1993 FORD MONDEO check transmission fluid
[x] Cancel search: check transmission fluidPage 5 of 279

Working on your car can be dangerous.
This page shows just some of the potential
risks and hazards, with the aim of creating a
safety-conscious attitude.
General hazards
Scalding
• Don’t remove the radiator or expansion
tank cap while the engine is hot.
• Engine oil, automatic transmission fluid or
power steering fluid may also be dangerously
hot if the engine has recently been running.
Burning
• Beware of burns from the exhaust system
and from any part of the engine. Brake discs
and drums can also be extremely hot
immediately after use.
Crushing
• When working under or near
a raised vehicle, always
supplement the
jack with axle
stands, or use
drive-on ramps.
Never venture
under a car
which is only
supported by
a jack.
• Take care if loosening or tightening high-
torque nuts when the vehicle is on stands.
Initial loosening and final tightening should
be done with the wheels on the ground.
Fire
• Fuel is highly flammable; fuel vapour is
explosive.
• Don’t let fuel spill onto a hot engine.
• Do not smoke or allow naked lights
(including pilot lights) anywhere near a
vehicle being worked on. Also beware of
creating sparks
(electrically or by use of tools).
• Fuel vapour is heavier than air, so don’t
work on the fuel system with the vehicle over
an inspection pit.
• Another cause of fire is an electrical
overload or short-circuit. Take care when
repairing or modifying the vehicle wiring.
• Keep a fire extinguisher handy, of a type
suitable for use on fuel and electrical fires.
Electric shock
• Ignition HT
voltage can be
dangerous,
especially to
people with
heart problems
or a pacemaker.
Don’t work on or
near the ignition
system with the
engine running or the
ignition switched on.• Mains voltage is also dangerous. Make
sure that any mains-operated equipment is
correctly earthed. Mains power points should
be protected by a residual current device
(RCD) circuit breaker.
Fume or gas intoxication
• Exhaust fumes are
poisonous; they often
contain carbon
monoxide, which is
rapidly fatal if inhaled.
Never run the
engine in a
confined space
such as a garage
with the doors shut.
• Fuel vapour is also
poisonous, as are the vapours from some
cleaning solvents and paint thinners.
Poisonous or irritant substances
• Avoid skin contact with battery acid and
with any fuel, fluid or lubricant, especially
antifreeze, brake hydraulic fluid and Diesel
fuel. Don’t syphon them by mouth. If such a
substance is swallowed or gets into the eyes,
seek medical advice.
• Prolonged contact with used engine oil can
cause skin cancer. Wear gloves or use a
barrier cream if necessary. Change out of oil-
soaked clothes and do not keep oily rags in
your pocket.
• Air conditioning refrigerant forms a
poisonous gas if exposed to a naked flame
(including a cigarette). It can also cause skin
burns on contact.
Asbestos
• Asbestos dust can cause cancer if inhaled
or swallowed. Asbestos may be found in
gaskets and in brake and clutch linings.
When dealing with such components it is
safest to assume that they contain asbestos.
Special hazards
Hydrofluoric acid
• This extremely corrosive acid is formed
when certain types of synthetic rubber, found
in some O-rings, oil seals, fuel hoses etc, are
exposed to temperatures above 400
0C. The
rubber changes into a charred or sticky
substance containing the acid. Once formed,
the acid remains dangerous for years. If it
gets onto the skin, it may be necessary to
amputate the limb concerned.
• When dealing with a vehicle which has
suffered a fire, or with components salvaged
from such a vehicle, wear protective gloves
and discard them after use.
The battery
• Batteries contain sulphuric acid, which
attacks clothing, eyes and skin. Take care
when topping-up or carrying the battery.
• The hydrogen gas given off by the battery
is highly explosive. Never cause a spark or
allow a naked light nearby. Be careful when
connecting and disconnecting battery
chargers or jump leads.
Air bags
• Air bags can cause injury if they go off
accidentally. Take care when removing the
steering wheel and/or facia. Special storage
instructions may apply.
Diesel injection equipment
• Diesel injection pumps supply fuel at very
high pressure. Take care when working on
the fuel injectors and fuel pipes.
Warning: Never expose the
hands, face or any other part of
the body to injector spray; the
fuel can penetrate the skin with
potentially fatal results.
Remember...
DO
• Do use eye protection when using power
tools, and when working under the vehicle.
• Do wear gloves or use barrier cream to
protect your hands when necessary.
• Do get someone to check periodically
that all is well when working alone on the
vehicle.
• Do keep loose clothing and long hair well
out of the way of moving mechanical parts.
• Do remove rings, wristwatch etc, before
working on the vehicle – especially the
electrical system.
• Do ensure that any lifting or jacking
equipment has a safe working load rating
adequate for the job.
A few tips
DON’T
• Don’t attempt to lift a heavy component
which may be beyond your capability – get
assistance.
• Don’t rush to finish a job, or take
unverified short cuts.
• Don’t use ill-fitting tools which may slip
and cause injury.
• Don’t leave tools or parts lying around
where someone can trip over them. Mop
up oil and fuel spills at once.
• Don’t allow children or pets to play in or
near a vehicle being worked on.
