1993 CHEVROLET DYNASTY service
[x] Cancel search: servicePage 247 of 2438
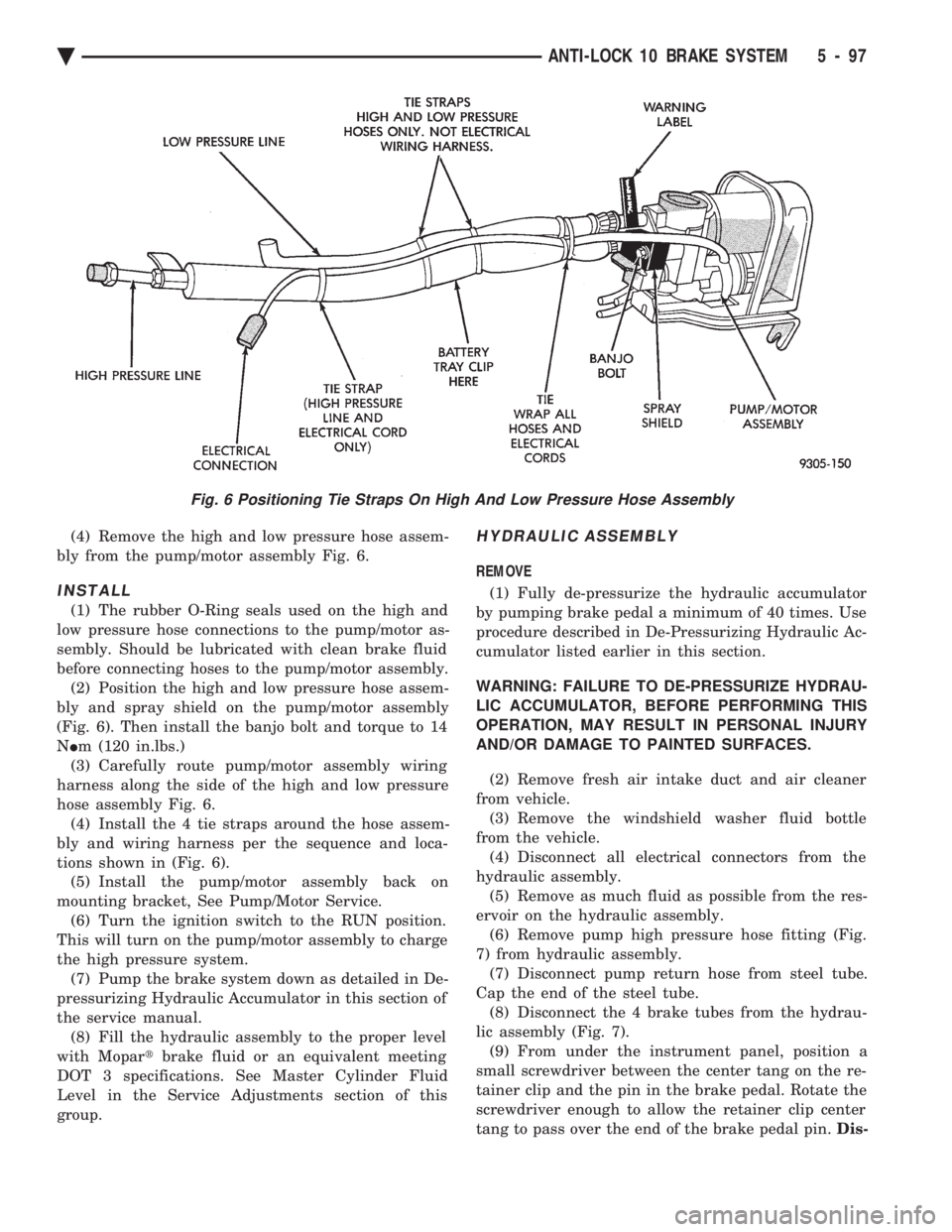
(4) Remove the high and low pressure hose assem-
bly from the pump/motor assembly Fig. 6.
INSTALL
(1) The rubber O-Ring seals used on the high and
low pressure hose connections to the pump/motor as-
sembly. Should be lubricated with clean brake fluid
before connecting hoses to the pump/motor assembly. (2) Position the high and low pressure hose assem-
bly and spray shield on the pump/motor assembly
(Fig. 6). Then install the banjo bolt and torque to 14
N Im (120 in.lbs.)
