1993 DODGE TRUCK transmission fluid
[x] Cancel search: transmission fluidPage 14 of 1502
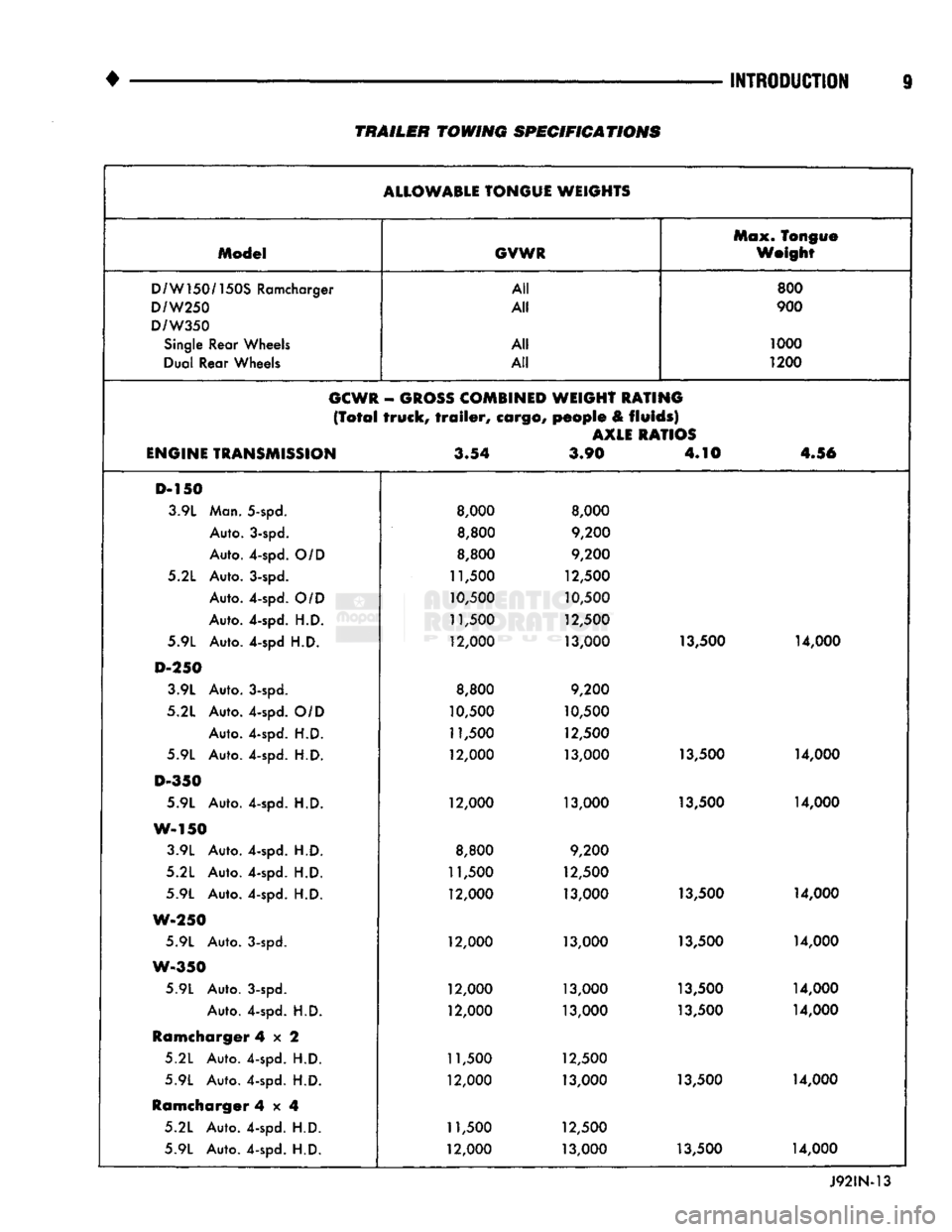
TRAILER TOWING
SPECIFICATIONS
ALLOWABLE
TONGUE WEIGHTS Max. Tongue
Model
GVWR
Weight
D/W150/150S
Ramcharger All
800
D/W250
All
900
D/W350
Single
Rear Wheels All
1000
Dual Rear Wheels All
1200
GCWR
-
GROSS
COMBINED
WEIGHT RATING
(Total
truck,
trailer,
cargo,
people
&
fluids)
AXLE
RATIOS
ENGINE
TRANSMISSION
3.54
3.90 4.10
4.56
D-150 3.9L Man. 5-spd.
8,000 8,000
Auto. 3-spd.
8,800
9,200
Auto. 4-spd.
O/D
8,800
9,200
5.2L Auto. 3-spd.
11,500
12,500
Auto. 4-spd.
O/D
10,500
10,500
Auto. 4-spd.
H.D.
11,500
12,500
5.9L Auto. 4-spd
H.D.
12,000
13,000 13,500
14,000
D-250
3.9L Auto. 3-spd.
8,800
9,200
5.2L Auto. 4-spd.
O/D
10,500 10,500
Auto. 4-spd.
H.D.
11,500
12,500
5.9L Auto. 4-spd.
H.D.
12,000
13,000 13,500
14,000
D-350
5.9L Auto. 4-spd.
H.D.
12,000
13,000 13,500 14,000
W-150 3.9L Auto. 4-spd.
