1994 JEEP CHEROKEE brake rotor
[x] Cancel search: brake rotorPage 184 of 1784

(9) Coat cylinder bore, pistons, cups and expander
with brake fluid and reassemble cylinder compo-
nents. Be sure piston cup lips face expander.
WHEEL CYLINDER INSTALLATION
(1) Apply small bead of silicone sealer around cyl-
inder mounting surface of support plate.
(2) Start brakeline in wheel cylinder fitting by
hand.
(3) Align and seat wheel cylinder on support plate
(Fig. 10).
(4) Install cylinder mounting bolts (Fig. 10).
Tighten bolts to 10 Nzm (90 in. lbs.) torque.
(5) Tighten brakeline fitting to 15 Nzm (132 in.
lbs.) torque.
(6) Install brakeshoes. Adjust shoes to drum with
brake gauge.
(7) Install brake drums and lower vehicle.
(8) Fill master cylinder and bleed brakes.
SUPPORT PLATE REPLACEMENT
The support plate should cleaned and inspected
whenever the drum brake components are being ser-
viced.
Check the support plate for wear, or rust through
at the contact pads and replace the plate if neces-
sary. Be sure to lubricate the contact pads with Mo-
par multi-mileage grease before shoe installation.
Lubrication will avoid noisy operation and shoe bind.
(1) Raise vehicle and remove wheel/tire assembly.(2) Remove brake drum, brakeshoes, and wheel
cylinder.
(3) Remove axle shaft as described in Group 3.
(4) Remove support plate attaching nuts and re-
move support plate.
(5) Clean axle tube flange. If gasket is not used on
flange, apply thin bead of silicone adhesive/sealer to
flange.
(6) Position new support plate on axle tube flange.
(7) Apply Mopar Lock N9Seal, or Loctite 242 to
support plate attaching nuts. Then install and
tighten nuts.
(8) Apply light coat of Mopar multi-mileage grease
to contact pads of new support plate.
(9) Install wheel cylinder and brakeshoes.
(10) Adjust brakeshoes to drums. Refer to proce-
dure in this section.
(11) Bleed brakes.
(12) Install wheel and tire assembly.
(13) Adjust parking brake cable tensioner. Refer to
procedure in Parking Brake section.
(14) Lower vehicle and verify proper service brake
and parking brake operation.
BRAKE DRUM REFINISHING
Brake drums can be machined to restore the brak-
ing surface. Use a brake lathe to clean up light scor-
ing and wear.
CAUTION: Never refinish a brake drum if machining
will cause the drum to exceed maximum allowable
brake surface diameter.
Brake drums that are warped, distorted, or se-
verely tapered should be replaced. Do not refinish
drums exhibiting these conditions. Brake drums that
are heat checked or have hard spots should also be
replaced.
If the brake drums are heavily coated with rust,
clean and inspect them carefully. Rust damage on
high mileage drums can be severe enough to require
replacement.
The maximum allowable diameter for the drum
braking surface is usually indicated on the drum
outer face (Fig. 11).
WHEEL NUT TIGHTENING
The wheel attaching lug nuts must be tightened
properly to ensure efficient brake operation. Over-
tightening the nuts or tightening them in the wrong
sequence can cause distortion of the brake rotors and
drums.
Impact wrenches are not recommended for tighten-
ing wheel nuts. A torque wrench should be used for
this purpose.
A light coat of LPS Anti-Corrosion spray lube
around the hub face and on the studs will cut down
on rust/corrosion formation.
Fig. 9 Wheel Cylinder (10-Inch Brake)
Fig. 10 Wheel Cylinder Mounting
JBRAKES 5 - 37
Page 185 of 1784

The correct tightening sequence is important in
avoiding rotor and drum distortion. The correct se-
quence is in a diagonal crossing pattern (Fig. 12).
Recommended torque range for XJ/YJ wheel lug
nuts is 109-150 Nzm (80-110 ft. lbs.).
Seat the wheel and install the wheel nuts finger
tight. Tighten the nuts in the sequence to half the
required torque. Then repeat the tightening sequence
to final specified torque.
