1993 FORD MONDEO check engine
[x] Cancel search: check enginePage 152 of 279
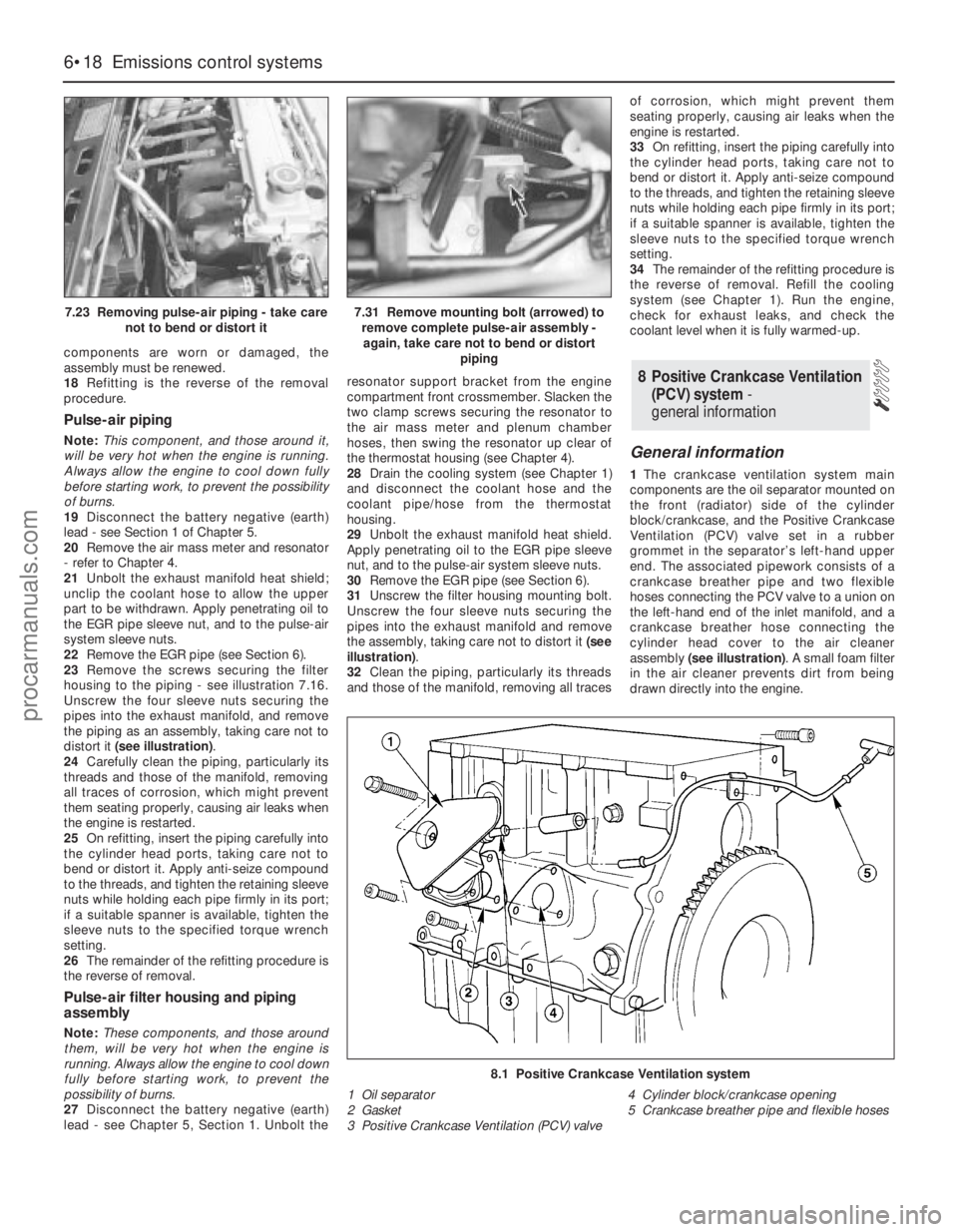
components are worn or damaged, the
assembly must be renewed.
18Refitting is the reverse of the removal
procedure.
Pulse-air piping
Note:This component, and those around it,
will be very hot when the engine is running.
Always allow the engine to cool down fully
before starting work, to prevent the possibility
of burns.
19Disconnect the battery negative (earth)
lead - see Section 1 of Chapter 5.
20Remove the air mass meter and resonator
- refer to Chapter 4.
21Unbolt the exhaust manifold heat shield;
unclip the coolant hose to allow the upper
part to be withdrawn. Apply penetrating oil to
the EGR pipe sleeve nut, and to the pulse-air
system sleeve nuts.
22Remove the EGR pipe (see Section 6).
23Remove the screws securing the filter
housing to the piping - see illustration 7.16.
Unscrew the four sleeve nuts securing the
pipes into the exhaust manifold, and remove
the piping as an assembly, taking care not to
distort it (see illustration).
24Carefully clean the piping, particularly its
threads and those of the manifold, removing
all traces of corrosion, which might prevent
them seating properly, causing air leaks when
the engine is restarted.
25On refitting, insert the piping carefully into
the cylinder head ports, taking care not to
bend or distort it. Apply anti-seize compound
to the threads, and tighten the retaining sleeve
nuts while holding each pipe firmly in its port;
if a suitable spanner is available, tighten the
sleeve nuts to the specified torque wrench
setting.
26The remainder of the refitting procedure is
the reverse of removal.
