1995 GMC SIERRA wheel
[x] Cancel search: wheelPage 326 of 488
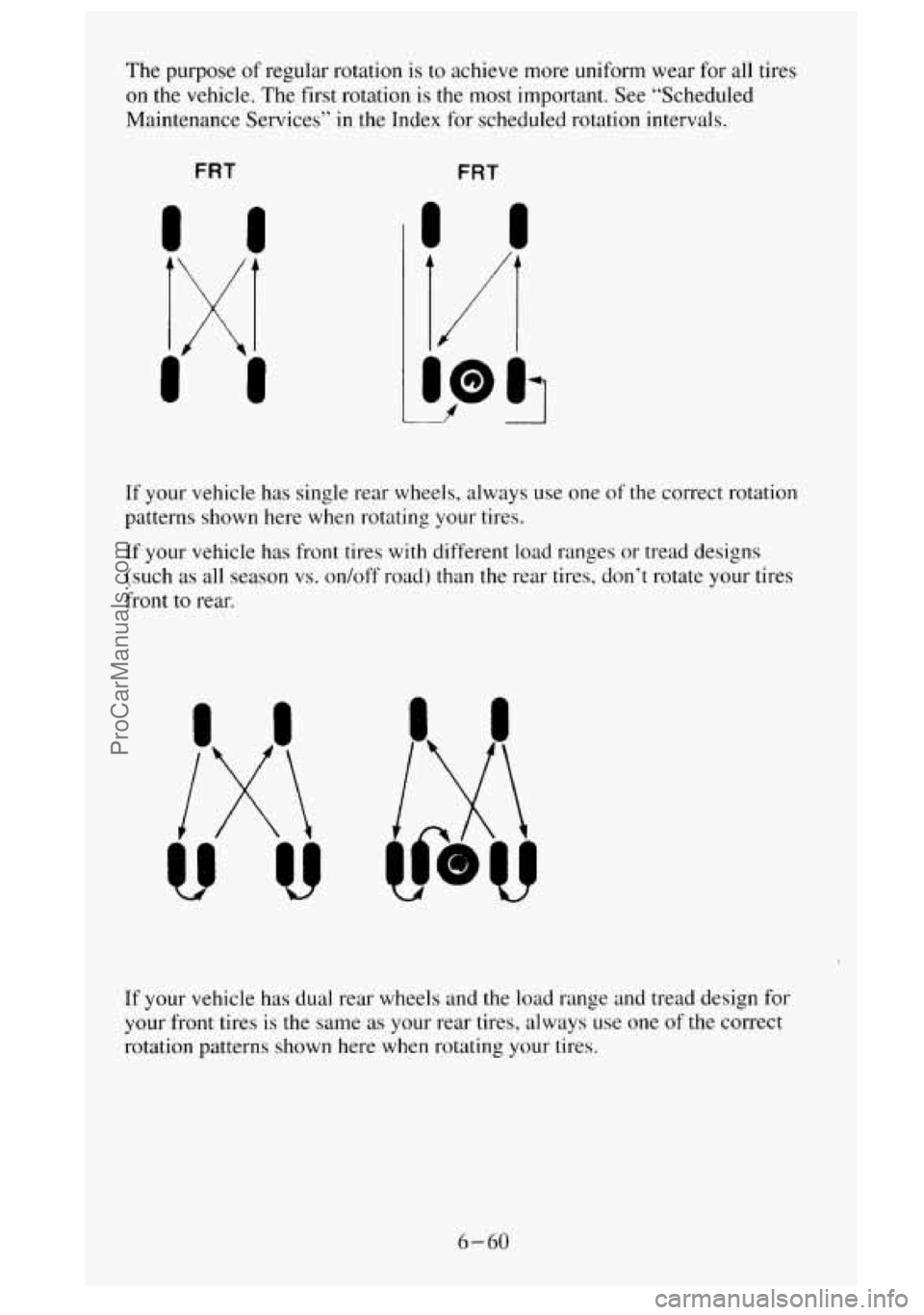
The purpose of regular rotation is to achieve more uniform wear for all tires
on the vehicle. The first rotation is the most important. See “Scheduled
Maintenance Services”
in the Index for scheduled rotation intervals.
FRT
I
II
FRT
If your vehicle has single rear wheels, always use one of the correct rotation
patterns shown here when rotating your tires.
If your vehicle has front tires with different load ranges
or tread designs
(such as all season vs. on/off road) than the rear tires. don‘t rotate your tires
front
to rear.
W v
If your vehicle has dual rear wheels and the load range and tread design for
your front tires
is the same as your rear tires, always use one of the correct
rotation patterns shown here when rotating your tires.
6-60
ProCarManuals.com
Page 327 of 488