0•5Safety First!
procarmanuals.com
Page 15 of 279

Chapter 1 Routine maintenance and servicing
Air conditioning system check . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 14
Air filter element renewal . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 29
Automatic transmission fluid level check . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7
Automatic transmission linkage lubrication . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 18
Auxiliary drivebelt check and renewal . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 11
Battery check, maintenance and charging . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9
Brake check . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 23
Brake fluid renewal . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 34
Clutch pedal adjustment . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 17
Coolant renewal . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2, 28
Door and bonnet check and lubrication . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 24
Driveshaft rubber gaiter and CV joint check . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 20
Electrical system check . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8
Engine compartment wiring check . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 13
Engine oil and filter change . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 15
Exhaust system check . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 21
Fluid level checks . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3
Fuel filter renewal . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 33
Idle speed and mixture check and adjustment . . . . . . See Chapter 4Ignition timing check . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . See Chapter 5
Introduction . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1
Manual transmission oil level check . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 16
Positive Crankcase Ventilation (PCV) system check
and filter cleaning . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 30
Power steering fluid level check . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5
Road test . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 26
Roadwheel nut tightness check . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 25
Seat belt check . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10
Spark plug renewal . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 31
Specifications . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . See end of Chapter
Steering, suspension and roadwheel check . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 19
Timing belt renewal . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 32
Tyre and tyre pressure checks . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4
Underbody and fuel/brake line check . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 22
Underbonnet check for fluid leaks and hose condition . . . . . . . . . . 12
Ventilation system pollen filter renewal . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 27
Windscreen/tailgate washer system and wiper blade check . . . . . . 6
1•1
Easy,suitable for
novice with little
experienceFairly easy,suitable
for beginner with
some experienceFairly difficult,suitable
for competent DIY
mechanicDifficult,suitable for
experienced DIY
mechanicVery difficult,
suitable for expert DIY
or professional
Degrees of difficulty Contents
1
procarmanuals.com
Page 17 of 279

Ford Mondeo maintenance schedule
1•3
1
Maintenance schedule
The manufacturer’s recommended maintenance schedule for these
vehicles is as described below - note that the schedule starts from the
vehicle’s date of registration. These are the minimum maintenance
intervals recommended by the factory for Mondeos driven daily, but
subjected only to “normal” use. If you wish to keep your vehicle in
peak condition at all times, you may wish to perform some of these
procedures even more often. Because frequent maintenance
enhances the efficiency, performance and resale value of your vehicle,
we encourage you to do so. If your usage is not “normal”, shorter
intervals are also recommended - the most important examples of
these are noted in the schedule. These shorter intervals apply
particularly if you drive in dusty areas, tow a caravan or trailer, sit with
the engine idling or drive at low speeds for extended periods (ie, in
heavy traffic), or drive for short distances (less than four miles) in
below-freezing temperatures.
When your vehicle is new, it should be serviced by a Ford dealer
service department to protect the factory warranty. In many cases, the
initial maintenance check is done at no cost to the owner. Note that
this first free service (carried out by the selling dealer 1500 miles or 3
months after delivery), although an important check for a new vehicle,
is not part of the regular maintenance schedule, and is therefore not
mentioned here.
Weekly checks
m mCheck the engine oil level, and top-up if necessary
(Section 3)
m mCheck the brake fluid level, and top-up if necessary
(Section 3). If repeated topping-up is required, check the
system for leaks or damage at the earliest possible
opportunity (Sections 12 and 22)
m mCheck the windscreen/tailgate washer fluid level, and top-
up if necessary (Section 3)
m mCheck the tyre pressures, including the spare (Section 4)
m mVisually check the tyres for excessive tread wear, or
damage (Section 4)
m mCheck the operation of all (exterior and interior) lights and
the horn, wipers and windscreen/tailgate washer system
(Sections 6 and 8). Renew any blown bulbs (Chapter 12),
and clean the lenses of all exterior lights
Monthly checks
m mCheck the coolant level, and top-up if necessary (Sec-
tion 3)
m mCheck the battery electrolyte level, where applicable
(Section 3)
m mCheck the power steering fluid level, and top-up if
necessary (Section 5)
m mVisually check all reservoirs, hoses and pipes for leakage
(Section 12)
m mCheck the operation of the air conditioning system
(Section 14)
m mCheck the operation of the handbrake (Section 23)
m mCheck the aim of the windscreen/tailgate/headlight
washer jets, correcting them if required (Section 6)
m mCheck the condition of the wiper blades, renewing them if
worn or no longer effective - note that the manufacturer
recommends renewing the blades as a safety precaution,
irrespective of their apparent condition, at least once a
year (Section 6)
Every 10 000 miles or 12 months,
whichever occurs first
Note:If the vehicle is used regularly for very short (less than
10 miles), stop/go journeys, the oil and filter should be renewed
between services (ie, every 5000 miles/6 months).
