1993 DODGE TRUCK trailer
[x] Cancel search: trailerPage 6 of 1502

INTRODUCTION
INTRODUCTION
DESIGNATIONS,
LABELS/PLATES/DECALS,
CODES
AND DIMENSIONS/WEIGHTS .
CONTENTS
page
MEASUREMENT
AND TORQUE
... 1 SPECIFICATIONS
page
. 11
DESIGNATIONS, LABELS/PLATES/DECALS, CODES
AND
DIMENSIONS/WEIGHTS
INDEX
page
Engine
and
Transmission/Transfer
Case
Identification
2
Engine/Transmission/GVWR
4
Equipment
Identification
Plate
3
International
Vehicle Control
and
Display
Symbols
10
Major Component
Identification 3
VEHICLE DESIGNATIONS The Vehicle Code chart lists description and code
for Ram Truck and Sport Utility vehicles. The codes are used to identify vehicle types in charts, captions
and in service procedures. The vehicle codes are
dif
ferent than the Vehicle Identification Number (VIN) or the wheelbase/model code.
VEHICLE SAFETY CERTIFICATION
LABEL
A certification label is attached to the left side
B-pillar. The label certifies that the vehicle conforms
to Federal Motor Vehicle Safety Standards (FMVSS).
The label also lists the: • Month and year of vehicle manufacture
• Gross Vehicle Weight Rating (GVWR). The gross
front and rear axle weight ratings (GAWR's) are
based on a minimum rim size and maximum cold tire inflation pressure Vehicle Identification Number (VIN)
Type of vehicle
Type of rear wheels (single or dual) Bar code
Month, Day and Hour (MDH) of final assembly
VEHICLE IDENTIFICATION NUMBER (VIN) PLATE The Vehicle Identification Number (VIN) plate is
attached to the top left side of the instrument panel.
The VIN contains 17 characters that provide data
concerning the vehicle. Refer to the decoding chart to
determine the identification of a vehicle.
page
Trailer
Towing Specifications
4
Vehicle Code Plate
2
Vehicle Designations
1
Vehicle Dimension
4
Vehicle
Identification
