1994 JEEP CHEROKEE tire type
[x] Cancel search: tire typePage 1218 of 1784
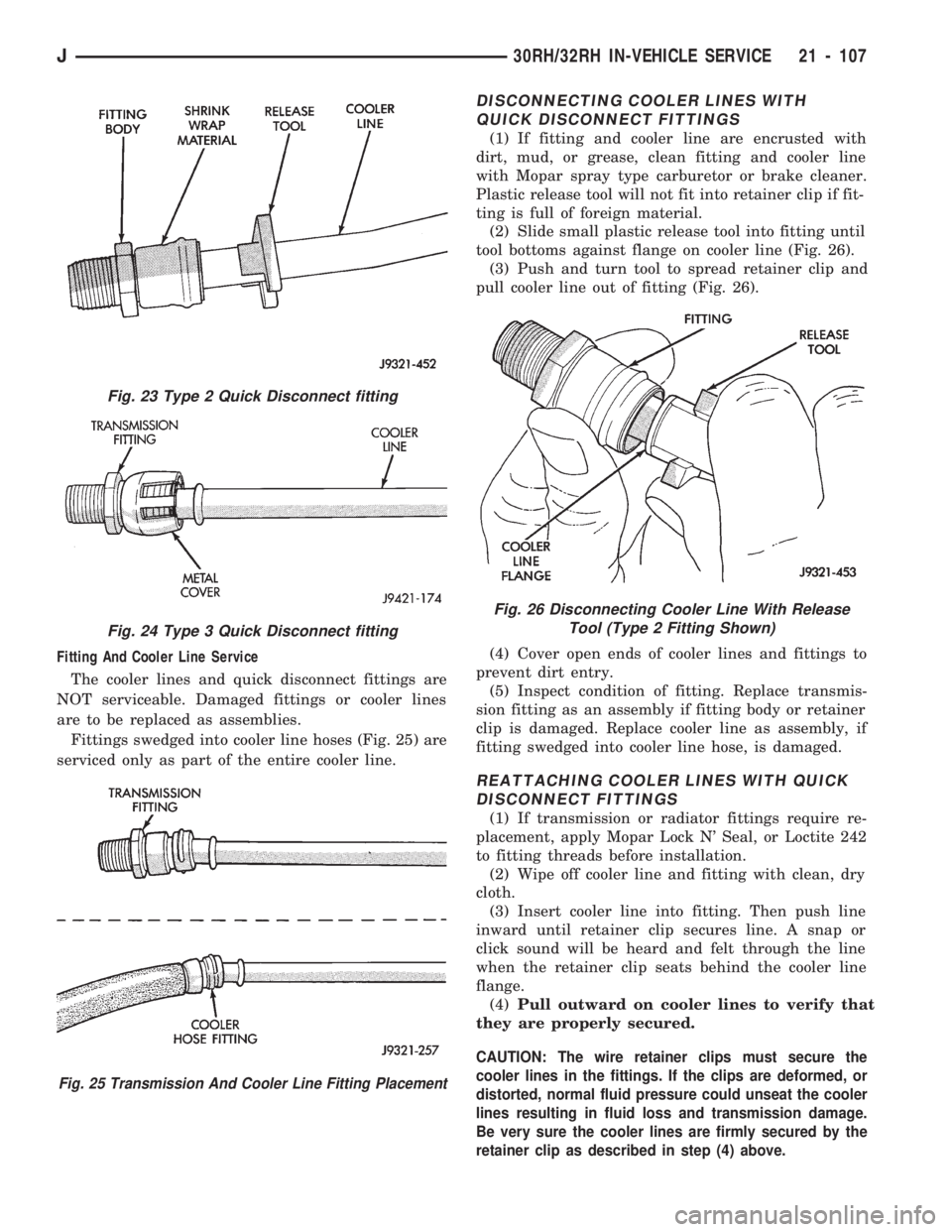
Fitting And Cooler Line Service
The cooler lines and quick disconnect fittings are
NOT serviceable. Damaged fittings or cooler lines
are to be replaced as assemblies.