m mCheck the electrical system (Section 8)
m mCheck the battery (Section 9)
m mCheck the seat belts (Section 10)
m mCheck the auxiliary drivebelt (Section 11)
m mCheck for fluid leaks and hose condition (Section 12)
m mCheck the condition of all wiring (Section 13)
m mCheck all air conditioning components (Section 14)
m mChange the engine oil and filter (Section 15)
m mCheck the manual transmission oil level (Section 16)
m mCheck the adjustment of the clutch pedal (Section 17)
m mLubricate the automatic transmission linkage (Section 18)
m mCheck the steering, suspension and wheels (Section 19)
m mCheck the driveshaft gaiters and CV joints (Section 20)
m mCheck the exhaust system (Section 21)
m mCheck the underbody, and all fuel/brake lines (Section 22)
m mCheck the brake system (Section 23)
m mCheck and lubricate the doors and bonnet (Section 24)
m mCheck the security of all roadwheel nuts (Section 25)
m mRoad test (Section 26). Check the level of the automatic
transmission fluid with the engine still hot, after the road
test (Section 7)
Every 20 000 miles or 2 years,
whichever occurs first
Carry out all operations listed above, plus the following:
m mRenew the ventilation system pollen filter (Section 27)
m mRenew the coolant (Sections 2 and 28)
Every 30 000 miles or 3 years,
whichever occurs first
Carry out all operations listed above, plus the following:
m mRenew the air filter element (Section 29). Note that this
task must be carried out at more frequent intervals if the
vehicle is used in dusty or polluted conditions
m mCheck the Positive Crankcase Ventilation (PCV) system,
and clean the filter (Section 30)
m mRenew the spark plugs (Section 31)
Every 60 000 miles
Carry out all operations listed above, plus the following:
m
mRenew the timing belt (Section 32)
m mRenew the fuel filter (Section 33)
Every 3 years
(regardless of mileage)
m mRenew the brake fluid (Section 34)
procarmanuals.com
Page 25 of 279
Every 10 000 miles or 12 months
1•11
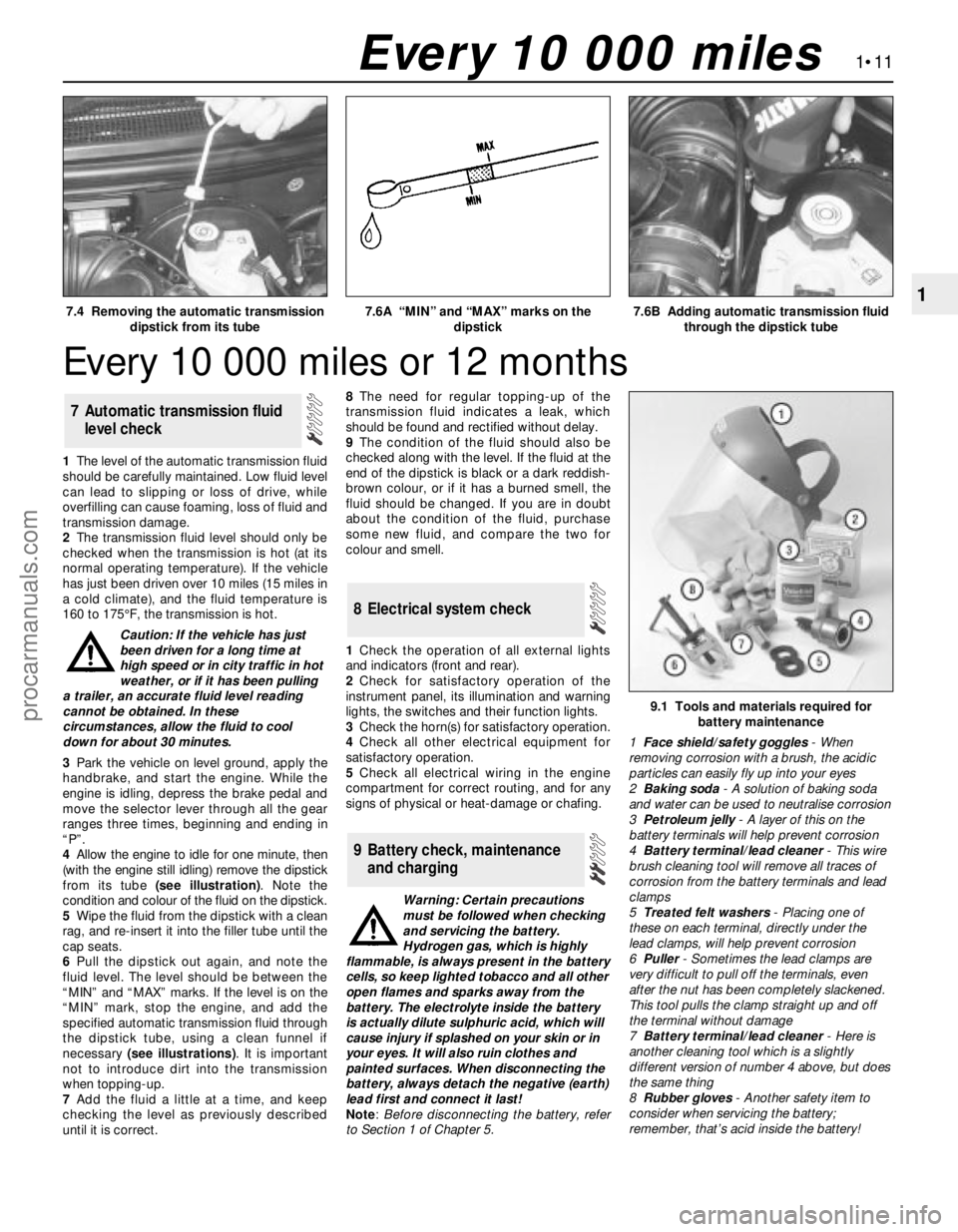
17.4 Removing the automatic transmission
dipstick from its tube7.6A “MIN” and “MAX” marks on the
dipstick7.6B Adding automatic transmission fluid
through the dipstick tube
Every 10 000 miles
1The level of the automatic transmission fluid
should be carefully maintained. Low fluid level
can lead to slipping or loss of drive, while
overfilling can cause foaming, loss of fluid and
transmission damage.
2The transmission fluid level should only be
checked when the transmission is hot (at its
normal operating temperature). If the vehicle
has just been driven over 10 miles (15 miles in
a cold climate), and the fluid temperature is
160 to 175°F, the transmission is hot.
Caution: If the vehicle has just
been driven for a long time at
high speed or in city traffic in hot
weather, or if it has been pulling
a trailer, an accurate fluid level reading
cannot be obtained. In these
circumstances, allow the fluid to cool
down for about 30 minutes.
3Park the vehicle on level ground, apply the
handbrake, and start the engine. While the
engine is idling, depress the brake pedal and
move the selector lever through all the gear
ranges three times, beginning and ending in
“P”.