Number (VIN) Plate
1
Vehicle Safety
Certification
Label
............. 1
Vehicle Weights
4
VEHICLE CODE
DESIGNATIONS
VEHICLE CODE
= AD
(DODGE
RAM
PICKUP
&
CHASSIS
CAB)
VEHICLE
FAMILY LINE DESCRIPTION
AD1
D150
AD2
D250
AD3
D350
PICKUP
4x2
AD5
W150
AD6
W250
AD7
W350
PICKUP
4x4
AD2
D250
AD3
D350
CHASSIS
CAB
4x2
AD6
W250
AD7
W350
CHASSIS
CAB
4x4
AD4
AD100
AD4
AD150
SPORT
UTILITY
4x2
AD8
AD100
AD8 AD
150
SPORT
UTILITY
4x4
J90IN-32
Page 9 of 1502
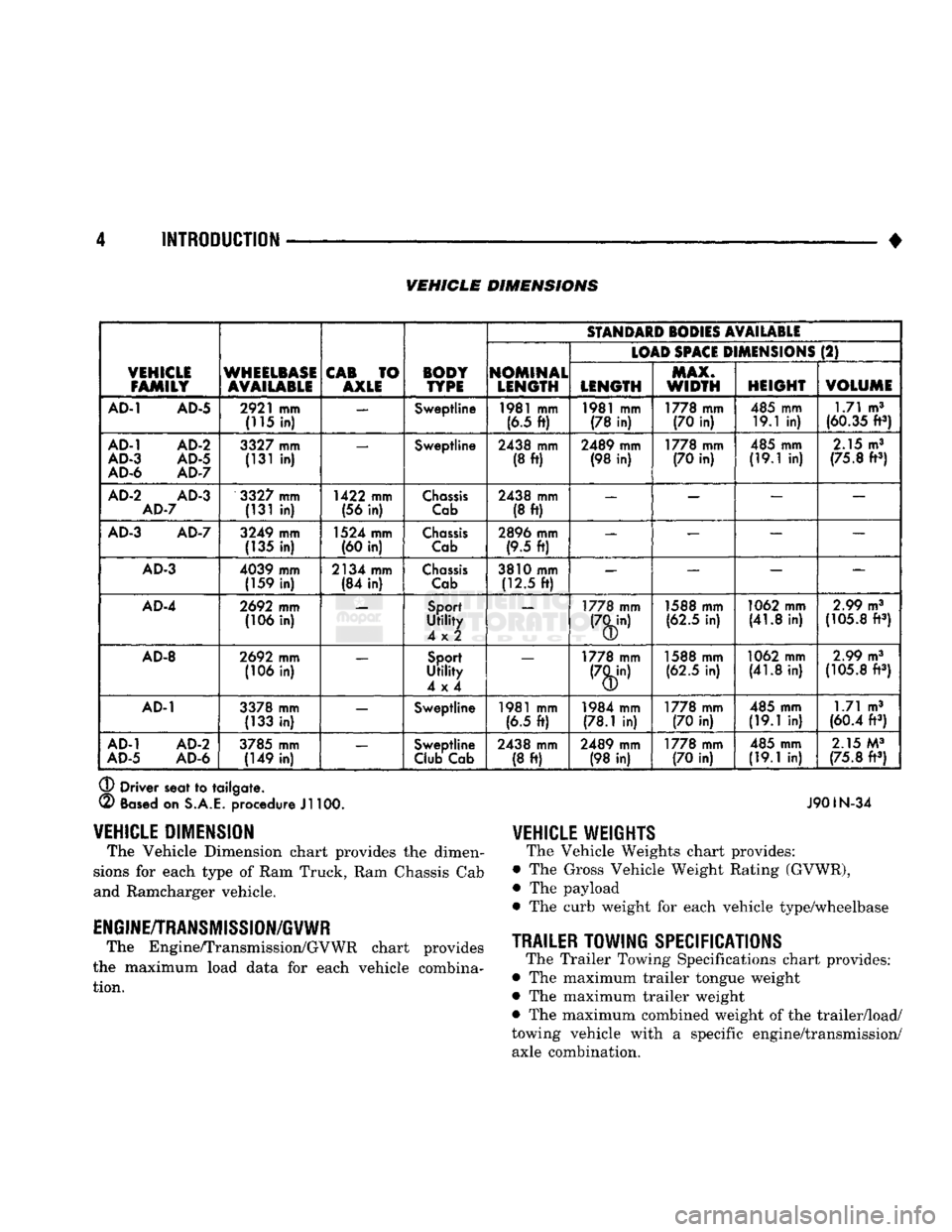
4 INTRODUCTION
• VEHICLE DIMENSIONS
VEHICLE
FAMILY
WHEELBASE
AVAILABLE
CAB
TO
AXLE BODY
TYPE
SfANDAID
SODIES
AVAILABLE
VEHICLE
FAMILY
WHEELBASE
AVAILABLE
CAB
TO
AXLE BODY
TYPE
NOMINAL
LENGTH
(LOAD
SPACE
D
MENSIONS
(2)
VEHICLE
FAMILY
WHEELBASE
AVAILABLE
CAB
TO
AXLE BODY
TYPE
NOMINAL
LENGTH LENGTH MAX.
WIDTH
HEIGHT
VOLUME
AD-1
AD-5
2921
mm
(115
in) —
Sweptline
1981
mm
(6.5
ft)
1981
mm
(78
in)
1778 mm
(70
in)
485 mm
19.1
in) 1.71 m3
(60.35
ft3)
AD-1
AD-2
AD-3
AD-5
AD-6
AD-7
3327
mm
(131
in) —
Sweptline
2438 mm
(8
ft)
2489 mm
(98
in)
1778 mm
(70
in)
485 mm
(19.1
in)
2.15
m3
(75.8
ft3)
AD-2
AD-3
AD-7
3327
mm
(131
in)
1422 mm
(56
in)
Chassis
Cab
2438 mm
(8
ft)
—
— — —
AD-3
AD-7
3249 mm
(135
in)
1524 mm
(60
in)
Chassis
Cab
2896 mm
(9.5
ft) —
— — —
AD-3
4039 mm
(159
in)
2134 mm
(84
in)
Chassis
Cab
3810 mm
(12.5
ft)
—
— —
AD-4
2692
mm
(106
in)
Sport
Utility
4x2
—
1778 mm 1588 mm
(62.5
in)
1062 mm
(41.8
in)
2.99
m3
(105.8
ft3)
AD-8
2692
mm
(106
in)
Sport
Utility
4x4
—
1778 mm 1588 mm
(62.5
in)
1062 mm
(41.8
in)
2.99
m3
(105.8
ft3)
AD-1
3378 mm
(133
in) —
Sweptline
1981
mm
(6.5
ft)
1984 mm
(78.1
in)
1778 mm
(70
in)
485 mm
(19.1
in) 1.71 m3
(60.4
ft3)
AD-1
AD-2
AD-5
AD-6
3785 mm
(149
in) —
Sweptline
Club
Cab 2438 mm
(8
ft)
2489 mm
(98
in)
1778 mm
(70
in)
485 mm
(19.1
in)
2.15
M3
(75.8
ft3)
®
Driver seat
to
tailgate.