Fittings swedged into cooler line hoses (Fig. 25) are
serviced only as part of the entire cooler line.
DISCONNECTING COOLER LINES WITH
QUICK DISCONNECT FITTINGS
(1) If fitting and cooler line are encrusted with
dirt, mud, or grease, clean fitting and cooler line
with Mopar spray type carburetor or brake cleaner.
Plastic release tool will not fit into retainer clip if fit-
ting is full of foreign material.
(2) Slide small plastic release tool into fitting until
tool bottoms against flange on cooler line (Fig. 26).
(3) Push and turn tool to spread retainer clip and
pull cooler line out of fitting (Fig. 26).
(4) Cover open ends of cooler lines and fittings to
prevent dirt entry.
(5) Inspect condition of fitting. Replace transmis-
sion fitting as an assembly if fitting body or retainer
clip is damaged. Replace cooler line as assembly, if
fitting swedged into cooler line hose, is damaged.
REATTACHING COOLER LINES WITH QUICK
DISCONNECT FITTINGS
(1) If transmission or radiator fittings require re-
placement, apply Mopar Lock N' Seal, or Loctite 242
to fitting threads before installation.
(2) Wipe off cooler line and fitting with clean, dry
cloth.
(3) Insert cooler line into fitting. Then push line
inward until retainer clip secures line. A snap or
click sound will be heard and felt through the line
when the retainer clip seats behind the cooler line
flange.
(4)Pull outward on cooler lines to verify that
they are properly secured.
CAUTION: The wire retainer clips must secure the
cooler lines in the fittings. If the clips are deformed, or
distorted, normal fluid pressure could unseat the cooler
lines resulting in fluid loss and transmission damage.
Be very sure the cooler lines are firmly secured by the
retainer clip as described in step (4) above.
Fig. 23 Type 2 Quick Disconnect fitting
Fig. 24 Type 3 Quick Disconnect fitting
Fig. 25 Transmission And Cooler Line Fitting Placement
Fig. 26 Disconnecting Cooler Line With Release
Tool (Type 2 Fitting Shown)
J30RH/32RH IN-VEHICLE SERVICE 21 - 107
Page 1444 of 1784

WHEELS AND TIRES
CONTENTS
page page
SPECIFICATIONS....................... 11
TIRES................................. 1VEHICLE VIBRATION..................... 9
WHEELS............................... 6
TIRES
INDEX
page page
Cleaning of Tires.......................... 2
General Information........................ 1
Pressure Gauges......................... 2
Repairing Leaks.......................... 3
Replacement Tires........................ 2Rotation................................ 3
Tire Inflation Pressures..................... 2
Tire Noise or Vibration..................... 4
Tire Wear Patterns........................ 4
Tread Wear Indicators...................... 3
GENERAL INFORMATION
Tires are designed for each specific vehicle. They
provide the best overall performance for normal op-
eration. The ride and handling characteristics match
the vehicle's requirements. With proper care they
will give excellent reliability, traction, skid resis-
tance, and tread life. These tires have specific load
carrying capacities. When correctly inflated, they
will operate properly.
Tires used in cool climates, and with light loads
will have a longer life than tires used in hot climates
with heavy loads. Abrasive road surfaces will accel-
erate tire wear.
Driving habits have more effect on tire life than
any other factor. Careful drivers will obtain much
greater mileage than careless drivers.
