1991 FORD FESTIVA fuse
[x] Cancel search: fusePage 284 of 454

Since DVOMs update their display roughly two to five times a second, all measurements in between are averaged. Because a potential voltage
drop is visible for such a small amount of time, it ge t s "a ve r a ge d o u t ", c a u sin g yo u t o miss it .
Only a DVOM that has a "min-max" function that checks EVERY MILLISECOND will catch this fault consistently (if used in that mode). The
Fluke 87 among others has this capability.
A "min-max" DVOM with a lower frequency of checking (100 millisecond) can miss the fault because it will probably check when the injector
is not on. This is especially true with current controlled driver circuits. The Fluke 88, among others fall into this category.
Outside of using a Fluke 87 (or equivalent) in the 1 mS "min-max" mode, the only way to catch a voltage drop fault is with a lab scope. You
will be able to see a voltage drop as it happens.
One final note. It is important to be aware that an injector circuit with a solenoid resistor will always show a voltage drop when the circuit is
energized. This is somewhat obvious and normal; it is a designed-in voltage drop. What can be unexpected is what we already covered--a
voltage drop disappears when the circuit is unloaded. The unloaded injector circuit will show normal battery voltage at the injector.
Remember this and do not get confused.
Checking Injector On-Time With Built-In Function
Several DVOMs have a feature that allows them to measure injector on-time (mS pulse width). While they are accurate and fast to hookup,
they have three limitations you should be aware of:
They only work on voltage controlled injector drivers (e.g "Saturated Switch"), NOT on current controlled injector drivers (e.g. "Peak &
Hold").
A few unusual conditions can cause inaccurate readings.
Varying engine speeds can result in inaccurate readings.
Regarding the first limitation, DVOMs need a well-defined injector pulse in order to determine when the injector turns ON and OFF. Voltage
controlled drivers provide this because of their simple switch-like operation. They completely close the circuit for the entire duration of the
pulse. This is easy for the DVOM to interpret.
The other type of driver, the current controlled type, start off well by completely closing the circuit (until the injector pintle opens), but then
they throttle back the voltage/current for the duration of the pulse. The DVOM understands the beginning of the pulse but it cannot figure out
the throttling action. In other words, it cannot distinguish the throttling from an open circuit (de-energized) condition.
Yet current controlled injectors will still yield a millisecond on-time reading on these DVOMs. You will find it is also always the same,
regardless of the operating conditions. This is because it is only measuring the initial completely-closed circuit on-time, which always takes the
same amount of time (to lift the injector pintle off its seat). So even though you get a reading, it is useless.
The second limitation is that a few erratic conditions can cause inaccurate readings. This is because of a DVOM's slow display rate; roughly
two to five times a second. As we covered earlier, measurements in between display updates get averaged. So conditions like skipped injector
pulses or intermittent long/short injector pulses tend to get "averaged out", which will cause you to miss important details.
The last limitation is that varying engine speeds can result in inaccurate readings. This is caused by the quickly shifting injector on-time as the
engine load varies, or the RPM moves from a state of acceleration to stabilization, or similar situations. It too is caused by the averaging of all
measurements in between DVOM display periods. You can avoid this by checking on-time when there are no RPM or load changes.
A lab scope allows you to overcome each one of these limitations.
Checking Injector On-Time With Dwell Or Duty
If no tool is available to directly measure injector millisecond on-time measurement, some techs use a simple DVOM dwell or duty cycle
functions as a replacement.
While this is an approach of last resort, it does provide benefits. We will discuss the strengths and weaknesses in a moment, but first we will
look at how a duty cycle meter and dwell meter work.
How A Duty Cycle Meter and Dwell Meter Work
All readings are obtained by comparing how long something has been OFF to how long it has been ON in a fixed time period. A dwell meter
and duty cycle meter actually come up with the same answers using different scales. You can convert freely between them. See
RELATIONSHIP BETWEEN DWELL & DUTY CYCLE READINGS TABLE
.
The DVOM display updates roughly one time a second, although some DVOMs can be a little faster or slower. All measurements during this
update period are tallied inside the DVOM as ON time or OFF time, and then the total ratio is displayed as either a percentage (duty cycle) or
degrees (dwell meter).
For example, let's say a DVOM had an update rate of exactly 1 second (1000 milliseconds). Let's also say that it has been measuring/tallying
an injector circuit that had been ON a total of 250 mS out of the 1000 mS. That is a ratio of one-quarter, which would be displayed as 25%
duty cycle or 15° dwell (six-cylinder scale). Note that most duty cycle meters can reverse the readings by selecting the positive o r n e ga t ive
slope to trigger on. If this reading were reversed, a duty cycle meter would display 75%.
Strengths of Dwell/Duty Meter
The obvious strength of a dwell/duty meter is that you can compare injector on-time against a known-good reading. This is the only practical
way to use a dwell/duty meter, but requires you to have known-good values to compare against.
Another strength is that you can roughly convert injector mS on-time into dwell reading with some computations.
A final strength is that because the meter averages everything together it does not miss anything (though this is also a severe weakness that we
will look at later). If an injector has a fault where it occasionally skips a pulse, the meter registers it and the reading changes accordingly.