(2)
Based
on
S.A.E.
procedure
Jl
100. J901N-34
VEHICLE
WEIGHTS
The Vehicle Weights chart provides:
• The Gross Vehicle Weight Rating (GVWR),
• The payload
• The curb weight
for
each vehicle type/wheelbase
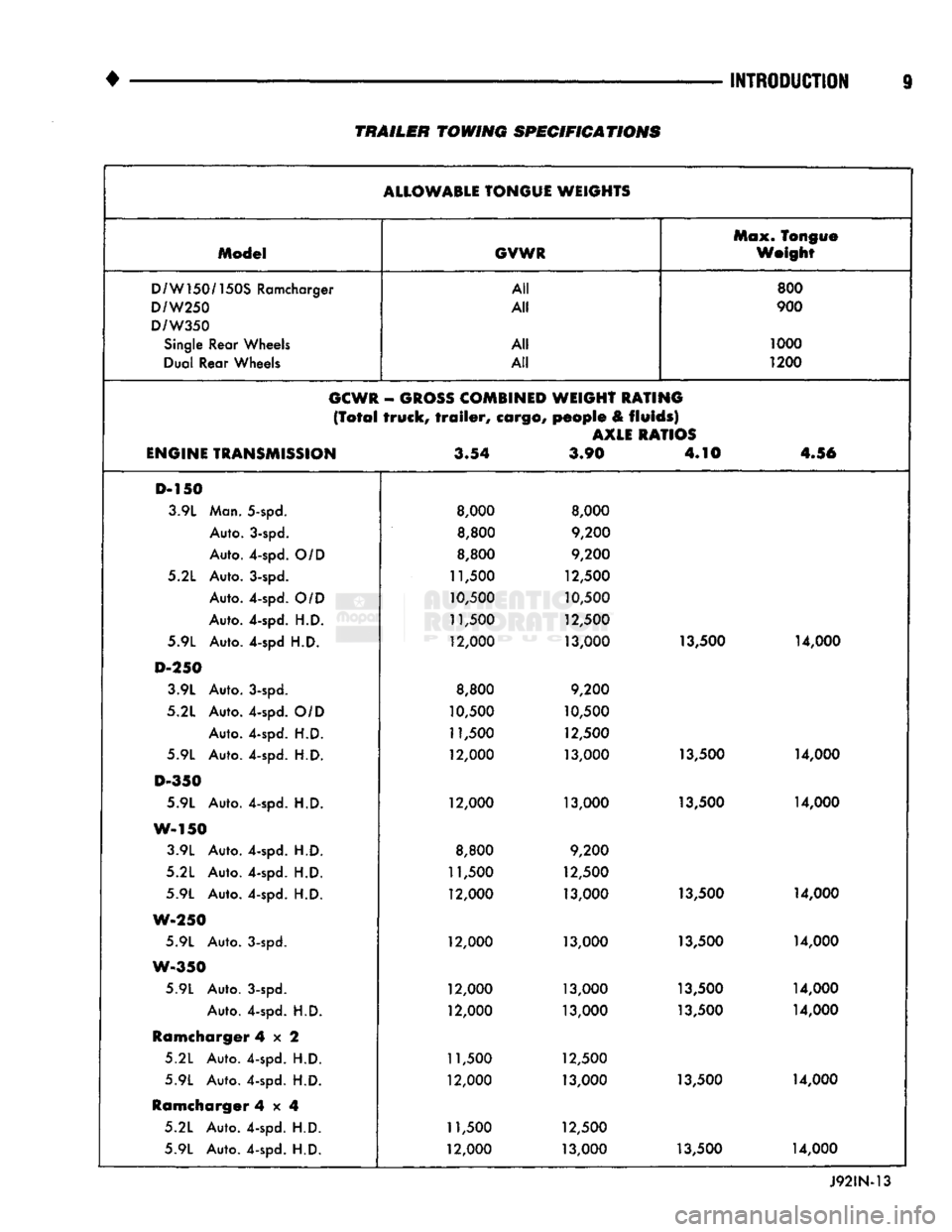
TRAILER
TOWING
SPECIFICATIONS
The Trailer Towing Specifications chart provides:
• The maximum trailer tongue weight
• The maximum trailer weight
• The maximum combined weight of the trailer/load/
towing vehicle with
a
specific engine/transmission/ axle combination.