Driving habits that shorten the life of any tire;
²Rapid acceleration and deceleration
²Severe application of brakes
²High-speed driving
²Taking turns at excessive speeds
²Striking curbs and other obstacles
It is very important to follow the tire rotation in-
terval
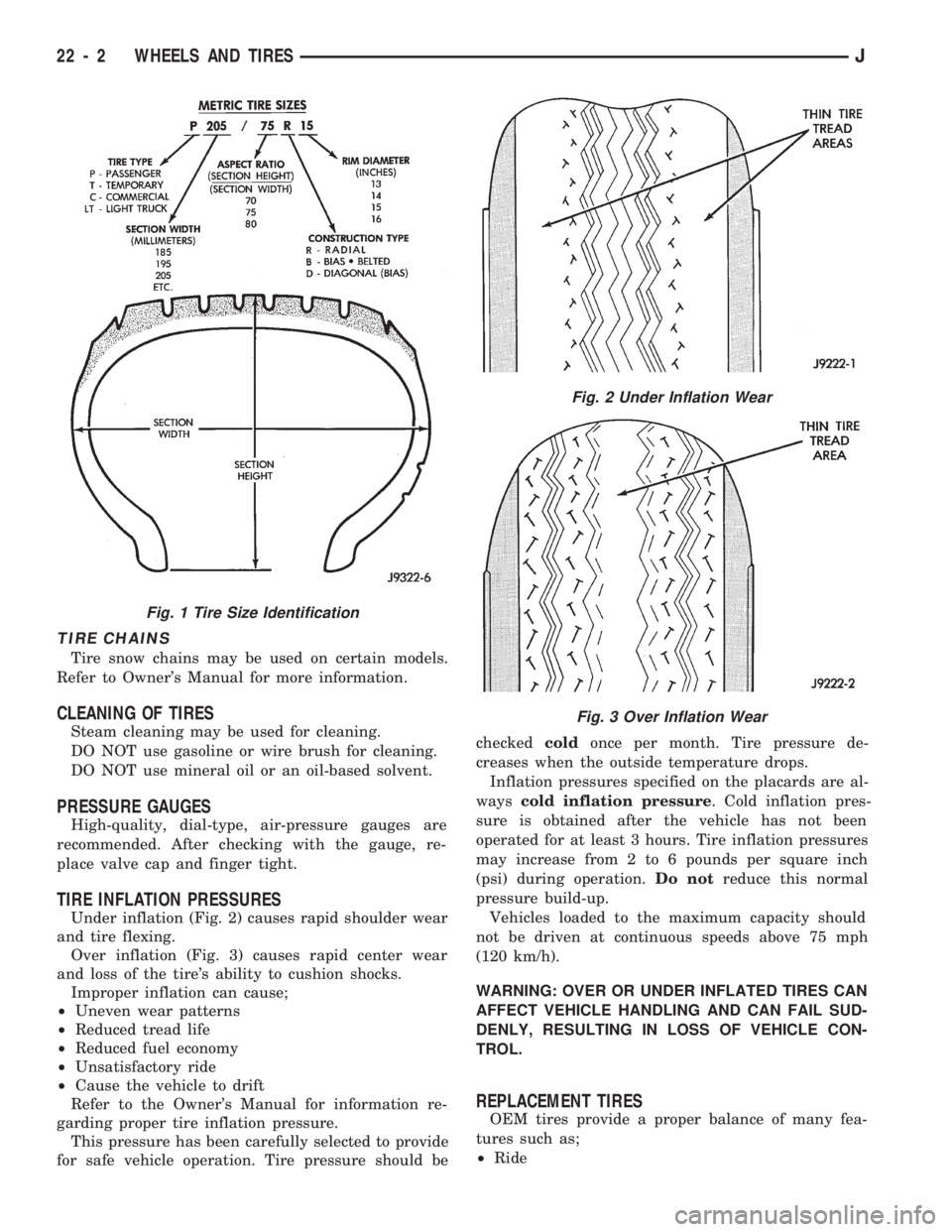
IDENTIFICATION
Tire type, size, aspect ratio and speed rating are
encoded in the letters and numbers imprinted on the
side wall of the tire. Refer to the chart to decipher
the tire identification code (Fig. 1).
Performance tires will have a speed rating letter
after the aspect ratio number. The speed rating isnot always printed on the tire sidewall. The letterS
indicates that the tire is speed rated up to 112 mph.
²Qup to 100 mph
²Tup to 118 mph
²Uup to 124 mph
²Hup to 130 mph
²Vup to 149 mph
²Zmore than 149 mph (consult the tire manufac-
turer for the specific speed rating)
An All Season type tire will have eitherM+S,M
&SorMÐS(indicating mud and snow traction) im-
printed on the side wall.
RADIAL-PLY TIRES
Radial-ply tires improve handling, tread life, ride
quality and decrease rolling resistance.
