1995 JEEP CHEROKEE automatic transmission
[x] Cancel search: automatic transmissionPage 1167 of 2198

(3) Remove the fan and shroud.
(4) Disconnect the radiator overflow tube, radiator
hoses, automatic transmission fluid cooler pipes (if
equipped).
(5) Remove the radiator.
(6) If equipped with air conditioning:
CAUTION: DO NOT loosen or disconnect any air
conditioner system fittings. Move the condenser
and receiver/drier aside as a complete assembly.
(a) Remove the A/C compressor serpentine drive
belt idler pulley.
(b) Disconnect and remove the generator.
(c) Remove the A/C condenser attaching bolts
and move the condenser and receiver/drier assem-
bly up and out of the way.
(7) Remove the serpentine drive belt.
(8) Remove the crankshaft vibration damper.
(9) Remove the timing case cover. Clean the gasket
material from the cover.
(10) Remove the thrust pin and tension spring
from the preload bolt head.
(11) Rotate crankshaft until the crankshaft
sprocket timing mark is closest to and on the center
line with the camshaft sprocket timing mark (Fig.
10).
(12) Remove the camshaft sprocket preload retain-
ing bolt and washer.
(13) Remove the crankshaft oil slinger.
(14) Remove the sprockets and chain as an assem-
bly.
CAUTION: The following procedural step must be
accomplished to prevent the camshaft from damag-
ing the rear camshaft plug during pin installation.
(15) Inspect the damaged camshaft pin.
(16) If the pin is a spring-type pin, remove the bro-
ken pin by inserting a self-tapping screw into the pin
and carefully pulling the pin from the camshaft.(17) If the pin is a dowel-type pin, center-punch it.
Ensure the exact center is located when center-
punching the pin.
CAUTION: Cover the opened oil pan area to prevent
metal chips from entering the pan.
(18) Drill into the pin center witha4mm(5/32
inch) drill bit.
(19) Insert a self-tapping screw into the drilled pin
and carefully pull the pin from the camshaft.
CAMSHAFT BEARINGS
The camshaft rotates within four steel-shelled, bab-
bitt-lined bearings that are pressed into the cylinder
block and then line reamed. The camshaft bearing
bores and bearing diameters are not the same size.
They are stepped down in 0.254 mm (0.010 inch) in-
crements from the front bearing (largest) to the rear
bearing (smallest). This permits easier removal and
installation of the camshaft. The camshaft bearings
are pressure lubricated.
It is not advisable to attempt to replace cam-
shaft bearings unless special removal and in-
stallation tools are available.
Camshaft end play is maintained by the load
placed on the camshaft by the sprocket preload bolt
tension spring and thrust pin.
INSTALLATION
(1) Clean the camshaft pin hole.
(2) Compress the center of the replacement spring
pin with vise grips.
(3) Carefully drive the pin into the camshaft pin
hole until it is seated.
(4) Install the camshaft sprocket, crankshaft
sprocket and timing chain with the timing marks
aligned (Fig. 10).
(5) To verify correct installation of the timing
chain, turn the crankshaft to position the camshaft
sprocket timing mark as shown in Fig. 11. Count the
number of chain pins between the timing marks of
both sprockets. There must be 15 pins.
(6) Install the crankshaft oil slinger.
(7) Tighten the camshaft sprocket preload bolt to
108 Nzm (80 ft. lbs.) torque.
(8) Check the valve timing.
(9) Lubricate the tension spring, the thrust pin
and the pin bore in the preload bolt with Mopar En-
gine Oil Supplement, or equivalent. Install the spring
and thrust pin in the preload bolt head.
(10) Coat both sides of the replacement timing case
cover gasket with gasket sealer. Applya3mm(1/8
inch) bead of Mopar Silicone Rubber Adhesive Seal-
ant, or equivalent to the joint formed at the oil pan
and cylinder block.
(11) Position the timing case cover on the oil pan
gasket and the cylinder block.
Fig. 10 Timing Chain AlignmentÐTypical
9 - 76 4.0L ENGINEJ
Page 1168 of 2198

(12) Place Timing Case Cover Alignment and Seal
Installation Tool 6139 in the crankshaft opening in
the cover (Fig. 12).
(13) Install the timing case cover-to-cylinder block
bolts. Install the oil pan-to-timing case cover bolts.