H.D.
8,800
9,200
5.2L Auto. 4-spd.
H.D.
11,500
12,500
5.9L Auto. 4-spd.
H.D.
12,000
13,000 13,500
14,000
W-250
5.9L Auto. 3-spd.
12,000
13,000 13,500 14,000
W-350
5.9L Auto. 3-spd.
12,000 13,000 13,500 14,000
Auto. 4-spd.
H.D.
12,000
13,000 13,500 14,000
Ramcharger
4x2
5.2L Auto. 4-spd.
H.D.
11,500 12,500
5.9L Auto. 4-spd.
H.D.
12,000 13,000 13,500 14,000
Ramcharger
4x4
5.2L Auto. 4-spd.
H.D.
11,500 12,500
5.9L Auto. 4-spd.
H.D.
12,000
13,000 13,500 14,000
Page 28 of 1502
•
LUBRICATION AND MAINTENANCE
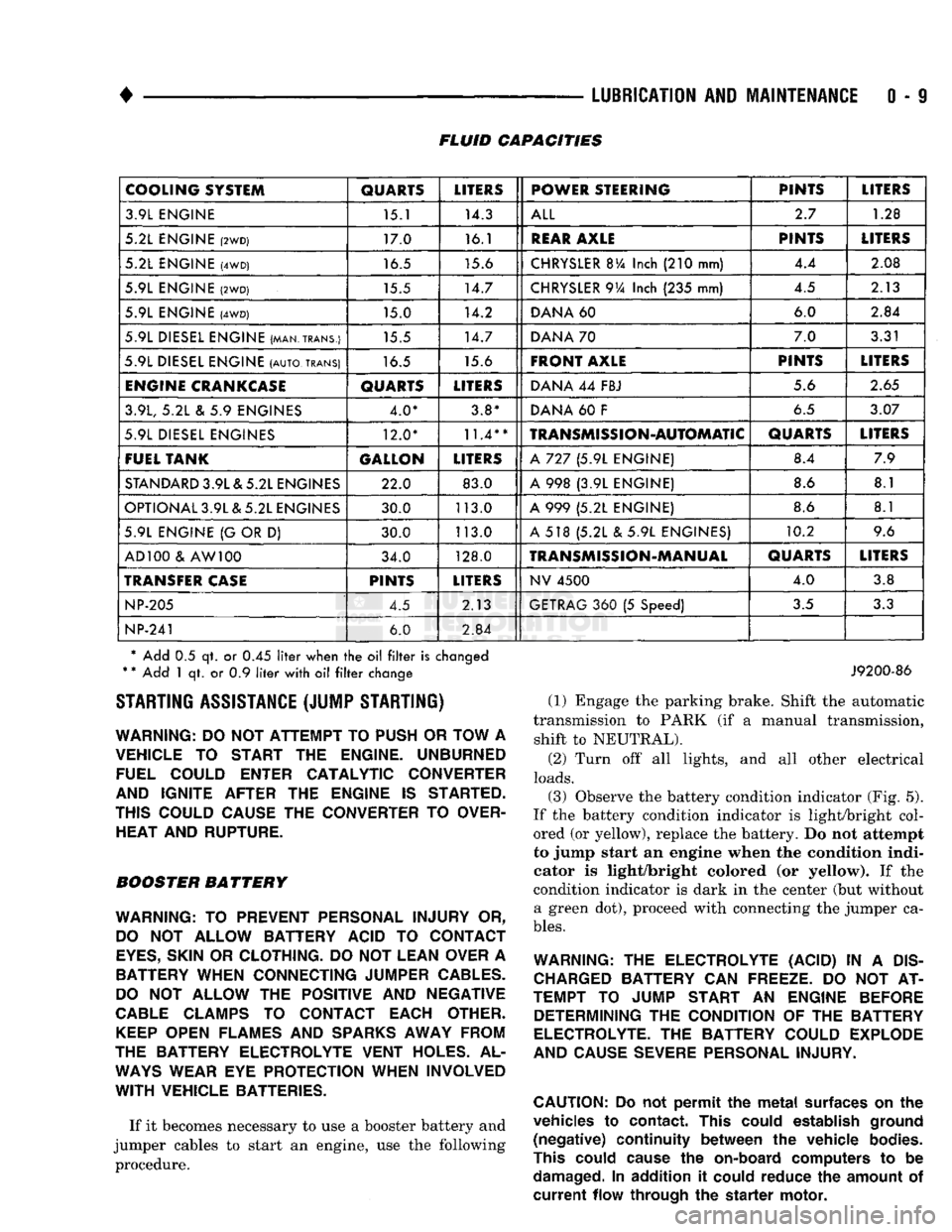
0 - 9 FLUID CAPACITIES
COOLING SYSTEM
QUARTS
LITERS
POWER STEERING PINTS
LITERS
3.9L ENGINE 15.1 14.3
ALL
2.7
1.28
5.2L ENGINE
(2WD)
17.0 16.1
REAR
AXLE
PINTS
LITERS
5.2L ENGINE
(4WD)
16.5 15.6
CHRYSLER
BVa
Inch
(210
mm) 4.4
2.08
5.9L ENGINE
(2WD)
15.5 14.7
CHRYSLER
9Va
Inch
(235
mm) 4.5
2.13
5.9L ENGINE
(4WD)
15.0 14.2
DANA
60 6.0
2.84
5.9L DIESEL ENGINE (MAN.TRANS.) 15.5 14.7
DANA
70 7.0
3.31
5.9L DIESEL ENGINE
(AUTO,
TRANS)
16.5 15.6
FRONT AXLE
PINTS
LITERS
ENGINE
CRANKCASE
QUARTS
LITERS
DANA
44
FBJ 5.6
2.65
3.9L,
5.2L & 5.9
ENGINES 4.0* 3.8*
DANA
60 F
6.5
3.07
5.9L DIESEL ENGINES 12.0*
11.4**
TRANSMISSION-AUTOMATIC
QUARTS
LITERS
FUEL TANK GALLON
LITERS
A
727 (5.9L
ENGINE) 8.4
7.9
STANDARD
3.9L & 5.2L ENGINES 22.0 83.0
A
998 (3.9L
ENGINE) 8.6
8.1
OPTIONAL 3.9L & 5.2L ENGINES 30.0 113.0
A
999 (5.2L
ENGINE) 8.6
8.1
5.9L ENGINE
{G
OR
D)
30.0 113.0
A
518 (5.2L & 5.9L
ENGINES) 10.2
9.6
AD 100
&
AW 100 34.0 128.0
TRANSMISSION-MANUAL
QUARTS
LITERS
TRANSFER
CASE
PINTS
LITERS
NV
4500
4.0
3.8
NP-205
4.5 2.13
GETRAG
360 (5
Speed)
3.5
3.3
NP-241
6.0
2.84
* Add
0.5 qt. or 0.45
liter
when
the oil filter
is
changed
*
*
Add
1 qt. or 0.9
liter
with
oil filter
change STARTING ASSISTANCE (JUMP STARTING)
WARNING:
DO NOT