4Allow the engine to idle for one minute, then
(with the engine still idling) remove the dipstick
from its tube (see illustration). Note the
condition and colour of the fluid on the dipstick.
5Wipe the fluid from the dipstick with a clean
rag, and re-insert it into the filler tube until the
cap seats.
6Pull the dipstick out again, and note the
fluid level. The level should be between the
“MIN” and “MAX” marks. If the level is on the
“MIN” mark, stop the engine, and add the
specified automatic transmission fluid through
the dipstick tube, using a clean funnel if
necessary (see illustrations). It is important
not to introduce dirt into the transmission
when topping-up.
7Add the fluid a little at a time, and keep
checking the level as previously described
until it is correct.8The need for regular topping-up of the
transmission fluid indicates a leak, which
should be found and rectified without delay.
9The condition of the fluid should also be
checked along with the level. If the fluid at the
end of the dipstick is black or a dark reddish-
brown colour, or if it has a burned smell, the
fluid should be changed. If you are in doubt
about the condition of the fluid, purchase
some new fluid, and compare the two for
colour and smell.
1Check the operation of all external lights
and indicators (front and rear).
2Check for satisfactory operation of the
instrument panel, its illumination and warning
lights, the switches and their function lights.
3Check the horn(s) for satisfactory operation.
4Check all other electrical equipment for
satisfactory operation.
5Check all electrical wiring in the engine
compartment for correct routing, and for any
signs of physical or heat-damage or chafing.
Warning: Certain precautions
must be followed when checking
and servicing the battery.
Hydrogen gas, which is highly
flammable, is always present in the battery
cells, so keep lighted tobacco and all other
open flames and sparks away from the
battery. The electrolyte inside the battery
is actually dilute sulphuric acid, which will
cause injury if splashed on your skin or in
your eyes. It will also ruin clothes and
painted surfaces. When disconnecting the
battery, always detach the negative (earth)
lead first and connect it last!
Note: Before disconnecting the battery, refer
to Section 1 of Chapter 5.
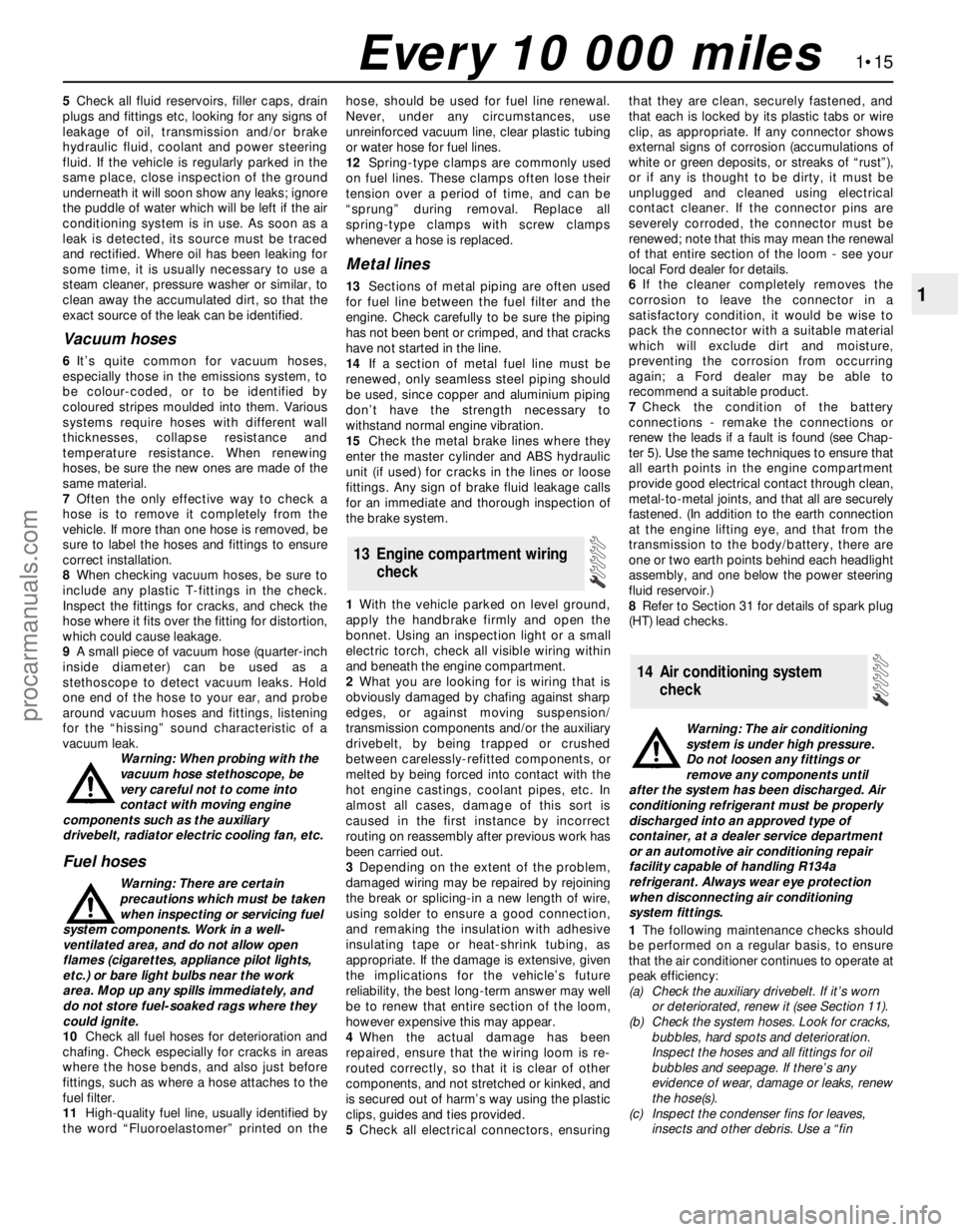
9 Battery check, maintenance
and charging
8 Electrical system check
7 Automatic transmission fluid
level check
9.1 Tools and materials required for
battery maintenance
1Face shield/safety goggles- When
removing corrosion with a brush, the acidic
particles can easily fly up into your eyes
2Baking soda- A solution of baking soda
and water can be used to neutralise corrosion
3Petroleum jelly- A layer of this on the
battery terminals will help prevent corrosion
4Battery terminal/lead cleaner- This wire
brush cleaning tool will remove all traces of
corrosion from the battery terminals and lead
clamps
5Treated felt washers- Placing one of
these on each terminal, directly under the
lead clamps, will help prevent corrosion
6Puller- Sometimes the lead clamps are
very difficult to pull off the terminals, even
after the nut has been completely slackened.
