1994 JEEP CHEROKEE front
[x] Cancel search: frontPage 177 of 1784
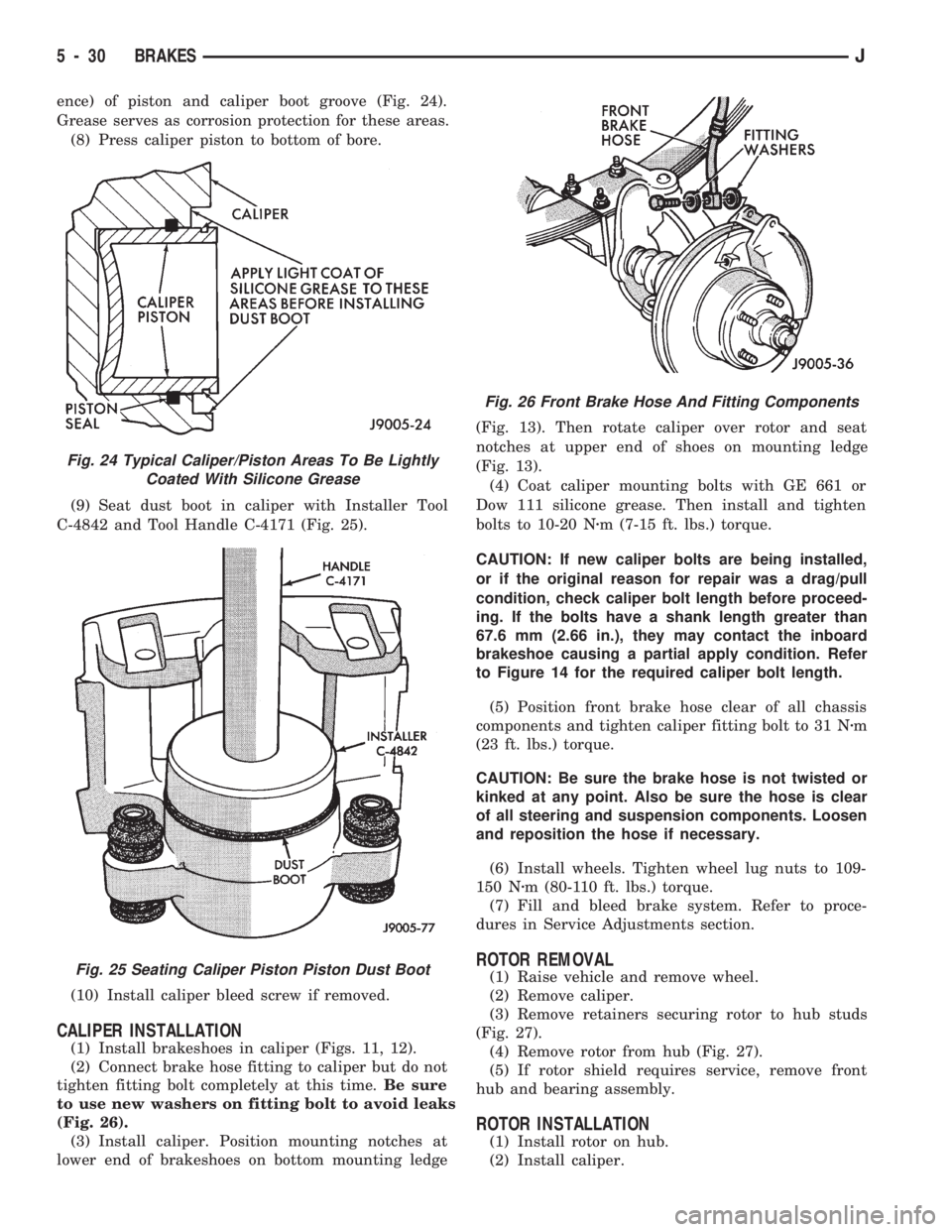
ence) of piston and caliper boot groove (Fig. 24).
Grease serves as corrosion protection for these areas.
(8) Press caliper piston to bottom of bore.
(9) Seat dust boot in caliper with Installer Tool
C-4842 and Tool Handle C-4171 (Fig. 25).
(10) Install caliper bleed screw if removed.
CALIPER INSTALLATION
(1) Install brakeshoes in caliper (Figs. 11, 12).
(2) Connect brake hose fitting to caliper but do not
tighten fitting bolt completely at this time.Be sure
to use new washers on fitting bolt to avoid leaks
(Fig. 26).
