1993 CHEVROLET PLYMOUTH ACCLAIM cooling
[x] Cancel search: coolingPage 2305 of 2438

HEATING AND AIR CONDITIONING
CONTENTS
page page
AUTOMATIC TEMPERATURE CONTROL (ATC) .............................. 66
COMPONENT SERVICE PROCEDURES ...... 47
FIXED DISPLACEMENT COMPRESSORÐ MODEL 10PA17 ...................... 24
FIXED DISPLACEMENT COMPRESSORÐ MODEL SD709P ...................... 38 FIXED DISPLACEMENT COMPRESSORÐ
MODEL TR105 ....................... 32
GENERAL INFORMATION .................. 1
HEATER AND A/C PERFORMANCE TESTS .... 6
REFRIGERANT SERVICE PROCEDURES ...... 8
VACUUM CONTROL SYSTEM DIAGNOSIS .... 4
VARIABLE DISPLACEMENT COMPRESSORÐ MODEL 6C17 ......................... 13
GENERAL INFORMATION INDEX
page page
A/C System Identification ................... 1
Cooling System Precautions ................. 3
Description and Operation ................... 1
Engine Cooling System Requirements .......... 2 Handling Tubing and Fittings
................. 3
Safety Precautions and Warnings ............. 3
Side Window Demisters .................... 2
System Airflow ........................... 1
A/C SYSTEM IDENTIFICATION
The terms Fixed Displacement Compressor and
Variable Displacement Compressor will be used to
describe the two types of A/C systems used through-
out this Group. Refer to (Figs. 1, 2, 3 and 4). The Variable Displacement Compressor can be
identified by the location of the high pressure line. It
is mounted to the end of the compressor case (Fig. 4).
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
Both the heater and the heater/air conditioning
systems share many of the same functioning compo-
nents. This Group will deal with both systems to-
gether when component function is common, and
separately when they are not. For proper operation of the instrument panel con-
trols, refer to the Owner's Manual provided with the
vehicle. All vehicles are equipped with a common A/C-heat-