(14) Tighten the 1/4 inch cover-to-block bolts to 7
Nzm (60 in. lbs.) torque. Tighten the 5/16 inch front
cover-to-block bolts to 22 Nzm (192 in. lbs.) torque.
Tighten the oil pan-to-cover 1/4 inch bolts to 14 Nzm
(120 in. lbs.) torque. Tighten the oil pan-to-cover 5/16
inch bolts to 18 Nzm (156 in. lbs.) torque.
(15) Remove the cover alignment tool and install a
replacement oil seal into the cover.(16) Install the vibration damper on the crank-
shaft.
(17) Lubricate and tighten the damper bolt to 108
Nzm (80 ft. lbs.) torque.
(18) If equipped with air conditioning:
(a) Install the A/C compressor serpentine drive
belt idler pulley.
(b) Install the generator.
(c) Install the A/C condenser and receiver/drier
assembly.
(19) Install the serpentine drive belt on the pulleys
and tighten (refer to Group 7, Cooling System for the
specifications and procedures).
(20) Install the radiator. Connect the radiator
hoses and automatic transmission fluid cooler pipes,
if equipped. Fill the cooling system.
(21) Install the fan and shroud.
(22) Connect negative cable to battery.
OIL PAN
REMOVAL
(1) Disconnect negative cable from battery.
(2) Raise the vehicle.
(3) Remove the oil pan drain plug and drain the
engine oil.
(4) Disconnect the exhaust pipe at the exhaust
manifold.
(5) Disconnect the exhaust hanger at the catalytic
converter and lower the pipe.
(6) Remove the starter motor.
(7) Remove the engine flywheel and transmission
torque converter housing access cover.
(8) If equipped with an oil level sensor, disconnect
the sensor.
(9) Position a jack stand directly under the engine
vibration damper.
(10) Place a piece of wood (2 x 2) between the jack
stand and the engine vibration damper.
(11) Remove the engine mount through bolts.
(12) Using the jack stand, raise the engine until
adequate clearance is obtained to remove the oil pan.
(13) Remove the oil pan bolts. Carefully slide the
oil pan and gasket to the rear. If equipped with an oil
level sensor, take care not to damage the sensor.
CLEANING
Clean the block and pan gasket surfaces.
INSTALLATION
(1) Fabricate 4 alignment dowels from 1/4 x 1 1/2
inch bolts. Cut the head off the bolts and cut a slot
into the top of the dowel. This will allow easier in-
stallation and removal with a screwdriver (Fig. 1).
(2) Install two dowels in the timing case cover. In-
stall the other two dowels in the cylinder block (Fig.
2).
Fig. 11 Verify CrankshaftÐCamshaft InstallationÐ
Typical
Fig. 12 Timing Case Cover Alignment and Seal
Installation Tool 6139
J4.0L ENGINE 9 - 77
Page 1234 of 2198

MULTI-PORT FUEL INJECTION (MFI)ÐCOMPONENT DESCRIPTION/SYSTEM
OPERATION
INDEX
page page
Air Cleaner.............................. 29
Air Conditioning (A/C) Clutch RelayÐPCM Output . 26
Air Conditioning (A/C) ControlsÐPCM Input...... 21
Auto Shutdown (ASD) RelayÐPCM Output...... 26
Automatic Shutdown (ASD) SenseÐPCM Input . . . 21
Battery VoltageÐPCM Input................. 21
Brake SwitchÐPCM Input................... 22
Camshaft Position SensorÐPCM Input......... 22
Crankshaft Position SensorÐPCM Input........ 22
Data Link ConnectorÐPCM Input............. 22
Data Link ConnectorÐPCM Output............ 27
EMR LampÐPCM Output................... 27
Engine Coolant Temperature SensorÐPCM Input . 23
Extended Idle SwitchÐPCM Input............. 23
Fuel InjectorsÐPCM Output................. 27
Fuel Pressure Regulator.................... 33
Fuel Pump RelayÐPCM Output.............. 27
Fuel Rail................................ 33
General Information....................... 19
Generator FieldÐPCM Output................ 27
Generator LampÐPCM Output............... 27
Idle Air Control (IAC) MotorÐPCM Output....... 27
Ignition Circuit SenseÐPCM Input............. 23
Ignition CoilÐPCM Output................... 28Intake Manifold Air Temperature SensorÐ
PCM Input............................. 22
Malfunction Indicator LampÐPCM Output....... 28
Manifold Absolute Pressure (MAP) SensorÐPCM
Input................................. 23
Open Loop/Closed Loop Modes of Operation..... 30