Pulse-air filter housing and piping
assembly
Note:These components, and those around
them, will be very hot when the engine is
running. Always allow the engine to cool down
fully before starting work, to prevent the
possibility of burns.
27Disconnect the battery negative (earth)
lead - see Chapter 5, Section 1. Unbolt theresonator support bracket from the engine
compartment front crossmember. Slacken the
two clamp screws securing the resonator to
the air mass meter and plenum chamber
hoses, then swing the resonator up clear of
the thermostat housing (see Chapter 4).
28Drain the cooling system (see Chapter 1)
and disconnect the coolant hose and the
coolant pipe/hose from the thermostat
housing.
29Unbolt the exhaust manifold heat shield.
Apply penetrating oil to the EGR pipe sleeve
nut, and to the pulse-air system sleeve nuts.
30Remove the EGR pipe (see Section 6).
31Unscrew the filter housing mounting bolt.
Unscrew the four sleeve nuts securing the
pipes into the exhaust manifold and remove
the assembly, taking care not to distort it (see
illustration).
32Clean the piping, particularly its threads
and those of the manifold, removing all tracesof corrosion, which might prevent them
seating properly, causing air leaks when the
engine is restarted.
33On refitting, insert the piping carefully into
the cylinder head ports, taking care not to
bend or distort it. Apply anti-seize compound
to the threads, and tighten the retaining sleeve
nuts while holding each pipe firmly in its port;
if a suitable spanner is available, tighten the
sleeve nuts to the specified torque wrench
setting.
34The remainder of the refitting procedure is
the reverse of removal. Refill the cooling
system (see Chapter 1). Run the engine,
check for exhaust leaks, and check the
coolant level when it is fully warmed-up.
General information
1The crankcase ventilation system main
components are the oil separator mounted on
the front (radiator) side of the cylinder
block/crankcase, and the Positive Crankcase
Ventilation (PCV) valve set in a rubber
grommet in the separator’s left-hand upper
end. The associated pipework consists of a
crankcase breather pipe and two flexible
hoses connecting the PCV valve to a union on
the left-hand end of the inlet manifold, and a
crankcase breather hose connecting the
cylinder head cover to the air cleaner
assembly (see illustration). A small foam filter
in the air cleaner prevents dirt from being
drawn directly into the engine.
8 Positive Crankcase Ventilation
(PCV) system -
general information
6•18 Emissions control systems
7.23 Removing pulse-air piping - take care
not to bend or distort it7.31 Remove mounting bolt (arrowed) to
remove complete pulse-air assembly -
again, take care not to bend or distort
piping
8.1 Positive Crankcase Ventilation system
1 Oil separator
2 Gasket
3 Positive Crankcase Ventilation (PCV) valve4 Cylinder block/crankcase opening
5 Crankcase breather pipe and flexible hoses
procarmanuals.com
Page 153 of 279

2The function of these components is to
reduce the emission of unburned
hydrocarbons from the crankcase, and to
minimise the formation of oil sludge. By
ensuring that a depression is created in the
crankcase under most operating conditions,
particularly at idle, and by positively inducing
fresh air into the system, the oil vapours and
“blow-by” gases collected in the crankcase
are drawn from the crankcase, through the oil
separator, into the inlet tract, to be burned by
the engine during normal combustion.
Checking
3Checking procedures for the system
components are included in Chapter 1.
Component renewal
Cylinder head-to-air cleaner hose
4See Chapter 1.
Positive Crankcase Ventilation (PCV)
valve
5The valve is plugged into the oil separator.
Depending on the tools available, access to
the valve may be possible once the pulse-air
assembly has been removed (see Section 7).
If this is not feasible, proceed as outlined in
paragraph 6 below.
Oil separator
6Remove the exhaust manifold (see Chap-
ter 2, Part A). The Positive Crankcase
Ventilation (PCV) valve can now be unplugged
and flushed, or renewed, as required, as
described in Chapter 1.
7Unbolt the oil separator from the cylinder
block/crankcase, and withdraw it; remove and
discard the gasket.
8Flush out or renew the oil separator, as
required (see Chapter 1).
9On reassembly, fit a new gasket, and
tighten the fasteners to the torque wrench
settings given in the Specifications Section of
Chapter 2, Part B.
10The remainder of the refitting procedure is
the reverse of removal. Refill the cooling
system (see Chapter 1). Run the engine,
check for exhaust leaks, and check the
coolant level when it is fully warmed-up.
General information
1The exhaust gases of any petrol engine
(however efficient or well-tuned) consist
largely (approximately 99 %) of nitrogen (N
2),
carbon dioxide (CO
2), oxygen (O2), other inert
gases and water vapour (H
2O). The remaining
1 % is made up of the noxious materials
which are currently seen (CO
2apart) as the
major polluters of the environment: carbon
monoxide (CO), unburned hydrocarbons (HC),oxides of nitrogen (NO
x) and some solid
matter, including a small lead content.
2Left to themselves, most of these pollutants
are thought eventually to break down naturally
(CO and NO
x, for example, break down in the
upper atmosphere to release CO
2) having first
caused ground-level environmental problems.
The massive increase world-wide in the use of
motor vehicles, and the current popular
concern for the environment has caused the
introduction in most countries of legislation, in
varying degrees of severity, to combat the
problem.
3The device most commonly used to clean
up vehicle exhausts is the catalytic converter.
