1993 CHEVROLET PLYMOUTH ACCLAIM cooling
[x] Cancel search: coolingPage 1764 of 2438
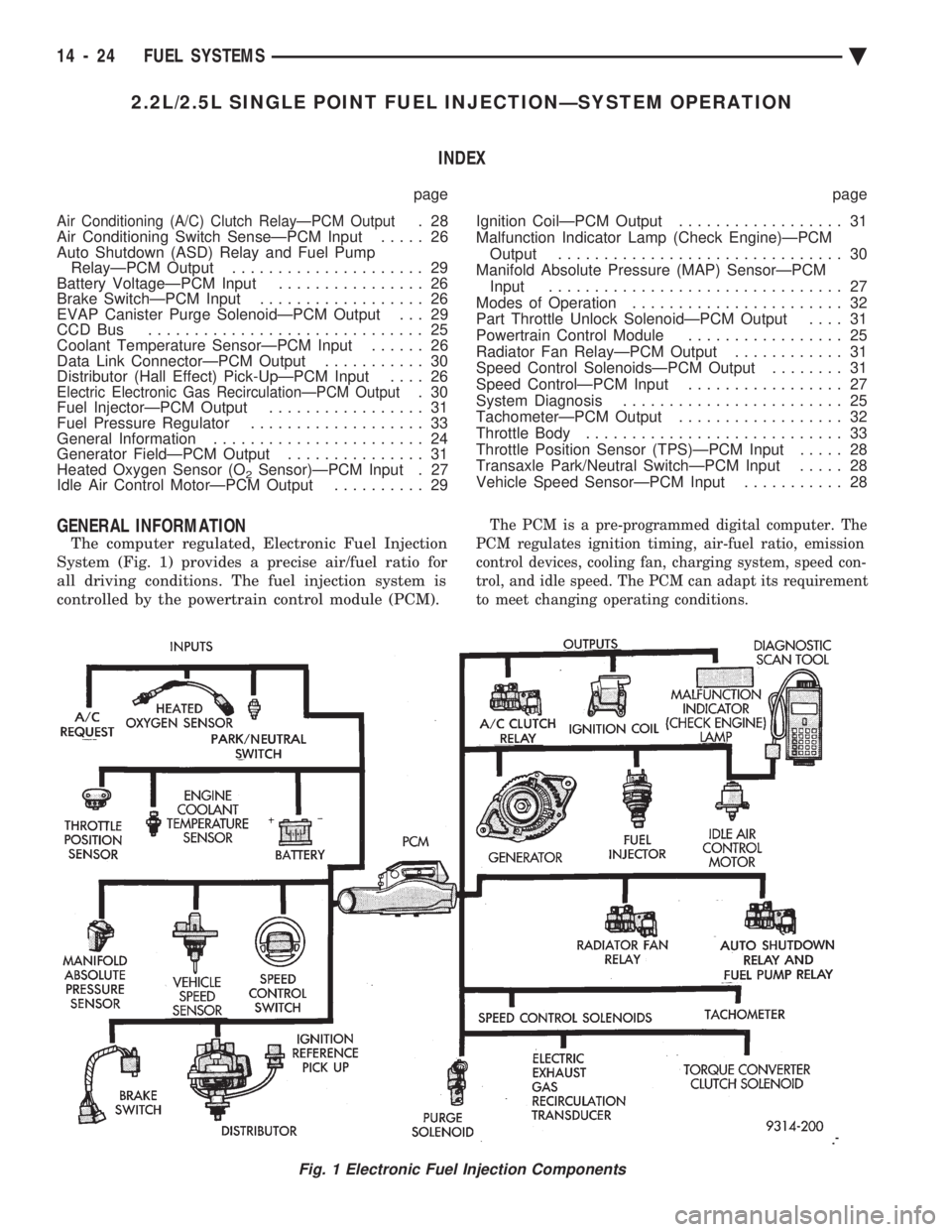
2.2L/2.5L SINGLE POINT FUEL INJECTIONÐSYSTEM OPERATION INDEX
page page
Air Conditioning (A/C) Clutch RelayÐPCM Output.28
Air Conditioning Switch SenseÐPCM Input ..... 26
Auto Shutdown (ASD) Relay and Fuel Pump RelayÐPCM Output ..................... 29
Battery VoltageÐPCM Input ................ 26
Brake SwitchÐPCM Input .................. 26
EVAP Canister Purge SolenoidÐPCM Output . . . 29
CCD Bus .............................. 25
Coolant Temperature SensorÐPCM Input ...... 26
Data Link ConnectorÐPCM Output ........... 30
Distributor (Hall Effect) Pick-UpÐPCM Input .... 26
Electric Electronic Gas RecirculationÐPCM Output.30
Fuel InjectorÐPCM Output ................. 31
Fuel Pressure Regulator ................... 33
General Information ....................... 24
Generator FieldÐPCM Output ............... 31
Heated Oxygen Sensor (O
2Sensor)ÐPCM Input . 27
Idle Air Control MotorÐPCM Output .......... 29 Ignition CoilÐPCM Output
.................. 31
Malfunction Indicator Lamp (Check Engine)ÐPCM Output ............................... 30
Manifold Absolute Pressure (MAP) SensorÐPCM Input ................................ 27
Modes of Operation ....................... 32
Part Throttle Unlock SolenoidÐPCM Output .... 31
Powertrain Control Module ................. 25
Radiator Fan RelayÐPCM Output ............ 31
Speed Control SolenoidsÐPCM Output ........ 31
Speed ControlÐPCM Input ................. 27
System Diagnosis ........................ 25
TachometerÐPCM Output .................. 32
Throttle Body ............................ 33
Throttle Position Sensor (TPS)ÐPCM Input ..... 28
Transaxle Park/Neutral SwitchÐPCM Input ..... 28
Vehicle Speed SensorÐPCM Input ........... 28
GENERAL INFORMATION
The computer regulated, Electronic Fuel Injection
System (Fig. 1) provides a precise air/fuel ratio for
all driving conditions. The fuel injection system is
controlled by the powertrain control module (PCM).