Page 3 of 19 MITCHELL 1 ARTICLE - GENERAL INFORMATION Waveforms - Injector Pattern Tutorial
3/10/2009 http://www.eautorepair.net/app/PrintItems.asp?S0=2097152&S1=0&SG=%7B9B990D68%2D660A%2D45E9%2D8F46%2DE
...
Page 345 of 454

Back To Article
HEAT ER SYST EM
1990-92 HEAT ER SYST EMS Ford Motor Co.
DESCRIPTION
The heater system consists of control panel, blower case, heater case, air control doors and ducts. The control panel incorporates 3 control
levers and a 3-speed fan switch. The control panel is located in the center of the instrument panel. All air control doors are cable operated
from the control panel.
The blower case is mounted on the bulkhead, behind the instrument panel on passenger's side of vehicle. The blower case houses a blower
motor, blower motor resistor and the fresh/recirculation air door. The heater case contains mode select door, temperature air mix door and
heater core.
OPERATION
Three control levers, temperature mix, fresh/recirculation and mode select, mechanically operate their associated cables and doors. The
temperature control lever adjusts the mix of fresh or recirculated air with heated air. In full heat position, all airflow goes through the heater
core.
In full cool position, the mix air door closes, allowing airflow to by-pass the heater core. The mode select lever, directs airflow to selected
vents. The fresh/recirculation control lever allows selection of fresh (outside) air or recirculated compartment air.
AJUSTMENT
FRESH/RECIRCULATION CONTROL CABLE
Remove the glove box. Remove fresh/recirculation cable retaining clip. Move control lever to RECIRCULATION position, while holding the
lever door in RECIRCULATION position. Ensure control lever does not move. Install fresh/recirculation cable retaining clip.
MODE SELECT CABLE
Remove mode select cable retaining clip. Move mode select lever to VENT position. Hold mode select lever downward against its stop.
Ensure that mode select lever does not move. Install mode select cable retaining clip.
TEMPERATURE CONTROL CABLE
Set temperature control lever to maximum cold position. Remove temperature cable retaining clip. Hold temperature control lever upward and
against its stop. Ensure that temperature lever does not move. Install temperature cable retaining clip.
TROUBLE SHOOTING
BLOWER MOTOR INOPERATIVE
Check blown motor fuse. Check for defective blower motor and/or blower motor resistor. Check blower motor switch. Check for open in
ground wire. Check for loose electrical connectors or poor connections. See WIRING DIAGRAMS
in this article.
BLOWER DOES NOT CHANGE SPEED
Check for defective blower motor. Check blower motor wiring harness. Check blower motor resistor. Check for blower motor fan switch. See
WIRING DIAGRAMS
in this article.
BLOWER RUNS CONSTANTLY
Check for defective blower motor resistor. Check for short in blower switch or wiring. See WIRING DIAGRAMS
in this article.
HEATER TEMPERATURE INSUFFICIENT
Check for proper coolant level. Check water pump for noise, leaks or wear. Check heater hoses for leaks or restrictions. Check heater core for
leaks, plugs or restrictions. Check inlet and outlet heater hoses for hot water flow. Check thermostat condition and operation. Check air mix
door position and adjust cable if necessary.
IMPROPER WARM AIR DISTRIBUTION
Check air mix door position. Adjust cable as necessary. Check function control door position. Adjust cable as necessary. Check for restriction
in ventilation air duct assembly. Repair as necessary.
TESTING BLOWER MOTOR & RESISTOR
1. Ensure 15-amp blower motor fuse is okay. Using voltmeter, check for battery voltage at blower motor Blue/Yellow terminal. If battery
voltage is present, go to next step. If battery voltage is not present, repair open in Blue/Yellow wire between blower motor and fuse box.
2. Disconnect blower motor connector. Using a jumper wire, apply battery voltage to Blue/Yellow terminal and ground the Blue/Red
terminal. If blower motor does not run, replace blower motor. If blower motor runs, go to next step.
3. Reconnect blower motor connector. Turn ignition on. Turn blower motor off. Disconnect the blower motor resistor connector. Using a
voltmeter, measure voltage at Blue/Red terminal of resistor connector. If battery voltage is not present, repair open in Blue/Red wire
between resistor and blower motor. If voltage is present, go to next step.
4. Using a jumper wire, ground Blue/Black, Blue/Yellow and Blue/White terminals of the blower fan switch one at a time. If the motor
runs at 3 different speeds, go to next step. If not, repair open in wire that failed to operate blower motor.
Page 1 of 4 MITCHELL 1 ARTICLE - HEATER SYSTEM 1990-92 HEATER SYSTEMS Ford Motor Co.
3/10/2009 http://www.eautorepair.net/app/PrintItems.asp?S0=2097152&S1=0&SG=%7B9B990D68%2D660A%2D45E9%2D8F46%2DE
...
Page 346 of 454

5. Check blower motor fan switch continuity. Resistance should not exceed 4 ohms. See BLOWER MOTOR FAN SWITCH
CONTINUITY table. If continuity is not present, replace fan switch. If continuity is okay, repair open in Black wire from blower motor
switch to ground.