It is fitted into the vehicle’s exhaust system,
and uses precious metals (platinum and
palladium or rhodium) as catalysts to speed
up the reaction between the pollutants and
the oxygen in the vehicle’s exhaust gases, CO
and HC being oxidised to form H
2O and CO2and (in the three-way type of catalytic
converter) NO
xbeing reduced to N2. Note:
The catalytic converter is not a filter in the
physical sense; its function is to promote a
chemical reaction, but it is not itself affected
by that reaction.
4The converter consists of an element (or
“substrate”) of ceramic honeycomb, coated
with a combination of precious metals in such
a way as to produce a vast surface area over
which the exhaust gases must flow; the whole
being mounted in a stainless-steel box. A
simple “oxidation” (or “two-way”) catalytic
converter can deal with CO and HC only,
while a “reduction” (or “three-way”) catalytic
converter can deal with CO, HC and NO
x.
Three-way catalytic converters are further
sub-divided into “open-loop” (or
“uncontrolled”) converters which can remove
50 to 70 % of pollutants and “closed-loop”
(also known as “controlled” or “regulated”)
converters which can remove over 90 % of
pollutants.
5The catalytic converter fitted to the Mondeo
models covered in this manual is of the three-
way closed-loop type.
6The catalytic converter is a reliable and
simple device, which needs no maintenance
in itself, but there are some facts of which an
owner should be aware if the converter is to
function properly for its full service life.
(a) DO NOT use leaded petrol in a vehicle
equipped with a catalytic converter - the
lead will coat the precious metals,
reducing their converting efficiency, and
will eventually destroy the converter; it will
also affect the operation of the oxygen
sensor, requiring its renewal if lead-
fouled. Opinions vary as to how much
leaded fuel is necessary to affect the
converter’s performance, and whether it
can recover even if only unleaded petrol is
used afterwards; the best course of action
is, therefore, to assume the worst, and to
ensure that NO leaded petrol is used at
any time.
(b) Always keep the ignition and fuel systemswell-maintained in accordance with the
manufacturer’s schedule (Chapter 1) -
particularly, ensure that the air filter
element, the fuel filter and the spark plugs
are renewed at the correct intervals. If the
intake air/fuel mixture is allowed to
become too rich due to neglect, the
unburned surplus will enter and burn in
the catalytic converter, overheating the
element and eventually destroying the
converter.
(c) If the engine develops a misfire, do not
drive the vehicle at all (or at least as little
as possible) until the fault is cured - the
misfire will allow unburned fuel to enter
the converter, which will result in its
overheating, as noted above. For the
same reason, do not persist if the engine
refuses to start - either trace the problem
and cure it yourself, or have the vehicle
checked immediately by a qualified
mechanic.
(d) Avoid allowing the vehicle to run out of
petrol.
(e) DO NOT push- or tow-start the vehicle
unless no other alternative exists,
especially if the engine and exhaust are at
normal operating temperature. Starting
the engine in this way may soak the
catalytic converter in unburned fuel,
causing it to overheat when the engine
does start - see (b) above.
(f) DO NOT switch off the ignition at high
engine speeds, in particular, do not “blip”
the throttle immediately before switching
off. If the ignition is switched off at
anything above idle speed, unburned fuel
will enter the (very hot) catalytic converter,
with the possible risk of its igniting on the
element and damaging the converter.
(g) Avoid repeated successive cold starts
followed by short journeys. If the
converter is never allowed to reach its
proper working temperature, it will gather
unburned fuel, allowing some to pass into
the atmosphere and the rest to soak in
the element, causing it to overheat when
a long journey is made - see (b) above.
(h) DO NOT use fuel or engine oil additives -
these may contain substances harmful to
the catalytic converter. Similarly, DO NOT
use silicone-based sealants on any part of
the engine or fuel system, and do not use
exhaust sealants on any part of the
exhaust system upstream of the catalytic
converter. Even if the sealant itself does
not contain additives harmful to the
converter, pieces of it may break off and
foul the element, causing local
overheating.
(i) DO NOT continue to use the vehicle if the
engine burns oil to the extent of leaving a
visible trail of blue smoke. Unburned
carbon deposits will clog the converter
passages and reduce its efficiency; in
severe cases, the element will overheat.
(j) Remember that the catalytic converter
operates at very high temperatures -
9 Catalytic converter -
general information, checking
and component renewal
Emissions control systems 6•19
6
procarmanuals.com
Page 154 of 279

hence the heat shields on the vehicle
underbody - and the casing will become
hot enough to ignite combustible
materials which brush against it. DO NOT,
therefore, park the vehicle in dry
undergrowth, over long grass or piles of
dead leaves.
(k) Remember that the catalytic converter is
FRAGILE. Do not strike it with tools
during servicing work, and take great care
when working on the exhaust system (see
Chapter 4). Ensure that the converter is
well clear of any jacks or other lifting gear
used to raise the vehicle. Do not drive the
vehicle over rough ground, road humps,
etc, in such a way as to “ground” the
exhaust system.
(l) In some cases, particularly when the
vehicle is new and/or is used for
stop/start driving, a sulphurous smell (like
that of rotten eggs) may be noticed fromthe exhaust. This is common to many
catalytic converter-equipped vehicles,
and seems to be due to the small amount
of sulphur found in some petrols reacting
with hydrogen in the exhaust, to produce
hydrogen sulphide (H
2S) gas; while this
gas is toxic, it is not produced in sufficient
amounts to be a problem. Once the
vehicle has covered a few thousand miles,
the problem should disappear - in the
meanwhile, a change of driving style, or of
the brand of petrol used, may effect a
solution.