VEHICLE
DIMENSION
The Vehicle Dimension chart provides
the
dimen
sions
for
each type
of
Ram Truck, Ram Chassis Cab
and Ramcharger vehicle.
ENGINE/TRANSMISSION/GVWR
The Engine/Transmission/GVWR chart provides
the maximum load data
for
each vehicle combina tion.
Page 14 of 1502
TRAILER TOWING
SPECIFICATIONS
ALLOWABLE
TONGUE WEIGHTS Max. Tongue
Model
GVWR
Weight
D/W150/150S
Ramcharger All
800
D/W250
All
900
D/W350
Single
Rear Wheels All
1000
Dual Rear Wheels All
1200
GCWR
-
GROSS
COMBINED
WEIGHT RATING
(Total
truck,
trailer,
cargo,
people
&
fluids)
AXLE
RATIOS
ENGINE
TRANSMISSION
3.54
3.90 4.10
4.56
D-150 3.9L Man. 5-spd.
8,000 8,000
Auto. 3-spd.
8,800
9,200
Auto. 4-spd.
O/D
8,800
9,200
5.2L Auto. 3-spd.
11,500
12,500
Auto. 4-spd.
O/D
10,500
10,500
Auto. 4-spd.
H.D.
11,500
12,500
5.9L Auto. 4-spd
H.D.
12,000
13,000 13,500
14,000
D-250
3.9L Auto. 3-spd.
8,800
9,200
5.2L Auto. 4-spd.
O/D
10,500 10,500
Auto. 4-spd.
H.D.
11,500
12,500
5.9L Auto. 4-spd.
H.D.
12,000
13,000 13,500
14,000
D-350
5.9L Auto. 4-spd.
H.D.
12,000
13,000 13,500 14,000
W-150 3.9L Auto. 4-spd.
H.D.
8,800
9,200
5.2L Auto. 4-spd.
H.D.
11,500
12,500
5.9L Auto. 4-spd.
H.D.
12,000
13,000 13,500
14,000
W-250
5.9L Auto. 3-spd.
12,000
13,000 13,500 14,000
W-350
5.9L Auto. 3-spd.
12,000 13,000 13,500 14,000
Auto. 4-spd.
H.D.
12,000
13,000 13,500 14,000
Ramcharger
4x2
5.2L Auto. 4-spd.
H.D.
11,500 12,500
5.9L Auto. 4-spd.
H.D.
12,000 13,000 13,500 14,000
Ramcharger
4x4
5.2L Auto. 4-spd.
H.D.
11,500 12,500
5.9L Auto. 4-spd.
H.D.
12,000
13,000 13,500 14,000
Page 20 of 1502

•
• —
LUiRICATlON
AND
MAINTENANCE
0 - 1
CONTENTS
page
page
CHASSIS
AND
BODY
28
ENGINE MAINTENANCE
14
DRIVETRAIN
.,,, 22
GENERAL INFORMATION
1
GENERAL
INFORMATION INDEl
page
Classification
of
Lubricants
. 3
Components
Requiring
No
Lubrication
4
Fuel Requirements
. 2
Introduction
1
Lubrication
and
Replacement Parts Recommendation
3
page
Routine Maintenance
2
Starting
Assistance (Jump Starting)
9
Vehicle
Lifting
Recommendations
............ 10
Vehicle Noise
Control
2
Vehicle Towing Recommendations
11
INTRODUCTION
Lubrication and maintenance is divided into re
quired and recommended service tasks. The required service tasks must be completed to verify the emis
sion controls function correctly. The recommended
service tasks should be completed to maintain safety
and durability. This information will assist the service personnel
in providing maximum protection for each owner's
vehicle. Conditions can vary with individual driving habits.