BLOWER MOTOR FAN SWITCH CONTINUITY
REMOVAL & INSTALLATION
CONTROL PANEL
1. Remove bezel screws and accessory bezel. Remove radio. Remove 4 screws securing control panel to instrument panel. Remove glove
box attaching screws and glove box. Remove the retaining clip and disconnect fresh/recirculation air door cable from mode door lever.
2. Disconnect mode select cable at mode control door lever. Disconnect temperature control cable at temperature control mode door lever.
Pull control panel away from instrument panel. Disconnect blower motor switch connector. Disconnect illumination electrical
connector. Remove control panel. To install, reverse removal procedure. Adjust control cables. See ADJUSTMENTS in this article.
BLOWER MOTOR FAN SWITCH
Remove control panel. See CONTROL PANEL R & I
. Remove blower motor fan switch knob. Remove attaching nut. To install, reverse
removal procedure.
HEATER CORE
1. Disconnect negative battery cable. Remove steering wheel by prying out center trim insert and removing steering wheel retaining nut.
Remove 2 steering wheel cover retaining screws and remove cover. Using a steering wheel puller, remove steering wheel.
2. Remove 5 screws and remove lower and upper steering column covers. Disconnect electrical connections and remove multifunction
switch. Remove 5 screws and pull instrument cluster hood rearward. Disconnect electrical connections and remove instrument cluster
hood.
3. Disconnect speedometer cable at transaxle. Remove 4 instrument cluster screws. Pull instrument cluster rearward and disconnect
speedometer cable and electrical connections. Remove instrument cluster.
4. Remove 2 center bracket mounting bolts under steering column and remove bracket. Remove glove box attaching screws and remove
glove box. Remove left and right heater ducts. Remove fuse panel cover. Remove 2 screws securing fuse panel and push fuse panel
inward. DO NOT remove fuse panel.
5. Slide both seats to most forward position. Remove 2 console attaching screws, located in front of seat belt anchors. Slide both seats to
rearmost position. Remove parking brake console insert. Using a Phillips screwdriver, remove push retainer insert, located at front lower
edge of parking brake console. Pull back on parking brake lever and remove parking brake console.
6. Remove gearshift knob. Remove screws and remove shift console. Remove radio/heater control panel bezel screws and remove bezel.
Remove 4 radio attaching screws. Pull radio out and disconnect antenna lead and electrical connections. Disconnect radio ground lead
and remove radio.
7. Remove 4 screws attaching heater control panel. Disconnect control cables and electrical connections. Remove control panel, while
pulling cables through opening.
8. Pry out bolt cover trim inserts in top corners of dash. Remove bolts located under trim panels. Remove 7 instrument panel attaching
bolts and 2 nuts. Pull instrument panel rearward. Disconnect any harness connectors and clips. Remove instrument panel.
9. Disconnect electrical connections at blower and resistor. Remove harness from routing brackets on heater box. Loosen clamp screw
securing air inlet housing. Remove attaching nuts at top and bottom of heater box. Disconnect defroster ducts and remove heater
assembly.
10. Disconnect link connecting 2 defroster doors. Remove attaching screw just above and to right of blower resistor. Turn heater assembly
around and remove screw just to left of blower motor opening. Remove clips securing 2 halves of heater assembly. Separate halves. Lift
out heater core.
11. To install, reverse removal procedure. Ensure all heater control cables are routed and adjusted properly. See ADJUSTMENTS in this
article. Fill cooling system. Check for leaks.
BLOWER MOTOR & RESISTOR
Disconnect negative battery cable. Remove instrument panel spacer brace located below steering column. Remove airflow duct below steering
column. Disconnect blower motor or resistor wiring. Remove 3 blower motor attaching screws or 2 resistor attaching screws and remove
component. To install, reverse removal procedure.
Switch PositionContinuity Between Wire Colors
1Black-to-Blue/White
2Black-to-Blue/Yellow & Blue/Yellow-to-Blue/Red
3Black-to-Blue/Black & Blue/Black-to-Blue/Red
Page 2 of 4 MITCHELL 1 ARTICLE - HEATER SYSTEM 1990-92 HEATER SYSTEMS Ford Motor Co.
3/10/2009 http://www.eautorepair.net/app/PrintItems.asp?S0=2097152&S1=0&SG=%7B9B990D68%2D660A%2D45E9%2D8F46%2DE
...
Page 361 of 454

tube from evaporator core fins while removing thermostatic switch. To install, reverse removal procedure. Evacuate and recharge system.
THERMOSTATIC EXPANSION VALVE
Removal & Installation
1. Discharge A/C system using approved refrigerant recovery/recycling equipment. Remove evaporator housing. See EVAPORATOR
HOUSING under REMOVAL & INSTALLATION. Remove air inlet duct. See Fig. 1 .
2. Remove insulation from sensing bulb. Disconnect thermostatic expansion valve at evaporator tube fitting and inlet tube fitting (from
receiver-drier). See Fig. 3
. Remove thermostatic expansion valve. To install, reverse removal procedure. Use new "O" rings. Evacuate
and recharge system.
A/C RELAYS
Removal & Installation
A/C relays are located in left front corner of engine compartment, near battery. Unclip relay holder from its mounting bracket. Disconnect
relay wiring. DO NOT pull on wiring connector to remove relay from holder. Remove relay from holder. To install, reverse removal procedure.