er unit housing assembly. On heater only systems,
the evaporator and recirculating air door are omitted
(Fig. 5).
SYSTEM AIRFLOW
The system pulls outside (ambient) air through the
cowl opening at the base of the windshield. Then it
goes into the plenum chamber above the A/C-heater unit housing. On air conditioned vehicles, the air
passes through the evaporator. Air flow can be di-
rected either through or around the heater core. This
Fig. 1 Fixed Displacement CompressorÐModel 10PA17
Ä HEATING AND AIR CONDITIONING 24 - 1
Page 2306 of 2438
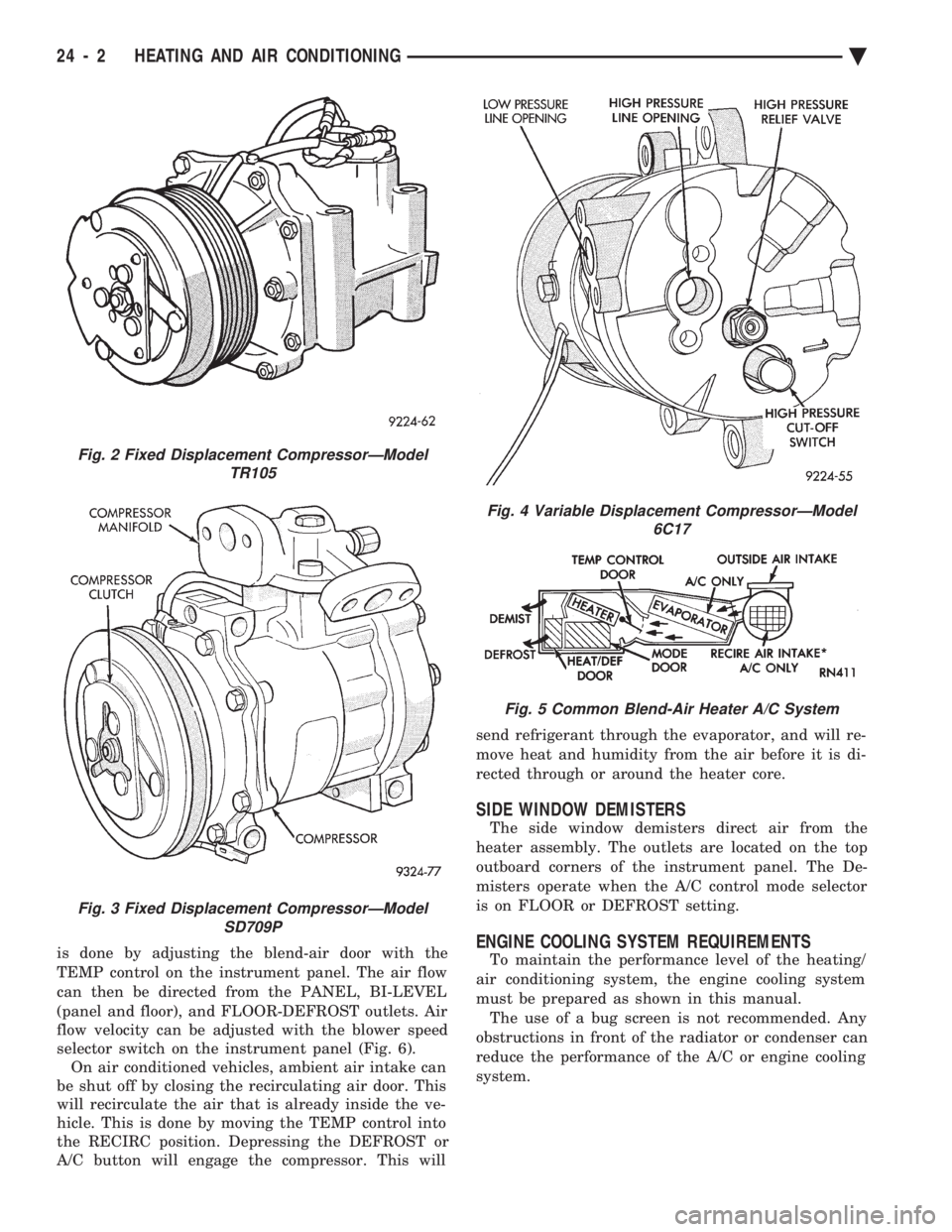
is done by adjusting the blend-air door with the
TEMP control on the instrument panel. The air flow
can then be directed from the PANEL, BI-LEVEL
(panel and floor), and FLOOR-DEFROST outlets. Air
flow velocity can be adjusted with the blower speed
selector switch on the instrument panel (Fig. 6). On air conditioned vehicles, ambient air intake can
be shut off by closing the recirculating air door. This
will recirculate the air that is already inside the ve-
hicle. This is done by moving the TEMP control into
the RECIRC position. Depressing the DEFROST or
A/C button will engage the compressor. This will send refrigerant through the evaporator, and will re-
move heat and humidity from the air before it is di-
rected through or around the heater core.
SIDE WINDOW DEMISTERS
The side window demisters direct air from the
heater assembly. The outlets are located on the top
outboard corners of the instrument panel. The De-
misters operate when the A/C control mode selector
is on FLOOR or DEFROST setting.
ENGINE COOLING SYSTEM REQUIREMENTS
To maintain the performance level of the heating/
air conditioning system, the engine cooling system
must be prepared as shown in this manual. The use of a bug screen is not recommended. Any
obstructions in front of the radiator or condenser can
reduce the performance of the A/C or engine cooling
system.