Fig. 11 Typical Location Of Brake Drum Refinish
Limit
Fig. 12 Wheel Nut Tightening Sequence
5 - 38 BRAKESJ
Page 194 of 1784
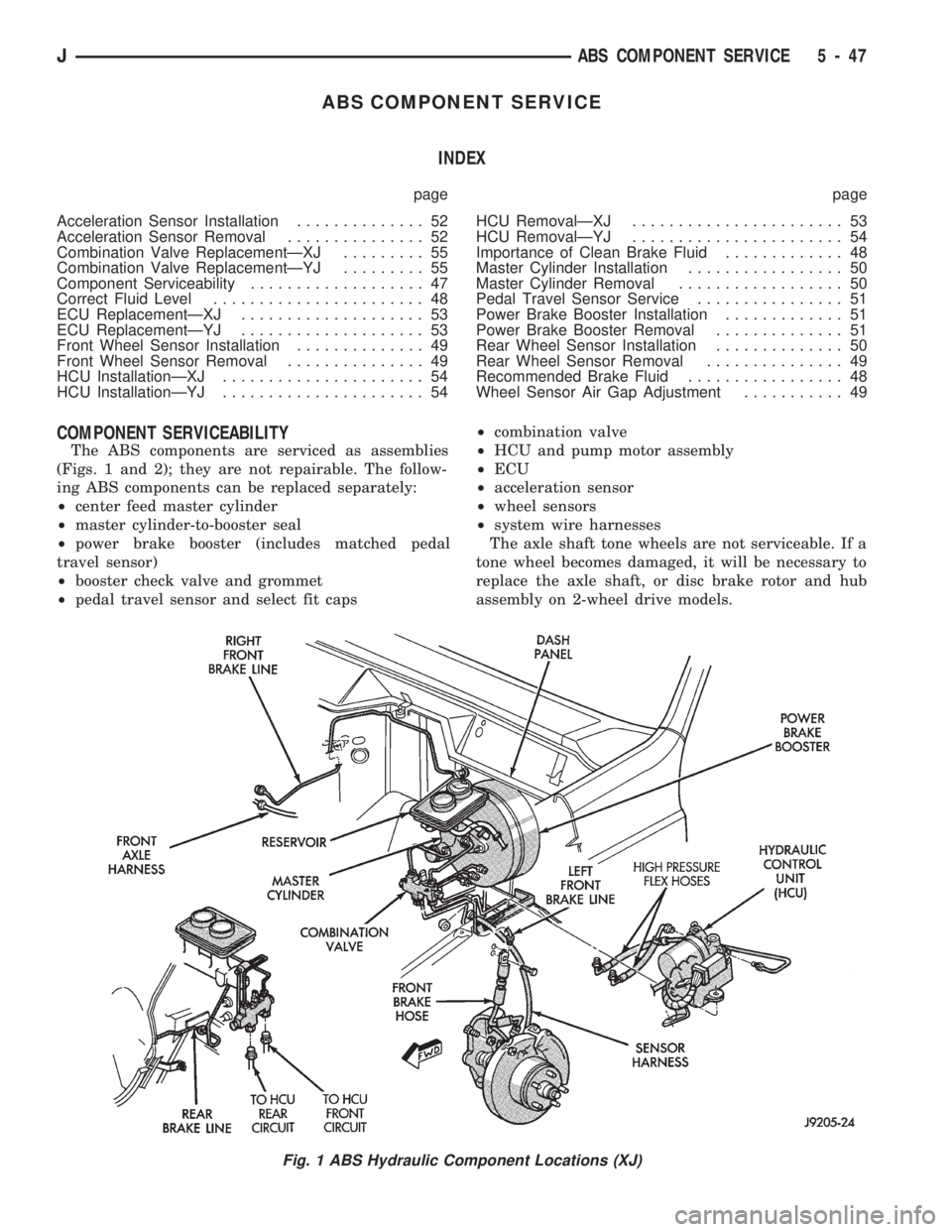
ABS COMPONENT SERVICE
INDEX
page page
Acceleration Sensor Installation.............. 52
Acceleration Sensor Removal............... 52
Combination Valve ReplacementÐXJ......... 55
Combination Valve ReplacementÐYJ......... 55
Component Serviceability................... 47
Correct Fluid Level....................... 48
ECU ReplacementÐXJ.................... 53
ECU ReplacementÐYJ.................... 53
Front Wheel Sensor Installation.............. 49
Front Wheel Sensor Removal............... 49
HCU InstallationÐXJ...................... 54
HCU InstallationÐYJ...................... 54HCU RemovalÐXJ....................... 53
HCU RemovalÐYJ....................... 54
Importance of Clean Brake Fluid............. 48
Master Cylinder Installation................. 50
Master Cylinder Removal.................. 50
Pedal Travel Sensor Service................ 51
Power Brake Booster Installation............. 51
Power Brake Booster Removal.............. 51
Rear Wheel Sensor Installation.............. 50
Rear Wheel Sensor Removal............... 49
Recommended Brake Fluid................. 48
Wheel Sensor Air Gap Adjustment........... 49
COMPONENT SERVICEABILITY
The ABS components are serviced as assemblies
(Figs. 1 and 2); they are not repairable. The follow-
ing ABS components can be replaced separately:
²center feed master cylinder
²master cylinder-to-booster seal
²power brake booster (includes matched pedal
travel sensor)
²booster check valve and grommet
²pedal travel sensor and select fit caps²combination valve
²HCU and pump motor assembly
²ECU
²acceleration sensor
²wheel sensors
²system wire harnesses
The axle shaft tone wheels are not serviceable. If a
tone wheel becomes damaged, it will be necessary to
replace the axle shaft, or disc brake rotor and hub
assembly on 2-wheel drive models.