A/C-HEATER CONTROL ASSEMBLY
Removal & Installation
1. A/C control module is located above radio. Remove accessory bezel. Remove radio (if necessary) and glove box. Disconnect
recirculated/fresh air cable from door lever. See Fig. 5
. Disconnect mode select cable from door lever. See Fig. 6 .
2. Disconnect temperature control cable from door lever. See Fig. 4
. Pull control assembly away from dash, and disconnect wiring
connectors. Remove control assembly.
3. To install, reverse removal procedure. Check and adjust temperature control, recirculated/fresh air and mode cables. See
ADJUSTMENTS. Test control assembly operation.
BLOWER MOTOR
Removal & Installation
Disconnect negative battery cable. Remove A/C air outlet duct located below steering column. See Fig. 2 . Disconnect blower motor wiring.
Remove blower motor attaching screws and blower motor. Remove blower wheel attaching nut. Remove blower wheel and washer. To install,
reverse removal procedure.
BLOWER MOTOR RESISTOR
Removal & Installation
Disconnect negative battery cable. Remove air duct located below steering column. See Fig. 2 . Disconnect blower motor resistor wiring.
Remove blower resistor attaching screws and resistor. To install, reverse removal procedure.
AIR DISTRIBUTION PLENUM
Removal & Installation
1. Remove instrument panel. See INSTRUMENT PANEL under REMOVAL & INSTALLATION. Drain cooling system. Disconnect
heater hoses in engine compartment. Disconnect wiring for blower motor and blower resistor. Disengage wiring harness and antenna
lead from bracket on front of air distribution housing.
2. Loosen connector duct-to-air inlet clamp screw. Remove upper and lower mounting nuts from plenum. Disengage and remove plenum
from defroster ducts. To install, reverse removal procedure. Refill cooling system, and check for leaks.
HEATER CORE
Removal & Installation
1. Remove air distribution plenum. See AIR DISTRIBUTION PLENUM under REMOVAL & INSTALLATION. Disconnect linkage
connecting defroster doors. Remove attaching screw located near blower resistor. Turn housing around and remove attaching screw
located near blower motor opening.
2. Remove clips retaining blower housing halves. Separate blower housing halves. Remove heater core. Remove tube insert from heater
core. To install, reverse removal procedure. Test system for proper operation.
INSTRUMENT PANEL
Removal & Installation
1. Disconnect negative battery cable. Remove steering wheel, steering column covers and multifunction switch assembly. Disconnect
electrical connectors from switches on instrument panel. Remove instrument cluster hood.
2. Disconnect speedometer cable from transmission. Remove 4 instrument cluster screws. Pull instrument cluster out from instrument
panel cluster enough to disconnect wiring and speedometer cable. Remove instrument cluster.
3. Remove steering column shield. Remove shield bracket. Remove glove box. Remove fuse panel cover and 4 fuse panel screws. Pull fu se
panel out, but DO NOT remove. Remove shift lever console and mount brackets. CAUTION: DO NOT rem ove screw in front of blower resistor, or blower resistor m ounting plate will fall into air