(3) Install caliper. Position mounting notches at
lower end of brakeshoes on bottom mounting ledge(Fig. 13). Then rotate caliper over rotor and seat
notches at upper end of shoes on mounting ledge
(Fig. 13).
(4) Coat caliper mounting bolts with GE 661 or
Dow 111 silicone grease. Then install and tighten
bolts to 10-20 Nzm (7-15 ft. lbs.) torque.
CAUTION: If new caliper bolts are being installed,
or if the original reason for repair was a drag/pull
condition, check caliper bolt length before proceed-
ing. If the bolts have a shank length greater than
67.6 mm (2.66 in.), they may contact the inboard
brakeshoe causing a partial apply condition. Refer
to Figure 14 for the required caliper bolt length.
(5) Position front brake hose clear of all chassis
components and tighten caliper fitting bolt to 31 Nzm
(23 ft. lbs.) torque.
CAUTION: Be sure the brake hose is not twisted or
kinked at any point. Also be sure the hose is clear
of all steering and suspension components. Loosen
and reposition the hose if necessary.
(6) Install wheels. Tighten wheel lug nuts to 109-
150 Nzm (80-110 ft. lbs.) torque.
(7) Fill and bleed brake system. Refer to proce-
dures in Service Adjustments section.
ROTOR REMOVAL
(1) Raise vehicle and remove wheel.
(2) Remove caliper.
(3) Remove retainers securing rotor to hub studs
(Fig. 27).
(4) Remove rotor from hub (Fig. 27).
(5) If rotor shield requires service, remove front
hub and bearing assembly.
ROTOR INSTALLATION
(1) Install rotor on hub.
(2) Install caliper.
Fig. 24 Typical Caliper/Piston Areas To Be Lightly
Coated With Silicone Grease
Fig. 25 Seating Caliper Piston Piston Dust Boot
Fig. 26 Front Brake Hose And Fitting Components
5 - 30 BRAKESJ
Page 186 of 1784

ABS SYSTEM OPERATION
INDEX
page page
Acceleration Switch....................... 41
Combination Valve....................... 42
Electronic Control Unit (ECU)............... 41
General Information....................... 39
Hydraulic Control Unit (HCU)................ 39
Ignition Switch........................... 42Master Cylinder.......................... 40
Pedal Travel Sensor...................... 41
Power Brake Booster..................... 40
System Relays.......................... 42
System Warning Lights.................... 42
Wheel Speed Sensors..................... 41
GENERAL INFORMATION
The Jeep antilock brake system (ABS) is an elec-
tronically operated, all-wheel brake control system.
Major components include the master cylinder, vac-
uum power brake booster, ECU, hydraulic control
unit (HCU) and various control sensors (Fig. 1). The
ABS brake system is available on XJ and YJ models.
The antilock hydraulic system is a three channel de-
sign. The front wheel brakes are controlled individually
and the rear wheel brakes in tandem (Fig. 2).
The antilock system is designed to retard wheel
lockup during periods of high wheel slip when brak-
ing. Retarding wheel lockup is accomplished by mod-
ulating fluid pressure to the wheel brake units.
The ABS electronic control system is separate from
other electrical circuits in the vehicle. A specially
programmed electronic control unit (ECU) is used to
operate the system components.
System components include:
²electronic control unit (ECU)
²wheel speed sensors and axle shaft tone rings²hydraulic control unit (HCU)
²tandem master cylinder with central valves
²vacuum power brake booster
²pedal travel sensor
²acceleration switch
²main relay and pump motor relay
²ABS warning light
²pump motor sensor
HYDRAULIC CONTROL UNIT (HCU)
The hydraulic control unit (HCU) consists of a
valve body and pump/motor assembly (Fig. 3).
The valve body contains the electrically operated
solenoid valves. It is the solenoid valves that modu-
late brake fluid apply pressure during antilock brak-
ing. The valves are operated by the antilock
electronic control unit (ECU).
Fig. 1 Antilock Components (XJ Shown)
Fig. 2 AntiLock System Basic Layout
JBRAKES 5 - 39
Page 187 of 1784

The HCU provides three channel pressure control
to the front and rear brakes. One channel controls
the rear wheel brakes in tandem. The two remaining
channels control the front wheel brakes individually.
During antilock braking, the solenoid valves are
opened and closed as needed. The valves are not static.
They are cycled rapidly and continuously to modulate
pressure and control wheel slip and deceleration.
The pump/motor assembly provides the extra vol-
ume of fluid needed during antilock braking. The
pump is connected to the master cylinder reservoir
by supply and return hoses.