Oxygen (O2S) SensorÐPCM Input............ 24
Park/Neutral SwitchÐPCM Input.............. 24
Power Ground........................... 24
Power Steering Pressure SwitchÐPCM Input.... 24
Powertrain Control Module (PCM)............. 20
Radiator Fan RelayÐPCM Output............. 28
SCI ReceiveÐPCM Input................... 24
SCI TransmitÐPCM Output.................. 29
Sensor ReturnÐPCM Input.................. 25
Shift IndicatorÐPCM Output................. 29
Speed ControlÐPCM Input.................. 25
Speed ControlÐPCM Output................. 29
TachometerÐPCM Output................... 29
Throttle Body............................ 33
Throttle Position Sensor (TPS)ÐPCM Input...... 25
Torque Converter Clutch RelayÐPCM Output.... 29
Vehicle Speed SensorÐPCM Input............ 25
GENERAL INFORMATION
All 2.5L 4-cylinder and 4.0L 6-cylinder engines are
equipped with sequential Multi-Port Fuel Injection
(MFI). The MFI system provides precise air/fuel ra-
tios for all driving conditions.
The Powertrain Control Module (PCM) operates
the fuel system. The PCM was formerly referred to
as the SBEC or engine controller. The PCM is a pre-
programmed, dual microprocessor digital computer. It
regulates ignition timing, air-fuel ratio, emission con-
trol devices, charging system, speed control, air con-
ditioning compressor clutch engagement and idle
speed. The PCM can adapt its programming to meet
changing operating conditions.
Powertrain Control Module (PCM) Inputsrep-
resent the instantaneous engine operating conditions.
Air-fuel mixture and ignition timing calibrations for
various driving and atmospheric conditions are pre-
programmed into the PCM. The PCM monitors and
analyzes various inputs. It then computes engine fuel
and ignition timing requirements based on these in-
puts. Fuel delivery control and ignition timing will
then be adjusted accordingly.
Other inputs to the PCM are provided by the brake
light switch, air conditioning select switch and the
speed control switches. All inputs to the PCM are
converted into signals.
Electrically operated fuel injectors spray fuel inprecise metered amounts into the intake port directly
above the intake valve. The injectors are fired in a
specific sequence by the PCM. The PCM maintains
an air/fuel ratio of 14.7 to 1 by constantly adjusting
injector pulse width. Injector pulse width is the
length of time that the injector opens and sprays fuel
into the chamber. The PCM adjusts injector pulse
width by opening and closing the ground path to the
injector.
Manifold absolute pressure (air density) and engine
rpm (speed) are the primary inputs that determine
fuel injector pulse width. The PCM also monitors
other inputs when adjusting air-fuel ratio.
Inputs That Effect Fuel Injector Pulse Width:
²Exhaust gas oxygen content
²Engine coolant temperature
²Manifold absolute pressure (MAP)
²Engine speed
²Throttle position
²Battery voltage
²Air conditioning selection
²Transmission gear selection (automatic transmis-
sions only)
²Speed control
The powertrain control module (PCM) adjusts igni-
tion timing by controlling ignition coil operation. The
ignition coil receives battery voltage when the igni-
tion key is in the run or starter position. The PCM
JFUEL SYSTEM COMPONENT DESCRIPTION/SYSTEM OPERATION 14 - 19
Page 1235 of 2198

provides a ground for the ignition coil. The coil dis-
charges when the PCM supplies a ground. By switch-
ing the ground path on and off, the PCM regulates
ignition timing.
The sensors and switches that provide inputs to
the powertrain control module (PCM) comprise the
Engine Control System. It is also comprised of the
PCM Outputs (engine control devices that the are op-
erated by the PCM).
SYSTEM DIAGNOSIS
The powertrain control module (PCM) tests many
of its own input and output circuits. If a Diagnostic
Trouble Code (DTC) is found in a major system, this
information is stored in the PCM memory. Refer to
On-Board Diagnostics in the MFI SystemÐGeneral
Diagnosis section of this group for DTC information.