Fig. 2 Fixed Displacement CompressorÐModel TR105
Fig. 3 Fixed Displacement CompressorÐModelSD709P
Fig. 4 Variable Displacement CompressorÐModel 6C17
Fig. 5 Common Blend-Air Heater A/C System
24 - 2 HEATING AND AIR CONDITIONING Ä
Page 2307 of 2438

SAFETY PRECAUTIONS AND WARNINGS
WARNING: WEAR EYE PROTECTION WHEN SER-
VICING THE AIR CONDITIONING REFRIGERANT
SYSTEM. SERIOUS EYE INJURY CAN RESULT
FROM EYE CONTACT WITH REFRIGERANT. IF EYE
CONTACT IS MADE, SEEK MEDICAL ATTENTION
IMMEDIATELY. DO NOT EXPOSE REFRIGERANT TO OPEN
FLAME. POISONOUS GAS IS CREATED WHEN RE-
FRIGERANT IS BURNED. AN ELECTRONIC TYPE
LEAK DETECTOR IS RECOMMENDED. LARGE AMOUNTS OF REFRIGERANT RELEASED
IN A CLOSED WORK AREA WILL DISPLACE THE
OXYGEN AND CAUSE SUFFOCATION. THE EVAPORATION RATE OF (R-12) REFRIGER-
ANT AT AVERAGE TEMPERATURE AND ALTITUDE
IS EXTREMELY HIGH. AS A RESULT, ANYTHING
THAT COMES IN CONTACT WITH THE REFRIGER-
ANT WILL FREEZE. ALWAYS PROTECT SKIN OR
DELICATE OBJECTS FROM DIRECT CONTACT
WITH REFRIGERANT.
CAUTION: Liquid refrigerant is corrosive to metal
surfaces. Follow the operating instructions supplied
with equipment being used.
COOLING SYSTEM PRECAUTIONS
WARNING: ANTIFREEZE IS AN ETHYLENE GLYCOL
BASE COOLANT AND IS HARMFUL IF SWAL-
LOWED OR INHALED. IF SWALLOWED, DRINK
TWO GLASSES OF WATER AND INDUCE VOMIT-
ING. IF INHALED, MOVE TO FRESH AIR AREA.
SEEK MEDICAL ATTENTION IMMEDIATELY. DO NOT STORE IN OPEN OR UNMARKED CON-
TAINERS. WASH SKIN AND CLOTHING THOROUGHLY AF-
TER COMING IN CONTACT WITH ETHYLENE GLY-
COL. KEEP OUT OF REACH OF CHILDREN AND PETS.
DO NOT OPEN A COOLING SYSTEM WHEN THE
ENGINE IS AT RUNNING TEMPERATURE. PER-
SONAL INJURY CAN RESULT.
The engine cooling system is designed to develop
internal pressure of 97 to 123 kPa (14 to 18 psi). Al-
low the vehicle 15 minutes (or until a safe tempera-
ture and pressure are attained) before opening the
cooling system. Refer to Group 7, Cooling System.
HANDLING TUBING AND FITTINGS
Kinks in the refrigerant tubing or sharp bends in
the refrigerant hose lines will greatly reduce the ca-
pacity of the entire system. High pressures are pro-
duced in the system when it is operating. Extreme
care must be exercised to make sure that all connec-
tions are pressure tight. Dirt and moisture can enter
the system when it is opened for repair or replace-
ment of lines or components. The refrigerant oil will
absorb moisture readily out of the air. This moisture
will convert into acids within a closed system. The following precautions must be observed:
The system must be completely empty before open-
ing any fitting or connection in the refrigeration sys-
tem. Open fittings with caution even after the
system has been emptied. If any pressure is noticed
as a fitting is loosened, allow trapped pressure to
bleed off very slowly. A good rule for the flexible hose lines is to keep the
radius of all bends at least 10 times the diameter of
the hose. Sharper bends will reduce the flow of re-
frigerant. The flexible hose lines should be routed so
they are at least 3 inches (80 mm) from the exhaust
manifold. Inspect all flexible hose lines to make sure
they are in good condition and properly routed. Unified plumbing connections with aluminum gas-
kets cannot be serviced with O-rings. These gaskets
are not reusable and do not require lubrication be-
fore installing. The use of correct wrenches when making connec-
tions is very important. Improper wrenches or im-
proper use of wrenches can damage the fittings. The A/C system will remain chemical stabile as
long as pure-moisture-free R-12 and refrigerant oil is
used. Abnormal amounts of dirt, moisture or air can
upset the chemical stability. This condition could
cause operational troubles or even serious damage if
present in more than very small quantities. When it is necessary to open the refrigeration sys-
tem, have everything needed to service the system
ready. The system should not be left open any longer
than necessary. Cap or plug all lines and fittings as
soon as they are opened to prevent the entrance or
dirt and moisture. All lines and components in parts
stock should be capped or sealed until they are ready
to be used. All tools, including the refrigerant dispensing man-
ifold, the manifold gauge set, and test hoses should
be kept clean and dry.