ATTEMPT
TO
PUSH
OR
TOW
A
VEHICLE
TO
START
THE
ENGINE. UNBURNED FUEL COULD ENTER CATALYTIC CONVERTER
AND IGNITE AFTER
THE
ENGINE
IS
STARTED.
THIS COULD CAUSE
THE
CONVERTER
TO
OVER HEAT AND RUPTURE.
BOOSTER BATTERY
WARNING:
TO
PREVENT PERSONAL INJURY
OR,
DO
NOT
ALLOW BATTERY ACID
TO
CONTACT
EYES,
SKIN
OR
CLOTHING.
DO NOT
LEAN OVER
A
BATTERY WHEN CONNECTING JUMPER
CABLES.
DO
NOT
ALLOW
THE
POSITIVE
AND
NEGATIVE
CABLE
CLAMPS
TO
CONTACT EACH OTHER.
KEEP
OPEN FLAMES
AND
SPARKS
AWAY FROM
THE BATTERY ELECTROLYTE VENT HOLES.
AL
WAYS
WEAR
EYE
PROTECTION WHEN INVOLVED
WITH
VEHICLE BATTERIES.
If it becomes necessary to use a booster battery and
jumper cables to start an engine, use the following procedure.
J9200-86
(1) Engage the parking brake. Shift the automatic
transmission to PARK (if a manual transmission, shift to NEUTRAL).
(2) Turn off all lights, and all other electrical
loads.
(3)
Observe the battery condition indicator (Fig. 5).
If the battery condition indicator is light/bright col
ored (or yellow), replace the battery. Do not attempt
to jump start an engine when the condition indi
cator is light/bright colored (or yellow). If the
condition indicator is dark in the center (but without a green dot), proceed with connecting the jumper ca
bles.
WARNING:
THE
ELECTROLYTE (ACID)
IN A
DIS
CHARGED
BATTERY
CAN
FREEZE.
DO NOT AT
TEMPT
TO
JUMP START
AN
ENGINE BEFORE DETERMINING
THE
CONDITION
OF THE
BATTERY
ELECTROLYTE.
THE
BATTERY COULD EXPLODE
AND CAUSE SEVERE PERSONAL INJURY.
CAUTION:
Do not
permit
the
metal
surfaces
on the
vehicles
to
contact.
This
could
establish
ground
(negative)
continuity
between
the
vehicle
bodies.
This
could
cause
the
on-board
computers
to be
damaged.
In
addition
it
could
reduce
the
amount
of
current
flow
through
the
starter
motor.