(3) Carefully route pump/motor assembly wiring
harness along the side of the high and low pressure
hose assembly Fig. 6. (4) Install the 4 tie straps around the hose assem-
bly and wiring harness per the sequence and loca-
tions shown in (Fig. 6). (5) Install the pump/motor assembly back on
mounting bracket, See Pump/Motor Service. (6) Turn the ignition switch to the RUN position.
This will turn on the pump/motor assembly to charge
the high pressure system. (7) Pump the brake system down as detailed in De-
pressurizing Hydraulic Accumulator in this section of
the service manual. (8) Fill the hydraulic assembly to the proper level
with Mopar tbrake fluid or an equivalent meeting
DOT 3 specifications. See Master Cylinder Fluid
Level in the Service Adjustments section of this
group.
HYDRAULIC ASSEMBLY
REMOVE
(1) Fully de-pressurize the hydraulic accumulator
by pumping brake pedal a minimum of 40 times. Use
procedure described in De-Pressurizing Hydraulic Ac-
cumulator listed earlier in this section.
WARNING: FAILURE TO DE-PRESSURIZE HYDRAU-
LIC ACCUMULATOR, BEFORE PERFORMING THIS
OPERATION, MAY RESULT IN PERSONAL INJURY
AND/OR DAMAGE TO PAINTED SURFACES.
(2) Remove fresh air intake duct and air cleaner
from vehicle. (3) Remove the windshield washer fluid bottle
from the vehicle. (4) Disconnect all electrical connectors from the
hydraulic assembly. (5) Remove as much fluid as possible from the res-
ervoir on the hydraulic assembly. (6) Remove pump high pressure hose fitting (Fig.
7) from hydraulic assembly. (7) Disconnect pump return hose from steel tube.
Cap the end of the steel tube. (8) Disconnect the 4 brake tubes from the hydrau-
lic assembly (Fig. 7). (9) From under the instrument panel, position a
small screwdriver between the center tang on the re-
tainer clip and the pin in the brake pedal. Rotate the
screwdriver enough to allow the retainer clip center
tang to pass over the end of the brake pedal pin. Dis-
Fig. 6 Positioning Tie Straps On High And Low Pressure Hose Assembly
Ä ANTI-LOCK 10 BRAKE SYSTEM 5 - 97
Page 249 of 2438

(7) Install high pressure hose to hydraulic assem-
bly (Fig. 7). Tighten the hose, to hydraulic assembly
fitting to 16 N Im (145 in. lbs)
(8) Fill hydraulic assembly brake fluid reservoir to
top of screen on the reservoir filter/strainer Fig. 9.
(9) Connect all electrical connectors to the hydrau-
lic assembly. (10) Bleed the entire brake system, see Bleeding
Brake System in this section of the Service Manual. (11) Replace all fresh air intake ducts, air cleaner
and washer bottle. (12) Check that the brake fluid in the hydraulic
assembly is at the correct level before moving vehicle
(Fig. 9). (See Checking Brake Fluid Level in this sec-
tion of the service manual).
BRAKE FLUID RESERVOIR
REMOVE
(1) Fully de-pressurize the hydraulic accumulator
by pumping brake pedal a minimum of 40 times. Use
procedure described in De-Pressurizing Hydraulic Ac-
cumulator listed earlier in this section.
WARNING: FAILURE TO DE-PRESSURIZE HYDRAU-
LIC ACCUMULATOR, BEFORE PERFORMING THIS
OPERATION, MAY RESULT IN PERSONAL INJURY
AND/OR DAMAGE TO PAINTED SURFACES.
(2) Remove as much brake fluid as possible from
the fluid reservoir, using a syringe or equivalent
method. (3) Using Oil Filter Band Wrench, Special Tool
C-4065 or equivalent loosen bladder accumulator. Then remove the bladder accumulator and brake
fluid spray shield from the hydraulic assembly (Fig.
10). Remove high pressure banjo fitting from hydrau-
lic assembly.
(4) Using needle nose pliers, remove the three
fluid reservoir retaining pins from the hydraulic as-
sembly (Fig. 11). Compress the barb on the opposite
side of retaining pin to prevent pin from breaking.