Fig. 6 Heater only or HeaterÐA/C Controls
Ä HEATING AND AIR CONDITIONING 24 - 3
Page 2310 of 2438

HEATER AND A/C PERFORMANCE TESTS
HEATER OUTPUT TEST
PRE-DIAGNOSTIC PREPARATIONS
Review Safety Precautions and Warnings before
performing the following procedures. Check the radiator coolant level, drive belt tension,
and engine vacuum line connections. Also check ra-
diator air flow and radiator fan operation. Start en-
gine and allow to warm up to normal operating
temperature.
WARNING: DO NOT REMOVE RADIATOR CAP
WHEN ENGINE IS HOT, PERSONAL INJURY CAN
RESULT.
If vehicle has been run recently, wait 15 minutes
before removing cap. Place a rag over the cap and
turn it to the first safety stop. Allow pressure to es-
cape through the overflow tube. When the system
stabilizes, remove the cap completely.
MAXIMUM HEATER OUTPUT: TEST AND ACTION
Engine coolant is provided to the heater system by
two 16 mm (5/8 inch inside diameter) heater hoses.
With engine idling at normal running temperature,
set the control to maximum heat, floor, and high
blower setting. Using a test thermometer, check the
air temperature coming from the floor outlets, refer
to Temperature Reference chart.
If the floor outlet air temperature is low, refer to
Group 7, Cooling System for coolant temperature
specifications. Both heater hoses should be HOT to
the touch. The coolant return hose should be slightly
cooler than the supply hose. If coolant return hose is
much cooler than the supply hose, locate and repair
engine coolant flow obstruction in heater system.
POSSIBLE LOCATIONS OR CAUSE OF OBSTRUCTED
COOLANT FLOW
(a) Pinched or kinked heater hoses.
(b) Improper heater hose routing. (c) Plugged heater hoses or supply and return
ports at cooling system connections, refer to Group
7, Cooling System. (d) Plugged heater core.
If proper coolant flow through heater system is ver-
ified and outlet air temperature is still low, a me-
chanical problem may exist.
POSSIBLE LOCATION OR CAUSE OF INSUFFICIENT HEAT
(a) Obstructed cowl air intake.
(b) Obstructed heater system outlets.
(c) Blend-air door not functioning properly.
TEMPERATURE CONTROL If temperature cannot be adjusted with the TEMP
lever on the control panel, or TEMP lever is difficult
to move, the following could require service: (a) Blend-air door binding.
(b) Control cables miss-routed, pinched, kinked,
or disconnected. (c) Improper engine coolant temperature.A/C PERFORMANCE TEST
The air conditioning system is designed to remove
heat and humidity from the air entering the passen-
ger compartment. The evaporator, located in the
heater A/C unit behind the instrument panel, is
cooled to temperatures near the freezing point. As
warm damp air passes over the fins in the evapora-
tor, moisture in the air condenses to water, dehumid-
ifying the air. Condensation on the evaporator fins
reduces the evaporators ability to absorb heat. Dur-
ing periods of high heat and humidity an A/C system
will be less effective than during periods of high heat
and low humidity. With the instrument control set to
RECIRC, only air from the passenger compartment
passes through the evaporator. As the passenger
compartment air dehumidifies, A/C performance lev-
els rise.