Page 41 of 1502
0
- 22
LUBRICATION
AND
MAINTENANCE
DRIVETRAIN
INDEX
page
Axles
25
Clutch
and
Brake Pedal
Bushings
............ 22
Clutch Master Cylinder
22
Drive Shafts
26
page
Front Axle U-Joint
and
Pivot Bearings
......... 26
Transfer
Case
(4WD
Vehicles)
. . ........ 24
Transmissions
. 22
CLUTCH
AND
BRAKE PEDAL
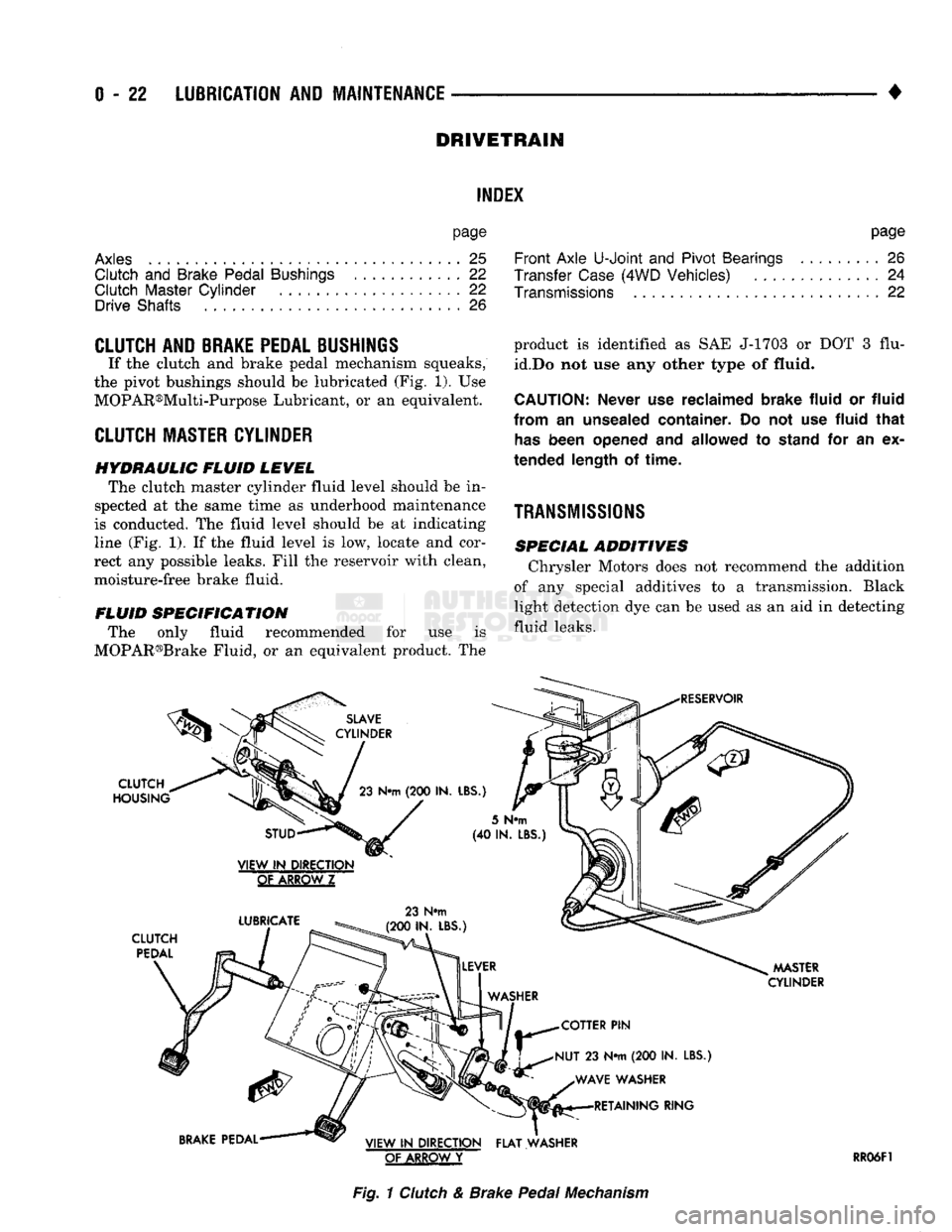
If the clutch and brake pedal mechanism squeaks,
the pivot bushings should be lubricated (Fig. 1). Use
MOPAR®Multi-Purpose Lubricant, or an equivalent.
CLUTCH
MASTER CYLINDER
HYDRAULIC FLUID LEVEL The clutch master cylinder fluid level should be in
spected at the same time as underhood maintenance
is conducted. The fluid level should be at indicating
line (Fig. 1). If the fluid level is low, locate and cor
rect any possible leaks. Fill the reservoir with clean,
moisture-free brake fluid.
FLUID SPECIFICATION The only fluid recommended for use is
MOPAR®Brake Fluid, or an equivalent product. The
SLAVE
CYLINDER
CLUTCH
HOUSING
23
N«m
(200 IN.
LBS.)
product is identified as SAE J-1703 or DOT 3 flu
id.Do not use any other type of
fluid.
CAUTION:
Never
use
reclaimed brake fluid
or
fluid
from
an
unsealed container.
Do not use
fluid that
has
been opened
and
allowed
to
stand
for an ex
tended length
of
time.
TRANSMISSIONS
SPECIAL ADDITIVES Chrysler Motors does not recommend the addition
of any special additives to a transmission. Black
light detection dye can be used as an aid in detecting
fluid leaks.
RESERVOIR
STUD
VIEW
IN
DIRECTION
GtAKBQWZ
LUBRICATE
CLUTCH
PEDAL
23 N#m
(200 IN. LBS.)
5
N«m
(40 IN.
LBS
MASTER
CYLINDER
COTTER
PIN
NUT
23 N*m (200 IN.
LBS.) WAVE WASHER RETAINING RING
BRAKE
PEDAL VIEW
IN
DIRECTION FLAT WASHER
OF ARROW
Y
RR06F1
Fig.