(5) Remove reservoir from hydraulic assembly by
CAREFULLY prying between reservoir and hydrau-
Fig. 9 ABS Fill Level On Filter/Strainer
Fig. 10 Removing Bladder Accumulator
Fig. 11 Remove Reservoir Retaining Pins
Ä ANTI-LOCK 10 BRAKE SYSTEM 5 - 99
Page 252 of 2438
WARNING: FAILURE TO DE-PRESSURIZE HYDRAU-
LIC ASSEMBLY/ACCUMULATOR PRIOR PERFORM-
ING THIS OPERATION. MAY RESULT IN PERSONAL
INJURY AND/OR DAMAGE TO PAINTED SURFACES
OF THE VEHICLE.
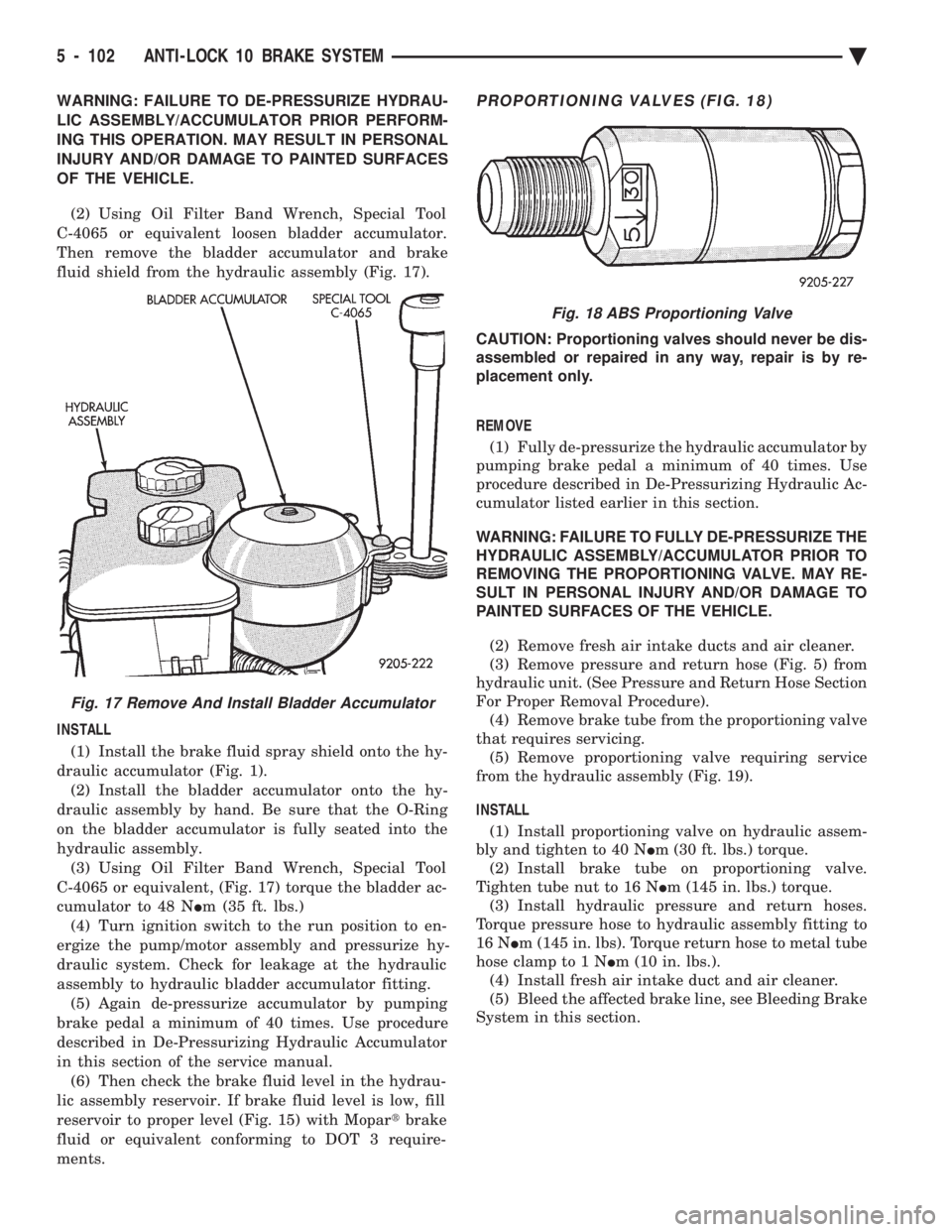
(2) Using Oil Filter Band Wrench, Special Tool
C-4065 or equivalent loosen bladder accumulator.