PERFORMANCE TEST PROCEDURE
Review Safety Precautions and Warnings before
proceeding with this procedure. Air temperature in
test room and on vehicle must be 70ÉF (21ÉC) mini-
mum for this test. (1) Connect a tachometer and manifold gauge set.
(2) Set control to A/C, RECIRC, PANEL, or MAX
A/C, temperature lever on full cool and blower on
high. (3) Start engine and hold at 1000 rpm with A/C
clutch engaged. (4) Engine should be warmed up with doors and
windows closed.
TEMPERATURE REFERENCE CHART
24 - 6 HEATING AND AIR CONDITIONING Ä
Page 2314 of 2438

backed off, immediately point the end of hose toward
floor, as possibly trapped refrigerant in the hose will
be released.(e) Install service port cap.
DISCHARGE (HIGH PRESSURE) GAUGE CONNECTION (1) Remove the service port cap from the 1/4 in.
service port. (2) Check all valves on the equipment being used to
verify they are closed. (3) Inspect the hose gasket in the service port con-
nector at the end of the (RED) hose. If the gasket is
flawed, replace it. (4) Use a suitable (3/8 in. male to 1/4 in. female)
adapter (Fig. 5), threaded securely into the end of the
(RED) hose connector.
(5) Thread the 1/4 in. hose adapter connector onto
the service port. Quickly secure adapter connector to
service port to avoid loosing refrigerant. To disconnect the discharge gauge (RED) hose:(a) Wrap the end of hose with a shop towel.
(b) Loosen the hose connector.
(c) Push and hold the end of hose toward the
service port to keep the gasket in contact with service
port. (d) Quickly rotate the connector counterclockwise.
When the hose connector is completely backed off,
immediately point the end of hose toward floor, as
possibly trapped refrigerant in the hose will be
released. (e) Install service port cap.
EVACUATION/RECOVERY/RECYCLING/CHARGING LINE CON-
NECTION
The center manifold (YELLOW) or (WHITE) hose is
used to recycle, recover, evacuate, and charge the
refrigerant system. When the discharge or suction
valves on the manifold gauge set are opened, the
refrigerant in the system will escape through this hose. This hose should be attached to a R-12
Recovery/Recycling device. Refer to the
Recovery/Recycling devices operators manual
for procedures. For disconnection of this hose, refer to Disconnect-
ing the Discharge Gauge (RED) hose in the preced-
ing paragraphs.
TESTING FOR REFRIGERANT LEAKS
If the A/C system is not cooling properly, deter-
mine if the refrigerant system is fully charged with
R-12. Follow the procedures in the Performance Test
Procedures section of this Group. If the refrigerant
system is empty or low in refrigerant charge, a leak
at any line fitting or component seal is likely. To de-
tect a leak in the refrigerant system, perform one of
the following procedures as indicated by the symp-
toms.
EMPTY REFRIGERANT SYSTEM LEAK TEST
CAUTION: Review Safety Precautions and Warnings
in General Information section of this Group.
(1) Evacuate the refrigerant system to the lowest
degree of vacuum possible. (2) Prepare a 10 oz. refrigerant (R-12) charge to be
injected into the system. Refer to Charging Refriger-
ant System for instructions. (3) Connect and dispense 10 ozs. of refrigerant into
the evacuated refrigerant system. (4) Proceed to step two of Low Refrigerant Level
Leak Test.
LOW REFRIGERANT LEVEL LEAK TEST
Caution: Review Safety Precautions and Warnings
in the General Information section of this group.