The pump is operated by an integral electric motor.
The DC type motor is controlled by the ECU.
The pump mechanism consists of two opposing pis-
tons operated by an eccentric cam. One piston sup-
plies the primary hydraulic circuit. The opposite
piston supplies the secondary hydraulic circuit. In op-
eration, one piston draws fluid from the master cyl-
inder reservoir. The opposing piston then pumps
fluid to the valve body solenoids. The pump cam is
operated by the electric motor.
MASTER CYLINDER
A new style tandem master cylinder is used with the
ABS system (Fig. 4). It is a center feed design. The pri-
mary and secondary pistons each contain a central
valve which is a unique feature. The valves are used in
place of the conventional piston and seal assemblies.
The valves close and open the cylinder pressure cham-
bers during brake application and release.
The only repairable components on the ABS master
cylinder are the reservoir, reservoir grommets and
the connecting hoses. The cylinder itself cannot be
disassembled and is serviced only as an assembly.
POWER BRAKE BOOSTER
A dual diaphragm, vacuum operated power brake
booster is used with the ABS master cylinder (Fig.
Fig. 3 AntiLock Hydraulic Control Unit (HCU)
Fig. 4 ABS Power Brake Booster/Master Cylinder Assembly
5 - 40 BRAKESJ
Page 188 of 1784

4). The engine intake manifold serves as the vacuum
source for booster operation.
The booster is mounted on the engine compartment
side of the dash panel. The master cylinder is
mounted on attaching studs at the front of the
booster. The master cylinder central valves are di-
rectly actuated by the booster push rod.
The pedal travel sensor is mounted in the forward
face of the booster shell. The sensor plunger is actu-
ated by the booster diaphragm plate.
PEDAL TRAVEL SENSOR
The pedal travel sensor signals brake pedal posi-
tion to the antilock ECU. The sensor signal is based
on changes in electrical resistance. The resistance
changes occur in steps that are generated by changes
in brake pedal position. A resistance signal gener-
ated by changing brake pedal position, will cause the
ECU to run the antilock pump when necessary.
The sensor is a plunger-type, electrical switch
mounted in the forward housing of the power brake
booster (Fig. 5). The sensor plunger is actuated by
movement of the booster diaphragm plate.
The tip on the sensor plunger is color coded. The
tip must be matched to the color dot on the face of
the brake booster front shell (Fig. 5).
WHEEL SPEED SENSORS
A sensor is used at each wheel. The sensors convert
wheel speed into an electrical signal. This signal is trans-
mitted to the antilock electronic control unit (ECU).
A gear-type tone ring serves as the trigger mecha-
nism for each sensor. The tone rings are mounted at
the outboard ends of the front and rear axle shafts.
Different sensors are used at the front and rear
wheels (Fig. 6). The front/rear sensors have the same
electrical values but are not interchangeable.
ELECTRONIC CONTROL UNIT (ECU)
A separate electronic control unit (ECU) monitors,
operates and controls the antilock system (Fig. 7).
The ECU contains dual microprocessors. The logic
block in each microprocessor receives identical sensor
signals. These signals are processed and compared si-
multaneously (Fig. 8).
The ECU is located under the instrument panel. It
is located at the right side of the steering column.
The power up voltage source for the ECU is through
the ignition switch in the On and Run positions.
The antilock ECU is separate from the other vehi-
cle electronic control units. It contains a self check
program that illuminates the amber warning light
when a system fault is detected. Faults are stored in
a diagnostic program memory and are accessible
with the DRB II scan tool.
ABS faults remain in memory until cleared, or until af-
ter the vehicle is started approximately 50 times. Stored
faults arenoterased if the battery is disconnected.
ACCELERATION SWITCH
An acceleration switch (Fig. 9), provides an addi-
tional vehicle deceleration reference during 4-wheel
drive operation. The switch is monitored by the anti-
lock ECU at all times.
The switch reference signal is utilized by the ECU
when all wheels are decelerating at the same speed.
Equal wheel speeds occur during braking in undiffer-
entiated 4-wheel ranges.
Fig. 5 Pedal Travel Sensor Location
Fig. 6 Wheel Speed Sensors
JBRAKES 5 - 41
Page 189 of 1784
SYSTEM RELAYS
The ABS system has two relays, which are the
main and motor pump relays. The motor pump relay
is used for the motor pump only. The main relay is
used for the solenoid valves and remaining system
components. The main relay is connected to the ECU
at the power control relay terminal.