The PCM is a pre-programmed digital computer. The
PCM regulates ignition timing, air-fuel ratio, emission
control devices, cooling fan, charging system, speed con-
trol, and idle speed. The PCM can adapt its requirement
to meet changing operating conditions.
Fig. 1 Electronic Fuel Injection Components
14 - 24 FUEL SYSTEMS Ä
Page 1765 of 2438

Various sensors provide the inputs necessary for
the PCM to correctly regulate fuel flow at the fuel
injector. These include the manifold absolute pres-
sure, throttle position, oxygen sensor, coolant tem-
perature, and vehicle speed sensors. In addition to
the sensors, various switches and relays provide im-
portant information and system control. The inputs
include the park/neutral switch and air conditioning
clutch switch. The outputs include the auto shutdown
relay and fuel pump relay. All inputs to the PCM are converted into signals.
Based on these inputs the PCM adjusts air-fuel ratio,
ignition timing and other controlled outputs. The
PCM adjusts the air-fuel ratio by changing the injec-
tor pulse width. Injector pulse width is the period of
time the injector is energized.
SYSTEM DIAGNOSIS
The PCM tests many of its own input and output
circuits. If a fault is found in a major system, the in-
formation is stored in memory. Technicians can dis-
play fault information through the instrument panel
Malfunction Indicator lamp (instrument panel Check
Engine lamp) or by connecting the DRBII scan tool.
For diagnostic trouble code information, refer to On
Board Diagnostics in 2.2L/2.5L Single Point Fuel In-
jectionÐGeneral Diagnosis section of this group.
CCD BUS
Various modules exchange information through a
communications port called the CCD Bus. The pow-
ertrain control module (PCM) transmits vehicle load
data on the CCD Bus.
POWERTRAIN CONTROL MODULE
The powertrain control module (PCM) is a digital
computer containing a microprocessor (Fig. 2). The
PCM receives input signals from various switches
and sensors that are referred to as PCM Inputs.