Then remove the bladder accumulator and brake
fluid shield from the hydraulic assembly (Fig. 17).
INSTALL
(1) Install the brake fluid spray shield onto the hy-
draulic accumulator (Fig. 1). (2) Install the bladder accumulator onto the hy-
draulic assembly by hand. Be sure that the O-Ring
on the bladder accumulator is fully seated into the
hydraulic assembly. (3) Using Oil Filter Band Wrench, Special Tool
C-4065 or equivalent, (Fig. 17) torque the bladder ac-
cumulator to 48 N Im (35 ft. lbs.)
(4) Turn ignition switch to the run position to en-
ergize the pump/motor assembly and pressurize hy-
draulic system. Check for leakage at the hydraulic
assembly to hydraulic bladder accumulator fitting. (5) Again de-pressurize accumulator by pumping
brake pedal a minimum of 40 times. Use procedure
described in De-Pressurizing Hydraulic Accumulator
in this section of the service manual. (6) Then check the brake fluid level in the hydrau-
lic assembly reservoir. If brake fluid level is low, fill
reservoir to proper level (Fig. 15) with Mopar tbrake
fluid or equivalent conforming to DOT 3 require-
ments.PROPORTIONING VALVES (FIG. 18)
CAUTION: Proportioning valves should never be dis-
assembled or repaired in any way, repair is by re-
placement only.
REMOVE (1) Fully de-pressurize the hydraulic accumulator by
pumping brake pedal a minimum of 40 times. Use
procedure described in De-Pressurizing Hydraulic Ac-
cumulator listed earlier in this section.
WARNING: FAILURE TO FULLY DE-PRESSURIZE THE
HYDRAULIC ASSEMBLY/ACCUMULATOR PRIOR TO
REMOVING THE PROPORTIONING VALVE. MAY RE-
SULT IN PERSONAL INJURY AND/OR DAMAGE TO
PAINTED SURFACES OF THE VEHICLE.
(2) Remove fresh air intake ducts and air cleaner.
(3) Remove pressure and return hose (Fig. 5) from
hydraulic unit. (See Pressure and Return Hose Section
For Proper Removal Procedure). (4) Remove brake tube from the proportioning valve
that requires servicing. (5) Remove proportioning valve requiring service
from the hydraulic assembly (Fig. 19).
INSTALL (1) Install proportioning valve on hydraulic assem-
bly and tighten to 40 N Im (30 ft. lbs.) torque.
(2) Install brake tube on proportioning valve.
Tighten tube nut to 16 N Im (145 in. lbs.) torque.
(3) Install hydraulic pressure and return hoses.
Torque pressure hose to hydraulic assembly fitting to
16 N Im (145 in. lbs). Torque return hose to metal tube
hose clamp to 1 N Im (10 in. lbs.).
(4) Install fresh air intake duct and air cleaner.
(5) Bleed the affected brake line, see Bleeding Brake
System in this section.
Fig. 17 Remove And Install Bladder Accumulator
Fig. 18 ABS Proportioning Valve
5 - 102 ANTI-LOCK 10 BRAKE SYSTEM Ä
Page 260 of 2438

(7) Using needle nose pliers, install the 3 brake fluid
reservoir to hydraulic assembly retaining pins (Fig.
14). Be sure retaining pins are fully installed with
barbs extending out past reservoir on opposite
side. (8) Install high pressure hose banjo fitting onto
hydraulic assembly and install banjo fitting attaching
bolt. Torque banjo fitting to hydraulic assembly banjo
bolt to 13 N Im (10 ft. lbs.).
(9) Install brake fluid spray shield onto hydraulic
assembly. Install bladder accumulator into hydraulic
assembly by hand (using care not to cross thread
accumulator) until O-ring seal is fully seated into
hydraulic assembly. (10) Using Oil Filter Band Wrench, Special Tool
C-4065 or equivalent, (Fig. 12) torque bladder accumu-
lator to 48 N Im (35 ft. lbs.).
(11) Fill hydraulic assembly fluid reservoir to the top
of the screen on the filter rainer. Use only fresh clean
brake fluid conforming to DOT 3 requirements, such as
Mopar tor equivalent.