(1) Using the refrigerant level sight glass, deter-
mine if there is any (R-12) refrigerant in the system. (2) Position the vehicle in a wind free work area.
This will aid in detecting small leaks. (3) Bring the refrigerant system up to operating
temperature and pressure. This is done by allowing
the engine to run for five minutes. (4) With the engine not running, use an Electronic
Leak Detector (or equivalent) and search for leaks.
Fittings, lines, or components that appear to be oily
usually will indicate a refrigerant leak. To inspect
the evaporator core for leaks, it is possible to insert
the leak detector probe into the recirculating air door
opening (Fig. 6).
ADDING PARTIAL REFRIGERANT CHARGE
After all leaks have been corrected and it was not
necessary to empty the refrigerant system, a partial
refrigerant charge can be added.
CAUTION:Review all Safety Precautions and Warn-
ings before attempting to add refrigerant to the sys-
tem. Do not add refrigerant to a system that is
known to have a leak.
Fig. 5 Discharge Hose Adapter
24 - 10 HEATING AND AIR CONDITIONING Ä
Page 2316 of 2438

WARNING: REVIEW SAFETY PRECAUTIONS AND
WARNINGS BEFORE CHARGING THE REFRIGER-
ANT SYSTEM.
After the system has been tested for leaks and
evacuated, a refrigerant charge can be injected into
the system. (1) Connect manifold gauge set.
(2) Measure refrigerant (refer to capacities) and
heat to 52ÉC (125ÉF) with the charging station. Refer
to the instructions provided with the equipment be-
ing used.
REFRIGERANT CAPACITIES:
² Without Rear A/C = 907 g (32 oz.)
² With Rear A/C = 1219 g (43 oz.)
(3) Open the suction and discharge valves. Open
the charge valve to allow the heated refrigerant to
flow into the system. When the transfer of refriger-
ant has stopped, close the suction and discharge
valve. (4) If all of the refrigerant charge did not transfer
from the dispensing device, start engine and hold at
idle (1400 rpm). Set the A/C control to A/C, low
blower speed, and open windows. If the A/C compres-
sor does not engage, test the compressor clutch con-
trol circuit and correct any failure. Refer to Group
8W, Wiring Diagrams. (5) Open the suction valve to allow the remaining
refrigerant to transfer to the system.
WARNING: TAKE CARE NOT TO OPEN THE DIS-
CHARGE (HIGH-PRESSURE) VALVE AT THIS TIME.
(6) Close all valves and test the A/C system perfor-
mance. Refer to Heater and A/C Performance Tests
in this Group. (7) Disconnect the charging station or manifold
gauge set. Install the service port caps.
OIL LEVEL
It is important to have the correct amount of oil in
the A/C system to ensure proper lubrication of the
compressor. Too little oil will result in damage to the
compressor. Too much oil will reduce the cooling ca-
pacity of the system. The oil used in the compressor is a 500 SUS viscos-
ity, wax-free refrigerant oil. Only refrigerant oil of
the same type should be used to service the system.
Do not use any other oil. The oil container should be
kept tightly capped until it is ready for use, and then
tightly capped after use to prevent contamination
from dirt and moisture. Refrigerant oil will quickly
absorb any moisture it comes in contact with. It will not be necessary to check oil level in the
compressor or to add oil unless there has been an oil
loss. This may be due to a ruptured line, shaft seal leakage, leakage from the evaporator, condenser
leak, filter drier or loss of refrigerant due to a colli-
sion. Oil loss at a the leak point will be evident by
the presence of a wet, shiny surface around the leak.