Based on these inputs, the PCM adjusts various en-
gine and vehicle operations through devices that are
referred to as PCM Outputs. PCM Inputs:
² Air Conditioning Controls
² Battery Voltage
² Brake Switch
² Coolant Temperature Sensor
² Distributor (Hall Effect) Pick-up
² Manifold Absolute Pressure (MAP) Sensor
² Oxygen Sensor
² SCI Receive
² Speed Control System Controls
² Throttle Position Sensor
² Park/Neutral Switch (automatic transaxle)
² Vehicle Speed Sensor
PCM Outputs:
² Air Conditioning Clutch Relay
² Generator Field ²
Idle Air Control Motor
² Auto Shutdown (ASD) Relay
² Canister Purge Solenoid
² Malfunction Indicator (Check Engine) Lamp
² Data Link Connector (Diagnostic Connector)
² Electronic EGR Transducer
² Fuel Injector
² Ignition Coil
² Part Throttle Unlock Solenoid (Automatic Tran-
saxle)
² Radiator Fan Relay
² Speed Control Solenoids
² Tachometer Output
Based on inputs it receives, the PCM adjusts fuel
injector pulse width, idle speed, ignition spark ad-
vance, ignition coil dwell and canister purge opera-
tion. The PCM regulates operation of the EGR,
cooling fan, A/C and speed control systems. The PCM
changes generator charge rate by adjusting the gen-
erator field. The PCM adjusts injector pulse width (air-fuel ra-
tio) based on the following inputs.
² battery voltage
² coolant temperature
² exhaust gas content
² engine speed (distributor pick-up)
² manifold absolute pressure
² throttle position
The PCM adjusts ignition timing based on the fol-
lowing inputs.
² coolant temperature
² engine speed (distributor pick-up)
² manifold absolute pressure
² throttle position
The Auto Shutdown (ASD) and Fuel Pump relays
are mounted externally, but turned on and off by the
PCM through the same circuit. The distributor pick-up signal is sent to the PCM.
If the PCM does not receive a distributor signal
within approximately one second of engine cranking,
Fig. 2 PCM
Ä FUEL SYSTEMS 14 - 25
Page 1766 of 2438

it de-activates the ASD relay and fuel pump relay.
When these relays are deactivated, power is shut off
from the fuel injector, fuel pump, ignition coil, and
oxygen sensor heater element. The PCM contains a voltage converter that
changes battery voltage to a regulated 8.0 volts to
power the distributor pick-up and vehicle speed sen-
sor. The PCM also provides a 5.0 volts supply for the
coolant temperature sensor, manifold absolute pres-
sure sensor and throttle position sensor.
AIR CONDITIONING SWITCH SENSEÐPCM INPUT
ALL VEHICLES EXCEPT AC-BODY
When the air conditioning or defrost switch is put
in the ON position and the low pressure and high
pressure switches are closed, the PCM receives an in-
put indicating that the air conditioning has been se-
lected. After receiving this input, the PCM activates
the A/C compressor clutch by grounding the A/C
clutch relay. The PCM also adjusts idle speed to a
scheduled RPM to compensate for increased engine
load.
AC-BODY VEHICLES
When the air conditioning or defrost switch is put
in the ON position and the low pressure switch, high
pressure switch and electronic cycling switch close,
the PCM receives an air conditioning select input.
After receiving this input, the PCM activates the
A/C compressor clutch by grounding the A/C com-
pressor clutch relay. The PCM also adjusts idle speed
to a scheduled RPM to compensate for increased en-
gine load.
BATTERY VOLTAGEÐPCM INPUT
The PCM monitors the battery voltage input to de-
termine fuel injector pulse width and generator field
control. If battery voltage is low, the PCM increases
injector pulse width.
BRAKE SWITCHÐPCM INPUT
When the brake switch is activated, the PCM re-
ceives an input indicating that the brakes are being
applied. After receiving the input, the PCM vents the
speed control servo. Venting the servo turns the
speed control system off.