If your vehicle has dual rear wheels and the load range or tread design for
your front tires is different from your rear tires, always use the correct
rotation pattern shown here when rotating your tires. The dual tires are
rotated as a pair, and the inside rear tires become the outside rear tires.
When you install dual wheels, be sure the vent holes in the inner and outer
wheels
on each side are lined up.
After the tires have been rotated, adjust the front and rear inflation pressures
as shown on the Certificatioflire label. Make certain that all wheel nuts are
properly tightened. See “Wheel Nut Torque” in the Index.
6-61
ProCarManuals.com
Page 328 of 488

When it’s Time for New Tires
You need a new tire if:
Tread Wear
Indicators
One way to tell when
it’s time for new tires
is to check the
treadwear indicators,
which will appear
when your tires have
only
1/16 inch (1.6
mm)
or less of tread
remaining.
0 You can see the indicators at three or more places around the tire.
0 You can see cord or fabric showing through the tire’s rubber.
The tread or sidewall is cracked, cut or snagged deep enough to show
cord
or fabric.
The tire has a bump, bulge or split.
The tire has a puncture, cut, or other damage that can‘t be repaired well
because
of the size or location of the damage.
Dual Tire Operation
When the vehicle is new, or whenever a wheel, wheel bolt or wheel nut is
replaced, check the wheel
nut torque after 100, 1,000 and 6,000 miles (160,
1 600 and 10 000 km) of driving. For proper torque see “Wheel Nut
Torque” in the Index.
The outer tire
on a dual wheel setup generally wears faster than the inner
tire. Your tires will wear more evenly and last longer
if you rotate the tires
periodically. If you’re going to be doing
a lot of driving on high-crown
roads, you can reduce tire wear by adding
5 psi (35 kPa) to the tire pressure
in the outer tires. Be sure to return
to the recommended pressures when no
longer driving under those conditions.
6-62
ProCarManuals.com
Page 329 of 488

A CAUTION:
If you operate your vehicle with a tire that is badly
underinflated, the tire can overheat. An overheated tire
can lose
air suddenly or catch fire. You or others could be injured. Be
sure all tires (including the spare, if any) are properly inflated.
Buying New Tires
To find out what kind and size of tires you need, look at the
CertificationRire label.
The tires installed on your vehicle when
it was new a Tire Performance
Criteria Specification (TPC Spec) number on each tire’s sidewall. When you
get new tires, get ones with that same TPC Spec number. That way, your
vehicle will continue to have tires that are designed to give proper
endurance, handling, speed rating, traction, ride and other things during
normal service on your vehicle.
If your tires have an all-season tread
design, the TPC number will be followed by an
“MS” (for mud and snow).
If you ever replace your tires with those not having a TPC Spec number,
make sure they are the same. size, load range, speed rating and construction
type (bias, bias-belted or radial) as your original tires.
I A CAUTION:
Mixing tires could cause you to lose control while driving. If you
mix tires of different sizes or types (radial and bias-belted tires),
the vehicle may not handle properly, and you could have
a crash.
Be sure to use the same size and type tires on all four wheels.
Uniform Tire Quality Grading
The following information relates to the system developed by the United
States National Highway Traffic Safety Administration which grades tires
by treadwear, traction and temperature performance.
(This applies only to
vehicles sold in the United States.)
6-63
ProCarManuals.com
Page 330 of 488

Treadwear
The treadwear grade is a comparative rating based on the wear rate of the
tire when tested under controlled conditions on
a specified government test
course. For example,
a tire graded 150 would wear one and a half (1 1/2)
times as well on the government course as a tire graded 100. The relative
performance
of tires depends upon the actual conditions of their use,
however, and may depart significantly from the norm due to variations
in
driving habits, service practices and differences in road characteristics and
climate.
Traction - A, B, C
The traction grades, from highest to lowest are: A, B, and C. They represent
the tire’s ability to stop on wet pavement
as measured under controlled
conditions on specified government test surfaces of asphalt and concrete.
A
tire marked C may have poor traction performance.
Warning: The traction grade assigned to this tire
is based on braking
(straight-ahead) traction tests and does not include cornering (turning)
traction.
Temperature - A, B, C
The temperature grades are A (the highest), B, and C, representing the tire’s
resistance to the generation
of heat and its ability to dissipate heat when
tested under controlled conditions on a specified indoor laboratory test
wheel. Sustained high temperature can cause the material
of the tire to
degenerate and reduce tire life, and excessive temperature can lead
to
sudden tire failure. The grade C corresponds to a level of performance
which all passenger car tires must meet under the Federal Motor Vehicle
Safety Standard
No. 109. Grades B and A represent higher levels of
performance
on the laboratory test wheel than the minimum required by
law.
Warning: The temperature grade for this tire is established for a tire that is
properly inflated and
not overloaded. Excessive speed, underinflation, or
excessive loading, either separately or in combination, can cause heat
buildup and possible tire failure.
These grades are molded on the sidewalls of passenger car tires.
While the tires available as standard or optional equipment on General
Motors vehicles may vary with respect to these grades, all such tires meet
General Motors performance standards and have been approved for use on
General Motors vehicles.
All passenger type (P Metric) tires must conform
to Federal safety requirements in addition to these grades.
6-64
ProCarManuals.com
Page 331 of 488