Radial-ply tires must always be used in sets of
four. Under no circumstances should they be used on
the front only. They may be mixed with temporary
spare tires when necessary, but reduced speeds are
recommended.
Radial-ply tires have the same load-carrying capac-
ity as other types of tires of the same size. They use
the same recommended inflation pressures.
SPARE TIRE (TEMPORARY)
The compact spare tire is designed for emergency
use only. The original tire should be repaired and re-
installed at the first opportunity. Refer to Owner's
Manual for complete details.
JWHEELS AND TIRES 22 - 1
Page 1445 of 1784
TIRE CHAINS
Tire snow chains may be used on certain models.
Refer to Owner's Manual for more information.
CLEANING OF TIRES
Steam cleaning may be used for cleaning.
DO NOT use gasoline or wire brush for cleaning.
DO NOT use mineral oil or an oil-based solvent.
PRESSURE GAUGES
High-quality, dial-type, air-pressure gauges are
recommended. After checking with the gauge, re-
place valve cap and finger tight.
TIRE INFLATION PRESSURES
Under inflation (Fig. 2) causes rapid shoulder wear
and tire flexing.
Over inflation (Fig. 3) causes rapid center wear
and loss of the tire's ability to cushion shocks.
Improper inflation can cause;
²Uneven wear patterns
²Reduced tread life
²Reduced fuel economy
²Unsatisfactory ride
²Cause the vehicle to drift
Refer to the Owner's Manual for information re-
garding proper tire inflation pressure.
This pressure has been carefully selected to provide
for safe vehicle operation. Tire pressure should becheckedcoldonce per month. Tire pressure de-
creases when the outside temperature drops.
Inflation pressures specified on the placards are al-
wayscold inflation pressure. Cold inflation pres-
sure is obtained after the vehicle has not been
operated for at least 3 hours. Tire inflation pressures
may increase from 2 to 6 pounds per square inch
(psi) during operation.Do notreduce this normal
pressure build-up.
Vehicles loaded to the maximum capacity should
not be driven at continuous speeds above 75 mph
(120 km/h).
WARNING: OVER OR UNDER INFLATED TIRES CAN
AFFECT VEHICLE HANDLING AND CAN FAIL SUD-
DENLY, RESULTING IN LOSS OF VEHICLE CON-
TROL.
REPLACEMENT TIRES
OEM tires provide a proper balance of many fea-
tures such as;
²Ride
Fig. 1 Tire Size Identification
Fig. 2 Under Inflation Wear
Fig. 3 Over Inflation Wear
22 - 2 WHEELS AND TIRESJ
Page 1452 of 1784

Radial runout of more than 1.5 mm (.060 inch)
measured at the center line of the tread may cause
the vehicle to shake.
Lateral runout of more than 2.0 mm (.080 inch)
measured near the shoulder of the tire may cause the
vehicle to shake.
Sometimes radial runout can be reduced. Relocate
the wheel and tire assembly on the mounting studs
(See Method 1). If this does not reduce runout to an
acceptable level, the tire can be rotated on the wheel.
(See Method 2).
METHOD 1 (RELOCATE WHEEL ON HUB)
Check accuracy of the wheel mounting surface; ad-
just wheel bearings.
Drive vehicle a short distance to eliminate tire flat
spotting from a parked position.
Make sure all wheel nuts are properly torqued.
Relocate wheel on the mounting, two studs over
from the original position.
Re-tighten wheel nuts until all are properly
torqued, to eliminate brake distortion.
Check radial runout. If still excessive, mark tire
sidewall, wheel, and stud at point of maximum
runout and proceed to Method 2.
METHOD 2 (RELOCATE TIRE ON WHEEL)
Rotating tire on wheel is particularly effective
when there is runout in both tire and wheel.Remove tire from wheel and re-mount wheel on
hub in former position.
Check wheel radial runout (Fig. 9).
²STEEL WHEELS: Radial runout 0.040 in., Lateral
runout 0.045 in.
²ALUMINUM WHEELS: Radial runout 0.030 in.,
Lateral runout 0.035 in.
If point of greatest runout is near original chalk
mark, remount tire 180 degrees. Recheck runout.