COOLANT TEMPERATURE SENSORÐPCM INPUT
The coolant temperature sensor is installed behind
the thermostat housing and ignition coil in the hot
box. The sensor provides an input voltage to the
PCM (Fig. 3). As coolant temperature varies, the sen-
sors resistance changes, resulting in a different input
voltage to the PCM. The PCM demands slightly richer air-fuel mixtures
and higher idle speeds until the engine reaches nor-
mal operating temperature. This sensor is also used for cooling fan control.
DISTRIBUTOR (HALL EFFECT) PICK-UPÐPCM
INPUT
The distributor pick-up supplies engine speed to
the PCM. The distributor pick-up is a Hall Effect de-
vice (Fig. 4).
A shutter (sometimes referred to as an interrupter)
is attached to the distributor shaft. The shutter con-
tains four blades, one per engine cylinder. A switch
plate is mounted to the distributor housing above the
Fig. 3 Coolant Temperature Sensor
Fig. 4 Distributor Pick-UpÐTypical
14 - 26 FUEL SYSTEMS Ä
Page 1771 of 2438

FUEL INJECTORÐPCM OUTPUT
The Fuel Injector is an electric solenoid operated
by the PCM (Fig. 15).
Based on sensor inputs, the PCM determines when
and how long the fuel injector should operate. The
amount of time the injector fires is referred to as in-
jector pulse width. The auto shutdown (ASD) relay
supplies battery voltage to the injector. The PCM
supplies the ground path. By switching the ground
path on and off, the PCM adjusts injector pulse
width. When the PCM supplies a ground path, a
spring loaded needle or armature lifts from its seat.
Fuel flows through the orifice and deflects off the
sharp edge of the injector nozzle. The resulting fuel
sprays forms a 45É cone shaped pattern before enter-
ing the air stream in the throttle body. Fuel is supplied to the injector constantly at regu-
lated 270 Kpa (39 psi). Unused fuel returns to the
fuel tank.
GENERATOR FIELDÐPCM OUTPUT
The PCM regulates the charging system voltage
within a range of 12.9 to 15.0 volts. Refer to Group
8A for charging system information.
IGNITION COILÐPCM OUTPUT
The PCM provides a ground contact (circuit) for en-
ergizing the ignition coil. When the PCM breaks the
contact, the energy in the coil primary transfers to
the secondary causing the spark. The PCM will de-
energize the ASD relay if it does not receive an input
from the distributor pick-up. Refer to Auto Shutdown
(ASD) Relay/Fuel Pump RelayÐPCM Output in this
section for relay operation. The ignition coil is mounted on the hot box next to
the thermostat housing (Fig. 16).
PART THROTTLE UNLOCK SOLENOIDÐPCM
OUTPUT
Three-speed automatic transaxles use a part throt-
tle unlock solenoid. The PCM controls the lock-up of
the torque convertor through the part throttle unlock
solenoid. The transaxle is locked up only in direct
drive mode. Refer to Group 21 for transaxle informa-
tion.
RADIATOR FAN RELAYÐPCM OUTPUT
The radiator fan is energized by the PCM through
the radiator fan relay. The PCM grounds the radia-
tor fan relay when engine coolant reaches a predeter-
mined temperature. For more information, refer to
Group 7, Cooling Systems. On AC, AG and AJ models, the radiator fan relay
is located in the power distribution center. Refer to
the Wiring and Component Identification section of
Group 8W. On AA and AP models, the radiator fan relay is
mounted on the drivers side fender well, next to the
strut tower (Fig. 10).
SPEED CONTROL SOLENOIDSÐPCM OUTPUT
The speed control vacuum and vent solenoids are
operated by the PCM. When the PCM supplies a
ground to the vacuum and vent solenoids, the speed
control system opens the throttle blade. When the
PCM supplies a ground only to the vent solenoid, the
throttle blade holds position. When the PCM removes
the ground from both the vacuum and vent solenoids,
the throttle blade closes. The PCM balances the two
solenoids to maintain the set speed. Refer to Group
8H for speed control information.