POWERTRAIN CONTROL MODULE (PCM)
The PCM operates the fuel system. The PCM was
formerly referred to as the SBEC or engine control-
ler. The PCM is a pre-programmed, dual microproces-
sor digital computer. It regulates ignition timing, air-
fuel ratio, emission control devices, charging system,
speed control, air conditioning compressor clutch en-
gagement and idle speed. The PCM can adapt its
programming to meet changing operating conditions.
On XJ models, the PCM is located in the engine
compartment next to the air cleaner (Fig. 1). On YJ
models, the PCM is located in the engine compart-
ment behind the windshield washer fluid reservoir
(Fig. 2).
The PCM receives input signals from various
switches and sensors. Based on these inputs, the
PCM regulates various engine and vehicle operations
through different system components. These compo-
nents are referred to as PCM Outputs. The sensors
and switches that provide inputs to the PCM are con-
sidered PCM Inputs.The PCM adjusts ignition timing based upon in-
puts it receives from sensors that react to: engine
rpm, manifold absolute pressure, coolant tempera-
ture, throttle position, transmission gear selection
(automatic transmission), vehicle speed and the
brake switch.
The PCM adjusts idle speed based on inputs it re-
ceives from sensors that react to: throttle position,
vehicle speed, transmission gear selection, coolant
temperature and from inputs it receives from the air
conditioning clutch switch and brake switch.
Based on inputs that it receives, the PCM adjusts
ignition coil dwell. The PCM also adjusts the gener-
ator charge rate through control of the generator
field and provides speed control operation.
Powertrain Control Module (PCM) Inputs:
²Generator output
²A/C request (if equipped with factory A/C)
²A/C select (if equipped with factory A/C)
²Auto shutdown (ASD) sense
²Intake manifold air temperature sensor
²Battery voltage
²Brake switch
²Engine coolant temperature sensor
²Crankshaft position sensor
²Ignition circuit sense (ignition switch in run posi-
tion)
²Manifold absolute pressure sensor
²Overdrive/override switch
²Oxygen sensor
²Park/neutral switch (auto. trans. only)
²SCI receive (DRB scan tool connection)
²Speed control resume switch
²Speed control set switch
²Speed control on/off switch
²Camshaft position sensor signal
²Throttle position sensor
²Vehicle speed sensor
²Sensor return
²Power ground
Fig. 1 PCM LocationÐXJ Models
Fig. 2 PCM LocationÐYJ Models
14 - 20 FUEL SYSTEM COMPONENT DESCRIPTION/SYSTEM OPERATIONJ
Page 1236 of 2198

²Signal ground
Powertrain Control Module (PCM) Outputs:
²A/C clutch relay
²Idle air control (IAC) motor
²Auto shutdown (ASD) relay
²Generator field
²Malfunction indicator lamp (Check Engine Lamp)
²Fuel injectors
²Fuel pump relay
²Ignition coil
²SCI transmit (DRB scan tool connection)
²Shift indicator lamp (manual transmission only)
²Speed control vacuum solenoid
²Speed control vent solenoid
²Tachometer (on instrument panel, if equipped)
²Torque converter clutch relay (3-speed auto. trans.
only)
The PCM contains a voltage convertor. This con-
verts battery voltage to a regulated 8.0 volts. It is
used to power the crankshaft position sensor, cam-
shaft position sensor and vehicle speed sensor. The
PCM also provides a five (5) volt supply for the Man-
ifold Absolute Pressure (MAP) sensor and Throttle
Position Sensor (TPS).
AIR CONDITIONING (A/C) CONTROLSÐPCM INPUT
The A/C control system information applies to fac-
tory installed air conditioning units only.
A/C SELECT SIGNAL:When the A/C switch is in
the ON position and the A/C low-pressure switch is
closed, an input signal is sent to the powertrain con-
trol module (PCM). The signal informs the PCM that
the A/C has been selected. The PCM adjusts idle
speed to a pre-programmed rpm through the idle air
control (IAC) motor to compensate for increased en-
gine load.