It is necessary to schedule maintenance as a time in
terval as well as a distance interval. It is the owner's responsibility to determine the ap
plicable driving condition. Also to have the vehicle serviced according to the maintenance schedule, and
to pay for the necessary parts and labor. Vehicles with a Gross Vehicle Weight Rating
(GVWR) of 3 855 kg (8,500 lbs.) or less must conform
to light duty emission standards. Vehicles with a Gross Vehicle Weight Rating (GVWR) of 3 856 kg
(8,501 lbs.) or more must conform to heavy duty
emission standards. The GVWR for each vehicle is listed on the Safety
Certification Label. This label is affixed to the driver
side door pillar (Fig. 1).
Additional maintenance and lubrication informa
tion is listed in the Owner's Manual.
Mm
rv
CHRYSLER
DATE
OF MFR
MFD BY CORPORATION
GVWR
GAWR FRONT
GAWR REAR
WITH
TIRES
WITH
TIRES
RIMS
AT
RIMS
AT
PSI
COLD
PSI
COLD THIS VEHICLE CONFORMS
TO
ALL APPLICABLE FEDERAL MOTOR VEHICLE SAFETY
STANDARDS
IN
EFFECT ON
THE
DATE
OF
MANUFACTURE SHOWN ABOVE.
SINGLE
DUAL
BAR
CODE
VEHICLE MADE
IN
4648503
J9UN-25
Fig. 1 Vehicle Safety
Certification
Label
SEVERE DRIVING
CONDITIONS
Vehicles subjected to severe driving conditions
should decrease the interval between component
maintenance. Severe driving conditions are defined
as:
• Frequent short trip driving less than 24 km (15
miles)
• Frequent driving in dusty conditions
• Trailer towing
• Extensive engine idling
• Sustained high speed operation
• Desert operation
• Frequent starting and stopping
• Cold climate operation
LUBRICATION
AND
MAINTENANCE
Page 42 of 1502

•
LUBRICATION
AND
MAINTENANCE
0 - 23 GEAR SHIFTER BOOTS
Inspect the shifter boots periodically for stone and
heat damage. Replace, if necessary.
SEVERE DRIVING CONDITIONS The interval between the transmission drain and
refill maintenance should be decreased to:
• NV4500 manual transmission—every 29 000 km (18,000 miles)
• Automatic transmission—every 19 000 km (12,000
miles)
A severe driving condition includes:
• Extended operation with heavy cargo loads
• Driving in deep mud or snow
• Off-road operation (4WD)
• Trailer towing
• Operation as a commercial vehicle
• Snow plowing
MANUAL TRANSMISSIONS
INSPECTION/LUBE
OIL
LEVEL
The transmission should be checked for leaks when
other service is necessary under the vehicle. To check
the lube oil level, remove the fill hole plug (Fig. 2 ). If the level is below the bottom of the fill hole, raise
the level to the bottom of the fill hole with:
• Castrol Syntorq for NV4500 transmissions
• SAE 5W-30 engine oil (API Service SG, SG/CD or
SG/CE) for Getrag 360 transmissions.
Fig.
2 NV4500 Manual
Transmission
DRAIN
AND
FILL
The NV4500 transmission fluid should be changed
according to the intervals listed in the Manual
Transmission—Drain & Refill Intervals chart below.
Also,
refer to the Fluid Capacities chart.
AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSIONS
FLUID
LEWEL
It is recommended that the fluid (ATF) level in au
tomatic transmissions be checked while involved
with other underhood maintenance.
Vehicle operation with an incorrect ATF level
will greatly reduce the life of the transmission.
Fig.
3 Getrag 360 Manual
Transmission
MANUAL TRANSMISSION-DRAIN & REFILL INTERVALS
Normal
Service
Light
Duty
Cycle
60 000
km
37,500
miles
Heavy
Duty
Cycle
58 000
km
36,000
miles
Severe
Service
29 000
km
18,000
miles
J9000-43
The condition of the ATF also should be deter
mined. If the ATF is dark in color and has a strong odor, the fluid should be changed. Also the filter should be replaced and the bands adjusted.
The following procedure must be used to check the
automatic transmission fluid (ATF) level.
(1) Position the vehicle on level ground.
(2) Operate the engine at idle speed.