Fig. 15 Fuel Injector
Fig. 16 Ignition Coil
Ä FUEL SYSTEMS 14 - 31
Page 1796 of 2438
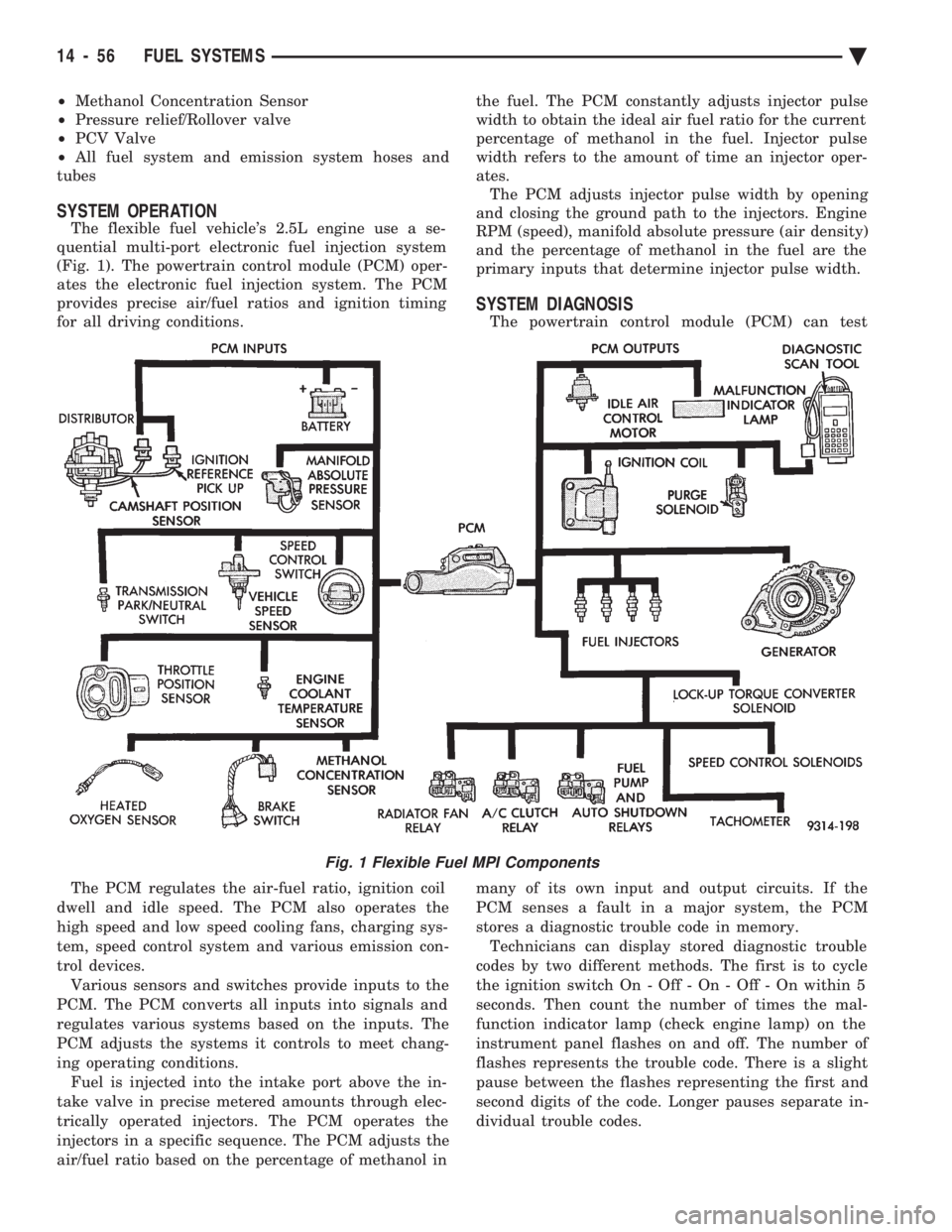
² Methanol Concentration Sensor
² Pressure relief/Rollover valve
² PCV Valve
² All fuel system and emission system hoses and
tubes
SYSTEM OPERATION
The flexible fuel vehicle's 2.5L engine use a se-
quential multi-port electronic fuel injection system
(Fig. 1). The powertrain control module (PCM) oper-
ates the electronic fuel injection system. The PCM
provides precise air/fuel ratios and ignition timing
for all driving conditions.