(12) Bleed the brake hydraulic system using proce-
dure shown in Bleeding Brake System in this section of
the service manual.
DIFFERENTIAL PRESSURE SWITCH
REMOVE
WARNING: FAILURE TO FULLY DE-PRESSURIZE THE
HYDRAULIC BLADDER ACCUMULATOR PRIOR TO
REMOVING DIFFERENTIAL PRESSURE SWITCH.
WILL RESULT IN PERSONAL INJURY AND/OR DAM-
AGE TO PAINTED SURFACES OF THE VEHICLE.
To remove the differential pressure switch (Fig. 18),
from the hydraulic assembly, removal of the hydraulic
assembly from the vehicle is notrequired. (1) De-pressurize hydraulic bladder accumulator on
hydraulic assembly by pumping the brake pedal a
minimum of 40 times. Refer to the procedure as de-
scribed in De-Pressurizing Hydraulic Accumulator
listed earlier in this section. (2) Disconnect the hydraulic assembly wiring har-
ness connector from the primary pressure transducer
(Fig. 19).
(3) Disconnect differential pressure switch wiring
harness connector from hydraulic assembly wiring
harness (Fig. 19). Do not attempt to remove wiring
harness from differential pressure switch. (4) Raise vehicle on a frame contact type hoist. See
Hoisting in the Lubrication And Maintenance section
of this manual, for the required lifting procedure to be
used for this vehicle. (5) Using a long extension and Socket, Special Tool
6684 loosen and remove differential pressure switch
from bottom of hydraulic assembly (Fig. 20)
Fig. 18 Differential Pressure Switch Location
Fig. 19 Primary Pressure Transducer And Differen- tial Pressure Switch Wiring Harness Connectors
Fig. 17 Primary Pressure Transducer Removal And Replacement
5 - 110 ANTI-LOCK 10 BRAKE SYSTEM Ä
Page 263 of 2438
ANTI-LOCK BRAKE SYSTEMÐBENDIX ANTI-LOCK 6 AA,AG,AJ,AP BODY INDEX
page page
ABS Brake System Diagnosis .............. 123
ABS Brake System Diagnostic Features ...... 125
ABS Computer System Service Precautions . . . 124
ABS General Service Precautions ........... 124
Anti-Lock Brake System Components ........ 116
Anti-Lock Brake System Definitions .......... 113
Anti-Lock Brakes Operation and Performance . . 115
Anti-Lock System Relays and Warning Lamps . . 120
Controller Anti-Lock Brake (CAB) ............ 119
Diagnostic Connector ..................... 120
Electronic Components ................... 130 General Information
...................... 113
Hydraulic Circuits and Valve Operation ....... 121
Major Components ...................... 114
Mechanical Diagnostics and Service Procedures . 125
Normal Braking System Function ............ 114
On-Car ABS Brake System Service .......... 126
Specifications .......................... 135
System Self-Diagnostics .................. 115
Vehicle Performance ..................... 115
Warning Systems Operation ............... 116
GENERAL INFORMATION
The purpose of the Anti-Lock Brake System (ABS)
is to prevent wheel lock-up under heavy braking con-
ditions on virtually any type of road surface. Anti-
Lock Braking is desirable because a vehicle which is
stopped without locking the wheels will retain direc-
tional stability and some steering capability. This al-
lows the driver to retain greater control of the
vehicle during heavy braking. This section of the service manual covers the de-
scription, diagnostics, and on car service for the Ben-
dix Anti-Lock 6 Brake System. If other service is required on the non ABS related components of the
brake system. Refer to the appropriate section in this
group of the manual for the specific service procedure
required.
ANTI-LOCK BRAKE SYSTEM DEFINITIONS
In this section of the manual several abbreviations
are used for the components that are in the Anti-
Lock Braking System They are listed below for your
reference.
² CABÐController Anti-Lock Brake
² ABSÐAnti-Lock Brake System
Fig. 1 Four-Wheel Anti-Lock Brake System Components AA/AG/AJ Body
Ä ANTI-LOCK 6 BRAKE SYSTEM 5 - 113
Page 266 of 2438

If the vehicle is not set in motion within 3 minutes
from the time the ignition switch is set in the on po-
sition. The solenoid test is bypassed but the pump/
motor is activated briefly to verify that it is
operating correctly.