This tool pulls the clamp straight up and off
the terminal without damage
7Battery terminal/lead cleaner- Here is
another cleaning tool which is a slightly
different version of number 4 above, but does
the same thing
8Rubber gloves- Another safety item to
consider when servicing the battery;
remember, that’s acid inside the battery!
procarmanuals.com
Page 29 of 279
5Check all fluid reservoirs, filler caps, drain
plugs and fittings etc, looking for any signs of
leakage of oil, transmission and/or brake
hydraulic fluid, coolant and power steering
fluid. If the vehicle is regularly parked in the
same place, close inspection of the ground
underneath it will soon show any leaks; ignore
the puddle of water which will be left if the air
conditioning system is in use. As soon as a
leak is detected, its source must be traced
and rectified. Where oil has been leaking for
some time, it is usually necessary to use a
steam cleaner, pressure washer or similar, to
clean away the accumulated dirt, so that the
exact source of the leak can be identified.
Vacuum hoses
6It’s quite common for vacuum hoses,
especially those in the emissions system, to
be colour-coded, or to be identified by
coloured stripes moulded into them. Various
systems require hoses with different wall
thicknesses, collapse resistance and
temperature resistance. When renewing
hoses, be sure the new ones are made of the
same material.
7Often the only effective way to check a
hose is to remove it completely from the
vehicle. If more than one hose is removed, be
sure to label the hoses and fittings to ensure
correct installation.
8When checking vacuum hoses, be sure to
include any plastic T-fittings in the check.
Inspect the fittings for cracks, and check the
hose where it fits over the fitting for distortion,
which could cause leakage.
9A small piece of vacuum hose (quarter-inch
inside diameter) can be used as a
stethoscope to detect vacuum leaks. Hold
one end of the hose to your ear, and probe
around vacuum hoses and fittings, listening
for the “hissing” sound characteristic of a
vacuum leak.
Warning: When probing with the
vacuum hose stethoscope, be
very careful not to come into
contact with moving engine
components such as the auxiliary
drivebelt, radiator electric cooling fan, etc.
Fuel hoses
Warning: There are certain
precautions which must be taken
when inspecting or servicing fuel
system components. Work in a well-
ventilated area, and do not allow open
flames (cigarettes, appliance pilot lights,
etc.) or bare light bulbs near the work
area. Mop up any spills immediately, and
do not store fuel-soaked rags where they
could ignite.
10Check all fuel hoses for deterioration and
chafing. Check especially for cracks in areas
where the hose bends, and also just before
fittings, such as where a hose attaches to the
fuel filter.
11High-quality fuel line, usually identified by
the word “Fluoroelastomer” printed on thehose, should be used for fuel line renewal.
Never, under any circumstances, use
unreinforced vacuum line, clear plastic tubing
or water hose for fuel lines.
12Spring-type clamps are commonly used
on fuel lines. These clamps often lose their
tension over a period of time, and can be
“sprung” during removal. Replace all
spring-type clamps with screw clamps
whenever a hose is replaced.
Metal lines
13Sections of metal piping are often used
for fuel line between the fuel filter and the
engine. Check carefully to be sure the piping
has not been bent or crimped, and that cracks
have not started in the line.
14If a section of metal fuel line must be
renewed, only seamless steel piping should
be used, since copper and aluminium piping
don’t have the strength necessary to
withstand normal engine vibration.
15Check the metal brake lines where they
enter the master cylinder and ABS hydraulic
unit (if used) for cracks in the lines or loose
fittings. Any sign of brake fluid leakage calls
for an immediate and thorough inspection of
the brake system.
1With the vehicle parked on level ground,
apply the handbrake firmly and open the
bonnet. Using an inspection light or a small
electric torch, check all visible wiring within
and beneath the engine compartment.
2What you are looking for is wiring that is
obviously damaged by chafing against sharp
edges, or against moving suspension/
transmission components and/or the auxiliary
drivebelt, by being trapped or crushed
between carelessly-refitted components, or
melted by being forced into contact with the
hot engine castings, coolant pipes, etc. In
almost all cases, damage of this sort is
caused in the first instance by incorrect
routing on reassembly after previous work has
been carried out.
3Depending on the extent of the problem,
damaged wiring may be repaired by rejoining
the break or splicing-in a new length of wire,
using solder to ensure a good connection,
and remaking the insulation with adhesive
insulating tape or heat-shrink tubing, as
appropriate. If the damage is extensive, given
the implications for the vehicle’s future
reliability, the best long-term answer may well
be to renew that entire section of the loom,
however expensive this may appear.