Wheel Alignment and Tire Balance
The wheels on your vehicle were aligned and balanced carefully at the
factory
to give you the longest tire life and best overall performance.
In most cases, you will not need to have your wheels aligned again.
However, if
you notice unusual tire wear or your vehicle pulling one way or
the other,
the alignment may need to be reset. If you notice your vehicle
vibrating when driving
on a smooth road, your wheels may need to be
rebalanced.
Wheel Replacement
Replace any wheel that is bent, cracked, or badly rusted or corroded. If
wheel nuts keep coming loose, the wheel, wheel bolts, and wheel nuts
should be replaced.
If the wheel leaks air, replace it (except some aluminum
wheels, which can sometimes be repaired). See your
GM dealer if any of
these conditions exist.
Your dealer will know the kind of wheel you need.
Each new wheel should have the same load carrying capacity, diameter,
width, offset, and be mounted the same way as the one
it replaces.
If you need to replace any of your wheels, wheel bolts, or wheel nuts,
replace them only with new
GM original equipment parts. This way, you
will be sure to have the right wheel, wheel bolts, and wheel nuts for your
vehicle.
A CAUTION:
Using the wrong replacement wheels, wheel bolts, or wheel nuts
on your vehicle can be dangerous. It could affect the braking
and handling
of your vehicle, make your tires lose air and make
you lose control, You could have a collision in which
you or
others could be injured. Always use the correct wheel, wheel
bolts, and wheel
nuts for replacement.
NOTICE:
The wrong wheel can also cause problems with bearing life,
brake cooling, speedometer/odometer calibration, headlamp
aim, bumper height, vehicle ground clearance, and tire or tire
chain clearance to the body and chassis.
6-65
ProCarManuals.com
Page 332 of 488

Whenever a wheel, wheel bolt or wheel nut is replaced on a dual wheel
setup, check the wheel nut torque after 100, 1,000 and 6,000 miles ( 160,
1 600 and 10 000 km) of driving. For proper torque, see “Wheel Nut
Torque” in the Index.
Used Replacement Wheels
A CAUTION:
Putting a used wheel on your vehicle is dangerous. You can’t
know
how it’s been used or how many miles it’s been driven. It
could fail suddenly and cause an accident. If you have to replace
a wheel use a new GM original equipment wheel.
7
c
‘ire Chains
NOTICE:
If your vehicle has dual wheels or LT265/75R16 size tires, don’t
use tire chains; they can damage your vehicle.
If you don’t have dual wheels or if you have a tire size other
than
LT26975R16, use tire chains only where legal and only
when you must. Use chains that are the proper size for your
tires. Install them on the tires of the rear axle.
Don’t use chains on the tires
of the front axle.
Tighten them
as tightly as possible with the ends securely
fastened. Drive slowly and follow the chain manufacturer’s
instructions. If you can hear the chains contacting your vehicle,
stop and retighten them. If the contact continues, slow down
until it stops. Driving too fast
or spinning the wheels with chains
on
will damage your vehicle.
6-66
ProCarManuals.com
Page 339 of 488

Protecting Exterior Bright Metal Parts
Bright metal parts should be cleaned regularly to keep their luster. Washing
with water is all that is usually needed. However, you may use
GM Chrome
Polish on chrome or stainless steel trim, if necessary.
Use special care with aluminum trim.
To avoid damaging protective trim,
never use auto or chrome polish, steam or caustic soap to clean aluminum.
A coating of wax, rubbed to high polish, is recommended for all bright
metal parts.
Aluminum Wheels (If So Equipped)
Your aluminum wheels have a protective coating similar to the painted
surface of your vehicle. Don’t use strong soaps, chemicals, chrome polish,
abrasive cleaners or abrasive cleaning brushes
on them because you could
damage this coating. After rinsing thoroughly, a wax may be applied.
I NOTICE:
If you have aluminum wheels, don’t use an automatic car wash
that has hard silicon carbide cleaning brushes. These brushes can take the protective coating
off your aluminum wheels.
Tires
To clean your tires, use a stiff brush with a tire cleaner.
When applying a tire dressing always take care to wipe off any overspray or
splash from painted surfaces. Petroleum-based products may damage the
paint finish.
Sheet Metal Damage
If your vehicle is damaged and requires sheet metal repair or replacement,
make sure the body repair shop applies anti-corrosion material to the parts
repaired or replaced to restore corrosion protection.
Foreign Material
Calcium chloride and other salts, ice melting agents, road oil and tar, tree
sap, bird droppings, chemicals from industrial chimneys, and other foreign \
matter can damage your vehicle’s finish if they remain on painted surfaces.
Use cleaners that are marked safe for painted surfaces to remove foreign
matter.
6.- 73
ProCarManuals.com