A/C REQUEST SIGNAL:Once A/C has been se-
lected, the PCM receives the A/C request signal from
the evaporator switch. The input indicates that the
evaporator temperature is in the proper range for
A/C application. The PCM uses this input to cycle the
A/C compressor clutch (through the A/C relay). It will
also determine the correct engine idle speed through
the IAC motor position.
If the A/C low-pressure switch opens (indicating a
low refrigerant level), the PCM will not receive an
A/C select signal. The PCM will then remove the
ground from the A/C relay. This will deactivate the
A/C compressor clutch.
If the evaporator switch opens, (indicating that
evaporator is not in proper temperature range), the
PCM will not receive the A/C request signal. The
PCM will then remove the ground from the A/C relay,
deactivating the A/C compressor clutch.
AUTOMATIC SHUTDOWN (ASD) SENSEÐPCM
INPUT
A 12 volt signal at this input indicates to the PCM
that the ASD has been activated. The ASD relay is
located in the power distribution center (PDC) in the
engine compartment (Figs. 3 or 4). It is used to con-
nect the ignition coil, generator field winding and
fuel injectors to 12 volt + power supply. Also refer to
Automatic Shutdown RelayÐPCM Output.
This input is used only to sense that the ASD relay
is energized. If the PCM does not see 12 volts at this
input when the ASD should be activated, it will set a
Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC).
BATTERY VOLTAGEÐPCM INPUT
The battery voltage input provides power to the
powertrain control module (PCM). It also informs the
PCM what voltage level is supplied to the ignition
coil and fuel injectors.
If battery voltage is low, the PCM will increase in-
jector pulse width (period of time that the injector is
Fig. 3 Power Distribution CenterÐYJ Models
Fig. 4 Power Distribution CenterÐXJ Models
JFUEL SYSTEM COMPONENT DESCRIPTION/SYSTEM OPERATION 14 - 21
Page 1237 of 2198

energized). This is done to compensate for the re-
duced flow through injector caused by the lowered
voltage.
BRAKE SWITCHÐPCM INPUT
When the brake light switch is activated, the pow-
ertrain control module (PCM) receives an input indi-
cating that the brakes are being applied. After
receiving this input, the PCM maintains idle speed to
a scheduled rpm through control of the idle air con-
trol (IAC) motor. The brake switch input is also used
to operate the speed control system.
CAMSHAFT POSITION SENSORÐPCM INPUT
A sync signal is provided by the camshaft position
sensor located in the distributor (Fig. 5). The sync
signal from this sensor works in conjunction with the
crankshaft position sensor to provide the powertrain
control module (PCM) with inputs. This is done to es-
tablish and maintain correct injector firing order.
Refer to Camshaft Position Sensor in Group 8D, Ig-
nition System for more information.
DATA LINK CONNECTORÐPCM INPUT
The data link connector (diagnostic scan tool con-
nector) links the DRB scan tool with the powertrain
control module (PCM). The data link connector is lo-
cated in the engine compartment (Figs. 6 or 7). For
operation of the DRB scan tool, refer to the appropri-
ate Powertrain Diagnostic Procedures service man-
ual.
The data link connector uses two different pins on
the PCM. One is for Data Link Transmit and the
other is for Data Link Receive.
INTAKE MANIFOLD AIR TEMPERATURE SENSORÐ
PCM INPUT
The intake manifold air temperature sensor is in-
stalled in the intake manifold with the sensor ele-
ment extending into the air stream (Figs. 8 or 9). Thesensor provides an input voltage to the powertrain
control module (PCM) indicating intake manifold air
temperature. The input is used along with inputs
from other sensors to determine injector pulse width.
As the temperature of the air-fuel stream in the
manifold varies, the sensor resistance changes. This
results in a different input voltage to the PCM.
CRANKSHAFT POSITION SENSORÐPCM INPUT
This sensor is a Hall Effect device that detects
notches in the flywheel (manual transmission), or
flexplate (automatic transmission).
This sensor is used to indicate to the powertrain
control module (PCM) that a spark and or fuel injec-
tion event is to be required. The output from this
sensor, in conjunction with the camshaft position sen-
sor signal, is used to differentiate between fuel injec-
tion and spark events. It is also used to synchronize
the fuel injectors with their respective cylinders.
Refer to Group 8D, Ignition System for more crank-
shaft position sensor information.