VEHICLE VIBRATION
Vehicle vibration can be caused by:
²Tire/wheel unbalance or excessive runout
²Defective tires with extreme tread wear
²Nylon overlay flat spots (performance tires only)
²Incorrect wheel bearing adjustment (if applicable)
²Loose or worn suspension/steering components
²Certain tire tread patterns
²Incorrect drive shaft angles or excessive drive
shaft/yoke runout
²Defective or worn U-joints
²Excessive brake rotor or drum runout
²Loose engine or transmission supports/mounts
²And by engine operated accessories
Refer to the appropriate Groups in this man-
ual for additional information.
VIBRATION TYPES
There are two types of vehicle vibration:
²Mechanical
²Audible.
Mechanical vehicle vibration can be felt through
the seats, floor pan and/or steering wheel.
Audible vehicle vibration is heard above normal
background noise. The sound can be a droning or
drumming noise.Vibrations are sensitive to change in engine
torque, vehicle speed or engine speed.
ENGINE TORQUE SENSITIVE VIBRATION
This vibration can be increased or decreased by:
²Accelerating
²Decelerating
²Coasting
²Maintaining a constant vehicle speed
VEHICLE SPEED SENSITIVE VIBRATION
This vibration condition always occurs at the same
vehicle speed regardless of the engine torque or en-
gine speed.
ENGINE SPEED (RPM) SENSITIVE VIBRATION
This vibration occurs at varying engine speeds. It
can be isolated by increasing or decreasing the en-
gine speed with the transmission in NEUTRAL posi-
tion.
VIBRATION DIAGNOSIS
A vibration diagnosis should always begin with a
10 mile (16 km) trip (to warm the vehicle and tires).
Then a road test to identify the vibration. Corrective
Fig. 9 Checking Wheel Runout
JWHEELS AND TIRES 22 - 9
Page 1453 of 1784

action should not be attempted until the vibration
type has been identified via a road test.
During the road test, drive the vehicle on a smooth
surface. If vibration exists, note and record the fol-
lowing information:
²Identify the vehicle speed range when the vibra-
tion occurs
²Identify the type of vibration
²Identify the vibration sensitivity
²Determine if the vibration is affected by changes
in vehicle speed, engine speed and engine torque.
When the vibration has been identified, refer to the
Vibration Diagnosis chart for causes. Consider cor-
recting only those causes coded in the chart that are
related to the vibration condition.
Refer to the following cause codes and descriptions
for explanations when referring to the chart.
TRRÐTire and Wheel Radial Runout:Vehicle
speed sensitive, mechanical vibration. The runout
will not cause vibration below 20 mph (32 km/h).
WHÐWheel Hop:Vehicle speed sensitive, me-
chanical vibration. The wheel hop generates rapid
up-down movement in the steering wheel. The vibra-
tion is most noticeable in the 20 - 40 mph (32 - 64
km/h) range. The wheel hop will not cause vibration
below 20 mph (32 km/h). Wheel hop is caused by a
tire/wheel that has a radial runout of more than
0.045 of-an-inch (1.14 mm). If wheel runout is accept-able and combined runout cannot be reduced by re-
positioning the tire on wheel, replace tire.
TBÐTire/Wheel Balance:Vehicle speed sensitive,
mechanical vibration. Static tire/wheel unbalance
will not cause vibration below 30 mph (46 km/h). Dy-
namic tire/wheel unbalance will not cause vibration
below 40 mph (64 km/h).
TLRÐTire/Wheel Lateral runout:Vehicle speed
sensitive, mechanical vibration. The runout will not
cause vibration below 50 - 55 mph (80 - 88 km/h).
Excessive lateral runout will also cause front-end
shimmy.
TWÐTire Wear:Vehicle speed sensitive, audible
vibration. Abnormal tire wear causes small vibration
in the 30 - 55 mph (88 km/h) range. This will pro-
duce a whine noise at high speed. The whine will
change to a growl noise when the speed is reduced.