(3) Apply the parking brake.
(4) Place the gear selector in N (neutral).
(5) Remove the dipstick from the tube. Wipe it
clean and determine if the ATF is hot or warm.
Hot ATF has a temperature of approximately
82°C (180°F). Warm ATF is when its temperature
is between 29-52°C (85-125°F). (6) Wipe the dipstick clean and completely insert it
into the tube. Remove the dipstick from the tube and
observe the ATF level.
(7) If the ATF is hot, the level should be in the
crosshatched area that is marked OK.
(8) If the ATF is warm, the level should be be
tween the two dimples.
Page 272 of 1502
COOLING SYSTEM
CONTENTS page
DIAGNOSIS
... 4
ENGINE
ACCESSORY
DRIVE BELTS
40
ENGINE
BLOCK HEATERS
48
GENERAL
INFORMATION
Throughout this group, references are made to partic
ular vehicle models by alphabetical designation or by
the particular vehicle nameplate. A chart showing a
breakdown of alphabetical designations is included in
the Introduction section at the beginning of this man
ual.
5.9L gas powered engines will be' referred to as ei
ther: LDC (Light Duty Cycle) or HDC (Heavy Duty
Cycle).
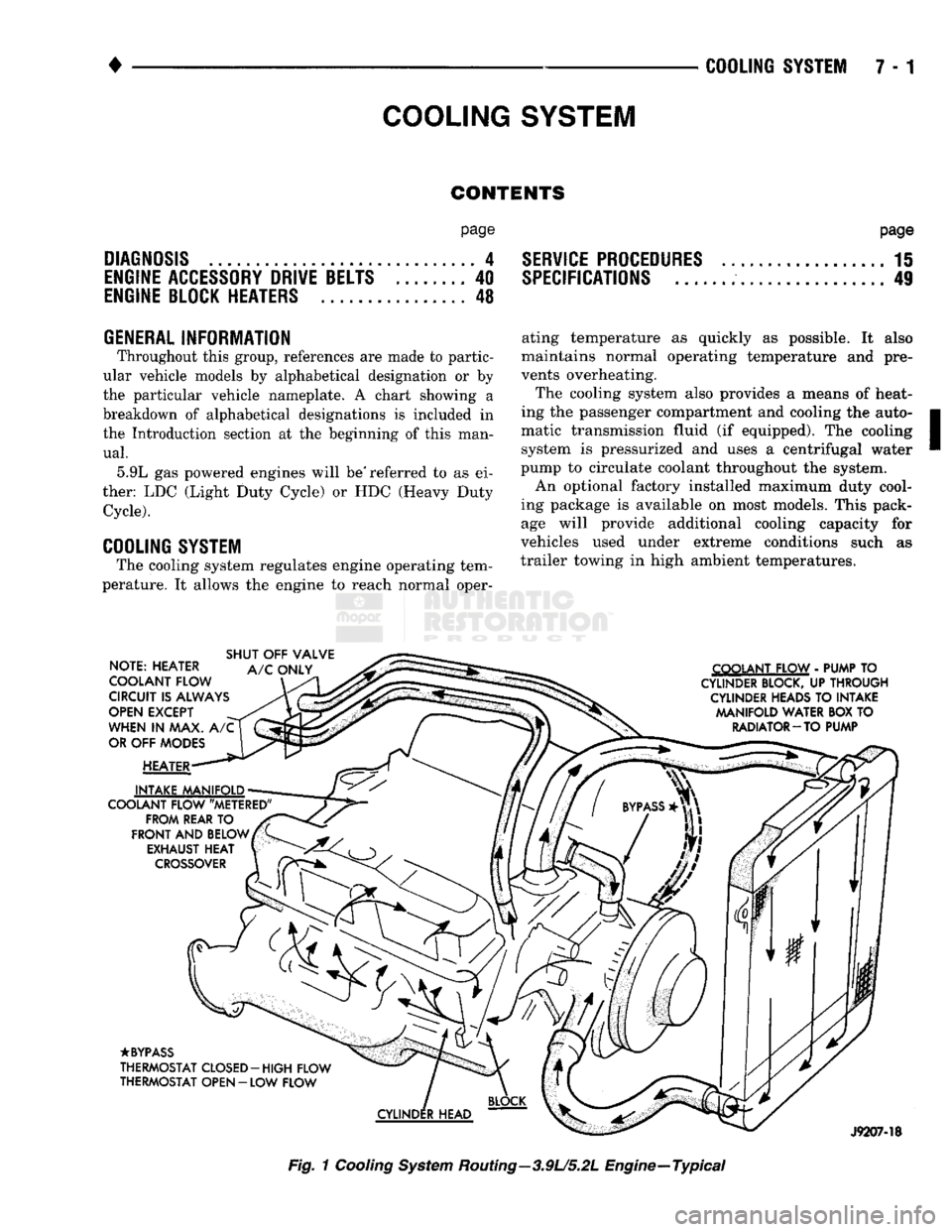
COOLING
SYSTEM
The cooling system regulates engine operating tem
perature. It allows the engine to reach normal oper-
page
SERVICE
PROCEDURES
15
SPECIFICATIONS
; 49
ating temperature as quickly as possible. It also
maintains normal operating temperature and pre
vents overheating.