(m) The catalytic converter on a well-
maintained and well-driven vehicle should
last for between 50 000 and 100 000
miles. From this point on, careful checks
should be made at regular intervals to
ensure that the converter is still operating
efficiently. If the converter is no longer
effective, it must be renewed.
Checking
7Checking the operation of a catalytic
converter requires expensive and
sophisticated diagnostic equipment, starting
with a high-quality exhaust gas analyser. If the
level of CO in the exhaust gases is too high, a
full check of the engine management system
must be carried out (see Section 3 of this
Chapter) to eliminate all other possibilities
before the converter is suspected of being
faulty.
8The vehicle should be taken to a Ford
dealer for this work to be carried out using the
correct diagnostic equipment; do not waste
time trying to test the system without such
facilities.
Component renewal
9The catalytic converter is part of the
exhaust system front downpipe - see Chap-
ter 4 for details of removal and refitting.
6•20 Emissions control systems
procarmanuals.com
Page 160 of 279

11Locate one of the circlips in the outer
groove of the knuckle.
12Press or drive the new bearing into the
knuckle until it contacts the circlip, using a
length of metal tube of diameter slightly less
than the outer race. Do not apply any
pressure to the inner race.
13Locate the remaining circlip in the inner
groove of the knuckle.
14Support the inner race on a length of
metal tube, then press or drive the hub fully
into the bearing.
15Refit the steering knuckle and hub
assembly as described in Section 2.
Removal
1Apply the handbrake, then jack up the front
of the vehicle and support it on axle stands.
Remove the appropriate front wheel.
2Unbolt the brake hose support bracket from
the front of the suspension strut (see
illustration).
3Remove the brake caliper as described in
Chapter 9, but do not disconnect the flexible
hydraulic hose from the caliper. Suspend the
caliper from a suitable point under the wheel
arch, taking care not to strain the hose.
4Extract the split pin from the track rod end
balljoint nut. Unscrew the nut, and detach the
rod from the arm on the steering knuckleusing a conventional balljoint removal tool.
Take care not to damage the balljoint seal.
5Remove the ABS sensor (when fitted) from
the steering knuckle, as described in Chapter 9.
6Remove the clip securing the driveshaft
inner gaiter to the inner CV joint. Disconnect
the gaiter from the CV joint housing.
7Remove the nut and disconnect the anti-roll
bar link from the strut. Note that, on models
fitted with ABS, the ABS wheel sensor wiring
support bracket is located beneath the nut
(see illustration).
8Note which way round the lower arm
balljoint clamp bolt is fitted, then unscrew and
remove it from the knuckle assembly. Lever
the balljoint down from the knuckle; if it is
tight, prise the clamp open carefully using a
large flat-bladed tool. Take care not to
damage the balljoint seal during the
separation procedure.
9Where applicable, disconnect the adaptive
damping wiring multi-plug at the strut, and
unclip the wire.
10Support the strut and steering knuckle on
an axle stand. Working inside the engine
compartment, remove the strut cap (if fitted).
Unscrew and remove the front suspension
strut upper mounting nut, holding the piston
rod stationary with an 8 mm Allen key (see
illustration).
11Lower the suspension strut, together with
the driveshaft and steering knuckle, from
under the wheel arch, withdrawing the tripod
on the inner end of the driveshaft from the CV
joint housing.12Unscrew and remove the pinch-bolt
securing the steering knuckle assembly to the
front suspension strut, noting which way
round it is fitted. Prise open the clamp using a
wedge-shaped tool, and release the knuckle
from the strut (see illustrations).
Refitting
13With the clamp prised open, locate the
front suspension strut on the steering knuckle,
and refit the pinch-bolt with its head facing
forwards. Tighten the bolt to the specified
torque.
14Locate the suspension strut (together with
the driveshaft and steering knuckle) in its
upper mounting, and loosely screw on the
nut.
15Locate the tripod on the inner end of the
driveshaft in the CV joint housing, then
manipulate the gaiter onto the housing, and fit
a new clip.
16Where applicable, reconnect the adaptive
damping multi-plug, and fit the wire in the clip.
17Locate the lower arm balljoint fully in the
bottom of the steering knuckle. Refit the
clamp bolt and tighten it to the specified
torque.
18Reconnect the anti-roll bar link to the
strut, and tighten the nut to the specified
torque. On models fitted with ABS, do not
forget to locate the sensor wiring support
bracket beneath the nut.
19Where fitted, refit the ABS sensor as
described in Chapter 9.
20Refit the track rod end balljoint to the
steering knuckle, and tighten the nut to the
specified torque. Check that the split pin
holes are aligned; if necessary, turn the nut to
the nearest alignment, making sure that the
torque wrench setting is still within the
specified range. Insert a new split pin, and
bend it back to secure.
21Refit the brake caliper as described in
Chapter 9.
22Refit the brake hose support bracket to
the strut, and tighten the bolt.
23Refit the wheel, and lower the vehicle to
the ground. Tighten the wheel nuts to the
specified torque.
24Tighten the suspension strut upper
mounting nut to the specified torque, while
4 Front suspension strut -
removal and refitting
10•6 Suspension and steering systems
4.2 Removing the brake hose support
bracket from the front of the front
suspension strut4.7 Removing the anti-roll bar link and
ABS sensor wiring bracket4.10 Front suspension strut upper
mounting nut
4.12A Steering knuckle-to-strut pinch-bolt4.12B Releasing the knuckle from the strut
procarmanuals.com
Page 162 of 279

spring must now be carefully released from
the compressor. If it is to be re-used, the
spring can be left in compression.