1
Clutch
& Brake
Pedal
Mechanism
Page 42 of 1502

•
LUBRICATION
AND
MAINTENANCE
0 - 23 GEAR SHIFTER BOOTS
Inspect the shifter boots periodically for stone and
heat damage. Replace, if necessary.
SEVERE DRIVING CONDITIONS The interval between the transmission drain and
refill maintenance should be decreased to:
• NV4500 manual transmission—every 29 000 km (18,000 miles)
• Automatic transmission—every 19 000 km (12,000
miles)
A severe driving condition includes:
• Extended operation with heavy cargo loads
• Driving in deep mud or snow
• Off-road operation (4WD)
• Trailer towing
• Operation as a commercial vehicle
• Snow plowing
MANUAL TRANSMISSIONS
INSPECTION/LUBE
OIL
LEVEL
The transmission should be checked for leaks when
other service is necessary under the vehicle. To check
the lube oil level, remove the fill hole plug (Fig. 2 ). If the level is below the bottom of the fill hole, raise
the level to the bottom of the fill hole with:
• Castrol Syntorq for NV4500 transmissions
• SAE 5W-30 engine oil (API Service SG, SG/CD or
SG/CE) for Getrag 360 transmissions.
Fig.
2 NV4500 Manual
Transmission
DRAIN
AND
FILL
The NV4500 transmission fluid should be changed
according to the intervals listed in the Manual
Transmission—Drain & Refill Intervals chart below.
Also,
refer to the Fluid Capacities chart.
AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSIONS
FLUID
LEWEL
It is recommended that the fluid (ATF) level in au
tomatic transmissions be checked while involved
with other underhood maintenance.
Vehicle operation with an incorrect ATF level
will greatly reduce the life of the transmission.
Fig.
3 Getrag 360 Manual
Transmission
MANUAL TRANSMISSION-DRAIN & REFILL INTERVALS
Normal
Service
Light
Duty
Cycle
60 000
km
37,500
miles
Heavy
Duty
Cycle
58 000
km
36,000
miles
Severe
Service
29 000
km
18,000
miles
J9000-43
The condition of the ATF also should be deter
mined. If the ATF is dark in color and has a strong odor, the fluid should be changed. Also the filter should be replaced and the bands adjusted.
The following procedure must be used to check the
automatic transmission fluid (ATF) level.
(1) Position the vehicle on level ground.
(2) Operate the engine at idle speed.
(3) Apply the parking brake.
(4) Place the gear selector in N (neutral).
(5) Remove the dipstick from the tube. Wipe it
clean and determine if the ATF is hot or warm.
Hot ATF has a temperature of approximately
82°C (180°F). Warm ATF is when its temperature
is between 29-52°C (85-125°F). (6) Wipe the dipstick clean and completely insert it
into the tube. Remove the dipstick from the tube and
observe the ATF level.
(7) If the ATF is hot, the level should be in the
crosshatched area that is marked OK.
(8) If the ATF is warm, the level should be be
tween the two dimples.
Page 43 of 1502
0
- 24
LUBRICATION
AND
MAINTENANCE
•
CAUTION:
Do not
overfill
the
transmission.
(9) Adjust
the
level
of the ATF
accordingly.
It
is
important
to use the
correct fluid
in an
automatic transmission. MOPAR®ATF PLUS
(ATF Type
7176)
should
be
used. Dexron®
II
ATF
can be
used
if the
recommended fluid
is not
available,
(10) Insert
the
dipstick into
the
tube.
DRAIN, FILTER CHANGE, BAND ADJUSTMENT AND REFILL
The chart below lists
the
intervals
at
which
the
transmission should
be
serviced. Also, refer
to the
Fluid Capacities chart
for
fill capacity.
AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION SERVICE
IN-
TERVALS
Normal
Usage
Light
Duty
Cycle
60 000
km
37,500
miles
Heavy
Duty
Cycle
38
000 km 24,000
miles
Severe
Usage
19 000 km 12,000
miles
J9100-19
It
is
very important
to use the
correct fluid
in
an automatic transmission. MOPAR®ATF PLUS
(ATF Type
7176)
should
be
used.
An
equivalent
Dexron®
II ATF
could
be
used only
if the
recom
mended fluid
is not
available.
The torque converter does
not
have
a
drain plug.
No attempt should
be
made
to
drain
the
converter.
Refer
to
Group
21
—Transmissions
for
transmission
drain
and
refill procedures.