The cooling system also provides a means of heat
ing the passenger compartment and cooling the auto
matic transmission fluid (if equipped). The cooling system is pressurized and uses a centrifugal water
pump to circulate coolant throughout the system.
An optional factory installed maximum duty cool
ing package is available on most models. This pack age will provide additional cooling capacity for
vehicles used under extreme conditions such as
trailer towing in high ambient temperatures.
NOTE: HEATER
COOLANT FLOW
CIRCUIT
IS
ALWAYS
OPEN
EXCEPT
WHEN
IN MAX. A/C
OR
OFF
MODES
HEATER
INTAKE MANIFOLD
COOLANT FLOW "METERED" FROM REAR
TO
FRONT
AND
BELOW EXHAUST
HEAT
CROSSOVER
SHUT
OFF
VALVE
A/C
ONLY COOLANT FLOW
-
PUMP
TO
CYLINDER BLOCK,
UP
THROUGH CYLINDER HEADS
TO
INTAKE MANIFOLD WATER
BOX TO
RADIATOR-TO PUMP
•BYPASS
THERMOSTAT CLOSED-HIGH FLOW
THERMOSTAT OPEN
- LOW
FLOW
J9207-18
Fig.
1
Cooling
System
Routing—3.9U5.2L Engine—Typical
Page 275 of 1502

DIAGNOSIS
PRELIMINARY
CHECKS
ENGINE COOLING SYSTEM OVERHEATING Establish what driving conditions caused the com
plaint. Abnormal loads on the cooling system such as
the following may be the cause:
1.
PROLONGED IDLE, VERY HIGH AMBI
ENT TEMPERATURE, SLIGHT TAIL WIND AT
IDLE, SLOW TRAFFIC, TRAFFIC JAMS, HIGH SPEED OR STEEP GRADES.
Driving techniques that avoid overheating are:
• Idle with A/C off when temperature gauge is at
end of normal range. * Increasing engine speed for more air flow is recom
mended.
2.
TRAILER TOWING: Consult Trailer Towing section of owners manual.
Do not exceed limits.
3.
AIR CONDITIONING; ADD-ON OR AFTER
MARKET: A maximum cooling package should have been or
dered with vehicle if add-on or after market A/C is
SYMPTOM AND ACTION
SYMPTOM
installed. If not, maximum cooling system compo
nents should be installed for model involved per
manufacturer's specifications.
4.
RECENT SERVICE OR ACCIDENT RE
PAIR:
Determine if any recent service has been performed
on vehicle that may effect cooling system. This may
be:
• Engine adjustments (incorrect timing)
• Slipping engine accessory drive belt(s) • Brakes (possibly dragging)
• Changed parts. Incorrect water pump or pump ro
tating in wrong direction due to belt not correctly
routed
• Reconditioned radiator or cooling system refilling (possibly under filled or air trapped in system).
If investigation reveals none of the above as a
cause for an engine overheating complaint, refer to
the following Symptom and Action chart:
PRELIMINARY FIRST) ACTION
Blinking Engine Temperature
Warning Light or High Gauge indication - Without Coolant Loss
Normal during temporary operation
with
heavy load, towing
a
trailer,
high
outdoor temperatures, and/or on
a
steep
Loss
grade.