7With the strut assembly now completely
dismantled, examine all the components for
wear and damage, and check the bearing for
smoothness of operation. Renew components
as necessary.
8Examine the strut for signs of fluid leakage.
Check the strut piston for signs of pitting
along its entire length, and check the strut
body for signs of damage. Test the operation
of the strut, while holding it in an upright
position, by moving the piston through a full
stroke, and then through short strokes of 50
to 100 mm. In both cases, the resistance felt
should be smooth and continuous. If the
resistance is jerky, uneven, or if there is any
visible sign of wear or damage to the strut,
renewal is necessary.
9Reassembly is a reversal of dismantling,
noting the following points:
(a) Make sure that the coil spring ends are
correctly located in the upper and lower
seats before releasing the compressor.
(b) Check that the bearing is correctly fitted
to the piston rod seat.
(c) Tighten the thrust bearing retaining nut to
the specified torque.
Removal
1Apply the handbrake, jack up the front of
the vehicle and support it on axle stands.
Remove both front wheels.
2Unscrew the nuts, and disconnect the anti-
roll bar links from the front suspension struts
on both sides of the vehicle. Note that, on
models with ABS, the wheel sensor wiring
support brackets are located beneath the nuts
(see illustrations).
3Unscrew and remove the anti-roll bar
mounting bolts from the engine subframe on
both sides of the vehicle.
4Withdraw the anti-roll bar from one side of
the vehicle, taking care not to damage the
surrounding components.5If necessary, unscrew the nuts and remove
the links from the anti-roll bar.
Refitting
6Refitting is a reversal of the removal
procedure.
Removal
1Apply the handbrake, jack up the front of
the vehicle and support it on axle stands.
Remove the appropriate wheel.
2If removing the right-hand side lower arm,
remove the auxiliary drivebelt cover where
necessary.
3Unscrew and remove the nuts and bolts
securing the lower arm to the subframe (see
illustration).
4Unscrew the nuts and disconnect the anti-
roll bar links from the anti-roll bar on both
sides. Swivel the anti-roll bar upwards away
from the lower arm.
5Extract the split pin from the track rod end
balljoint nut. Unscrew the nut, and detach the
rod from the arm on the steering knuckle
using a conventional balljoint removal tool.
Take care not to damage the balljoint seal.
6Remove the clip securing the driveshaft
inner gaiter to the inner CV joint, and
disconnect the gaiter from the CV joint
housing. This is necessary to prevent damageto the gaiter when the steering knuckle is
moved outwards to remove the lower arm.
7Note which way round the front suspension
lower arm balljoint clamp bolt is fitted, then
unscrew and remove it from the knuckle
assembly. Lever the balljoint down from the
knuckle; if it is tight, prise the joint open carefully
using a large flat-bladed tool. Take care not to
damage the balljoint seal during the separation
procedure. Support the inner end of the
driveshaft on an axle stand (see illustrations).
8Remove the lower arm from the subframe,
and withdraw it from the vehicle.
Overhaul
9Examine the rubber bushes and the
suspension lower balljoint for wear and
damage. The balljoint may be renewed as
described in Section 8. The rubber bushes
may be removed using a press, or a length of
metal tubing together with a long bolt,
washers and nut.
10Note that the front and rear bushes are
different. The front one has a solid rubber
bush with a cylindrical inner tube, whereas the
rear one has a voided rubber bush with a
barrel-shaped inner tube (see illustration).
11Press the new bushes into the lower arm,
using the same method as used for removal.
Note that, when fitting the rear bush, the voids
must be in line with the front bush location.
On later models, a pip on the rear bush must
be aligned with a triangular alignment mark on
the arm.
7 Front suspension lower arm -
removal, overhaul and refitting
6 Front anti-roll bar and links -
removal and refitting
10•8 Suspension and steering systems
6.2A Unscrew the nut . . .6.2B . . . and disconnect the anti-roll bar
link and (on ABS models) the sensor wiring
support bracket
7.3 One of the nuts and bolts securing the
lower arm to the subframe7.7A Unscrew the lower arm balljoint
clamp bolt . . .7.7B . . . and disconnect the balljoint from
the knuckle
procarmanuals.com
Page 174 of 279

15Locate the steering column shaft on the
flexible coupling, swivel the clamp plate
round, then insert the bolt and tighten to the
specified torque.
16Refit the driver’s side lower trim panel.
17Refit the steering column upper and lower
shrouds.
18Reconnect the battery negative lead.
Removal
1Disconnect the battery negative (earth) lead
(refer to Chapter 5, Section 1).
2Turn the steering wheel so that the front
wheels are in the straight-ahead position.
Remove the ignition key, then turn the
steering wheel slightly as necessary until the
steering lock engages.
3Unscrew the clamp plate bolt securing the
steering column shaft to the flexible coupling.
Swivel the clamp plate around, and disengage
it from the flexible coupling stub.
4Carefully prise the rubber boot from the
bulkhead, and withdraw it into the passenger
compartment. Take care not to damage the
sealing lip of the boot.
5Using an Allen key, unscrew the clamp bolt
securing the flexible coupling to the pinion
shaft on the steering gear, and withdraw the
coupling from inside the vehicle.
Refitting
6Refitting is a reversal of the removal
procedure, but tighten the clamp bolts to the
specified torque. Make sure that the rubber
boot engages correctly in the bulkhead and
on the flexible coupling.
Removal
1Remove the steering column flexible
coupling as described in Section 29.
2Apply the handbrake, then jack up the frontof the vehicle and support it on axle stands.