distribution plenum . T o retrieve plate, disassem ble instrum ent panel.
Page 13 of 14 MITCHELL 1 ARTICLE - 1991 AIR CONDITIONING & HEAT MANUAL A/C
3/10/2009 http://www.eautorepair.net/app/PrintItems.asp?S0=2097152&S1=0&SG=%7B9B990D68%2D660A%2D45E9%2D8F46%2DE
...
Page 369 of 454
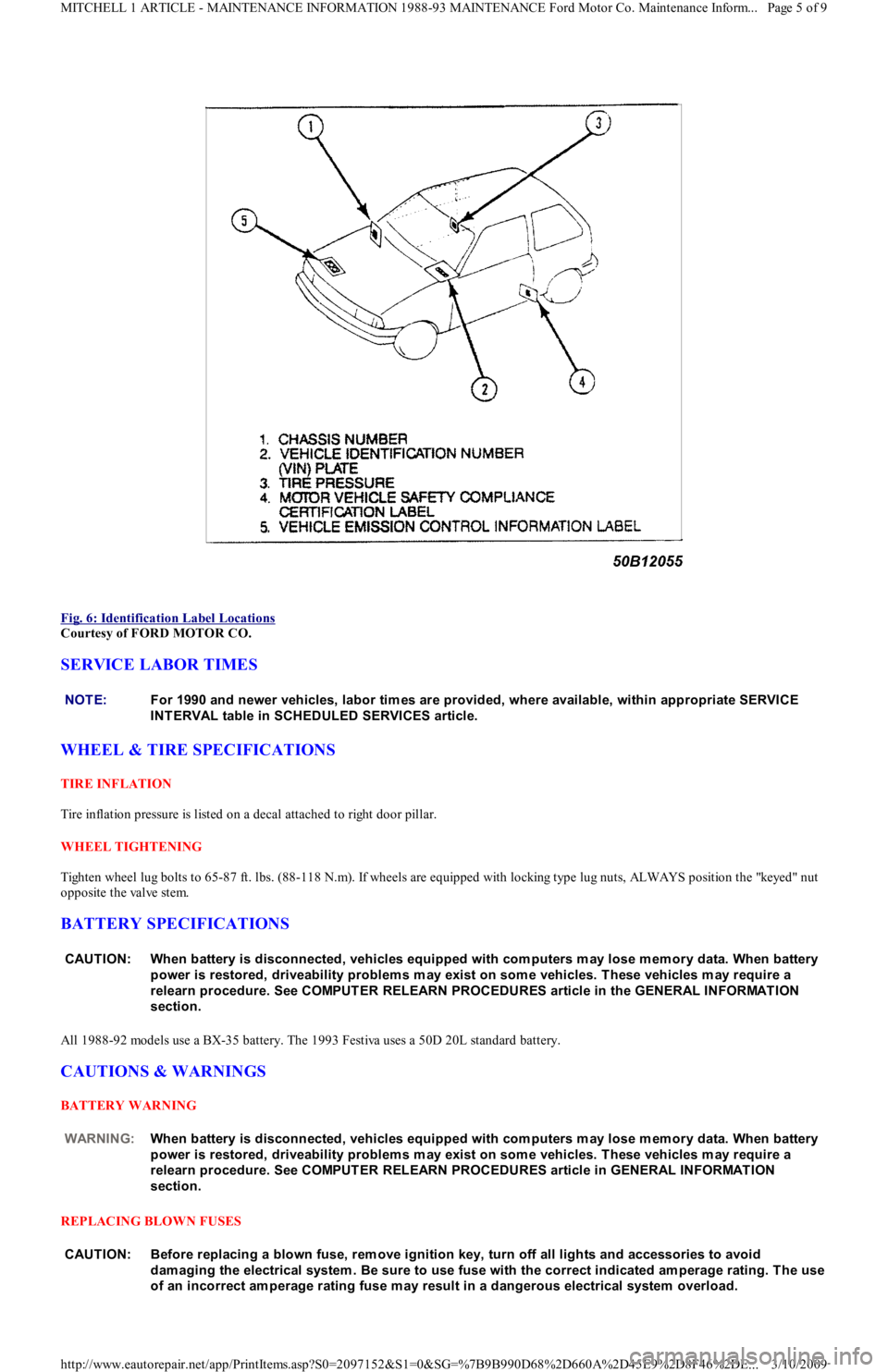
Fig. 6: Identification Label Locations
Courtesy of FORD MOTOR CO.
SERVICE LABOR TIMES
WHEEL & TIRE SPECIFICATIONS
TIRE INFLATION
Tire inflation pressure is listed on a decal attached to right door pillar.
WHEEL TIGHTENING
Tighten wheel lug bolts to 65-87 ft. lbs. (88-118 N.m). If wheels are equipped with locking type lug nuts, ALWAYS position the "keyed" nut
opposite the valve stem.
BATTERY SPECIFICATIONS
All 1988-92 models use a BX-35 battery. The 1993 Festiva uses a 50D 20L standard battery.
CAUTIONS & WARNINGS
BATTERY WARNING
REPLACING BLOWN FUSES
NOTE:For 1990 and newer vehicles, labor tim es are provided, where available, within appropriate SERVICE
INT ERVAL table in SCHEDULED SERVICES article.
CAUT ION: When battery is disconnected, vehicles equipped with com puters m ay lose m em ory data. When battery
power is restored, driveability problem s m ay exist on som e vehicles. T hese vehicles m ay require a
relearn procedure. See COMPUT ER RELEARN PROCEDURES article in the GENERAL INFORMAT ION
section.
WARNING:When battery is disconnected, vehicles equipped with com puters m ay lose m em ory data. When battery
power is restored, driveability problem s m ay exist on som e vehicles. T hese vehicles m ay require a
relearn procedure. See COMPUT ER RELEARN PROCEDURES article in GENERAL INFORMAT ION
section.
CAUT ION: Before replacing a blown fuse, rem ove ignition key, turn off all lights and accessories to avoid
dam aging the electrical system . Be sure to use fuse with the correct indicated am perage rating. T he use
of an incorrect am perage rating fuse m ay result in a dangerous electrical system overload.
Page 5 of 9 MITCHELL 1 ARTICLE - MAINTENANCE INFORMATION 1988-93 MAINTENANCE Ford Motor Co. Maintenance Inform...
3/10/2009 http://www.eautorepair.net/app/PrintItems.asp?S0=2097152&S1=0&SG=%7B9B990D68%2D660A%2D45E9%2D8F46%2DE
...
Page 371 of 454

whichever occurs first.
POWERTRAIN WARRANTY
Under this warranty, certain parts of the engine, transmission, axle and driveline are warranted against defects in materials and workmanship
for either 4 years/50,000 or 6 years/60,000 miles, depending on the model year. This coverage begins after 12 months or 12,000 miles. See
copy of warranty for specific components covered and length of coverage.
BUMPER-TO-BUMPER COVERAGE
All 1992-93 vehicles have complete warranty coverage against defects in materials and workmanship for 3 years or 36,000 miles, whichever
occurs first. There is no deductible with this warranty. Items not covered include tires and parts that are subject to normal wear and tear, such
as windshield wiper blades, brake linings, brake pads, clutch linings and scheduled maintenance items. There is no extended powertrain
coverage included in this warranty.