WÐTire Waddle:Vehicle speed sensitive, mechan-
ical vibration. Irregular tire uniformity can cause
side-to-side motion during speeds up to 15 mph (24
km/h). If the motion is excessive, identify the defec-
tive tire and replace it.
UAJÐUniversal Joint (Drive Shaft) Angles:
Torque/vehicle speed sensitive, mechanical/audible
vibration. Incorrect drive shaft angles cause mechan-
ical vibration below 20 mph (32 km/h) and in the 70
VIBRATION DIAGNOSIS
22 - 10 WHEELS AND TIRESJ
Page 1543 of 1784
The reinforcement bracket is held on the
frame rail with two blind rivets.
(2) Remove the bracket and tow hook from frame
rail.
INSTALLATION
(1) Position bracket and tow hook on the frame
rail.
(2) Install bolts that attach tow hook bracket to
frame rail and reinforcement bracket. Tighten bolts
to 75 Nzm (55 ft-lbs) torque.
TRAILER HITCHES
CLASS III HITCHÐXJ VEHICLES
A class III weight-distributing/equalizer type hitch
can be used to tow a trailer:
²having a maximum gross weight of 5,000 lbs/2250
kg, and
²having a maximum tongue weight of 750 lbs/332
kg).
The following vehicle basic equipment is required
for class III trailer towing:
²P205/75R15 or larger tires;
²full size spare tire;
²trailer sway control;
²trailer tow wire harness and connector;
²heavy duty turn signal flasher element;
²heavy duty axle (with synthetic lubricant);²heavy duty cooling system;
²heavy duty generator/battery;
²auxiliary automatic transmission fluid cooler; and
²I-6, 4.0L engine.
Wide-angle type door mirrors are recommended but
not required.
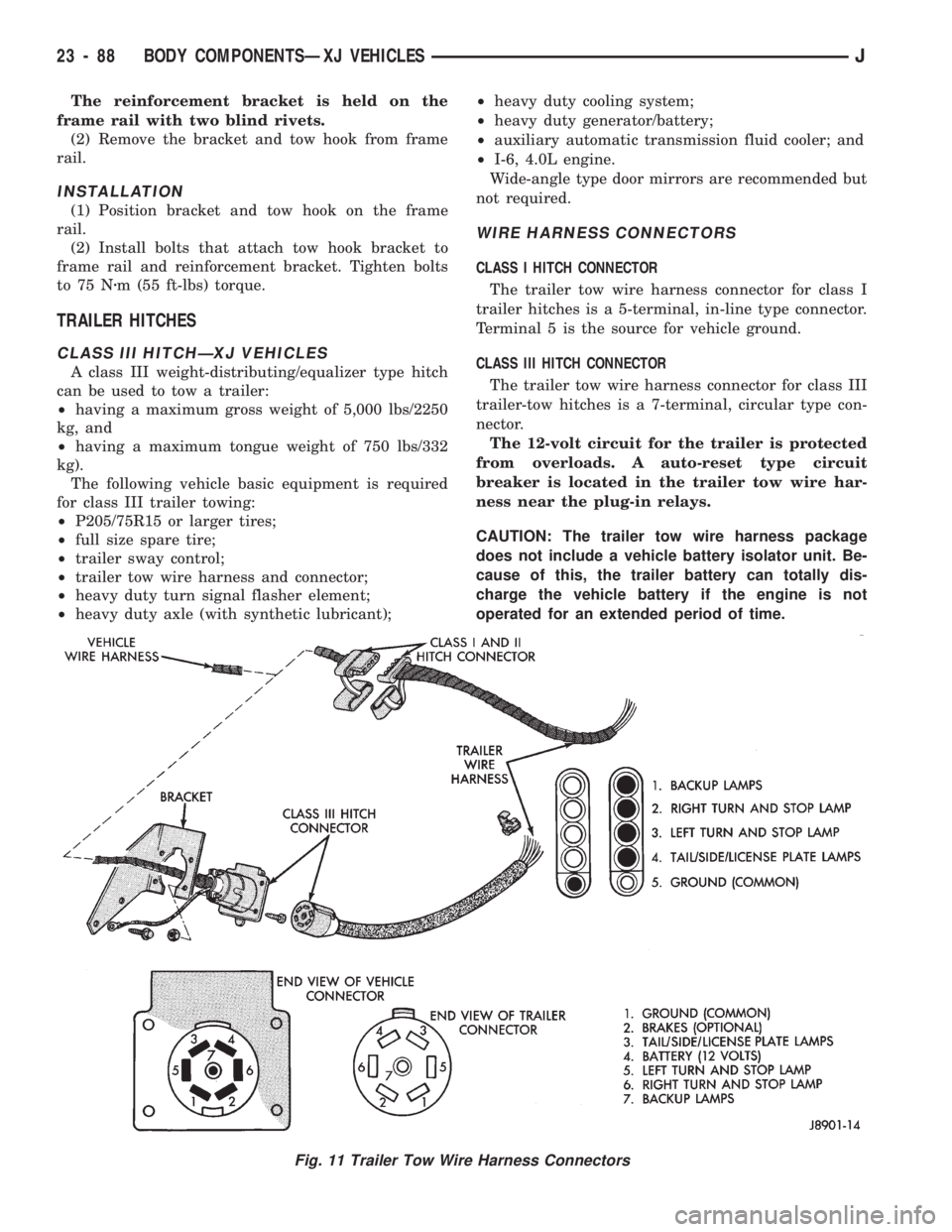
WIRE HARNESS CONNECTORS
CLASS I HITCH CONNECTOR
The trailer tow wire harness connector for class I
trailer hitches is a 5-terminal, in-line type connector.
Terminal 5 is the source for vehicle ground.
CLASS III HITCH CONNECTOR
The trailer tow wire harness connector for class III
trailer-tow hitches is a 7-terminal, circular type con-
nector.
The 12-volt circuit for the trailer is protected
from overloads. A auto-reset type circuit
breaker is located in the trailer tow wire har-
ness near the plug-in relays.
CAUTION: The trailer tow wire harness package
does not include a vehicle battery isolator unit. Be-