Remove both front wheels.
3Working beneath the vehicle, unbolt the
rear engine mounting from the transmission
and underbody.
4Extract the split pins from the track rod end
balljoint nuts, then unscrew the nuts, and
detach the rods from the arms on the steering
knuckles using a conventional balljoint
removal tool. Take care not to damage the
balljoint seals.
5Position a suitable container beneath the
steering gear, then unscrew the union nuts
securing the power steering fluid supply,
return, and cooler lines to the steering gear.
Identify the lines for position, then unbolt the
clamps, disconnect the lines, and allow the
fluid to drain into the container. Cover the
apertures in the steering gear and also the
ends of the fluid pipes, to prevent the ingress
of dust and dirt into the hydraulic circuit.
6Unscrew and remove the steering gear
mounting bolts. The bolts are located on top
of the steering gear, and are difficult to reach.
Ideally, the special U-shaped Ford spanner
should be used, but it is just possible to reach
them with a normal spanner (see illustration).
7Withdraw the steering gear through the
wheel arch.
Refitting
8If the steering gear is being replaced with a
new one, the new unit will be supplied
together with union nuts already fitted. The
new nuts must only be used with new feed
and return lines - otherwise, they must be
removed and discarded. If the original lines
and union nuts are being used, the Teflon
rings on the union nuts must be renewed. To
do this, the rings must be expanded
individually onto a fitting adaptor (see
illustration), then located in the grooves of
the union nuts.
9Locate the steering gear on the subframe,
and insert the two mounting bolts. Tighten the
bolts to the specified torque (see illustration).
Note that, if the special Ford tool is being
used, the bottom of the tool must be turned
anti-clockwise in order to tighten the
mounting bolts.10Remove the covers from the apertures on
the steering gear, then reconnect the fluid
lines and tighten the union nuts to the
specified torque. Refit the clamps and tighten
the bolts.
11Refit the track rod end balljoints to the
steering knuckles, and tighten the nuts to the
specified torque. Check that the split pin
holes are aligned; if necessary, turn the nuts
to the nearest alignment, making sure that the
torque wrench setting is still within the
specified range. Insert new split pins, and
bend them back to secure.
12Refit the rear engine mounting to the
transmission and underbody, and tighten the
bolts to the specified torque.
13Refit the front wheels, and lower the
vehicle to the ground.
14Refit the steering column flexible coupling
with reference to Section 29.
15Bleed the power steering hydraulic
system as described in Section 33.
16Have the front wheel alignment checked,
and if necessary adjusted, at the earliest
opportunity (refer to Section 36).Removal
1Disconnect the battery negative (earth) lead
(refer to Chapter 5, Section 1).
2Working inside the vehicle, unscrew the
clamp plate bolt securing the steering column
shaft to the flexible coupling. Swivel the clamp
plate around, and disengage it from the
flexible coupling stub.
3Apply the handbrake, then jack up the front
of the vehicle and support it on axle stands.
Remove both wheels.
4On manual transmission models,
disconnect the gearchange linkage and
support rods from the transmission, as
described in Chapter 7, Part A.
5Remove the exhaust downpipe complete,
as described in Chapter 4.
6Remove the cover from under the radiator
by unscrewing the screws and releasing the
clips.
31 Power steering gear
(left-hand-drive models with
ABS) - removal and refitting
30 Power steering gear (all except
left-hand-drive models with
ABS) - removal and refitting
29 Steering column flexible
coupling - removal and refitting
10•20 Suspension and steering systems
30.6 U-shaped Ford spanner for
unscrewing the steering gear mounting
bolts
30.8 Using an adaptor to fit the Teflon
rings to the union nuts
1 Adaptor 2 Teflon ring 3 Union nut
4 Groove location for the Teflon ring
30.9 Tightening the steering gear
mounting bolts using the U-shaped
spanner (arrowed)
procarmanuals.com
Page 175 of 279

7Support the radiator in its raised position,
by inserting split pins through the small holes
in the radiator mounting extensions which
protrude through the upper mountings (see
illustration).
8Unbolt and remove the radiator lower
mounting brackets.
9Where applicable, unscrew the bolts
securing the air conditioning accumulator to
the subframe.
10Working beneath the vehicle, unbolt the
engine rear mounting from the transmission
and underbody.
11Unscrew the front engine mounting-to-
cylinder block bolts, and also the through-
bolt.
12Extract the split pins from the track rod
end balljoint nuts, then unscrew the nuts, and
detach the rods from the arms on the steering
knuckles using a conventional balljoint
removal tool. Take care not to damage the
balljoint seals.
13Working on each side in turn, unscrew the
mounting nuts, and remove the anti-roll bar
links from the front suspension struts. Note
that, on models fitted with ABS, the ABS
sensor wiring support brackets are located
beneath the nuts.
14Working on each side in turn, note which
way round the front suspension lower arm
balljoint clamp bolt is fitted, then unscrew and
remove it from the knuckle assembly. Lever
the balljoint down from the knuckle - if it is
tight, prise the joint open carefully using a
large flat-bladed tool. Take care not to
damage the balljoint seal during the
separation procedure.
15Support the weight of the front subframe
assembly on two trolley jacks (or two scissor
jacks).
16Unscrew and remove the subframe
mounting bolts, then lower the subframe
sufficiently to gain access to the power
steering fluid pipes on top of the steering
gear. Note that the front subframe mountingbolts are gold in colour - the rear ones are
silver.
17Position a suitable container beneath the
steering gear, then unscrew the union nuts
securing the power steering fluid supply,
return, and cooler lines to the steering gear.