BATTERY COVERAGE
Begins at warranty start date and lasts up to 3 years or 36,000 miles, whichever occurs first. For the first 12 months in service (less than
36,000 miles), battery will be replaced at no charge. After that, battery will be replaced on a customer-participation basis: For the 13th-24th
month in service, Ford will pay 50%; for the 25th-36th month, Ford will pay 25%. Labor is covered for 3 years or 36,000 miles, whichever
occurs first.
SAFETY RESTRAINT SYSTEM COVERAGE
Begins at warranty start date and lasts for 5 years or 50,000 miles, whichever occurs first. Covers safety restraint problems not related to
comfort or appearance. Coverage for model years earlier than 1990 is 3 years with unlimited miles.
CORROSION COVERAGE
Begins at warranty start date and lasts for 6 years or 60,000 miles, whichever occurs first. 1992-93 models are covered for 6 years or 100,000
miles, whichever occurs first. Covers any holes in body sheet metal caused by corrosion.
EMISSIONS DEFECT & PERFORMANCE WARRANTIES (EXCEPT CALIFORNIA)
Defect Warranty ensures that vehicle meets applicable EPA regulations and that vehicle's emission control system is free from defects in
materials and workmanship for a period of 5 years or 50,000 miles, whichever occurs first.
The Performance Warranty covers all costs of repairing or adjusting any components or parts as needed for the vehicle to pass a Federally
required state or local emissions test.
Other emission control parts related to these components are covered by the Performance Warranty, where applicable. If another part fails due
to the failure of one of these components, both parts are covered. See customer's copy of warranty information for specific items co vered .
Performance Warranty coverage is limited to fewer components after 2 years or 24,000 miles.
EMISSIONS PERFORMANCE WARRANTY (CALIFORNIA)
If vehicle fails a Smog Check inspection, all necessary repairs and adjustments will be made by manufacturer to ensure that vehicle passes the
inspection. Warranty begins at warranty start date and lasts for a period of 3 years or 50,000 miles, whichever occurs first.
EMISSIONS DEFECT WARRANTY (CALIFORNIA)
If any emission-related part on the vehicle is defective, the part will be repaired or replaced by manufacturer. Warranty begins at warranty start
date and lasts for a period of 3 years or 50,000 miles, whichever occurs first.
Some emission-related parts are warranted for 7 years or 70,000 miles whichever occurs first, and will be repaired or replaced by manufacturer
if found to be defective in material or workmanship. See customer's copy of warranty information for specific items covered.
FUSES & FUSIBLE LINKS