WARNING SYSTEMS OPERATION
The ABS system uses an Amber Anti-Lock Warn-
ing Lamp, located in the instrument cluster. The
purpose of the warning lamp is discussed in detail
below. The Amber Anti-Lock Warning Light will turn on
when the (CAB) detects a condition which results in
a shutdown of the Anti-Lock function. The Amber
Anti-Lock Warning Lamp is normally on until the
(CAB) completes its self tests and turns the lamp off
(approximately 1-2 seconds). When the Amber Anti-
Lock Warning Light is on only the Anti-Lock func-
tion of the brake system if affected. The standard
brake system and the ability to stop the car will not
be affected when only the Amber Anti-Lock Warning
Light is on.
NORMAL OPERATION OF WARNING LAMP
With the ignition in the Crank position, the Red
Brake Warning Lamp will turn on as a bulb check.
The Amber Anti-Lock Warning Lamp will stay on for
1-2 seconds then turn off. Once verification of the self
diagnosis is completed.
ANTI-LOCK BRAKE SYSTEM COMPONENTS
The following is a detailed description of the Anti-
Lock Brake System components. For information on
servicing the Four Wheel Disk Brake System, see the
standard Brake section of this Service Manual.
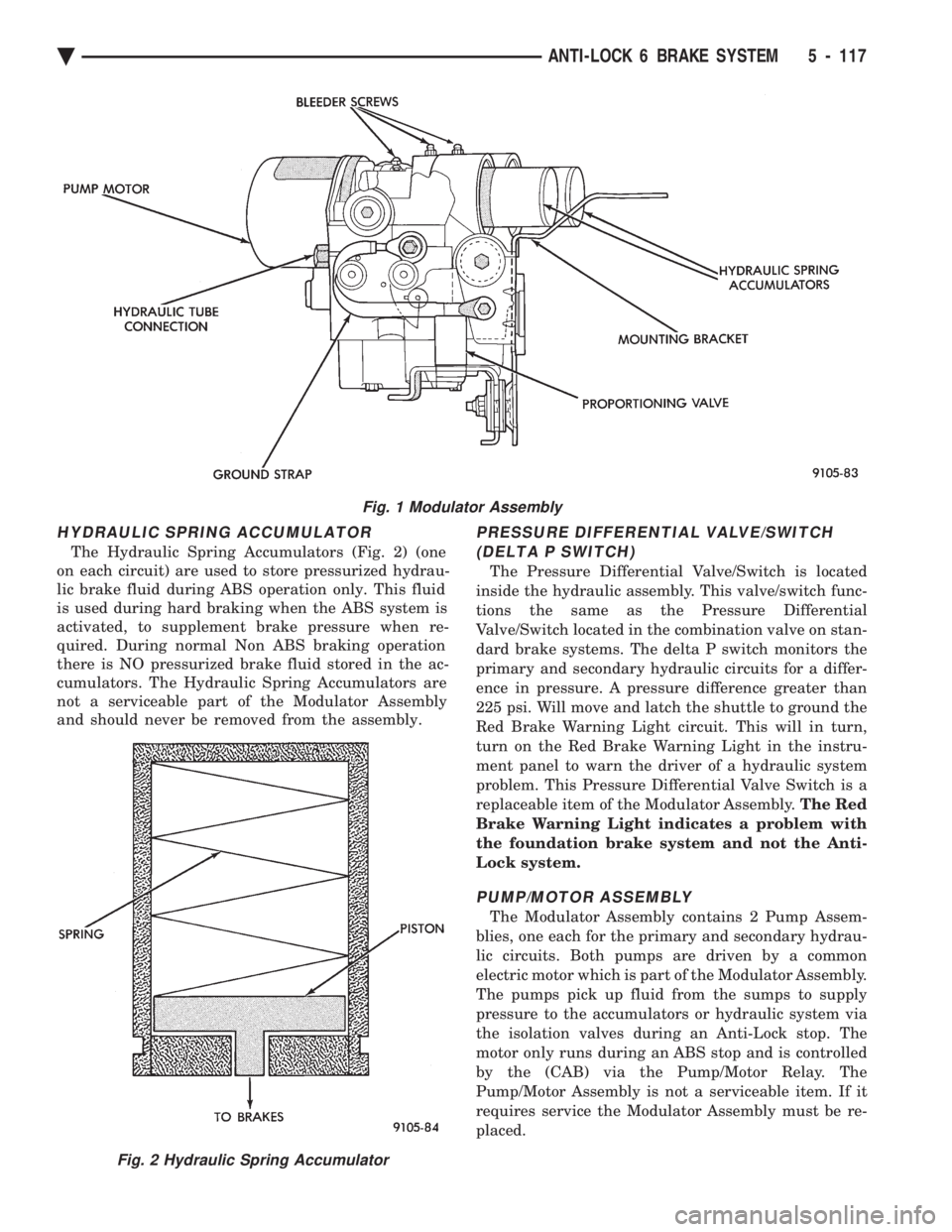
MODULATOR ASSEMBLY
WARNING: THE ONLY PART OF THE MODULATOR
ASSEMBLY THAT IS A SERVICEABLE COMPONENT
IS THE DELTA P SWITCH. THE REMAINING COM-
PONENTS OF THE MODULATOR ASSEMBLY ARE
NOT SERVICEABLE ITEMS. NO ATTEMPT SHOULD
BE MADE TO REMOVE OR SERVICE ANY OTHER
PARTS OF THE MODULATOR ASSEMBLY.