Coolant Loss
Hot Vehicle (Not Engine) Heat Damage,
Hot Carpet, Seat,
Hot
Catalytic
Converter,
Smoke, Burnt Odor
Hot Engine Crackling Noise Hot Smell
Severe Local Hot Spots
Coolant Color
Coolant Reserve Bottle Level Changes
Coolant Not Returning To Radiator
Improper refilling procedures
can
result
in
trapped air
in
the
system.
Subsequent
operation
of the
pressure cap and coolant reserve system
will
deaereate
the
cooling
system.
A low
coolant
level
will
then result
in the
Coolant Reserve
Tank. Add coolant.
If
condition persists,
refer
to
System
Diagnosis.
Check
heat shielding, exhaust
system,
engine emission controls, ignition
timing, engine misfiring.
A
moderate amount
of
sound from heating
metal
can
be
expected
with
any
vehicle. However,
a
crackling sound from
trie
thermostat
housing,
a hot
smell and/or severe local
hot
spots on
an
engine can indicate blocked coolant
passages,
bad castina, core sand deposits and subsequent blockage,
cracked cylinder block
or
head,
or
blown cylinder head gasket. Usually
accompanied
with
coolant
loss.
Coolant
color is
not
necessarily
an
indication
of
adequate
temperature
or
corrosion
protection.
Level changes
are to be
expected as coolant volume fluctuates
with
engine
temperature.
If the
level
in the
bottle
is
between
the
Maximum and Minimum
marks
at
normal engine operating temperature,
the
level
should
return
to
within
that
range
after
operation
at
elevated temperatures.
Coolant
will
not
return
to the
radiator
if the
radiator cap vent valve does
not
function,
if
an
air
leak destroys vacuum,
or if the
overflow
passage
is
blocked
or
restricted. Inspect
all
portions
of the
overflow
passage,
pressure
cap,
filler
neck nipple, hose, and
passages
within
the
bottle
for
vacuum leak
only. Coolant
return
failure
will
be
evident
by a low
level
in the
radiator.
Reserve
bottle
level
should increase during heat-up.
J9207-31
Page 277 of 1502

7 - 6
COOLING
SYSTEM
• COOLING SYSTEM DIAGNOSIS (EXCEPT DIESEL)—CONTINUED
Condition and Checks
Diagnosis
(7) Other possible
causes.
(7) a — If
symptom
occurs
during high speed operation inspect for
plugged
air
inlet
side of the radiator or condenser,
plugged
radiator core tubes, add on A/C package
without
proper radiator, engine not operating
within
specifications,
dragging
brakes,
trailer
towing or
hill
climbing, or an insect screen.
b — If
symptom
occurs
during high or low
speed
operation inspect for: thermostat being stuck
partially
open if ambient
temperature
is
below
70°F
and
the vehicle
has
high
mileage,
plugged
air
inlet
side of the radiator or
condenser, add on
A/C
with
incorrect radiator.
c
— If
symptom
occurs
during low
speed
operation only, inspect the radiator fan drive. Repair as necessary.
TEMPERATURE
GAUGE
READS
HOT.
PRESSURE
CAP
VENTS
RESULTING
IN
STEAM
AND
COOLANT
TRANSFER
TO
COOLANT
RESERVE
TANK.
(1) Coolant
level
low in radiator and coolant reserve tank. (1) a —
Fill
cooling
system
and vent trapped air.
b — Inspect for leaks. Repair as necessary.
c
—
Ensure
that
pressure cap
is
completely shut and
seals.
d
— If
level
is low in radiator but normal in the coolant reserve tank, check the
filler
cap to coolant reserve
bottle
connection and pressure cap seal.
(2) Test coolant
freeze
point. (2) Adjust coolant to
50/50
mix of
anti-freeze
and
water.
Refer to
Coolant
section in this group.
(3)
Ensure
coolant
is
flowing through system. (3) a — With the coolant
level
low and the thermostat open, check
for coolant flow through the radiator at the
filler
neck.
b — If a
metal
cracking
sound
is heard, inspect for core sand restricting coolant flow through the
water
jacket
and/or a
faulty
cylinder head casting.
(4) Thermostat stuck in the
closed
position
(prevalent
in cold ambient temperatures). (4) Replace thermostat if found to be stuck in
closed
position.
Refer
to the Thermostat Testing section in this group.
(5) Cylinder head gasket leak. (5) Inspect for leaking cylinder head gasket
with
a commercially
available Block Leak Tester.
J9007-57