FUSE PANEL & FUSIBLE LINK BLOCK LOCATIONS
The vehicle has a fuse block with fusible links and a fuse panel with circuit fuses. The fuse panel is located behind the instrument panel, left o
f
the steering column. The fuse block is located under the hood.
FUSE PANEL IDENTIFICATION NOTE:Powertrain Warranty varies in coverage length (4 years/50,000 m iles or 6 years/60,000 m iles) depending
on model year.
Page 7 of 9 MITCHELL 1 ARTICLE - MAINTENANCE INFORMATION 1988-93 MAINTENANCE Ford Motor Co. Maintenance Inform...
3/10/2009 http://www.eautorepair.net/app/PrintItems.asp?S0=2097152&S1=0&SG=%7B9B990D68%2D660A%2D45E9%2D8F46%2DE
...
Page 372 of 454
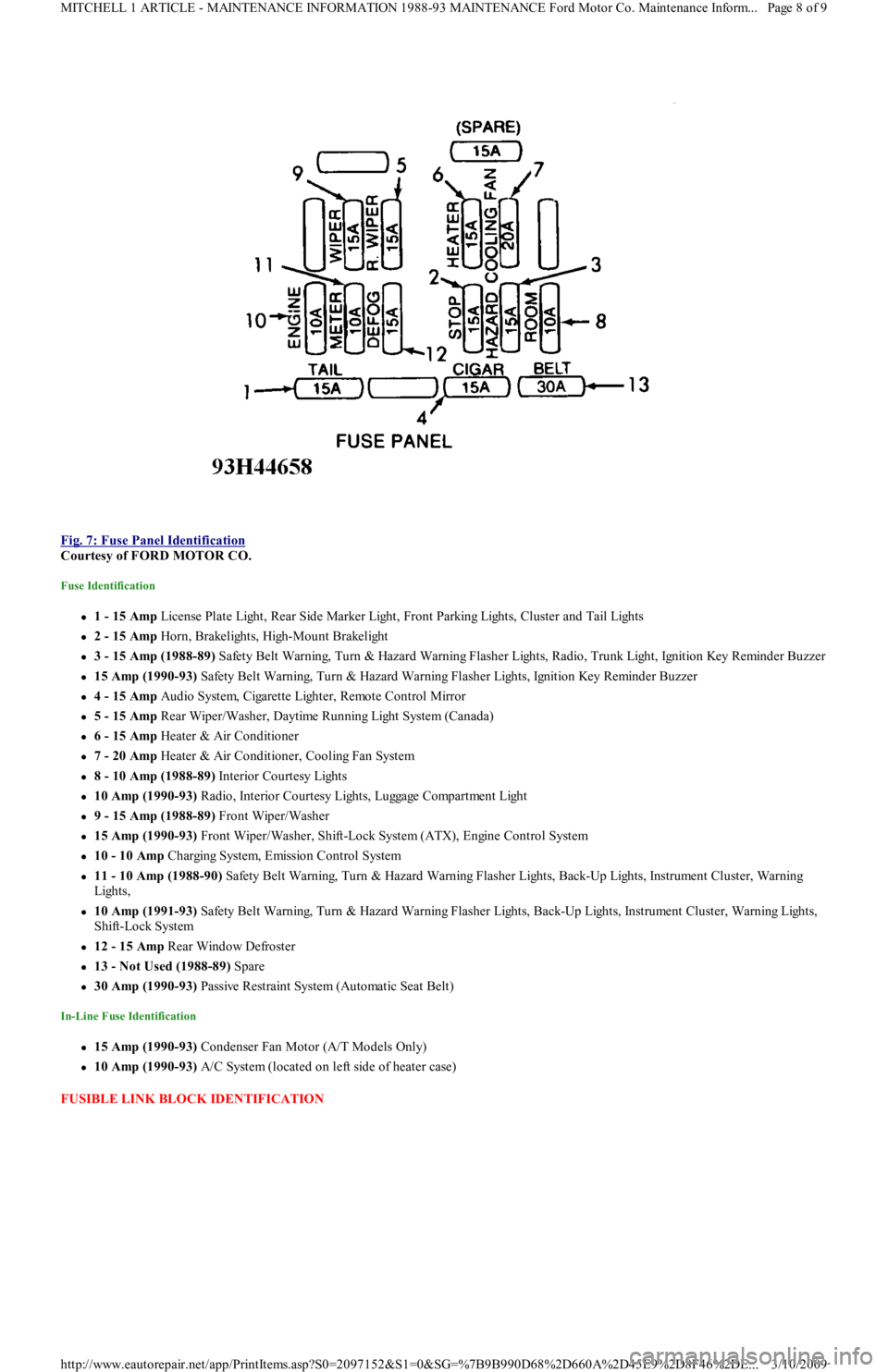
Fig. 7: Fuse Panel Identification
Courtesy of FORD MOTOR CO.
Fuse Identification
1 - 15 Amp License Plate Light, Rear Side Marker Light, Front Parking Lights, Cluster and Tail Lights
2 - 15 Amp Horn, Brakelights, High-Mount Brakelight
3 - 15 Amp (1988-89) Safety Belt Warning, Turn & Hazard Warning Flasher Lights, Radio, Trunk Light, Ignition Key Reminder Buzzer
15 Amp (1990-93) Safety Belt Warning, Turn & Hazard Warning Flasher Lights, Ignition Key Reminder Buzzer
4 - 15 Amp Audio System, Cigarette Lighter, Remote Control Mirror
5 - 15 Amp Rear Wiper/Washer, Daytime Running Light System (Canada)
6 - 15 Amp Heater & Air Conditioner
7 - 20 Amp Heater & Air Conditioner, Cooling Fan System
8 - 10 Amp (1988-89) Interior Courtesy Lights
10 Amp (1990-93) R a d io , In t e r io r C o u r t e sy Ligh t s, Lu gga ge C o mp a r t me n t Ligh t
9 - 15 Amp (1988-89) Front Wiper/Washer
15 Amp (1990-93) Front Wiper/Washer, Shift-Lock System (ATX), Engine Control System
10 - 10 Amp Charging System, Emission Control System
11 - 10 Amp (1988-90) Safety Belt Warning, Turn & Hazard Warning Flasher Lights, Back-Up Lights, Instrument Cluster, Warning
Lights,
10 Amp (1991-93) Safety Belt Warning, Turn & Hazard Warning Flasher Lights, Back-Up Lights, Instrument Cluster, Warning Lights,
Shift-Lock System
12 - 15 Amp Rear Window Defroster
13 - Not Used (1988-89) Spare
30 Amp (1990-93) Passive Restraint System (Automatic Seat Belt)
In-Line Fuse Identification
15 Amp (1990-93) Condenser Fan Motor (A/T Models Only)
10 Amp (1990-93) A/C System (located on left side of heater case)
FUSIBLE LINK BLOCK IDENTIFICATION
Page 8 of 9 MITCHELL 1 ARTICLE - MAINTENANCE INFORMATION 1988-93 MAINTENANCE Ford Motor Co. Maintenance Inform...
3/10/2009 http://www.eautorepair.net/app/PrintItems.asp?S0=2097152&S1=0&SG=%7B9B990D68%2D660A%2D45E9%2D8F46%2DE
...
Page 414 of 454
Differential Noise
ATF contaminated or level incorrect. Bearings worn or has excessive preload. Teeth on gears worn or damaged or has excessive backlash.