The PCM regulates the air-fuel ratio, ignition coil
dwell and idle speed. The PCM also operates the
high speed and low speed cooling fans, charging sys-
tem, speed control system and various emission con-
trol devices. Various sensors and switches provide inputs to the
PCM. The PCM converts all inputs into signals and
regulates various systems based on the inputs. The
PCM adjusts the systems it controls to meet chang-
ing operating conditions. Fuel is injected into the intake port above the in-
take valve in precise metered amounts through elec-
trically operated injectors. The PCM operates the
injectors in a specific sequence. The PCM adjusts the
air/fuel ratio based on the percentage of methanol in the fuel. The PCM constantly adjusts injector pulse
width to obtain the ideal air fuel ratio for the current
percentage of methanol in the fuel. Injector pulse
width refers to the amount of time an injector oper-
ates. The PCM adjusts injector pulse width by opening
and closing the ground path to the injectors. Engine
RPM (speed), manifold absolute pressure (air density)
and the percentage of methanol in the fuel are the
primary inputs that determine injector pulse width.
SYSTEM DIAGNOSIS
The powertrain control module (PCM) can test
many of its own input and output circuits. If the
PCM senses a fault in a major system, the PCM
stores a diagnostic trouble code in memory. Technicians can display stored diagnostic trouble
codes by two different methods. The first is to cycle
the ignition switch On - Off - On - Off - On within 5
seconds. Then count the number of times the mal-
function indicator lamp (check engine lamp) on the
instrument panel flashes on and off. The number of
flashes represents the trouble code. There is a slight
pause between the flashes representing the first and
second digits of the code. Longer pauses separate in-
dividual trouble codes.
Fig. 1 Flexible Fuel MPI Components
14 - 56 FUEL SYSTEMS Ä
Page 1798 of 2438

A/C clutch relay. To compensate for increased engine
load, the PCM also adjusts idle speed to a scheduled
RPM.
BATTERY VOLTAGEÐPCM INPUT
The powertrain control module (PCM) monitors the
battery voltage input to determine fuel injector pulse
width and generator field control. If battery voltage
is low, the PCM increases injector pulse width to
compensate.
BRAKE SWITCHÐPCM INPUT
When the brake switch activates, the powertrain
control module (PCM) receives an input indicating
that the brakes are being applied. After receiving the
input, the PCM vents the speed control servo. Vent-
ing the servo turns the speed control system off.
ENGINE COOLANT TEMPERATURE SENSORÐPCM
INPUT
The coolant temperature sensor is installed behind
the thermostat housing and ignition coil in the ther-
mostat housing (hot box). The PCM supplies 5 volts
to the coolant temperature sensor. The sensor pro-
vides an input voltage to the PCM (Fig. 3). As cool-
ant temperature varies, the coolant temperature
sensor resistance changes resulting in a different in-
put voltage to the PCM. The PCM demands slightly richer air-fuel mixtures
and higher idle speeds until the engine reaches nor-
mal operating temperature. This sensor is also used for cooling fan control.
CAMSHAFT POSITION SENSORÐPCM INPUT
The camshaft position sensor (distributor pick-up)
supplies engine speed and the injector sync signal to
the powertrain control module (PCM). The sensor is
a Hall Effect device (Fig. 4). A shutter (sometimes referred to as an interrupter)
is attached to the distributor shaft. The shutter con-
tains four blades, one per engine cylinder. A switch plate is mounted to the distributor housing above the
shutter. The switch plate contains the camshaft posi-
tion sensor (distributor pick-up) through which the
shutter blades rotate. As the shutter blades pass
through the pick-up, they interrupt the magnetic
field. The Hall effect device in the pick-up senses the
change in the magnetic field and switches on and off
(which creates pulses), generating the input signal to
the PCM. The PCM calculates engine speed through
the number of pulses generated. One of the shutter blades has a window cut into it.