The pump motor relay starts/stops the pump motor
when signaled by the ECU. The start/stop signal tothe ECU is generated by the pedal travel sensor. Re-
fer to the ABS schematic at the end of this section
for circuit details.
IGNITION SWITCH
The antilock ECU and warning light are in
standby mode with the ignition switch in Off or Ac-
cessory position. No operating voltage is supplied to
the system components.
A 12 volt power feed is supplied to the ECU, re-
lays, solenoid valves, and warning light when the ig-
nition switch is in the ON, Start and Run positions.
Refer to the ABS system schematic at the end of this
section for details.
SYSTEM WARNING LIGHTS
Two warning lights are used. The standard brake
system light is red. The antilock system light is am-
ber. Both lights are in the instrument cluster. The
amber ABS light is in circuit with the ECU and op-
erates independently of the red brake light.
The amber light indicates antilock system condi-
tion. It is in circuit with the valve body solenoids and
main relay. The light illuminates (flashes) at
start-up for the self check. The light then goes out
when the self check program determines system op-
eration is normal.
If an ABS fault occurs either during the start-up
self check, or during normal operation, the amber
light remains on until the fault is corrected.
COMBINATION VALVE
A combination valve is used with the ABS system
(Fig. 2). The valve contains a front/rear brake pres-
sure switch and proportioning valve. The valve is
connected between the master cylinder and hydraulic
control unit (HCU).
Fig. 7 Anti-Lock ECU
Fig. 8 ECU Dual Microprocessor Schematic
Fig. 9 Acceleration Switch
5 - 42 BRAKESJ
Page 190 of 1784

ANTILOCK BRAKE SYSTEM OPERATION
INDEX
page page
ABS Operation in Antilock Braking Mode....... 43
ABS Operation in Normal Braking Mode....... 43
Acceleration Switch Operation............... 45
ECY Operation.......................... 46HCU Pump and Pedal Travel Sensor Operation . 44
HCU Solenoid Valve Operation.............. 43
System Power-Up and Initialization........... 43
Wheel Speed Sensor Operation............. 45
SYSTEM POWER-UP AND INITIALIZATION
The antilock system is in standby mode with the
ignition switch in Off or Accessory position. The an-
tilock electrical components are not operational.
Turning the ignition switch to On or Run position
allows battery voltage to flow through the switch to
the ECU ignition terminal.
The ABS system is activated when battery voltage
is supplied to the ECU. The ECU performs a system
initialization procedure at this point. Initialization
consists of a static and dynamic self check of system
electrical components.
The static check occurs immediately after the igni-
tion switch is turned to the On position. The dynamic
check occurs when vehicle road speed reaches ap-
proximately 10 kph (6 mph). During the dynamic
check, the ECU briefly cycles the pump to verify op-
eration. The HCU solenoids are checked continu-
ously.
If an ABS component exhibits a fault during ini-
tialization, the ECU illuminates the amber warning
light and registers a fault code in the microprocessor
memory.
ABS OPERATION IN NORMAL BRAKING MODE
The ECU monitors wheel speed sensor inputs con-
tinuously while the vehicle is in motion. However,
the ECU will not activate any ABS components as
long as sensor inputs and the acceleration switch in-
dicate normal braking.
During normal braking, the master cylinder, power
booster and wheel brake units all function as they
would in a vehicle without ABS. The HCU compo-
nents are not activated.
ABS OPERATION IN ANTILOCK BRAKING MODE
The purpose of the antilock system is to prevent
wheel lockup during periods of high wheel slip. Pre-
venting lockup helps maintain vehicle braking action
and steering control.
The antilock ECU activates the system whenever
sensor signals indicate periods of high wheel slip.
High wheel slip can be described as the point where
wheel rotation begins approaching zero (or lockup)
during braking. Periods of high wheel slip occur
when brake stops involve high pedal pressure and
rate of vehicle deceleration.The antilock system retards lockup during high
slip conditions by modulating fluid apply pressure to
the wheel brake units.
Brake fluid apply pressure is modulated according
to wheel speed, degree of slip and rate of decelera-
tion. A sensor at each wheel converts wheel speed
into electrical signals. These signals are transmitted
to the ECU for processing and determination of
wheel slip and deceleration rate.
The Jeep ABS system has three fluid pressure con-
trol channels. The front brakes are controlled sepa-
rately and the rear brakes in tandem (Fig. 10). A
speed sensor input signal indicating high slip condi-
tions activates the ECU antilock program.