Fig. 5 Camshaft Position Sensor
Fig. 6 Data Link ConnectorÐYJ ModelsÐTypical
Fig. 7 Data Link ConnectorÐXJ ModelsÐTypical
14 - 22 FUEL SYSTEM COMPONENT DESCRIPTION/SYSTEM OPERATIONJ
Page 1244 of 2198

coolant temperature drops to 98ÉC (208ÉF). Refer to
Group 7, Cooling Systems for more information.
The relay is located in the power distribution cen-
ter (PDC) (Fig. 25).
The electric radiator cooling fan is not used on YJ
models.
SCI TRANSMITÐPCM OUTPUT
SCI Transmit is the serial data communication
transmit circuit for the DRB scan tool. The power-
train control module (PCM) transmits data to the
DRB through the SCI Transmit circuit.
SHIFT INDICATORÐPCM OUTPUT
Vehicles equipped with manual transmissions have
an Up-Shift indicator lamp. The lamp is controlled by
the powertrain control module (PCM). The lamp illu-
minates on the instrument panel to indicate when
the driver should shift to the next highest gear for
best fuel economy. The PCM will turn the lamp OFF
after 3 to 5 seconds if the shift of gears is not per-
formed. The up-shift lamp will remain off until vehi-
cle stops accelerating and is brought back to range of
up-shift lamp operation. This will also happen if ve-
hicle is shifted into fifth gear.
The indicator lamp is normally illuminated when
the ignition switch is turned on and it is turned off
when the engine is started up. With the engine run-
ning, the lamp is turned on/off depending upon en-
gine speed and load.
SPEED CONTROLÐPCM OUTPUT
Speed control operation is regulated by the power-
train control module (PCM). The PCM controls the
vacuum to the throttle actuator through the speed
control vacuum and vent solenoids. Refer to Group
8H for speed control information.
TACHOMETERÐPCM OUTPUT
The powertrain control module (PCM) supplies en-
gine rpm values to the instrument cluster tachometer
(if equipped). Refer to Group 8E for tachometer infor-
mation.
TORQUE CONVERTER CLUTCH RELAYÐPCM
OUTPUT
ALL 2.5L 4 CYL. WITH 3-SPEED AUTO. TRANS
4.0L 6 CYL. YJ MODELS WITH 3-SPEED AUTO.
TRANS
The transmission mounted torque converter clutch
(TCC) solenoid is used to control the torque con-
verter. The solenoid is controlled through the power-
train control module (PCM) and by the TCC relay.
This relay is used only on vehicles equipped with a
3-speed automatic transmission.
An electrical output signal is sent from the PCM to
the TCC relay after the PCM receives information
from the vehicle speed, MAP, throttle position and
engine coolant temperature sensors. After the TCC
relay receives this necessary information, it will send
a signal to the torque converter clutch solenoid to
control the torque converter.
On YJ models the TCC relay is located in the en-
gine compartment, on the cowl panel and near the
battery (Fig. 26). On XJ models the TCC relay is lo-
cated in the power distribution center (PDC) (Fig.
25).
AIR CLEANER
The air cleaner assembly used on all models (Figs.
27 or 28) is open to ambient air. The blend air door
and vacuum motor that was used on engines of pre-
vious model years to supply heated air, is no longer
used. The air cleaner housing contains the engine air
cleaner element.