Identify the lines for position, then unbolt the
clamps, disconnect the lines, and allow the
fluid to drain into the container. Cover the
apertures in the steering gear and also the
ends of the fluid pipes, to prevent the ingress
of dust and dirt into the hydraulic circuit.
18Lower the subframe, together with the
power steering gear, to the ground.
19Unscrew the mounting bolts and remove
the power steering gear from the subframe.
20Using a suitable Allen key, unscrew the
clamp bolt securing the flexible coupling to
the pinion shaft on the steering gear, and
withdraw the coupling.
21Refer to Section 30, paragraph 8 for
details of renewing the Teflon rings.Refitting
22Refit the flexible coupling to the pinion
shaft on the steering gear, then insert and
tighten the clamp bolt using an Allen key.
23Locate the power steering gear on the
subframe, then insert the mounting bolts and
tighten to the specified torque.
24Raise the subframe until it is possible to
refit the fluid lines. Tighten the union nuts and
clamps.
25Raise the subframe, making sure that the
alignment holes are in line with the holes in
the underbody. At the same time, make sure
that the flexible coupling locates correctly on
the steering column. Ford technicians use a
special tool to ensure that the subframe is
correctly aligned - refer to Chapter 2 for more
details of the alignment procedure. With the
subframe aligned, insert and tighten the
mounting bolts to the specified torque. Note
that the front mounting bolts are gold in
colour - the rear bolts are silver.
26Working on each side in turn, refit the
front suspension lower arm balljoint to the
knuckle assembly, and insert the clamp bolt
with its head facing forwards. Refit the nut
and tighten to the specified torque.
27Working on each side in turn, refit the
anti-roll bar links and tighten the mounting
nuts to the specified torque. On models fitted
with ABS, don’t forget to locate the wheel
sensor wiring support brackets beneath the
nuts.
28Refit the track rod end balljoints to the
steering knuckles, and tighten the nuts to the
specified torque. Check if the split pin holes
are aligned, and if necessary turn the nuts to
the nearest alignment, making sure that the
torque wrench setting is still within the
specified range. Insert new split pins, and
bend them back to secure.
29Refit and tighten the engine front
mounting bolts.
30Refit the engine rear mounting and tighten
the bolts.31Where applicable, insert and tighten the
air conditioning accumulator bolts.
32Refit the radiator lower mounting brackets
and tighten the bolts.
33Remove the split pins supporting the
radiator in its raised position.
34Refit the cover under the radiator.
35Refit the exhaust downpipe as described
in Chapter 4.
36On manual transmission models,
reconnect the gearchange linkage and
support rods.
37Refit the front wheels, and lower the
vehicle to the ground.
38Working inside the vehicle, reconnect the
steering column clamp plate, then insert the
bolt and tighten to the specified torque.
39Reconnect the battery negative lead.
40Bleed the power steering hydraulic
system as described in Section 33.
41Have the front wheel alignment checked,
and if necessary adjusted, at the earliest
opportunity (refer to Section 36).
1Remove the track rod end and its locknut
from the track rod, as described in Section 35.
Make sure that a note is made of the exact
position of the track rod end on the track rod,
in order to retain the front wheel alignment
setting on refitting.
2Release the outer retaining clip and inner
plastic clamp band, and disconnect the gaiter
from the steering gear housing.
3Disconnect the breather from the gaiter,
then slide the gaiter off the track rod.
4Scrape off all grease from the old gaiter,
and apply to the track rod inner joint. Wipe
clean the seating areas on the steering gear
housing and track rod.
5Slide the new gaiter onto the track rod and
steering gear housing, and reconnect the
breather.
6Fit a new inner plastic clamp band and
outer retaining clip.
7Refit the track rod end as described in
Section 35.
8Have the front wheel alignment checked,
and if necessary adjusted, at the earliest
opportunity (refer to Section 36).
1Following any operation in which the power
steering fluid lines have been disconnected,
the power steering system must be bled, to
remove any trapped air.
2With the front wheels in the straight-ahead
position, check the power steering fluid level
in the reservoir and, if low, add fresh fluid until
it reaches the “MAX” or “MAX COLD” mark.
Pour the fluid slowly, to prevent air bubbles
forming, and use only the specified fluid (refer
to Chapter 1 Specifications).
33 Power steering hydraulic
system - bleeding
32 Power steering gear rubber
gaiters - renewal
Suspension and steering systems 10•21
10
31.7 Method of supporting the radiator in
its raised position
1 Radiator upper mounting extension
2 Small hole
3 Pin or split pin inserted through hole
procarmanuals.com
Page 176 of 279

3Start the engine, and allow it to run at a fast
idle. Check the hoses and connections for
leaks.
4Stop the engine, and recheck the fluid level.
Add more if necessary, up to the “MAX” or
“MAX COLD” mark.
5Start the engine again, allow it to idle, then
bleed the system by slowly turning the
steering wheel from side to side several times.
This should purge the system of all internal
air. However, if air remains in the system
(indicated by the steering operation being very
noisy), leave the vehicle overnight, and repeat
the procedure again the next day.
6If air still remains in the system, it may be
necessary to resort to the Ford method of
bleeding, which uses a vacuum pump. Turn
the steering to the right until it is near the stop,
then fit the vacuum pump to the fluid
reservoir, and apply 0.15 bars of vacuum.
Maintain the vacuum for a minimum of
5 minutes, then repeat the procedure with the
steering turned to the left.