Fig. 1 ABS Hydraulic Component Locations (XJ)
JABS COMPONENT SERVICE 5 - 47
Page 195 of 1784

The wheel brake components such as the calipers,
brakeshoes, wheel cylinders, rotors and drums are all
serviced the same as standard brake system compo-
nents.
RECOMMENDED BRAKE FLUID
Recommended brake fluid for the Jeep ABS system
is Mopar DOT 3 brake fluid. If Mopar fluid is not
readily available, a top quality fluid meeting SAE
J1703 and DOT 3 standards can be used.
Brake fluid used in the ABS system must meet the
SAE and DOT quality standards and be exception-
ally clean.Never use substandard fluid, fluid not
meeting the SAE and DOT standards, reclaimed
fluid, or fluid from open containers.
CORRECT FLUID LEVEL
Correct brake fluid level is marked on the driver
side of the master cylinder reservoir (Fig. 3).
Preferred fluid level is to the MAX indicator mark.
Acceptable fluid level is between the MAX and MIN
marks.
If fluid level is at or below the MIN mark, the
brake hydraulic system should be checked for leaks.
CAUTION: Clean the reservoir caps and exterior
thoroughly before checking fluid level. Do not allow
any dirt or foreign material to enter the reservoirwhile checking fluid level. Such materials can inter-
fere with solenoid valve operation causing an ABS
malfunction.
IMPORTANCE OF CLEAN BRAKE FLUID
The antilock system brake fluid must be kept clean
and uncontaminated. Foreign material in the fluid,
or non-recommended fluids will cause system mal-
functions.
Fig. 2 ABS Hydraulic Component Locations (YJ)
Fig. 3 Reservoir Fluid Level Indicators
5 - 48 ABS COMPONENT SERVICEJ
Page 1268 of 1784

The valve body solenoids are controlled by signals
from the transmission control module (TCM). Signal
sequence is determined by vehicle speed and throttle
position.
Fourth gear is an 0.75:1 ratio overdrive range.
First, second, third and reverse gear are conventional
ranges. Third gear ratio is 1:1. A separate planetary
gear set provides overdrive operation in fourth gear.
TRANSMISSION RANGES AND SHIFT LEVER
POSITIONS
The AW-4 transmission has six ranges and shift le-
ver positions. Park, Reverse and Neutral are conven-
tional and mechanically operated. The 1-2, 3 and D
ranges provide electronically controlled shifting.
The 1-2 position provides first and second gear
only. The 3 position provides first, second and third
gear.
The D range provides first through fourth gear.
Overdrive fourth gear range is available only when
the shift lever is in D position (Fig. 2).
TRANSMISSION IDENTIFICATION
The transmission I.D. plate is attached to the case
(Fig. 3). The plate contains the transmission serial
and model numbers. Refer to the information on this
plate when ordering service parts.
COMPONENTS AND OPERATION
ELECTRONIC CONTROLS
The AW-4 is electronically controlled in the 1, 2, 3
and D ranges. Controls consist of the transmission
control module (TCM), valve body solenoids and var-ious sensors. The sensors monitor vehicle speed,
throttle opening, shift lever position and brake pedal
application.
TRANSMISSION CONTROL MODULE (TCM)
The module determines shift and converter clutch
engagement timing based on signals from the sen-
sors. The valve body solenoids are activated, or deac-
tivated accordingly.
The module has a self diagnostic program. Compo-
nent and circuitry malfunctions can be diagnosed
with the DRB II scan tool. Once a malfunction is
noted and stored in control module memory, it is re-
tained even after the problem has been corrected. To
cancel a stored malfunction, simply disconnect and
reconnect the9Trans.9fuse in the module harness.
TRANSMISSION VALVE BODY SOLENOIDS
The solenoids are mounted on the valve body and
operated by the transmission control module. The so-
lenoids control operation of the converter clutch and
shift valves in response to input signals from the
module.