4When the actual damage has been
repaired, ensure that the wiring loom is re-
routed correctly, so that it is clear of other
components, and not stretched or kinked, and
is secured out of harm’s way using the plastic
clips, guides and ties provided.
5Check all electrical connectors, ensuringthat they are clean, securely fastened, and
that each is locked by its plastic tabs or wire
clip, as appropriate. If any connector shows
external signs of corrosion (accumulations of
white or green deposits, or streaks of “rust”),
or if any is thought to be dirty, it must be
unplugged and cleaned using electrical
contact cleaner. If the connector pins are
severely corroded, the connector must be
renewed; note that this may mean the renewal
of that entire section of the loom - see your
local Ford dealer for details.
6If the cleaner completely removes the
corrosion to leave the connector in a
satisfactory condition, it would be wise to
pack the connector with a suitable material
which will exclude dirt and moisture,
preventing the corrosion from occurring
again; a Ford dealer may be able to
recommend a suitable product.
7Check the condition of the battery
connections - remake the connections or
renew the leads if a fault is found (see Chap-
ter 5). Use the same techniques to ensure that
all earth points in the engine compartment
provide good electrical contact through clean,
metal-to-metal joints, and that all are securely
fastened. (In addition to the earth connection
at the engine lifting eye, and that from the
transmission to the body/battery, there are
one or two earth points behind each headlight
assembly, and one below the power steering
fluid reservoir.)
8Refer to Section 31 for details of spark plug
(HT) lead checks.
Warning: The air conditioning
system is under high pressure.
Do not loosen any fittings or
remove any components until
after the system has been discharged. Air
conditioning refrigerant must be properly
discharged into an approved type of
container, at a dealer service department
or an automotive air conditioning repair
facility capable of handling R134a
refrigerant. Always wear eye protection
when disconnecting air conditioning
system fittings.
1The following maintenance checks should
be performed on a regular basis, to ensure
that the air conditioner continues to operate at
peak efficiency:
(a) Check the auxiliary drivebelt. If it’s worn
or deteriorated, renew it (see Section 11).
(b) Check the system hoses. Look for cracks,
bubbles, hard spots and deterioration.
Inspect the hoses and all fittings for oil
bubbles and seepage. If there’s any
evidence of wear, damage or leaks, renew
the hose(s).
(c) Inspect the condenser fins for leaves,
insects and other debris. Use a “fin
14 Air conditioning system
check
13 Engine compartment wiring
check
1•15
1
Every 10 000 miles
procarmanuals.com
Page 30 of 279

comb” or compressed air to clean the
condenser.
Warning: Wear eye protection
when using compressed air!
(d) Check that the drain tube from the front
of the evaporator is clear - note that it is
normal to have clear fluid (water) dripping
from this while the system is in operation,
to the extent that quite a large puddle can
be left under the vehicle when it is parked.
2It’s a good idea to operate the system forabout 30 minutes at least once a month,
particularly during the winter. Long term
non-use can cause hardening, and
subsequent failure, of the seals.
3Because of the complexity of the air
conditioning system and the special
equipment necessary to service it, in-depth
fault diagnosis and repairs are not included in
this manual. For more complete information
on the air conditioning system, refer to the
Haynes Automotive Heating and Air
Conditioning Manual.
4The most common cause of poor cooling is
simply a low system refrigerant charge. If a
noticeable drop in cool air output occurs, the
following quick check will help you determine
if the refrigerant level is low.
5Warm the engine up to normal operating
temperature.
6Place the air conditioning temperature
selector at the coldest setting, and put the
blower at the highest setting. Open the doors
- to make sure the air conditioning system
doesn’t cycle off as soon as it cools the
passenger compartment.
7With the compressor engaged - the clutch
will make an audible click, and the centre of
the clutch will rotate - feel the inlet and outlet
pipes at the compressor. One side should be
cold, and one hot. If there’s no perceptible
difference between the two pipes, there’s
something wrong with the compressor or the
system. It might be a low charge - it might be
something else. Take the vehicle to a dealer
service department or an automotive air
conditioning specialist.1Make sure that you have all the necessary
tools before you begin this procedure (see
illustration). You should also have plenty of
rags or newspapers handy, for mopping up
any spills.
2To avoid any possibility of scalding, and to
protect yourself from possible skin irritants
and other harmful contaminants in used
engine oils, it is advisable to wear gloves
when carrying out this work.
3Access to the underside of the vehicle is
greatly improved if the vehicle can be lifted on
a hoist, driven onto ramps, or supported by
axle stands.
Warning: Do not work under a
vehicle which is supported only
by an hydraulic or scissors-type
jack, or by bricks, blocks of
wood, etc.
4If this is your first oil change, get under the
vehicle and familiarise yourself with the
position of the engine oil drain plug, which is
located at the rear of the sump. The engine
and exhaust components will be warm during
the actual work, so try to anticipate any
potential problems while the engine and
accessories are cool.
5The oil should preferably be changed when
the engine is still fully warmed-up to normal
operating temperature, just after a run (the
needle on the temperature gauge should be in
the “Normal” sector of the gauge); warm oil
and sludge will flow out more easily. Park the
vehicle on firm, level ground, apply the
handbrake firmly, then select 1st or reverse
gear (manual transmission) or the “P” position
(automatic transmission). Open the bonnet
and remove the engine oil filler cap from the
cylinder head cover, then remove the oil level
dipstick from its tube (see Section 3).
6Raise the front of the vehicle, and support it
securely on axle stands. Remove the front
right-hand roadwheel to provide access to the
oil filter; if the additional working clearance is
required, remove also the auxiliary drivebelt
cover (two fasteners).