REFRIGERANT OIL LEVEL CHECK
When an A/C system is assembled at the factory,
all components (except the compressor) are refriger-
ant oil free. After the system has been charged with
R-12 and operated, the oil in the compressor is dis-
persed through the lines and components. The evap-
orator, condenser, and filter-drier will retain a
significant amount of oil. (Refer to the Refrigerant
Oil Capacities chart). When a component is replaced,
the specified amount of refrigerant oil must be
added. When the compressor is replaced, the amount
of oil that is retained in the rest of the system must
be drained from the replacement compressor. When a
refrigerant line or component has ruptured and it
has released an unknown amount of oil. The A/C
compressor should be removed and drained through
the suction port. The filter-drier must be replaced
along with the ruptured part. Then the oil capacity
of the system (minus the amount of oil still in the re-
maining components) can be poured into the suction
port of the compressor. Example: The evaporator retains 60 ml (2 oz). The
condenser retains 30 ml (1 oz) of oil, and system ca-
pacity may be 214 ml (7.25 oz) of oil. 214 ml minus 90 ml = 124 ml (4.25 oz).
VERIFY REFRIGERANT OIL LEVEL
(1) Using a refrigerant recovery machine, remove
refrigerant from the A/C system. (2) Remove refrigerant lines from A/C compressor.
(3) Remove compressor from vehicle.
(4) From suction port on top of compressor, drain
refrigerant oil from compressor. (5) Add system oil capacity minus the capacity of
components that have not been replaced. Refer to the
Refrigerant Oil Capacity chart. Add oil through suc-
tion port on compressor. (6) Install compressor, connect refrigerant lines,
evacuate, and charge refrigerant system.
REFRIGERANT OIL CAPACITIES
24 - 12 HEATING AND AIR CONDITIONING Ä
Page 2317 of 2438

VARIABLE DISPLACEMENT COMPRESSORÐMODEL 6C17 INDEX
page page
Clutch Coil Tests ......................... 17
Compressor ............................. 17
Compressor Clutch Inoperative .............. 13
Compressor Clutch/Coil Assembly ............ 19
Compressor Diagnosis ..................... 13
Compressor Front Shaft Seal ............... 20 Compressor High Pressure Cut-Out Switch
..... 21
Compressor High Pressure Relief Valve (HPR) . . 22
Compressor Identification ................... 13
Compressor Main or Sub Control Valves ....... 22
Compressor Noise ........................ 13
General Information ....................... 13
GENERAL INFORMATION
The Variable Displacement Compressor (VDC) pro-
vides maximum A/C performance under most condi-
tions. It is designed to operate continuously without
any cycling of the compressor clutch. The compressor
has a variable angle wobble plate with six axially
oriented cylinders. During vehicle A/C system operation, the compres-
sor will change its displacement to match the vehi-
cles A/C cooling demands. When the A/C system
needs more cooling capacity, the compressor will in-
crease its pumping capacity. This is done by increas-
ing the wobble plate angle to increase the piston
stroke. When the A/C system cooling demand is low,
the compressor will decrease its pumping capacity by
reducing the piston pumping stroke. The low cooling
capacity will prevent evaporator from freezing.
COMPRESSOR IDENTIFICATION
The Variable Displacement Compressor can be
identified by the location of the high pressure line. It
is mounted to the end of the compressor case (Fig. 1).
COMPRESSOR DIAGNOSIS
(1) Verify that refrigerant system is at full charge.
Refer to the Refrigerant Service Procedures section
in this Group. (2) Perform A/C Performance Test. Refer to Heater
and A/C Performance Test section in this Group. (3) If performance is not acceptable, perform ex-
pansion valve tests. Refer to Expansion Valve Tests
in this section. (4) If expansion valve test is correct, refer to the
Variable Displacement Compressor Diagnosis charts.
COMPRESSOR NOISE
Excessive noise that occurs when the air condition-
ing is being used, can be caused by:
² Loose bolts
² Mounting brackets
² Loose clutch
² Excessive high refrigerant system operating pres-
sure Verify compressor drive belt condition, proper re-
frigerant charge and head pressure before compressor
repair is performed. For noise diagnostic procedures, refer to the Com-
pressor Noise and Compressor Clutch Diagnosis
chart in this section.