Fig. 25 PDCÐXJ Models
Fig. 26 TCC Relay LocationÐYJ Models
JFUEL SYSTEM COMPONENT DESCRIPTION/SYSTEM OPERATION 14 - 29
Page 1255 of 2198
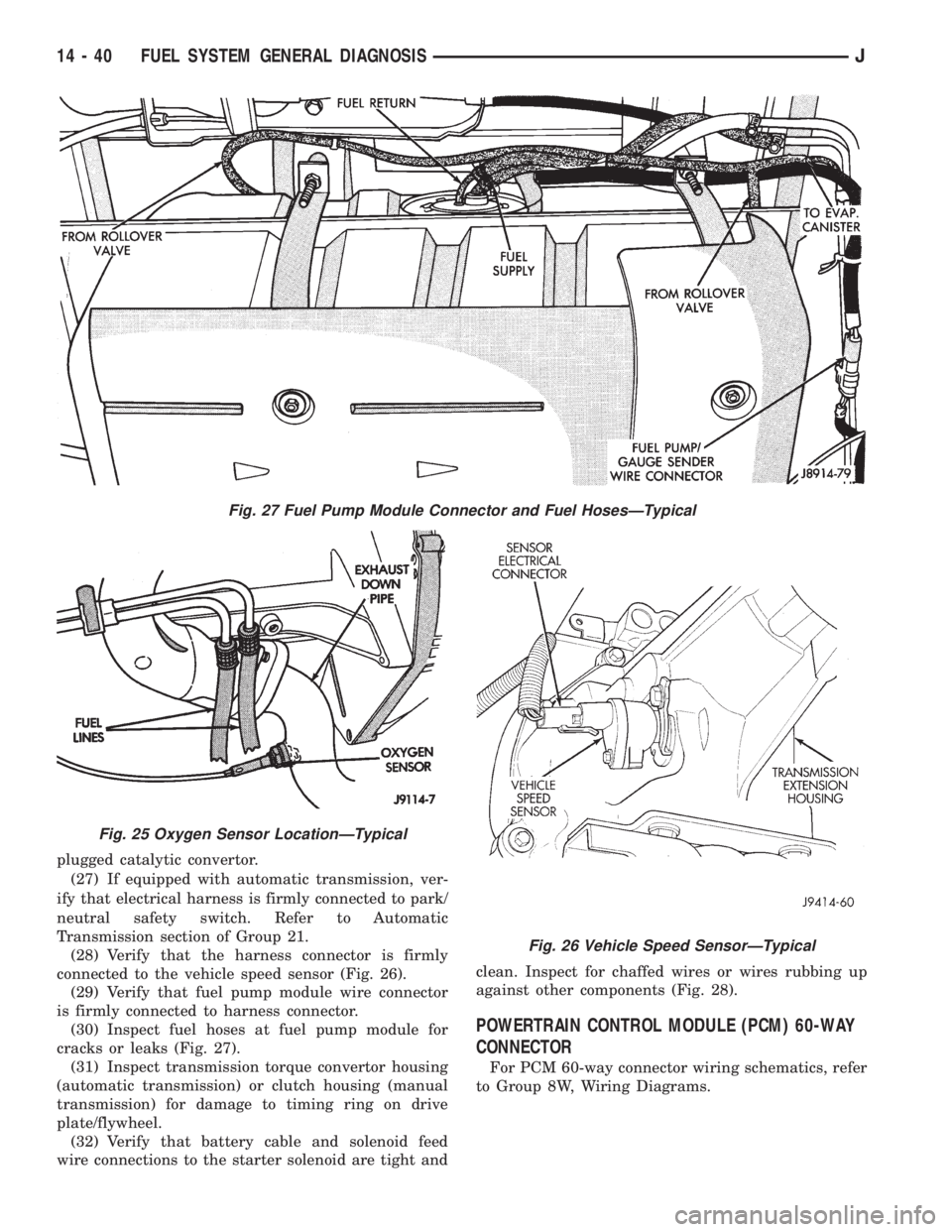
plugged catalytic convertor.
(27) If equipped with automatic transmission, ver-
ify that electrical harness is firmly connected to park/
neutral safety switch. Refer to Automatic
Transmission section of Group 21.
(28) Verify that the harness connector is firmly
connected to the vehicle speed sensor (Fig. 26).
(29) Verify that fuel pump module wire connector
is firmly connected to harness connector.
(30) Inspect fuel hoses at fuel pump module for
cracks or leaks (Fig. 27).
(31) Inspect transmission torque convertor housing
(automatic transmission) or clutch housing (manual
transmission) for damage to timing ring on drive
plate/flywheel.
(32) Verify that battery cable and solenoid feed
wire connections to the starter solenoid are tight andclean. Inspect for chaffed wires or wires rubbing up
against other components (Fig. 28).
POWERTRAIN CONTROL MODULE (PCM) 60-WAY
CONNECTOR
For PCM 60-way connector wiring schematics, refer
to Group 8W, Wiring Diagrams.
Fig. 27 Fuel Pump Module Connector and Fuel HosesÐTypical
Fig. 25 Oxygen Sensor LocationÐTypical
Fig. 26 Vehicle Speed SensorÐTypical
14 - 40 FUEL SYSTEM GENERAL DIAGNOSISJ