Two solenoid valves are used in each antilock con-
trol channel (Fig. 11). The valves are all located
within the HCU valve body and work in pairs to ei-
ther increase, hold, or decrease apply pressure as
needed in the individual control channels.
The solenoid valves are not static during antilock
braking. They are cycled continuously to modulate
pressure. Solenoid cycle time in antilock mode can be
measured in milliseconds.
HCU SOLENOID VALVE OPERATION
Normal Braking
During normal braking, the HCU solenoid valves
and pump are not activated. The master cylinder and
power booster operate the same as a vehicle without
an ABS brake system.
Antilock Pressure Modulation
Solenoid valve pressure modulation occurs in three
stages which are: pressure increase, pressure hold,
and pressure decrease. The valves are all contained
in the valve body portion of the HCU.
Pressure Decrease
The outlet valve is opened and the inlet valve is
closed during the pressure decrease cycle (Fig. 11).
A pressure decrease cycle is initiated when speed
sensor signals indicate high wheel slip at one or
more wheels. At this point, the ECU opens the outlet
valve. Opening the outlet valve also opens the hy-
draulic return circuit to the master cylinder reser-
JANTILOCK BRAKE SYSTEM OPERATION 5 - 43
Page 192 of 1784

At the start of antilock braking, pedal height will
decrease as the volume of fluid in the master cylin-
der is used up. When pedal height drops a predeter-
mined amount, the pedal travel sensor will signal
the ECU to run the pump. At this point, the pump is
activated to supply the extra fluid volume and re-
store pedal height at the same time.
The pump does not run continuously. It cycles on/
off according to signals from the travel sensor and
ECU. The pump is connected directly to the mastercylinder reservoir by hoses. During antilock braking,
the additional volume of fluid needed is drawn by the
pump from the reservoir.
WHEEL SPEED SENSOR OPERATION
Wheel speed input signals are generated by a sen-
sor and tone ring at each wheel. The sensors, which
are connected directly to the ECU, are mounted on
brackets attached to the front steering knuckles and
rear brake support plates.
The sensor triggering devices are the tone rings
which are similar in appearance to gears. The tone
rings are located on the outboard end of each front/
rear axle shaft. The speed sensors generate a signal
whenever a tone ring tooth rotates past the sensor
pickup face.
The wheel speed sensors provide the input signal to
the ECU. If input signals indicate ABS mode brak-
ing, the ECU causes the HCU solenoids to decrease,
hold, or increase fluid apply pressure as needed.
The HCU solenoid valves are activated only when
wheel speed input signals indicate that a wheel is
approaching a high slip, or lockup condition. At this
point, the ECU will cycle the appropriate wheel con-
trol channel solenoid valves to prevent slip or lockup.
The wheel sensors provide speed signals whenever
the vehicle wheels are rotating. The ECU examines
these signals for degree of deceleration and wheel
slip. If signals indicate normal braking, the solenoid
valves are not activated. However, when incoming
signals indicate the approach of wheel slip, or lockup,
the ECU cycles the solenoid valves as needed.
ACCELERATION SWITCH OPERATION
The ECU monitors the acceleration switch at all
times. The switch assembly contains three mercury
switches that monitor vehicle ride height and decel-
eration rates (G-force). Sudden, rapid changes in ve-
hicle and wheel deceleration rate, triggers the switch
sending a signal to the ECU. The switch assembly
provides three deceleration rates; two for forward
braking and one for rearward braking.
Fig. 12 Solenoid Valves In Pressure Hold Cycle
Fig. 13 Solenoid Valves In Pressure Increase Cycle
Fig. 14 Pedal Travel Sensor Actuation
JANTILOCK BRAKE SYSTEM OPERATION 5 - 45
Page 193 of 1784

ECU OPERATION
The antilock ECU controls all phases of antilock
operation. It monitors and processes input signals
from all of the system sensors.
It is the ECU that activates the solenoid valves to
modulate apply pressure during antilock braking.
The ECU program is able to determine which wheel
control channel requires modulation and which fluid
pressure modulation cycle to use.
The ECU cycles the solenoid valves through thepressure decrease, hold and increase phases to retard
and prevent wheel lock during periods of high wheel
slip.
Solenoid valve operation is selective. The solenoid
valves may not be cycled simultaneously, nor are
they all cycled in the same pressure modulation
phase at the same time. The ECU cycles the valves
in each control channel as needed. For example, sen-
sor inputs may indicate that only the left front wheel
requires modulation during a period of high slip.
5 - 46 ANTILOCK BRAKE SYSTEM OPERATIONJ