
Page 1555 of 2158
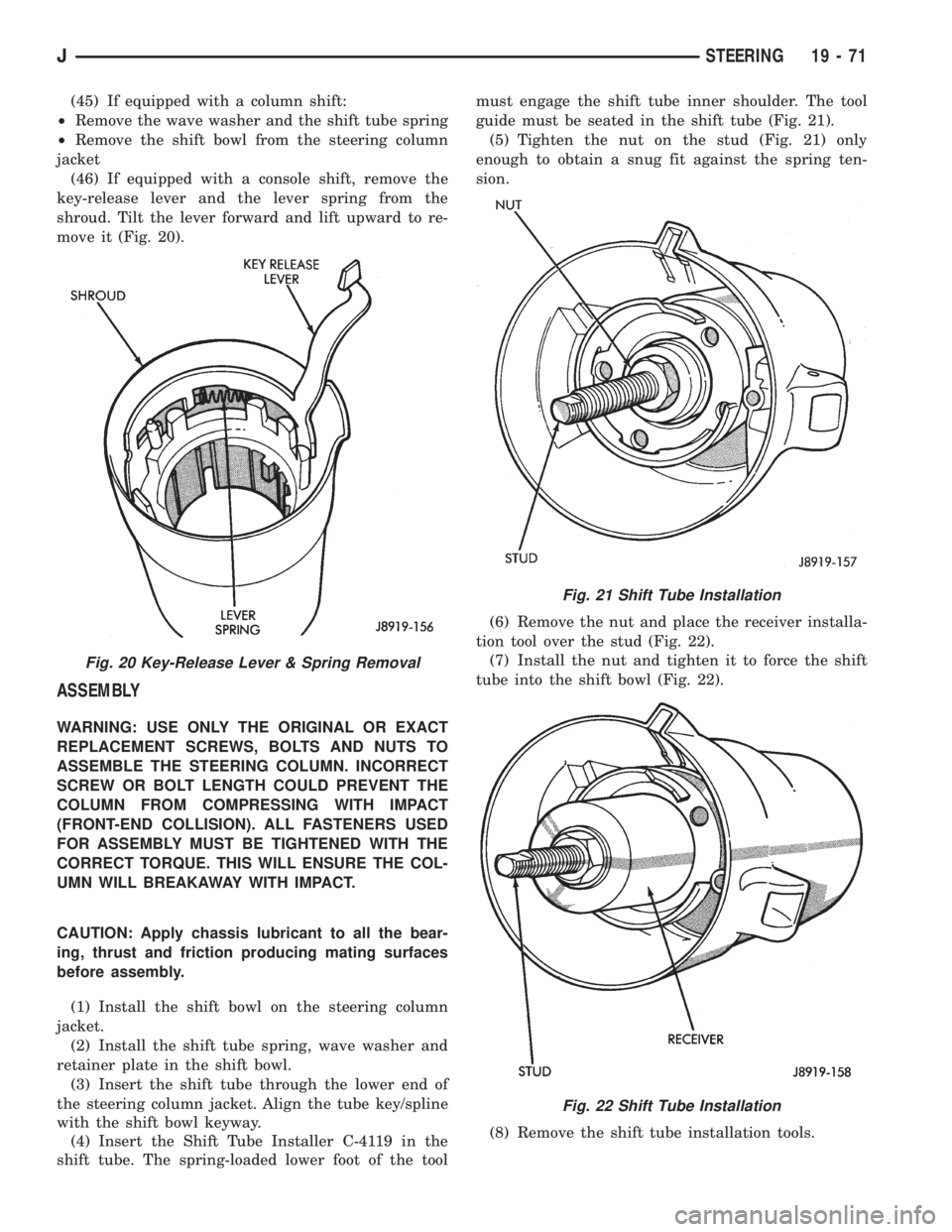
(45) If equipped with a column shift:
²Remove the wave washer and the shift tube spring
²Remove the shift bowl from the steering column
jacket
(46) If equipped with a console shift, remove the
key-release lever and the lever spring from the
shroud. Tilt the lever forward and lift upward to re-
move it (Fig. 20).
ASSEMBLY
WARNING: USE ONLY THE ORIGINAL OR EXACT
REPLACEMENT SCREWS, BOLTS AND NUTS TO
ASSEMBLE THE STEERING COLUMN. INCORRECT
SCREW OR BOLT LENGTH COULD PREVENT THE
COLUMN FROM COMPRESSING WITH IMPACT
(FRONT-END COLLISION). ALL FASTENERS USED
FOR ASSEMBLY MUST BE TIGHTENED WITH THE
CORRECT TORQUE. THIS WILL ENSURE THE COL-
UMN WILL BREAKAWAY WITH IMPACT.
CAUTION: Apply chassis lubricant to all the bear-
ing, thrust and friction producing mating surfaces
before assembly.
(1) Install the shift bowl on the steering column
jacket.
(2) Install the shift tube spring, wave washer and
retainer plate in the shift bowl.
(3) Insert the shift tube through the lower end of
the steering column jacket. Align the tube key/spline
with the shift bowl keyway.
(4) Insert the Shift Tube Installer C-4119 in the
shift tube. The spring-loaded lower foot of the toolmust engage the shift tube inner shoulder. The tool
guide must be seated in the shift tube (Fig. 21).
(5) Tighten the nut on the stud (Fig. 21) only
enough to obtain a snug fit against the spring ten-
sion.
(6) Remove the nut and place the receiver installa-
tion tool over the stud (Fig. 22).
(7) Install the nut and tighten it to force the shift
tube into the shift bowl (Fig. 22).
(8) Remove the shift tube installation tools.
Fig. 20 Key-Release Lever & Spring Removal
Fig. 21 Shift Tube Installation
Fig. 22 Shift Tube Installation
JSTEERING 19 - 71