15 Engine oil and filter change
1•16
15.1 These tools are required when
changing the engine oil and filter
1Drain pan- It should be fairly shallow in
depth, but wide to prevent spills
2Rubber gloves- When removing the drain
plug and filter, it is inevitable that you will get
oil on your hands (the gloves will prevent
burns from hot oil)
3Breaker bar- Sometimes the oil drain plug
is pretty tight, and a long breaker bar is
needed to loosen it
4Socket- To be used with the breaker bar
or a ratchet (must be the correct size to fit the
drain plug)
5Filter wrench- This is a metal band-type
wrench, which requires clearance around the
filter to be effective
6Filter wrench- This type fits on the
bottom of the filter, and can be turned with a
ratchet or breaker bar (different size wrenches
are available for different types of filters)
15.7 Use the correct-size spanner or
socket to remove the oil drain plug and
avoid rounding it off15.9 Since the oil filter is usually on very
tight, you’ll need a special wrench for
removal. DO NOT use the wrench to
tighten the new filter. Pack rag under the
filter before removal to minimise the mess
Every 10 000 miles
Frequent oil changes are the
best preventive maintenance
the home mechanic can give
the engine, because ageing
oil becomes diluted and contaminated,
which leads to premature engine wear.
Note: It is
antisocial and
illegal to dump
oil down the
drain. To find
the location of
your local oil
recycling bank,
call this
number free.
procarmanuals.com
Page 34 of 279

brake shoes is not less than the
recommendation given in the Specifications.
14If it is difficult to determine the exact
thickness of the brake shoe linings, or if you
are at all concerned about the condition of the
shoes, then remove the rear drums for a more
comprehensive inspection (refer to Chapter 9)
(see illustration).
15With the drum removed, check the shoe
return and hold-down springs for correct
installation, and check the wheel cylinders for
leakage of brake fluid. Check the friction
surface of the brake drums for scoring and
discoloration. If excessive, the drum should
be resurfaced or renewed.
16Before refitting the wheels, check all
brake lines and hoses (refer to Chapter 9). On
completion, apply the handbrake and check
that the rear wheels are locked. The
handbrake is self-adjusting, and no manual
adjustment is possible.
1Check that the doors, bonnet and
tailgate/boot lid close securely. Check that
the bonnet safety catch operates correctly.
Check the operation of the door check straps.
2Lubricate the hinges, door check straps,
the striker plates and the bonnet catch
sparingly with a little oil or grease.1Apply the handbrake.
2Remove the wheel covers, using the flat
end of the wheelbrace supplied in the tool kit
(on models with the RS trim kit, it will be
necessary to unscrew the retaining bolts with
the special key).
3Check that the roadwheel nuts are tightened
to the specified torque wrench setting.
4Refit the wheel covers.
Check the operation and
performance of the braking
system
1Make sure that the vehicle does not pull to
one side when braking, and that the wheels
do not lock prematurely when braking hard.
2Check that there is no vibration through the
steering when braking.
3Check that the handbrake operates
correctly, without excessive movement of the
lever, and that it holds the vehicle stationary
on a slope.
4With the engine switched off, test the
operation of the brake servo unit as follows.
Depress the footbrake four or five times to
exhaust the vacuum, then start the engine. As
the engine starts, there should be a noticeable
“give” in the brake pedal as vacuum builds
up. Allow the engine to run for at least two
minutes, and then switch it off. If the brake
pedal is now depressed again, it should be
possible to detect a hiss from the servo as the
pedal is depressed. After about four or five
applications, no further hissing should be
heard, and the pedal should feel considerably
harder.
Steering and suspension
5Check for any abnormalities in the steering,
suspension, handling or road “feel”.
6Drive the vehicle, and check that there are
no unusual vibrations or noises.
7Check that the steering feels positive, with
no excessive sloppiness or roughness, andcheck for any suspension noises when
cornering and driving over bumps.
Drivetrain
8Check the performance of the engine,
transmission and driveshafts.
9Check that the engine starts correctly, both
when cold and when hot.
10Listen for any unusual noises from the
engine and transmission.
11Make sure that the engine runs smoothly
when idling, and that there is no hesitation
when accelerating.
12On manual transmission models, check
that all gears can be engaged smoothly
without noise, and that the gear lever action is
not abnormally vague or “notchy”.
13On automatic transmission models, make
sure that all gearchanges occur smoothly
without snatching, and without an increase in
engine speed between changes. Check that
all the gear positions can be selected with the
vehicle at rest. If any problems are found, they
should be referred to a Ford dealer.
14Listen for a metallic clicking sound from
the front of the vehicle as the vehicle is driven
slowly in a circle with the steering on full-lock.
Carry out this check in both directions. If a
clicking noise is heard, this indicates wear in a
driveshaft joint, in which case renew the joint
if necessary.
Clutch
15Check that the clutch pedal moves
smoothly and easily through its full travel, and
that the clutch itself functions correctly, with
no trace of slip or drag. If the movement is
uneven or stiff in places, check that the cable
is routed correctly, with no sharp turns.
16Inspect both ends of the clutch inner
cable, both at the gearbox end and inside the
car, for signs of wear and fraying.
17Check the pedal stroke as described in
Chapter 8, Section 3, and adjust if necessary.
Instruments and electrical
equipment
18Check the operation of all instruments
and electrical equipment.
19Make sure that all instruments read
correctly, and switch on all electrical
equipment in turn, to check that it functions
properly.