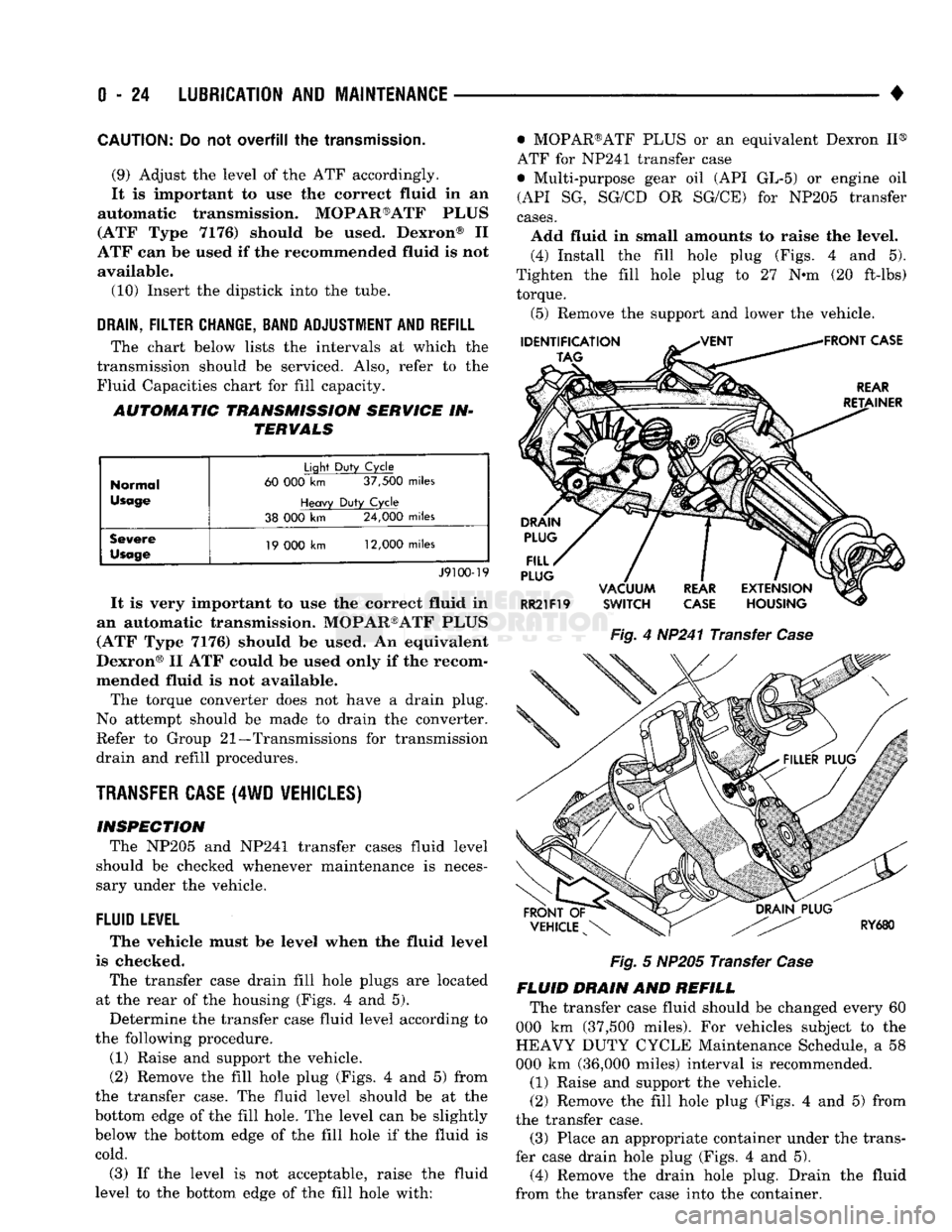
TRANSFER
CASE
(4WD
VEHICLES)
INSPECTION The NP205
and
NP241 transfer cases fluid level
should
be
checked whenever maintenance
is
neces
sary under
the
vehicle.
FLUID
LEVEL
The vehicle must
be
level when
the
fluid level
is checked.
The transfer case drain fill hole plugs
are
located
at
the
rear
of the
housing (Figs.
4 and 5).
Determine
the
transfer case fluid level according
to
the following procedure.
(1) Raise
and
support
the
vehicle.
(2) Remove
the
fill hole plug (Figs.
4 and 5)
from
the transfer case.
The
fluid level should
be at the
bottom edge
of the
fill hole.
The
level
can be
slightly
below
the
bottom edge
of the
fill hole
if the
fluid
is
cold.
(3)
If the
level
is not
acceptable, raise
the
fluid
level
to the
bottom edge
of the
fill hole with: • MOPAR®ATF PLUS
or an
equivalent Dexron
II®
ATF
for
NP241 transfer case
• Multi-purpose gear
oil (API GL-5) or
engine
oil
(API
SG,
SG/CD
OR
SG/CE)
for
NP205 transfer
cases.
Add fluid
in
small amounts
to
raise
the
level. (4) Install
the
fill hole plug (Figs.
4 and 5).
Tighten
the
fill hole plug
to 27 N-m (20
ft-lbs) torque.
(5) Remove
the
support
and
lower
the
vehicle.
Fig.
4
HP241 Transfer
Case
Fig.
5
NP205 Transfer
Case
FLUID DRAIN
AND
REFILL The transfer case fluid should
be
changed every
60
000
km
(37,500 miles).
For
vehicles subject
to the
HEAVY DUTY CYCLE Maintenance Schedule,
a 58
000
km
(36,000 miles) interval
is
recommended.
(1) Raise
and
support
the
vehicle.
(2) Remove
the
fill hole plug (Figs.
4 and 5)
from
the transfer case. (3) Place
an
appropriate container under
the
trans
fer case drain hole plug (Figs.
4 and 5).
(4) Remove
the
drain hole plug. Drain
the
fluid
from
the
transfer case into
the
container.
Page 44 of 1502

•
LUBRICATION
AND
MAINTENANCE
0 - 25
CAUTION:
Do not
over-tighten
the
drain
and fill
hole
plugs.
Over-tightening
can strip the
hole
threads
and/or crack
the
aluminum housing.