COMPRESSOR CLUTCH INOPERATIVE
The air conditioning compressor clutch electrical
circuit is controlled by the engine controller. The
controller is located in the engine compartment out-
board of the battery. If the compressor clutch does not engage:
Verify refrigerant charge. Refer to Refrigerant Ser-
vice Procedures in this section. If the compressor clutch still does not engage:
Check for battery voltage at the differential pres-
sure cut-off switch located on the expansion valve. If
voltage is not detected, refer to: (1) Group 8W, Wiring Diagrams.
Fig. 1 Variable Displacement CompressorÐModel 6C17
Ä HEATING AND AIR CONDITIONING 24 - 13
Page 2321 of 2438

(2) The appropriate Powertrain Diagnostic Proce-
dures Manual for diagnostic information. (3) The Compressor Clutch DiagnosisÐVariable
Displacement Compressor chart in this section. (4) On 2.2 L Turbo III engines, check for battery
voltage at the Thermal Limiter Switch located on the
compressor. If voltage is found at the cut-off and/or thermal
limiter switch, reconnect switch. Then check for bat-
tery voltage between the compressor clutch connector
terminals. If voltage is detected, perform A/C Clutch Coil
Tests. Refer to Clutch Coil Tests in this section.
CLUTCH COIL TESTS
(1) Verify battery state of charge. (Test indicator
in battery should be green). (2) Connect an ammeter (0-10 ampere scale) in se-
ries with the clutch coil terminal. Use a volt meter
(0-20 volt scale) with clip leads measuring voltage
across the battery and A/C clutch. (3) With A/C control in A/C mode and blower at
low speed, start the engine and run at normal idle. (4) The A/C clutch should engage immediately and
the clutch voltage should be within two volts of the
battery voltage. If the A/C clutch does not engage,
test the fusible link. (5) The A/C clutch coil is acceptable if the current
draw is 2.0 to 3.7 amperes at 11.5-12.5 volts at clutch
coil. This is with the work area temperature at 21ÉC
(70ÉF). If voltage is more than 12.5 volts, add electri-
cal loads by turning on electrical accessories until
voltage reads below 12.5 volts. If coil current reads zero, the coil is open and
should be replaced. If the ammeter reading is 4 am-
peres or more, the coil is shorted and should be re-
placed. If the coil voltage is not within two volts of
the battery voltage, test clutch coil feed circuit for
excessive voltage drop.
COMPRESSOR
The A/C compressor may be removed and posi-
tioned without discharging the refrigerant system.
Discharging is not necessary if removing the A/C
compressor clutch/coil assembly, engine, cylinder
head, or generator.
WARNING: REFRIGERANT PRESSURES REMAIN HIGH
EVEN THOUGH THE ENGINE MAY BE TURNED OFF.
BEFORE REMOVING A FULLY CHARGED COMPRES-
SOR, REVIEW THE SAFETY PRECAUTIONS AND
WARNINGS SECTION IN THIS GROUP. DO NOT TWIST
OR KINK THE REFRIGERANT LINES WHEN REMOV-
ING A FULLY CHARGED COMPRESSOR. SAFETY
GLASSES MUST BE WORN.
REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION
(1) Disconnect NEGATIVE battery cable.
(2) Loosen and remove drive belts (Refer to Group
7, Cooling System) and disconnect compressor clutch
wire lead. (3) Remove refrigerant lines from compressor (if
necessary). (4) Remove compressor attaching nuts and bolts
(Fig. 2 or 3).
(5) Remove compressor. If refrigerant lines were
not removed, lift compressor/clutch assembly and tie
it to a suitable component. To install, reverse the preceding operation.
Fig. 2 A/C Compressor Removal and InstallationÐ3.3L Engines
Fig. 3 A/C Compressor Removal and InstallationÐ3.0 L Engine
Ä HEATING AND AIR CONDITIONING 24 - 17