7Keep the fluid level topped-up throughout
the bleeding procedure; note that, as the fluid
temperature increases, the level will rise.
8On completion, switch off the engine, and
return the front wheels to the straight-ahead
position.
Removal
1Disconnect the battery negative (earth) lead
(refer to Chapter 5, Section 1).
2Unscrew and remove the bolt securing the
hydraulic fluid line support to the engine lifting
bracket on the right-hand side of the engine.
3Unscrew and remove the bolt securing the
hydraulic fluid line support to the pump
mounting bracket.
4Position a suitable container beneath the
power steering pump, to catch spilt fluid.
5Loosen the clip, and disconnect the fluid
supply hose from the pump inlet. Plug the
hose, to prevent the ingress of dust and dirt.
6Unscrew the union nut, and disconnect the
high-pressure line from the pump. Allow the
fluid to drain into the container.
7Apply the handbrake, then jack up the front
of the vehicle and support it on axle stands.
Remove the right-hand front wheel.
8Unbolt and remove the lower drivebelt
cover.
9Using a spanner, rotate the drivebelt
tensioner in a clockwise direction to release
the belt tension, then slip the drivebelt off the
pulleys and remove from the vehicle. Refer to
Chapter 1 if necessary.
10Unscrew and remove the four mounting
bolts, and withdraw the power steering pump
from its bracket. Access to the bolts on the
right-hand side of the engine is gained by
turning the pump pulley until a hole lines up
with the bolt.
Refitting
11Locate the power steering pump on the
mounting bracket, and secure with the four
bolts. Tighten the bolts to the specified
torque.
12Slip the drivebelt over the pulleys, then
rotate the drivebelt tensioner in a clockwise
direction, and locate the drivebelt on it.
Release the tensioner to tension the drivebelt.
13Refit the lower belt cover.
14Refit the right-hand front wheel, and lower
the vehicle to the ground.
15If necessary, the sealing ring on the high-
pressure outlet should be renewed, using the
same procedure as described in Section 30,
paragraph 8.
16Reconnect the high-pressure line to the
pump, and tighten the union nut.
17Reconnect the fluid supply hose to the
pump inlet, and tighten the clip.
18Refit the hydraulic fluid line support to the
pump mounting bracket, and tighten the bolt.
19Refit the hydraulic fluid line support to the
engine lifting bracket on the right-hand side of
the engine, and tighten the bolt.
20Reconnect the battery negative lead.
21Bleed the power steering hydraulic
system as described in Section 33.
1Apply the handbrake, then jack up the front
of the vehicle and support it on axle stands.
Remove the appropriate front roadwheel.
2Using a suitable spanner, slacken the
locknut on the track rod by a quarter-turn.
Hold the track rod end stationary with another
spanner engaged with the special flats while
loosening the locknut.
3Extract the split pin, then unscrew and
remove the track rod end balljoint retaining
nut.
4To release the tapered shank of the balljoint
from the steering knuckle arm, use a balljoint
separator tool (if the balljoint is to be re-used,
take care not to damage the dust cover when
using the separator tool) (see illustration).
5Count the number of exposed threads
visible on the inner section of the track rod,
and record this figure.
6Unscrew the track rod end from the track
rod, counting the number of turns necessary
to remove it. If necessary, hold the track rod
stationary with grips.
Refitting
7Screw the track rod end onto the track rod
by the number of turns noted during removal,
until it just contacts the locknut.
8Engage the shank of the balljoint with the
steering knuckle arm, and refit the nut.
Tighten the nut to the specified torque. If the
balljoint shank turns while the nut is being
tightened, press down on the balljoint. The
tapered fit of the shank will lock it, and
prevent rotation as the nut is tightened.9Check that the split pin holes in the nut and
balljoint shank are aligned. If necessary turn
the nut to the nearest alignment, making sure
that the torque wrench setting is still within
the specified range. Insert a new split pin, and
bend it back to secure.
10Now tighten the locknut, while holding the
track rod end as before.
11Refit the roadwheel, and lower the vehicle
to the ground.
12Finally check, and if necessary adjust, the
front wheel alignment as described in Sec-
tion 29.
1Accurate front wheel alignment is essential
to provide positive steering, and to prevent
excessive tyre wear. Before considering the
steering/suspension geometry, check that the
tyres are correctly inflated, that the front
wheels are not buckled, and that the steering
linkage and suspension joints are in good
order, without slackness or wear.
2Wheel alignment consists of four factors
(see illustration):
Camberis the angle at which the front
wheels are set from the vertical, when viewed
from the front of the vehicle. “Positive
camber” is the amount (in degrees) that the
wheels are tilted outward at the top of the
vertical. Castoris the angle between the
steering axis and a vertical line, when viewed
from each side of the car. “Positive castor” is
when the steering axis is inclined rearward at
the top.
Steering axis inclinationis the angle (when
viewed from the front of the vehicle) between
the vertical and an imaginary line drawn
through the suspension strut upper mounting
and the lower suspension arm balljoint.
Toe settingis the amount by which the
distance between the front inside edges of the
roadwheels (measured at hub height) differs
from the diametrically-opposite distance
measured between the rear inside edges of
the front roadwheels.
3With the exception of the toe setting, all
other steering angles are set during
manufacture, and no adjustment is possible. It
36 Wheel alignment and steering
angles - general information35 Track rod end - renewal34 Power steering pump -
removal and refitting
10•22 Suspension and steering systems
35.4 Using a balljoint separator tool to
release the track rod end balljoint
procarmanuals.com