(5) Install the drain hole plug (Figs. 4 and 5) in
the transfer case. Tighten the drain hole plug to 27 N*m (20 ft-lbs) torque. (6) Fill the transfer case to the bottom edge of the
fill hole (Figs. 4 and 5) with: • MOPAR®ATF PLUS or an equivalent Dexron II®
ATF for NP241 transfer cases
• Multi-purpose gear oil (API GL-5) or engine oil (API SG, SG/CD or SG/CE) for NP205 transfer cases. (7) Install the fill hole plug (Figs. 4 and 5) in the
transfer case. Tighten the plug to 27 N«m (20 ft-lbs) torque.
(8) Remove the support and lower the vehicle.
FLUID SPECIFICATION
• MOPAR®ATF PLUS or an equivalent Dexron II®
ATF for NP241 transfer cases • Multi-purpose gear oil (API GL-5) or engine oil (API SG, SG/CD or SG/CE) for NP205 transfer cases
NP20I
MULTI-PURPOSE GEAR OIL/ENGINE
OIL
SELECTION
MULTI-PURPOSE GEAR OIL-if the anticipated
minimum temperature will: • Be above 32°C (90°F)-use SAE 140, API GL-5;
• Decrease to as low as -23°C (-10°F)-use SAE 90,
API GL-5; and • Be below -23°C (-10°F)-use SAE 80, API GL-5. ENGINE OIL—if the anticipated minimum tem
perature will be: ® Above 0°C (32°F)-use SAE 50, API SG, SG/CD or
SG/CE;
• Below 0°C (32°F)-use SAE 30, API SG, SG/CD or SG/CE.
SHIFT MECHANISM-NP241 AND NP205 The transfer case shift mechanism should be
cleaned and lubricated as necessary.
Lubricate the pivot, the sliding contact areas and
the shift linkage pivot ends with light-weight engine oil (Figs. 6 and 7).
AXLES
INSPECTION/LUBRICANT LEVEL For normal vehicle operation, periodic axle lubri
cant level checks are not necessary. The exterior of
the axle housing should be inspected for leakage. Check the lubricant level to confirm the leakage.
LUBRICANT LEVEL
(1) Raise the vehicle with an axle or wheel type
hoist. Support the vehicle.
(2) The rear axle differential housings have a rub
ber, PRESS-IN type fill plug (Fig. 8). Pry the fill
TRANSMISSION
ASSEMBLY
GEARSHIFT
MECHANISM TRANSFER CASE
SCREWS
(2)
50
FT. LBS.
(68 N*m)
CLAMP
SHIFT
ROD
SCREW
80 IN.
LBS.
(9 N*m)
RP1091
Fig.
6 Shift
Mechanism
Lubrication—NP241 Transfer
Case
Fig.
RY682
7 Shift
Mechanism
Lubrication—NP205 Transfer
Case
plug from the differential housing. The front axle (4WD vehicles)*differential housings have a thread
ed-type fill plug (Fig. 9). Un-thread the fill plug from
the differential housing.
(3) The lubricant level should be within 12 mm
(1/2 in) of the fill hole for the 8.25 and 9.25 rear ax
les.
The lubricant level should be between 12mm (1/2
in) and 24mm (1 in.) of the fill hole for the Dana ax
les.
(4) If necessary, add lubricant to raise the level to
the acceptable position.
(5) Install the fill hole plug in the differential
housing (Figs. 8 and 9).
DRAIN
AND
REFILL
Periodic axle lubricant change for normal vehicle
operation is not necessary. Refer to the chart below-
Page 189 of 1502

5 - 2 BRAKES
• CAUTION:
Never
use gasoline,
kerosene,
alcohol,
motor
oil, transmission
fluid,
or any
fluid
containing
mineral
oil to
clean
the system
components.
These
fluids
damage
rubber
cups and seals. If system
contamination
is suspected,
check
the
fluid
for
dirt,
discoloration,
or
separation
into
distinct
layers.
Drain
and
flush
the system
with
new
brake
fluid
if
contamination
is suspected.
BRAKE
SAFETY PRECAUTIONS WARNING: DUST AND DIRT ON BRAKE PARTS
THAT
ACCUMULATES DURING NORMAL USE MAY CONTAIN ASBESTOS FIBERS. BREATHING
EXCES
SIVE
CONCENTRATIONS OF ASBESTOS FIBERS
CAN
CAUSE SERIOUS BODILY HARM. EXERCISE
CARE
WHEN SERVICING BRAKE COMPONENTS.
DO NOT CLEAN BRAKE COMPONENTS
WITH
COM
PRESSED
AIR OR BY DRY BRUSHING. USE A VAC UUM CLEANER SPECIFICALLY DESIGNED FOR
REMOVING BRAKE DUST
THAT
MAY ASBESTOS
FIBERS.
IF A SUITABLE VACUUM CLEANER IS NOT
AVAILABLE,
CLEANING SHOULD BE DONE USING
A
WATER DAMPENED CLOTH. DO NOT CREATE DUST BY SANDING, GRINDING, OR SHAVING
BRAKE
LININGS UNLESS PROPERLY VENTED
EQUIPMENT IS USED. DISPOSE OF ALL DUST AND
DIRT
THAT
MAY CONTAIN ASBESTOS FIBERS IN
SEALED
BAGS OR CONTAINERS. THIS WILL MINI MIZE EXPOSURE TO YOURSELF AND OTHERS.