SENSORS
The sensors include the throttle position sensor
(TPS), transmission output speed sensor, vehicle
speed sensor, park/neutral position switch and brake
switch.
The throttle position sensor is mounted on the
throttle body. It electronically determines throttle po-
sition and relays this information to the transmission
control module to determine shift points and con-
verter clutch engagement.
The transmission speed sensor consists of a rotor
and magnet on the transmission output shaft and a
switch in the extension housing or adapter. The sen-
sor switch is activated each time the rotor and mag-
Fig. 2 AW-4 Shift Lever Positions And Transmission
Ranges
Fig. 3 Transmission Identification
JAW-4 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION 21 - 157
Page 1284 of 1784

AW-4 IN-VEHICLE SERVICE
INDEX
page page
Accumulator Pistons and Springs........... 179
Adapter Housing Seal Replacement.......... 182
Checking Fluid Level and Condition.......... 173
Manual Valve Shaft Seal Replacement....... 178
Park Interlock Cable Adjustment............ 186
Park Rod and Pawl Service................ 181
Park/Neutral Position Switch............... 173
Second Coast Brake Servo................ 181
Shift Cable Adjustment................... 186
Speed Sensor.......................... 182Speed Sensor RotorÐSpeedometer Drive Gear . 183
Throttle Position Sensor (TPS) Service....... 184
Transmission Control Module (TCM) Service . . . 173
Transmission Cooler Line Fittings........... 187
Transmission Cooler Service............... 187
Transmission Throttle Cable Adjustment....... 185
Transmission Throttle Cable Replacement..... 184
Transmission Valve Body Installation......... 177
Transmission Valve Body Removal.......... 176
Transmission Valve Body Solenoids.......... 175
CHECKING FLUID LEVEL AND CONDITION
Recommended fluid for AW-4 transmissions is Mo-
par Dexron IIE/Mercon. Mopar Dexron II may be
used if Mercon fluid is not readily available.
CHECKING FLUID LEVEL
(1) Be sure transmission fluid is at normal operat-
ing temperature. Normal operating temperature is
reached after approximately 15 miles (25 km) of op-
eration.
(2) Position vehicle on level surface. This is impor-
tant for an accurate fluid level check.
(3) Shift transmission through all gear ranges and
back to Park.
(4) Apply parking brakes.
(5) Verify that transmission is in Park.
(6) Wipe off dipstick handle to prevent dirt from
entering fill tube. Then remove dipstick and check
fluid level and condition.
(7) Correct fluid level isto FULL mark on dip-
stick when fluid is at normal operating temper-
ature(Fig. 1).
(8) If fluid level is low, top off level with Mopar
Dexron IIE/Mercon. Mopar Dexron II may also be
used if Mercon is not available.Do not overfill
transmission. Add only enough fluid to bring
level to Full mark.
CHECKING FLUID CONDITION
Inspect the appearance of the fluid during the fluid
level check. The fluid should be clear and free of for-eign material or particles. If the fluid is dark brown
or black in color and smells burnt, the fluid has been
overheated and should be replaced.
Transmission operation should also be checked if
the fluid is severely discolored and contains quanti-
ties of foreign material, metal particles, or clutch disc
friction material.
A small quantity of friction material or metal
particles in the oil pan is normal. The particles
are usually generated during the break-in pe-
riod and indicate normal seating of the various
transmission components.
TRANSMISSION CONTROL MODULE (TCM)
SERVICE
Use the DRB II scan tool to diagnose transmission
control module function whenever a fault is sus-
pected. Replace the module only when actually faulty.
TRANSMISSION CONTROL MODULE
REPLACEMENT
The transmission control module is mounted under
the instrument panel. On left hand drive models, it is
at the driver side of the lower finish panel (Fig. 2).
On right hand drive models, it is at the passenger
side of the lower finish panel (Fig. 3).
To remove the module, disconnect the wire harness,
remove the mounting screws and remove the module
from the finish panel. Tighten the module mounting
screws securely after installation. Also be sure the
wire harness is not twisted, kinked or touching any
body panels.
PARK/NEUTRAL POSITION SWITCH
SWITCH TESTING
Test switch continuity with an ohmmeter. Discon-
nect the switch and check continuity at the connector
terminal positions and in the gear ranges indicated
in Figure 3. Switch continuity should be as follows:Fig. 1 Transmission Fluid Level
JAW-4 IN-VEHICLE SERVICE 21 - 173
Page 1293 of 1784
(8) Install park rod and bracket (Fig. 33). Tighten
bracket bolts to 10 Nzm (7 ft. lbs.) torque.