cause of this, the trailer battery can totally dis-
charge the vehicle battery if the engine is not
operated for an extended period of time.
Fig. 11 Trailer Tow Wire Harness Connectors
23 - 88 BODY COMPONENTSÐXJ VEHICLESJ
Page 1642 of 1784

CAUTION: Be prepared to install the windshield
glass immediately after applying the adhesive. The
adhesive begins to cure within 10-15 minutes.
(12) Align the windshield with the grease pencil
marks (or the tape strips) and position windshield on
frame flanges.
(13) Force the windshield glass inward just enough
to wet-out and set urethane. Use care to avoid exces-
sive squeeze-out of adhesive.
(14) Water test the windshield with a cold water
spray after installation. Do not direct high pressure
streams of water directly at the urethane. Use a
moderate spray only. If any leaks are detected, apply
urethane as necessary.
(15) Install the windshield reveal moulding and (if
used) remove the masking tape from the inner sur-
face of the glass.
(16) Install all removed components and clean the
vehicle. If necessary, refer to the applicable installa-
tion procedures.
(17) Open windows and liftgate to prevent pres-
sure build-up while the urethane is curing.
(18) Install the rearview mirror on the bracket and
tighten the mirror setscrew with 2 Nzm (15 in-lbs)
torque.
INSTALLATIONÐEXTENDED METHOD
Normally, after a windshield is installed, the rear-
view mirror bracket also requires installation.Do not
install the bracket until after the windshield in-
stallation is completed.
(1) Remove all of the original urethane from all the
frame pinchweld flanges. Use an electric hot knife
and a plow-type knife blade to remove the adhesive.
(2) Inspect and repair the windshield frame and
the pinchweld flanges as necessary.
(3) Inspect and replace the reveal moulding if the
retainers are damaged.(4) Prime the frame pinchweld flanges with a ure-
thane base primer. However, if the flange is top-
coated with paint, prime the flanges with a paint
finish primer.This is important because ure-
thane adhesive will not adhere to all top coat
paints.
(5) Install the replacement interior trim moulding
(Fig. 5) on the frame pinchweld flanges (Fig. 5).