FOLLOW ALL RECOMMENDED PRACTICES PRE
SCRIBED
BY THE OCCUPATIONAL SAFETY AND HEALTH ADMINISTRATION AND THE ENVIRON
MENTAL PROTECTION AGENCY FOR THE HAN
DLING, PROCESSING, AND DISPOSITION OF DUST
OR DIRT WHICH MAY CONTAIN ASBESTOS FI
BERS.
Page 190 of 1502

•
BRAKES
i - 3 BRAKE DIAGNOSIS
INDEX
page
Brake
Warning Lights
3
Diagnosing
Brake Problems .................
4
Diagnosis
Procedures
3
Low
Vacuum
Switch—Diesel
Models
3
page
Master
Cylinder/Power Booster Test
5
Power
Booster
Check
Valve Test .............
6
Power
Booster
Vacuum
Test .................
6
Testing Diesel
Engine
Vacuum
Pump
Output
.... 6
DIAGNOSIS
PROCEDURES
Brake diagnosis involves determining
if the
prob
lem
is
related
to a
mechanical, hydraulic
or
vacuum
operated component.
A
preliminary check, road test
ing
and
component inspection
can all be
used
to de
termine
a
problem cause. Road testing will either verify proper brake opera
tion
or
confirm
the
existence
of a
problem. Compo nent inspection will,
in
most cases, identify
the
actual part causing
a
problem. The first diagnosis step
is the
preliminary check. This
involves inspecting fluid level, parking brake action,
wheel
and
tire condition, checking
for
obvious leaks
or
component damage
and
testing brake pedal response. A road test will confirm
the
existence
of a
problem.
Final diagnosis procedure involves road test analysis and
a
visual inspection
of
brake components.
BRAKE
WARNING LIGHTS
The
red
brake warning light
is
connected
to the
parking brake switch
and to the
pressure differential switch
in the
combination valve. The
red
light will illuminate when
the
parking
brakes
are
applied
or
when
a
fluid pressure drop
oc
curs
in the
front
or
rear brake circuit.
The
light will
also illuminate
for
approximately
2-4
seconds
at en
gine start
up.
This
is a
self test feature designed
to
check bulb
and
circuit operation each time
the en
gine
is
started. The amber antilock light
is
connected
to the
anti-
lock rear brake hydraulic valve.
The
light will illu
minate
if a
fault occurs within
the
antilock system.
LOW VACUUM SWITCH-DIESEL MODELS
On diesel models,
the red
brake warning light
is
also
used
to
alert
the
driver
of a low
brake booster vacuum
condition.
The
warning light
is in
circuit with
a
vacuum
warning switch mounted
on the
driver side fender
panel.
The
vacuum side
of the
switch
is
connected
to the
power brake booster.
The
electrical side
of the
switch
is
connected
to the
brake warning light. The
low
vacuum switch monitors booster vacuum
level whenever
the
engine
is
running.
If
booster vac
uum falls below
8.5
inches vacuum
for a
minimum
of
10 seconds,
the
switch completes
the
circuit
to the
warning light causing
it to
illuminate.
The
warning light
is
designed
to
differentiate between
a low
vac
uum condition
and a
hydraulic circuit fault.
PRELIMINARY
BRAKE CHECK
(1) Check condition
of
tires
and
wheels. Damaged
wheels
and
worn, damaged,
or
underinflated tires
can
cause pull, shudder, tramp,
and a
condition similar
to
grab.
(2)
If
complaint
was
based
on
noise when braking,
check suspension components. Jounce front
and
rear
of
vehicle
and
listen
for
noise that might
be
caused
by
loose, worn
or
damaged suspension
or
steering compo
nents.
(3) Inspect brake fluid level
and
condition. Note
that
the
front disc brake reservoir fluid level will drop
in
proportion
to
normal lining wear. Also note
that brake fluid tends
to
darken over time. This
is normal
and
should
not be
mistaken
for
con
tamination.
If the
fluid
is
still clear
and
free
of
foreign material,
it is OK.
(a)
If
fluid level
is
abnormally
low,
look
for
evi
dence
of
leaks
at
calipers, wheel cylinders, brake-
lines
and
master cylinder.
(b)
If
fluid appears contaminated, drain
out a
sample.
If
fluid
is
separated into layers,
or
obvi
ously contains
oil or a
substance other than brake
fluid,
the
system seals
and
cups will have
to be re
placed
and the
hydraulic system flushed.
(4) Check parking brake operation. Verify free
movement
and
full release
of
cables
and
pedal. Also
note
if
vehicle
was
being operated with parking
brake partially applied.
(5) Check brake pedal operation. Verify that pedal
does
not
bind
and has
adequate free play.
If
pedal
lacks free play, check pedal
and
power booster
for be
ing loose
or for
bind condition.
Do not
road test until
condition
is
corrected.
(6)
If
components checked appear
OK,
road test
the
vehicle.
ROAD
TESTING (1)
If
complaint involved
low
brake pedal, pump
the pedal
and
note
if the
pedal comes back
up to
nor mal height.
(2) Check brake pedal response with transmission
in Neutral
and
engine running. Pedal should remain
firm under steady foot pressure.