26 Road test
25 Roadwheel nut tightness
check
24 Door and bonnet check and
lubrication
1•20
23.14 If the lining is bonded to the brake
shoe, measure the lining thickness from
the outer surface to the metal shoe, as
shown here; if the lining is riveted to the
shoe, measure from the lining outer
surface to the rivet head
Every 20 000 miles
Every 20 000 miles or 2 years
1The air entering the vehicle’s ventilation
system is passed through a very fine pleated-
paper air filter element, which removes
particles of pollen, dust and other airborne
foreign matter. To ensure its continued
effectiveness, this filter’s element must be
renewed at regular intervals.2Remove the left-hand side windscreen
wiper arm (Chapter 12).
3Prise off their trim caps, then unscrew the two
screws securing the windscreen edge of the cowl
grille panel; open the bonnet and remove the
remaining three retaining screws (see illustration).
4Peel back the rubber seal and withdraw the
cowl grille panel.
5Releasing the clip at each end, lift out the
pollen filter housing, and withdraw the
element (see illustrations).6Wipe out the ventilation system intake and
the filter housing, removing any leaves, dead
insects etc.
7If carrying out a routine service, the element
must be renewed regardless of its apparent
condition. If you are checking the element for
any other reason, inspect its front surface; if it
is very dirty, renew the element. If it is only
moderately dusty, it can be re-used by
blowing it clean from the rear to the front
surface with compressed air. Because it is a
27 Ventilation system pollen
filter renewal
procarmanuals.com
Page 59 of 279

then an ordinary socket extension bar and an
angle gauge, to tighten the cylinder head
bolts in the stages given in the Specifications
Section of this Chapter (see illustrations).
Note:Once tightened correctly, following this
procedure, the cylinder head bolts do not
require check-tightening, and must notbe re-
torqued.
33Refit the hydraulic tappets (if removed),
the camshafts, their oil seals and pulleys (see
Sections 10, 11, 12 and 13, as appropriate).
Temporarily refit the crankshaft pulley, and
rotate the crankshaft clockwise to return the
pulley notches to the position described in
paragraph 8 of Section 10.
34Refit the timing belt and covers, checking
the camshaft alignment (valve timing) and
setting the timing belt tension, as described in
Section 10.
35The remainder of reassembly is the
reverse of the removal procedure, noting the
following points:
(a) Tighten all fasteners to the torque wrench
settings specified.
(b) When reassembling the
engine/transmission right-hand mounting,
renew the self-locking nuts, and do not
allow the mounting to twist as the middle
two of the bracket’s six nuts are
tightened.
(c) Refill the cooling system, and top-up the
engine oil.
(d) Check all disturbed joints for signs of oil
or coolant leakage, once the engine has
been restarted and warmed-up to normal
operating temperature.
Removal
Note:To carry out this task with the
engine/transmission installed in the vehicle
requires the assistance of at least one person,
plus the equipment necessary to raise and
support the front of the vehicle (high enough
that the sump can be withdrawn from
underneath), and to lift and support the
complete engine/transmission unit 2 to 3 inches from its mountings while the vehicle
is raised. Precise details of the procedure will
depend on the equipment available - the
following is typical.
The full procedure outlined below must be
followed, so that the mating surfaces can be
cleaned and prepared to achieve an oil-tight
joint on reassembly, and so that the sump
can be aligned correctly; depending on your
skill and experience, and the tools and
facilities available, it may be that this task can
be carried out only with the engine removed
from the vehicle.
Note that the sump gasket must be
renewed whenever it is disturbed.
1With the vehicle parked on firm level
ground, open the bonnet and disconnect the
battery negative (earth) lead - see Chapter 5,
Section 1.
2Drain the engine oil, then clean and refit the
engine oil drain plug, tightening it to the
specified torque wrench setting. Although not
strictly necessary as part of the dismantling
procedure, owners are advised to remove
and discard the oil filter, so that it can be
renewed with the oil (see Chapter 1).
3Drain the cooling system (see Chapter 1).
4Disconnect the radiator bottom hose from
the radiator union and from the (heater)
coolant pipe. Unbolt the coolant pipe from
the sump; if they will prevent sump removal,
disconnect or release the coolant hoses from
the oil cooler unions (where fitted).
5Unscrew the two bolts securing the powersteering system pipes to the right-hand side
of the subframe.
6Unplug the electrical connector(s) to
disconnect the oxygen sensor and, where
fitted, the oil level sensor wiring - unclip the
connectors to release the wiring where
necessary.
7Where the vehicle is fitted with automatic
transmission, trace the fluid cooler lines from
the transmission to the radiator, and release
them from any clips etc, so that they have as
much movement as possible.
8Remove the auxiliary drivebelt cover (see
Chapter 1).
9Unscrew the nuts to disconnect the
exhaust system front downpipe from the
manifold, then either unhook all the system’s
rubber mountings and withdraw the complete
exhaust system from under the vehicle, or
remove only the downpipe/catalytic converter
(see Chapter 4 for details).
10Unscrew the sump-to-transmission bolts,
also any securing the engine/transmission
lower adaptor plate.
11Unplugging the two electrical connectors,
disconnecting the vacuum hose (where fitted)
and disconnecting the crankcase breather
hose from the cylinder head cover, remove
the complete air cleaner assembly with the air
mass meter, the resonator and the plenum
chamber (see Chapter 4).
12Take the weight of the engine/
transmission unit using the lifting eyes
provided on the cylinder head; bolt on
15 Sump - removal and refitting
In-car engine repair procedures 2A•19
2A
14.32B . . . and to third stage using angle
gauge14.32C Cylinder head bolt tightening
sequence
Note:View from rear of vehicle15.12 Equipment must be available to raise
and support engine/transmission unit while
vehicle is raised, to allow sump removal
14.30 Refitting cylinder head - note
fabricated guide studs (arrowed)14.32A Tightening cylinder head bolts (to
first and second stages) using torque
wrench . . .
procarmanuals.com