The window tells the PCM which injector to energize.
MANIFOLD ABSOLUTE PRESSURE (MAP)
SENSORÐPCM INPUT
The powertrain control module (PCM) supplies 5
volts to the MAP sensor. The MAP sensor converts
intake manifold pressure into voltage. The PCM
monitors the MAP sensor output voltage. As vacuum
increases, MAP sensor voltage decreases proportion-
ately. Also, as vacuum decreases, MAP sensor volt-
age increases proportionately. During cranking, before the engine starts running,
the PCM determines atmospheric air pressure from
the MAP sensor voltage. While the engine operates,
the PCM determines intake manifold pressure from
the MAP sensor voltage. Based on MAP sensor volt-
age and inputs from other sensors, the PCM adjusts
spark advance and the air/fuel mixture. The MAP sensor mounts on the dash panel inside
the engine compartment (Fig. 5). A vacuum hose con-
nects the sensor to the throttle body.
Fig. 3 Coolant Temperature Sensor
Fig. 4 Camshaft Position Sensor (Distributor Pick-Up)
14 - 58 FUEL SYSTEMS Ä
Page 1803 of 2438

mode, the PCM compensates for the failure of certain
components that send incorrect signals. The PCM
substitutes for the incorrect signals with inputs from
other sensors and by using stored default values.Signals that can trigger the Malfunction Indi-
cator (Check Engine) Lamp.
² An emission system component
² Battery Voltage Input
² Charging system
² Engine Coolant Temperature Sensor
² Manifold Absolute Pressure Sensor
² Methanol Concentration Sensor
² Throttle Position Sensor
The malfunction indicator lamp can also display
diagnostic trouble codes. Cycle the ignition switch on,
off, on, off, on, within five seconds and the PCM
displays any diagnostic trouble codes stored in
memory. Refer to the 2.5L Flexible Fuel Multi-Port
Fuel InjectionÐOn Board Diagnostics section in this
group for diagnostic trouble code descriptions.
RADIATOR FAN RELAYÐPCM OUTPUT
The radiator fan is energized by the PCM through
the radiator fan relay. The PCM grounds the radiator
fan relay when engine coolant reaches a predetermined
temperature. For more information, refer to Group 7,
Cooling Systems. The radiator fan relay is mounted on the drivers side
fender well, next to the strut tower (Fig. 11).
SPEED CONTROL SOLENOIDSÐPCM OUTPUT
The speed control vacuum and vent solenoids are
operated by the PCM. When the PCM supplies a
ground to the vacuum and vent solenoids, the speed
control system opens the throttle blade. When the PCM
supplies a ground only to the vent solenoid, the throttle
blade holds position. When the PCM removes the
ground from both the vacuum and vent solenoids, the
throttle blade closes. The PCM balances the two sole-
noids to maintain the set speed. Refer to Group 8H for
speed control information.
TACHOMETERÐPCM OUTPUT
The PCM supplies engine RPM to the instrument
panel tachometer. Refer to Group 8 for tachometer
information.
TORQUE CONVERTER CLUTCH SOLENOIDÐPCM
OUTPUT
Three-speed automatic transaxles use a torque con-
verter clutch solenoid. The PCM controls the lock-up of
the torque convertor through the solenoid. The tran-
saxle is locked up only in direct drive mode. Refer to
Group 21 for transaxle information.