The Modulator Assembly (Fig. 1) is located under
the battery tray and is covered with an acid shield.
The Modulator Assembly contains the following com-
ponents for controlling the Anti-Lock braking sys-
tem. 2 Isolation Valves, 4 Build/Decay Valves, 4
Shuttle Orifices, 2 Fluid Sumps, 2 Accumulators, a
Pump/Motor and a Pressure Differential Valve/
Switch. Also attached to the Modulator Assembly are
4 brake tubes which are connected to an 8 way con-
nector block. The connector block is mounted to the
left frame rail below the master cylinder in the same location as the non ABS equipped combination valve.
The wheel brake lines are attached to the system via
the connector block.
ISOLATION VALVES
The Isolation Valves are used to isolate the master
cylinder from the rest of the brake hydraulic circuit
during an Anti-Lock stop. Two Isolation Valves are
used, one for the primary circuit and one for the sec-
ondary circuit. The Isolation Valves are spring
loaded in the released position. In the released posi-
tion the Isolation Valves provide a fluid path from
the master cylinder outputs to the wheel brakes via
the Build/Decay valves. When actuated it provides a
fluid path from the accumulator (which was charged
by the Pump/Motor during ABS operation) to the
Build/Decay valves through the Shuttle Orifices.
BUILD/DECAY VALVES
There are 4 Build/Decay valves, one for each
wheel. In the released position they provide a fluid
path from the wheel brakes to the Isolation Valve
through the shuttle orifices. In the actuated (decay)
position, they provide a fluid path from the wheel
brakes to the sump. The Build/Decay valves are
spring loaded in the released (build) position.
SHUTTLE ORIFICE
There are 4 Shuttle Orifice Valves, one for each
wheel. The Shuttle Orifice Valve is a hydraulically
actuated valve which shuttles when the Build/Decay
valve is actuated. Actuating of the Build/Decay valve
causes a pressure differential to be created across the
Shuttle Orifice Valve. This acts like placing an ori-
fice (restriction) in the line between the Isolation
Valve and the Build/Decay Valve. This restriction
provides a controlled build rate to each wheel brake
during an Anti-Lock stop. The Shuttle Orifice Valve
will remain in the orificed position until the ABS cy-
cle is complete. When the ABS cycle has been com-
pleted the Isolation and Build/Decay valves will
return to their released position which will equalize
the pressure across the Shuttle Orifice Valves. When
the pressure equalizes, the spring loaded Shuttle Or-
ifice valves will return to the unrestricted position.
FLUID SUMPS
There are two Fluid Sumps in the Hydraulic As-
sembly, one each for the primary and secondary hy-
draulic circuits. The Fluid Sumps store the brake
fluid that is decayed from the wheel brakes during
ABS cycle. This fluid is then pumped to an accumu-
lator and/or the hydraulic system in order to provide
build pressure. The typical pressure in the sumps is
50 psi, During ABS operation only.