(6) Install and inspect the fit of the windshield
glass on the pinchweld flanges according to the fol-
lowing instructions:
²position the windshield glass on the flanges and
adjust the position until it is correctly aligned within
the windshield frame;
²measure the gap between the frame and the glass
around the entire perimeter of the glass and the
flange;
²the gap should be at least 3 mm (1/8 in) but no
more than 6 mm (1/4 in) at any point around the pe-
rimeter; and
²the flanges should in complete contact with the
glass around the perimeter of the frame.
(7) If the pinchweld flanges require repair, remove
the windshield glass and straighten, align, or repair
the flange(s) as necessary.
(8) Position the windshield on the flanges and in-
spect the windshield fit again. If the fit is acceptable,
mark windshield final position on the glass and the
frame. The marks (or masking tape) will be used for
installation alignment reference.
(9) If the replacement windshield glass does not
have blackout primer:
²attach a 25-mm (1-in) wide masking tape band
around the interior side of the glass 16 mm (5/8 in)
from the edge of the glass (Fig. 6);
²attach the tape only to the interior side of
the glass;
²thoroughly mix and apply blackout primer to the
16 mm (5/8 in) surface area around the interior side
of the glass (Fig. 6); then
²allow the primer to dry for at least 10-12 minutes.
(10) Cut the urethane adhesive applicator nozzle
according to the instructions in Figure 7.
(11) Apply a 3-mm (1/8-in) diameter bead of ure-
thane to the surface area.
CAUTION: Be prepared to install the windshield
glass immediately after applying the adhesive. The
adhesive begins to cure within 10-15 minutes.
(12) Align windshield with reference marks (or the
tape strips) and position it on the frame pinchweld
flanges.
(13) Force the windshield glass inward just enough
to wet-out and set urethane. Use care to avoid exces-
sive squeeze-out of adhesive.
(14) Water test the windshield with a cold water
spray after installation. Do not direct high pressure
Fig. 7 Applicator Nozzle Preparation
JBODY COMPONENTSÐXJ VEHICLES 23 - 187
Page 1735 of 1784

INTRODUCTION
CONTENTS
page page
DESIGNATIONS, LABELS/PLATES, CODES
AND DIMENSIONS..................... 1SPECIFICATIONS........................ 8
DESIGNATIONS, LABELS/PLATES, CODES AND DIMENSIONS
INDEX
page page
Engine and Transmission/Transfer Case Identification.3
International Vehicle Control and Display Symbols . 3
Major Component Identification............... 3
Tire Inflation Pressure Label................. 3
Vehicle Code Plate........................ 2Vehicle Designations....................... 1
Vehicle Dimension Data.................... 3
Vehicle Identification Number (VIN) Plate....... 1
Vehicle Load Data........................ 3
Vehicle Safety Certification Label............. 1
VEHICLE DESIGNATIONS
The Vehicle Designation Codes chart lists the vehi-
cle description(s) and the corresponding vehicle des-
ignation code for each type of Jeeptvehicle (Figs. 1,
2, and 3 ). The vehicle designation codes are different
from the Vehicle Identification Number (VIN) or
body-type/style codes.
VEHICLE SAFETY CERTIFICATION LABEL
A vehicle safety certification label (Fig. 4) is at-
tached to each Jeeptvehiclee. The label also lists
the:
²gross vehicle weight rating (GVWR) and the gross
front and rear axle weight ratings (GAWR's) based
on a minimum tire rim size and a maximum cold tire
inflation pressure;²month and year of vehicle manufacture;
²vehicle identification number (VIN);
²type of vehicle and
²month, day and hour (MDH) of final assembly.
The label is located on the driver's side door edge.
VEHICLE IDENTIFICATION NUMBER (VIN) PLATE
The vehicle identification number (VIN) plate is at-
tached to the top left side of the instrument panel at
the base of the windshield. Each VIN contains 17 al-
pha-numerical characters. Refer to the decoding
chart to determine the actual identification of a
Jeeptvehicle.
VEHICLE DESIGNATION CODES
Fig. 1 YJÐWrangler Multi-Purpose Vehicle (With
Hard Top)
JINTRODUCTION1