(9) Install valve body, oil screen and oil pan as out-
lined in this section.
ADAPTER HOUSING SEAL REPLACEMENT
(1) Raise vehicle.
(2) Disconnect or remove components necessary to
gain access to seal (e.g. propeller shaft, crossmember,
shift linkage, transfer case, exhaust components,
hoses, wires).
(3) Remove dust shield and remove seal from
adapter housing (Fig. 36).
(4) Install new seal with appropriate size seal in-
staller and install dust shield.(5) Reinstall components removed to gain access to
seal.
(6) Top off transmission fluid if necessary.SPEED SENSOR
SPEED SENSOR TESTING
Test the speed sensor with an ohmmeter. Place the
ohmmeter leads on the terminals in the sensor con-
nector (Fig. 37).
Rotate the transmission output shaft and observe
the ohmmeter needle. The needle should deflect indi-
cating the switch is opening/closing as the rotor
Fig. 34 Removing/Installing Park Rod
Fig. 35 Removing/Installing Park Pawl, Pin And
Spring
Fig. 32 Second Coast Brake Servo Components
Fig. 33 Removing/Installing Park Rod Bracket
21 - 182 AW-4 IN-VEHICLE SERVICEJ
Page 1452 of 1784

Radial runout of more than 1.5 mm (.060 inch)
measured at the center line of the tread may cause
the vehicle to shake.
Lateral runout of more than 2.0 mm (.080 inch)
measured near the shoulder of the tire may cause the
vehicle to shake.
Sometimes radial runout can be reduced. Relocate
the wheel and tire assembly on the mounting studs
(See Method 1). If this does not reduce runout to an
acceptable level, the tire can be rotated on the wheel.
(See Method 2).
METHOD 1 (RELOCATE WHEEL ON HUB)
Check accuracy of the wheel mounting surface; ad-
just wheel bearings.
Drive vehicle a short distance to eliminate tire flat
spotting from a parked position.
Make sure all wheel nuts are properly torqued.
Relocate wheel on the mounting, two studs over
from the original position.
Re-tighten wheel nuts until all are properly
torqued, to eliminate brake distortion.
Check radial runout. If still excessive, mark tire
sidewall, wheel, and stud at point of maximum
runout and proceed to Method 2.
METHOD 2 (RELOCATE TIRE ON WHEEL)
Rotating tire on wheel is particularly effective
when there is runout in both tire and wheel.Remove tire from wheel and re-mount wheel on
hub in former position.
Check wheel radial runout (Fig. 9).
²STEEL WHEELS: Radial runout 0.040 in., Lateral
runout 0.045 in.
²ALUMINUM WHEELS: Radial runout 0.030 in.,
Lateral runout 0.035 in.
If point of greatest runout is near original chalk
mark, remount tire 180 degrees. Recheck runout.
VEHICLE VIBRATION
Vehicle vibration can be caused by:
²Tire/wheel unbalance or excessive runout
²Defective tires with extreme tread wear
²Nylon overlay flat spots (performance tires only)
²Incorrect wheel bearing adjustment (if applicable)
²Loose or worn suspension/steering components
²Certain tire tread patterns
²Incorrect drive shaft angles or excessive drive
shaft/yoke runout
²Defective or worn U-joints
²Excessive brake rotor or drum runout
²Loose engine or transmission supports/mounts
²And by engine operated accessories
Refer to the appropriate Groups in this man-
ual for additional information.
VIBRATION TYPES
There are two types of vehicle vibration:
²Mechanical
²Audible.
Mechanical vehicle vibration can be felt through
the seats, floor pan and/or steering wheel.
Audible vehicle vibration is heard above normal
background noise. The sound can be a droning or
drumming noise.Vibrations are sensitive to change in engine
torque, vehicle speed or engine speed.
ENGINE TORQUE SENSITIVE VIBRATION
This vibration can be increased or decreased by:
²Accelerating
²Decelerating
²Coasting
²Maintaining a constant vehicle speed
VEHICLE SPEED SENSITIVE VIBRATION
This vibration condition always occurs at the same
vehicle speed regardless of the engine torque or en-
gine speed.
ENGINE SPEED (RPM) SENSITIVE VIBRATION
This vibration occurs at varying engine speeds. It
can be isolated by increasing or decreasing the en-
gine speed with the transmission in NEUTRAL posi-
tion.
VIBRATION DIAGNOSIS
A vibration diagnosis should always begin with a
10 mile (16 km) trip (to warm the vehicle and tires).
Then a road test to identify the vibration. Corrective
Fig. 9 Checking Wheel Runout
JWHEELS AND TIRES 22 - 9