5 - 116 ANTI-LOCK 6 BRAKE SYSTEM Ä
Page 267 of 2438
HYDRAULIC SPRING ACCUMULATOR
The Hydraulic Spring Accumulators (Fig. 2) (one
on each circuit) are used to store pressurized hydrau-
lic brake fluid during ABS operation only. This fluid
is used during hard braking when the ABS system is
activated, to supplement brake pressure when re-
quired. During normal Non ABS braking operation
there is NO pressurized brake fluid stored in the ac-
cumulators. The Hydraulic Spring Accumulators are
not a serviceable part of the Modulator Assembly
and should never be removed from the assembly.
PRESSURE DIFFERENTIAL VALVE/SWITCH
(DELTA P SWITCH)
The Pressure Differential Valve/Switch is located
inside the hydraulic assembly. This valve/switch func-
tions the same as the Pressure Differential
Valve/Switch located in the combination valve on stan-
dard brake systems. The delta P switch monitors the
primary and secondary hydraulic circuits for a differ-
ence in pressure. A pressure difference greater than
225 psi. Will move and latch the shuttle to ground the
Red Brake Warning Light circuit. This will in turn,
turn on the Red Brake Warning Light in the instru-
ment panel to warn the driver of a hydraulic system
problem. This Pressure Differential Valve Switch is a
replaceable item of the Modulator Assembly. The Red
Brake Warning Light indicates a problem with
the foundation brake system and not the Anti-
Lock system.
PUMP/MOTOR ASSEMBLY
The Modulator Assembly contains 2 Pump Assem-
blies, one each for the primary and secondary hydrau-
lic circuits. Both pumps are driven by a common
electric motor which is part of the Modulator Assembly.
The pumps pick up fluid from the sumps to supply
pressure to the accumulators or hydraulic system via
the isolation valves during an Anti-Lock stop. The
motor only runs during an ABS stop and is controlled
by the (CAB) via the Pump/Motor Relay. The
Pump/Motor Assembly is not a serviceable item. If it
requires service the Modulator Assembly must be re-
placed.
Fig. 1 Modulator Assembly
Fig. 2 Hydraulic Spring Accumulator
Ä ANTI-LOCK 6 BRAKE SYSTEM 5 - 117
Page 268 of 2438

PROPORTIONING VALVES
Two Proportioning Valves (Fig. 3) are used in the
system, one for each rear brake hydraulic circuit.
The Proportioning Valves function the same as in a
standard brake system. The Proportioning Valves are
located on the bottom of the hydraulic assembly (Fig.
1). They are the same screw in type as the ones used
on the Bendix Anti-Lock 10 and Bosh Anti-Lock
Brake systems.
WHEEL SPEED SENSORS
One Wheel Speed Sensor (WSS), is located at each
wheel (Fig. 4 and 5), and sends a small (AC) signal
to the control module (CAB). This signal is generated
by magnetic induction. The magnetic induction is
created, when a toothed sensor ring Tone Wheel (Fig.
6) passes a stationary magnetic Wheel Speed Sensor.
The (CAB) converts the (AC) signal generated at
each wheel into a digital signal. If a wheel locking
tendency is detected, the (CAB) will then modulate
hydraulic pressure to prevent the wheel(s) from lock-
ing. The front Wheel Speed Sensor is attached to a boss
in the steering knuckle (Fig. 4). The tone wheel is
part of the outboard constant velocity joint. The rear
Wheel Speed Sensor is mounted to the caliper adap-
tor (Fig. 5) and the rear tone wheel is an integral
part of the rear wheel hub (Fig. 6). The speed sensor
air gap is NOT adjustable. The four Wheel Speed Sensors are serviced individ-
ually. The front Tone Wheels are serviced as an as-
sembly with the outboard constant velocity joint. The
rear Tone Wheels are serviced as an assembly with
the rear brake hub. Correct Anti-Lock system operation is dependent
on the vehicle's wheel speed signals, that are gener-
ated by the Wheel Speed Sensors. The vehicle's
wheels and tires must all be the same size and type
to generate accurate signals. In addition, the tires
must be inflated to the recommended pressures for
optimum system operation. Variations in wheel and
tire size or significant variations in inflation pres-
sure can produce inaccurate wheel speed signals.
Fig. 3 Proportioning Valve Identification
Fig. 4 Front Wheel Speed Sensor
Fig. 5 Rear Wheel Speed Sensor
5 - 118 ANTI-LOCK 6 BRAKE SYSTEM Ä