MODES OF OPERATION
As input signals to the PCM change, the PCM
adjusts its response to the output devices. For example, the PCM must calculate a different injector pulse
width and ignition timing for idle than it does for wide
open throttle (WOT). There are several different modes
of operation that determine how the PCM responds to
the various input signals. There are two different areas of operation, Open
Loop and Closed Loop. During Open Loop modes, the PCM receives input
signals and responds according to preset PCM pro-
gramming. Input from the oxygen (O
2) sensor is not
monitored during Open Loop modes. During CLOSED LOOP modes, the PCM does moni-
tor the oxygen (O
2) sensor input. The input indicates if
the calculated injector pulse width results in the ideal
air-fuel ratio for the current percentage of methanol in
the fuel. By monitoring the exhaust oxygen content
through the O
2sensor, the PCM can fine tune the
injector pulse width to achieve optimum fuel economy
combined with low emissions. The 2.5L flexible fuel multi-port fuel injection system
has the following modes of operation:
² Ignition switch ON - Zero RPM
² Engine start-up
² Engine warm-up
² Cruise (Idle)
² Acceleration
² Deceleration
² Wide Open Throttle
² Ignition switch OFF
The engine start-up (crank), engine warm-up, and
wide open throttle modes are OPEN LOOP modes. The
acceleration, deceleration, and cruise modes, with the
engine at operating temperature are CLOSED
LOOP modes (under most operating conditions).
IGNITION SWITCH ON (ZERO RPM) MODE
When the ignition switch cycles and past the On
position, the fuel injection system activates and the
following actions occur:
² For two seconds at key ON (and during cranking),
the methanol concentration sensor calibrates the PCM.
During the calibration period the sensor sends 4.45
volts to the PCM as a correction factor. After the
calibration period, the methanol concentration sensor
output represents the methanol percentage in the fuel.
² The PCM calculates basic fuel strategy by determin-
ing atmospheric air pressure from the MAP sensor
input.
² The PCM monitors the coolant temperature sensor
and throttle position sensor input. The PCM modifies
fuel strategy based on this input. When the key is in the ON position and the engine is
not running, the auto shutdown (ASD) relay and fuel
pump relay are not energized. Therefore battery volt-
age is not supplied to the fuel pump, ignition coil, fuel
injector or oxygen sensor heating element.
Ä FUEL SYSTEMS 14 - 63
Page 1813 of 2438

THROTTLE BODY MINIMUM AIR FLOW CHECK
PROCEDURE
(1) Warm engine in Park or neutral until the cooling
fan has cycled on and off at least once. (2) Hook-up timing check device and Tachometer.
(3) Disconnect the coolant temperature sensor and
set basic timing to 12É BTDC 62É BTDC.
(4) Shut off engine. Connect harness connector to
coolant temperature sensor. (5) Disconnect the PCV valve hose from the nipple
on the intake manifold. (6) Attach Air Metering Fitting #6457 (0.125 in.
orifice) to the intake manifold PCV nipple (Fig. 2).
(7) Connect DRBII scan tool to the data link connec-
tor. The connector is located next to the powertrain
control module (PCM) (Fig. 1). (8) Restart engine. Allow engine to idle for at least
one minute. (9) Using the DRBII scan tool, access Min. Airflow
Idle Spd. The following will then occur:
² idle air control motor fully closes ²
Idle spark advance becomes fixed
² The DRBII scan tool displays engine RPM
(10) Check idle RPM with tachometer, if idle RPM is
within the specifications then the throttle body mini-
mum airflow is set correctly.
If the idle RPM is not within specification, replace
the throttle body. (11) Shut off engine.
(12) Remove Air Metering Fitting #6457 from the
intake manifold PCV nipple. Reinstall the PCV valve
hose. (13) Remove DRBII scan tool.
(14) Disconnect timing light and tachometer.
IGNITION TIMING PROCEDURE
Refer to Group 8D Ignition System.
POWERTRAIN CONTROL MODULE 60-WAY CON-
NECTOR
Check the powertrain control module (PCM) 60-way
connector for the following.
² Spread terminals
² Stretched or pulled out wires
² Undertightened or overtightened 60 way connector
Tighten the PCM connector to 4 N Im (35 in. lbs.)
torque. When checking terminal pin outs, refer to the
Powertrain Control Module 60-Way Connector Dia-
gram for circuit wire colors and cavity numbers.
Fig. 2 Checking Minimum Air Flow Using Special Tool 6457
IDLE SPECIFICATIONS
Ä FUEL SYSTEMS 14 - 73