TESTING
PARK/NEUTRAL SWITCH TEST
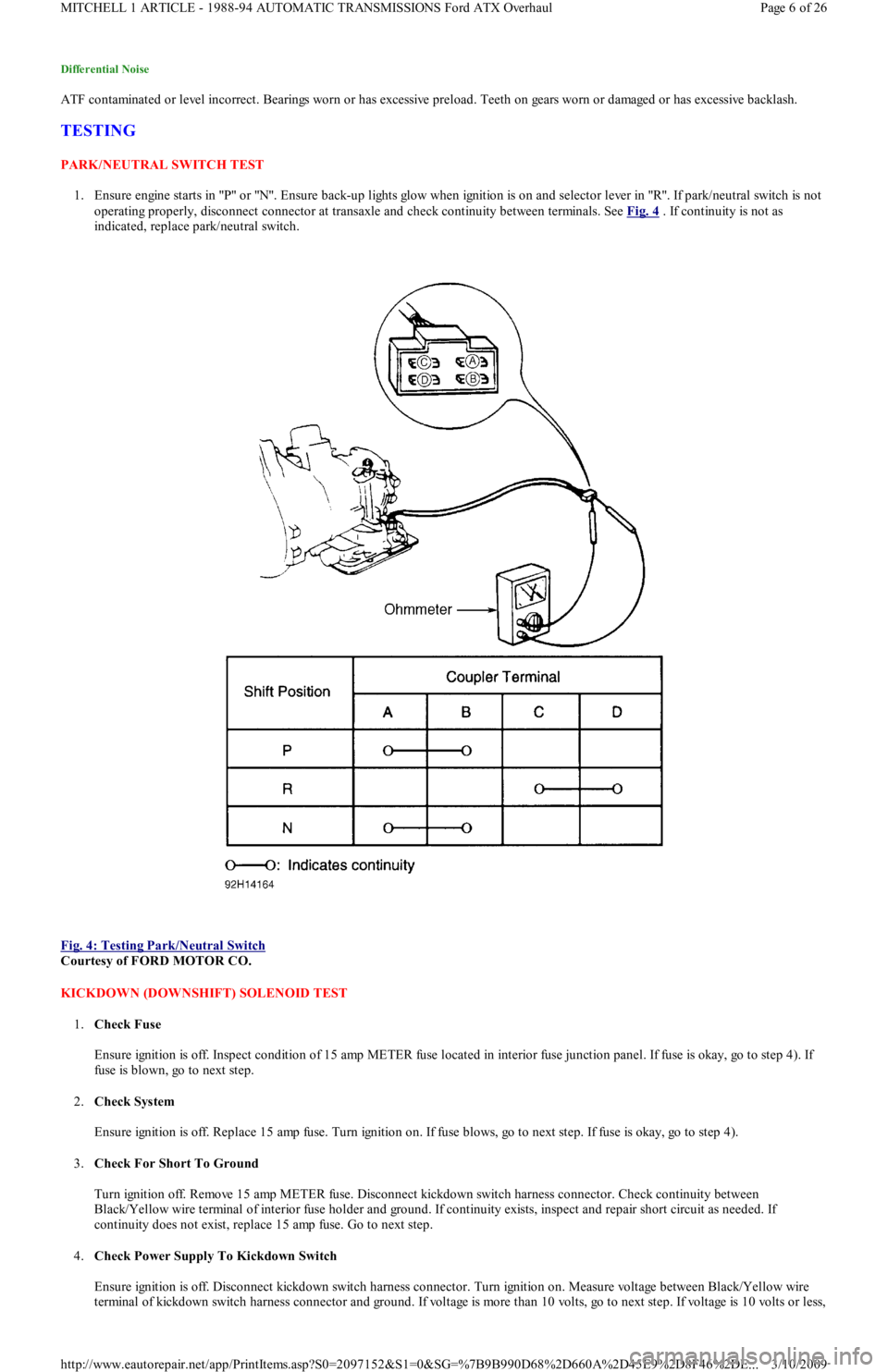
1. Ensure engine starts in "P" or "N". Ensure back-up lights glow when ignition is on and selector lever in "R". If park/neutral switch is not
operating properly, disconnect connector at transaxle and check continuity between terminals. See Fig. 4
. If continuity is not as
indicated, replace park/neutral switch.
Fig. 4: Testing Park/Neutral Switch
Courtesy of FORD MOTOR CO.
KICKDOWN (DOWNSHIFT) SOLENOID TEST
1.Check Fuse
Ensure ignition is off. Inspect condition of 15 amp METER fuse located in interior fuse junction panel. If fuse is okay, go to step 4). If
fuse is blown, go to next step.
2.Check System
Ensure ignition is off. Replace 15 amp fuse. Turn ignition on. If fuse blows, go to next step. If fuse is okay, go to step 4).
3.Check For Short To Ground
Turn ignition off. Remove 15 amp METER fuse. Disconnect kickdown switch harness connector. Check continuity between
Black/Yellow wire terminal of interior fuse holder and ground. If continuity exists, inspect and repair short circuit as needed. If
continuity does not exist, replace 15 amp fuse. Go to next step.
4.Check Power Supply To Kickdown Switch
Ensure ignition is off. Disconnect kickdown switch harness connector. Turn ignition on. Measure voltage between Black/Yellow wire
terminal of kickdown switch harness connector and ground. If voltage is more than 10 volts, go to next step. If voltage is 10 volts or less,
Page 6 of 26 MITCHELL 1 ARTICLE - 1988-94 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSIONS Ford ATX Overhaul
3/10/2009 http://www.eautorepair.net/app/PrintItems.asp?S0=2097152&S1=0&SG=%7B9B990D68%2D660A%2D45E9%2D8F46%2DE
...